corporate strategy.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 45
 Concept of Strategy Word Strategy is derived from Greek word “Strategtia” The concept of strategy defined as “ the common thread among the organization , activities and products markets, that defines the essential nature of business that the organization was or planned to be in future” Igor Ansoff
Concept of Strategy Word Strategy is derived from Greek word “Strategtia” The concept of strategy defined as “ the common thread among the organization , activities and products markets, that defines the essential nature of business that the organization was or planned to be in future” Igor Ansoff
 Concept of Strategy In other words: • Strategy is defined as “the unified comprehensive and integrated plan that relates the strategy advantage of the firm to challenges of the environment and is designed to ensure that basic objectives of the enterprise and achieved through implementation process” William Glueck
Concept of Strategy In other words: • Strategy is defined as “the unified comprehensive and integrated plan that relates the strategy advantage of the firm to challenges of the environment and is designed to ensure that basic objectives of the enterprise and achieved through implementation process” William Glueck
 Features of Corporate Strategy • It is related mostly to external environment. • It is being formulated at the higher level of management. • It integrates three distinct and closely related activities in strategy making. • It is related in long term. • It requires systems and norms for its efficient adoption in any organization. • It provides overall framework for guiding enterprise thinking and action. • It is concerned with a unified direction and efficient allocation of organization resources.
Features of Corporate Strategy • It is related mostly to external environment. • It is being formulated at the higher level of management. • It integrates three distinct and closely related activities in strategy making. • It is related in long term. • It requires systems and norms for its efficient adoption in any organization. • It provides overall framework for guiding enterprise thinking and action. • It is concerned with a unified direction and efficient allocation of organization resources.
 Components of Corporate Strategy Major components of corporate strategy are: • • • Purpose and objectives. Vector. Competitive advantage. Synergy. Personal values. Aspirations and social obligations.
Components of Corporate Strategy Major components of corporate strategy are: • • • Purpose and objectives. Vector. Competitive advantage. Synergy. Personal values. Aspirations and social obligations.
 Objectives Corporate objectives should be stated in such a way so that it may provide a clear idea about the scope of the enterprise’s business. They should: • • • Have proper timeframe Attainable Challenging Understandable Measurable and controllable
Objectives Corporate objectives should be stated in such a way so that it may provide a clear idea about the scope of the enterprise’s business. They should: • • • Have proper timeframe Attainable Challenging Understandable Measurable and controllable
 Vector • Vector gives the directions within an industry and across industry boundaries which the firm proposes to pursue. • It signifies that a series of decisions are taken in the same directions to accomplish the objectives.
Vector • Vector gives the directions within an industry and across industry boundaries which the firm proposes to pursue. • It signifies that a series of decisions are taken in the same directions to accomplish the objectives.
 Competitive Advantage • Corporate strategy is relative by nature and when the corporative strategies are formulate, one cannot ignore competitors. • If organization ignores this aspect, than it cannot survive in a dynamic environment and can’t build their internal strength of the organization.
Competitive Advantage • Corporate strategy is relative by nature and when the corporative strategies are formulate, one cannot ignore competitors. • If organization ignores this aspect, than it cannot survive in a dynamic environment and can’t build their internal strength of the organization.
 Functions of Corporate Strategy Various functions of corporate strategy are: • It exploits the most effective means to overcome difficulties and face competition. • It assists in the deployment of scarce resources among critical activities. • It focuses upon charges in the organizational setup. • It furnishes the management with a perspective whereby, the latter gives equal importance to present and future opportunities. • It provides the management with a mechanism to cope with highly complex environment characterized by diversity of cultural, social, political and competitive forces.
Functions of Corporate Strategy Various functions of corporate strategy are: • It exploits the most effective means to overcome difficulties and face competition. • It assists in the deployment of scarce resources among critical activities. • It focuses upon charges in the organizational setup. • It furnishes the management with a perspective whereby, the latter gives equal importance to present and future opportunities. • It provides the management with a mechanism to cope with highly complex environment characterized by diversity of cultural, social, political and competitive forces.
 Levels of Corporate Strategy Corporate strategy exists at three levels in an organization. The three levels are: • Corporate level Strategy • Business level Strategy • Operating level Strategy
Levels of Corporate Strategy Corporate strategy exists at three levels in an organization. The three levels are: • Corporate level Strategy • Business level Strategy • Operating level Strategy
 Corporate Level Strategy • At corporate level, board of directors and chief executive officers, corporate planners and consultants are involved in strategy making. • These strategies are futuristic, innovative and pervasive in nature. • Decision like spreading the range of business interests, acquisition, diversification, structural redesigning, mergers takeovers, etc. comes under corporate level strategies.
Corporate Level Strategy • At corporate level, board of directors and chief executive officers, corporate planners and consultants are involved in strategy making. • These strategies are futuristic, innovative and pervasive in nature. • Decision like spreading the range of business interests, acquisition, diversification, structural redesigning, mergers takeovers, etc. comes under corporate level strategies.
 Business Level Strategy • Strategic Business Unit (SBU) managers are involved at this level in taking strategic decisions. • These strategies relate to a unit within an organization and objectives are formulated for SBU’s • These strategies are more specific and action oriented. It relates mainly with “how” aspect.
Business Level Strategy • Strategic Business Unit (SBU) managers are involved at this level in taking strategic decisions. • These strategies relate to a unit within an organization and objectives are formulated for SBU’s • These strategies are more specific and action oriented. It relates mainly with “how” aspect.
 Operating Level Strategy • This level of strategy is at the operating end of the organization. Decisions related to training, investing in plant, advertising, sales promotion, total quality management, market segmentation, etc are taken at this level. • They deal with a relatively restricted plan providing objectives for specific function, allocation of resources among different operations within the functional area and coordination between them.
Operating Level Strategy • This level of strategy is at the operating end of the organization. Decisions related to training, investing in plant, advertising, sales promotion, total quality management, market segmentation, etc are taken at this level. • They deal with a relatively restricted plan providing objectives for specific function, allocation of resources among different operations within the functional area and coordination between them.
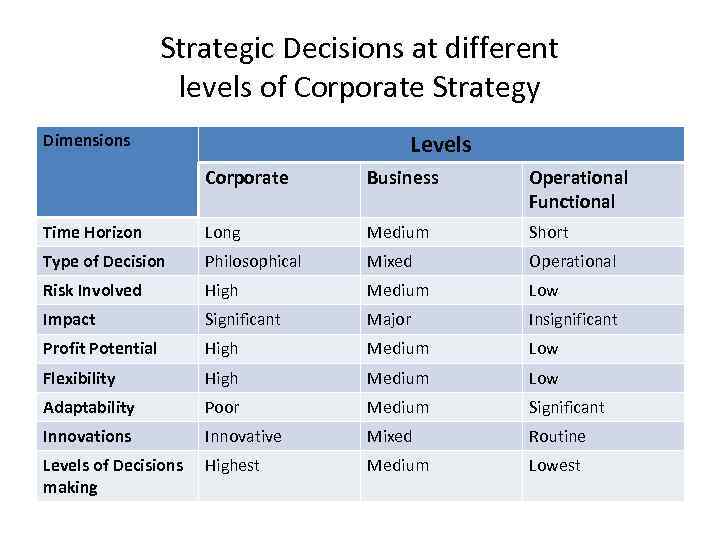 Strategic Decisions at different levels of Corporate Strategy Levels Dimensions Corporate Business Operational Functional Time Horizon Long Medium Short Type of Decision Philosophical Mixed Operational Risk Involved High Medium Low Impact Significant Major Insignificant Profit Potential High Medium Low Flexibility High Medium Low Adaptability Poor Medium Significant Innovations Innovative Mixed Routine Levels of Decisions making Highest Medium Lowest
Strategic Decisions at different levels of Corporate Strategy Levels Dimensions Corporate Business Operational Functional Time Horizon Long Medium Short Type of Decision Philosophical Mixed Operational Risk Involved High Medium Low Impact Significant Major Insignificant Profit Potential High Medium Low Flexibility High Medium Low Adaptability Poor Medium Significant Innovations Innovative Mixed Routine Levels of Decisions making Highest Medium Lowest
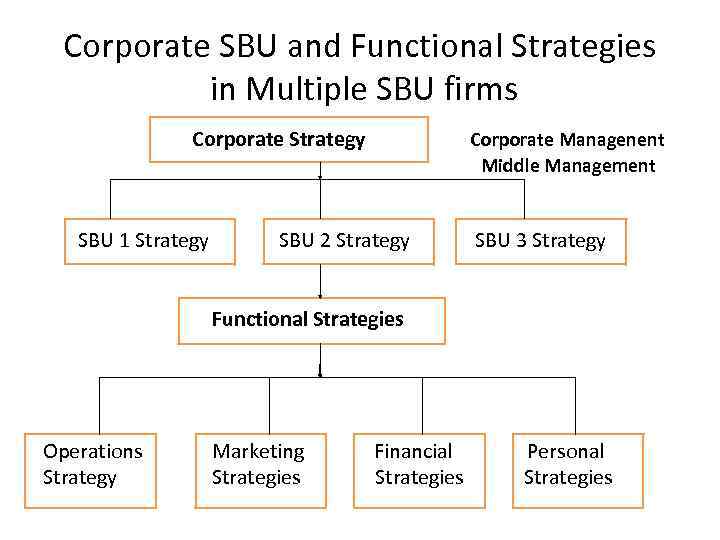 Corporate SBU and Functional Strategies in Multiple SBU firms Corporate Strategy SBU 1 Strategy Corporate Managenent Middle Management SBU 2 Strategy SBU 3 Strategy Functional Strategies Operations Strategy Marketing Strategies Financial Strategies Personal Strategies
Corporate SBU and Functional Strategies in Multiple SBU firms Corporate Strategy SBU 1 Strategy Corporate Managenent Middle Management SBU 2 Strategy SBU 3 Strategy Functional Strategies Operations Strategy Marketing Strategies Financial Strategies Personal Strategies
 Types of Corporate Strategy Four types of grand strategies: • Stability Strategy • Expansion Strategy • Retrenchment Strategy • Combination Strategies
Types of Corporate Strategy Four types of grand strategies: • Stability Strategy • Expansion Strategy • Retrenchment Strategy • Combination Strategies
 Stability Strategy • It is adopted by an organization when it attempts to improve functional performance. They are further classified as: • No change strategy • Profit strategy • Pause/Proceed with caution strategy
Stability Strategy • It is adopted by an organization when it attempts to improve functional performance. They are further classified as: • No change strategy • Profit strategy • Pause/Proceed with caution strategy
 Expansion Strategy • It is followed when an organization aims at high growth. They operate through – • • • Concentration Integration Diversification Cooperation Internationalization
Expansion Strategy • It is followed when an organization aims at high growth. They operate through – • • • Concentration Integration Diversification Cooperation Internationalization
 Retrenchment Strategy It is followed when an organization aims at a contraction of its activities. It is done through turnaround, disinvestment and liquidation in either of the following three modes: • Compulsory winding up • Voluntary winding up • Winding up under supervision of the court
Retrenchment Strategy It is followed when an organization aims at a contraction of its activities. It is done through turnaround, disinvestment and liquidation in either of the following three modes: • Compulsory winding up • Voluntary winding up • Winding up under supervision of the court
 Combination Strategies It is followed when an organization adopts a combination of stability, expansion and retrenchment either at the same time in different businesses or at different times in the same business.
Combination Strategies It is followed when an organization adopts a combination of stability, expansion and retrenchment either at the same time in different businesses or at different times in the same business.
 Significance of Corporate Strategy • It rationalizes allocation of scarce resources. • It motivates employees examples to share their work in the context of shared corporate goals. • It assists management to meet unanticipated future changes. • Organizational effectiveness is ensured through implementing and evaluating the strategy. • Strategy planning system provides an objective basis for measuring performance. • It encourages management to choose the best course of action to realize the objectives.
Significance of Corporate Strategy • It rationalizes allocation of scarce resources. • It motivates employees examples to share their work in the context of shared corporate goals. • It assists management to meet unanticipated future changes. • Organizational effectiveness is ensured through implementing and evaluating the strategy. • Strategy planning system provides an objective basis for measuring performance. • It encourages management to choose the best course of action to realize the objectives.
 Limitation of Corporate Strategy • Process of forming the corporate strategy is complex, cumbersome and complicated. • They are useful for long range problems. • They are not effective to overcome current exigencies. • Developing appropriate strategy is not simple and economical proposition. • As future is uncertain and can not be predicted accurately, the strategic planning system based on hazy and uncertain estimated is not exact.
Limitation of Corporate Strategy • Process of forming the corporate strategy is complex, cumbersome and complicated. • They are useful for long range problems. • They are not effective to overcome current exigencies. • Developing appropriate strategy is not simple and economical proposition. • As future is uncertain and can not be predicted accurately, the strategic planning system based on hazy and uncertain estimated is not exact.
 What is Strategy? • Strategy is the direction and scope of an organization over the long term, which achieves advantage in a changing environment through its configuration of resources and competences with the aim of fulfilling stakeholder expectations.
What is Strategy? • Strategy is the direction and scope of an organization over the long term, which achieves advantage in a changing environment through its configuration of resources and competences with the aim of fulfilling stakeholder expectations.
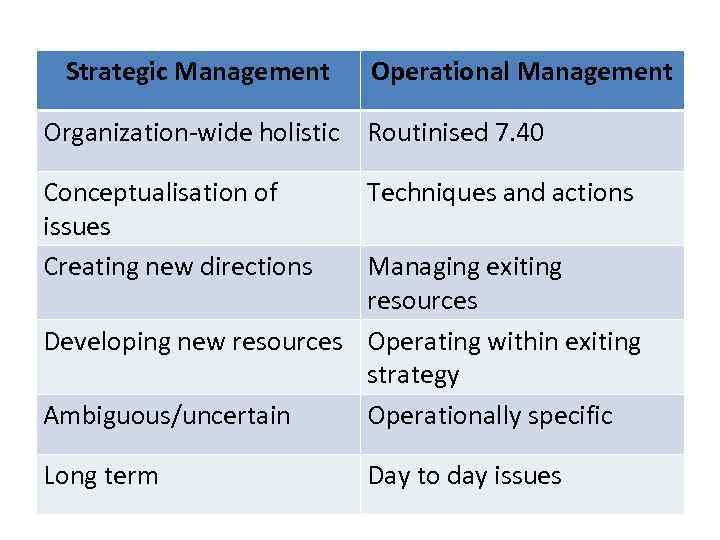 Strategic Management Operational Management Organization-wide holistic Routinised 7. 40 Conceptualisation of issues Creating new directions Techniques and actions Long term Day to day issues Managing exiting resources Developing new resources Operating within exiting strategy Ambiguous/uncertain Operationally specific
Strategic Management Operational Management Organization-wide holistic Routinised 7. 40 Conceptualisation of issues Creating new directions Techniques and actions Long term Day to day issues Managing exiting resources Developing new resources Operating within exiting strategy Ambiguous/uncertain Operationally specific
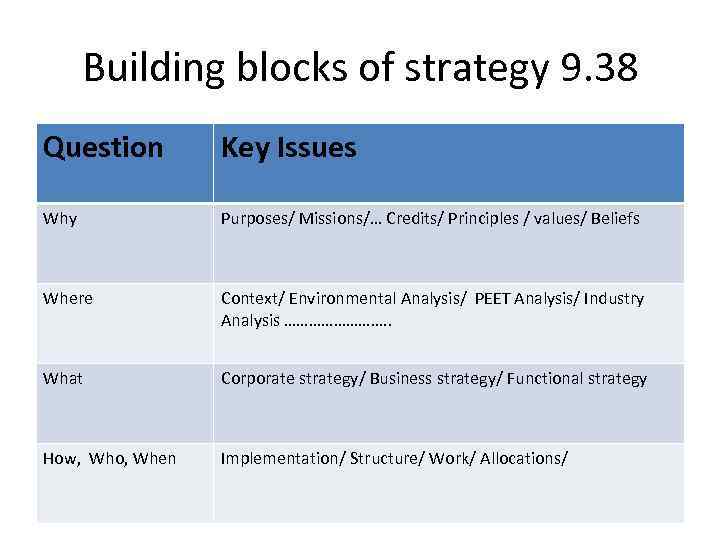 Building blocks of strategy 9. 38 Question Key Issues Why Purposes/ Missions/… Credits/ Principles / values/ Beliefs Where Context/ Environmental Analysis/ PEET Analysis/ Industry Analysis …………. . What Corporate strategy/ Business strategy/ Functional strategy How, Who, When Implementation/ Structure/ Work/ Allocations/
Building blocks of strategy 9. 38 Question Key Issues Why Purposes/ Missions/… Credits/ Principles / values/ Beliefs Where Context/ Environmental Analysis/ PEET Analysis/ Industry Analysis …………. . What Corporate strategy/ Business strategy/ Functional strategy How, Who, When Implementation/ Structure/ Work/ Allocations/
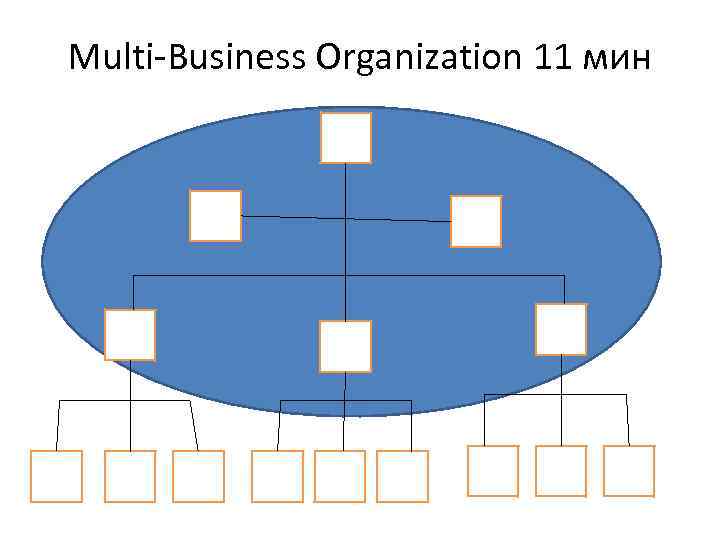 Multi-Business Organization 11 мин
Multi-Business Organization 11 мин
 Levels of Strategy • Corporate Strategy • Business Strategy • Functional Strategy
Levels of Strategy • Corporate Strategy • Business Strategy • Functional Strategy
 Corporate Strategy Issues • Rational for the Portfolio What business to be in their characteristic? Portfolio Rationalization (Matrix / Core Competency? ) • Growth – M&As greenfield – Means of getting there • Managing the Business – Parenting
Corporate Strategy Issues • Rational for the Portfolio What business to be in their characteristic? Portfolio Rationalization (Matrix / Core Competency? ) • Growth – M&As greenfield – Means of getting there • Managing the Business – Parenting
 Rational for the Portfolio • What business to be in their characteristic? • GE: Industry Leadership for individual businesses and profitability • Tatas: Decision to be in Seven Core Areas
Rational for the Portfolio • What business to be in their characteristic? • GE: Industry Leadership for individual businesses and profitability • Tatas: Decision to be in Seven Core Areas
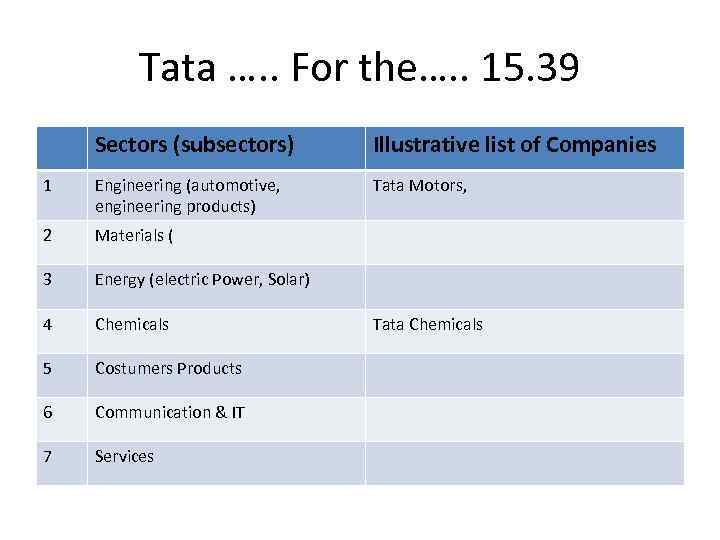 Tata …. . For the…. . 15. 39 Sectors (subsectors) Illustrative list of Companies 1 Engineering (automotive, engineering products) Tata Motors, 2 Materials ( 3 Energy (electric Power, Solar) 4 Chemicals 5 Costumers Products 6 Communication & IT 7 Services Tata Chemicals
Tata …. . For the…. . 15. 39 Sectors (subsectors) Illustrative list of Companies 1 Engineering (automotive, engineering products) Tata Motors, 2 Materials ( 3 Energy (electric Power, Solar) 4 Chemicals 5 Costumers Products 6 Communication & IT 7 Services Tata Chemicals
 Portfolio Analysis • Each business has different financial characteristics • They offer different strategy options • Examine them separately • The only extent of the-up between business would be for Cash flow from one to another • The transfer depends upon whether the recipient designed for market share expansion
Portfolio Analysis • Each business has different financial characteristics • They offer different strategy options • Examine them separately • The only extent of the-up between business would be for Cash flow from one to another • The transfer depends upon whether the recipient designed for market share expansion
 Two Considerations • Growth of the business (prospects of industry) What is the rate of growth of the industry • Relative Market share (strength of the SBU) Relative Market Position (Share of the SBU Share of the largest other competitor)
Two Considerations • Growth of the business (prospects of industry) What is the rate of growth of the industry • Relative Market share (strength of the SBU) Relative Market Position (Share of the SBU Share of the largest other competitor)
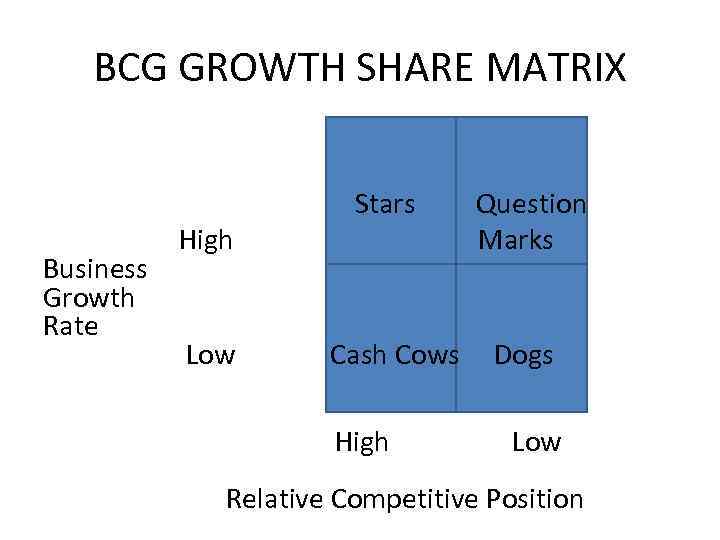 BCG GROWTH SHARE MATRIX Business Growth Rate High Low Stars Cash Cows High Question Marks Dogs Low Relative Competitive Position
BCG GROWTH SHARE MATRIX Business Growth Rate High Low Stars Cash Cows High Question Marks Dogs Low Relative Competitive Position
 Business Strategy • Cash Cows: insist of high profitability, least capital spending, tight financial for cost leadership • Stars: Plough back returns towards capital spending to maintain share, built for future • Question marks: Identify which would become stars (and invest in market share) and which dogs (insist of minimum returns and divest opportunistically) • Dogs: No capital spending, be aware of any cross subsidy, insist of minimum returns, divest away ASAP
Business Strategy • Cash Cows: insist of high profitability, least capital spending, tight financial for cost leadership • Stars: Plough back returns towards capital spending to maintain share, built for future • Question marks: Identify which would become stars (and invest in market share) and which dogs (insist of minimum returns and divest opportunistically) • Dogs: No capital spending, be aware of any cross subsidy, insist of minimum returns, divest away ASAP
 Corporate Strategy • Evolve separate business strategies for each business. • Try evolving the mix towards having big cash caws and having the stars who will in turn become cash cows in future. • Similarly have some questions marks that will turn out to be Stars at some later date. • Divest selected question marks and dogs when opportunity arrives. • Keep a healthy mix with the eye on the future.
Corporate Strategy • Evolve separate business strategies for each business. • Try evolving the mix towards having big cash caws and having the stars who will in turn become cash cows in future. • Similarly have some questions marks that will turn out to be Stars at some later date. • Divest selected question marks and dogs when opportunity arrives. • Keep a healthy mix with the eye on the future.
 BCG-Type Matrix-Advantages • Tells what to do with different businesses • Allows for tracking changes. Can be used a control mechanism • Sends the message that differential performance of Businesses can only be expected • Allows for balance in terms of cash flow management
BCG-Type Matrix-Advantages • Tells what to do with different businesses • Allows for tracking changes. Can be used a control mechanism • Sends the message that differential performance of Businesses can only be expected • Allows for balance in terms of cash flow management
 BCG-Type Matrix-Disadvantages • It tells you what to do with existing businesses. Is does not tell what to acquire. • It ignores synergy. Assumes no tie-ins between businesses. • It does not take into account the need for balancing the portfolio and diversifying risk.
BCG-Type Matrix-Disadvantages • It tells you what to do with existing businesses. Is does not tell what to acquire. • It ignores synergy. Assumes no tie-ins between businesses. • It does not take into account the need for balancing the portfolio and diversifying risk.
 Modifications to BCG-Type Matrix Models • Map potential companies that could be acquired • Develop a separate matrix that shows how the businesses are dependent upon each other. Be aware of these connections before suggesting any change in the portfolio / divestment. • Ask whether balancing is one of the objectives. If yes connect up these businesses like above.
Modifications to BCG-Type Matrix Models • Map potential companies that could be acquired • Develop a separate matrix that shows how the businesses are dependent upon each other. Be aware of these connections before suggesting any change in the portfolio / divestment. • Ask whether balancing is one of the objectives. If yes connect up these businesses like above.
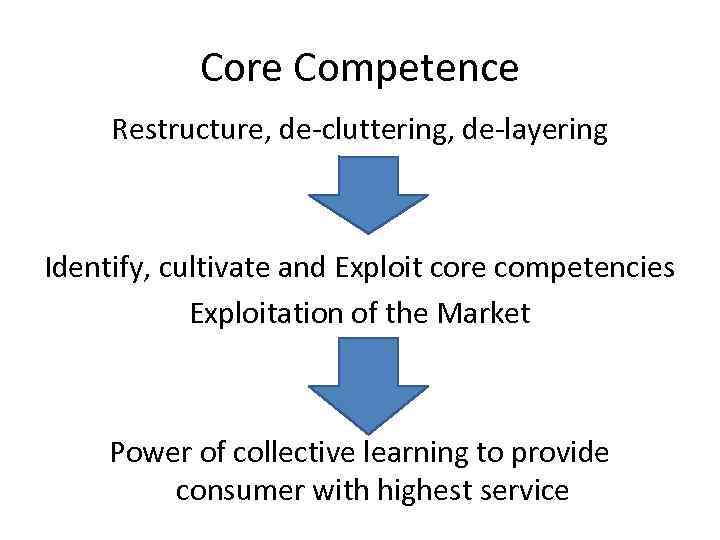 Core Competence Restructure, de-cluttering, de-layering Identify, cultivate and Exploit core competencies Exploitation of the Market Power of collective learning to provide consumer with highest service
Core Competence Restructure, de-cluttering, de-layering Identify, cultivate and Exploit core competencies Exploitation of the Market Power of collective learning to provide consumer with highest service
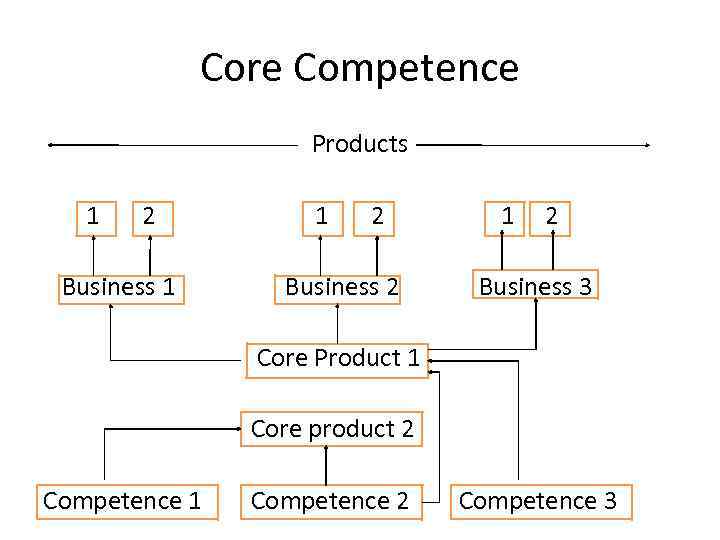 Core Competence Products 1 2 Business 1 1 2 Business 2 1 2 Business 3 Core Product 1 Core product 2 Competence 1 Competence 2 Competence 3
Core Competence Products 1 2 Business 1 1 2 Business 2 1 2 Business 3 Core Product 1 Core product 2 Competence 1 Competence 2 Competence 3
 Example of Core Competence -1 3 M • End Products: Post in notes, magnetic tape, Photographic film • Businesses: Office Stationary, Industrial abrasives • Core product: Surface coasted materials • Competencies: 1) Substrate materials (material technology) 2) Coasting technology
Example of Core Competence -1 3 M • End Products: Post in notes, magnetic tape, Photographic film • Businesses: Office Stationary, Industrial abrasives • Core product: Surface coasted materials • Competencies: 1) Substrate materials (material technology) 2) Coasting technology
 Example of Core Competence – 2 Honda • End Products: High and Low end cars (from Automobile business), Range of two wheelers etc. • Business: Automobiles, Small generators • Core product: Petrol Engine, Small-sized Diesel Engines, Transmission Assembly • Competencies: 1) Internal Combustion Engines, Material technology, 2)Coatings, 3)Multi-Fuel systems
Example of Core Competence – 2 Honda • End Products: High and Low end cars (from Automobile business), Range of two wheelers etc. • Business: Automobiles, Small generators • Core product: Petrol Engine, Small-sized Diesel Engines, Transmission Assembly • Competencies: 1) Internal Combustion Engines, Material technology, 2)Coatings, 3)Multi-Fuel systems
 Core Competence – the Acid Tests • Core competence provides potential access to a wide variety of markets • The CC should provide significant contribution to the perceived customer benefits • CC should be difficult for the customer to imitate
Core Competence – the Acid Tests • Core competence provides potential access to a wide variety of markets • The CC should provide significant contribution to the perceived customer benefits • CC should be difficult for the customer to imitate
 Means of Growth strategy Results of M&A Greater Market Share Greenfied Horizontal M&A Vertical M&A Related M&A Unrelated M&A Long term contacts Vertically integrated Corporate conglomerates
Means of Growth strategy Results of M&A Greater Market Share Greenfied Horizontal M&A Vertical M&A Related M&A Unrelated M&A Long term contacts Vertically integrated Corporate conglomerates
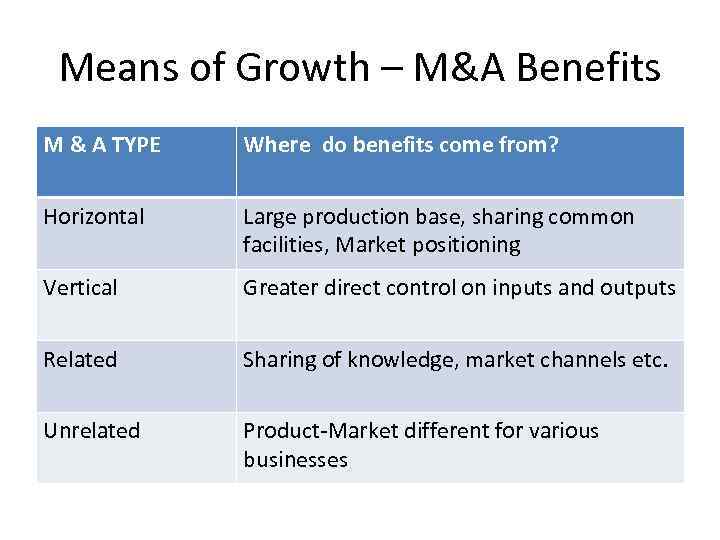 Means of Growth – M&A Benefits M & A TYPE Where do benefits come from? Horizontal Large production base, sharing common facilities, Market positioning Vertical Greater direct control on inputs and outputs Related Sharing of knowledge, market channels etc. Unrelated Product-Market different for various businesses
Means of Growth – M&A Benefits M & A TYPE Where do benefits come from? Horizontal Large production base, sharing common facilities, Market positioning Vertical Greater direct control on inputs and outputs Related Sharing of knowledge, market channels etc. Unrelated Product-Market different for various businesses
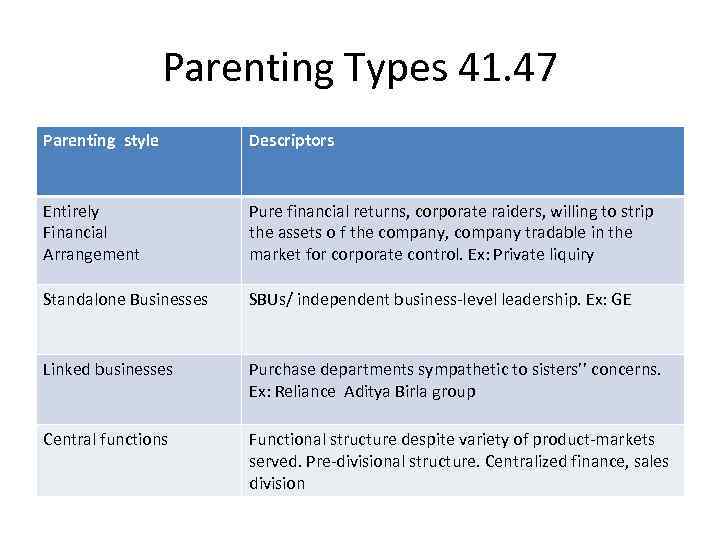 Parenting Types 41. 47 Parenting style Descriptors Entirely Financial Arrangement Pure financial returns, corporate raiders, willing to strip the assets o f the company, company tradable in the market for corporate control. Ex: Private liquiry Standalone Businesses SBUs/ independent business-level leadership. Ex: GE Linked businesses Purchase departments sympathetic to sisters’’ concerns. Ex: Reliance Aditya Birla group Central functions Functional structure despite variety of product-markets served. Pre-divisional structure. Centralized finance, sales division
Parenting Types 41. 47 Parenting style Descriptors Entirely Financial Arrangement Pure financial returns, corporate raiders, willing to strip the assets o f the company, company tradable in the market for corporate control. Ex: Private liquiry Standalone Businesses SBUs/ independent business-level leadership. Ex: GE Linked businesses Purchase departments sympathetic to sisters’’ concerns. Ex: Reliance Aditya Birla group Central functions Functional structure despite variety of product-markets served. Pre-divisional structure. Centralized finance, sales division


