6fddf3ec64a9dc394df41e93a148250d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

Computers and Internet in Bioinformatics Dr Tan Tin Wee Director Bioinformatics Centre

Internet and Bioinformatics • Computing Technology in Biology biocomputing • Molecular biology was one of first to use latest Internet technologies such as mailing list, newsgroups, WAIS, Gopher and World Wide Web • Internet Boom occurred at the same time as Genome Project data explosion • Close synergies between the two
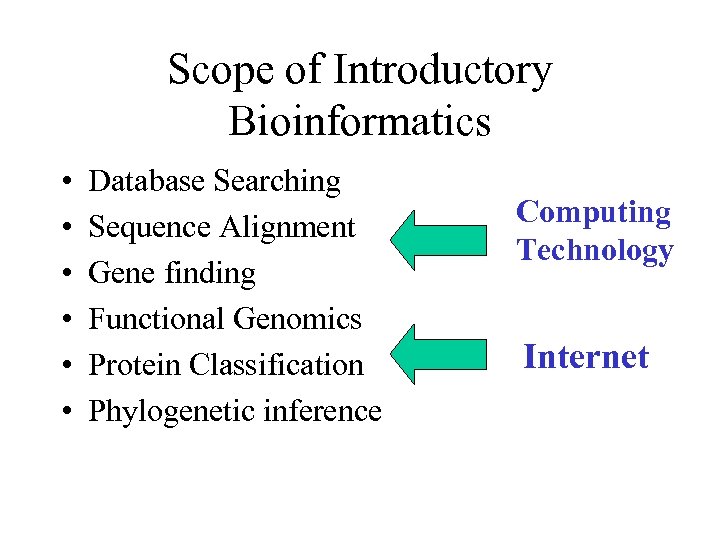
Scope of Introductory Bioinformatics • • • Database Searching Sequence Alignment Gene finding Functional Genomics Protein Classification Phylogenetic inference Computing Technology Internet
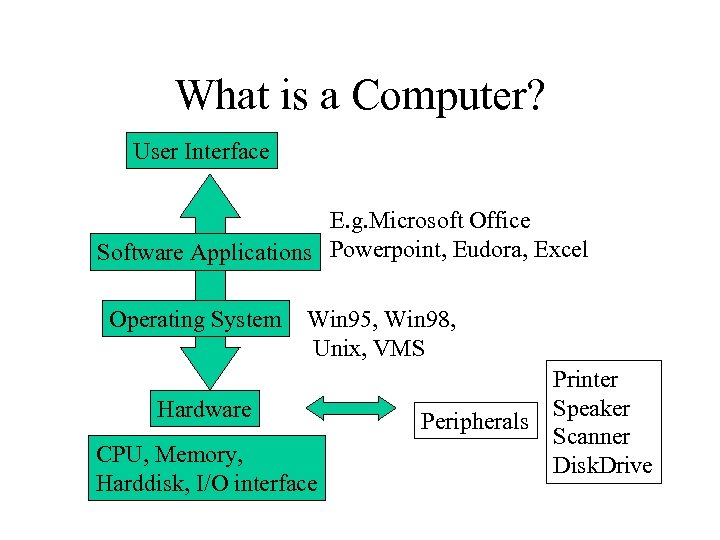
What is a Computer? User Interface E. g. Microsoft Office Software Applications Powerpoint, Eudora, Excel Operating System Win 95, Win 98, Unix, VMS Hardware CPU, Memory, Harddisk, I/O interface Peripherals Printer Speaker Scanner Disk. Drive

What is a Computer Program • Set of instructions which tells the computer • Machine language eg. 010011010010 • Assembly Language eg. MOV AX, 2 command for programming chips eg Intel SPARCs, Digital Alpha chip, Z 80, Motorola 6008 • Higher level Programming language Interpreted - BASIC, PERL Byte. Code - Java Compilable - C, C++, COBOL, PASCAL etc

Programming Language • 1 GL - Machine • 2 GL - Assembly • 3 GL - Structured Programming - Fortran, Pascal, C, C++ (Object Oriented), PERL, BASIC, etc • 4 GL - Functional Programming - LISP, Standard ML, Prolog

Program Development Environment • • • Visual Basic (BASIC) Visual C (C programming) Visual J++ (Java) Delphi (Pascal) Assists software developer to develop programs faster.

Example • Microsoft Word • Developers use a variety of environments writing software for Windows operating system • Compile the code • End result is an executable. exe which when you double-click, powers up the application • Application allows you to compose document and save into harddisk or floppy
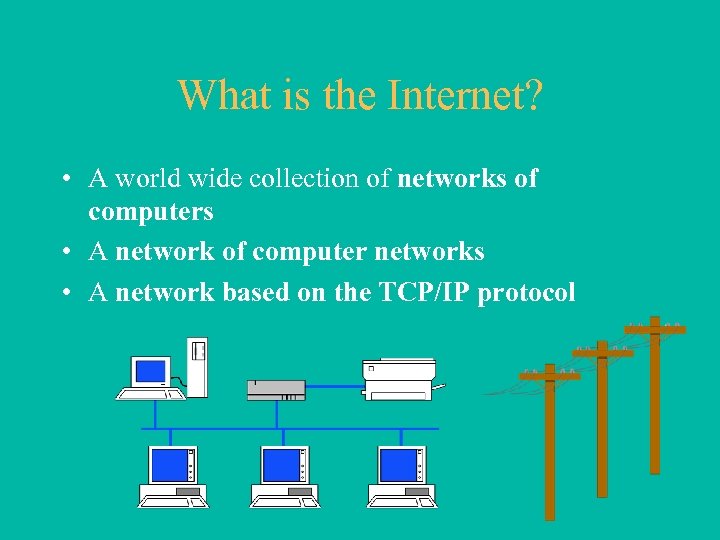
What is the Internet? • A world wide collection of networks of computers • A network of computer networks • A network based on the TCP/IP protocol
PC Standalone Computer Printer A typical setup at home Speakers
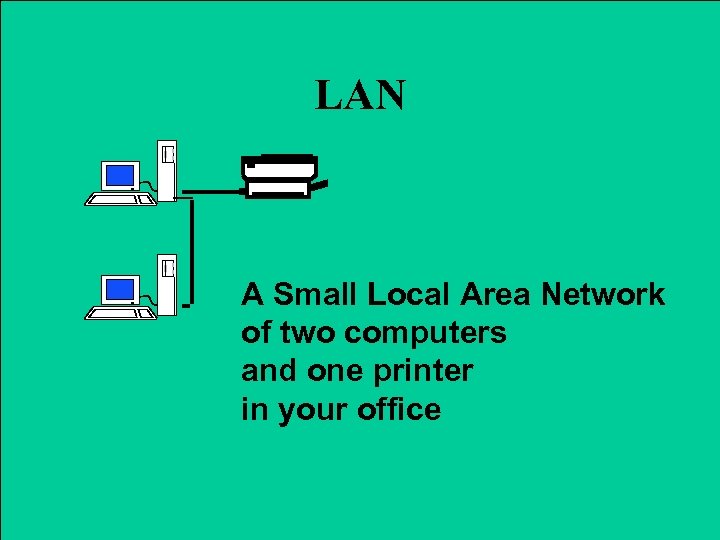
LAN A Small Local Area Network of two computers and one printer in your office
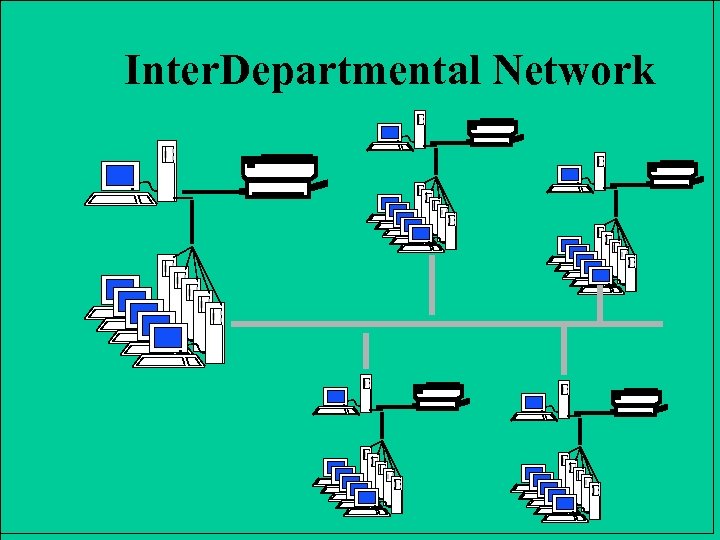
Inter. Departmental Network
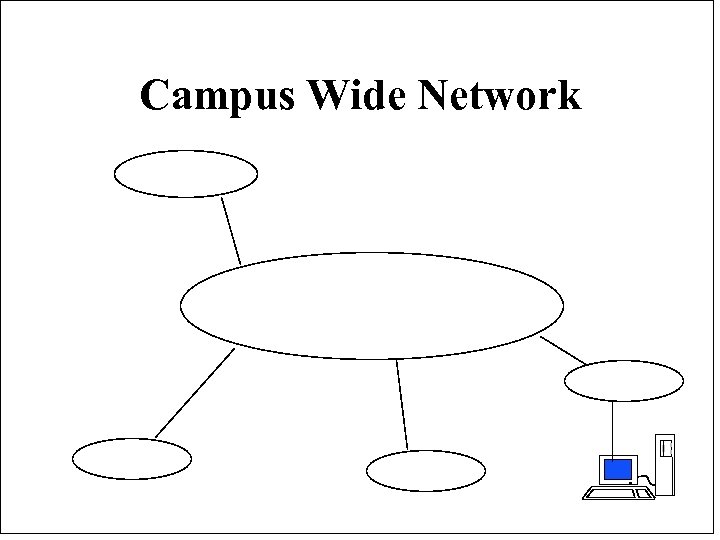
Campus Wide Network
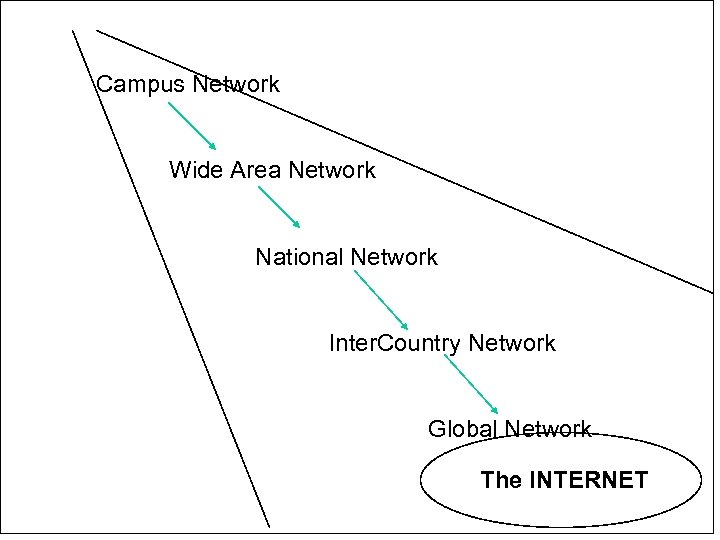
Campus Network Wide Area Network National Network Inter. Country Network Global Network The INTERNET
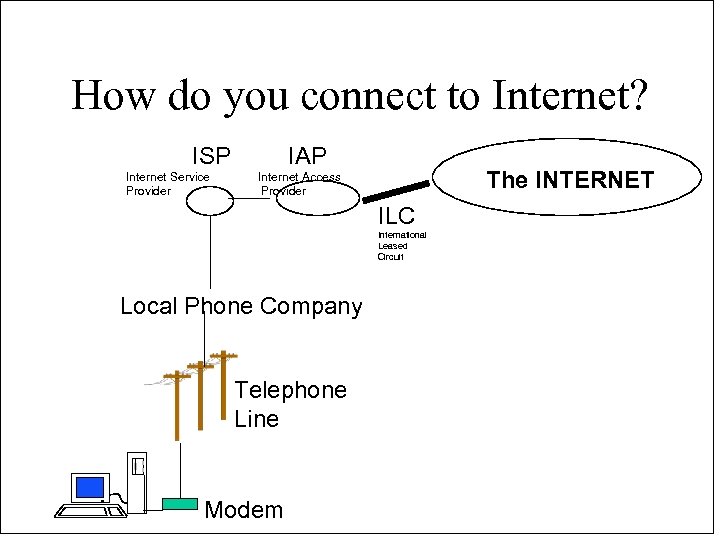
How do you connect to Internet? ISP Internet Service Provider IAP The INTERNET Internet Access Provider ILC International Leased Circuit Local Phone Company Telephone Line Modem
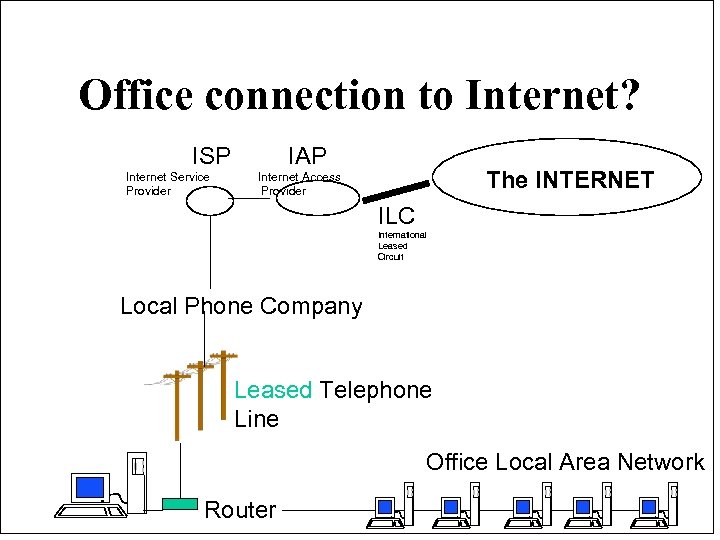
Office connection to Internet? ISP Internet Service Provider IAP The INTERNET Internet Access Provider ILC International Leased Circuit Local Phone Company Leased Telephone Line Office Local Area Network Router

What can you do with Internet? • • • INTERNET APPLICATIONS Electronic Mail (Email) Internet Talk/Chat (IRC) File Transfer (FTP) Remote Login (Telnet) Internet News (Usenet) Info retrieval (Gopher, World Wide Web) Virtual Reality (VRML) Audio. Video Conferencing (CU-See. Me, Mbone) Internet Phone
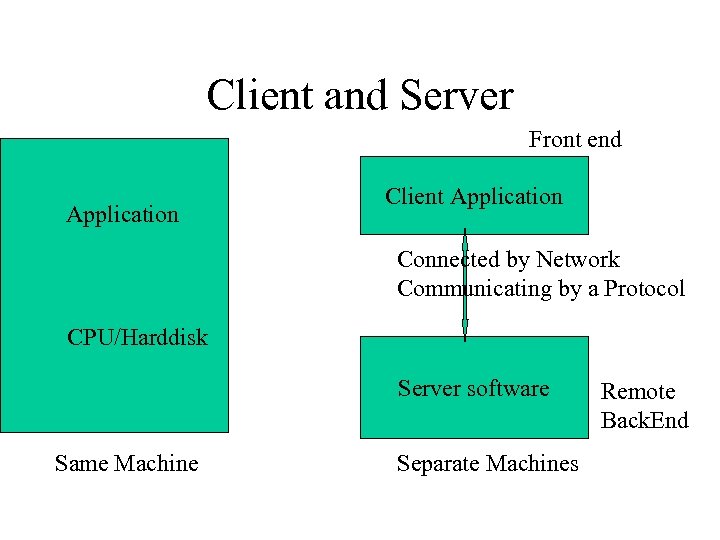
Client and Server Front end Application Client Application Connected by Network Communicating by a Protocol CPU/Harddisk Server software Same Machine Separate Machines Remote Back. End
Networks and Protocols • Many networks - BITNET, SNA (for IBM) and most famous and de facto global information infrastructure - INTERNET • Many different protocols - most famous is TCP/IP - a set of protocols for transferring information packets through a network • Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol

Technical Notes • • IP number Userid Domain Name Email address • URL 137. 132. 9. 61 tinwee biomed. nus. sg tinwee@biomed. nus. sg http: //biomed. nus. sg: 80/welcome. html

Internet Access in Singapore For Dialup, you will need: • • • An Internet account PC / Macintosh based computer Modem Phone line Communications Software For NUS, you will need: • Network card • configure built-in software

Internet Access in Singapore Internet Providers • • • Pacific Internet Cyberway Singnet Internet resellers Through Singapore ONE NUS, NTU and other educational institutions

Power of the Internet and Emergence of WWW • • • Hypertext Ted Nelson’s Project Xanadu (1969) CDROMs and Hypermedia Distributed Hypertext Distributed Hypermedia Mosaic, Netscape, Internet Explorer
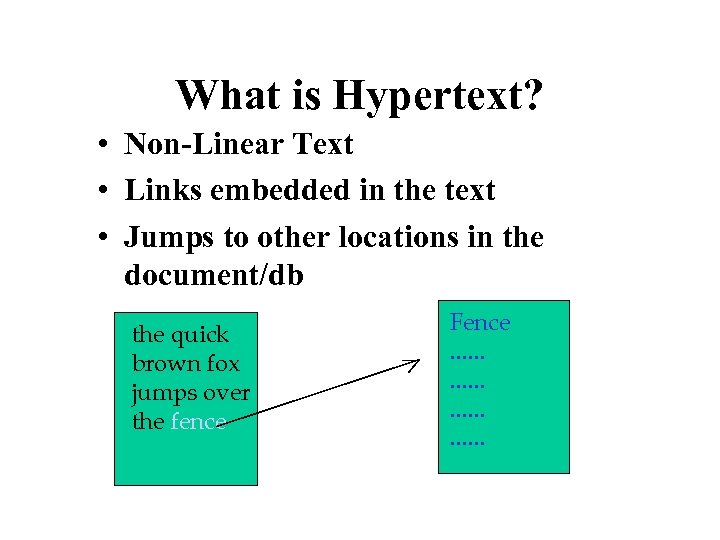
What is Hypertext? • Non-Linear Text • Links embedded in the text • Jumps to other locations in the document/db the quick brown fox jumps over the fence Fence. . .

Hypermedia & CDROMs • Ted Nelson’s visionary ideas in 1969 • Project Xanadu • Combine Text with Graphics, Pictures, Audio, Video, Movie clips etc • CDROMs
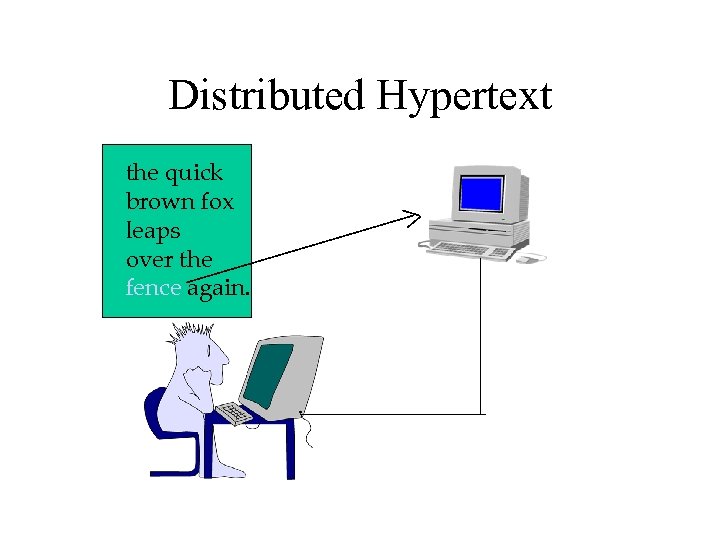
Distributed Hypertext the quick brown fox leaps over the fence again.
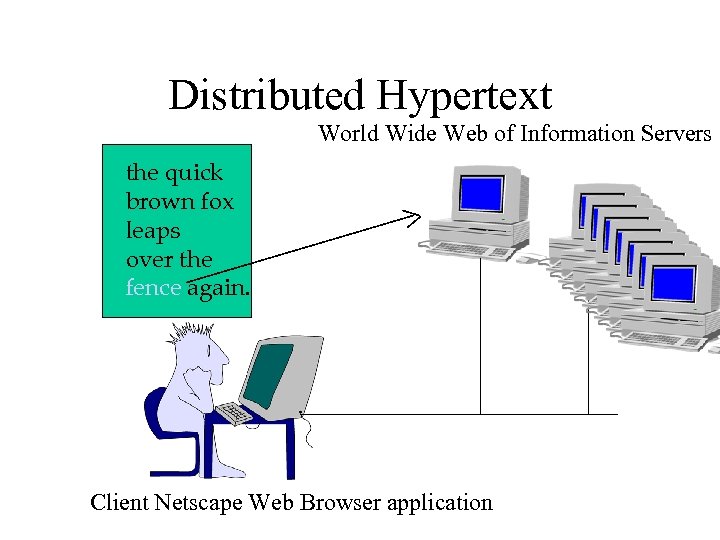
Distributed Hypertext World Wide Web of Information Servers the quick brown fox leaps over the fence again. Client Netscape Web Browser application

Distributed Hypertext/Hypermedia Document File Name + Internet Address Tim Berners-Lee CERN, Geneva Uniform Resource Locator: http: //www. sg/welcome. html http: //www. whitehouse. gov/welcome. au http: //biomed. nus. sg/logo. gif
Mosaic, Netscape, Internet Explorer WWW Browsers
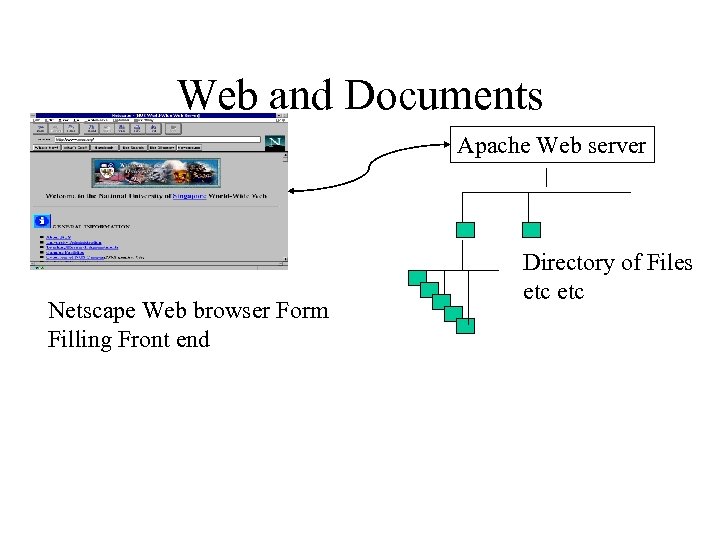
Web and Documents Apache Web server Netscape Web browser Form Filling Front end Directory of Files etc
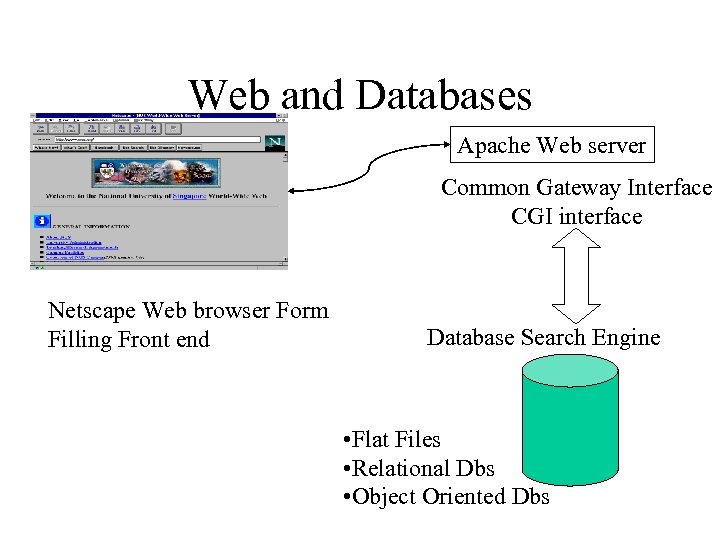
Web and Databases Apache Web server Common Gateway Interface CGI interface Netscape Web browser Form Filling Front end Database Search Engine • Flat Files • Relational Dbs • Object Oriented Dbs
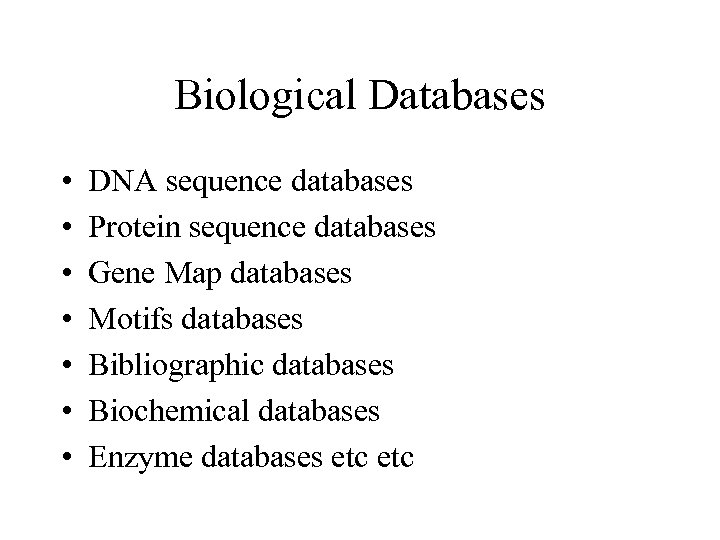
Biological Databases • • DNA sequence databases Protein sequence databases Gene Map databases Motifs databases Bibliographic databases Biochemical databases Enzyme databases etc
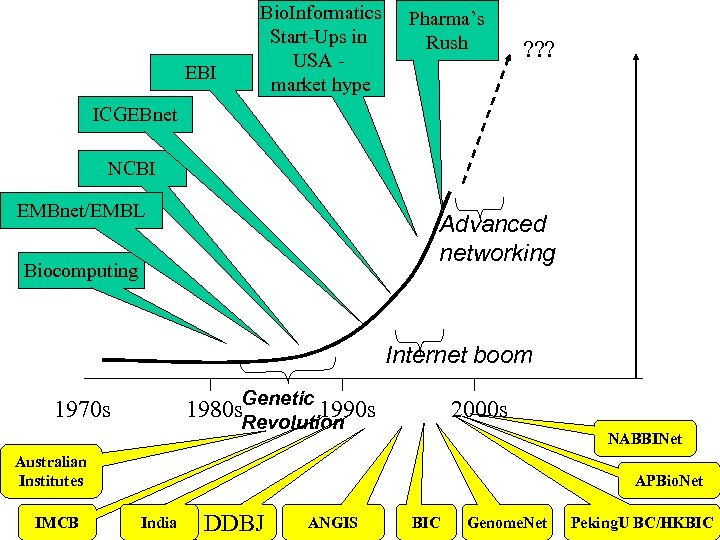
EBI Bio. Informatics Start-Ups in USA market hype Pharma’s Rush ? ? ? ICGEBnet NCBI EMBnet/EMBL Advanced networking Biocomputing Internet boom Genetic 1970 s 1980 s. Revolution 1990 s 2000 s NABBINet Australian Institutes IMCB APBio. Net India DDBJ ANGIS BIC Genome. Net Peking. U BC/HKBIC
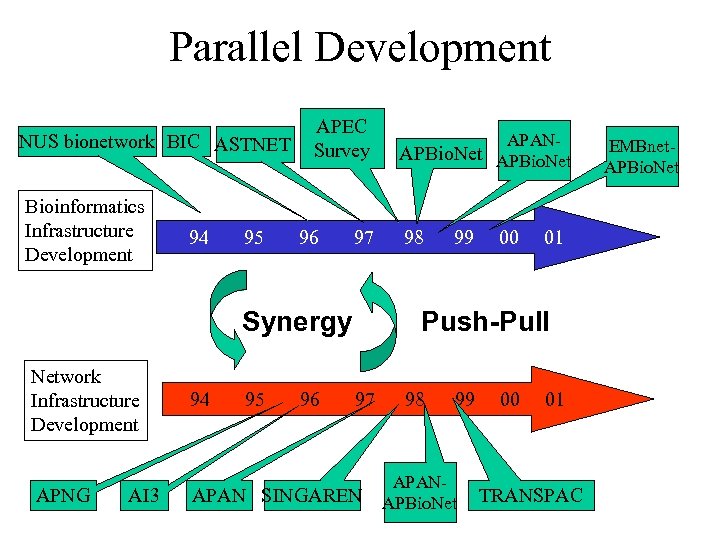
Parallel Development NUS bionetwork BIC ASTNET Bioinformatics Infrastructure Development 94 95 APEC Survey 96 97 Synergy Network Infrastructure Development APNG AI 3 94 95 96 APANAPBio. Net 98 99 00 01 Push-Pull 97 APAN SINGAREN 98 99 APANAPBio. Net 00 01 TRANSPAC EMBnet. APBio. Net

Life Scientists • Communication with each other through email, mailing lists, newsgroups and video conferencing • Information when and where needed • Rapid dissemination of information for global collaborations • Access to software applications freely • Access to computational resources freely

Conclusion • Computer and Internet Technologies has tremendous applications in the Life Sciences • Tremendous impact on the growth and evolution of Bioinformatics
6fddf3ec64a9dc394df41e93a148250d.ppt