ae0f198bd6eee11df5a82d8ca364628c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60
 Computer Science and Engineering The University of South Carolina Computer Science and Engineering 1 3/15/2018
Computer Science and Engineering The University of South Carolina Computer Science and Engineering 1 3/15/2018
 Faculty Research Interests Jason Bakos: VLSI, architecture, high performance interconnects Jason O’Kane: Robotics and Autonomous Systems John Bowles: Software and systems engineering Gang Quan: Real-time/embedded/poweraware systems, reconfigurable computing Duncan Buell: HPC, reconfigurable computing, security John Rose: Bioinformatics, data mining, probabilistic reasoning Caroline Eastman: Information retrieval, security, user interfaces Larry Stephens: Knowledge representation, computer security ontologies Csilla Farkas: Information assurance, web data integration, privacy Jijun Tang: Algorithms and bioinformatics Stephen Fenner: Theory of computing, quantum computing, complexity Homayoun Valafar: Computational Biology and Medicine, Bioinformatics Jianjun Hu: Bioinformatics, data mining Chin-Tser Huang: Intrusion detection, wireless security, protocols Marco Valtorta: Bayesian networks José Vidal: Multiagent systems, ecommerce, the semantic web Michael Huhns: Service-oriented computing, multiagent systems Song Wang: Computer vision, medical imaging Manton Matthews: Artificial intelligence, natural language processing Wenyuan Xu: Wireless networking and security, sensor networks Srihari Nelakuditi: Computer networking, multimedia streaming Computer Science and Engineering 2 3/15/2018
Faculty Research Interests Jason Bakos: VLSI, architecture, high performance interconnects Jason O’Kane: Robotics and Autonomous Systems John Bowles: Software and systems engineering Gang Quan: Real-time/embedded/poweraware systems, reconfigurable computing Duncan Buell: HPC, reconfigurable computing, security John Rose: Bioinformatics, data mining, probabilistic reasoning Caroline Eastman: Information retrieval, security, user interfaces Larry Stephens: Knowledge representation, computer security ontologies Csilla Farkas: Information assurance, web data integration, privacy Jijun Tang: Algorithms and bioinformatics Stephen Fenner: Theory of computing, quantum computing, complexity Homayoun Valafar: Computational Biology and Medicine, Bioinformatics Jianjun Hu: Bioinformatics, data mining Chin-Tser Huang: Intrusion detection, wireless security, protocols Marco Valtorta: Bayesian networks José Vidal: Multiagent systems, ecommerce, the semantic web Michael Huhns: Service-oriented computing, multiagent systems Song Wang: Computer vision, medical imaging Manton Matthews: Artificial intelligence, natural language processing Wenyuan Xu: Wireless networking and security, sensor networks Srihari Nelakuditi: Computer networking, multimedia streaming Computer Science and Engineering 2 3/15/2018
 High Performance Computing Computer Engineering Embedded Systems Reconfigurable Computing Computer Science and Engineering 3 3/15/2018
High Performance Computing Computer Engineering Embedded Systems Reconfigurable Computing Computer Science and Engineering 3 3/15/2018
 Parallel Computing The “Dead Computer Society” ILLIAC-4 CDC STAR-100 Denelcor HEP Tera Computer Corp. MPA Alliant Sequent Stardent Kendall Square Research (KSR) Intel Hypercube NCube BBN Butterfly NASA MPP Thinking Machines CM-2, CM-5 Mas. Par Successful Parallel Machines Cray T 3 D, T 3 E, XMP, YMP, X SGI Challenge, Origin, Altix Sun Enterprise HP-Convex DEC 84 xx Pittsburgh Terascale Do. E ASCI machines Beowulf clusters IBM SP-1, SP-2 Computer Science and Engineering 4 3/15/2018
Parallel Computing The “Dead Computer Society” ILLIAC-4 CDC STAR-100 Denelcor HEP Tera Computer Corp. MPA Alliant Sequent Stardent Kendall Square Research (KSR) Intel Hypercube NCube BBN Butterfly NASA MPP Thinking Machines CM-2, CM-5 Mas. Par Successful Parallel Machines Cray T 3 D, T 3 E, XMP, YMP, X SGI Challenge, Origin, Altix Sun Enterprise HP-Convex DEC 84 xx Pittsburgh Terascale Do. E ASCI machines Beowulf clusters IBM SP-1, SP-2 Computer Science and Engineering 4 3/15/2018
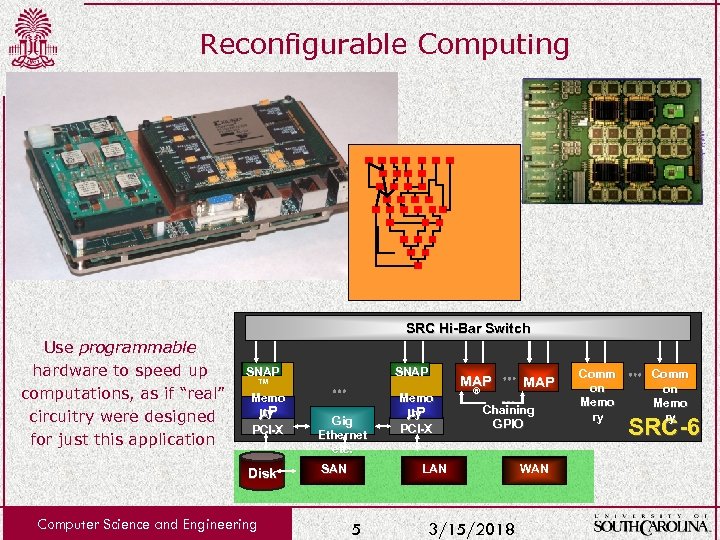 Reconfigurable Computing SRC Hi-Bar Switch Use programmable hardware to speed up computations, as if “real” circuitry were designed for just this application SNAP ™ Memo ry P PCI-X Disk Computer Science and Engineering SNAP Gig Ethernet etc. Memo ry P PCI-X MAP ® Chaining GPIO LAN SAN 5 MAP 3/15/2018 WAN Comm on Memo ry SRC-6
Reconfigurable Computing SRC Hi-Bar Switch Use programmable hardware to speed up computations, as if “real” circuitry were designed for just this application SNAP ™ Memo ry P PCI-X Disk Computer Science and Engineering SNAP Gig Ethernet etc. Memo ry P PCI-X MAP ® Chaining GPIO LAN SAN 5 MAP 3/15/2018 WAN Comm on Memo ry SRC-6
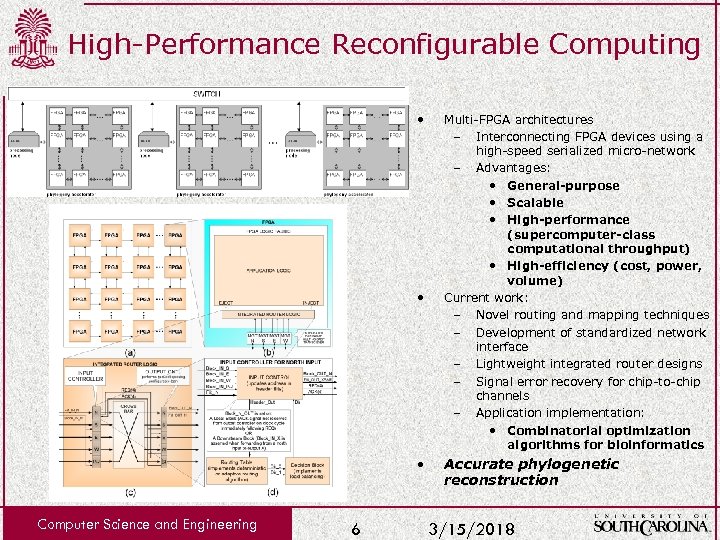 High-Performance Reconfigurable Computing • • • Computer Science and Engineering 6 Multi-FPGA architectures – Interconnecting FPGA devices using a high-speed serialized micro-network – Advantages: • General-purpose • Scalable • High-performance (supercomputer-class computational throughput) • High-efficiency (cost, power, volume) Current work: – Novel routing and mapping techniques – Development of standardized network interface – Lightweight integrated router designs – Signal error recovery for chip-to-chip channels – Application implementation: • Combinatorial optimization algorithms for bioinformatics Accurate phylogenetic reconstruction 3/15/2018
High-Performance Reconfigurable Computing • • • Computer Science and Engineering 6 Multi-FPGA architectures – Interconnecting FPGA devices using a high-speed serialized micro-network – Advantages: • General-purpose • Scalable • High-performance (supercomputer-class computational throughput) • High-efficiency (cost, power, volume) Current work: – Novel routing and mapping techniques – Development of standardized network interface – Lightweight integrated router designs – Signal error recovery for chip-to-chip channels – Application implementation: • Combinatorial optimization algorithms for bioinformatics Accurate phylogenetic reconstruction 3/15/2018
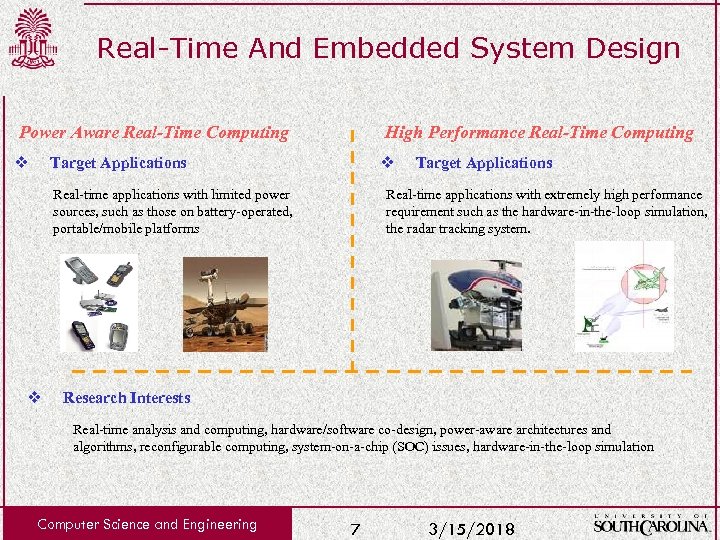 Real-Time And Embedded System Design Power Aware Real-Time Computing v High Performance Real-Time Computing v Target Applications Real-time applications with limited power sources, such as those on battery-operated, portable/mobile platforms v Target Applications Real-time applications with extremely high performance requirement such as the hardware-in-the-loop simulation, the radar tracking system. Research Interests Real-time analysis and computing, hardware/software co-design, power-aware architectures and algorithms, reconfigurable computing, system-on-a-chip (SOC) issues, hardware-in-the-loop simulation Computer Science and Engineering 7 3/15/2018
Real-Time And Embedded System Design Power Aware Real-Time Computing v High Performance Real-Time Computing v Target Applications Real-time applications with limited power sources, such as those on battery-operated, portable/mobile platforms v Target Applications Real-time applications with extremely high performance requirement such as the hardware-in-the-loop simulation, the radar tracking system. Research Interests Real-time analysis and computing, hardware/software co-design, power-aware architectures and algorithms, reconfigurable computing, system-on-a-chip (SOC) issues, hardware-in-the-loop simulation Computer Science and Engineering 7 3/15/2018
 Computer and Information Security Information Assurance Network Security Computer Science and Engineering 8 3/15/2018
Computer and Information Security Information Assurance Network Security Computer Science and Engineering 8 3/15/2018
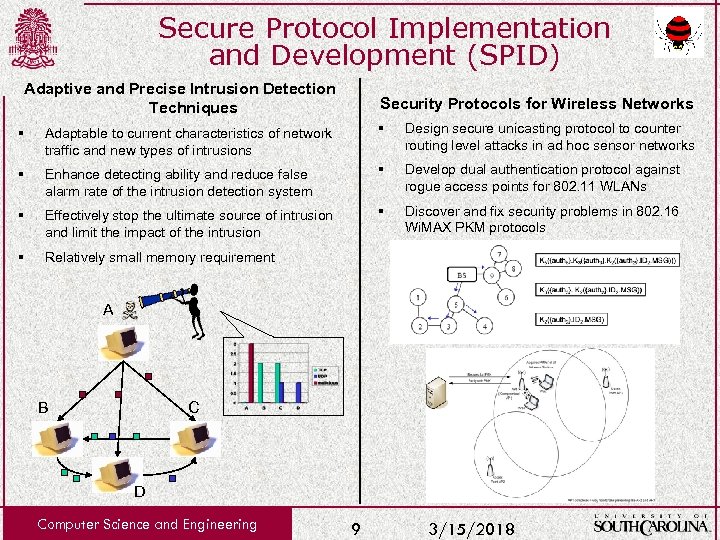 Secure Protocol Implementation and Development (SPID) Adaptive and Precise Intrusion Detection Techniques Security Protocols for Wireless Networks § Adaptable to current characteristics of network traffic and new types of intrusions § Design secure unicasting protocol to counter routing level attacks in ad hoc sensor networks § Enhance detecting ability and reduce false alarm rate of the intrusion detection system § Develop dual authentication protocol against rogue access points for 802. 11 WLANs § Effectively stop the ultimate source of intrusion and limit the impact of the intrusion § Discover and fix security problems in 802. 16 Wi. MAX PKM protocols § Relatively small memory requirement A B C D Computer Science and Engineering 9 3/15/2018
Secure Protocol Implementation and Development (SPID) Adaptive and Precise Intrusion Detection Techniques Security Protocols for Wireless Networks § Adaptable to current characteristics of network traffic and new types of intrusions § Design secure unicasting protocol to counter routing level attacks in ad hoc sensor networks § Enhance detecting ability and reduce false alarm rate of the intrusion detection system § Develop dual authentication protocol against rogue access points for 802. 11 WLANs § Effectively stop the ultimate source of intrusion and limit the impact of the intrusion § Discover and fix security problems in 802. 16 Wi. MAX PKM protocols § Relatively small memory requirement A B C D Computer Science and Engineering 9 3/15/2018
 Secure Protocol Implementation and Development (SPID) Selected Publications People C. -T. Huang and M. G. Gouda, Hop Integrity in the Internet, published by Springer, 2005. § Director: Dr. Chin-Tser Huang § § Graduate Assistants: § S. Xu, C. -T. Huang, "Attacks on PKM Protocols of IEEE 802. 16 and Its Later Versions", 3 rd Int’l Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems (ISWCS 2006). § J. Janies, N. L. Johnson, C. -T. Huang, "SUMP: A Secure Unicast Messaging Protocol for Wireless Ad Hoc Sensor Networks", Proc. of 2006 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC 2006). § C. -T. Huang, N. L. Johnson, J. Janies, and A. X. Liu, "On Capturing and Containing E-mail Worms", Proc. of the 25 th IEEE Int’l Performance Computing and Communications Conference (IPCCC 2006). § X. Zheng, C. Chen, C. -T. Huang, M. M. Matthews, and N. Santhapuri, "A Dual Authentication Protocol for IEEE 802. 11 Wireless LANs", Proc. of 2 nd Int’l Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems (ISWCS 2005). Alexander Alexandrov Shantnu Chaturvedi Jeff Janies Prasanth Kalakota Sen Xu Computer Science and Engineering 10 3/15/2018
Secure Protocol Implementation and Development (SPID) Selected Publications People C. -T. Huang and M. G. Gouda, Hop Integrity in the Internet, published by Springer, 2005. § Director: Dr. Chin-Tser Huang § § Graduate Assistants: § S. Xu, C. -T. Huang, "Attacks on PKM Protocols of IEEE 802. 16 and Its Later Versions", 3 rd Int’l Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems (ISWCS 2006). § J. Janies, N. L. Johnson, C. -T. Huang, "SUMP: A Secure Unicast Messaging Protocol for Wireless Ad Hoc Sensor Networks", Proc. of 2006 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC 2006). § C. -T. Huang, N. L. Johnson, J. Janies, and A. X. Liu, "On Capturing and Containing E-mail Worms", Proc. of the 25 th IEEE Int’l Performance Computing and Communications Conference (IPCCC 2006). § X. Zheng, C. Chen, C. -T. Huang, M. M. Matthews, and N. Santhapuri, "A Dual Authentication Protocol for IEEE 802. 11 Wireless LANs", Proc. of 2 nd Int’l Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems (ISWCS 2005). Alexander Alexandrov Shantnu Chaturvedi Jeff Janies Prasanth Kalakota Sen Xu Computer Science and Engineering 10 3/15/2018
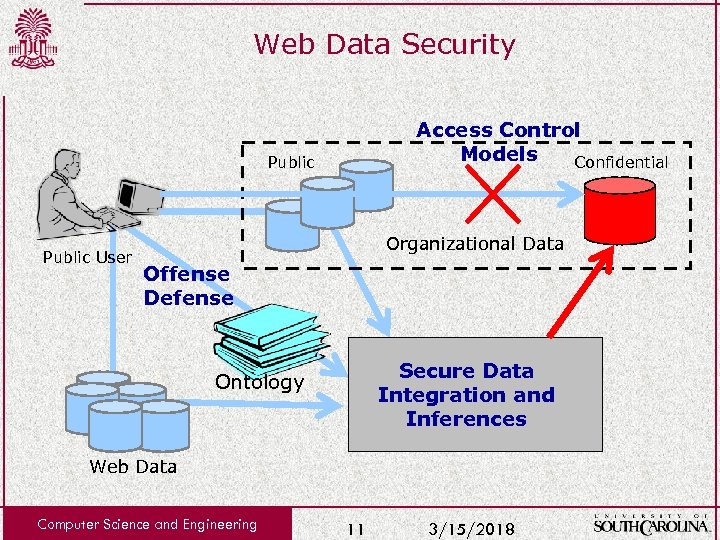 Web Data Security Access Control Models Confidential Public User Organizational Data Offense Defense Secure Data Integration and Inferences Ontology Web Data Computer Science and Engineering 11 3/15/2018
Web Data Security Access Control Models Confidential Public User Organizational Data Offense Defense Secure Data Integration and Inferences Ontology Web Data Computer Science and Engineering 11 3/15/2018
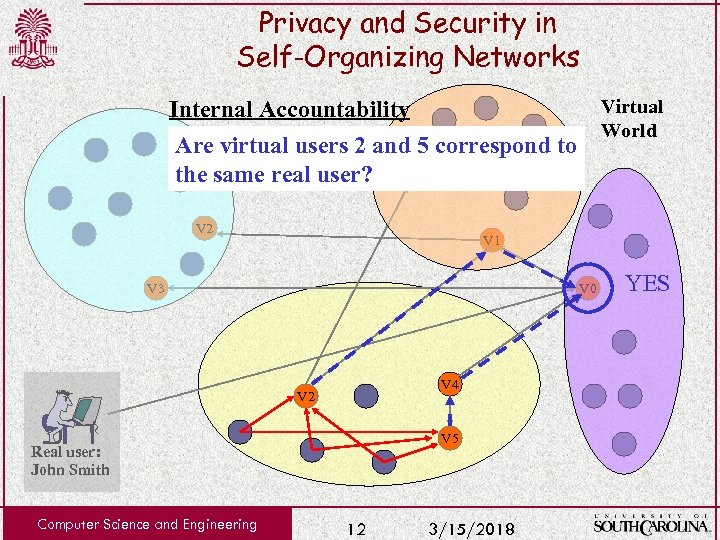 Privacy and Security in Self-Organizing Networks Virtual World Internal Accountability Are virtual users 2 and 5 correspond to the same real user? V 6 V 2 V 1 V 3 V 0 V 4 V 2 V 5 Real user: John Smith Computer Science and Engineering 12 3/15/2018 YES
Privacy and Security in Self-Organizing Networks Virtual World Internal Accountability Are virtual users 2 and 5 correspond to the same real user? V 6 V 2 V 1 V 3 V 0 V 4 V 2 V 5 Real user: John Smith Computer Science and Engineering 12 3/15/2018 YES
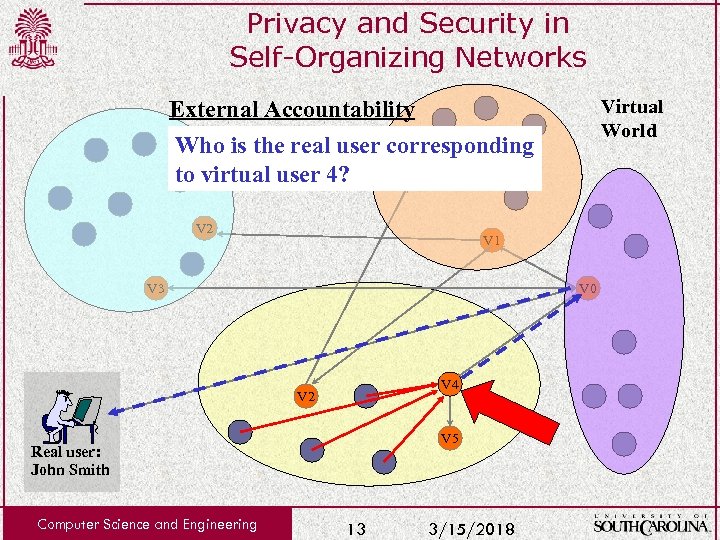 Privacy and Security in Self-Organizing Networks Virtual World External Accountability Who is the real user corresponding V 6 to virtual user 4? V 2 V 1 V 3 V 0 V 4 V 2 V 5 Real user: John Smith Computer Science and Engineering 13 3/15/2018
Privacy and Security in Self-Organizing Networks Virtual World External Accountability Who is the real user corresponding V 6 to virtual user 4? V 2 V 1 V 3 V 0 V 4 V 2 V 5 Real user: John Smith Computer Science and Engineering 13 3/15/2018
 VANETs: Vehicle Ad Hoc Networks Ontologies for Reconciling Security Among Dynamic Coalitions Information Systems Security Research Group Center for Information Assurance Engineering Computer Science and Engineering 14 3/15/2018
VANETs: Vehicle Ad Hoc Networks Ontologies for Reconciling Security Among Dynamic Coalitions Information Systems Security Research Group Center for Information Assurance Engineering Computer Science and Engineering 14 3/15/2018
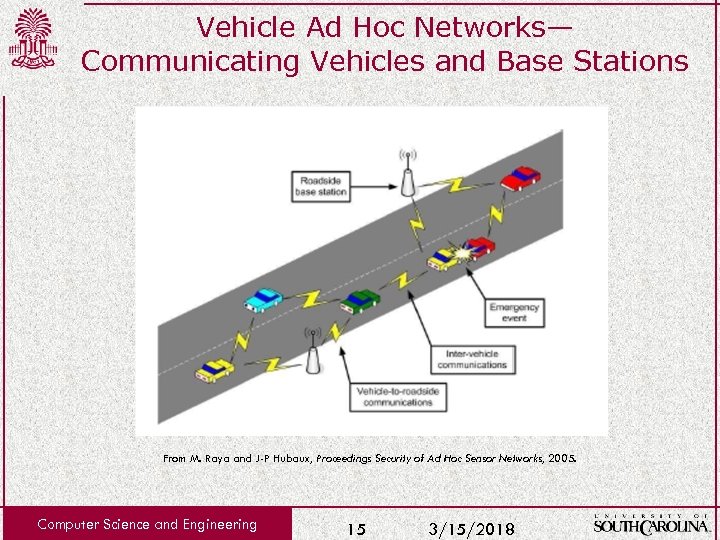 Vehicle Ad Hoc Networks— Communicating Vehicles and Base Stations From M. Raya and J-P Hubaux, Proceedings Security of Ad Hoc Sensor Networks, 2005. Computer Science and Engineering 15 3/15/2018
Vehicle Ad Hoc Networks— Communicating Vehicles and Base Stations From M. Raya and J-P Hubaux, Proceedings Security of Ad Hoc Sensor Networks, 2005. Computer Science and Engineering 15 3/15/2018
 VANET Coalition Security Issues • The VANET environment is dynamic and distributed. • Coalitions of vehicles form and dissolve based on proximity and traffic conditions. • As vehicles enter a coalition they bring their own unique representations (ontologies) for security and trust. • A major research issue is to represent and exchange these ontologies so that a vehicle seeking to enter a coalition can quickly be identified as a trusted member or else rejected. Computer Science and Engineering 16 3/15/2018
VANET Coalition Security Issues • The VANET environment is dynamic and distributed. • Coalitions of vehicles form and dissolve based on proximity and traffic conditions. • As vehicles enter a coalition they bring their own unique representations (ontologies) for security and trust. • A major research issue is to represent and exchange these ontologies so that a vehicle seeking to enter a coalition can quickly be identified as a trusted member or else rejected. Computer Science and Engineering 16 3/15/2018
 Bioinformatics Computer Science and Engineering 17 3/15/2018
Bioinformatics Computer Science and Engineering 17 3/15/2018
 Viral Genome Signatures Overview • Analysis of viral amino acids shows: – There is a correlation between usage and genome type – An efficient classifier can be constructed from amino acid data – In-frame sequences can be accurately classified • This observation can be used to support classification of novel viral pathogens. • This analysis can support phylogenetic reconstruction. Computer Science and Engineering 18 3/15/2018
Viral Genome Signatures Overview • Analysis of viral amino acids shows: – There is a correlation between usage and genome type – An efficient classifier can be constructed from amino acid data – In-frame sequences can be accurately classified • This observation can be used to support classification of novel viral pathogens. • This analysis can support phylogenetic reconstruction. Computer Science and Engineering 18 3/15/2018
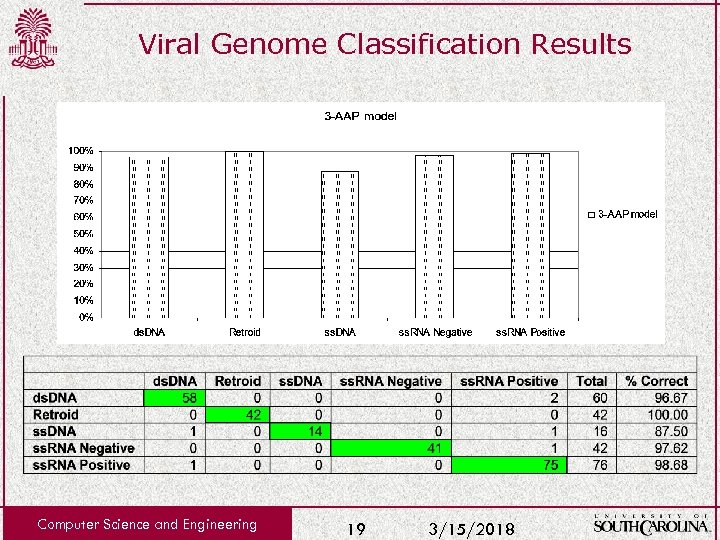 Viral Genome Classification Results Computer Science and Engineering 19 3/15/2018
Viral Genome Classification Results Computer Science and Engineering 19 3/15/2018
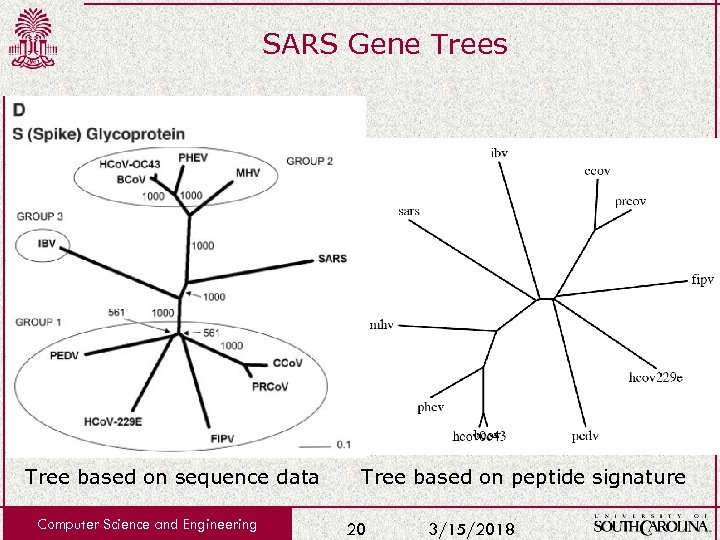 SARS Gene Trees Tree based on sequence data Computer Science and Engineering Tree based on peptide signature 20 3/15/2018
SARS Gene Trees Tree based on sequence data Computer Science and Engineering Tree based on peptide signature 20 3/15/2018
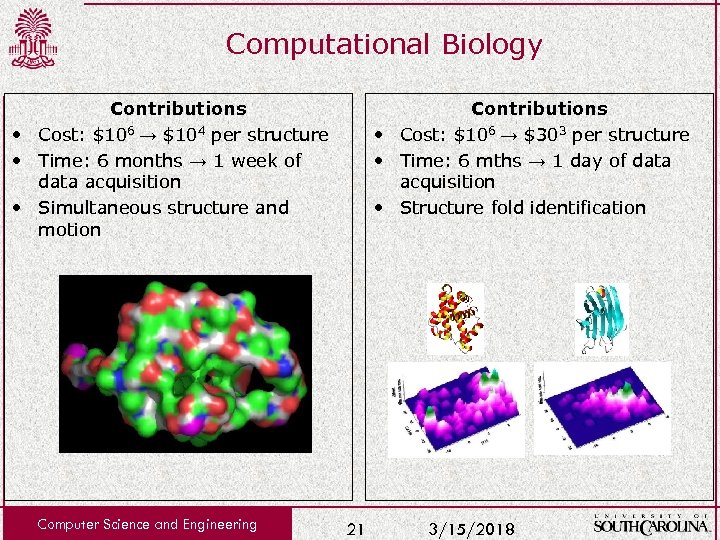 Computational Biology Contributions • Cost: $106 → $104 per structure • Time: 6 months → 1 week of data acquisition • Simultaneous structure and motion Computer Science and Engineering Contributions • Cost: $106 → $303 per structure • Time: 6 mths → 1 day of data acquisition • Structure fold identification 21 3/15/2018
Computational Biology Contributions • Cost: $106 → $104 per structure • Time: 6 months → 1 week of data acquisition • Simultaneous structure and motion Computer Science and Engineering Contributions • Cost: $106 → $303 per structure • Time: 6 mths → 1 day of data acquisition • Structure fold identification 21 3/15/2018
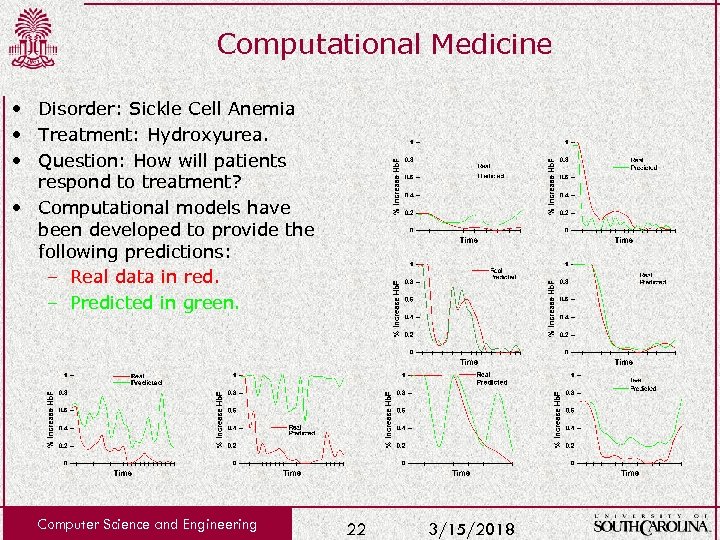 Computational Medicine • Disorder: Sickle Cell Anemia • Treatment: Hydroxyurea. • Question: How will patients respond to treatment? • Computational models have been developed to provide the following predictions: – Real data in red. – Predicted in green. Computer Science and Engineering 22 3/15/2018
Computational Medicine • Disorder: Sickle Cell Anemia • Treatment: Hydroxyurea. • Question: How will patients respond to treatment? • Computational models have been developed to provide the following predictions: – Real data in red. – Predicted in green. Computer Science and Engineering 22 3/15/2018
 Phylogenetic Reconstruction Fundamental to a wide range of bioinformatic applications Involves biologists, computer scientists and mathematicians Models, algorithms and highperformance tools for analysis from genome rearrangement data Current NIH funding with co-PIs from USC and U of North Carolina. Also part of the NSF CIPRES project, a large ITR providing new solutions for the difficult computational problems that arise in inferring evolutionary relationships. Computer Science and Engineering 23 3/15/2018
Phylogenetic Reconstruction Fundamental to a wide range of bioinformatic applications Involves biologists, computer scientists and mathematicians Models, algorithms and highperformance tools for analysis from genome rearrangement data Current NIH funding with co-PIs from USC and U of North Carolina. Also part of the NSF CIPRES project, a large ITR providing new solutions for the difficult computational problems that arise in inferring evolutionary relationships. Computer Science and Engineering 23 3/15/2018
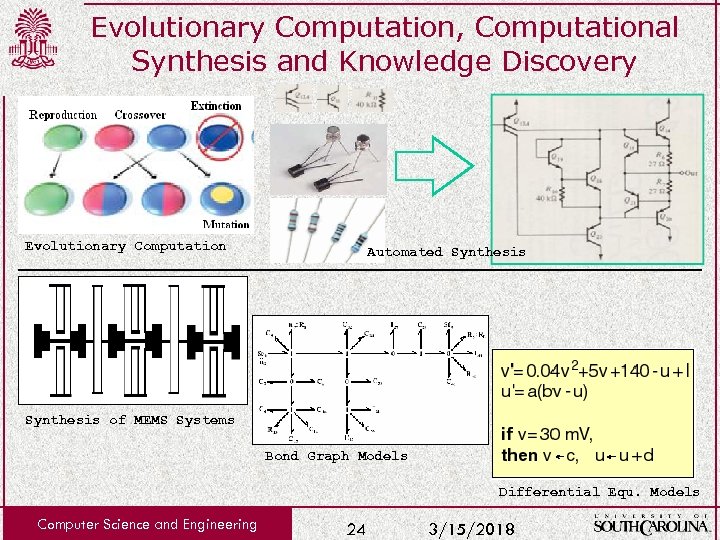 Evolutionary Computation, Computational Synthesis and Knowledge Discovery Evolutionary Computation Automated Synthesis of MEMS Systems Bond Graph Models Differential Equ. Models Computer Science and Engineering 24 3/15/2018
Evolutionary Computation, Computational Synthesis and Knowledge Discovery Evolutionary Computation Automated Synthesis of MEMS Systems Bond Graph Models Differential Equ. Models Computer Science and Engineering 24 3/15/2018
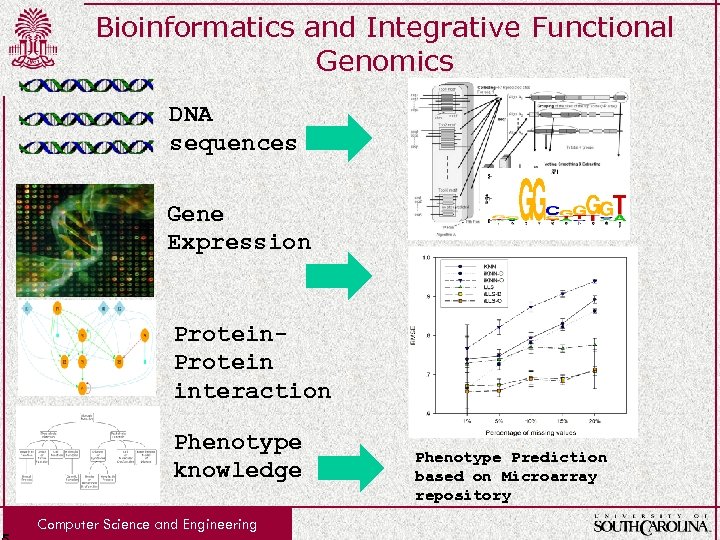 Bioinformatics and Integrative Functional Genomics DNA sequences Gene Expression Protein interaction Phenotype knowledge Computer Science and Engineering Phenotype Prediction based on Microarray repository
Bioinformatics and Integrative Functional Genomics DNA sequences Gene Expression Protein interaction Phenotype knowledge Computer Science and Engineering Phenotype Prediction based on Microarray repository
 Medical Image Processing Computer Vision Computer Science and Engineering 26 3/15/2018
Medical Image Processing Computer Vision Computer Science and Engineering 26 3/15/2018
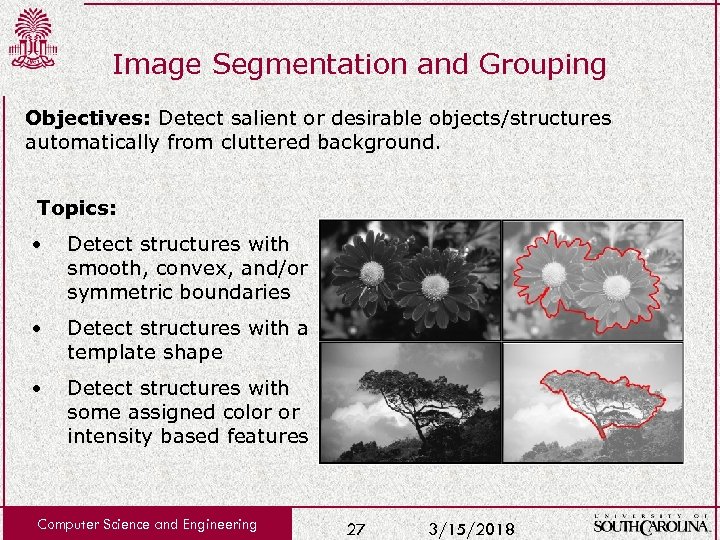 Image Segmentation and Grouping Objectives: Detect salient or desirable objects/structures automatically from cluttered background. Topics: • Detect structures with smooth, convex, and/or symmetric boundaries • Detect structures with a template shape • Detect structures with some assigned color or intensity based features Computer Science and Engineering 27 3/15/2018
Image Segmentation and Grouping Objectives: Detect salient or desirable objects/structures automatically from cluttered background. Topics: • Detect structures with smooth, convex, and/or symmetric boundaries • Detect structures with a template shape • Detect structures with some assigned color or intensity based features Computer Science and Engineering 27 3/15/2018
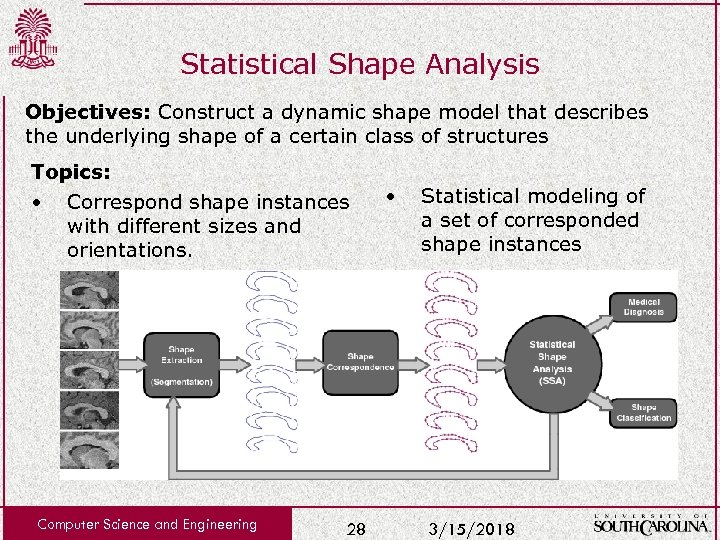 Statistical Shape Analysis Objectives: Construct a dynamic shape model that describes the underlying shape of a certain class of structures Topics: • Correspond shape instances with different sizes and orientations. Computer Science and Engineering 28 • Statistical modeling of a set of corresponded shape instances 3/15/2018
Statistical Shape Analysis Objectives: Construct a dynamic shape model that describes the underlying shape of a certain class of structures Topics: • Correspond shape instances with different sizes and orientations. Computer Science and Engineering 28 • Statistical modeling of a set of corresponded shape instances 3/15/2018
 Robust Software Cultural Decision Support and Computational Ethics Computer Science and Engineering 29 3/15/2018
Robust Software Cultural Decision Support and Computational Ethics Computer Science and Engineering 29 3/15/2018
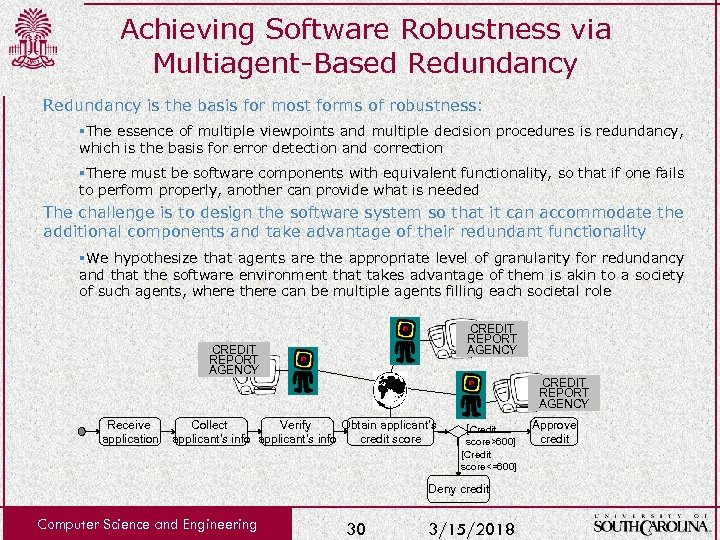 Achieving Software Robustness via Multiagent-Based Redundancy is the basis for most forms of robustness: §The essence of multiple viewpoints and multiple decision procedures is redundancy, which is the basis for error detection and correction §There must be software components with equivalent functionality, so that if one fails to perform properly, another can provide what is needed The challenge is to design the software system so that it can accommodate the additional components and take advantage of their redundant functionality §We hypothesize that agents are the appropriate level of granularity for redundancy and that the software environment that takes advantage of them is akin to a society of such agents, where there can be multiple agents filling each societal role CREDIT REPORT AGENCY Receive application CREDIT REPORT AGENCY Collect Verify Obtain applicant’s info credit score [Credit score>600] [Credit score<=600] Deny credit Computer Science and Engineering 30 3/15/2018 Approve credit
Achieving Software Robustness via Multiagent-Based Redundancy is the basis for most forms of robustness: §The essence of multiple viewpoints and multiple decision procedures is redundancy, which is the basis for error detection and correction §There must be software components with equivalent functionality, so that if one fails to perform properly, another can provide what is needed The challenge is to design the software system so that it can accommodate the additional components and take advantage of their redundant functionality §We hypothesize that agents are the appropriate level of granularity for redundancy and that the software environment that takes advantage of them is akin to a society of such agents, where there can be multiple agents filling each societal role CREDIT REPORT AGENCY Receive application CREDIT REPORT AGENCY Collect Verify Obtain applicant’s info credit score [Credit score>600] [Credit score<=600] Deny credit Computer Science and Engineering 30 3/15/2018 Approve credit
 “Winning the Peace” A Decision System for Commanders in Asymmetric Conflicts Vision Commanders in asymmetric conflicts need decision systems that will aid them in considering religious, cultural, historic, and economic factors, as well as battlefield tactics Individual warfighters need guidance in how to interact with a local populace having a different cultural background We will develop real-time decision aids for both commanders and warfighters that will guide their choice of the appropriate tactics in the appropriate context Challenges Accommodating different representations, reasoning methods, and abstractions for each contextual factor Acquiring domain knowledge for each factor Representing specific situations quickly and easily for useful contextual decisions Presenting recommended COAs with explanations in a helpful format Computer Science and Engineering Problem Commanders in asymmetric conflicts must make decisions that consider not only battlefield tactics, but also collateral effects on the local populace Military objectives must be to win both the tactical engagements and the good will of the local populace Short-term tactical decisions must be made in a long-term strategic context that includes religious, cultural, historic, political, and economic factors Current Prototype Provides cultural and tactical advice to warfighters Combines GPS, wi-fi, and Bluetooth to relay status to commanders and interact with other warfighters 31 3/15/2018
“Winning the Peace” A Decision System for Commanders in Asymmetric Conflicts Vision Commanders in asymmetric conflicts need decision systems that will aid them in considering religious, cultural, historic, and economic factors, as well as battlefield tactics Individual warfighters need guidance in how to interact with a local populace having a different cultural background We will develop real-time decision aids for both commanders and warfighters that will guide their choice of the appropriate tactics in the appropriate context Challenges Accommodating different representations, reasoning methods, and abstractions for each contextual factor Acquiring domain knowledge for each factor Representing specific situations quickly and easily for useful contextual decisions Presenting recommended COAs with explanations in a helpful format Computer Science and Engineering Problem Commanders in asymmetric conflicts must make decisions that consider not only battlefield tactics, but also collateral effects on the local populace Military objectives must be to win both the tactical engagements and the good will of the local populace Short-term tactical decisions must be made in a long-term strategic context that includes religious, cultural, historic, political, and economic factors Current Prototype Provides cultural and tactical advice to warfighters Combines GPS, wi-fi, and Bluetooth to relay status to commanders and interact with other warfighters 31 3/15/2018
 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Computer Science and Engineering 32 3/15/2018
Robotics and Autonomous Systems Computer Science and Engineering 32 3/15/2018
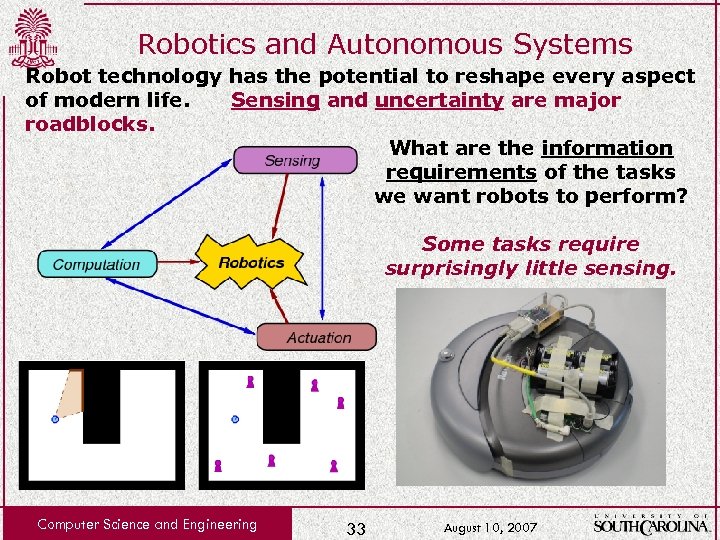 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Robot technology has the potential to reshape every aspect of modern life. Sensing and uncertainty are major roadblocks. What are the information requirements of the tasks we want robots to perform? Some tasks require surprisingly little sensing. Computer Science and Engineering 33 August 10, 2007
Robotics and Autonomous Systems Robot technology has the potential to reshape every aspect of modern life. Sensing and uncertainty are major roadblocks. What are the information requirements of the tasks we want robots to perform? Some tasks require surprisingly little sensing. Computer Science and Engineering 33 August 10, 2007
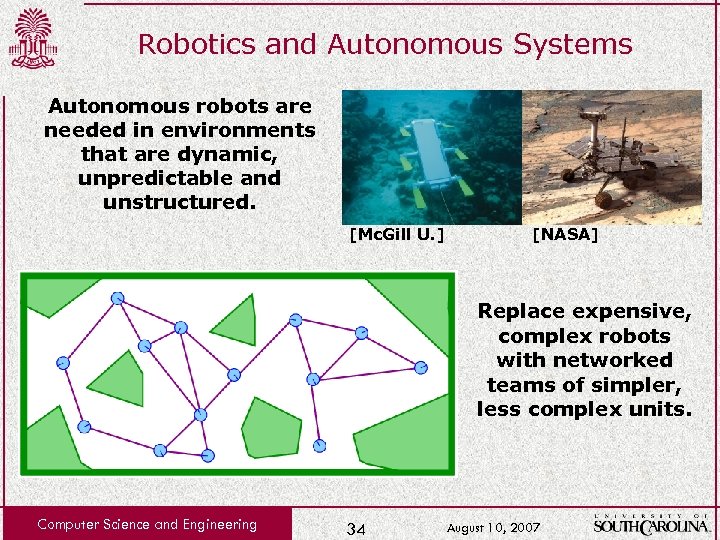 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Autonomous robots are needed in environments that are dynamic, unpredictable and unstructured. [Mc. Gill U. ] [NASA] Replace expensive, complex robots with networked teams of simpler, less complex units. Computer Science and Engineering 34 August 10, 2007
Robotics and Autonomous Systems Autonomous robots are needed in environments that are dynamic, unpredictable and unstructured. [Mc. Gill U. ] [NASA] Replace expensive, complex robots with networked teams of simpler, less complex units. Computer Science and Engineering 34 August 10, 2007
 Efficient Distributed Resource Allocation Computer Science and Engineering 35 3/15/2018
Efficient Distributed Resource Allocation Computer Science and Engineering 35 3/15/2018
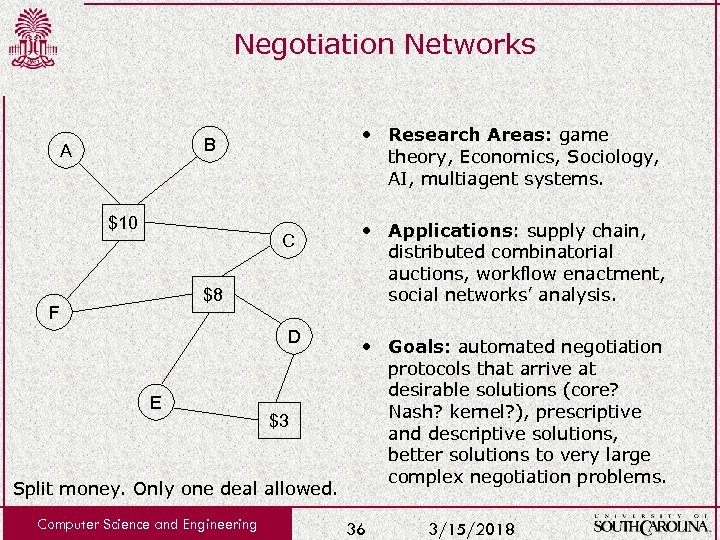 Negotiation Networks • Research Areas: game theory, Economics, Sociology, AI, multiagent systems. B A $10 C $8 F D E $3 Split money. Only one deal allowed. Computer Science and Engineering • Applications: supply chain, distributed combinatorial auctions, workflow enactment, social networks’ analysis. • Goals: automated negotiation protocols that arrive at desirable solutions (core? Nash? kernel? ), prescriptive and descriptive solutions, better solutions to very large complex negotiation problems. 36 3/15/2018
Negotiation Networks • Research Areas: game theory, Economics, Sociology, AI, multiagent systems. B A $10 C $8 F D E $3 Split money. Only one deal allowed. Computer Science and Engineering • Applications: supply chain, distributed combinatorial auctions, workflow enactment, social networks’ analysis. • Goals: automated negotiation protocols that arrive at desirable solutions (core? Nash? kernel? ), prescriptive and descriptive solutions, better solutions to very large complex negotiation problems. 36 3/15/2018
 Bayesian Networks Computer Science and Engineering 37 3/15/2018
Bayesian Networks Computer Science and Engineering 37 3/15/2018
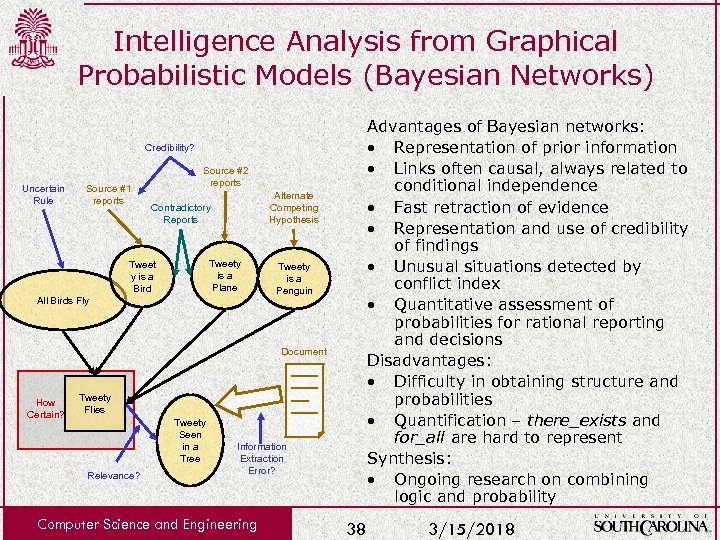 Intelligence Analysis from Graphical Probabilistic Models (Bayesian Networks) Advantages of Bayesian networks: • Representation of prior information • Links often causal, always related to conditional independence • Fast retraction of evidence • Representation and use of credibility of findings • Unusual situations detected by conflict index • Quantitative assessment of probabilities for rational reporting and decisions Disadvantages: • Difficulty in obtaining structure and probabilities • Quantification – there_exists and for_all are hard to represent Synthesis: • Ongoing research on combining logic and probability Credibility? Uncertain Rule Source #1 reports Source #2 reports Alternate Competing Hypothesis Contradictory Reports Tweety is a Plane Tweet y is a Bird All Birds Fly Tweety is a Penguin Document How Certain? Tweety Flies Tweety Seen in a Tree Relevance? Information Extraction Error? Computer Science and Engineering 38 3/15/2018
Intelligence Analysis from Graphical Probabilistic Models (Bayesian Networks) Advantages of Bayesian networks: • Representation of prior information • Links often causal, always related to conditional independence • Fast retraction of evidence • Representation and use of credibility of findings • Unusual situations detected by conflict index • Quantitative assessment of probabilities for rational reporting and decisions Disadvantages: • Difficulty in obtaining structure and probabilities • Quantification – there_exists and for_all are hard to represent Synthesis: • Ongoing research on combining logic and probability Credibility? Uncertain Rule Source #1 reports Source #2 reports Alternate Competing Hypothesis Contradictory Reports Tweety is a Plane Tweet y is a Bird All Birds Fly Tweety is a Penguin Document How Certain? Tweety Flies Tweety Seen in a Tree Relevance? Information Extraction Error? Computer Science and Engineering 38 3/15/2018
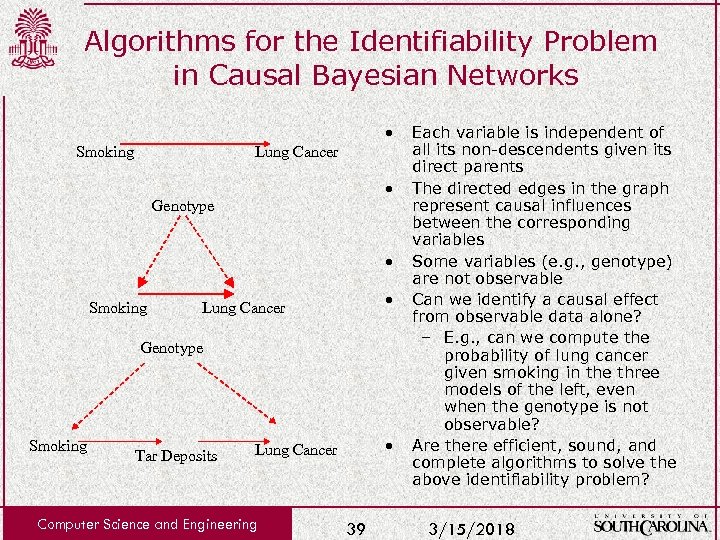 Algorithms for the Identifiability Problem in Causal Bayesian Networks • Smoking Lung Cancer • Genotype • Smoking • Lung Cancer Genotype Smoking Tar Deposits • Lung Cancer Computer Science and Engineering 39 Each variable is independent of all its non-descendents given its direct parents The directed edges in the graph represent causal influences between the corresponding variables Some variables (e. g. , genotype) are not observable Can we identify a causal effect from observable data alone? – E. g. , can we compute the probability of lung cancer given smoking in the three models of the left, even when the genotype is not observable? Are there efficient, sound, and complete algorithms to solve the above identifiability problem? 3/15/2018
Algorithms for the Identifiability Problem in Causal Bayesian Networks • Smoking Lung Cancer • Genotype • Smoking • Lung Cancer Genotype Smoking Tar Deposits • Lung Cancer Computer Science and Engineering 39 Each variable is independent of all its non-descendents given its direct parents The directed edges in the graph represent causal influences between the corresponding variables Some variables (e. g. , genotype) are not observable Can we identify a causal effect from observable data alone? – E. g. , can we compute the probability of lung cancer given smoking in the three models of the left, even when the genotype is not observable? Are there efficient, sound, and complete algorithms to solve the above identifiability problem? 3/15/2018
 Quantum Computing and Information Computational Complexity Computer Science and Engineering 40 3/15/2018
Quantum Computing and Information Computational Complexity Computer Science and Engineering 40 3/15/2018
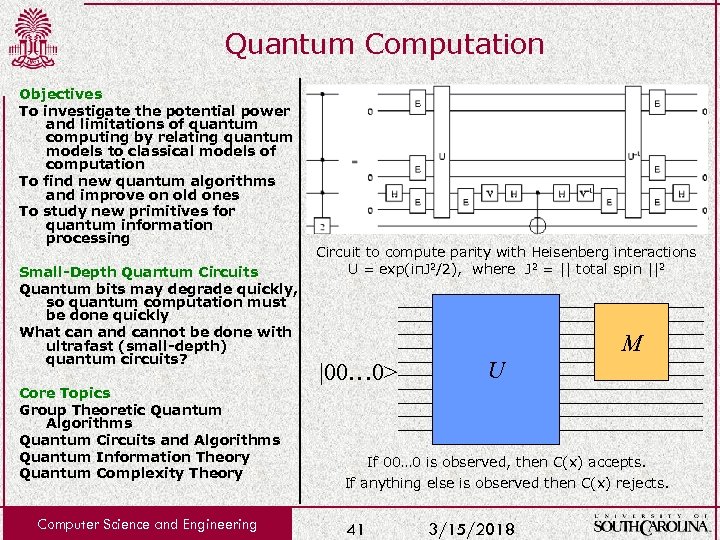 Quantum Computation Objectives To investigate the potential power and limitations of quantum computing by relating quantum models to classical models of computation To find new quantum algorithms and improve on old ones To study new primitives for quantum information processing Small-Depth Quantum Circuits Quantum bits may degrade quickly, so quantum computation must be done quickly What can and cannot be done with ultrafast (small-depth) quantum circuits? Core Topics Group Theoretic Quantum Algorithms Quantum Circuits and Algorithms Quantum Information Theory Quantum Complexity Theory Computer Science and Engineering Circuit to compute parity with Heisenberg interactions U = exp(iπJ 2/2), where J 2 = || total spin ||2 M |00… 0> U If 00… 0 is observed, then C(x) accepts. If anything else is observed then C(x) rejects. 41 3/15/2018
Quantum Computation Objectives To investigate the potential power and limitations of quantum computing by relating quantum models to classical models of computation To find new quantum algorithms and improve on old ones To study new primitives for quantum information processing Small-Depth Quantum Circuits Quantum bits may degrade quickly, so quantum computation must be done quickly What can and cannot be done with ultrafast (small-depth) quantum circuits? Core Topics Group Theoretic Quantum Algorithms Quantum Circuits and Algorithms Quantum Information Theory Quantum Complexity Theory Computer Science and Engineering Circuit to compute parity with Heisenberg interactions U = exp(iπJ 2/2), where J 2 = || total spin ||2 M |00… 0> U If 00… 0 is observed, then C(x) accepts. If anything else is observed then C(x) rejects. 41 3/15/2018
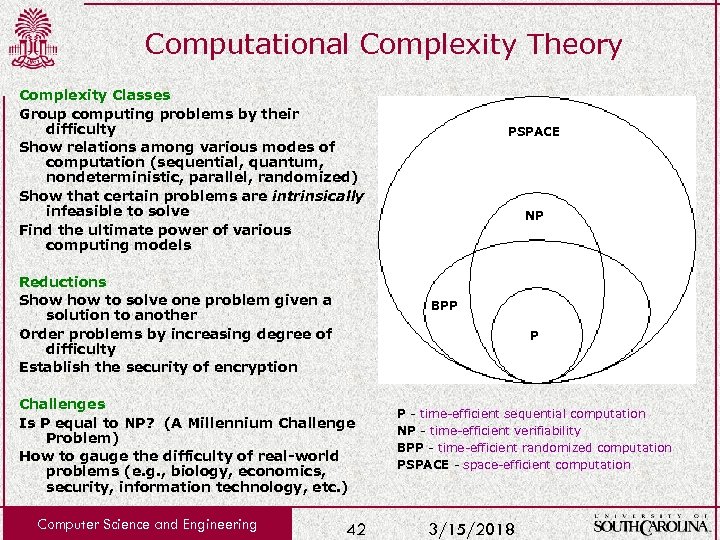 Computational Complexity Theory Complexity Classes Group computing problems by their difficulty Show relations among various modes of computation (sequential, quantum, nondeterministic, parallel, randomized) Show that certain problems are intrinsically infeasible to solve Find the ultimate power of various computing models Reductions Show to solve one problem given a solution to another Order problems by increasing degree of difficulty Establish the security of encryption NP BPP P Challenges Is P equal to NP? (A Millennium Challenge Problem) How to gauge the difficulty of real-world problems (e. g. , biology, economics, security, information technology, etc. ) Computer Science and Engineering PSPACE 42 P - time-efficient sequential computation NP - time-efficient verifiability BPP - time-efficient randomized computation PSPACE - space-efficient computation 3/15/2018
Computational Complexity Theory Complexity Classes Group computing problems by their difficulty Show relations among various modes of computation (sequential, quantum, nondeterministic, parallel, randomized) Show that certain problems are intrinsically infeasible to solve Find the ultimate power of various computing models Reductions Show to solve one problem given a solution to another Order problems by increasing degree of difficulty Establish the security of encryption NP BPP P Challenges Is P equal to NP? (A Millennium Challenge Problem) How to gauge the difficulty of real-world problems (e. g. , biology, economics, security, information technology, etc. ) Computer Science and Engineering PSPACE 42 P - time-efficient sequential computation NP - time-efficient verifiability BPP - time-efficient randomized computation PSPACE - space-efficient computation 3/15/2018
 Software Engineering Computer Science and Engineering 43 3/15/2018
Software Engineering Computer Science and Engineering 43 3/15/2018
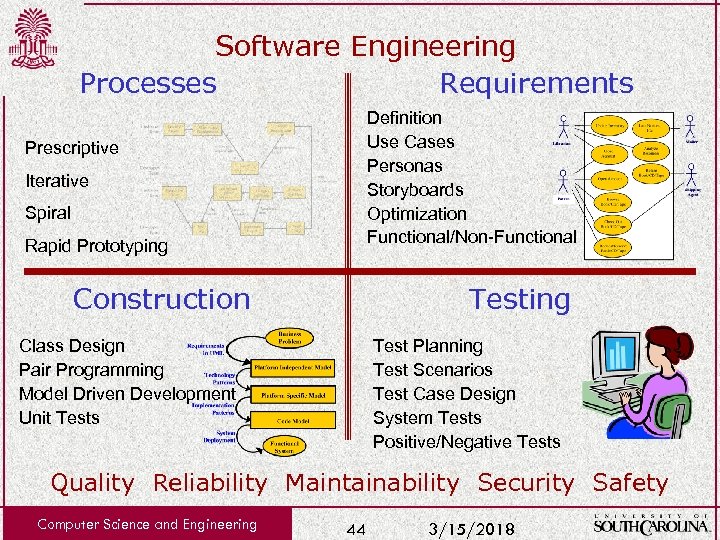 Software Engineering Processes Requirements Definition Use Cases Personas Storyboards Optimization Functional/Non-Functional Prescriptive Iterative Spiral Rapid Prototyping Construction Testing Test Planning Test Scenarios Test Case Design System Tests Positive/Negative Tests Class Design Pair Programming Model Driven Development Unit Tests Quality Reliability Maintainability Security Safety Computer Science and Engineering 44 3/15/2018
Software Engineering Processes Requirements Definition Use Cases Personas Storyboards Optimization Functional/Non-Functional Prescriptive Iterative Spiral Rapid Prototyping Construction Testing Test Planning Test Scenarios Test Case Design System Tests Positive/Negative Tests Class Design Pair Programming Model Driven Development Unit Tests Quality Reliability Maintainability Security Safety Computer Science and Engineering 44 3/15/2018
 Information Retrieval Computer Science and Engineering 45 3/15/2018
Information Retrieval Computer Science and Engineering 45 3/15/2018
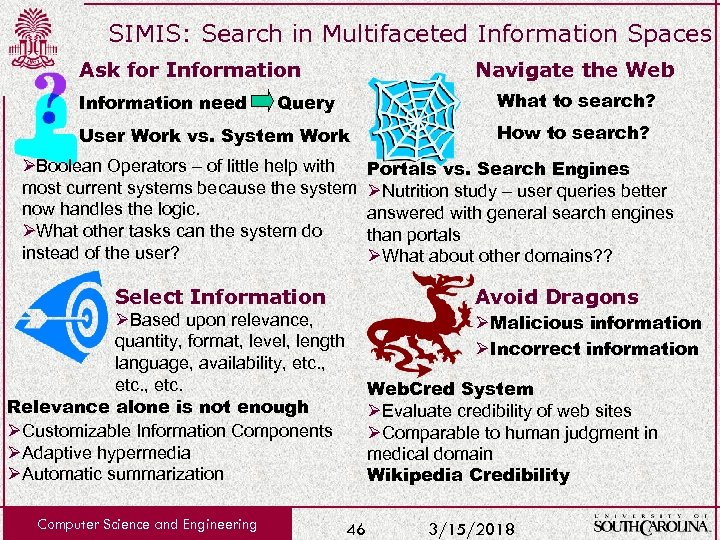 SIMIS: Search in Multifaceted Information Spaces Ask for Information need Navigate the Web What to search? Query User Work vs. System Work ØBoolean Operators – of little help with most current systems because the system now handles the logic. ØWhat other tasks can the system do instead of the user? Select Information Portals vs. Search Engines ØNutrition study – user queries better answered with general search engines than portals ØWhat about other domains? ? Avoid Dragons ØBased upon relevance, quantity, format, level, length language, availability, etc. Relevance alone is not enough ØCustomizable Information Components ØAdaptive hypermedia ØAutomatic summarization Computer Science and Engineering How to search? ØMalicious information ØIncorrect information Web. Cred System ØEvaluate credibility of web sites ØComparable to human judgment in medical domain Wikipedia Credibility 46 3/15/2018
SIMIS: Search in Multifaceted Information Spaces Ask for Information need Navigate the Web What to search? Query User Work vs. System Work ØBoolean Operators – of little help with most current systems because the system now handles the logic. ØWhat other tasks can the system do instead of the user? Select Information Portals vs. Search Engines ØNutrition study – user queries better answered with general search engines than portals ØWhat about other domains? ? Avoid Dragons ØBased upon relevance, quantity, format, level, length language, availability, etc. Relevance alone is not enough ØCustomizable Information Components ØAdaptive hypermedia ØAutomatic summarization Computer Science and Engineering How to search? ØMalicious information ØIncorrect information Web. Cred System ØEvaluate credibility of web sites ØComparable to human judgment in medical domain Wikipedia Credibility 46 3/15/2018
 Computer Networks Computer Science and Engineering 47 3/15/2018
Computer Networks Computer Science and Engineering 47 3/15/2018
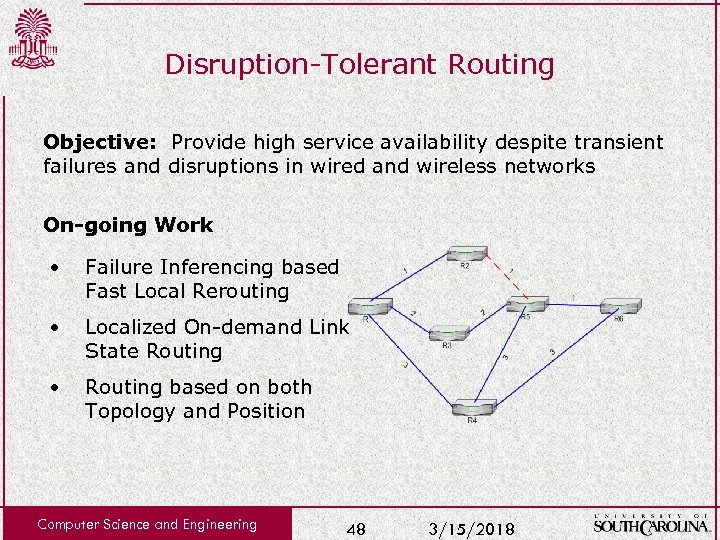 Disruption-Tolerant Routing Objective: Provide high service availability despite transient failures and disruptions in wired and wireless networks On-going Work • Failure Inferencing based Fast Local Rerouting • Localized On-demand Link State Routing • Routing based on both Topology and Position Computer Science and Engineering 48 3/15/2018
Disruption-Tolerant Routing Objective: Provide high service availability despite transient failures and disruptions in wired and wireless networks On-going Work • Failure Inferencing based Fast Local Rerouting • Localized On-demand Link State Routing • Routing based on both Topology and Position Computer Science and Engineering 48 3/15/2018
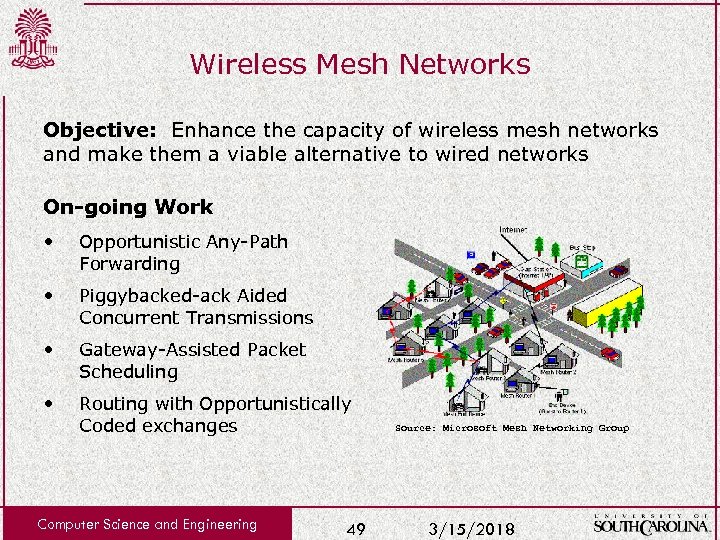 Wireless Mesh Networks Objective: Enhance the capacity of wireless mesh networks and make them a viable alternative to wired networks On-going Work • Opportunistic Any-Path Forwarding • Piggybacked-ack Aided Concurrent Transmissions • Gateway-Assisted Packet Scheduling • Routing with Opportunistically Coded exchanges Computer Science and Engineering 49 Source: Microsoft Mesh Networking Group 3/15/2018
Wireless Mesh Networks Objective: Enhance the capacity of wireless mesh networks and make them a viable alternative to wired networks On-going Work • Opportunistic Any-Path Forwarding • Piggybacked-ack Aided Concurrent Transmissions • Gateway-Assisted Packet Scheduling • Routing with Opportunistically Coded exchanges Computer Science and Engineering 49 Source: Microsoft Mesh Networking Group 3/15/2018
 Wireless networking and security Computer Science and Engineering 50 15 三月
Wireless networking and security Computer Science and Engineering 50 15 三月
 Radio Interference/Jamming Attacks in Wireless Networks Overview § @#$%%$# @&… Hi Hello Bob … Wireless networks § § § Communicate via shared media Channel access protocol: carrier sense based … Alic e Mr. X Unintentional radio interference: § § § Co-existing devices: 802. 11 b/g, cordless phone, Bluetooth, Microwave oven share the same frequency band Equipment accidentally transmits on a frequency band that doesn’t belong to it. Intentional jamming: § A transmitter, tuned to the same frequency as the receiving equipment, overrides any signal with enough power Computer Science and Engineering 51 15 三月
Radio Interference/Jamming Attacks in Wireless Networks Overview § @#$%%$# @&… Hi Hello Bob … Wireless networks § § § Communicate via shared media Channel access protocol: carrier sense based … Alic e Mr. X Unintentional radio interference: § § § Co-existing devices: 802. 11 b/g, cordless phone, Bluetooth, Microwave oven share the same frequency band Equipment accidentally transmits on a frequency band that doesn’t belong to it. Intentional jamming: § A transmitter, tuned to the same frequency as the receiving equipment, overrides any signal with enough power Computer Science and Engineering 51 15 三月
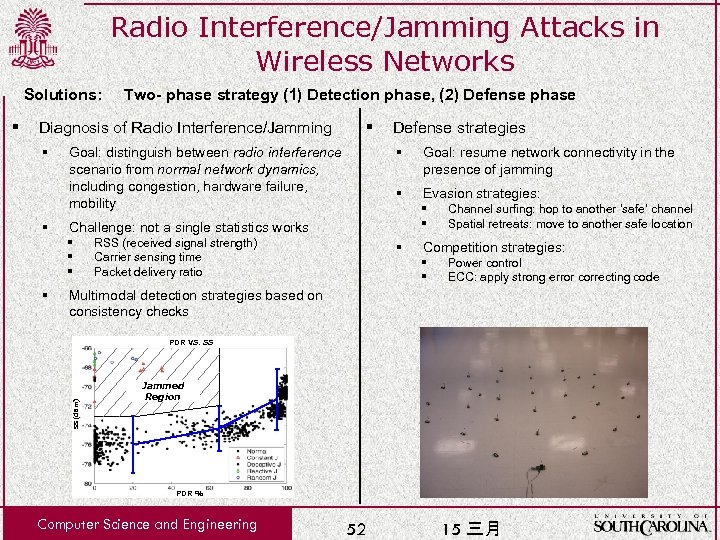 Radio Interference/Jamming Attacks in Wireless Networks Solutions: Diagnosis of Radio Interference/Jamming § § Defense strategies § Goal: resume network connectivity in the presence of jamming § Evasion strategies: § § Challenge: not a single statistics works § § § Goal: distinguish between radio interference scenario from normal network dynamics, including congestion, hardware failure, mobility RSS (received signal strength) Carrier sensing time Packet delivery ratio § Channel surfing: hop to another ‘safe’ channel Spatial retreats: move to another safe location Competition strategies: § § Power control ECC: apply strong error correcting code Multimodal detection strategies based on consistency checks PDR VS. SS SS(d. Bm) § Two- phase strategy (1) Detection phase, (2) Defense phase Jammed Region PDR % Computer Science and Engineering 52 15 三月
Radio Interference/Jamming Attacks in Wireless Networks Solutions: Diagnosis of Radio Interference/Jamming § § Defense strategies § Goal: resume network connectivity in the presence of jamming § Evasion strategies: § § Challenge: not a single statistics works § § § Goal: distinguish between radio interference scenario from normal network dynamics, including congestion, hardware failure, mobility RSS (received signal strength) Carrier sensing time Packet delivery ratio § Channel surfing: hop to another ‘safe’ channel Spatial retreats: move to another safe location Competition strategies: § § Power control ECC: apply strong error correcting code Multimodal detection strategies based on consistency checks PDR VS. SS SS(d. Bm) § Two- phase strategy (1) Detection phase, (2) Defense phase Jammed Region PDR % Computer Science and Engineering 52 15 三月
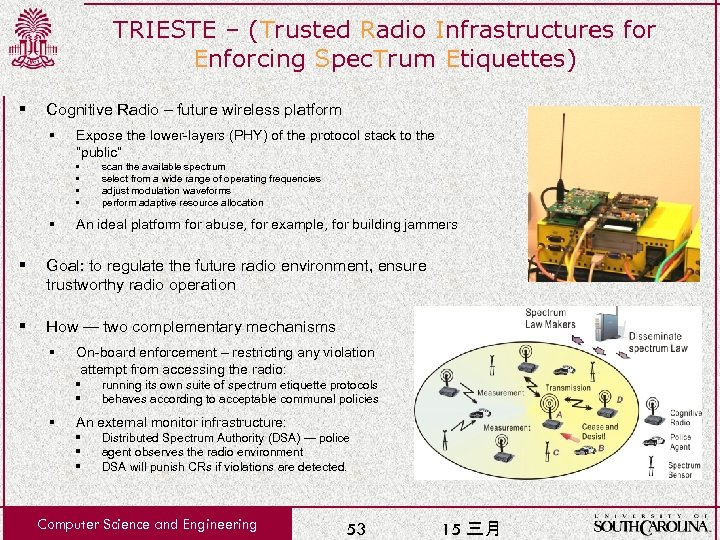 TRIESTE – (Trusted Radio Infrastructures for Enforcing Spec. Trum Etiquettes) § Cognitive Radio – future wireless platform § Expose the lower-layers (PHY) of the protocol stack to the “public” § § § scan the available spectrum select from a wide range of operating frequencies adjust modulation waveforms perform adaptive resource allocation An ideal platform for abuse, for example, for building jammers § Goal: to regulate the future radio environment, ensure trustworthy radio operation § How — two complementary mechanisms § On-board enforcement – restricting any violation attempt from accessing the radio: § § § running its own suite of spectrum etiquette protocols behaves according to acceptable communal policies An external monitor infrastructure: § § § Distributed Spectrum Authority (DSA) — police agent observes the radio environment DSA will punish CRs if violations are detected. Computer Science and Engineering 53 15 三月
TRIESTE – (Trusted Radio Infrastructures for Enforcing Spec. Trum Etiquettes) § Cognitive Radio – future wireless platform § Expose the lower-layers (PHY) of the protocol stack to the “public” § § § scan the available spectrum select from a wide range of operating frequencies adjust modulation waveforms perform adaptive resource allocation An ideal platform for abuse, for example, for building jammers § Goal: to regulate the future radio environment, ensure trustworthy radio operation § How — two complementary mechanisms § On-board enforcement – restricting any violation attempt from accessing the radio: § § § running its own suite of spectrum etiquette protocols behaves according to acceptable communal policies An external monitor infrastructure: § § § Distributed Spectrum Authority (DSA) — police agent observes the radio environment DSA will punish CRs if violations are detected. Computer Science and Engineering 53 15 三月
 Research Experiences for Undergraduates Computer Science and Engineering 54 3/15/2018
Research Experiences for Undergraduates Computer Science and Engineering 54 3/15/2018
 Research Experiences for Undergraduates Goals Research Areas ØEncourage students to consider graduate school and research careers ØEncourage students to work in areas of state and national interest ØProvide a supportive research group ØImproving information availability on the semantic web ØPromote greater cooperation among science and engineering professionals and K-12 teachers ØSpecifying security requirements during software design ØSupport provided in part by NSF Grant CNS-0353637 Computer Science and Engineering ØSoftware development for hand-held computers 55 3/15/2018
Research Experiences for Undergraduates Goals Research Areas ØEncourage students to consider graduate school and research careers ØEncourage students to work in areas of state and national interest ØProvide a supportive research group ØImproving information availability on the semantic web ØPromote greater cooperation among science and engineering professionals and K-12 teachers ØSpecifying security requirements during software design ØSupport provided in part by NSF Grant CNS-0353637 Computer Science and Engineering ØSoftware development for hand-held computers 55 3/15/2018
 The Job Market in Computing Computer Science and Engineering 56 3/15/2018
The Job Market in Computing Computer Science and Engineering 56 3/15/2018
 Computer Science and Engineering 57 3/15/2018
Computer Science and Engineering 57 3/15/2018
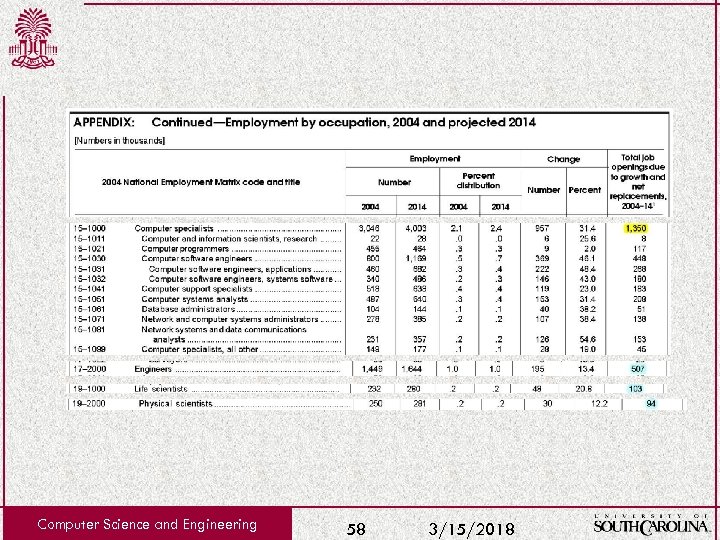 Computer Science and Engineering 58 3/15/2018
Computer Science and Engineering 58 3/15/2018
 cnnbestjobs. htm cnnbestjobspay. htm Computer Science and Engineering 59 3/15/2018
cnnbestjobs. htm cnnbestjobspay. htm Computer Science and Engineering 59 3/15/2018
 www. cse. sc. edu info@cse. sc. edu Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina Columbia, South Carolina 29208 803. 777. 2880 Computer Science and Engineering 60 3/15/2018
www. cse. sc. edu info@cse. sc. edu Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina Columbia, South Carolina 29208 803. 777. 2880 Computer Science and Engineering 60 3/15/2018


