b145312b270ce064bc9f84dc8c553992.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Computer Structure
Computer Structure
 We will look at: ¡ ¡ ¡ Four Box diagram CPU Memory Registers and their role Processing speed
We will look at: ¡ ¡ ¡ Four Box diagram CPU Memory Registers and their role Processing speed
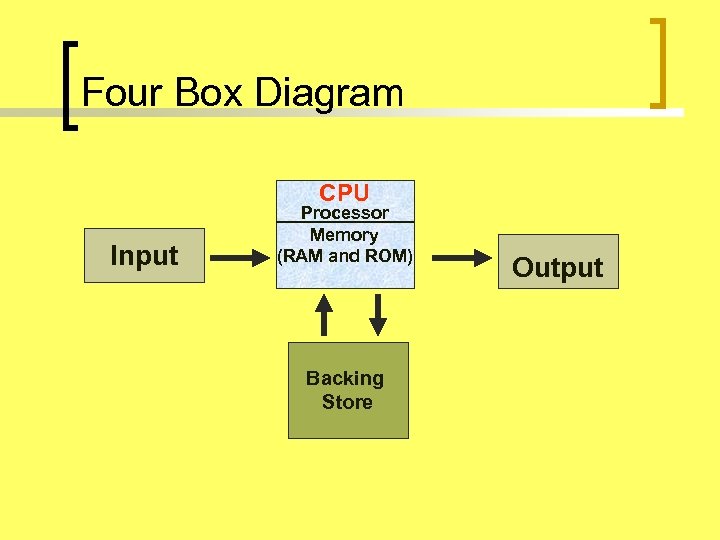 Four Box Diagram CPU Input Processor Memory (RAM and ROM) Backing Store Output
Four Box Diagram CPU Input Processor Memory (RAM and ROM) Backing Store Output
 Basic concepts - Hardware n Central Processing Unit (CPU) performs actual processing of data. n Data and programs are stored in memory, and moved to and from CPU as required. n Data travels between system components along electronic pathways, (sets of wires), called buses.
Basic concepts - Hardware n Central Processing Unit (CPU) performs actual processing of data. n Data and programs are stored in memory, and moved to and from CPU as required. n Data travels between system components along electronic pathways, (sets of wires), called buses.
 Three major components of the processor: n n n Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU), Control unit Registers
Three major components of the processor: n n n Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU), Control unit Registers
 Arithmetic Logic Unit: Functions The main functions of the ALU are: n To perform arithmetic calculations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) n To perform logic functions involving branching ( IF, THEN)
Arithmetic Logic Unit: Functions The main functions of the ALU are: n To perform arithmetic calculations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) n To perform logic functions involving branching ( IF, THEN)
 Control Unit: Functions The Control Unit n Controls the timing of operations within the processor. n Sends out signals that fetch instructions from the main memory. n Interpret instructions. n Carry out instructions that are fetched from the main memory.
Control Unit: Functions The Control Unit n Controls the timing of operations within the processor. n Sends out signals that fetch instructions from the main memory. n Interpret instructions. n Carry out instructions that are fetched from the main memory.
 Registers n These are temporary storage areas within the processor that are used to hold data that has been fetched from the memory or produced a calculation.
Registers n These are temporary storage areas within the processor that are used to hold data that has been fetched from the memory or produced a calculation.
 Main Memory n Main Memory is composed of Read only Memory (ROM) and Random Access Memory (RAM)
Main Memory n Main Memory is composed of Read only Memory (ROM) and Random Access Memory (RAM)
 Read Only Memory (ROM) n Features of ROM n n ROM is read-only memory, i. e. you cannot save data to ROM Data in ROM is permanent n Data in ROM is not lost when the computer is switched off.
Read Only Memory (ROM) n Features of ROM n n ROM is read-only memory, i. e. you cannot save data to ROM Data in ROM is permanent n Data in ROM is not lost when the computer is switched off.
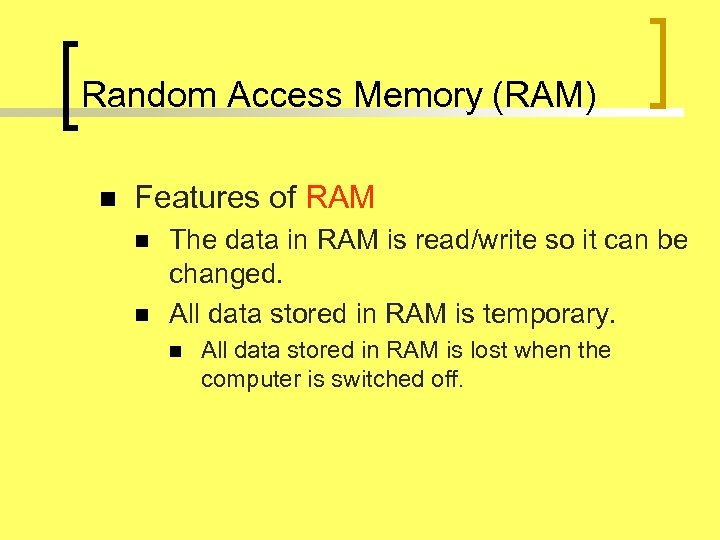 Random Access Memory (RAM) n Features of RAM n n The data in RAM is read/write so it can be changed. All data stored in RAM is temporary. n All data stored in RAM is lost when the computer is switched off.
Random Access Memory (RAM) n Features of RAM n n The data in RAM is read/write so it can be changed. All data stored in RAM is temporary. n All data stored in RAM is lost when the computer is switched off.
 Types of Computer Systems n n Desktop Computers Portable ( laptops, palmtops) Mainframe Computers Embedded Computer Systems
Types of Computer Systems n n Desktop Computers Portable ( laptops, palmtops) Mainframe Computers Embedded Computer Systems
 Important features to look for in a computer. n Type and speed of processor ¡ ¡ n The process or is run by a regular stream of electronic pulses, called the clock speed. The clock keeps everything working in time. The speed of the clock is measured in MHz (Megahertz) or GHz (Gigahertz). Size of main memory ¡ This is the measurement of RAM and is measured in Mb or GB
Important features to look for in a computer. n Type and speed of processor ¡ ¡ n The process or is run by a regular stream of electronic pulses, called the clock speed. The clock keeps everything working in time. The speed of the clock is measured in MHz (Megahertz) or GHz (Gigahertz). Size of main memory ¡ This is the measurement of RAM and is measured in Mb or GB
 Important features to look for in a computer. (continued) n Backing storage ¡ n A modern device should contain a number of backing storage devices Input and out put devices ¡ Will depend on the type of computer, i. e. desktop ot laptop, etc.
Important features to look for in a computer. (continued) n Backing storage ¡ n A modern device should contain a number of backing storage devices Input and out put devices ¡ Will depend on the type of computer, i. e. desktop ot laptop, etc.
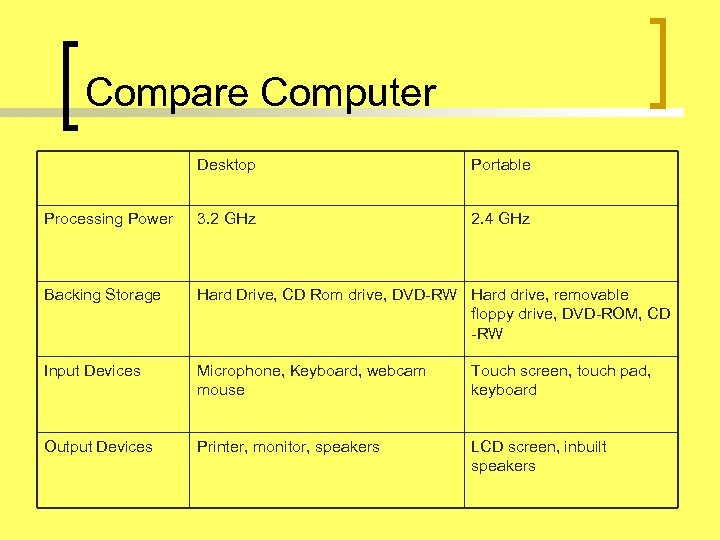 Compare Computer Desktop Portable Processing Power 3. 2 GHz 2. 4 GHz Backing Storage Hard Drive, CD Rom drive, DVD-RW Hard drive, removable floppy drive, DVD-ROM, CD -RW Input Devices Microphone, Keyboard, webcam mouse Touch screen, touch pad, keyboard Output Devices Printer, monitor, speakers LCD screen, inbuilt speakers
Compare Computer Desktop Portable Processing Power 3. 2 GHz 2. 4 GHz Backing Storage Hard Drive, CD Rom drive, DVD-RW Hard drive, removable floppy drive, DVD-ROM, CD -RW Input Devices Microphone, Keyboard, webcam mouse Touch screen, touch pad, keyboard Output Devices Printer, monitor, speakers LCD screen, inbuilt speakers
 Palmtops n n Palmtops are very small portable computers, they have limited memory and processor speed. You require a stylus to input data, some palmtops have a microphone so you can use voice input, they also have a (small) keyboard
Palmtops n n Palmtops are very small portable computers, they have limited memory and processor speed. You require a stylus to input data, some palmtops have a microphone so you can use voice input, they also have a (small) keyboard
 Laptops n n Laptops usual have devices that are removable this makes the laptop cheaper to buy as you only purchase the devices that you require. It also makes the laptop lighter, for carrying.
Laptops n n Laptops usual have devices that are removable this makes the laptop cheaper to buy as you only purchase the devices that you require. It also makes the laptop lighter, for carrying.
 Palmtop Applications n A palmtop can use most applications but they will be cut down version of the usual package with limited functions
Palmtop Applications n A palmtop can use most applications but they will be cut down version of the usual package with limited functions
 Mainframe Computer n n This system operates by sharing many processors between a large number of terminals. Mainframes support multi-access and multi-programming
Mainframe Computer n n This system operates by sharing many processors between a large number of terminals. Mainframes support multi-access and multi-programming
 Features of a Mainframe n n n A mainframe will have several processors that work together making the machine extremely powerful. There is usually vast amounts of memory It typically has 100 Gb of hard disk and tape drives are used for back ups. A keyboard is the input device Printers and monitors are the output devices.
Features of a Mainframe n n n A mainframe will have several processors that work together making the machine extremely powerful. There is usually vast amounts of memory It typically has 100 Gb of hard disk and tape drives are used for back ups. A keyboard is the input device Printers and monitors are the output devices.
 Embedded Computer Systems n This is a system which performs a specific task and is general part of a larger system that may not be a computer, it works in real-time and this is affected by time constraints.
Embedded Computer Systems n This is a system which performs a specific task and is general part of a larger system that may not be a computer, it works in real-time and this is affected by time constraints.
 Applications of Embedded Systems n n Products: washing machines, fridges, Electronics: cameras, camcorders, phones Industrial: printers, faxes, elevators, robots Multimedia: video conferencing, interactive games
Applications of Embedded Systems n n Products: washing machines, fridges, Electronics: cameras, camcorders, phones Industrial: printers, faxes, elevators, robots Multimedia: video conferencing, interactive games
 Written Task n You can now complete Exercise 4
Written Task n You can now complete Exercise 4


