ad4613aa40115f6e766f738a1a58f7f9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55

Concepts and Resources for Teaching Globalization (12 May’ 05) S. Tamer Cavusgil The John W. Byington Endowed Chair in Global Marketing, and Executive Director, Center for International Business Education and Research, Michigan State University 2005 International Business Institute East Lansing, Michigan 15 May 2005

S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 2

Rationale for Internationalization Faculty Professional development/enrichment; recognition Students Liberating minds; informed citizens; appreciation of diversity develop cosmopolitan orientations Business Become relevant; serve as resource and source of training Your College Create a total global culture; establish new traditions and behavior; become a viable competitor And… a goal common to all constituents: Build global competence as a source of competitive advantage. S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 3

What is Globalization? At the macro level… • Greater integration and interdependency of national economies • Freer movement of goods, services, capital, and knowledge • Prevalence of regional trading blocs • Emergence of monetary unions • Convergence of customer lifestyles, requirements, etc. S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 4

What is Globalization? For business enterprises… • Foreign market entry and expansion • Re-configuration and externalization of value chain • Collaborative ventures with foreign partners • Integration of operations on a global scale • Building global capabilities and a global organization S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 5

1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. The Many Dimensions of Globalization Value-adding activities Companies – The business enterprise Products and brands Economic assets Business risks Industries Countries, markets Regulations, laws, standards Cultural values, mindsets, consumer behavior Business practices S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 6

Phases of Globalization 1 st Phase: 1830, peaking around 1880 Aided by railroads, ocean transport, rise of manufacturing and trading companies 2 nd Phase: 1900, peaking around 1930 Fueled by electricity and steel 3 rd Phase: 1948, peaking around 1970 GATT, End of WWII, Marshall Plan… 4 th Phase: 1980, peaking around 1997 Technological advances, Internet, Privatization… S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 7

Perspectives on Globalization can be studied as a … • Process • As a cause or driver • Consequence S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 8

CURRICULAR INITIATIVES FOREIGN INSTITUTIONAL LINKAGES ENRICHMENT OF STUDENT EXPERIENCES (on campus and abroad) Comprehensive Agenda for Internationalization FACULTY MOTIVATION AND DEVELOPMENT COLLABORATION WITH BUSINESS CAPITALIZING ON INSTITUTIONAL STRENGTHS: BUILDING CAMPUS ALLIANCES S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 9

Motivating the Student • Companies face special challenges when operating in a broader, multi-country environment. • The foreign country environment (political, legal, cultural, etc. ) deserves special attention. • Knowledge and practices developed at home may not be valid in other country contexts. • Managers need to acquire new types of competence in order to compete in the global economy. • The consequences of a global economy are felt daily around us. S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 10

Three Dimensions of International Context • International/Cross Border dimension (Functional specialist) Cross-border management paradigm • Comparative dimension (Country enthusiast) Extension paradigm • Cross-cultural dimension (Behaviorist) Inter-cultural paradigm S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 11

Layers of Knowledge in International Business Cross-Cultural Knowledge Country/Regional Knowledge Cross-Border Transactions Knowledge Domestic Business Knowledge S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 12

Layers of Knowledge in International Business Cross-Cultural Knowledge Cultural Differences Negotiation Styles Ethical Values Language Decisionmaking Styles Attitudes Organizational towards IPR Features Country/Regional Knowledge Commercial Market Access Trade/ Entry Infrastructure Product Distribution Barriers Channels Standards Contract Law Role of Government in Business Cross-Border Transactions Knowledge Product Adaptation International SCM Letters of Credit Currency Markets Legal Agreements Payments Domestic Business Knowledge 13
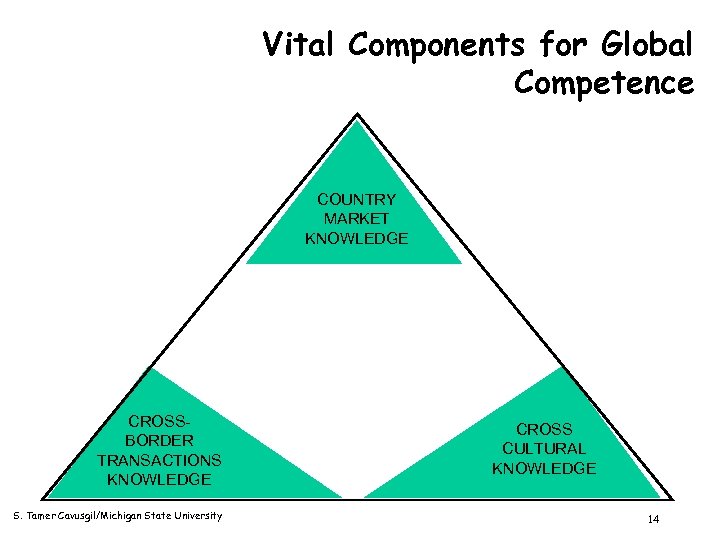
Vital Components for Global Competence COUNTRY MARKET KNOWLEDGE CROSSBORDER TRANSACTIONS KNOWLEDGE S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University CROSS CULTURAL KNOWLEDGE 14
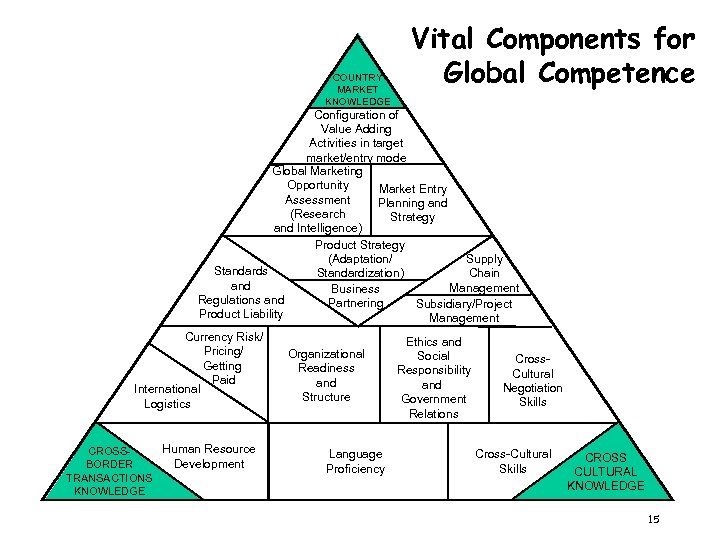
COUNTRY MARKET KNOWLEDGE Vital Components for Global Competence Configuration of Value Adding Activities in target market/entry mode Global Marketing Opportunity Market Entry Assessment Planning and (Research Strategy and Intelligence) Product Strategy Supply (Adaptation/ Standards Chain Standardization) and Management Business Regulations and Partnering Subsidiary/Project Product Liability Management Currency Risk/ Pricing/ Getting Paid International Logistics Human Resource CROSSDevelopment BORDER TRANSACTIONS KNOWLEDGE Organizational Readiness and Structure Language Proficiency Ethics and Social Responsibility and Government Relations Cross. Cultural Negotiation Skills Cross-Cultural Skills CROSS CULTURAL KNOWLEDGE 15

Leading IB Portal http: //globaledge. msu. edu 16

global. EDGE™ A knowledge web-portal that connects international business professionals worldwide to a wealth of information, insights, and learning resources on global business activities. The site offers: – Global Resources - more than 5, 000 online resources – Country Insights - a wealth of information on all countries – Community - an interactive forum for business professionals – Knowledge Room - latest issues in international business – Academy - extensive research and teaching resources – Diagnostic Tools - decision-support tools for managers global. EDGE™ - your source for global business knowledge S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 17

Globalization Themes for Economics • Comparative advantage; gains from trade • Drivers of globalization • Purchasing Power Parity • Global Competitiveness Index • Index of Economic Freedom • Culture and IB • International entrepreneurship • Attitudes toward work and leisure • Unionization; collective bargaining S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 18

Globalization Drivers: Seven Macro. Trends 1. Reduction of barriers to trade and investment 2. Regional trade agreements and economic blocs 3. Market liberalization and privatization 4. Industrialization, economic development and modernization 5. Integration of world financial markets 6. Transportation and communication technology 7. Information technology S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 19

The World Competitiveness Scoreboard 2004 Source: IMD World Competitiveness Yearbook 2004 20

Economic Freedom and Wealth 21

The Economist’s Big Mac Index The concept of Purchasing Power Parity refers to the notion that a dollar should buy the same bundle of goods in all countries. Comparing actual exchange rates with PPP indicates whether a currency is under- or overvalued. S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 22

Big Mac Currencies May 27 th 2004 From The Economist print edition The world economy looks very different once countries' output is adjusted for differences in prices 23

Capturing the Purchasing Power COUNTRY Argentina Brazil Bulgaria Canada China Hungary South Korea Mexico Russian Fed Turkey GNP per capita US $ Purchasing Power Parity adjusted GNP per capita 6, 950 2, 850 10, 980 7, 250 1, 790 22, 300 940 5, 280 9, 930 5, 910 2, 140 2, 500 6, 840 28, 070 4, 390 12, 810 16, 480 8, 540 7, 820 6, 120 Source: World Bank. Figures are for 2003. 24

Themes for Culture • The Iceberg Principle of Culture • Cultural stereotypes, idioms, metaphors • Cultural Dimensions (High Context; Collectivism, Power distance, Uncertainty avoidance, Masculinity) • Language as the expression of culture • Self Reference Criterion • Critical incidence analysis • Negotiation patterns S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 25

26

27

Critical Skills for the Manager • Cultural empathy / Open-mindedness • Tolerance for ambiguity • Flexibility/Adaptability/Self reliance • Perceptiveness • Curiosity • Premium on personal relationships • Good sense of humor • Warmth in human relationships S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 28

Is Globalization a Good Thing? The Critics • Benefits of globalization are not evenly distributed • Globalization causes dislocation of jobs • Wages for unskilled labor are declining • Manufacturing moves offshore to avoid workplace safety and health regulations • MNCs fail to protect the environment S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 29

Is Globalization a Good Thing? The Critics (cont. ) • Power shifts to multinational corporations and supranational organizations; nations loose sovereignty • Concentration of power by multinational corporations leads to monopoly • International financial markets are inherently unstable • Globalization results in loss of national cultural values and identity S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 30

Themes for General Business • Market entry, expansion, segmentation • Standardization /adaptation • Global brand success • Joint ventures/alliances/partnerships • Product liability laws; retail regulations • Global supply chain management • Emerging Markets; Family Conglomerates • Offshoring S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 31

Stage in Value Chain Research & Development Types of Collaboration Company Examples Strategic alliances Licensing/cross licensing Telecoms, computers, drugs, aircraft, satellite communication systems… Dow, Pharmacia-Upjohn Design contracting Software, autos, fashion goods, shoes, furniture… Manufacturing Global procurement Contract manufacturing Equity joint ventures (FDI) Agency agreements Licensing Automotive Marketing Exporting to distributors/ agents Franchising Gerber (Novartis) Product Design Distribution Sales & Service Exporting to end-users Business format franchising Agency/representative relationships IKEA, Guardian Industries Kmart, Manpower, Banks, Courier Services, Amway 32
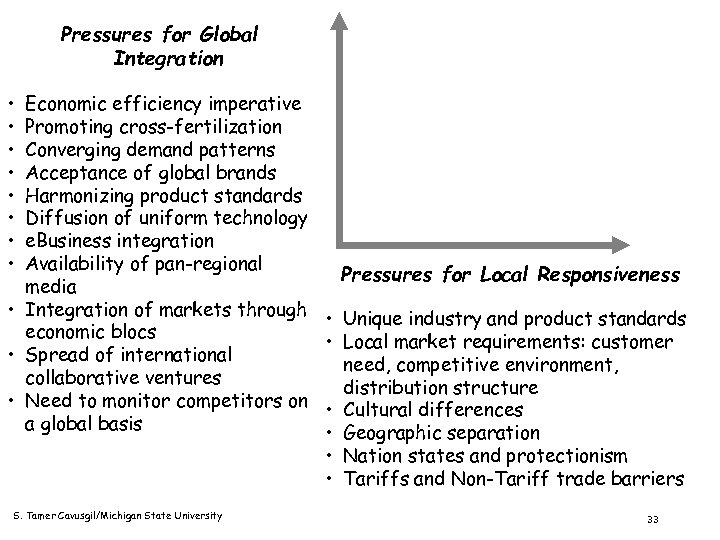
Pressures for Global Integration • • Economic efficiency imperative Promoting cross-fertilization Converging demand patterns Acceptance of global brands Harmonizing product standards Diffusion of uniform technology e. Business integration Availability of pan-regional Pressures for Local Responsiveness media • Integration of markets through • Unique industry and product standards economic blocs • Local market requirements: customer • Spread of international need, competitive environment, collaborative ventures distribution structure • Need to monitor competitors on • Cultural differences a global basis • Geographic separation • Nation states and protectionism • Tariffs and Non-Tariff trade barriers S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 33

34

Emerging Markets • High-growth, high-potential developing countries • Rapid transformation • Liberalization, modernization, industrialization • Rising middle class • Unique Aspects: Family Conglomerates; large informal economy; institutional vacuum; high risks… S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 35

Market Potential Indicators for Emerging Markets 36

37

S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 38
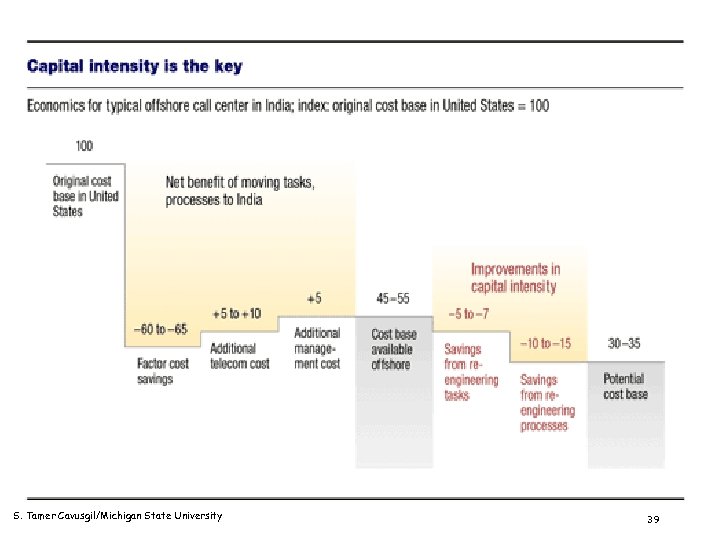
S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 39

Themes for Accounting • Exchange rates and trade • Currency risk; Euro in the E. U. • Harmonized accounting practices • Transfer pricing; Taxation of foreign income • Foreign Corrupt Practices Act • Operating in: High-inflation countries; Free Trade Areas • Listing in foreign stock markets S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 40

Four Types of Risks Commercial Risk Cross-Cultural Risk Cultural distance Negotiation patterns Decision-making styles Ethical practices Types of Risks in International Business Country (Political and Legal) Risk • Weak Partner • Operational Problems • Timing of entry • Competitive intensity • Poor execution of strategy Currency/Financial Risk • • Currency exposure Asset valuation Foreign taxation Inflationary and transfer pricing • Global sourcing • Social/political unrest and instability • Economic mismanagement; inflation • Distribution of income; size of middle class • Government intervention, bureaucracy, red tape • Market access; barriers; profit repatriation • Legal safeguards for intellectual property right 41

Themes for Information Systems / Technology • Internet and Information Technology as a driver of globalization • e. Business /On-line strategies • Virtual interconnectedness in the multinational corporation • Globalization of IT sector; India’s advantage in this area • Globalization of related industries such as office furniture industry (Steelcase, Herman Miller, etc. ) S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 42

43

44

Online IB Course Modules on the global. EDGE Organized by: • Countries / Geographic regions • Business functions • Culture • Exports S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 45

http: //global. EDGE. msu. edu Your company has developed a new product that is expected to achieve high penetration rates in all the countries where it is introduced, regardless of the average income status of the local population. Considering the costs of the product launch, the management team has decided to initially introduce the product only in countries that have a sizeable population base. You are required to prepare a preliminary report with the top ten countries of the world in terms of population size. Since growth opportunities are another major concern, the average population growth rates should be also listed for management’s consideration. How to? – – “Global Resources” on global. EDGE Research: Statistical Data Sources Search “Population” Source: “World Population Data Sheet” S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 46

http: //global. EDGE. msu. edu The Freedom in the World survey evaluates the state of political rights and civil liberties around the world. For a company location project, you need to provide a description of this survey and a ranking, in terms of “freedom” of the leaders and laggards of the world. What factors are taken into consideration in this survey when forming the rankings? How to? – “Global Resources” on global. EDGE – Research: Multi-Country – Search: “Freedom” – Result: “Freedom House Surveys” S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 47

http: //global. EDGE. msu. edu For a country selection project, you need to know which markets/countries are the most attractive in the global marketplace. Accordingly, the ranking of the top 25 countries in terms of FDI attractiveness is a crucial ingredient for your report. You have heard about the “FDI Confidence Index” which is updated periodically. Find this index, and provide additional information regarding how the index is constructed. How to? – “Global Resources on global. EDGE – Research: Rankings – Search: “FDI Confidence Index” – Result: “A. T. Kearney: FDI Confidence Index” S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 48

Web-Based Exercises and Projects for Internationalizing Business Courses • Handout S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 49

Market and Country Research • International Marketing Insight (IMI) Reports • Multilateral Development Bank (MDB) • Industry Sector Analysis Reports • Best Market Reports • Global Agriculture Information Network (GAIN) Ag. World Attaché reports • Country Commercial Guides 50

S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University

Company’s Overall Readiness to Export Product Readiness Organizational Readiness Competitive Capabilities in Domestic Market Motivation for Going International S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University Skill, Knowledge and Resources Commitment of Owners and Top Management Experience and Training 52
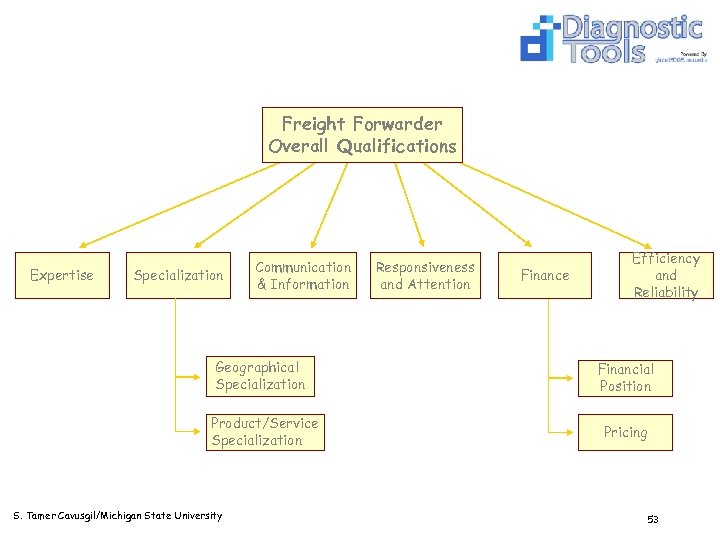
Freight Forwarder Overall Qualifications Expertise Specialization Communication & Information Geographical Specialization Product/Service Specialization S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University Responsiveness and Attention Finance Efficiency and Reliability Financial Position Pricing 53

global. EDGE™ is a global business knowledge web-portal that connects international business professionals worldwide to a wealth of information, insights, and learning resources on global business activities. By serving as a gateway to specialized knowledge on countries, crossborder business transactions, and cross-cultural management, global. EDGE™ responds to a real interest expressed by an increasing number of global business professionals. It also creates a virtual community of both executives and academics with like interests. 54

Additional Resources • Internationalizing Business Education: Issues and Recommendations by Leading Educators, (Cavusgil, Schechter, Yaprak), East Lansing, Michigan, MSU Press, March 1992 (28 pp. ). • Internationalizing Business Education: Toward Meeting the Challenge, (Cavusgil), East Lansing, Michigan, MSU Press, 1993 (342 pp. ) • Internationalizing the Business Curriculum, R. F. Scherer, S. T. Beaton, M. F. Ainina, Euclid, OH: Lakeshore Comm. • “Expanding Horizons with E-Learning” in A Field Guide to Internationalizing Business Education, R. F. Scherer, S. T. Beaton, M. F. Ainina and J. F. Meyer (eds. ), Second Edition, 2003, 183 -194, Cavusgil, I. Kiyak and T. Kiyak. • Study Abroad Programs in Business Schools, Issues and Recommendations by Leading Educators, East Lansing, MI, MSU Press, 2002. • Doing Business in Emerging Markets, Cavusgil, P. Ghauri and M. Agarwal, Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, Inc. , 2002. S. Tamer Cavusgil/Michigan State University 55
ad4613aa40115f6e766f738a1a58f7f9.ppt