5873898553919edb862c54f481d2de0a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 Computer Programming with JAVA Chapter 7. Event-Driven Programming Using the AWT n. Event-Driven Programming n. GUIs and the AWT n. Simple Window Interfaces n. Components, Containers, and Layout Managers n. Panels and Text Components n. Adding Menus n. Inner Classes
Computer Programming with JAVA Chapter 7. Event-Driven Programming Using the AWT n. Event-Driven Programming n. GUIs and the AWT n. Simple Window Interfaces n. Components, Containers, and Layout Managers n. Panels and Text Components n. Adding Menus n. Inner Classes
 Event-Driven Programming n n A different approach to program design Programs react to events, e. g. n n n n GUI: graphical user interface n n mouse click key press menu selection button selection message sent from printer etc. windows, scroll bars, menus, radio buttons, etc. a special case of event-driven programming the only type of event we will be concerned with in this chapter An event is an object
Event-Driven Programming n n A different approach to program design Programs react to events, e. g. n n n n GUI: graphical user interface n n mouse click key press menu selection button selection message sent from printer etc. windows, scroll bars, menus, radio buttons, etc. a special case of event-driven programming the only type of event we will be concerned with in this chapter An event is an object
 AWT n n n n Abstract Window Toolkit Implements GUI A standard part of Java Not fancy, but adequate Makes extensive use of inheritance Based on events and event handlers Firing an event: when an object generates an event Listener object n n n every object that can fire an event, such as a button, can have one or more listener objects Listener objects have methods (called event handlers) that perform actions depending on the event You the programmer write these event handlers
AWT n n n n Abstract Window Toolkit Implements GUI A standard part of Java Not fancy, but adequate Makes extensive use of inheritance Based on events and event handlers Firing an event: when an object generates an event Listener object n n n every object that can fire an event, such as a button, can have one or more listener objects Listener objects have methods (called event handlers) that perform actions depending on the event You the programmer write these event handlers
 WARNING! Programs that use the AWT can hang the computer Save your work before running a program using the AWT!
WARNING! Programs that use the AWT can hang the computer Save your work before running a program using the AWT!
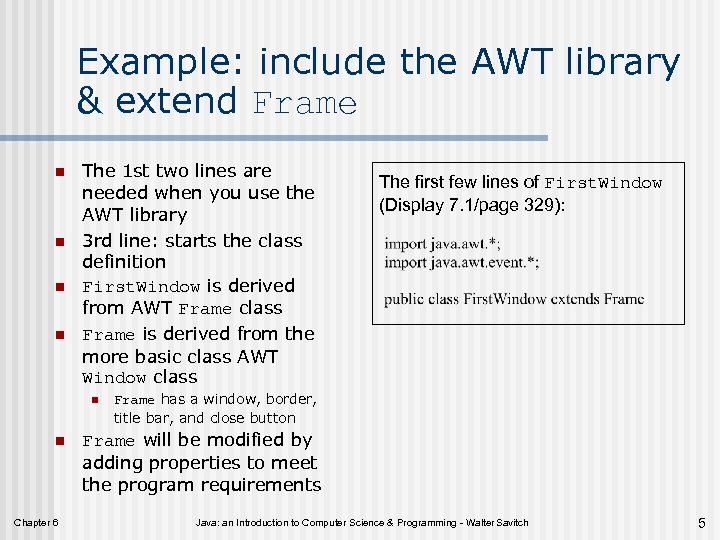 Example: include the AWT library & extend Frame n n The 1 st two lines are needed when you use the AWT library 3 rd line: starts the class definition First. Window is derived from AWT Frame class Frame is derived from the more basic class AWT Window class n n Chapter 6 The first few lines of First. Window (Display 7. 1/page 329): Frame has a window, border, title bar, and close button Frame will be modified by adding properties to meet the program requirements Java: an Introduction to Computer Science & Programming - Walter Savitch 5
Example: include the AWT library & extend Frame n n The 1 st two lines are needed when you use the AWT library 3 rd line: starts the class definition First. Window is derived from AWT Frame class Frame is derived from the more basic class AWT Window class n n Chapter 6 The first few lines of First. Window (Display 7. 1/page 329): Frame has a window, border, title bar, and close button Frame will be modified by adding properties to meet the program requirements Java: an Introduction to Computer Science & Programming - Walter Savitch 5
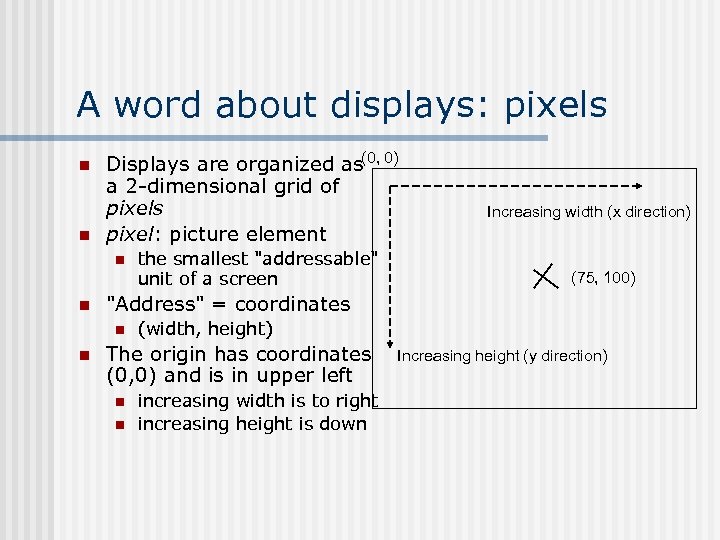 A word about displays: pixels n n Displays are organized as(0, 0) a 2 -dimensional grid of pixels pixel: picture element n n (75, 100) "Address" = coordinates n n the smallest "addressable" unit of a screen Increasing width (x direction) (width, height) The origin has coordinates (0, 0) and is in upper left n n increasing width is to right increasing height is down Increasing height (y direction)
A word about displays: pixels n n Displays are organized as(0, 0) a 2 -dimensional grid of pixels pixel: picture element n n (75, 100) "Address" = coordinates n n the smallest "addressable" unit of a screen Increasing width (x direction) (width, height) The origin has coordinates (0, 0) and is in upper left n n increasing width is to right increasing height is down Increasing height (y direction)
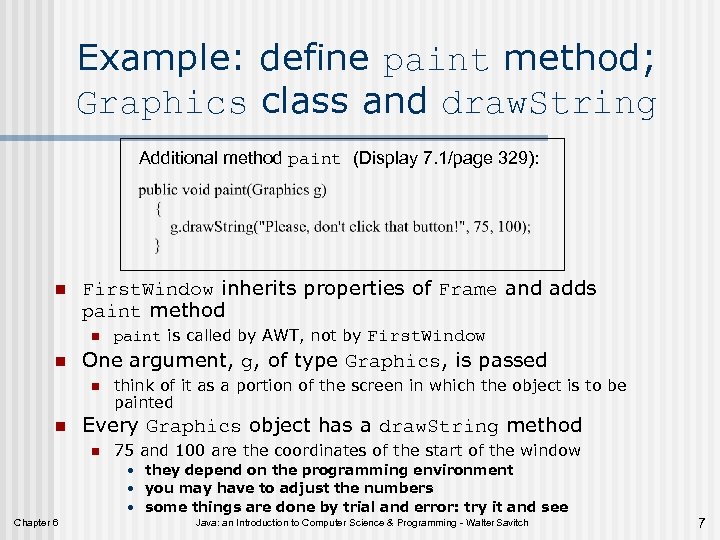 Example: define paint method; Graphics class and draw. String Additional method paint (Display 7. 1/page 329): n First. Window inherits properties of Frame and adds paint method n n One argument, g, of type Graphics, is passed n n paint is called by AWT, not by First. Window think of it as a portion of the screen in which the object is to be painted Every Graphics object has a draw. String method n 75 and 100 are the coordinates of the start of the window • they depend on the programming environment • you may have to adjust the numbers • some things are done by trial and error: try it and see Chapter 6 Java: an Introduction to Computer Science & Programming - Walter Savitch 7
Example: define paint method; Graphics class and draw. String Additional method paint (Display 7. 1/page 329): n First. Window inherits properties of Frame and adds paint method n n One argument, g, of type Graphics, is passed n n paint is called by AWT, not by First. Window think of it as a portion of the screen in which the object is to be painted Every Graphics object has a draw. String method n 75 and 100 are the coordinates of the start of the window • they depend on the programming environment • you may have to adjust the numbers • some things are done by trial and error: try it and see Chapter 6 Java: an Introduction to Computer Science & Programming - Walter Savitch 7
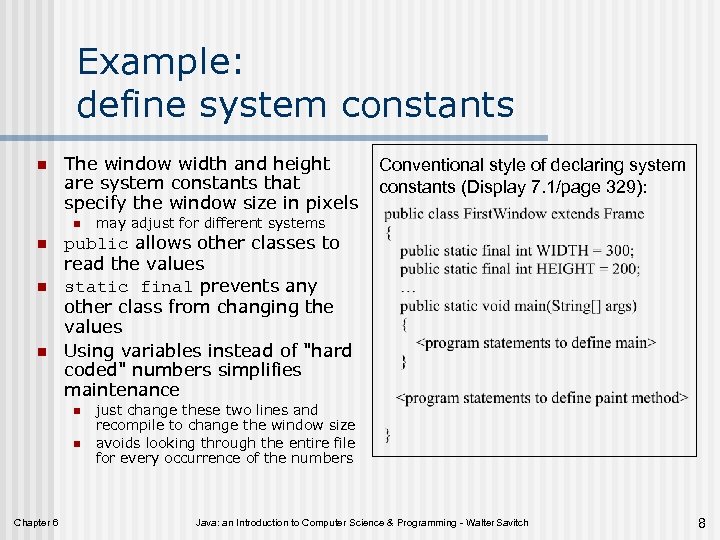 Example: define system constants n The window width and height are system constants that specify the window size in pixels n n may adjust for different systems public allows other classes to read the values static final prevents any other class from changing the values Using variables instead of "hard coded" numbers simplifies maintenance n n Chapter 6 Conventional style of declaring system constants (Display 7. 1/page 329): just change these two lines and recompile to change the window size avoids looking through the entire file for every occurrence of the numbers Java: an Introduction to Computer Science & Programming - Walter Savitch 8
Example: define system constants n The window width and height are system constants that specify the window size in pixels n n may adjust for different systems public allows other classes to read the values static final prevents any other class from changing the values Using variables instead of "hard coded" numbers simplifies maintenance n n Chapter 6 Conventional style of declaring system constants (Display 7. 1/page 329): just change these two lines and recompile to change the window size avoids looking through the entire file for every occurrence of the numbers Java: an Introduction to Computer Science & Programming - Walter Savitch 8
 Example: display window; define and register listeners 1) set. Size: a Frame method to set the size of the window 2) listener: an object of the window. Destroyer class n n n The main method (Display 7. 1/page 329): an object that receives events from an object should close window if "close window" button is clicked must be defined (written) 3) Registering the listener n n associates the listener object with an event-firing object the listener will listen for events fired by the associated object 4) set. Visible: a Frame method to make the Chapter 6 Java: window visible an Introduction to Computer Science & Programming - Walter Savitch 9
Example: display window; define and register listeners 1) set. Size: a Frame method to set the size of the window 2) listener: an object of the window. Destroyer class n n n The main method (Display 7. 1/page 329): an object that receives events from an object should close window if "close window" button is clicked must be defined (written) 3) Registering the listener n n associates the listener object with an event-firing object the listener will listen for events fired by the associated object 4) set. Visible: a Frame method to make the Chapter 6 Java: window visible an Introduction to Computer Science & Programming - Walter Savitch 9
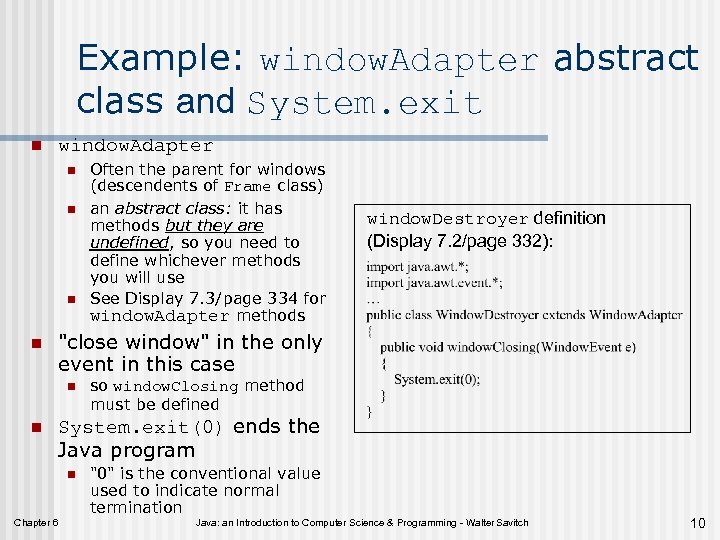 Example: window. Adapter abstract class and System. exit n window. Adapter n n window. Destroyer definition (Display 7. 2/page 332): "close window" in the only event in this case n n Often the parent for windows (descendents of Frame class) an abstract class: it has methods but they are undefined, so you need to define whichever methods you will use See Display 7. 3/page 334 for window. Adapter methods so window. Closing method must be defined System. exit(0) ends the Java program n Chapter 6 "0" is the conventional value used to indicate normal termination Java: an Introduction to Computer Science & Programming - Walter Savitch 10
Example: window. Adapter abstract class and System. exit n window. Adapter n n window. Destroyer definition (Display 7. 2/page 332): "close window" in the only event in this case n n Often the parent for windows (descendents of Frame class) an abstract class: it has methods but they are undefined, so you need to define whichever methods you will use See Display 7. 3/page 334 for window. Adapter methods so window. Closing method must be defined System. exit(0) ends the Java program n Chapter 6 "0" is the conventional value used to indicate normal termination Java: an Introduction to Computer Science & Programming - Walter Savitch 10
 Useful methods in Frame class n n set. Title inserts a string in the title bar of the window set. Background(Color. blue) specifies the background color of the window n Display 7. 6/page 343 lists other predefined color values n add. Window. Listener registers a listener for events set. Size and paint have already been described n etc. - see Display 7. 7/page 344 n
Useful methods in Frame class n n set. Title inserts a string in the title bar of the window set. Background(Color. blue) specifies the background color of the window n Display 7. 6/page 343 lists other predefined color values n add. Window. Listener registers a listener for events set. Size and paint have already been described n etc. - see Display 7. 7/page 344 n
 Two principle ways to create new classes from old ones One method: Inheritance n n Use extend to create a custom window based on an existing class For example: … First. Window extends Frame Another: Container class n n Use a container class Use the add method to place items in it n n Items placed in a container class are called components Three kinds of objects to deal with: 1. The container class itself (usually a window) 2. The components to add to it 3. The layout manager
Two principle ways to create new classes from old ones One method: Inheritance n n Use extend to create a custom window based on an existing class For example: … First. Window extends Frame Another: Container class n n Use a container class Use the add method to place items in it n n Items placed in a container class are called components Three kinds of objects to deal with: 1. The container class itself (usually a window) 2. The components to add to it 3. The layout manager
 AWT container class n AWT container classes: Window, Panel, Frame n n Custom windows are built by adding components to a container class, usually in the constructor Use the add method inherited from Container to place items in the new (container) class Components: items added to a container n n n All three are descendents of the class Container for windows: buttons, menus, text fields, etc. Component is also a class The AWT class hierarchy with Container and Component classes is shown on the next slide (Display 7. 9/page 350)
AWT container class n AWT container classes: Window, Panel, Frame n n Custom windows are built by adding components to a container class, usually in the constructor Use the add method inherited from Container to place items in the new (container) class Components: items added to a container n n n All three are descendents of the class Container for windows: buttons, menus, text fields, etc. Component is also a class The AWT class hierarchy with Container and Component classes is shown on the next slide (Display 7. 9/page 350)
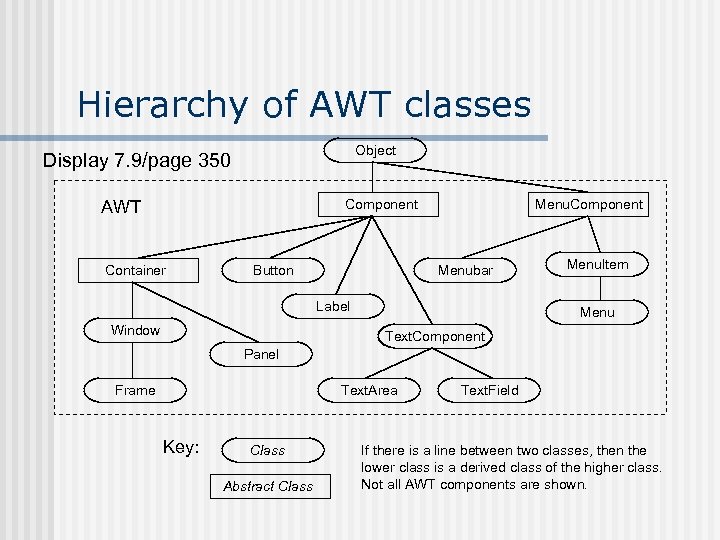 Hierarchy of AWT classes Object Display 7. 9/page 350 Component AWT Container Button Menu. Component Menubar Label Window Menu. Item Menu Text. Component Panel Frame Text. Area Key: Class Abstract Class Text. Field If there is a line between two classes, then the lower class is a derived class of the higher class. Not all AWT components are shown.
Hierarchy of AWT classes Object Display 7. 9/page 350 Component AWT Container Button Menu. Component Menubar Label Window Menu. Item Menu Text. Component Panel Frame Text. Area Key: Class Abstract Class Text. Field If there is a line between two classes, then the lower class is a derived class of the higher class. Not all AWT components are shown.
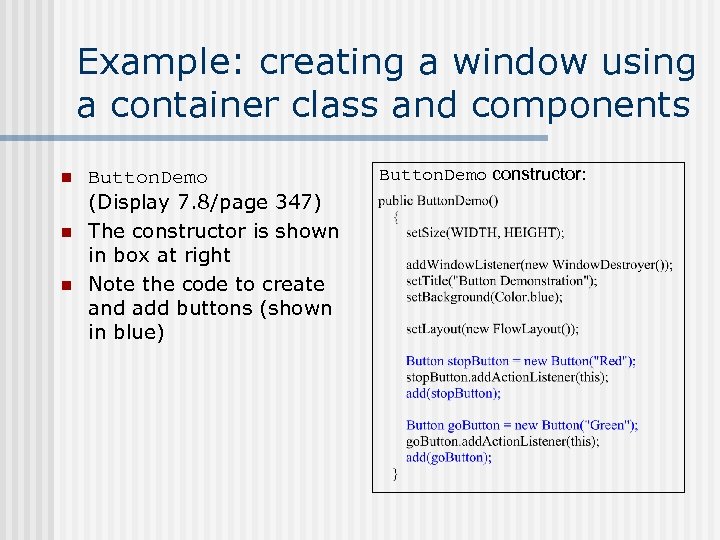 Example: creating a window using a container class and components n n n Button. Demo (Display 7. 8/page 347) The constructor is shown in box at right Note the code to create and add buttons (shown in blue) Button. Demo constructor:
Example: creating a window using a container class and components n n n Button. Demo (Display 7. 8/page 347) The constructor is shown in box at right Note the code to create and add buttons (shown in blue) Button. Demo constructor:
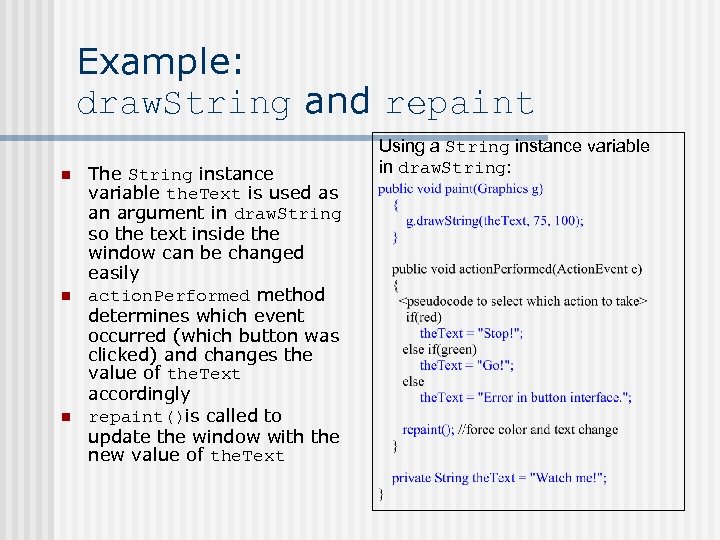 Example: draw. String and repaint n n n The String instance variable the. Text is used as an argument in draw. String so the text inside the window can be changed easily action. Performed method determines which event occurred (which button was clicked) and changes the value of the. Text accordingly repaint()is called to update the window with the new value of the. Text Using a String instance variable in draw. String:
Example: draw. String and repaint n n n The String instance variable the. Text is used as an argument in draw. String so the text inside the window can be changed easily action. Performed method determines which event occurred (which button was clicked) and changes the value of the. Text accordingly repaint()is called to update the window with the new value of the. Text Using a String instance variable in draw. String:
 Example: action listeners n n Different kinds of components require different kinds of listeners Buttons fire events of type Action. Event which require action listeners Action. Listener is not a class, it is a property (or interface) of a class To give the Action. Listener property to a class: 1. Add implements Action. Listener to the beginning of the class definition, e. g. : public class Button. Demo extends Frame implements Action. Listener {
Example: action listeners n n Different kinds of components require different kinds of listeners Buttons fire events of type Action. Event which require action listeners Action. Listener is not a class, it is a property (or interface) of a class To give the Action. Listener property to a class: 1. Add implements Action. Listener to the beginning of the class definition, e. g. : public class Button. Demo extends Frame implements Action. Listener {
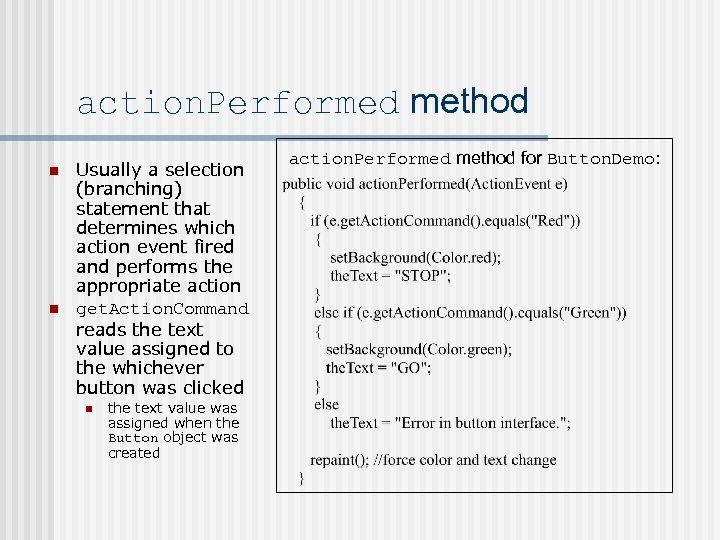 action. Performed method n n Usually a selection (branching) statement that determines which action event fired and performs the appropriate action get. Action. Command reads the text value assigned to the whichever button was clicked n the text value was assigned when the Button object was created action. Performed method for Button. Demo:
action. Performed method n n Usually a selection (branching) statement that determines which action event fired and performs the appropriate action get. Action. Command reads the text value assigned to the whichever button was clicked n the text value was assigned when the Button object was created action. Performed method for Button. Demo:
 Layout managers n Three basic layout managers provided with AWT: 1. Flow. Layout 2. Border. Layout 3. Grid. Layout n There are others but they are not covered in this text
Layout managers n Three basic layout managers provided with AWT: 1. Flow. Layout 2. Border. Layout 3. Grid. Layout n There are others but they are not covered in this text
 Flow. Layout n To create a Flow. Layout object: set. Layout(new Flow. Layout()); n Arranges components in the order they are added n n n starting in upper left of window (or other object) and proceeding to the right when the top line is full it goes to the next line, etc. Example: Button. Demo (Display 7. 8/page 347) uses a flow layout
Flow. Layout n To create a Flow. Layout object: set. Layout(new Flow. Layout()); n Arranges components in the order they are added n n n starting in upper left of window (or other object) and proceeding to the right when the top line is full it goes to the next line, etc. Example: Button. Demo (Display 7. 8/page 347) uses a flow layout
 Border. Layout n To create a Border. Layout object: set. Layout(new Border. Layout()); n Components can be placed in any one of five regions n n n "North" "South" "East" "West" "Center"
Border. Layout n To create a Border. Layout object: set. Layout(new Border. Layout()); n Components can be placed in any one of five regions n n n "North" "South" "East" "West" "Center"
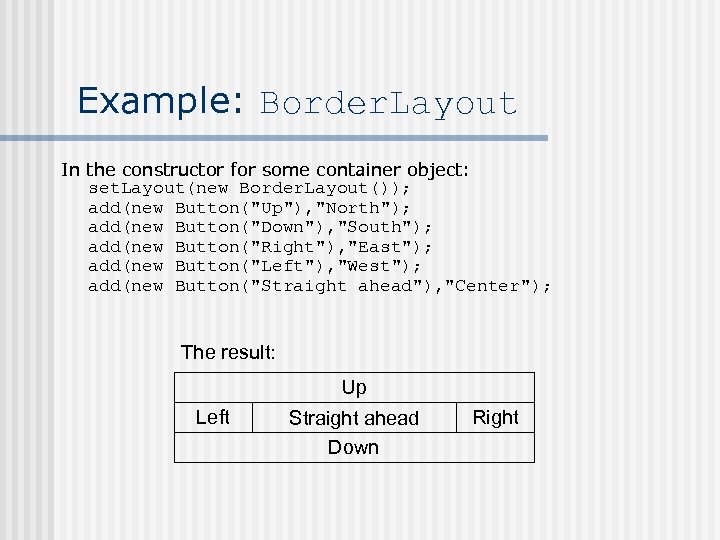 Example: Border. Layout In the constructor for some container object: set. Layout(new Border. Layout()); add(new Button("Up"), "North"); add(new Button("Down"), "South"); add(new Button("Right"), "East"); add(new Button("Left"), "West"); add(new Button("Straight ahead"), "Center"); The result: Up Left Straight ahead Down Right
Example: Border. Layout In the constructor for some container object: set. Layout(new Border. Layout()); add(new Button("Up"), "North"); add(new Button("Down"), "South"); add(new Button("Right"), "East"); add(new Button("Left"), "West"); add(new Button("Straight ahead"), "Center"); The result: Up Left Straight ahead Down Right
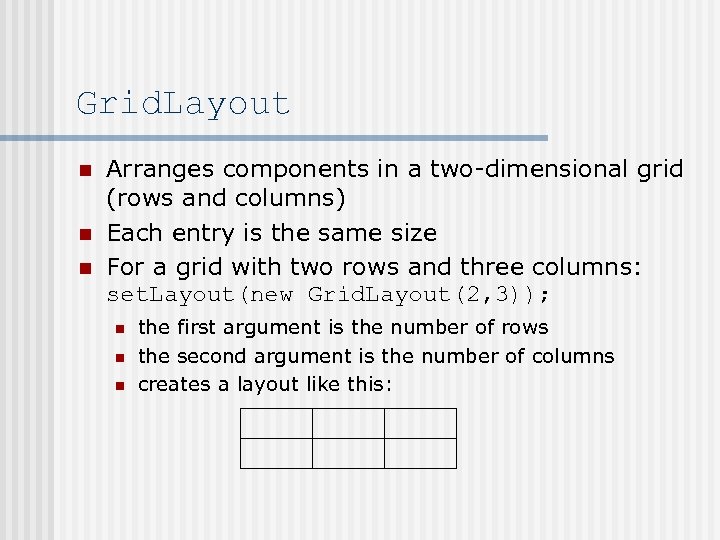 Grid. Layout n n n Arranges components in a two-dimensional grid (rows and columns) Each entry is the same size For a grid with two rows and three columns: set. Layout(new Grid. Layout(2, 3)); n n n the first argument is the number of rows the second argument is the number of columns creates a layout like this:
Grid. Layout n n n Arranges components in a two-dimensional grid (rows and columns) Each entry is the same size For a grid with two rows and three columns: set. Layout(new Grid. Layout(2, 3)); n n n the first argument is the number of rows the second argument is the number of columns creates a layout like this:
 Summary for creating simple window interface(1) 1. Derive a window object from Frame and add components. 2. You must register a window listener for the closewindow button n n e. g. , by adding the following to the GUI class definition within a constructor: add. Window. Listener(new Window. Destroyer()); See Display 7. 2/page 332 for a definition of Window. Destroyer. 3. Some components, e. g. buttons, generate action events, so the GUI (or some other class) must be made an action listener. n n Every component that generates an action event should have an action listener registered with it. Use add. Action. Listener to register an action listener.
Summary for creating simple window interface(1) 1. Derive a window object from Frame and add components. 2. You must register a window listener for the closewindow button n n e. g. , by adding the following to the GUI class definition within a constructor: add. Window. Listener(new Window. Destroyer()); See Display 7. 2/page 332 for a definition of Window. Destroyer. 3. Some components, e. g. buttons, generate action events, so the GUI (or some other class) must be made an action listener. n n Every component that generates an action event should have an action listener registered with it. Use add. Action. Listener to register an action listener.
 Summary for creating simple window interface(2) 4. Use implements Action. Listener at the beginning of the class definition to make your GUI (or other class) an action listener. n You also need to add a definition of the method action. Performed to the class. 5. There are other ways, but this one is simple and commonly used.
Summary for creating simple window interface(2) 4. Use implements Action. Listener at the beginning of the class definition to make your GUI (or other class) an action listener. n You also need to add a definition of the method action. Performed to the class. 5. There are other ways, but this one is simple and commonly used.
 Programming tips 1. Don't reinvent the wheel: copy a similar program and modify it. n Obviously there is a lot of detail to deal with, so start with a program similar to what you need - the sample programs in each chapter are often good starting points for doing the Programming Exercises at the end of the chapter. However, it is NOT ok to copy another student's work! 2. See Display 7. 11/page 360 for an outline of the code to create a simple GUI class. You may want to create this file and use it as a template: copy it and modify the copy to create a new GUI.
Programming tips 1. Don't reinvent the wheel: copy a similar program and modify it. n Obviously there is a lot of detail to deal with, so start with a program similar to what you need - the sample programs in each chapter are often good starting points for doing the Programming Exercises at the end of the chapter. However, it is NOT ok to copy another student's work! 2. See Display 7. 11/page 360 for an outline of the code to create a simple GUI class. You may want to create this file and use it as a template: copy it and modify the copy to create a new GUI.
 Window. Listener options 1. Make the window itself the button listener by implementing the Action. Listener interface n we did this when we placed buttons in a window 2. Make the window listener a separate class n we did this for the window-closing button by defining Window. Destroyer 3. Make the window itself the window listener by implementing the Window. Listener interface
Window. Listener options 1. Make the window itself the button listener by implementing the Action. Listener interface n we did this when we placed buttons in a window 2. Make the window listener a separate class n we did this for the window-closing button by defining Window. Destroyer 3. Make the window itself the window listener by implementing the Window. Listener interface
 More about interfaces n n n Interfaces are just a collection of undefined methods A Java class can be derived from only one base class but can implement more than one interface All methods in an interface must be defined n unused methods can be defined with empty bodies, e. g. public void window. Deiconified(Window. Event e) {} n Action. Listener has only one method (Action. Performed), but Window. Listener has seven methods n if you do not need the other methods, using Action. Listener instead of Window. Listener avoids having to write the empty method definitions
More about interfaces n n n Interfaces are just a collection of undefined methods A Java class can be derived from only one base class but can implement more than one interface All methods in an interface must be defined n unused methods can be defined with empty bodies, e. g. public void window. Deiconified(Window. Event e) {} n Action. Listener has only one method (Action. Performed), but Window. Listener has seven methods n if you do not need the other methods, using Action. Listener instead of Window. Listener avoids having to write the empty method definitions
 The Panel class n n A container class to group objects Used to subdivide a Frame into different areas For example, if you want two buttons in the south area of a border layout, put the two objects in a panel and place the panel in the south position Typical program organization: Create new panel set panel attributes, e. g. background color and panel layout create and add objects such as buttons Establish the overall layout and place the panel in the layout n Example code: Display 7. 13/page 366
The Panel class n n A container class to group objects Used to subdivide a Frame into different areas For example, if you want two buttons in the south area of a border layout, put the two objects in a panel and place the panel in the south position Typical program organization: Create new panel set panel attributes, e. g. background color and panel layout create and add objects such as buttons Establish the overall layout and place the panel in the layout n Example code: Display 7. 13/page 366
 Example: Panel. Demo constructor from Display 7. 13/page 366 create panel place panel in GUI Chapter 7 Java: an Introduction to Computer Science & Programming - Walter Savitch 30
Example: Panel. Demo constructor from Display 7. 13/page 366 create panel place panel in GUI Chapter 7 Java: an Introduction to Computer Science & Programming - Walter Savitch 30
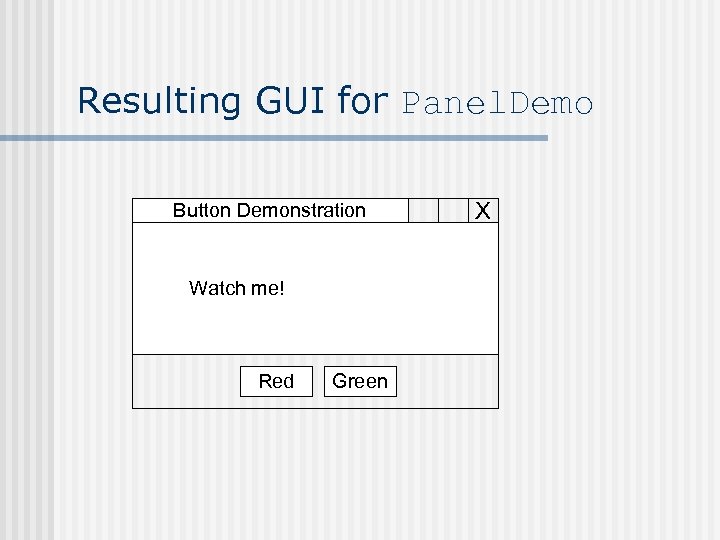 Resulting GUI for Panel. Demo Button Demonstration Watch me! Red Green X
Resulting GUI for Panel. Demo Button Demonstration Watch me! Red Green X
 Text. Area and Text. Field classes n Text. Area: defines an area to display text n n Text. Field: also defines an area to display text n n n specifies how many lines and how many characters per line to display but only the number of characters in the line is specified the field has only one line For both classes: n n n The user can enter text in the field get. Text reads text entered by the user set. Text writes text to the field more text can be written to the field than the specified size, but only an amount equal to the size will be displayed (the scroll bar must be used to see the remaining text) initial text can be specified when the object is created with new
Text. Area and Text. Field classes n Text. Area: defines an area to display text n n Text. Field: also defines an area to display text n n n specifies how many lines and how many characters per line to display but only the number of characters in the line is specified the field has only one line For both classes: n n n The user can enter text in the field get. Text reads text entered by the user set. Text writes text to the field more text can be written to the field than the specified size, but only an amount equal to the size will be displayed (the scroll bar must be used to see the remaining text) initial text can be specified when the object is created with new
 Example: Text. Area n The constructor for Text. Area. Demo (Display 7. 14/page 369) creates a panel with a text area 10 lines by 40 characters n The panel color is set to blue and the background of the text area to white n The panel is placed in the center of the window Creating a text area (excerpt from Display 7. 14/page 369):
Example: Text. Area n The constructor for Text. Area. Demo (Display 7. 14/page 369) creates a panel with a text area 10 lines by 40 characters n The panel color is set to blue and the background of the text area to white n The panel is placed in the center of the window Creating a text area (excerpt from Display 7. 14/page 369):
 Example: set. Text and get. Text Using the same example, Text. Area. Demo (Display 7. 14/page 369): n Clear the text area: the. Text. set. Text(""); n Read the text entered by the user into String instance variable memo 1: memo 1 = the. Text. get. Text();
Example: set. Text and get. Text Using the same example, Text. Area. Demo (Display 7. 14/page 369): n Clear the text area: the. Text. set. Text(""); n Read the text entered by the user into String instance variable memo 1: memo 1 = the. Text. get. Text();
 Label class n Used to label text fields or other components n Typical program organization to attach a label to a text field: Create new panel set panel attributes, e. g. background color and panel layout add text field and label Place the panel in the layout
Label class n Used to label text fields or other components n Typical program organization to attach a label to a text field: Create new panel set panel attributes, e. g. background color and panel layout add text field and label Place the panel in the layout
 Example: Label Excerpt from Label. Demo (Display 7. 15/page 374) name = new Text. Field(20); name. Panel. add(name, "South"); Label name. Label = new Label("Enter your name here: "); name. Panel. add(name. Label, "Center"); Resulting GUI: X Name Tester Enter your name here: A label A very good name! Test Clear
Example: Label Excerpt from Label. Demo (Display 7. 15/page 374) name = new Text. Field(20); name. Panel. add(name, "South"); Label name. Label = new Label("Enter your name here: "); name. Panel. add(name. Label, "Center"); Resulting GUI: X Name Tester Enter your name here: A label A very good name! Test Clear
 Inputting and outputting numbers in the AWT n Problem: the numbers read from or written to a text area are String type but we want numeric types n n all AWT input and output is String Conversion methods are needed n n to convert from numeric types to String, and to convert String to numeric types
Inputting and outputting numbers in the AWT n Problem: the numbers read from or written to a text area are String type but we want numeric types n n all AWT input and output is String Conversion methods are needed n n to convert from numeric types to String, and to convert String to numeric types
 Inputting numbers: methods, . . . Numeric wrapper classes have a value. Of method that converts text numbers to the wrapper numeric type (Integer, Double, etc. ) … … but we often want the corresponding primitive type, so we also need to use the appropriate "Value" method (int. Value, double. Value, etc. ) … … and we want to ignore white space before and after the input, so the trim method is also used
Inputting numbers: methods, . . . Numeric wrapper classes have a value. Of method that converts text numbers to the wrapper numeric type (Integer, Double, etc. ) … … but we often want the corresponding primitive type, so we also need to use the appropriate "Value" method (int. Value, double. Value, etc. ) … … and we want to ignore white space before and after the input, so the trim method is also used
 Example: reading an integer from a text area Combining all these results in a rather long statement, but it should make sense on careful analysis: Input example Read an integer from text field input. Output. Field: int n = Integer. value. Of(input. Output. Field. get. Text(). trim()). int. V alue();
Example: reading an integer from a text area Combining all these results in a rather long statement, but it should make sense on careful analysis: Input example Read an integer from text field input. Output. Field: int n = Integer. value. Of(input. Output. Field. get. Text(). trim()). int. V alue();
 Outputting numbers n n Not so many methods need to be strung together Just use to. String to convert a numeric value to String, and set. Text to write it to the text area. Output example Write an integer to text field input. Output. Field: int n = 31; input. Output. Field. set. Text(Integer. to. String(n));
Outputting numbers n n Not so many methods need to be strung together Just use to. String to convert a numeric value to String, and set. Text to write it to the text area. Output example Write an integer to text field input. Output. Field: int n = 31; input. Output. Field. set. Text(Integer. to. String(n));
 Adding menus n n In the AWT menus are not a component but are added in ways similar to adding components Three AWT classes are used n n Menu. Item The basic approach is to use an add method to n n put Menu. Items in a Menu and put Menus in a Menu.
Adding menus n n In the AWT menus are not a component but are added in ways similar to adding components Three AWT classes are used n n Menu. Item The basic approach is to use an add method to n n put Menu. Items in a Menu and put Menus in a Menu.
 Example: creating a menu Excerpt from Menu. Demo constructor (Display 7. 18/page 386) The resulting GUI before and after clicking Memos is shown on page 388 Note: the method to add a menu bar is set. Menu. Bar, not add Chapter 7 Java: an Introduction to Computer Science & Programming - Walter Savitch 42
Example: creating a menu Excerpt from Menu. Demo constructor (Display 7. 18/page 386) The resulting GUI before and after clicking Memos is shown on page 388 Note: the method to add a menu bar is set. Menu. Bar, not add Chapter 7 Java: an Introduction to Computer Science & Programming - Walter Savitch 42
 Inner classes n n n An inner class is a class that is defined inside another class A full description is beyond the scope of this text However, one situation has already been described: using the AWT to create GUIs n Another simple situation is common and is also described: helping classes n Moving the definition of a helping class inside the class definition has two advantages: n n n it allows the helping class to access all instance variables, including private ones it improves the level of information hiding For these reasons inner classes are often used as listeners to handle events fired within the outer class
Inner classes n n n An inner class is a class that is defined inside another class A full description is beyond the scope of this text However, one situation has already been described: using the AWT to create GUIs n Another simple situation is common and is also described: helping classes n Moving the definition of a helping class inside the class definition has two advantages: n n n it allows the helping class to access all instance variables, including private ones it improves the level of information hiding For these reasons inner classes are often used as listeners to handle events fired within the outer class
 Summary. . . n n n GUIs are written using event-driven programming In event-driven programming, a user action, like a mouse click, generates an event and the that event is automatically passed to an event-handling program to perform the appropriate action. Two main ways to build a GUI with the AWT: 1. Use inheritance to create a derived class from a preexisting one 2. Add components to a container n n A window is defined as a derived class of Frame A button is an object of the class button The add method is used to add components to a container Components in a container are arranged by a layout manager object
Summary. . . n n n GUIs are written using event-driven programming In event-driven programming, a user action, like a mouse click, generates an event and the that event is automatically passed to an event-handling program to perform the appropriate action. Two main ways to build a GUI with the AWT: 1. Use inheritance to create a derived class from a preexisting one 2. Add components to a container n n A window is defined as a derived class of Frame A button is an object of the class button The add method is used to add components to a container Components in a container are arranged by a layout manager object
 … summary, continued n n A panel is a container to organize objects inside a larger container. Text fields and text areas are used by GUIs for input and output of text, including numbers in text format n methods exist to convert numeric types to and from text n Menu. Bars are created by adding Menus and Menu. Items in a manner similar to putting components in containers, but they are not members of the classes Container or Components n Both buttons and menu items fire action events and so should have an Action. Listener registered with them to respond to the event
… summary, continued n n A panel is a container to organize objects inside a larger container. Text fields and text areas are used by GUIs for input and output of text, including numbers in text format n methods exist to convert numeric types to and from text n Menu. Bars are created by adding Menus and Menu. Items in a manner similar to putting components in containers, but they are not members of the classes Container or Components n Both buttons and menu items fire action events and so should have an Action. Listener registered with them to respond to the event


