a24ac9a03e0517b3df85a0da5898e126.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 99
 Computer Science 1 Week 12
Computer Science 1 Week 12
 This Week. . . • QBasic For Loops • Computer History w 1 st – 3 rd Generation computers • Website Project is Due!
This Week. . . • QBasic For Loops • Computer History w 1 st – 3 rd Generation computers • Website Project is Due!

 QBasic For Loops Looping a variable through a range
QBasic For Loops Looping a variable through a range
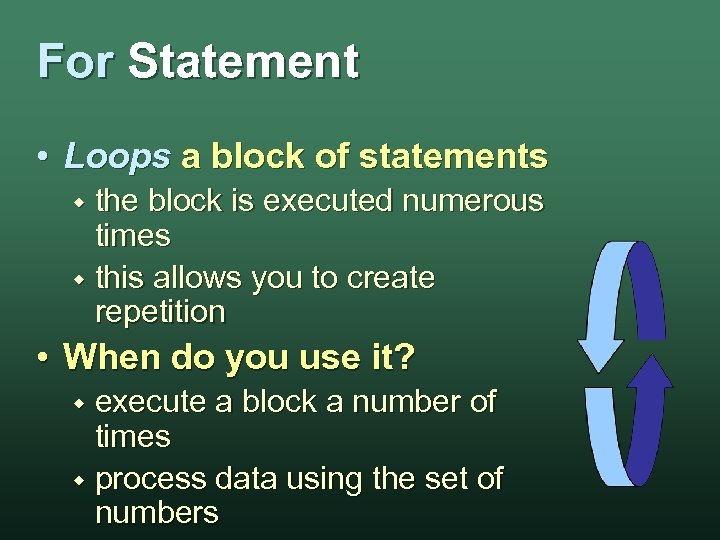 For Statement • Loops a block of statements the block is executed numerous times w this allows you to create repetition w • When do you use it? execute a block a number of times w process data using the set of numbers w
For Statement • Loops a block of statements the block is executed numerous times w this allows you to create repetition w • When do you use it? execute a block a number of times w process data using the set of numbers w
 For Statement • Uses a numeric variable w w w Default: increment by one (+ 1) in each loop automatically starts with an initial value changes its value for each loop stops once its value is greater than end value • Semantics. . . w w assigns the initial/next value to the variable executes the block if the variable is not greater than the end value
For Statement • Uses a numeric variable w w w Default: increment by one (+ 1) in each loop automatically starts with an initial value changes its value for each loop stops once its value is greater than end value • Semantics. . . w w assigns the initial/next value to the variable executes the block if the variable is not greater than the end value
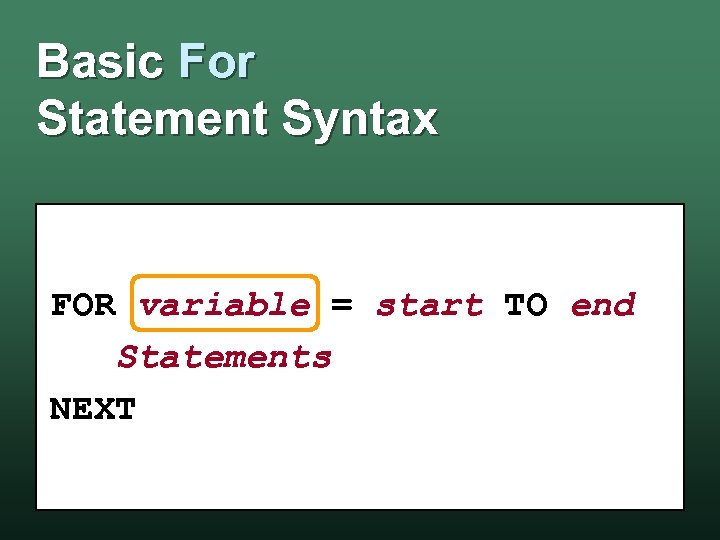 Basic For Statement Syntax FOR variable = start TO end Statements NEXT
Basic For Statement Syntax FOR variable = start TO end Statements NEXT
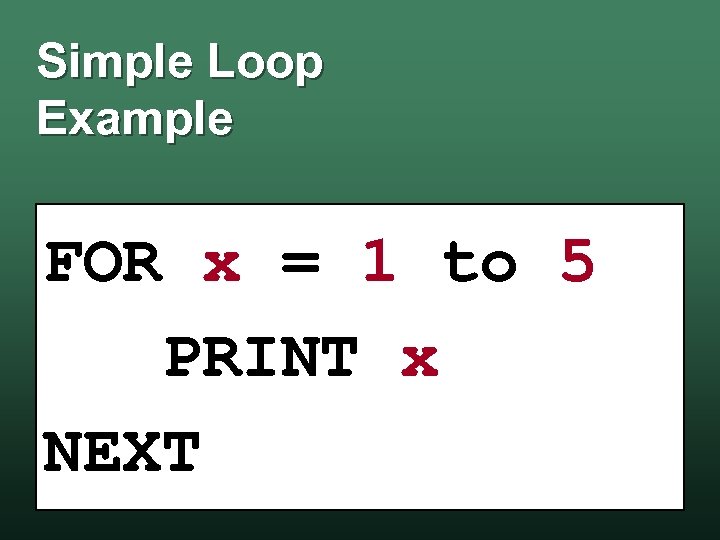 Simple Loop Example FOR x = 1 to 5 PRINT x NEXT
Simple Loop Example FOR x = 1 to 5 PRINT x NEXT
 Simple Loop Example Output 1 2 3 4 5
Simple Loop Example Output 1 2 3 4 5
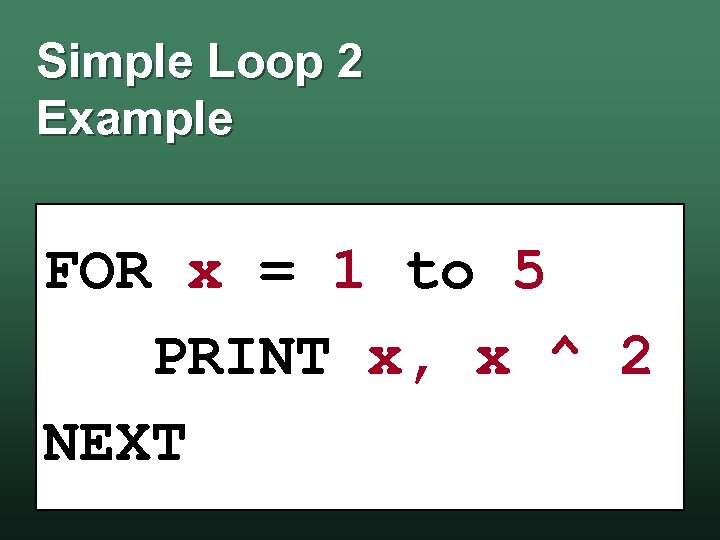 Simple Loop 2 Example FOR x = 1 to 5 PRINT x, x ^ 2 NEXT
Simple Loop 2 Example FOR x = 1 to 5 PRINT x, x ^ 2 NEXT
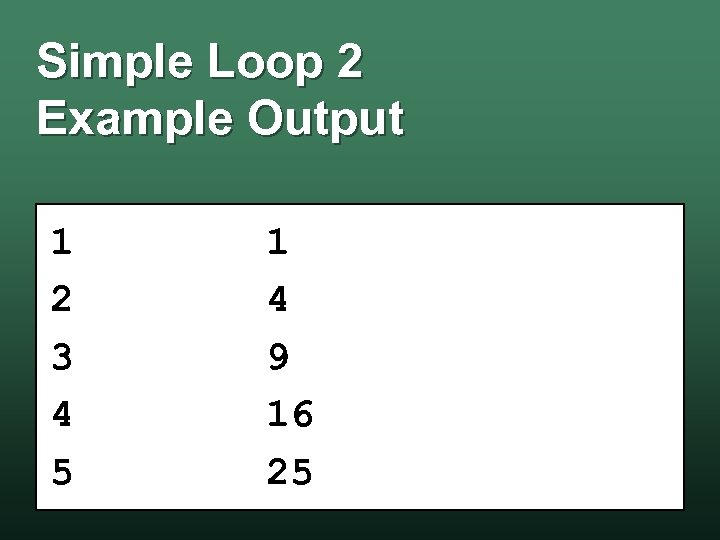 Simple Loop 2 Example Output 1 2 3 4 5 1 4 9 16 25
Simple Loop 2 Example Output 1 2 3 4 5 1 4 9 16 25
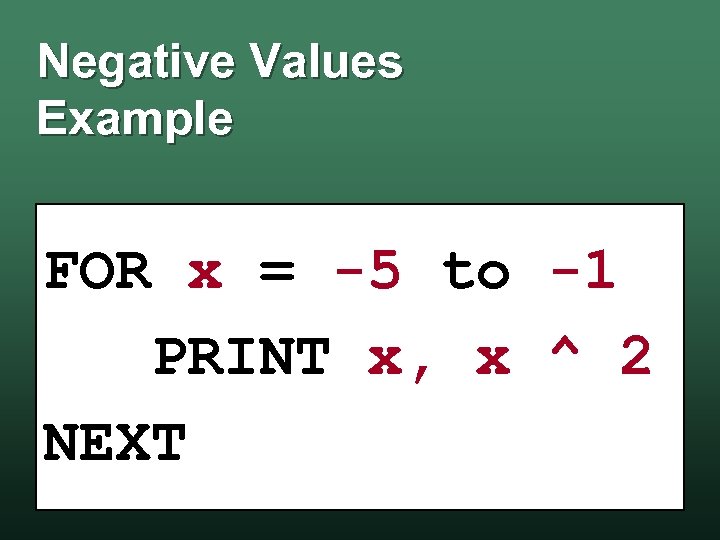 Negative Values Example FOR x = -5 to -1 PRINT x, x ^ 2 NEXT
Negative Values Example FOR x = -5 to -1 PRINT x, x ^ 2 NEXT
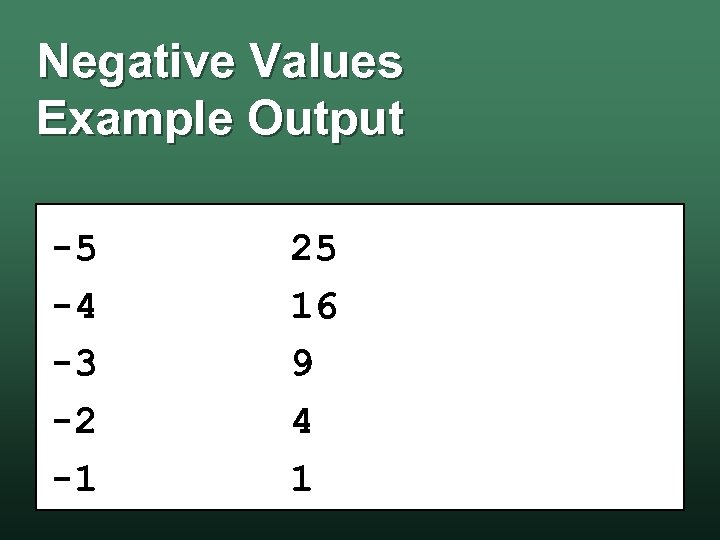 Negative Values Example Output -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 25 16 9 4 1
Negative Values Example Output -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 25 16 9 4 1
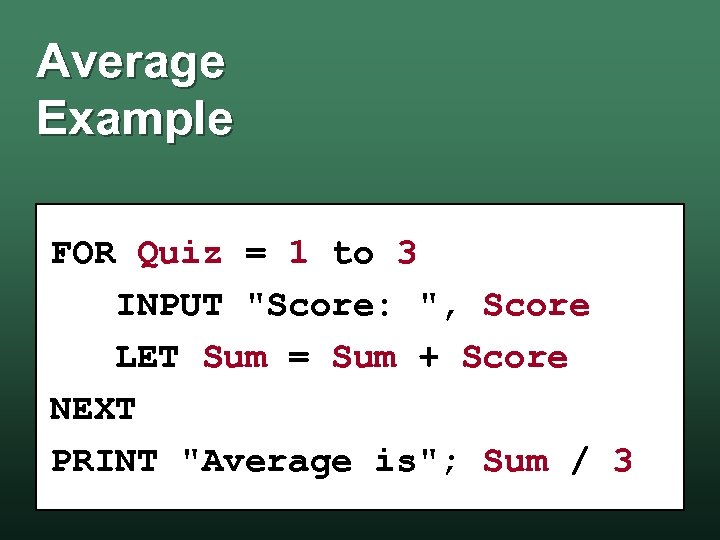 Average Example FOR Quiz = 1 to 3 INPUT "Score: ", Score LET Sum = Sum + Score NEXT PRINT "Average is"; Sum / 3
Average Example FOR Quiz = 1 to 3 INPUT "Score: ", Score LET Sum = Sum + Score NEXT PRINT "Average is"; Sum / 3
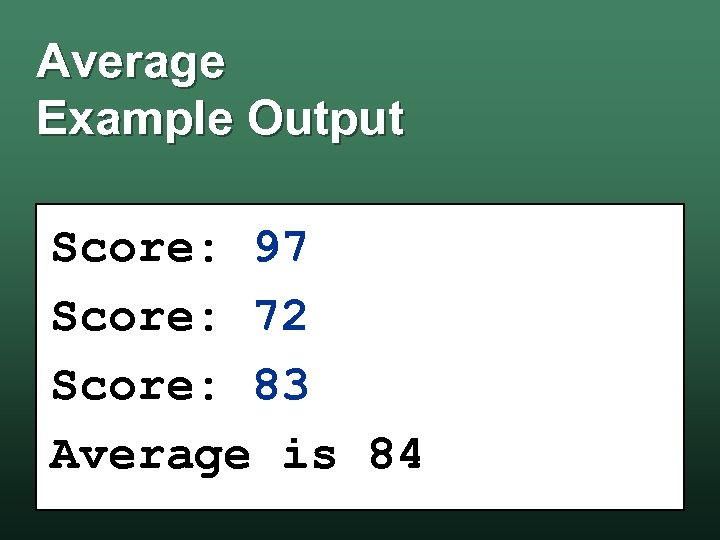 Average Example Output Score: 97 Score: 72 Score: 83 Average is 84
Average Example Output Score: 97 Score: 72 Score: 83 Average is 84
 Inner Loops • Like all QBasic blocks, you can put loops within loops • The loop in the inner-most block is an inner loop • The loop in the outer-most block is an outer loop
Inner Loops • Like all QBasic blocks, you can put loops within loops • The loop in the inner-most block is an inner loop • The loop in the outer-most block is an outer loop
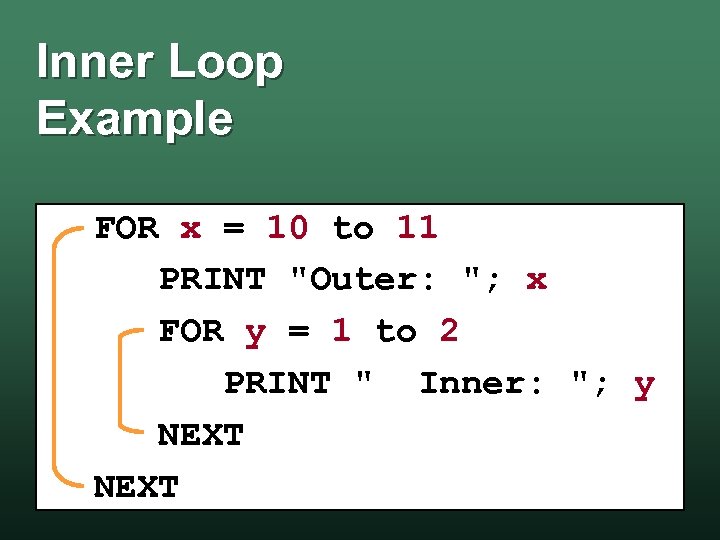 Inner Loop Example FOR x = 10 to 11 PRINT "Outer: "; x FOR y = 1 to 2 PRINT " Inner: "; y NEXT
Inner Loop Example FOR x = 10 to 11 PRINT "Outer: "; x FOR y = 1 to 2 PRINT " Inner: "; y NEXT
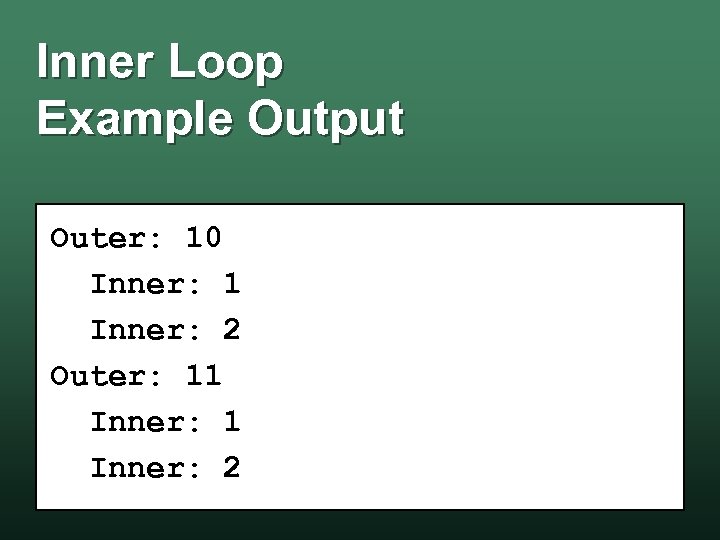 Inner Loop Example Output Outer: 10 Inner: 1 Inner: 2 Outer: 11 Inner: 2
Inner Loop Example Output Outer: 10 Inner: 1 Inner: 2 Outer: 11 Inner: 2
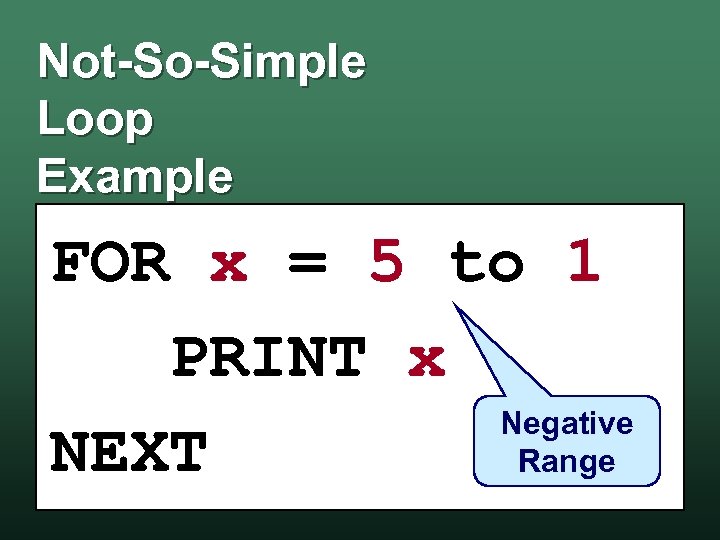 Not-So-Simple Loop Example FOR x = 5 to 1 PRINT x Negative NEXT Range
Not-So-Simple Loop Example FOR x = 5 to 1 PRINT x Negative NEXT Range
 Not-So-Simple Loop Example Output Nothing!
Not-So-Simple Loop Example Output Nothing!
 Not-So-Simple Loop Why? • The For. . . Next Statement starts at the first value w continues until the value of the variable is greater than the end value w • If the start value is greater than the end value, the loop never executes
Not-So-Simple Loop Why? • The For. . . Next Statement starts at the first value w continues until the value of the variable is greater than the end value w • If the start value is greater than the end value, the loop never executes
 The Step Clause • Normally, the For. . . Next Statement increments using +1 • The Step Clause allows you to change the increment value • This allows you to: create negative loops w create loops that jump by a specific value w
The Step Clause • Normally, the For. . . Next Statement increments using +1 • The Step Clause allows you to change the increment value • This allows you to: create negative loops w create loops that jump by a specific value w
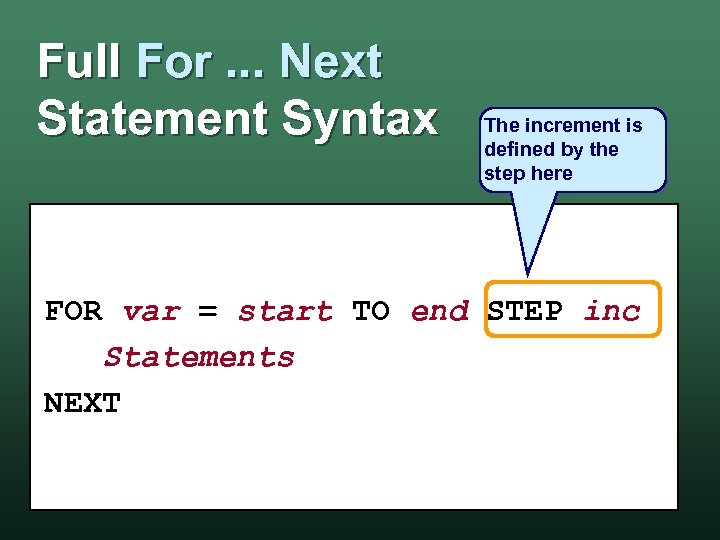 Full For. . . Next Statement Syntax The increment is defined by the step here FOR var = start TO end STEP inc Statements NEXT
Full For. . . Next Statement Syntax The increment is defined by the step here FOR var = start TO end STEP inc Statements NEXT
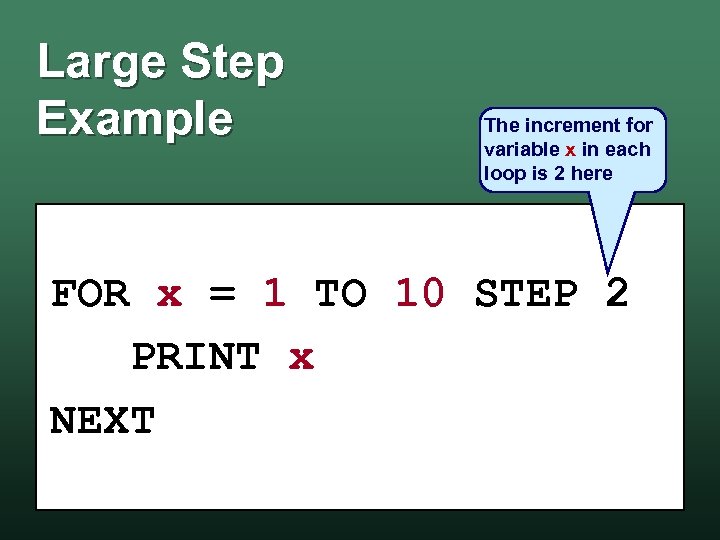 Large Step Example The increment for variable x in each loop is 2 here FOR x = 1 TO 10 STEP 2 PRINT x NEXT
Large Step Example The increment for variable x in each loop is 2 here FOR x = 1 TO 10 STEP 2 PRINT x NEXT
 Large Step Example Output 1 3 5 7 9
Large Step Example Output 1 3 5 7 9
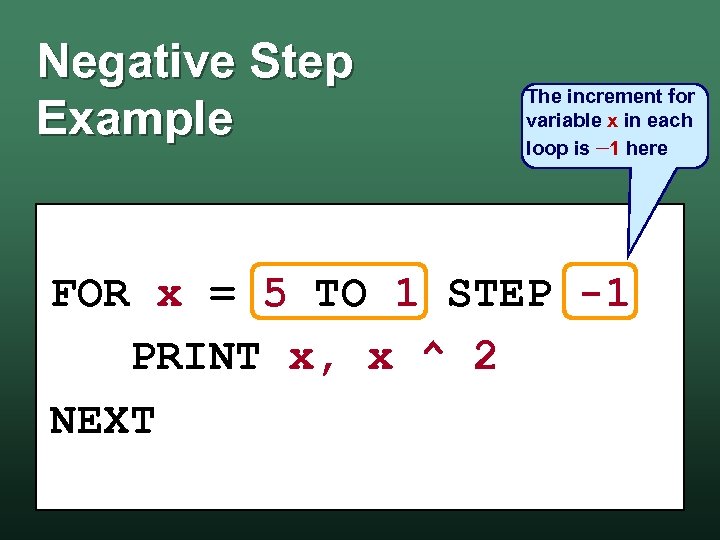 Negative Step Example The increment for variable x in each loop is 1 here FOR x = 5 TO 1 STEP -1 PRINT x, x ^ 2 NEXT
Negative Step Example The increment for variable x in each loop is 1 here FOR x = 5 TO 1 STEP -1 PRINT x, x ^ 2 NEXT
 Negative Step Example Output 5 4 3 2 1 25 16 9 4 1
Negative Step Example Output 5 4 3 2 1 25 16 9 4 1
 Zero Step Example FOR x = 1 TO 5 STEP 0 PRINT x, x ^ 2 NEXT
Zero Step Example FOR x = 1 TO 5 STEP 0 PRINT x, x ^ 2 NEXT
 Zero Step Example Output RUNTIME ERROR: Line 1 : Step value is zero
Zero Step Example Output RUNTIME ERROR: Line 1 : Step value is zero
 While Loop vs. For Loop • For Loop is a form of the While Loop • As a result: wa While Loop can implement any For Loop w the For Loop is used as a shortcut notation
While Loop vs. For Loop • For Loop is a form of the While Loop • As a result: wa While Loop can implement any For Loop w the For Loop is used as a shortcut notation
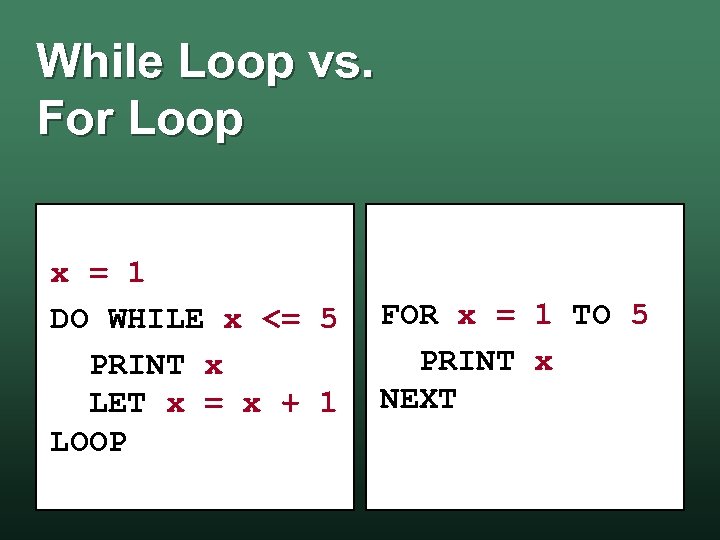 While Loop vs. For Loop x = 1 DO WHILE x <= 5 PRINT x LET x = x + 1 LOOP FOR x = 1 TO 5 PRINT x NEXT
While Loop vs. For Loop x = 1 DO WHILE x <= 5 PRINT x LET x = x + 1 LOOP FOR x = 1 TO 5 PRINT x NEXT
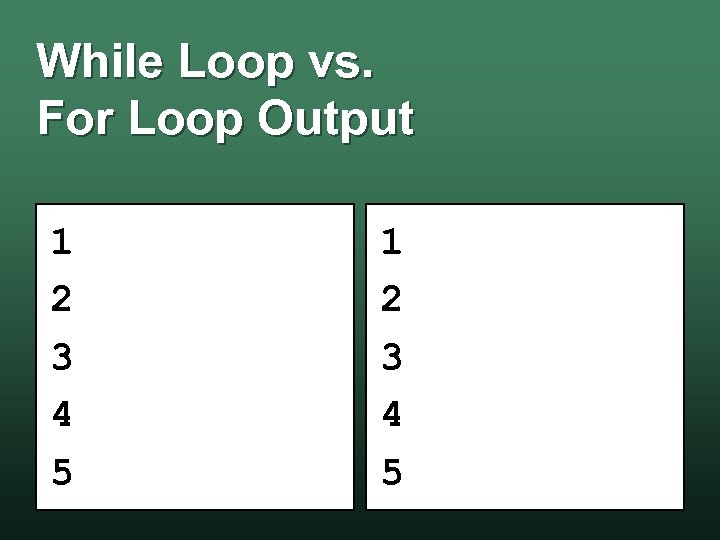 While Loop vs. For Loop Output 1 2 3 4 5
While Loop vs. For Loop Output 1 2 3 4 5
 QBasic Lab For Loops – 99 Bottles of Something
QBasic Lab For Loops – 99 Bottles of Something
 Lab: 99 Bottles of Something • Overview: You will use QBasic to print the 99 Bottles of Beer (Water) Song w Use another drink, water or juice w • Objectives: Use a For Statement to print the song w Use an If Statement inside the w
Lab: 99 Bottles of Something • Overview: You will use QBasic to print the 99 Bottles of Beer (Water) Song w Use another drink, water or juice w • Objectives: Use a For Statement to print the song w Use an If Statement inside the w
 Remember. . . • Turn your program & your output w to Lab 10 in Sac. CT • You must do your own work • If you do not turn in your program, you will not get credit!
Remember. . . • Turn your program & your output w to Lab 10 in Sac. CT • You must do your own work • If you do not turn in your program, you will not get credit!

 The First Computer History
The First Computer History
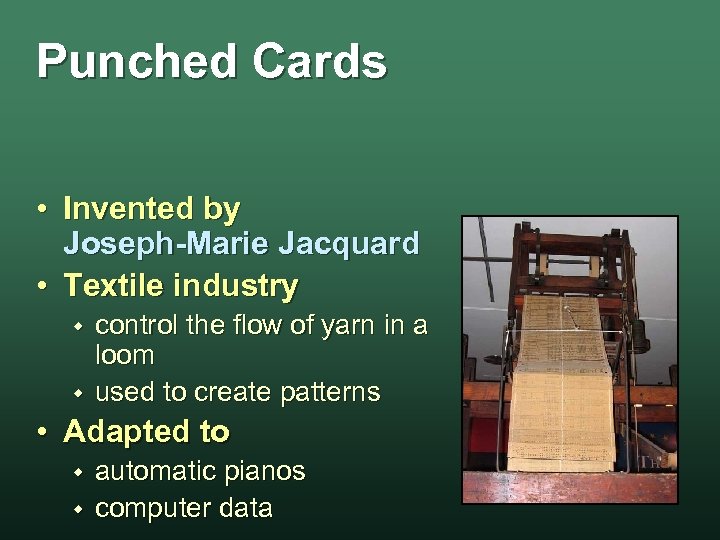 Punched Cards • Invented by Joseph-Marie Jacquard • Textile industry w w control the flow of yarn in a loom used to create patterns • Adapted to w w automatic pianos computer data
Punched Cards • Invented by Joseph-Marie Jacquard • Textile industry w w control the flow of yarn in a loom used to create patterns • Adapted to w w automatic pianos computer data
 Charles Babbage • Known as the “Father of Computers” • Created several calculators • Developed the first computer
Charles Babbage • Known as the “Father of Computers” • Created several calculators • Developed the first computer
 The Difference Engine • In the 1800’s log and trig tables were calculated manually w Babbage knew machines could compute these w • He designed the Difference Engine could compute logarithmic and trigonometric data w first machine to be automatic in action w
The Difference Engine • In the 1800’s log and trig tables were calculated manually w Babbage knew machines could compute these w • He designed the Difference Engine could compute logarithmic and trigonometric data w first machine to be automatic in action w
 The Difference Engine: continued in March 2008 at the • It was completed Science Museum, London 150 years after its original design, and is faithful to Babbage’s original design (1847 -49). • It is one of only two Babbage engines consisting of 8, 000 parts in bronze, cast iron and steel. • It weighs five tons and measures 11 feet long and 7 feet tall.
The Difference Engine: continued in March 2008 at the • It was completed Science Museum, London 150 years after its original design, and is faithful to Babbage’s original design (1847 -49). • It is one of only two Babbage engines consisting of 8, 000 parts in bronze, cast iron and steel. • It weighs five tons and measures 11 feet long and 7 feet tall.
 Computer History Museum, San Jose (June, 2012)
Computer History Museum, San Jose (June, 2012)
 Computer History Museum, San Jose (June, 2012)
Computer History Museum, San Jose (June, 2012)

 The Analytical Engine • A general-purpose calculating machine • He began work in 1834 w he never finished it w it has never been built • If built, it would have been one of the Wonders of the World
The Analytical Engine • A general-purpose calculating machine • He began work in 1834 w he never finished it w it has never been built • If built, it would have been one of the Wonders of the World
 The Analytical Engine • Use punched cards to run calculations • Had all the attributes of a modern computer Programs – looping, branching – "Barrels" w Memory – "The Store" w Arithmetic Logic Unit – "The Mill" w
The Analytical Engine • Use punched cards to run calculations • Had all the attributes of a modern computer Programs – looping, branching – "Barrels" w Memory – "The Store" w Arithmetic Logic Unit – "The Mill" w
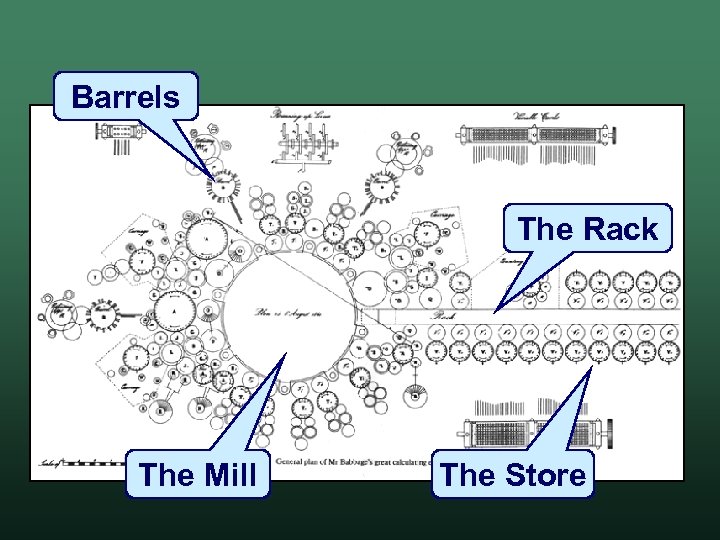 Barrels The Rack The Mill The Store
Barrels The Rack The Mill The Store
 Ada Lovelace • Mathematician • Spoke several languages • University of Turin lecturer w w During a nine-month period in 1842– 43, Lovelace translated Italian mathematician Luigi Menabrea's memoir (to English) on Babbage's Analytical Engine. With the article, she appended a set of notes that included a method for calculating a sequence of Bernoulli numbers with the Engine. Her method is recognized as the world’s first computer program.
Ada Lovelace • Mathematician • Spoke several languages • University of Turin lecturer w w During a nine-month period in 1842– 43, Lovelace translated Italian mathematician Luigi Menabrea's memoir (to English) on Babbage's Analytical Engine. With the article, she appended a set of notes that included a method for calculating a sequence of Bernoulli numbers with the Engine. Her method is recognized as the world’s first computer program.
 Ada Lovelace • She made extensive notes w several volumes, in fact w designed several programs w this included how to calculate Bernoulli numbers
Ada Lovelace • She made extensive notes w several volumes, in fact w designed several programs w this included how to calculate Bernoulli numbers

 The 1890 Census Crisis Computer History
The 1890 Census Crisis Computer History
 Census Crisis • The United States Federal Constitution population must be calculated - census w this must be done every 10 years w used in the House of Representatives w • However, the U. S. population had grown extremely large w the people could not be counted in 10 years w
Census Crisis • The United States Federal Constitution population must be calculated - census w this must be done every 10 years w used in the House of Representatives w • However, the U. S. population had grown extremely large w the people could not be counted in 10 years w
 Herman Hollerith • Developed: first automatic card-feed mechanism w enhanced card reading w the first key punch – 200 to 300 cards per hour w • Used electricity
Herman Hollerith • Developed: first automatic card-feed mechanism w enhanced card reading w the first key punch – 200 to 300 cards per hour w • Used electricity
 Herman Hollerith • His system was used for 1890 census w only took 9 months! w • Hollerith founded Tabulating Machine Company w it later became International Business Machines w
Herman Hollerith • His system was used for 1890 census w only took 9 months! w • Hollerith founded Tabulating Machine Company w it later became International Business Machines w
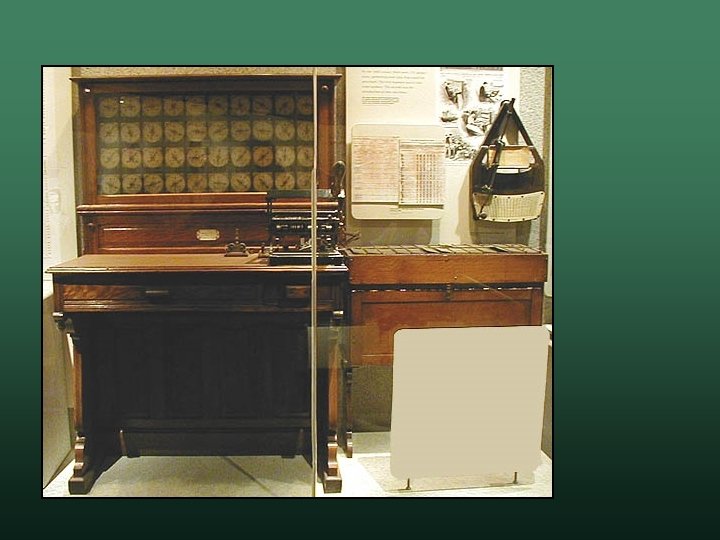
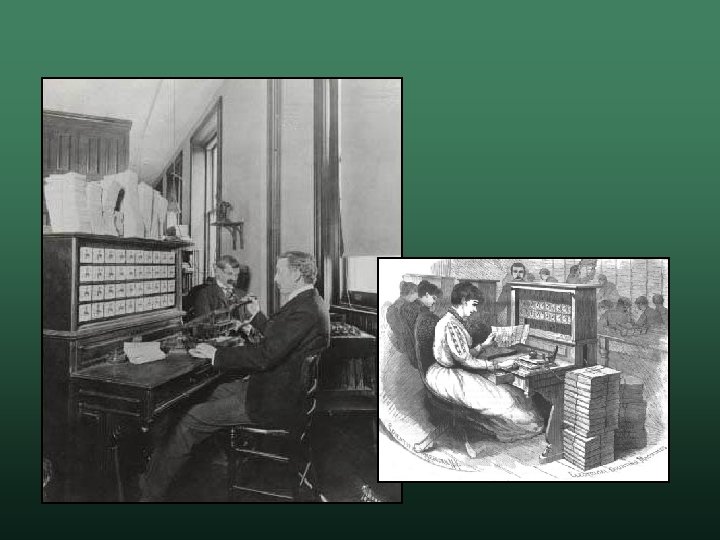



 Birth of Computer Science Computer History
Birth of Computer Science Computer History
 Alan Turing • Mathematician, logician & cryptographer • "Father of Computer Science" Highest award in Computer Science is the Turing Award w Developed Turing Machines w
Alan Turing • Mathematician, logician & cryptographer • "Father of Computer Science" Highest award in Computer Science is the Turing Award w Developed Turing Machines w
 Alan Turing's Major Works • Developed Turing Machines invented in 1937 w logical model – not an actual computer w proved programming w • Turing Test artificial Intelligence w no computer has yet passed it w
Alan Turing's Major Works • Developed Turing Machines invented in 1937 w logical model – not an actual computer w proved programming w • Turing Test artificial Intelligence w no computer has yet passed it w
 Computer Generations • Computers are historically classified by their generation • Each generation. . . marks a new, major, technology w changes how computers are built and/or used w their are currently four generations w
Computer Generations • Computers are historically classified by their generation • Each generation. . . marks a new, major, technology w changes how computers are built and/or used w their are currently four generations w

 st 1 Generation Computers Computer History
st 1 Generation Computers Computer History
 First Generation Computers • 1946 to 1958 • Used the vacuum tube w w they consumed a lot of power they also tended to burn out quickly • Programs written in machine language • Data w w read with Punched Cards stored with Magnetic Tape
First Generation Computers • 1946 to 1958 • Used the vacuum tube w w they consumed a lot of power they also tended to burn out quickly • Programs written in machine language • Data w w read with Punched Cards stored with Magnetic Tape
 Vacuum Tubes
Vacuum Tubes
 Atanasoff-Berry Computer • First electronic digital computer • Development John Atanasoff & Clifford Berry w Iowa State University w built from 1937 to 1942 w • Speed: 60 Hz
Atanasoff-Berry Computer • First electronic digital computer • Development John Atanasoff & Clifford Berry w Iowa State University w built from 1937 to 1942 w • Speed: 60 Hz
 Atanasoff-Berry Computer • Features: binary digits to represent all data w calculations using electronics w memory is separate from CPU w • Rebuilt in 1997 w cost of $350, 000
Atanasoff-Berry Computer • Features: binary digits to represent all data w calculations using electronics w memory is separate from CPU w • Rebuilt in 1997 w cost of $350, 000
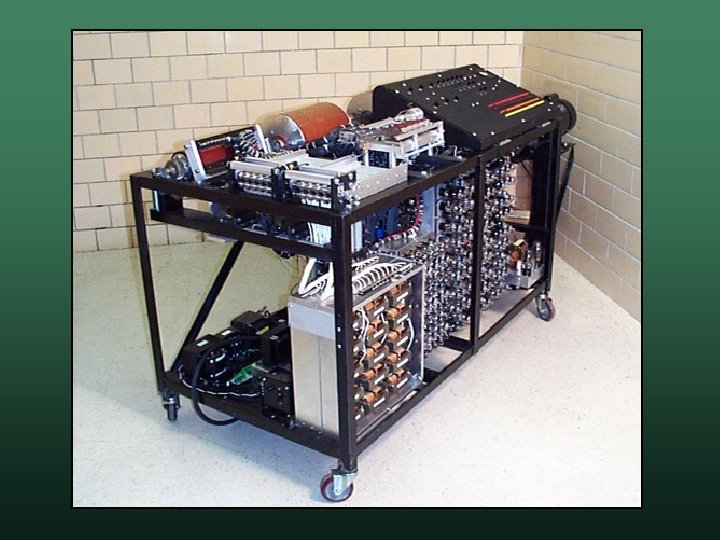

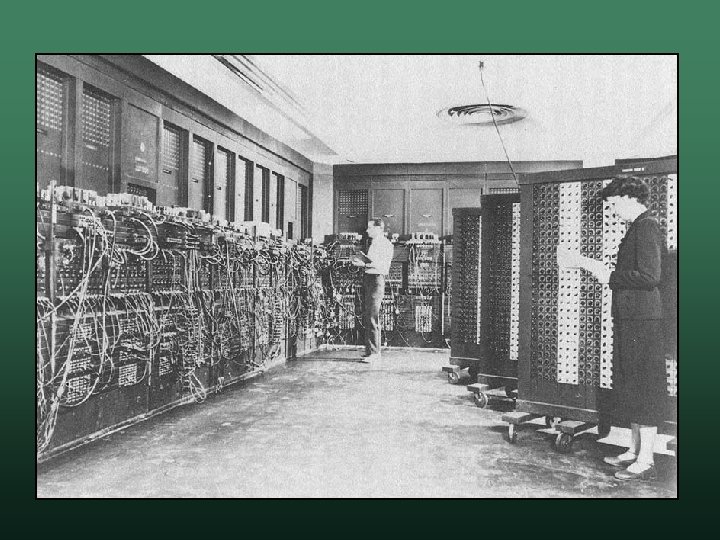
 ENIAC • Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer • Development John Eckert and John W. Mauchly w U. S. Ballistics Research Laboratory w Needed to fight World War II – then Cold War w Compute ballistic firing tables w
ENIAC • Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer • Development John Eckert and John W. Mauchly w U. S. Ballistics Research Laboratory w Needed to fight World War II – then Cold War w Compute ballistic firing tables w
 ENIAC • • • Designed to be Turing Complete Operational in February 1946 Features 5 KHz (5000 Hz) w programmed by rewiring – pre 1948 w based on decimal – not binary w weighed 30 tons, 18 feet high, 80 feet long w
ENIAC • • • Designed to be Turing Complete Operational in February 1946 Features 5 KHz (5000 Hz) w programmed by rewiring – pre 1948 w based on decimal – not binary w weighed 30 tons, 18 feet high, 80 feet long w
 ENIAC • A tube burned out once every 2 days • Retired in 1955 w operational for only 9 years w estimated to have performed more calculations than all of humanity had ever done prior
ENIAC • A tube burned out once every 2 days • Retired in 1955 w operational for only 9 years w estimated to have performed more calculations than all of humanity had ever done prior
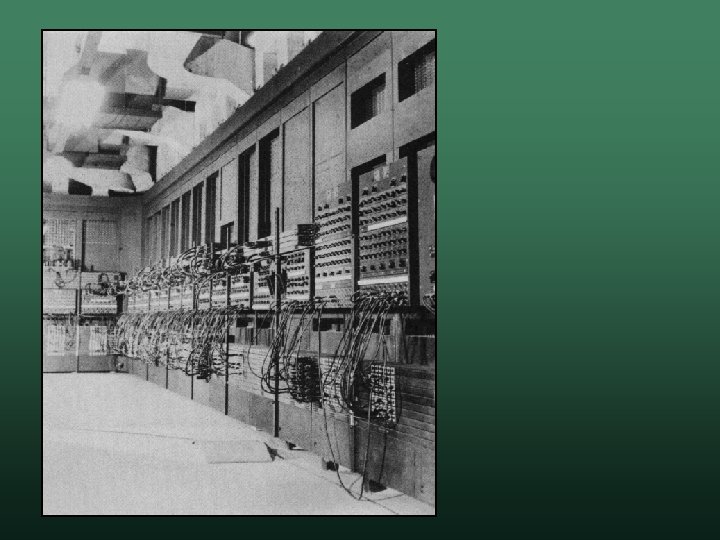

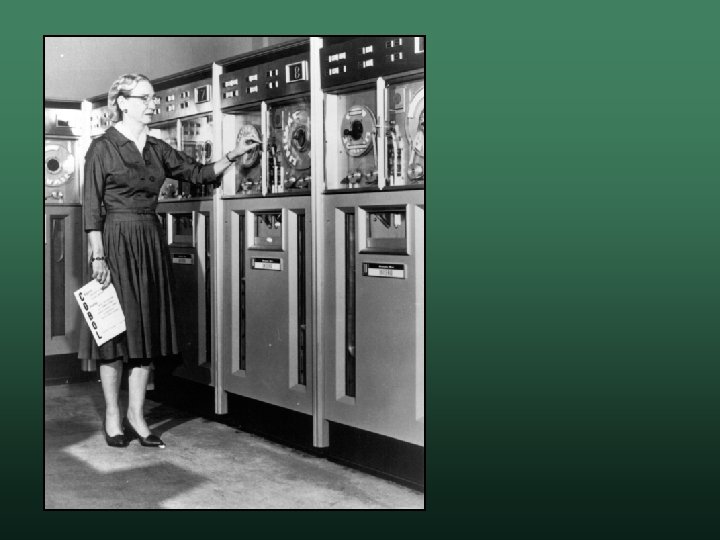
 Grace Hopper • • Admiral in the U. S. Navy Worked on several projects Mark II Mainframe w COBOL Programming Language w Compilers w Standardized software testing w • Discovered the first
Grace Hopper • • Admiral in the U. S. Navy Worked on several projects Mark II Mainframe w COBOL Programming Language w Compilers w Standardized software testing w • Discovered the first

 September 9, 1945
September 9, 1945
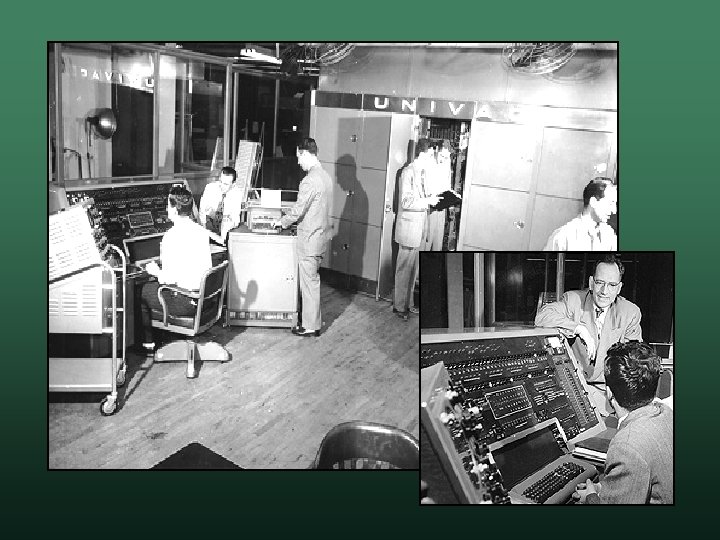
 UNIVAC • Universal Automatic Computer • Released in 1951 • First commercial computer w 43 were sold to government and industry w used to tabulate the census
UNIVAC • Universal Automatic Computer • Released in 1951 • First commercial computer w 43 were sold to government and industry w used to tabulate the census
 UNIVAC • Some features ran programs on punched cards w secondary storage: metal oxide tape w clock: 2. 25 MHz w • Predicted the 1952 election Eisenhower over Stevenson w news agencies held the results - great publicity w
UNIVAC • Some features ran programs on punched cards w secondary storage: metal oxide tape w clock: 2. 25 MHz w • Predicted the 1952 election Eisenhower over Stevenson w news agencies held the results - great publicity w
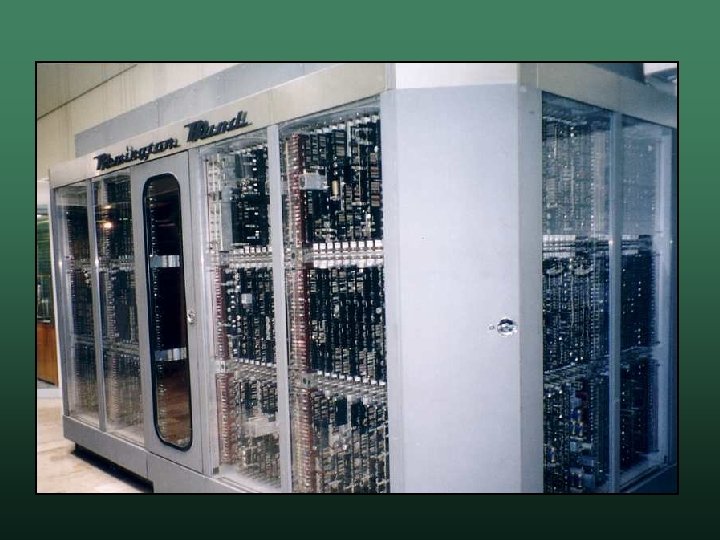


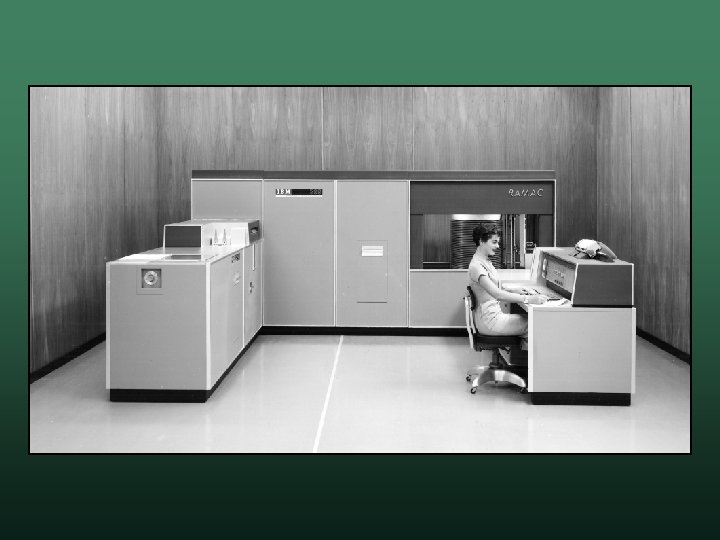
 IBM RAMAC 305 • Random Access Method of Accounting and Control • Released in 1956 • First computer to use a hard drive w based on record technology w could store 5 million 7 -bit characters
IBM RAMAC 305 • Random Access Method of Accounting and Control • Released in 1956 • First computer to use a hard drive w based on record technology w could store 5 million 7 -bit characters



 nd 2 Generation Computers Computer History
nd 2 Generation Computers Computer History
 Second Generation Computers • 1959 to 1964 • Used Transistors more reliable than vacuum tubes w required less power w • Compilers were developed • Disk Storage was developed
Second Generation Computers • 1959 to 1964 • Used Transistors more reliable than vacuum tubes w required less power w • Compilers were developed • Disk Storage was developed
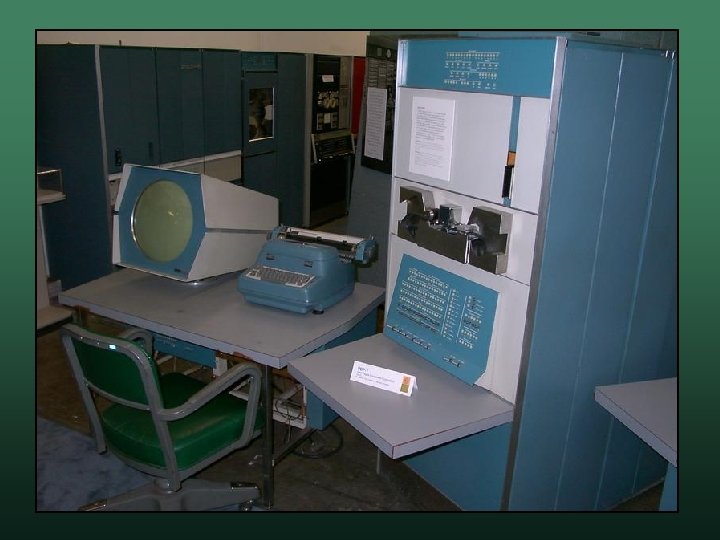
 DEC PDP-1 • • Programmed Data Processor-1 Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) Released 1960 Features w w read data from tape used a cathode ray tube (T. V. ) to display data • The first hacker computer • World's first digital video game: Space War
DEC PDP-1 • • Programmed Data Processor-1 Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) Released 1960 Features w w read data from tape used a cathode ray tube (T. V. ) to display data • The first hacker computer • World's first digital video game: Space War


 rd 3 Generation Computers Computer History
rd 3 Generation Computers Computer History
 Third Generation Computers • 1965 to 1970 • Used integrated circuits increased speed w smaller size w lower cost w even less electricity w • Birth of the minicomputer
Third Generation Computers • 1965 to 1970 • Used integrated circuits increased speed w smaller size w lower cost w even less electricity w • Birth of the minicomputer
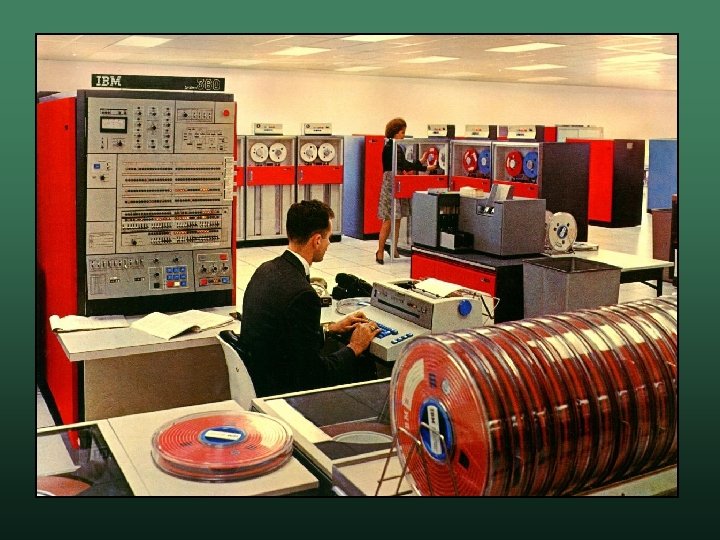
 IBM 360 • Most expensive computer project ever the "5 billion dollar gamble" w this is over 30 billion by today's dollars w • • Released 1964 Breakthrough architecture and implementation are different w microcode technology w
IBM 360 • Most expensive computer project ever the "5 billion dollar gamble" w this is over 30 billion by today's dollars w • • Released 1964 Breakthrough architecture and implementation are different w microcode technology w
 IBM 360 • It was the first platform computer all 360 computers would be compatible w initial models: 30, 40, 50, 62, and 70 w peripherals could be interchanged w • Huge success companies could buy the best model w companies could upgrade their systems later w
IBM 360 • It was the first platform computer all 360 computers would be compatible w initial models: 30, 40, 50, 62, and 70 w peripherals could be interchanged w • Huge success companies could buy the best model w companies could upgrade their systems later w

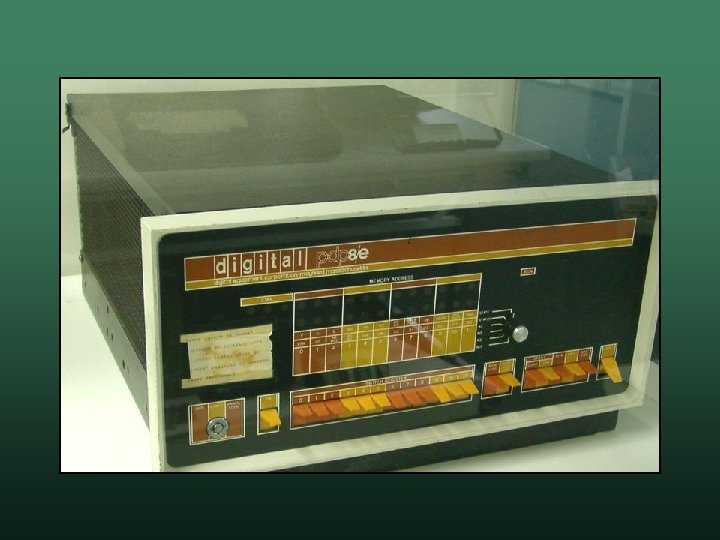
 DEC PDP-8 • First successful commercial minicomputer released in 1965 w it cost less than $20, 000 w • Features up to 32 k of RAM w 1 MHz – varied by model w multiple versions available w
DEC PDP-8 • First successful commercial minicomputer released in 1965 w it cost less than $20, 000 w • Features up to 32 k of RAM w 1 MHz – varied by model w multiple versions available w




