1f6d9763a69532a194cb945b6bc6939d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Concept of Knowledge Management and Process Documentation: Types and skills of process documentation Dr. A. K. Bhattacharyya Professor EEI(NE Region), AAU, Jorhat
Concept of Knowledge Management and Process Documentation: Types and skills of process documentation Dr. A. K. Bhattacharyya Professor EEI(NE Region), AAU, Jorhat
 Knowledge Management n Systematic Management of an organization’s knowledge assets for the purpose of creating value and meeting tactical and strategic requirements n It consists of the initiatives, processes, strategies and systems that sustains and enhances the storage, assessment, sharing, refinement and creation of knowledge
Knowledge Management n Systematic Management of an organization’s knowledge assets for the purpose of creating value and meeting tactical and strategic requirements n It consists of the initiatives, processes, strategies and systems that sustains and enhances the storage, assessment, sharing, refinement and creation of knowledge
 AKIS n In agricultural sector, AKIS is the best example that links people and institutions to promote mutual learning and generate, share and utilize agricultural related technology, knowledge and information n integrates farmers, agricultural educators, researchers and experiments, to harness knowledge and information from various sources for better farming and improved livelihoods.
AKIS n In agricultural sector, AKIS is the best example that links people and institutions to promote mutual learning and generate, share and utilize agricultural related technology, knowledge and information n integrates farmers, agricultural educators, researchers and experiments, to harness knowledge and information from various sources for better farming and improved livelihoods.
 Process documentation n Systematic way of capturing what happens in a process of change and to organize and disseminate the finding. n Process documentation helps project staff and stakeholders to track meaningful events in their project to discern more accurately what is happening, how it is happening and why it is happening.
Process documentation n Systematic way of capturing what happens in a process of change and to organize and disseminate the finding. n Process documentation helps project staff and stakeholders to track meaningful events in their project to discern more accurately what is happening, how it is happening and why it is happening.
 What is Documentation? The process of systematically collecting, organizing, storing, retrieving, and disseminating information. Output of documentation can be written, visual and audio information about an object, a practice, a product or an event.
What is Documentation? The process of systematically collecting, organizing, storing, retrieving, and disseminating information. Output of documentation can be written, visual and audio information about an object, a practice, a product or an event.
 Types of Documentation n n Annual Reports: A printed publication, submitted each year by the officers of a publicly held company or organisation to its governing body Books: A set of pages that have been fastened together inside a cover to be read or written in. Case Study: A detailed account giving information about the development of a person, group or thing, in order to show general principles Digest: A collection of previously published material, such as articles, essays, or reports, usually in edited or condensed form. Directories: A book which gives a list of names, addresses or other facts
Types of Documentation n n Annual Reports: A printed publication, submitted each year by the officers of a publicly held company or organisation to its governing body Books: A set of pages that have been fastened together inside a cover to be read or written in. Case Study: A detailed account giving information about the development of a person, group or thing, in order to show general principles Digest: A collection of previously published material, such as articles, essays, or reports, usually in edited or condensed form. Directories: A book which gives a list of names, addresses or other facts
 n n n n Guide: A book which gives you important information about a particular subject Handbooks: A book which contains instructions or advice about how to do something or the most important and useful information about a subject Journal: A serious magazine which is published regularly, usually about a specialist subject Manual: A book which gives you practical instructions on how to do something or how to use something. Newsletter or Bulletin: A printed document containing information about the recent activities of an organization, which is sent regularly to the organization's members Occasional Papers: Information Published on an event Pamphlet: A thin book with only a few pages which gives information or an opinion about something
n n n n Guide: A book which gives you important information about a particular subject Handbooks: A book which contains instructions or advice about how to do something or the most important and useful information about a subject Journal: A serious magazine which is published regularly, usually about a specialist subject Manual: A book which gives you practical instructions on how to do something or how to use something. Newsletter or Bulletin: A printed document containing information about the recent activities of an organization, which is sent regularly to the organization's members Occasional Papers: Information Published on an event Pamphlet: A thin book with only a few pages which gives information or an opinion about something
 n n n n Policy Briefings: A document which outlines the rationale for choosing a particular policy alternative or course of action. Position paper: A summary of a country's position on a topic Reports: (Project Reports, Research Reports, and Technical reports)- A formatted and organized presentation of data. Training Calendar: A document which gives total training programmes of an organisation in a calendar year. Working Papers: Working Papers are pre-publication versions of academic articles, book chapters, or reviews. Yearbooks: A book published every year by an organization, that gives various facts about the events and achievements of the previous or present year. Success Story: An account of achievement of something desired, planned, or attempted.
n n n n Policy Briefings: A document which outlines the rationale for choosing a particular policy alternative or course of action. Position paper: A summary of a country's position on a topic Reports: (Project Reports, Research Reports, and Technical reports)- A formatted and organized presentation of data. Training Calendar: A document which gives total training programmes of an organisation in a calendar year. Working Papers: Working Papers are pre-publication versions of academic articles, book chapters, or reviews. Yearbooks: A book published every year by an organization, that gives various facts about the events and achievements of the previous or present year. Success Story: An account of achievement of something desired, planned, or attempted.
 What to Document? n Who, where, what, when n Who all are involved, what exactly, when and where can you observe, why is it not happening, what is behind the surface, where the project life line makes the sharpest curves etc
What to Document? n Who, where, what, when n Who all are involved, what exactly, when and where can you observe, why is it not happening, what is behind the surface, where the project life line makes the sharpest curves etc
 How to Document? Observation of Meetings n Personal interviews n Focus group discussions n Documentation of anecdotes and stories n Diaries of project team members and/or stakeholders n Photography and Video n
How to Document? Observation of Meetings n Personal interviews n Focus group discussions n Documentation of anecdotes and stories n Diaries of project team members and/or stakeholders n Photography and Video n
 Disseminating channels Posters n Newsletters n Photographs n Videos n Blogs n
Disseminating channels Posters n Newsletters n Photographs n Videos n Blogs n
 n Summaries of meetings Success stories n Case studies n Radio/ TV programmes n Websites n
n Summaries of meetings Success stories n Case studies n Radio/ TV programmes n Websites n
 Written materials Keeping written materials short and presenting them well, with pictures, gives them a better chance of being appreciated and read.
Written materials Keeping written materials short and presenting them well, with pictures, gives them a better chance of being appreciated and read.
 Web blogs, wikis, discussion forums n Blogs n collaborative editing (wikis), n Much of the knowledge creation and sharing is carried out through a process of discussion with questions and answers (discussion forum).
Web blogs, wikis, discussion forums n Blogs n collaborative editing (wikis), n Much of the knowledge creation and sharing is carried out through a process of discussion with questions and answers (discussion forum).
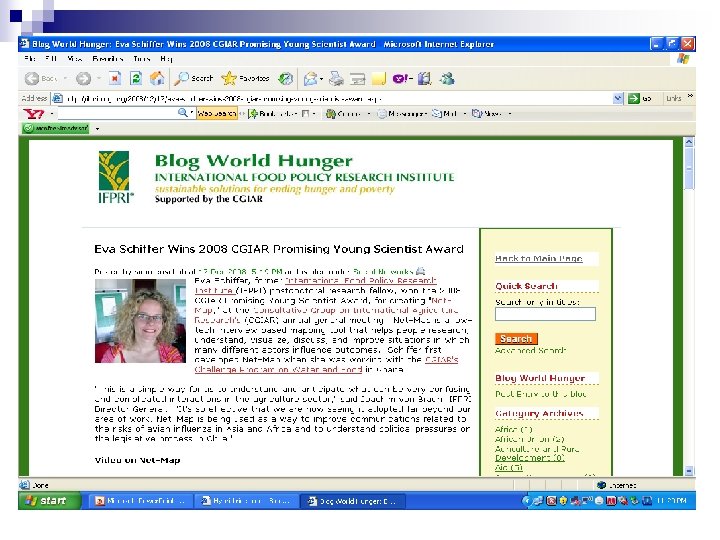
 Blogs n n Blog or "web log, ” is a site where contributors can post news, thoughts, comments, reflections etc. It is maintained by an individual with regular entries of commentary, descriptions of events, or other material such as graphics or video. ” Entries in a blog are commonly displayed in reversechronological order. A typical blog combines text, images, and links to other blogs, web pages, and other media related to its topic. A key feature is that it allows people to post comments to another person's blog.
Blogs n n Blog or "web log, ” is a site where contributors can post news, thoughts, comments, reflections etc. It is maintained by an individual with regular entries of commentary, descriptions of events, or other material such as graphics or video. ” Entries in a blog are commonly displayed in reversechronological order. A typical blog combines text, images, and links to other blogs, web pages, and other media related to its topic. A key feature is that it allows people to post comments to another person's blog.
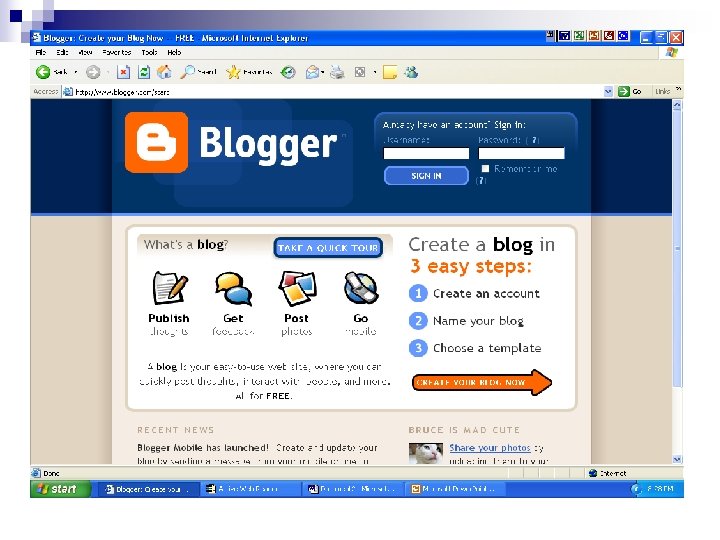
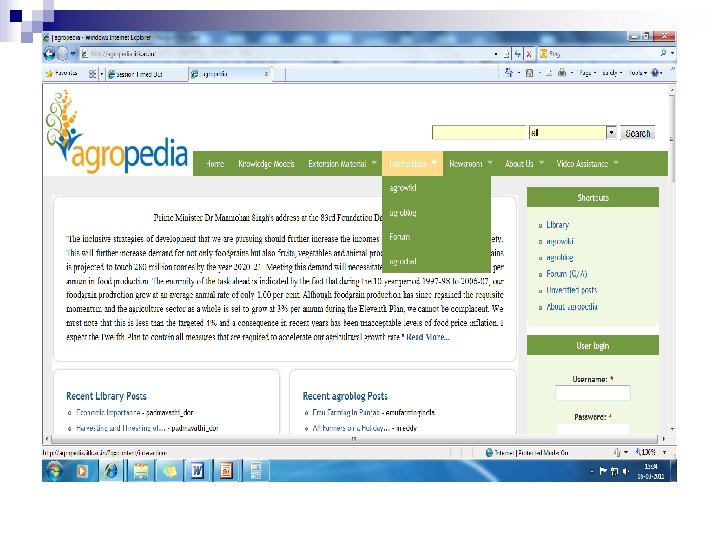
 Wiki n n Wikis are Web pages or sites where content can be added, edited and maintained by several people. Eg. Wikipedia http//en. wikipedia. org/wiki. It is an interactive and collaborative website. Registered users can add tools and methods, content, edit existing pages, insert comments and anecdotes. Documents can be written collaboratively
Wiki n n Wikis are Web pages or sites where content can be added, edited and maintained by several people. Eg. Wikipedia http//en. wikipedia. org/wiki. It is an interactive and collaborative website. Registered users can add tools and methods, content, edit existing pages, insert comments and anecdotes. Documents can be written collaboratively
 photos, on screen sub-titles and a soundtrack can be used to tell a story on You. Tube www. youtube. com n n Videos capturing stories on Digital. Green http: //www. digitalgreen. org/
photos, on screen sub-titles and a soundtrack can be used to tell a story on You. Tube www. youtube. com n n Videos capturing stories on Digital. Green http: //www. digitalgreen. org/
 Who Documents? Insiders – the project team Direct stakeholders Outsiders
Who Documents? Insiders – the project team Direct stakeholders Outsiders
 Skills § Writing skills § Editing § Convert information into stories that people like to read § Producing newsletter, posters etc.
Skills § Writing skills § Editing § Convert information into stories that people like to read § Producing newsletter, posters etc.
 Elements of Documentation n n Clarity on the subject and overall objective (what/why) Complete understanding of the programme information (aim, time period, location, resources, actors, process, end results) Familiarity with various tools and techniques for generating information (FGD, Interviews, etc) Selection of appropriate medium (written, audio, video), format, style as per the context Good facilitation skills
Elements of Documentation n n Clarity on the subject and overall objective (what/why) Complete understanding of the programme information (aim, time period, location, resources, actors, process, end results) Familiarity with various tools and techniques for generating information (FGD, Interviews, etc) Selection of appropriate medium (written, audio, video), format, style as per the context Good facilitation skills
 Good Writing vs. Bad Writing n n n n Good writing is clear, compelling, logically organized, precise, and interesting. Bad writing is opaque, unconvincing, disorderly, vague, and boring. Rules of good writing: Know your message. What are the most important things that you want your reader to come away with? Know your audience. What base of knowledge do you share? What do they already know, and what is it your job to explain? Present a connected argument. Does each sentence build logically on the previous one? Does each paragraph deal with a single central idea? Be precise. Have you said exactly what you meant to say, or just something Be interesting. Are you using language in a reader-friendly way?
Good Writing vs. Bad Writing n n n n Good writing is clear, compelling, logically organized, precise, and interesting. Bad writing is opaque, unconvincing, disorderly, vague, and boring. Rules of good writing: Know your message. What are the most important things that you want your reader to come away with? Know your audience. What base of knowledge do you share? What do they already know, and what is it your job to explain? Present a connected argument. Does each sentence build logically on the previous one? Does each paragraph deal with a single central idea? Be precise. Have you said exactly what you meant to say, or just something Be interesting. Are you using language in a reader-friendly way?
 How to write for different target group? n For scientists: ¨ The wolf spider is an effective predator of certain rice pests n For farmers: ¨ Wolf spiders are friends. They hunt and kill insects that harm the rice plant.
How to write for different target group? n For scientists: ¨ The wolf spider is an effective predator of certain rice pests n For farmers: ¨ Wolf spiders are friends. They hunt and kill insects that harm the rice plant.
 n He initiated and facilitated in the conduct of meetings and workshops. . . n He helped conduct meetings. . .
n He initiated and facilitated in the conduct of meetings and workshops. . . n He helped conduct meetings. . .
 THANKS
THANKS


