6918a57498273e54e2db1c44b5035fa6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Concord Consortium CILT@Tele. Learning 98
Concord Consortium CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 Prospect and Problems l l l Revolutionary potentials of LT but. . . Two decades of strong academic R&D on learning technologies had minimal influences on school practices or industry developments Fragmented field of LT researchers—uncoordinated critical mass, differential strengths rarely combined Fragmentation of LT practitioner craft wisdom— uncoordinated insights rarely shared In sum: weak coupling of research and practice CILT@Tele. Learning 98
Prospect and Problems l l l Revolutionary potentials of LT but. . . Two decades of strong academic R&D on learning technologies had minimal influences on school practices or industry developments Fragmented field of LT researchers—uncoordinated critical mass, differential strengths rarely combined Fragmentation of LT practitioner craft wisdom— uncoordinated insights rarely shared In sum: weak coupling of research and practice CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 A distributed center for tackling these problems l l l Seed funding from National Science Foundation ($1. 45 mil@year) An open structure for harvesting knowledge and leveraging efforts of diverse LT R&D Working on “theme teams” in high-priority areas Weaving the web—Creating “virtual critical mass” for a distributed learning organization, including industry CILT@Tele. Learning 98
A distributed center for tackling these problems l l l Seed funding from National Science Foundation ($1. 45 mil@year) An open structure for harvesting knowledge and leveraging efforts of diverse LT R&D Working on “theme teams” in high-priority areas Weaving the web—Creating “virtual critical mass” for a distributed learning organization, including industry CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 The hub of founding members Concord Consortium CILT@Tele. Learning 98
The hub of founding members Concord Consortium CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 CILT Leadership Council John Bransford Marcia Linn CILT@Tele. Learning 98 Roy Pea Robert Tinker Barbara Means
CILT Leadership Council John Bransford Marcia Linn CILT@Tele. Learning 98 Roy Pea Robert Tinker Barbara Means
 CILT Mission (http: //cilt. org) To catalyze the development and implementation of important, technologyenabled solutions to critical problems in K-14 science, mathematics, engineering, and technology learning CILT@Tele. Learning 98
CILT Mission (http: //cilt. org) To catalyze the development and implementation of important, technologyenabled solutions to critical problems in K-14 science, mathematics, engineering, and technology learning CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 The Central CILT Strategy l Foster partnerships of research, industry, schools, and other stakeholders through invitational workshops and “seed fund” CILT partnership projects that emerge as priorities for breakthrough developments CILT@Tele. Learning 98
The Central CILT Strategy l Foster partnerships of research, industry, schools, and other stakeholders through invitational workshops and “seed fund” CILT partnership projects that emerge as priorities for breakthrough developments CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 We provide a socio-technical framework. . . l l l For sharing what’s being learned and fostering greater synergies of ideas across disciplines, projects, sectors, and funders To identify high potential areas for collaborative R&D For rapid, flexible funding of promising concepts For establishing multi-organizational collaboratories and testbeds for LT R&D To train multidisciplinary professionals CILT@Tele. Learning 98
We provide a socio-technical framework. . . l l l For sharing what’s being learned and fostering greater synergies of ideas across disciplines, projects, sectors, and funders To identify high potential areas for collaborative R&D For rapid, flexible funding of promising concepts For establishing multi-organizational collaboratories and testbeds for LT R&D To train multidisciplinary professionals CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 CILT as a Knowledge Network l The vision is a coordinated web of organizations, individuals, industries, schools, foundations, government agencies and labs devoted to the production, sharing and use of new knowledge about how learning technologies can dramatically improve the processes and outcomes of learning and teaching. CILT@Tele. Learning 98
CILT as a Knowledge Network l The vision is a coordinated web of organizations, individuals, industries, schools, foundations, government agencies and labs devoted to the production, sharing and use of new knowledge about how learning technologies can dramatically improve the processes and outcomes of learning and teaching. CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 How CILT is organized l l l CILT Leadership Council Four R&D Theme Teams Plus Core Center functions l l l Industry Alliance Program Communications Program for Knowledge Networking Postdoctoral Program School Partner and Affiliates Program Advisory Board Evaluation Program CILT@Tele. Learning 98
How CILT is organized l l l CILT Leadership Council Four R&D Theme Teams Plus Core Center functions l l l Industry Alliance Program Communications Program for Knowledge Networking Postdoctoral Program School Partner and Affiliates Program Advisory Board Evaluation Program CILT@Tele. Learning 98
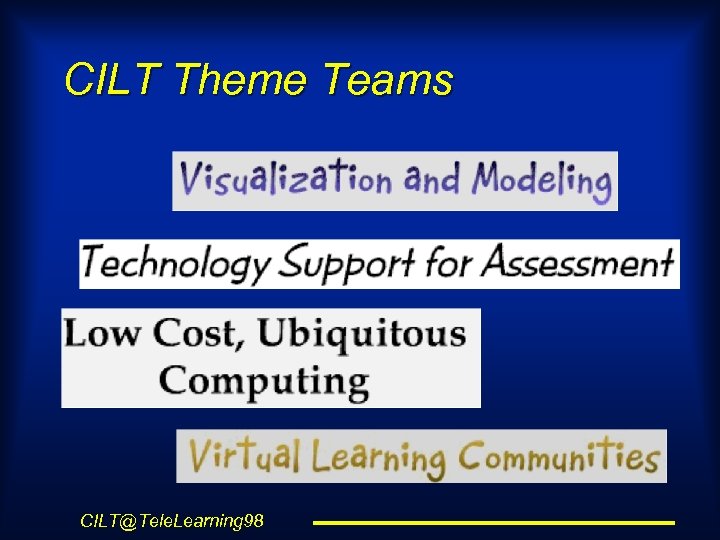 CILT Theme Teams CILT@Tele. Learning 98
CILT Theme Teams CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 How do CILT Theme Teams work? l Identify and recruit team members l Conduct partnership workshops l Community discussions on priorities l Select prototype projects and technologies with breakthrough opportunities l Foster widespread research and communication l Reflect on progress, re-consider directions l Provide context for training new professionals CILT@Tele. Learning 98
How do CILT Theme Teams work? l Identify and recruit team members l Conduct partnership workshops l Community discussions on priorities l Select prototype projects and technologies with breakthrough opportunities l Foster widespread research and communication l Reflect on progress, re-consider directions l Provide context for training new professionals CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 Four 1998 CILT Workshops l 367 attendees (300 individuals) l Over 200 projects l 150 different institutions represented • 81 universities and research organizations • 59 corporations • 10 schools CILT@Tele. Learning 98
Four 1998 CILT Workshops l 367 attendees (300 individuals) l Over 200 projects l 150 different institutions represented • 81 universities and research organizations • 59 corporations • 10 schools CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 Marcia Linn Andy di. Sessa Nancy Songer January 1998, U. California, Berkeley. 86 members, 44 institutions, 50 projects CILT@Tele. Learning 98
Marcia Linn Andy di. Sessa Nancy Songer January 1998, U. California, Berkeley. 86 members, 44 institutions, 50 projects CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 John Bransford Barbara Means February 1998: Vanderbilt University. 79 members, 31 institutions, 25 projects CILT@Tele. Learning 98
John Bransford Barbara Means February 1998: Vanderbilt University. 79 members, 31 institutions, 25 projects CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 Bob Tinker Bob Brodersen March 1998: SRI International 82 members, 59 institutions, 60 projects CILT@Tele. Learning 98
Bob Tinker Bob Brodersen March 1998: SRI International 82 members, 59 institutions, 60 projects CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 Roy Pea Jeremy Roschelle May 1998: SRI International 120 members, 69 institutions, 60 projects CILT@Tele. Learning 98
Roy Pea Jeremy Roschelle May 1998: SRI International 120 members, 69 institutions, 60 projects CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 CILT Theme Team R&D funding l l l Provides “seed” resources to fund CILT Partnership Projects, White Papers CILT Partnership Projects leverage LT research insights from a large proportion of US-funded work (>$50 Mil@Yr) CILT projects may enhance ongoing grants, lead to new grants, and/or be co-funded by industry CILT@Tele. Learning 98
CILT Theme Team R&D funding l l l Provides “seed” resources to fund CILT Partnership Projects, White Papers CILT Partnership Projects leverage LT research insights from a large proportion of US-funded work (>$50 Mil@Yr) CILT projects may enhance ongoing grants, lead to new grants, and/or be co-funded by industry CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 Criteria for Defining CILT projects l Idea potential l Leverage funding! l l Interdisciplinary collaboration and multiple institutions Rapid delivery—developing concepts, toolkits, environments others can use in under a year Prospects for successful integration into or impact on K-14 curricula Plan for testing, assessment CILT@Tele. Learning 98
Criteria for Defining CILT projects l Idea potential l Leverage funding! l l Interdisciplinary collaboration and multiple institutions Rapid delivery—developing concepts, toolkits, environments others can use in under a year Prospects for successful integration into or impact on K-14 curricula Plan for testing, assessment CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 1998 “CILT Headlines” l l Workshop model is a vital success; we will consolidate in one annual meeting (April 29 -May 2, San Jose CA) Participants expressed tremendous need for a forum and process like CILT 20 partnership projects approved Particular value to junior faculty, smaller institutions CILT@Tele. Learning 98
1998 “CILT Headlines” l l Workshop model is a vital success; we will consolidate in one annual meeting (April 29 -May 2, San Jose CA) Participants expressed tremendous need for a forum and process like CILT 20 partnership projects approved Particular value to junior faculty, smaller institutions CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 Some CILT Partnership Projects l Virtual Reality Solar System (Ken Hay, U. Ga. and Sasha Barab, Indiana U. ) l Visualizing the Amazonian Rain Forest (Douglas Gordin, MSU-SRI and Quinn Mc. Laughlin, Osiris) l Exploring Self-Explanatory Simulators for Middle-School-Science (Ken Forbus, Northwestern U. , and Jim Slotta, U. C. Berkeley) CILT@Tele. Learning 98
Some CILT Partnership Projects l Virtual Reality Solar System (Ken Hay, U. Ga. and Sasha Barab, Indiana U. ) l Visualizing the Amazonian Rain Forest (Douglas Gordin, MSU-SRI and Quinn Mc. Laughlin, Osiris) l Exploring Self-Explanatory Simulators for Middle-School-Science (Ken Forbus, Northwestern U. , and Jim Slotta, U. C. Berkeley) CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 Some CILT Partnership Projects l Technology Support for Assessment book (NEA, Vanderbilt, SRI, CILT presenters; broader community through Knowledge Mining) l CILT knowledge network (Chris Hoadley, SRI; Vanderbilt, Concord, U. California, Berkeley; UM; NWU and others) l Teacher Education and Professional Development: A systemic conversation among diverse institutions (Mark Schlager, SRI; Therese Laferriere, Universite Laval; Margaret Honey CCT; LA Unified Schools; Ray Rose, Concord Consortium; others) CILT@Tele. Learning 98
Some CILT Partnership Projects l Technology Support for Assessment book (NEA, Vanderbilt, SRI, CILT presenters; broader community through Knowledge Mining) l CILT knowledge network (Chris Hoadley, SRI; Vanderbilt, Concord, U. California, Berkeley; UM; NWU and others) l Teacher Education and Professional Development: A systemic conversation among diverse institutions (Mark Schlager, SRI; Therese Laferriere, Universite Laval; Margaret Honey CCT; LA Unified Schools; Ray Rose, Concord Consortium; others) CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 Some CILT Partnership Projects l Scenarios for interoperable components for shared active representations (Dan Suthers, U. Hawaii, and SRI, UM, CMU, NWU, MIT, Vanderbilt, Rutgers, schools, and more) l K-12 collaborative learning requirements (Geoffrey Fox, Syracuse U. , Denis Newman, IMS and a large group) l Envisioning a Future Product Line of Low-cost Computers (Michael Mills, IDEO; Jeremy Rochelle and Roy Pea, SRI; Robbie Berg, MIT; Charlie Patton, TI-83 inventor; Nick Jackiw, Key Curriculum Press; Yasmin Kafai, UCLA). . . l Sonar Ranger Application to the Palm Pilot (Stephen Bannasch, Concord Consortium; Evan Weis, MIT) CILT@Tele. Learning 98
Some CILT Partnership Projects l Scenarios for interoperable components for shared active representations (Dan Suthers, U. Hawaii, and SRI, UM, CMU, NWU, MIT, Vanderbilt, Rutgers, schools, and more) l K-12 collaborative learning requirements (Geoffrey Fox, Syracuse U. , Denis Newman, IMS and a large group) l Envisioning a Future Product Line of Low-cost Computers (Michael Mills, IDEO; Jeremy Rochelle and Roy Pea, SRI; Robbie Berg, MIT; Charlie Patton, TI-83 inventor; Nick Jackiw, Key Curriculum Press; Yasmin Kafai, UCLA). . . l Sonar Ranger Application to the Palm Pilot (Stephen Bannasch, Concord Consortium; Evan Weis, MIT) CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 Ubiquitous Computing l l l Current computing and communications products, developed primarily for business and research, have a combination of price, performance, and features that are sub-optimal for education and are a significant source of unacceptable inequities. Desktop computers do not meet students’ requirements for mobility and fail to empower students with personal ownership of their inquiry tools. Conjecture that major learning breakthroughs are possible when every learner has regular access to even limited computing, can use a computer anywhere, can easily access the Web CILT@Tele. Learning 98
Ubiquitous Computing l l l Current computing and communications products, developed primarily for business and research, have a combination of price, performance, and features that are sub-optimal for education and are a significant source of unacceptable inequities. Desktop computers do not meet students’ requirements for mobility and fail to empower students with personal ownership of their inquiry tools. Conjecture that major learning breakthroughs are possible when every learner has regular access to even limited computing, can use a computer anywhere, can easily access the Web CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 Ubiquitous Technologies l l For use in schools, homes, museums, and on the move. Inexpensive mobile computers Real-time data input Wireless networking Interoperable component software CILT@Tele. Learning 98
Ubiquitous Technologies l l For use in schools, homes, museums, and on the move. Inexpensive mobile computers Real-time data input Wireless networking Interoperable component software CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 What functionality is needed? l l l Fast interactivity Connections to the real world: probeware, actuators, force feedback Scaffolded learning environments Special representations for SMET: graphs, symbols, spreadsheets Communications tools including text, sketching, portfolios CILT@Tele. Learning 98
What functionality is needed? l l l Fast interactivity Connections to the real world: probeware, actuators, force feedback Scaffolded learning environments Special representations for SMET: graphs, symbols, spreadsheets Communications tools including text, sketching, portfolios CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 Research Needed l l Engineering: System and UI design. Interface development. Cost containment. Cognition: What MST topics can be learned readily in this new environment? Pedagogy: How do we connect experiential and formal learning? Education: How do we impact the school curriculum and the informal sector such as homes and museums? CILT@Tele. Learning 98
Research Needed l l Engineering: System and UI design. Interface development. Cost containment. Cognition: What MST topics can be learned readily in this new environment? Pedagogy: How do we connect experiential and formal learning? Education: How do we impact the school curriculum and the informal sector such as homes and museums? CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 Learning appliances l l l Palm Pilot hits the “form-function” sweet spot (63% global market) Fastest adopted HH computing device of all time: Over 2 million so far 10, 000 developers using the Palm OS CILT@Tele. Learning 98
Learning appliances l l l Palm Pilot hits the “form-function” sweet spot (63% global market) Fastest adopted HH computing device of all time: Over 2 million so far 10, 000 developers using the Palm OS CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 Concord Consortium Sonar Ranger (CCSR): CILT Project CILT@Tele. Learning 98
Concord Consortium Sonar Ranger (CCSR): CILT Project CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 CILT@Tele. Learning 98
CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 Goals of the CILT Industry Alliance Program l l l Significant contributions of cash and in-kind for CILT project support Access to state-of-the-art developments for advancing CILT partnership projects To influence developments in learning technologies for key industries l Good working relationships with key companies l First Alliance Partners: Intel, Net. Schools l Negotiating: Sun Microsystems, Oracle, 3 COM, In. Focus CILT@Tele. Learning 98
Goals of the CILT Industry Alliance Program l l l Significant contributions of cash and in-kind for CILT project support Access to state-of-the-art developments for advancing CILT partnership projects To influence developments in learning technologies for key industries l Good working relationships with key companies l First Alliance Partners: Intel, Net. Schools l Negotiating: Sun Microsystems, Oracle, 3 COM, In. Focus CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 Center for Innovative Learning Technologies http: //cilt. org CILT@Tele. Learning 98
Center for Innovative Learning Technologies http: //cilt. org CILT@Tele. Learning 98
 http: //www. sri. com/policy/ctl CILT@Tele. Learning 98
http: //www. sri. com/policy/ctl CILT@Tele. Learning 98


