9- Обмен веществ и энергии.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

Concept about a metabolism and energy. Main exchange. Lecture plan: Absorption of substances in various departments of a digestive tract. Types and absorption mechanism. The general concept about a metabolism and energy. Main exchange. Power "a working exchange". Methods of studying of an exchange of energy. Straight line and indirect calorimetry.

The general concept about a metabolism and energy The metabolism and energy is a set of physical, chemical and physiological processes of transformation of substances and energy in a human body. Distinguish 4 stages of a metabolism: Hydrolysis of feedstuffs in a digestive tract – fermentativny splitting of nutrients. Absorption of the final products of hydrolysis in blood and a lymph. Transport nutritious and O 2 in a cage – an intracellular metabolism and energy. Allocation of the final products of a metabolism.

In a metabolism and energy emit two interconnected, but multidirectional process: anabolism (assimilation) and catabolism (dissimilation). In the course of a metabolism there is an energy transformation: potential energy of the difficult organic compounds which have arrived with food, turns in thermal, mechanical, electric. In a healthy organism the balance between power education and power expenditure (the law of conservation of energy) remains

In a metabolism and energy emit two interconnected, but multidirectional process: anabolism (assimilation) and catabolism (dissimilation). In the course of a metabolism there is an energy transformation: potential energy of the difficult organic compounds which have arrived with food, turns in thermal, mechanical, electric. In a healthy organism the balance between power education and power expenditure (the law of conservation of energy) remains

The energy which was released in the course of biological oxidation is used for: ATF synthesis Mechanical work Chemical synthesis Transport of substances Osmotic and electric work Body temperature maintenance Ensuring activity, growth and organism development, etc. The energy formed in an organism, can be expressed in terms of heat – calories or joules (SI system)

Role of nutrients and their physiological norms ►A food - process of receipt of digestion, absorption and assimilation in an organism of feedstuffs (нутриентов), necessary for covering plastic and power needs of an organism, formation of physiologically active agents. ► Makronutriyenta (proteins, carbohydrates, lipids) at their oxidation the energy necessary for all processes of activity of an organism is released.

► Exchange of proteins ► The main source of protein for an organism – protein of food. ► Value of proteins: ► Plastic role - from protein are filled or again structural components of a cage are formed. ► The power - use of energy of the protein which is forming at their splitting ► Motive function (актин, myosin). ► Fermentativny function (enzymes - the proteins providing the main functions of an organism: breath, пище 6 варение, allocation.

Physiological norm: 90 -100 g per day. From 20 amino acids which are a part of proteins of an organism 12 are synthesized in an organism, 8 aren't synthesized (irreplaceable amino acids: methine, lysine, threonine and B'day). ► In an organism nitrogen contains in proteins. (I. e. its receipt and removal) it is possible to judge a protein exchange in size of the arrived and emitted nitrogen. The ratio of amount of the nitrogen arrived with food and emitted with urine and then, is called as nitrogenous balance. ► The adult has an amount of the nitrogen entered into an organism equally to amount of the nitrogen removed from an organism. - the nitrogenous balance remains. The positive nitrogenous balance - synthesis of protein prevails over disintegration (at children). The negative nitrogenous balance – allocation of nitrogen exceeds its receipt (at insufficient a food - the strengthened disintegration of proteins in an organism. ► Regulation of a proteinaceous exchange - the regulation Centers in kernels гипоталамуса. The sympathetic nervous system strengthens protein dissimilation. Parasympathetic strengthens synthesis of a squirrel. Strengthen synthesis of proteins – STG, трийодтироксин, thyroxine ►

► Exchange ► The of carbohydrates main source of energy arrive in the form of Dee polysaccharides, are soaked up a type of monosaccharides. In a liver from glucose the glycogen is synthesized. At reduction of glucose of blood – disintegration глюкогена a liver amplifies. ► Regulation exchange of carbohydrates: The hyperglycemia causes irritation гипоталамуса and a cerebral cortex, influence realization through vegetative nerves. The sympathetic nervous system strengthens glycogen-glikoliz disintegration. The parasympathetic nervous system strengthens glycogen synthesis from glucose

► Fat exchange ► Plastic, power role. Fats are soaked up from intestines in a lymph and blood in the form of glycerin and fatty acids (forming micelles with bilious acids). ► Regulation are carried out the gipotalamusy. Disintegration of fats happens under the influence of adrenaline, STG noradrenaline, and тироксина the Irritation of sympathetic nervous system – strengthens fat disintegration. ► The parasympathetic – promotes fat adjournment.

► The food consists of many components, proteins, fats, carbohydrates, macro - and microcells, vitamins, phytoncide and food fibers. A rational food is a food which satisfies energy, plastic and other needs of an organism and provides necessary level of an exchange. ► Main components of a balanced diet: ► 1) Balance ► 2) Diet ► 3) Power balance

Daily physiological norms of feedstuffs for the vrosly population: ► Belki- 80 -100 g a squirrel (not mey 1 g of protein on 1 kg of weight of a body) including % animal protein -55 ► Lipidy- 80 -100 g. (50 -60% animal fat, 30 -40% vegetable) ► Uglevody- 400 -500 g. ► Ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates: B: Zh: U-1: 1: 4, 6

Main exchange. Power "a working exchange" The main exchange – a minimum level of energy consumption for maintenance of activity of an organism in the conditions of rather absolute physical and emotional rest. Definition of the main exchange carry out in standard conditions: in the morning – on an empty stomach in 12 -14 hours after meal. in a prone position – at the maximum relaxation of muscles. in the conditions of temperature comfort – 18 -22 os For the adult average value of the main exchange equally to 1 kcal/kg/h For the adult man weighing 70 kg, growth 165 -170, age 35 -16 size of the main exchange = 1700 kcal/days For women = 1500 kcal/days

Dependence of sizes of power expenditure on weight of loading defines "a working exchange". Depending on intensity of work for adult able-bodied population recommended average sizes of consumption of energy, nutrients per day are made.

Power expenses of an organism at various intensity physical rabotyrekomenduyemy average sizes of consumption of energy, nutrients per day. group Kind of activity 1 the workers of the brainwork who haven't been occupied with physical work: heads of the enterprises and organizations; technical officers; medical workers (except doctors-surgeons, nurses); teachers; tutors; workers of science and literature; press; account; clerks, etc. 22002800 2 the workers occupied with easy physical work: the technical officers which work is connected with some physical conditions; the workers occupied on automated productions; agronomists; livestock specialists; nurses; trainers, etc. 23003000 3 workers of an average on weight of work: machine operators, servicemen, doctors-surgeons; textile workers; employees of the food industry; drivers of a various type of transport; railroad workers; printers. nurses; trainers, etc. 25003200 4 workers of hard physical work: construction workers; agricultural workers and machine operators; miners; employees of the oil and gas industry; derevoobrabotchik; carpenters. 29003700 5 workers of hard physical work: miners; steelmakers, valshchik of the wood, bricklayers, concreters, navvies, loaders. 39004300 Power expendit ure, kcal/days

Methods of studying of an exchange of energy 1. Direct calorimetry – the direct accounting of quantity of heat allocated by an organism in a biocalorimeter (Etuotera-Benedict's camera). 2. Indirect calorimetry – heat generation definition in an organism on its gas exchange – the accounting of amount of consumed oxygen and emitted carbon dioxide with the subsequent calculation of the main exchange of an organism (a way of Douglas, an oksispirografiya).

For determination of these parameters calculate Respiratory coefficient – DK=SO 2 (volume allocated) O 2 (oby absorbed) Depends on character of food Dkdlya of proteins =0, 8 Dkdlya of carbohydrates =1, 0 Dkdlya of fats =0, 7 Dkpri mixed пище=0, 85 2) KEK – a caloric equivalent of O 2 is a quantity of energy which is emitted at the use 1 l of O 2. At the mixed food = 4, 865 kcal. 3) Caloric coefficient of nutrients. Caloric or thermal coefficient – the quantity of heat which is releasing at combustion of 1 g of substance
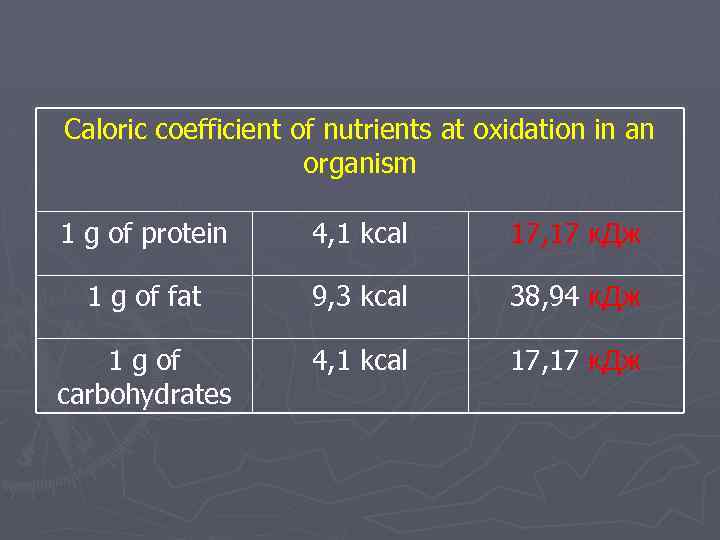
Caloric coefficient of nutrients at oxidation in an organism 1 g of protein 4, 1 kcal 17, 17 к. Дж 1 g of fat 9, 3 kcal 38, 94 к. Дж 1 g of carbohydrates 4, 1 kcal 17, 17 к. Дж
9- Обмен веществ и энергии.ppt