fe93325295b8ac43947a6b178682033e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Computer Science 101 Color, Fonts, Links, Design
Computer Science 101 Color, Fonts, Links, Design
 Body Attributes • Govern the entire body of the page • • BGCOLOR - the background color TEXT - the text color LINK - the color of all links VLINK - the color of a link after it’s been selected
Body Attributes • Govern the entire body of the page • • BGCOLOR - the background color TEXT - the text color LINK - the color of all links VLINK - the color of a link after it’s been selected
(hexadecimal number) " src="https://present5.com/presentation/fe93325295b8ac43947a6b178682033e/image-3.jpg" alt="Examples (uses defaults)
(hexadecimal number) " /> Examples (uses defaults)
(hexadecimal number)
 Hexadecimal Number System • Digits 0. . 9 and A. . F • base 16 • A 16 = 1010, etc. • Can say more with less - AA is 170 (10 * 16) + (10 * 1)
Hexadecimal Number System • Digits 0. . 9 and A. . F • base 16 • A 16 = 1010, etc. • Can say more with less - AA is 170 (10 * 16) + (10 * 1)
 Representing Colors • Almost 17 million colors on most computers • Use a six-digit hexadecimal number • #000000 is black, #FFFFFF is white
Representing Colors • Almost 17 million colors on most computers • Use a six-digit hexadecimal number • #000000 is black, #FFFFFF is white
 RGB Color System • Mixes three color components (red, green, blue) • Each component is given two hex digits #2 C 45 F 2 = 2 C 45 F 2 red green blue
RGB Color System • Mixes three color components (red, green, blue) • Each component is given two hex digits #2 C 45 F 2 = 2 C 45 F 2 red green blue
 Saturation Values • 00 is minimum saturation • FF is maximum saturation • In general, lower saturation produces darker shades, whereas higher saturation produces brighter shades
Saturation Values • 00 is minimum saturation • FF is maximum saturation • In general, lower saturation produces darker shades, whereas higher saturation produces brighter shades
 Web-Safe Colors • Only 216 colors are guaranteed on all browsers • 6 * 6 = 216, so only 6 different values per component • 00, 33, 66, 99, CC, and FF
Web-Safe Colors • Only 216 colors are guaranteed on all browsers • 6 * 6 = 216, so only 6 different values per component • 00, 33, 66, 99, CC, and FF
 Examples #666666 medium gray #660066 medium purple #FF 0000 brightest red
Examples #666666 medium gray #660066 medium purple #FF 0000 brightest red
 RGB on Most Monitors • 256 * 256 = 16, 777, 216 colors • If the browser does not support all these, then the nearest color among the Web-safe ones is used
RGB on Most Monitors • 256 * 256 = 16, 777, 216 colors • If the browser does not support all these, then the nearest color among the Web-safe ones is used
 The FONT Tag • some text • It’s deprecated, meaning it’s probably supported by most browsers but may not be in future releases
The FONT Tag • some text • It’s deprecated, meaning it’s probably supported by most browsers but may not be in future releases
 Font Attributes • SIZE – 3 (10 or 12 pt) is default • COLOR – as usual • FACE – Arial, Courier, Times, etc. • Relative size - +2, -2, etc.
Font Attributes • SIZE – 3 (10 or 12 pt) is default • COLOR – as usual • FACE – Arial, Courier, Times, etc. • Relative size - +2, -2, etc.
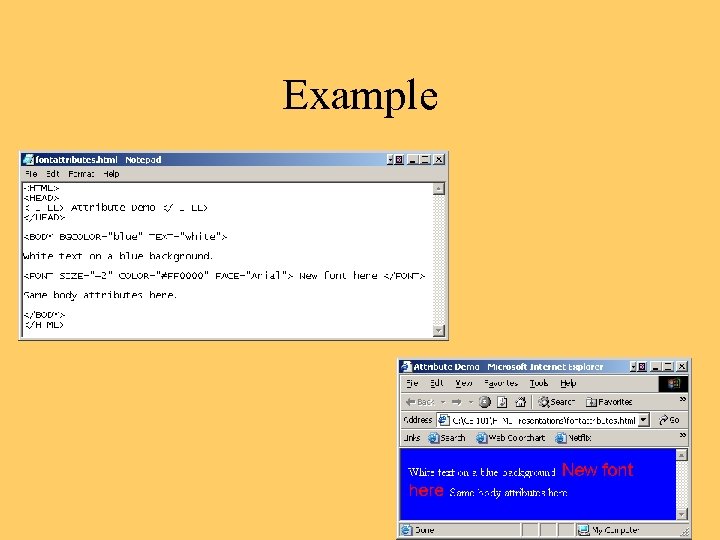 Example
Example
 Linking to Other Pages • The Web is a hyperspace • One navigates to various items by following links • The navigation path can be linear or nonlinear
Linking to Other Pages • The Web is a hyperspace • One navigates to various items by following links • The navigation path can be linear or nonlinear
 Basic Principles of Web Site Design • Distribute topics into a set of pages • Connect the pages with links • Each topic should be self-contained and contain links to related topics, allowing users to form a cognitive map easily
Basic Principles of Web Site Design • Distribute topics into a set of pages • Connect the pages with links • Each topic should be self-contained and contain links to related topics, allowing users to form a cognitive map easily
 The Top-Level Page • Serves as a platform for browsing the entire site • Many ways to lay it out, but the most simple is to provide – an introductory paragraph – a set of links to the main topics
The Top-Level Page • Serves as a platform for browsing the entire site • Many ways to lay it out, but the most simple is to provide – an introductory paragraph – a set of links to the main topics
 Example: A Simple Site • Top-level page (index. html) has links to my hobbies and my career information • Hobbies are discussed in hobbies. html • Career stuff is in career. html
Example: A Simple Site • Top-level page (index. html) has links to my hobbies and my career information • Hobbies are discussed in hobbies. html • Career stuff is in career. html
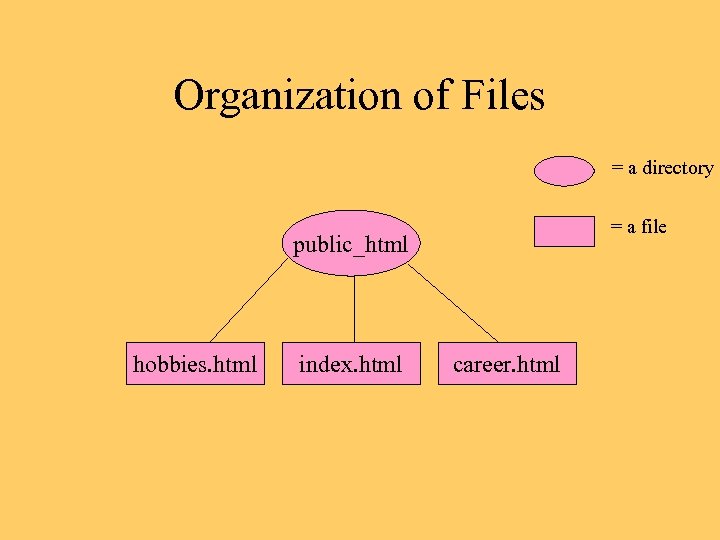 Organization of Files = a directory = a file public_html hobbies. html index. html career. html
Organization of Files = a directory = a file public_html hobbies. html index. html career. html
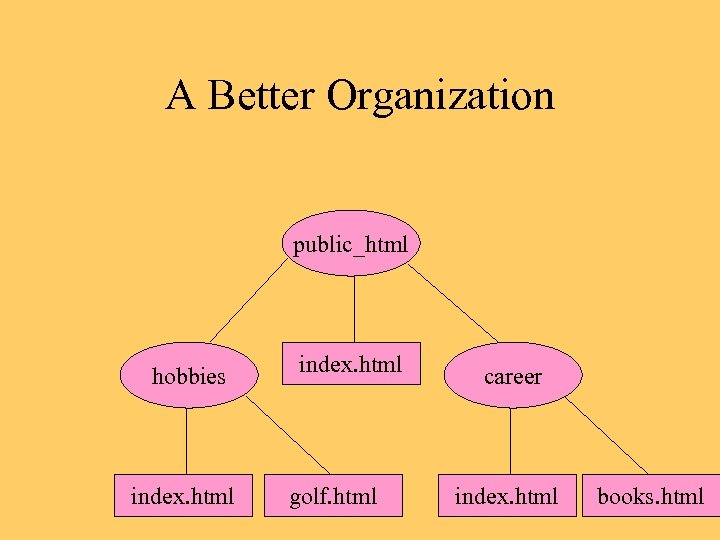 A Better Organization public_html hobbies index. html golf. html career index. html books. html
A Better Organization public_html hobbies index. html golf. html career index. html books. html
 Why Design? • Helps to divide up the work into manageable parts • Reduces cognitive overload on viewers of pages • Facilitates the construction of links
Why Design? • Helps to divide up the work into manageable parts • Reduces cognitive overload on viewers of pages • Facilitates the construction of links
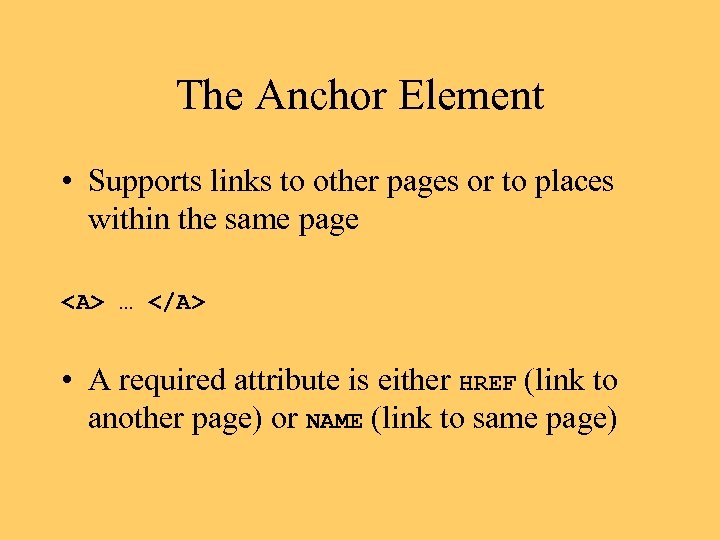 The Anchor Element • Supports links to other pages or to places within the same page … • A required attribute is either HREF (link to another page) or NAME (link to same page)
The Anchor Element • Supports links to other pages or to places within the same page … • A required attribute is either HREF (link to another page) or NAME (link to same page)
Lambert page The displayed text" src="https://present5.com/presentation/fe93325295b8ac43947a6b178682033e/image-22.jpg" alt="The HREF Anchor Lambert page The displayed text" />
The HREF Anchor Lambert page The displayed text of the link
 Absolute URLs • An absolute URL contains the complete address, including the server name – Example: http: //www. wlu. edu/~lambertk • Causes a linking request to the server for a page, which involves some overhead (ie, time)
Absolute URLs • An absolute URL contains the complete address, including the server name – Example: http: //www. wlu. edu/~lambertk • Causes a linking request to the server for a page, which involves some overhead (ie, time)
 Relative URLs • A relative URL contains just a path name (a file name or directory name and zero or more directory names) – Example: hobbies. html – Example: hobbies/golf. html • Link to server is already there, so this way is faster than with absolute URLs
Relative URLs • A relative URL contains just a path name (a file name or directory name and zero or more directory names) – Example: hobbies. html – Example: hobbies/golf. html • Link to server is already there, so this way is faster than with absolute URLs
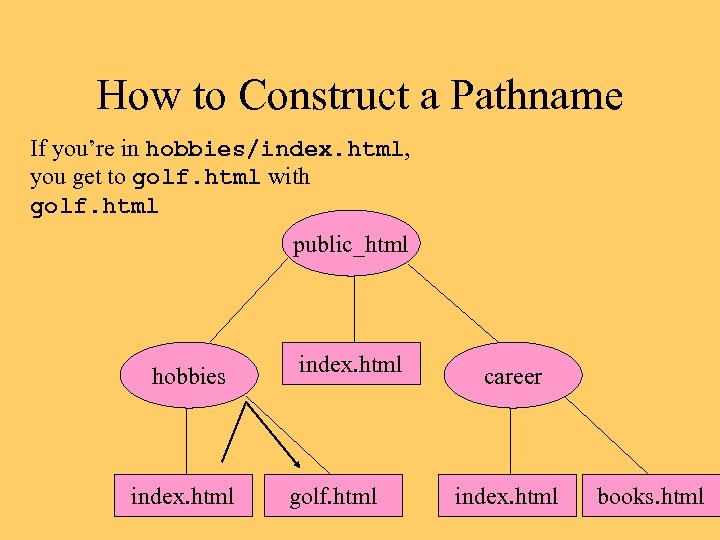 How to Construct a Pathname If you’re in hobbies/index. html, you get to golf. html with golf. html public_html hobbies index. html golf. html career index. html books. html
How to Construct a Pathname If you’re in hobbies/index. html, you get to golf. html with golf. html public_html hobbies index. html golf. html career index. html books. html
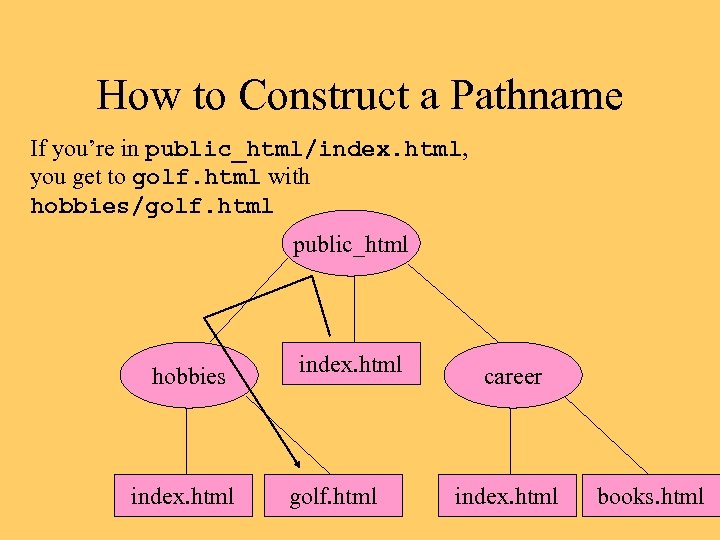 How to Construct a Pathname If you’re in public_html/index. html, you get to golf. html with hobbies/golf. html public_html hobbies index. html golf. html career index. html books. html
How to Construct a Pathname If you’re in public_html/index. html, you get to golf. html with hobbies/golf. html public_html hobbies index. html golf. html career index. html books. html
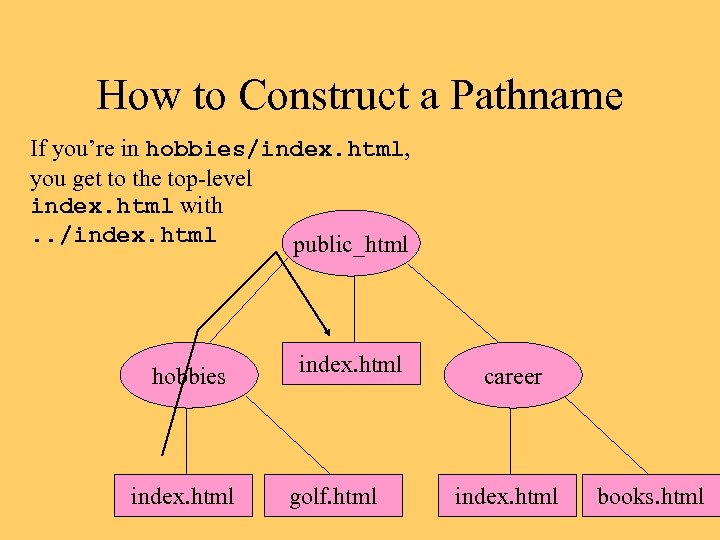 How to Construct a Pathname If you’re in hobbies/index. html, you get to the top-level index. html with. . /index. html public_html hobbies index. html golf. html career index. html books. html
How to Construct a Pathname If you’re in hobbies/index. html, you get to the top-level index. html with. . /index. html public_html hobbies index. html golf. html career index. html books. html
Back to index Back to index
Relative vs Absolute Back to index Back to index An absolute link causes a relink to the server, which can slow down navigation. Relative links are shorter and easier to remember and use. Absolute links can change, relative links are (relatively) stable
 More Basic Principles • Restrict content of each page to avoid cognitive overload (3 -7 rule) • Avoid superfluous links, such as back to previous page (the browser has a button for this already)
More Basic Principles • Restrict content of each page to avoid cognitive overload (3 -7 rule) • Avoid superfluous links, such as back to previous page (the browser has a button for this already)
 Other Design Tips • Draw a diagram of the file/directory system • Show also how the files are linked
Other Design Tips • Draw a diagram of the file/directory system • Show also how the files are linked
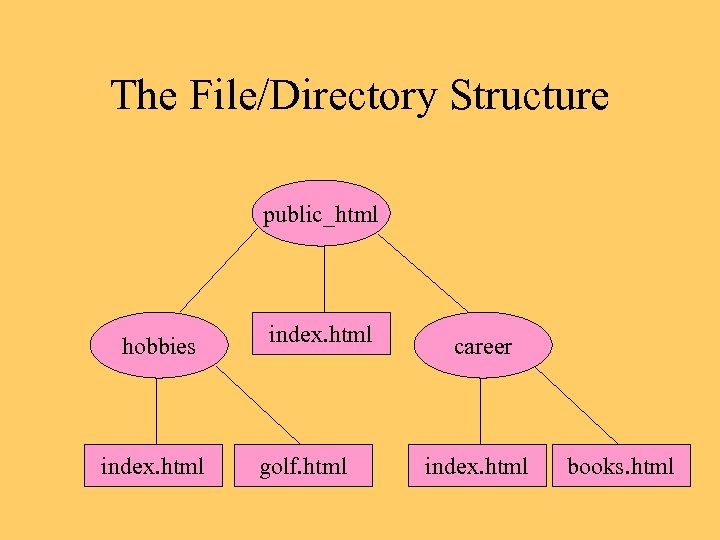 The File/Directory Structure public_html hobbies index. html golf. html career index. html books. html
The File/Directory Structure public_html hobbies index. html golf. html career index. html books. html
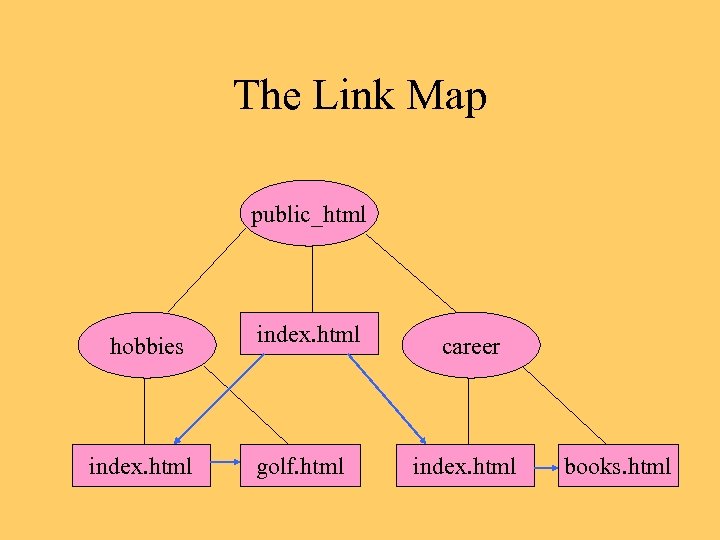 The Link Map public_html hobbies index. html golf. html career index. html books. html
The Link Map public_html hobbies index. html golf. html career index. html books. html


