28ddb954741d6cdecbeb769c93239677.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Computer security co-operation in Europe Jan Meijer, SURFnet-CERT jan. meijer@surfnet. nl Based on materials provided by TERENA TF-CSIRT © TERENA 2003
Computer security co-operation in Europe Jan Meijer, SURFnet-CERT jan. meijer@surfnet. nl Based on materials provided by TERENA TF-CSIRT © TERENA 2003
 Agenda • • Why co-operate? History of co-operation CSIRT Task Force (TF-CSIRT) Benefits: – Contacts – Trends and hot issues • Deliverables, including: – – © TERENA 2003 IRT database object Common format on incident data Training course for new CSIRTs Accreditation scheme for new teams • Questions
Agenda • • Why co-operate? History of co-operation CSIRT Task Force (TF-CSIRT) Benefits: – Contacts – Trends and hot issues • Deliverables, including: – – © TERENA 2003 IRT database object Common format on incident data Training course for new CSIRTs Accreditation scheme for new teams • Questions
 Why Co-operate? • Security incidents are international – Must work together to solve them • No team knows everything – Share knowledge, resources, tools – Compare working practices – Develop best practice & standards – Provide better and faster service © TERENA 2003
Why Co-operate? • Security incidents are international – Must work together to solve them • No team knows everything – Share knowledge, resources, tools – Compare working practices – Develop best practice & standards – Provide better and faster service © TERENA 2003
 Historical perspective • Pre-1990: CSIRTs in isolation (if at all) • During 1990 s: FIRST provides binding: – – Members meet members Basic notion of trust Exchange of operational information Less powerful in initiating innovation • Mid 1990 s: Euro. CERT pilot service: – Top-down approach – Operational work outsourced to 3 rd party • 2000: TF-CSIRT established © TERENA 2003
Historical perspective • Pre-1990: CSIRTs in isolation (if at all) • During 1990 s: FIRST provides binding: – – Members meet members Basic notion of trust Exchange of operational information Less powerful in initiating innovation • Mid 1990 s: Euro. CERT pilot service: – Top-down approach – Operational work outsourced to 3 rd party • 2000: TF-CSIRT established © TERENA 2003
 Influence of NRENs • National Research & Education Networks – Traditionally innovative – Low commercial profile • Natural “academic” way of working – Achievements based on collaboration – Results shared for society’s benefit – Free dissemination of expertise 1994: TERENA (see: www. terena. nl) © TERENA 2003
Influence of NRENs • National Research & Education Networks – Traditionally innovative – Low commercial profile • Natural “academic” way of working – Achievements based on collaboration – Results shared for society’s benefit – Free dissemination of expertise 1994: TERENA (see: www. terena. nl) © TERENA 2003
 Creation of TF-CSIRT • TERENA Task Force: – – – – Operation defined by Terms of Reference Two years recurring lifecycle with review Members and non-members of TERENA No membership fee, just travel & hotel costs Active participation by members Success depends on members’ commitment TERENA plays role of professional facilitator: • Secretarial tasks • Logistical support © TERENA 2003
Creation of TF-CSIRT • TERENA Task Force: – – – – Operation defined by Terms of Reference Two years recurring lifecycle with review Members and non-members of TERENA No membership fee, just travel & hotel costs Active participation by members Success depends on members’ commitment TERENA plays role of professional facilitator: • Secretarial tasks • Logistical support © TERENA 2003
 TF-CSIRT way of working • Meeting every four months • Venue rotates among members who volunteer to host • Two days: – 1 st day for seminars and presentations – 2 nd day for Task Force official meeting • Evening in-between: social event organised by the hosting member • Contacts between meetings provided by mailing list and project groups © TERENA 2003
TF-CSIRT way of working • Meeting every four months • Venue rotates among members who volunteer to host • Two days: – 1 st day for seminars and presentations – 2 nd day for Task Force official meeting • Evening in-between: social event organised by the hosting member • Contacts between meetings provided by mailing list and project groups © TERENA 2003
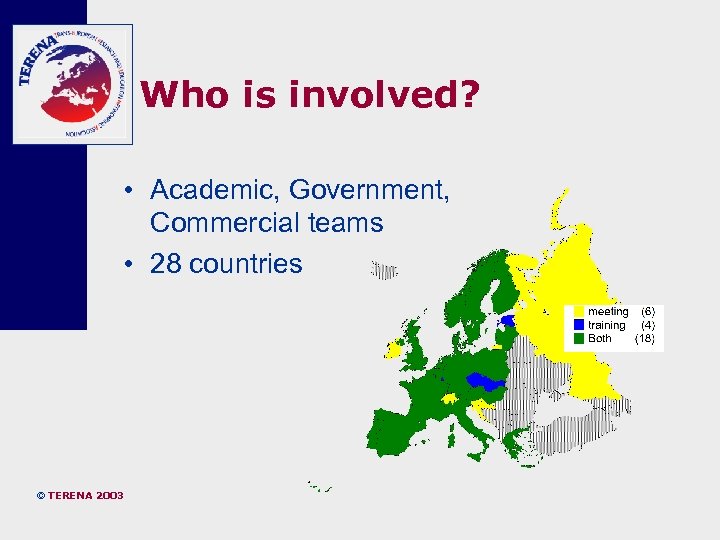 Who is involved? • Academic, Government, Commercial teams • 28 countries © TERENA 2003
Who is involved? • Academic, Government, Commercial teams • 28 countries © TERENA 2003
 Benefits - contacts • Operational people talk directly to each other – Trusted contacts for later work © TERENA 2003 • Little or no formalities, collaborative atmosphere • Ad-hoc subgroups working on concrete deliverables • Social event often proves to be a fruitful environment for new ideas
Benefits - contacts • Operational people talk directly to each other – Trusted contacts for later work © TERENA 2003 • Little or no formalities, collaborative atmosphere • Ad-hoc subgroups working on concrete deliverables • Social event often proves to be a fruitful environment for new ideas
 Benefits – trends and hot issues • Supportive peer review of other members’ organisation and operations • Members share and consume expertise (a win/win approach) • Atmosphere of understanding – no team has to fight common problems alone • Discussing trends and hot issues among peers make these trends and hot issues easier to understand assess © TERENA 2003
Benefits – trends and hot issues • Supportive peer review of other members’ organisation and operations • Members share and consume expertise (a win/win approach) • Atmosphere of understanding – no team has to fight common problems alone • Discussing trends and hot issues among peers make these trends and hot issues easier to understand assess © TERENA 2003
 Wider Co-operation • European Commission – Projects (e. CSIRT. net, EISPP, TRANSITS) – Legal handbook for CSIRTs – Network & Information Security Agency • National governments – Government CSIRTs – Consultation on new legislation • Law enforcement – Operations and invited speakers at meetings • Other regional initiatives © TERENA 2003
Wider Co-operation • European Commission – Projects (e. CSIRT. net, EISPP, TRANSITS) – Legal handbook for CSIRTs – Network & Information Security Agency • National governments – Government CSIRTs – Consultation on new legislation • Law enforcement – Operations and invited speakers at meetings • Other regional initiatives © TERENA 2003
 Deliverables and Projects • Trusted Introducer Service & Directory • Incident Object Description & Exchange Format • RIPE IRT object • Clearing House for Incident Handling Tools • CSIRT training course (TRANSITS) © TERENA 2003 Under development • Incident Information Exchange (e. CSIRT. net) • Vulnerability information exchange (EISPP) • Assistance to new CSIRTs • Incident Handling Procedures
Deliverables and Projects • Trusted Introducer Service & Directory • Incident Object Description & Exchange Format • RIPE IRT object • Clearing House for Incident Handling Tools • CSIRT training course (TRANSITS) © TERENA 2003 Under development • Incident Information Exchange (e. CSIRT. net) • Vulnerability information exchange (EISPP) • Assistance to new CSIRTs • Incident Handling Procedures
 Deliverables – Trusted Introducer (http: //www. ti. terena. nl/) © TERENA 2003 • Notion of ‘trust’ – is a contact trustworthy? • Currently, no scheme generically applicable • TF-CSIRT to work out a model of which it believes it fulfills criteria needed at operational level • Feasibility and sanity checks • Now, outsourced to a 3 rd party • TF-CSIRT retains control by TI Review Board
Deliverables – Trusted Introducer (http: //www. ti. terena. nl/) © TERENA 2003 • Notion of ‘trust’ – is a contact trustworthy? • Currently, no scheme generically applicable • TF-CSIRT to work out a model of which it believes it fulfills criteria needed at operational level • Feasibility and sanity checks • Now, outsourced to a 3 rd party • TF-CSIRT retains control by TI Review Board
 Deliverables – IODEF (http: //www. iodef. org/) • Incident Object Description & Exchange Format • Cross-platform, cross-language, cross common understanding • Need for a well-understood definition of an incident • Bottom-up working group • Lots of output, among which RFC 3067 • Now transferred to IETF (INCH) © TERENA 2003
Deliverables – IODEF (http: //www. iodef. org/) • Incident Object Description & Exchange Format • Cross-platform, cross-language, cross common understanding • Need for a well-understood definition of an incident • Bottom-up working group • Lots of output, among which RFC 3067 • Now transferred to IETF (INCH) © TERENA 2003
 Deliverables – IRT database object • Commonly perceived problem: correct points of contact in (RIPE) database • Practical approach: – what do we miss now? – how can we design it – how can we implement it? • Wishlist followed by discussion in RIPE database group • Lots of iterations, but eventually implemented and populated © TERENA 2003
Deliverables – IRT database object • Commonly perceived problem: correct points of contact in (RIPE) database • Practical approach: – what do we miss now? – how can we design it – how can we implement it? • Wishlist followed by discussion in RIPE database group • Lots of iterations, but eventually implemented and populated © TERENA 2003
 Deliverables – CHIHT (http: //chiht. dfn-cert. de/) • Clearing House for Incident Handling Tools • Share information on tools CSIRTs use – Help new and existing teams • Website listing tools by category – Evidence gathering & investigation, system recovery, CSIRT operations, remote access, proactive tools – Plan to add procedures and best practice • Contents suggested by active CSIRTs © TERENA 2003
Deliverables – CHIHT (http: //chiht. dfn-cert. de/) • Clearing House for Incident Handling Tools • Share information on tools CSIRTs use – Help new and existing teams • Website listing tools by category – Evidence gathering & investigation, system recovery, CSIRT operations, remote access, proactive tools – Plan to add procedures and best practice • Contents suggested by active CSIRTs © TERENA 2003
 Deliverables – TRANSITS (http: //www. ist-transits. org/) • Teams were seeking relevant training • Idea: best transfer of knowledge is from operational people to operational people • Conclusion: best people to write it are TFCSIRT members • Two day course developed in modules: – Operational, legal, technical, organisational, vulnerabilities • EC funding for delivery and updating © TERENA 2003 – Six presentations over three years – Materials available to members for own use
Deliverables – TRANSITS (http: //www. ist-transits. org/) • Teams were seeking relevant training • Idea: best transfer of knowledge is from operational people to operational people • Conclusion: best people to write it are TFCSIRT members • Two day course developed in modules: – Operational, legal, technical, organisational, vulnerabilities • EC funding for delivery and updating © TERENA 2003 – Six presentations over three years – Materials available to members for own use
 Deliverables – e. CSIRT. net (http: //www. ecsirt. net/) • Teams need to exchange incidents – To resolve them – To measure statistics and trends – To get early warnings • Need processes and standards – Language (using IDMEF & IODEF) – Meanings (definitions, trust & procedure) – Automation (to identify events and trends) • Develop/test these among trusted teams © TERENA 2003 – Build larger network using tested processes
Deliverables – e. CSIRT. net (http: //www. ecsirt. net/) • Teams need to exchange incidents – To resolve them – To measure statistics and trends – To get early warnings • Need processes and standards – Language (using IDMEF & IODEF) – Meanings (definitions, trust & procedure) – Automation (to identify events and trends) • Develop/test these among trusted teams © TERENA 2003 – Build larger network using tested processes
 Deliverables – EISPP (http: //www. eispp. org/) • Need technical skills to do security • How can small businesses cope? – Current advisories not suitable for them • Additional preventive services needed – Need to define services – And develop funding models • Service providers need to co-operate – Develop processes and technology © TERENA 2003
Deliverables – EISPP (http: //www. eispp. org/) • Need technical skills to do security • How can small businesses cope? – Current advisories not suitable for them • Additional preventive services needed – Need to define services – And develop funding models • Service providers need to co-operate – Develop processes and technology © TERENA 2003
 Questions? © TERENA 2003
Questions? © TERENA 2003


