ca4a542d26635c3609809ba052e92581.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Computers: Information Technology in Perspective Larry Long & Nancy Long Computers: Information Technology in Perspective By Long and Long Copyright 2002 Prentice Hall, Inc.
Computers: Information Technology in Perspective Larry Long & Nancy Long Computers: Information Technology in Perspective By Long and Long Copyright 2002 Prentice Hall, Inc.
 Inside the Computer Chapter 3 Computers: Information Technology in Perspective By Long and Long Copyright 2002 Prentice Hall, Inc.
Inside the Computer Chapter 3 Computers: Information Technology in Perspective By Long and Long Copyright 2002 Prentice Hall, Inc.
 Be Informed ! ! 3 Quit And, make good decisions when purchasing a PC. Monthly Technolo gy Update
Be Informed ! ! 3 Quit And, make good decisions when purchasing a PC. Monthly Technolo gy Update
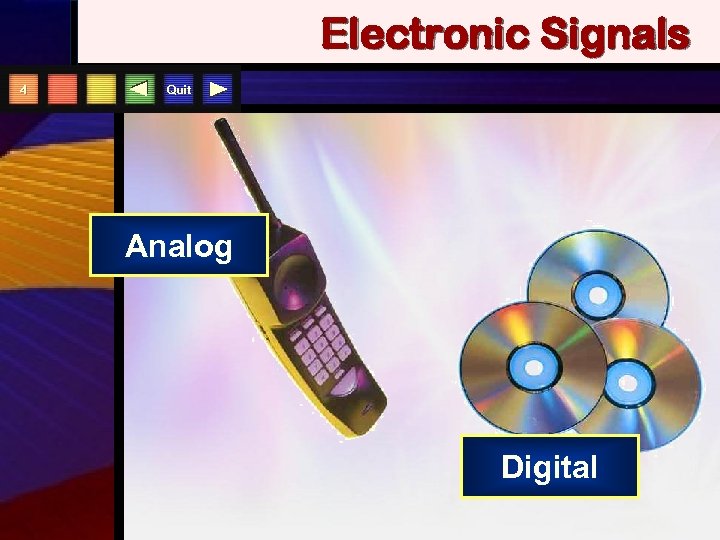 Electronic Signals 4 Quit Analog Digital
Electronic Signals 4 Quit Analog Digital
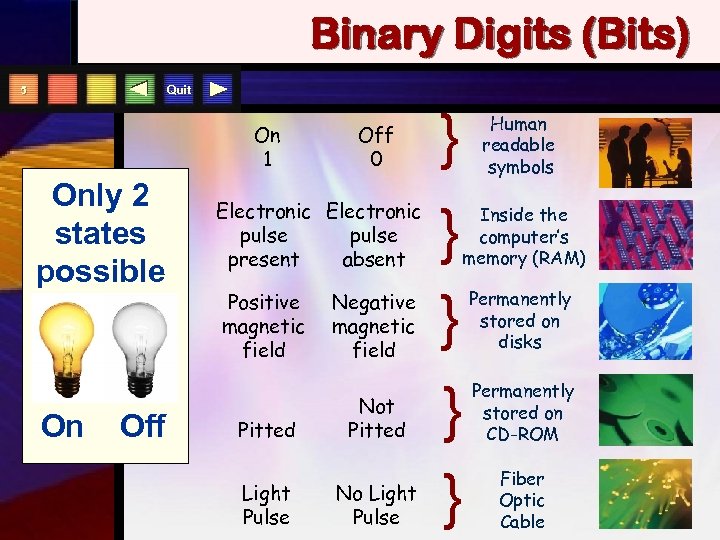 Binary Digits (Bits) Quit 5 On 1 Only 2 states possible On Off 0 Electronic pulse present absent Positive magnetic field Pitted Light Pulse Negative magnetic field Not Pitted No Light Pulse } } } Human readable symbols Inside the computer’s memory (RAM) } } Permanently stored on disks Permanently stored on CD-ROM Fiber Optic Cable
Binary Digits (Bits) Quit 5 On 1 Only 2 states possible On Off 0 Electronic pulse present absent Positive magnetic field Pitted Light Pulse Negative magnetic field Not Pitted No Light Pulse } } } Human readable symbols Inside the computer’s memory (RAM) } } Permanently stored on disks Permanently stored on CD-ROM Fiber Optic Cable
 Digitizing Data 6 Quit Digital Analog 001 0 111 100 00
Digitizing Data 6 Quit Digital Analog 001 0 111 100 00
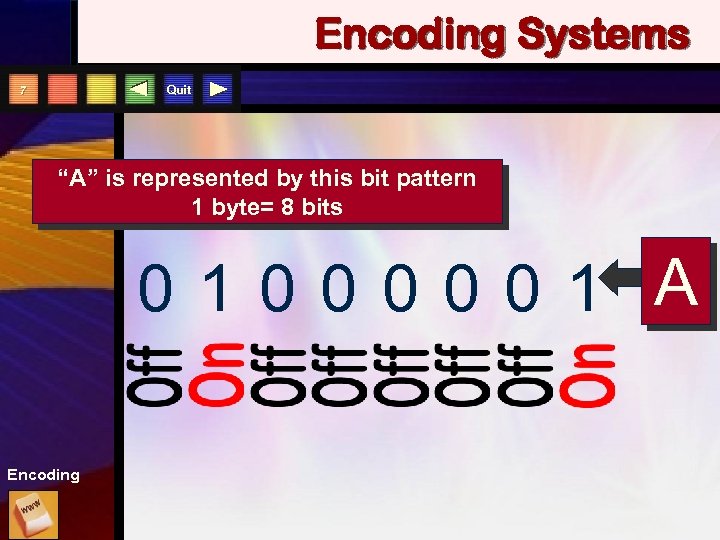 Encoding Systems Quit 7 “A” is represented by this bit pattern 1 byte= 8 bits 01000001 A Encoding
Encoding Systems Quit 7 “A” is represented by this bit pattern 1 byte= 8 bits 01000001 A Encoding
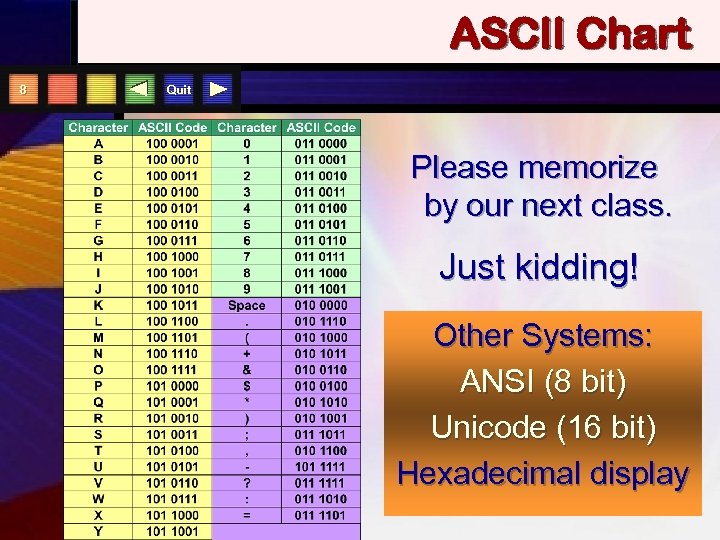 ASCII Chart 8 Quit Please memorize by our next class. Just kidding! Other Systems: ANSI (8 bit) Unicode (16 bit) Hexadecimal display
ASCII Chart 8 Quit Please memorize by our next class. Just kidding! Other Systems: ANSI (8 bit) Unicode (16 bit) Hexadecimal display
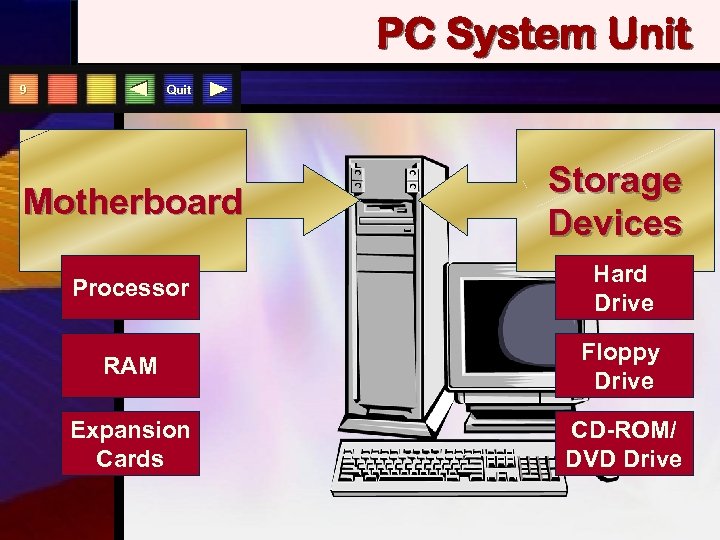 PC System Unit Quit 9 Motherboard Storage Devices Processor Hard Drive RAM Floppy Drive Expansion Cards CD-ROM/ DVD Drive
PC System Unit Quit 9 Motherboard Storage Devices Processor Hard Drive RAM Floppy Drive Expansion Cards CD-ROM/ DVD Drive
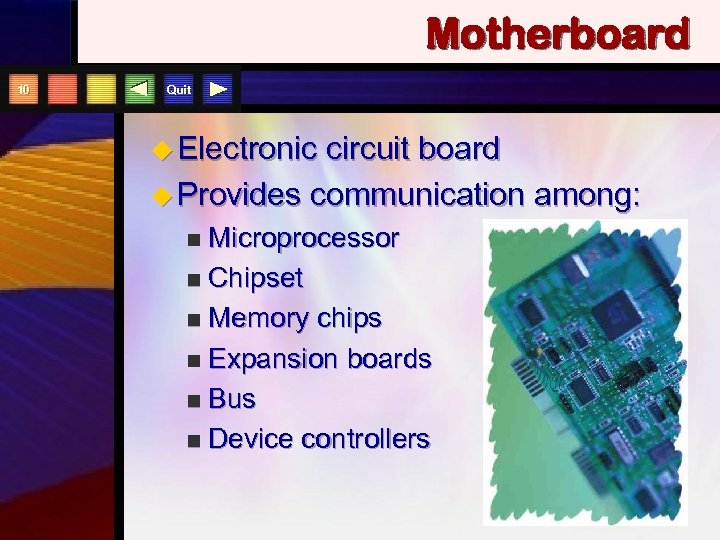 Motherboard 10 Quit u Electronic circuit board u Provides communication among: Microprocessor n Chipset n Memory chips n Expansion boards n Bus n Device controllers n
Motherboard 10 Quit u Electronic circuit board u Provides communication among: Microprocessor n Chipset n Memory chips n Expansion boards n Bus n Device controllers n
 Intel Processor Progression 11 Quit u 286, 386, 486 u Pentium® Pro u Pentium® III u Celeron® u Itanium™ Photo Courtesy of Intel Corporation
Intel Processor Progression 11 Quit u 286, 386, 486 u Pentium® Pro u Pentium® III u Celeron® u Itanium™ Photo Courtesy of Intel Corporation
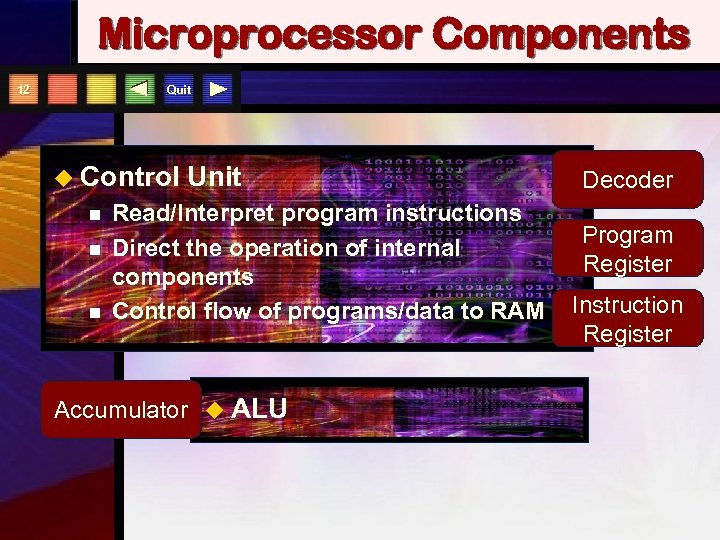 Microprocessor Components Quit 12 u Control n n n Unit Read/Interpret program instructions Direct the operation of internal components Control flow of programs/data to RAM Accumulator u ALU Decoder Program Register Instruction Register
Microprocessor Components Quit 12 u Control n n n Unit Read/Interpret program instructions Direct the operation of internal components Control flow of programs/data to RAM Accumulator u ALU Decoder Program Register Instruction Register
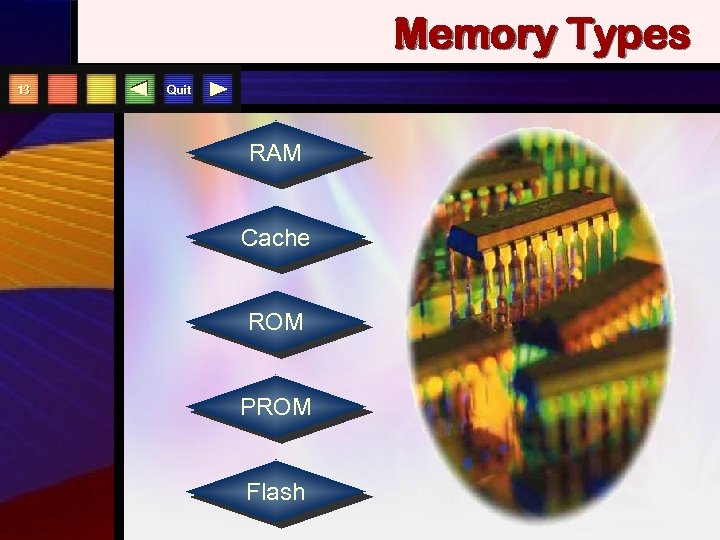 Memory Types 13 Quit RAM Cache ROM PROM Flash
Memory Types 13 Quit RAM Cache ROM PROM Flash
 RAM 14 Quit u Random Access Memory u Solid-state electronic circuitry u Holds current data and programs at a RAM address u Temporary or volatile storage
RAM 14 Quit u Random Access Memory u Solid-state electronic circuitry u Holds current data and programs at a RAM address u Temporary or volatile storage
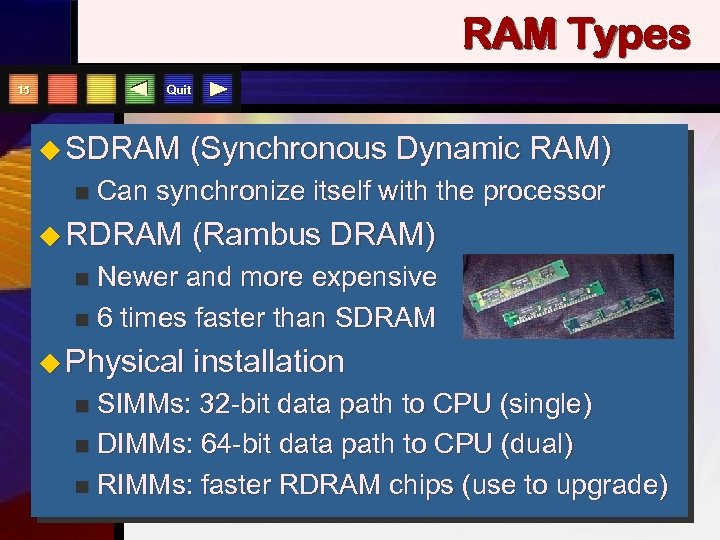 RAM Types Quit 15 u SDRAM n (Synchronous Dynamic RAM) Can synchronize itself with the processor u RDRAM (Rambus DRAM) Newer and more expensive n 6 times faster than SDRAM n u Physical installation SIMMs: 32 -bit data path to CPU (single) n DIMMs: 64 -bit data path to CPU (dual) n RIMMs: faster RDRAM chips (use to upgrade) n
RAM Types Quit 15 u SDRAM n (Synchronous Dynamic RAM) Can synchronize itself with the processor u RDRAM (Rambus DRAM) Newer and more expensive n 6 times faster than SDRAM n u Physical installation SIMMs: 32 -bit data path to CPU (single) n DIMMs: 64 -bit data path to CPU (dual) n RIMMs: faster RDRAM chips (use to upgrade) n
 Cache Memory 16 Quit u Faster and more costly than RAM u Much smaller capacity than RAM u Holds next likely instructions u Increases system throughput
Cache Memory 16 Quit u Faster and more costly than RAM u Much smaller capacity than RAM u Holds next likely instructions u Increases system throughput
 ROM 17 Quit u Read Only Memory u Permanent; user cannot change u Loads Operating System during boot process u PROM
ROM 17 Quit u Read Only Memory u Permanent; user cannot change u Loads Operating System during boot process u PROM
 Flash Memory 18 Quit u Type of PROM u Can be easily changed by user u Non-volatile u Upgrade by downloading software from the Web or disk u No longer need to replace chips or circuit boards
Flash Memory 18 Quit u Type of PROM u Can be easily changed by user u Non-volatile u Upgrade by downloading software from the Web or disk u No longer need to replace chips or circuit boards
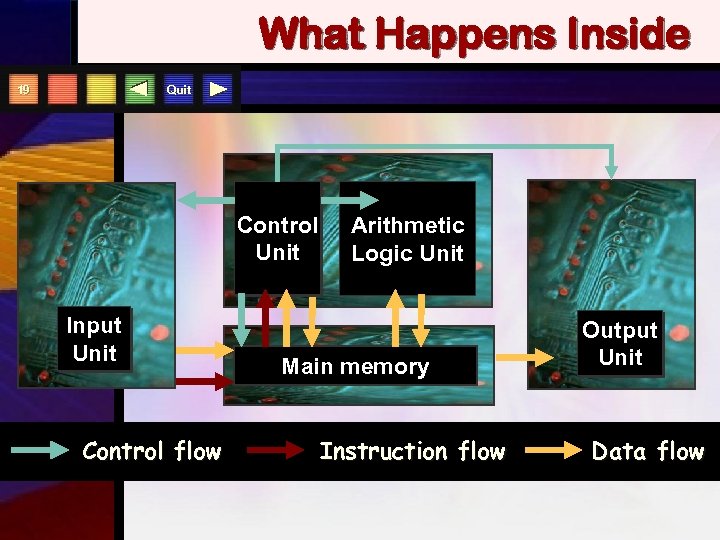 What Happens Inside Quit 19 Control Unit Input Unit Control flow Arithmetic Logic Unit Main memory Instruction flow Output Unit Data flow
What Happens Inside Quit 19 Control Unit Input Unit Control flow Arithmetic Logic Unit Main memory Instruction flow Output Unit Data flow
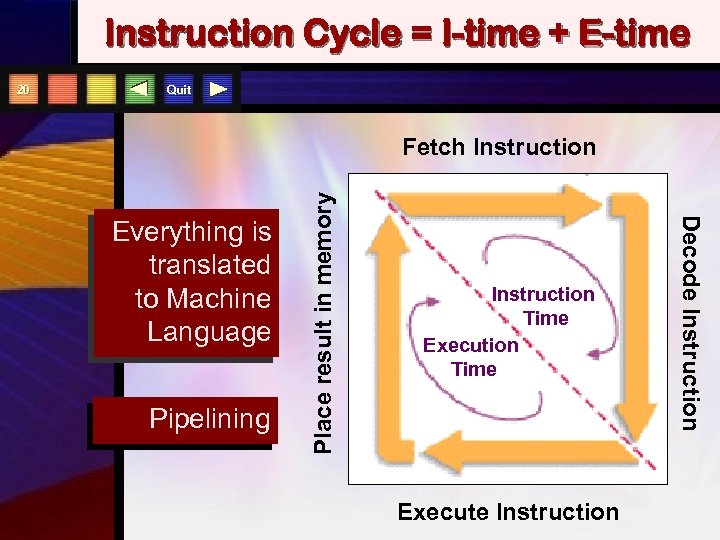 Instruction Cycle = I-time + E-time Quit Fetch Instruction Pipelining Instruction Time Execute Instruction Decode Instruction Everything is translated to Machine Language Place result in memory 20
Instruction Cycle = I-time + E-time Quit Fetch Instruction Pipelining Instruction Time Execute Instruction Decode Instruction Everything is translated to Machine Language Place result in memory 20
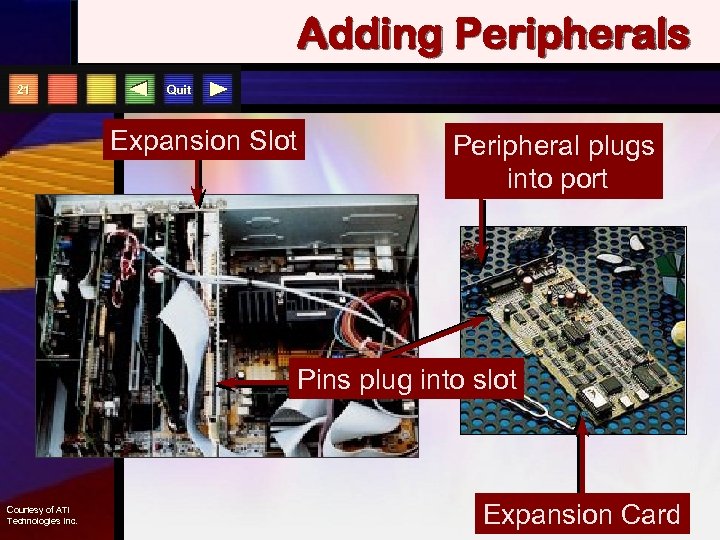 Adding Peripherals 21 Quit Expansion Slot Peripheral plugs into port Pins plug into slot Courtesy of ATI Technologies Inc. Expansion Card
Adding Peripherals 21 Quit Expansion Slot Peripheral plugs into port Pins plug into slot Courtesy of ATI Technologies Inc. Expansion Card
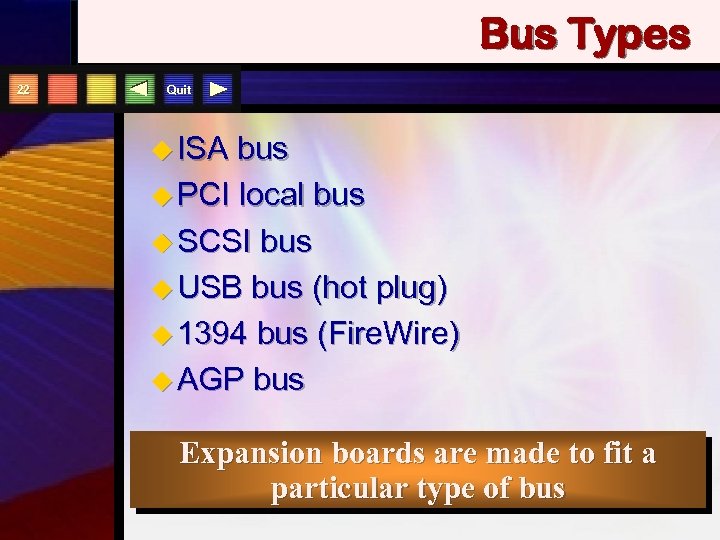 Bus Types 22 Quit u ISA bus u PCI local bus u SCSI bus u USB bus (hot plug) u 1394 bus (Fire. Wire) u AGP bus Expansion boards are made to fit a particular type of bus
Bus Types 22 Quit u ISA bus u PCI local bus u SCSI bus u USB bus (hot plug) u 1394 bus (Fire. Wire) u AGP bus Expansion boards are made to fit a particular type of bus
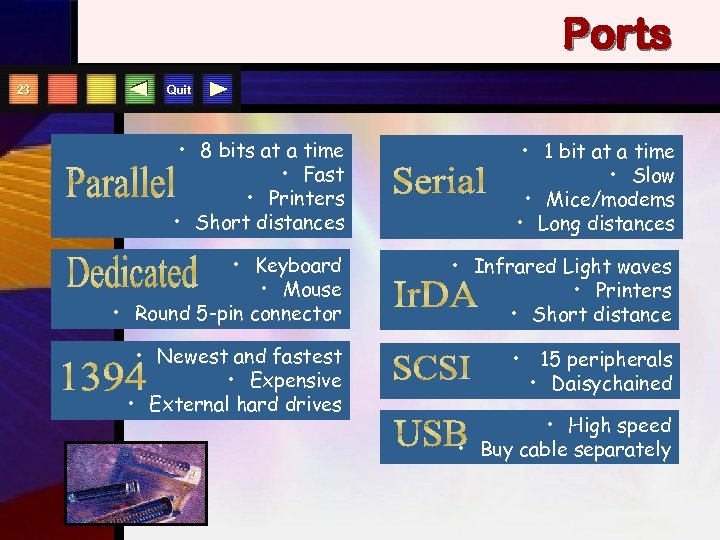 Ports 23 Quit • 8 bits at a time • Fast • Printers • Short distances • 1 bit at a time • Slow • Mice/modems • Long distances • Keyboard • Mouse • Round 5 -pin connector • Infrared Light waves • Printers • Short distance • Newest and fastest • Expensive • External hard drives • 15 peripherals • Daisychained • High speed • Buy cable separately
Ports 23 Quit • 8 bits at a time • Fast • Printers • Short distances • 1 bit at a time • Slow • Mice/modems • Long distances • Keyboard • Mouse • Round 5 -pin connector • Infrared Light waves • Printers • Short distance • Newest and fastest • Expensive • External hard drives • 15 peripherals • Daisychained • High speed • Buy cable separately
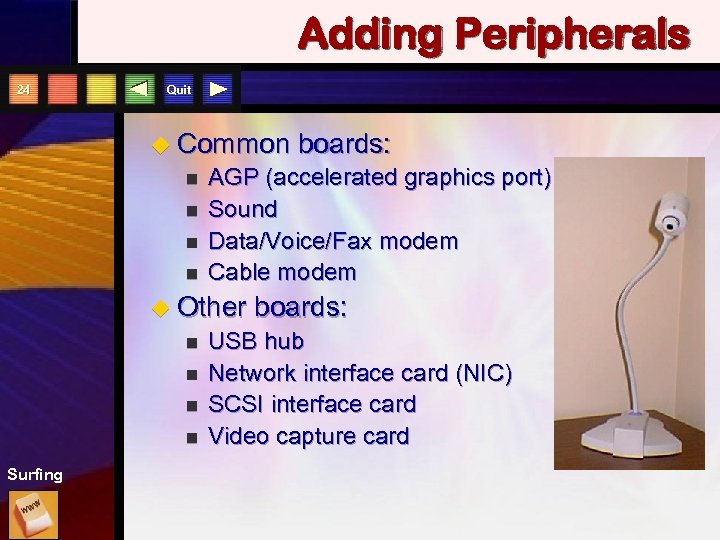 Adding Peripherals 24 Quit u Common n n AGP (accelerated graphics port) Sound Data/Voice/Fax modem Cable modem u Other n n Surfing boards: USB hub Network interface card (NIC) SCSI interface card Video capture card
Adding Peripherals 24 Quit u Common n n AGP (accelerated graphics port) Sound Data/Voice/Fax modem Cable modem u Other n n Surfing boards: USB hub Network interface card (NIC) SCSI interface card Video capture card
 PCMCIA Card 25 U. S. Robotics Mobile Communications Corporation Quit
PCMCIA Card 25 U. S. Robotics Mobile Communications Corporation Quit
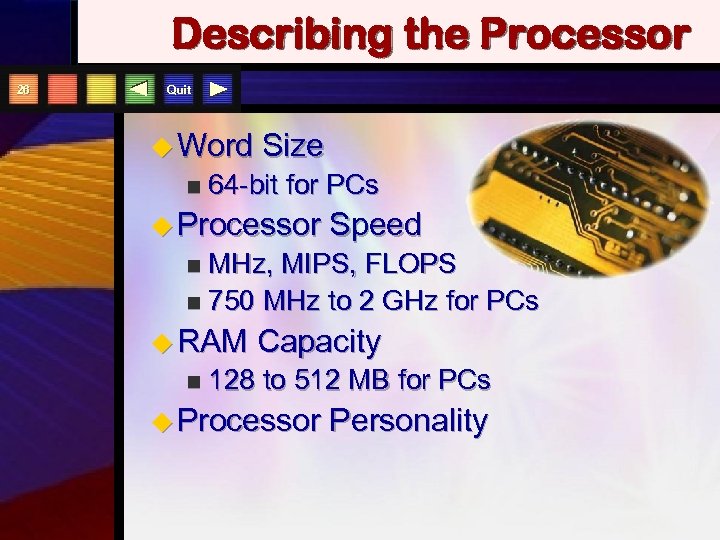 Describing the Processor 26 Quit u Word n Size 64 -bit for PCs u Processor Speed MHz, MIPS, FLOPS n 750 MHz to 2 GHz for PCs n u RAM n Capacity 128 to 512 MB for PCs u Processor Personality
Describing the Processor 26 Quit u Word n Size 64 -bit for PCs u Processor Speed MHz, MIPS, FLOPS n 750 MHz to 2 GHz for PCs n u RAM n Capacity 128 to 512 MB for PCs u Processor Personality
 Storage Capacity Quit u Byte - one character u Kilobyte (KB) - 1024 bytes u Megabyte (MB) - about 1 million bytes u Gigabyte (GB) - about 1 billion bytes u Terabyte (TB) - about 1 trillion bytes
Storage Capacity Quit u Byte - one character u Kilobyte (KB) - 1024 bytes u Megabyte (MB) - about 1 million bytes u Gigabyte (GB) - about 1 billion bytes u Terabyte (TB) - about 1 trillion bytes
 Processor Design 28 Quit u Parallel processing u Massively parallel processing u Neural networks
Processor Design 28 Quit u Parallel processing u Massively parallel processing u Neural networks
 Inside the Computer The End Computers: Information Technology in Perspective By Long and Long Copyright 2002 Prentice Hall, Inc.
Inside the Computer The End Computers: Information Technology in Perspective By Long and Long Copyright 2002 Prentice Hall, Inc.


