ccc76e83470e0bd680c24c1fa7b29170.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Computer Networks and Internets Spring 2005 Assistant Professor Jain. Shing Liu 1
Computer Networks and Internets Spring 2005 Assistant Professor Jain. Shing Liu 1
 Networks t. What is a network? electric net, telephone net, computer net l t. Network architectures t. Network payload (voice net, data network) t. Network protocols t. Circuit-switching vs. packet switching 2
Networks t. What is a network? electric net, telephone net, computer net l t. Network architectures t. Network payload (voice net, data network) t. Network protocols t. Circuit-switching vs. packet switching 2
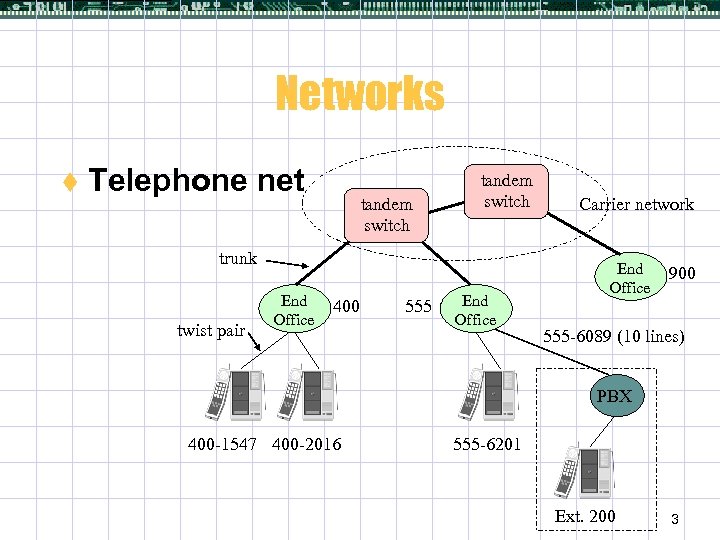 Networks t Telephone net tandem switch trunk twist pair End Office 400 555 End Office Carrier network End Office 900 555 -6089 (10 lines) PBX 400 -1547 400 -2016 555 -6201 Ext. 200 3
Networks t Telephone net tandem switch trunk twist pair End Office 400 555 End Office Carrier network End Office 900 555 -6089 (10 lines) PBX 400 -1547 400 -2016 555 -6201 Ext. 200 3
 Networks t Computer net LAN 4
Networks t Computer net LAN 4
 You Will Learn t. Using and Building Internet Applications (Part I) l. Motivation and tools l. Network programming and Applications 5
You Will Learn t. Using and Building Internet Applications (Part I) l. Motivation and tools l. Network programming and Applications 5
 You Will Learn (ctn. ) t Data Transmission (Part II) Transmission media l Local asynchronous communication (RS-232) l Long-Distance communication l 6
You Will Learn (ctn. ) t Data Transmission (Part II) Transmission media l Local asynchronous communication (RS-232) l Long-Distance communication l 6
 You Will Learn (ctn. ) t. Packet Transmission (Part III) l. Packet, frames, and error detection l. LAN technologies l. WAN technologies l. Protocols and layering 7
You Will Learn (ctn. ) t. Packet Transmission (Part III) l. Packet, frames, and error detection l. LAN technologies l. WAN technologies l. Protocols and layering 7
 You Will Learn (ctn. ) t. Internetworking (Part IV) l. Concepts and Protocols l. Internet Protocol (IP) datagram and Forwarding l. Address binding (ARP) l. Internet control messages (ICMP) l. User Datagram Protocol (UDP) l. Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) l. Network Address Translation (NAT) l. Internet Routing 8
You Will Learn (ctn. ) t. Internetworking (Part IV) l. Concepts and Protocols l. Internet Protocol (IP) datagram and Forwarding l. Address binding (ARP) l. Internet control messages (ICMP) l. User Datagram Protocol (UDP) l. Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) l. Network Address Translation (NAT) l. Internet Routing 8
 You Will Learn (ctn. ) t. Network applications (Part V) l. Client-server paradigm, Socket Interface l. Domain name system (DNS) l. Voice over IP (Vo. IP) l. E-mail, File transfer (FTP), Remote login (TELNET) l. Email transfer (SMTP) l. Web technologies and protocols l. SNMP 9
You Will Learn (ctn. ) t. Network applications (Part V) l. Client-server paradigm, Socket Interface l. Domain name system (DNS) l. Voice over IP (Vo. IP) l. E-mail, File transfer (FTP), Remote login (TELNET) l. Email transfer (SMTP) l. Web technologies and protocols l. SNMP 9
 What You Will NOT Learn t. Commercial aspects l. Products l. Vendors l. Prices l. Network operating systems t. How to purchase / configure / operate t. How to design / implement protocol software 10
What You Will NOT Learn t. Commercial aspects l. Products l. Vendors l. Prices l. Network operating systems t. How to purchase / configure / operate t. How to design / implement protocol software 10
 Ch 1. Introduction 11
Ch 1. Introduction 11
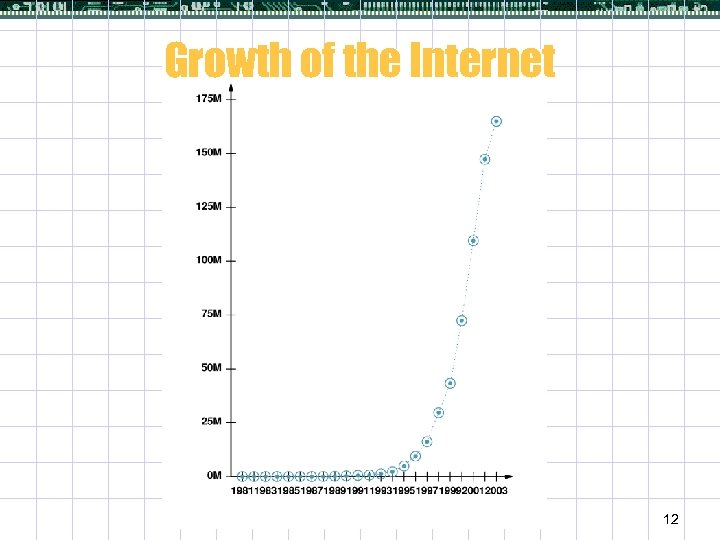 Growth of the Internet 12
Growth of the Internet 12
 Growth of Computer Networking t Computer networks are everywhere l Advertising, shopping, … An entire industry has emerged that develops networking technologies, products, and services t Produces a strong demand in all jobs for people with more networking expertise t Programmers are expected to design network application software 13 t
Growth of Computer Networking t Computer networks are everywhere l Advertising, shopping, … An entire industry has emerged that develops networking technologies, products, and services t Produces a strong demand in all jobs for people with more networking expertise t Programmers are expected to design network application software 13 t
 Ch 2. Motivation and Tools 14
Ch 2. Motivation and Tools 14
 Motivation for Networking t. Information sharing t. Resource sharing l. Computing power l. Peripheral devices such as a printer or a disk l. Human power t. Interaction among cooperative application programs l. E. g. , earthquake alarm 15
Motivation for Networking t. Information sharing t. Resource sharing l. Computing power l. Peripheral devices such as a printer or a disk l. Human power t. Interaction among cooperative application programs l. E. g. , earthquake alarm 15
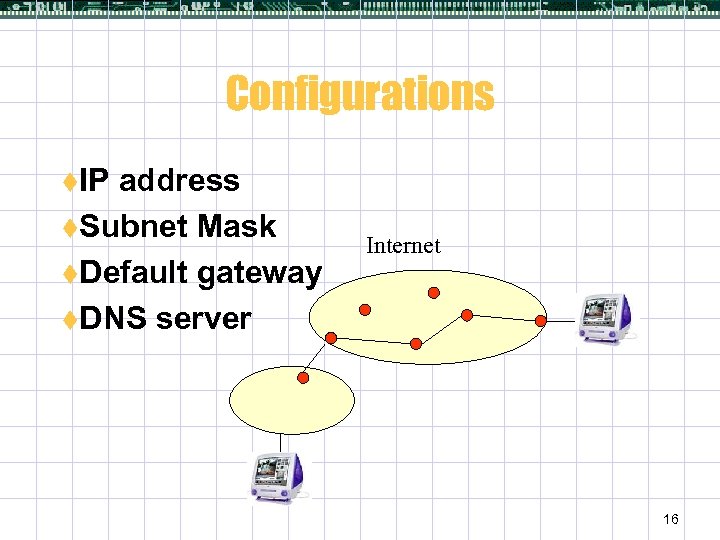 Configurations t. IP address t. Subnet Mask t. Default gateway t. DNS server Internet 16
Configurations t. IP address t. Subnet Mask t. Default gateway t. DNS server Internet 16
 17
17
 18
18
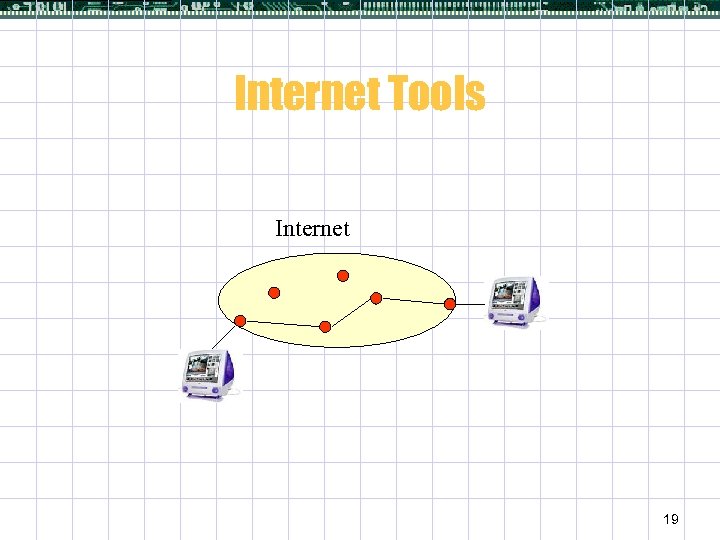 Internet Tools Internet 19
Internet Tools Internet 19
 Internet Tools t. Ping ping 163. 23. 1. 73 (or ping mail. dyu. edu. tw) l Pinging 163. 23. 1. 73 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 163. 23. 1. 73: bytes=32 time=2 ms TTL=249 Reply from 163. 23. 1. 73: bytes=32 time=1 ms TTL=249 Ping statistics for 163. 23. 1. 73: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 1 ms, Maximum = 2 ms, Average = 1 ms 20
Internet Tools t. Ping ping 163. 23. 1. 73 (or ping mail. dyu. edu. tw) l Pinging 163. 23. 1. 73 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 163. 23. 1. 73: bytes=32 time=2 ms TTL=249 Reply from 163. 23. 1. 73: bytes=32 time=1 ms TTL=249 Ping statistics for 163. 23. 1. 73: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 1 ms, Maximum = 2 ms, Average = 1 ms 20
 Internet Tools t traceroute (tracert for MS Windows) l tracert www. nctu. edu. tw Tracing route to mail. dyu. edu. tw [163. 23. 1. 73] over a maximum of 30 hops: 1 <1 ms 2 sch-g. pu. edu. tw [140. 128. 19. 254] 2 <1 ms ssrccc-mgt. pu. edu. tw [140. 128. 20. 254] 3 1 ms <1 ms frouter 1. pu. edu. tw [140. 128. 30. 253] 4 2 ms 140. 128. 251. 42 5 2 ms 140. 128. 251. 33 6 13 ms 12 ms 13 ms 163. 23. 32. 254 7 2 ms 1 ms 2 ms mail. dyu. edu. tw [163. 23. 1. 73] Trace complete. 21
Internet Tools t traceroute (tracert for MS Windows) l tracert www. nctu. edu. tw Tracing route to mail. dyu. edu. tw [163. 23. 1. 73] over a maximum of 30 hops: 1 <1 ms 2 sch-g. pu. edu. tw [140. 128. 19. 254] 2 <1 ms ssrccc-mgt. pu. edu. tw [140. 128. 20. 254] 3 1 ms <1 ms frouter 1. pu. edu. tw [140. 128. 30. 253] 4 2 ms 140. 128. 251. 42 5 2 ms 140. 128. 251. 33 6 13 ms 12 ms 13 ms 163. 23. 32. 254 7 2 ms 1 ms 2 ms mail. dyu. edu. tw [163. 23. 1. 73] Trace complete. 21


