16f6d6be53e24c6820cdb6ff3b554f7d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60
 Computer Network Security Hyun-Sung Kim Dept. of Computer Engineering Kyungil University kim@kiu. ac. kr
Computer Network Security Hyun-Sung Kim Dept. of Computer Engineering Kyungil University kim@kiu. ac. kr
 Computer Network Security Index n Necessity of network security n Services for network security n Security techniques for Internet service n Secure Internet banking example Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 2
Computer Network Security Index n Necessity of network security n Services for network security n Security techniques for Internet service n Secure Internet banking example Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 2
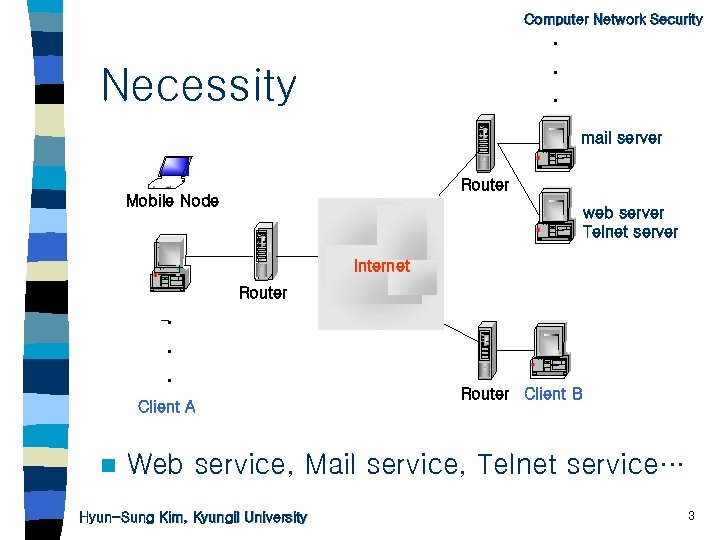 Computer Network Security . . . Necessity mail server Router Mobile Node web server Telnet server Internet Router . . . Client A n Router Client B Web service, Mail service, Telnet service… Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 3
Computer Network Security . . . Necessity mail server Router Mobile Node web server Telnet server Internet Router . . . Client A n Router Client B Web service, Mail service, Telnet service… Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 3
 Basic concerns
Basic concerns
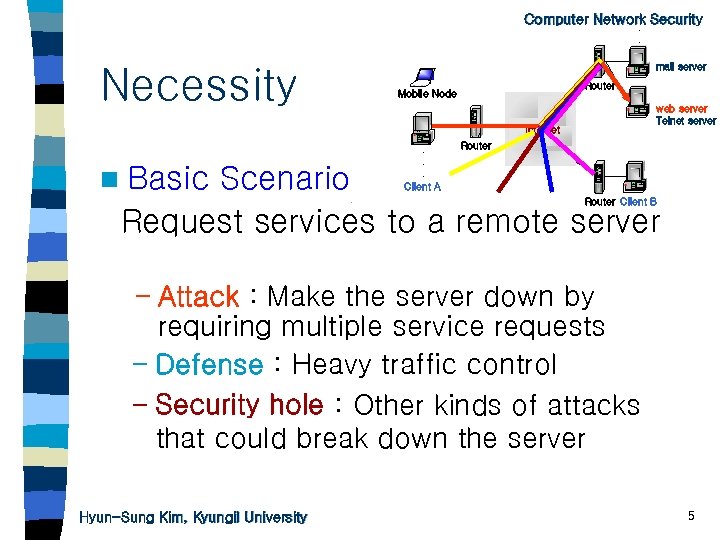 . Computer Network Security. . Necessity mail server Router Mobile Node web server Telnet server Internet n Basic . . . Client A Router Scenario Request services to a remote server Router Client B – Attack : Make the server down by requiring multiple service requests – Defense : Heavy traffic control – Security hole : Other kinds of attacks that could break down the server Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 5
. Computer Network Security. . Necessity mail server Router Mobile Node web server Telnet server Internet n Basic . . . Client A Router Scenario Request services to a remote server Router Client B – Attack : Make the server down by requiring multiple service requests – Defense : Heavy traffic control – Security hole : Other kinds of attacks that could break down the server Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 5
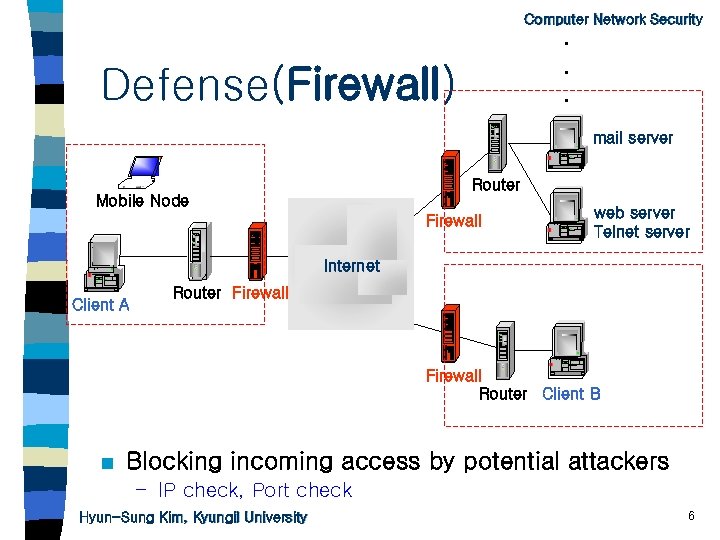 Computer Network Security . . . Defense(Firewall) mail server Router Mobile Node Firewall web server Telnet server Internet Client A Router Firewall Router Client B n Blocking incoming access by potential attackers – IP check, Port check Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 6
Computer Network Security . . . Defense(Firewall) mail server Router Mobile Node Firewall web server Telnet server Internet Client A Router Firewall Router Client B n Blocking incoming access by potential attackers – IP check, Port check Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 6
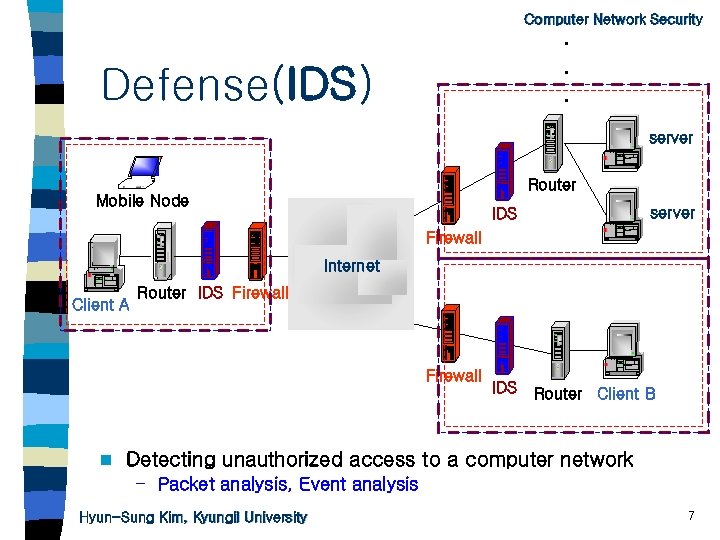 Computer Network Security . . . Defense(IDS) server Router Mobile Node server IDS Firewall Internet Client A Router IDS Firewall n IDS Router Client B Detecting unauthorized access to a computer network – Packet analysis, Event analysis Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 7
Computer Network Security . . . Defense(IDS) server Router Mobile Node server IDS Firewall Internet Client A Router IDS Firewall n IDS Router Client B Detecting unauthorized access to a computer network – Packet analysis, Event analysis Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 7
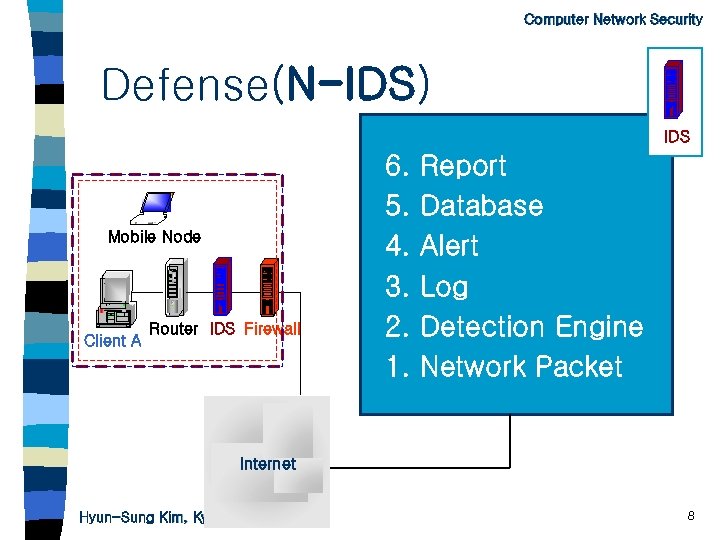 Computer Network Security Defense(N-IDS) IDS Mobile Node Client A Router IDS Firewall 6. 5. 4. 3. 2. 1. Report Database Alert Log Detection Engine Network Packet Internet Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 8
Computer Network Security Defense(N-IDS) IDS Mobile Node Client A Router IDS Firewall 6. 5. 4. 3. 2. 1. Report Database Alert Log Detection Engine Network Packet Internet Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 8
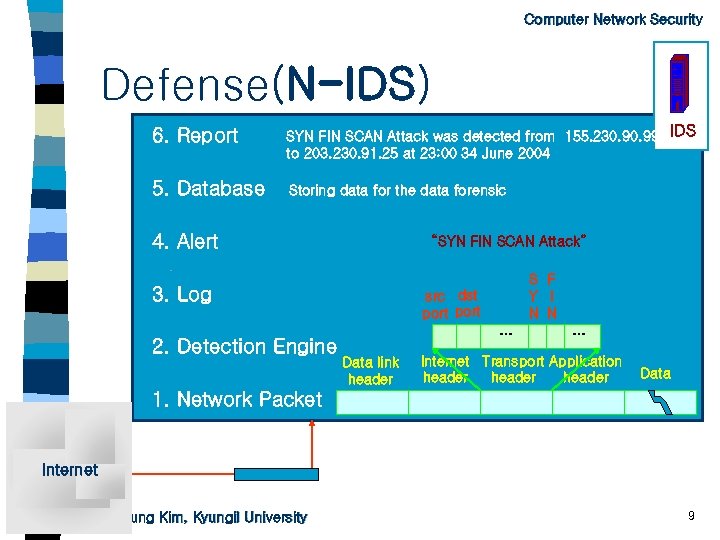 Computer Network Security Defense(N-IDS) 6. Report SYN FIN SCAN Attack was detected from 155. 230. 99 IDS to 203. 230. 91. 25 at 23: 00 34 June 2004 5. Database Storing data for the data forensic 4. Alert “SYN FIN SCAN Attack” 3. Log 2. Detection Engine S F Y I N N src dst port … Data link header … Internet Transport Application header Data 1. Network Packet Internet Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 9
Computer Network Security Defense(N-IDS) 6. Report SYN FIN SCAN Attack was detected from 155. 230. 99 IDS to 203. 230. 91. 25 at 23: 00 34 June 2004 5. Database Storing data for the data forensic 4. Alert “SYN FIN SCAN Attack” 3. Log 2. Detection Engine S F Y I N N src dst port … Data link header … Internet Transport Application header Data 1. Network Packet Internet Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 9
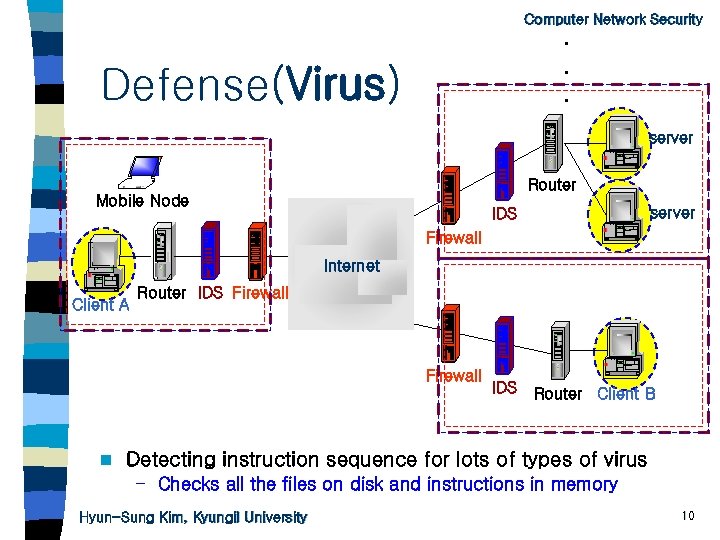 Computer Network Security . . . Defense(Virus) server Router Mobile Node server IDS Firewall Internet Client A Router IDS Firewall n IDS Router Client B Detecting instruction sequence for lots of types of virus – Checks all the files on disk and instructions in memory Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 10
Computer Network Security . . . Defense(Virus) server Router Mobile Node server IDS Firewall Internet Client A Router IDS Firewall n IDS Router Client B Detecting instruction sequence for lots of types of virus – Checks all the files on disk and instructions in memory Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 10
 Computer Network Security Is that all about the security ? server Router Mobile Node Client A Router IDS Firewall Internet Firewall Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University server Firewall IDS Router Client B 11
Computer Network Security Is that all about the security ? server Router Mobile Node Client A Router IDS Firewall Internet Firewall Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University server Firewall IDS Router Client B 11
 Other concerns
Other concerns
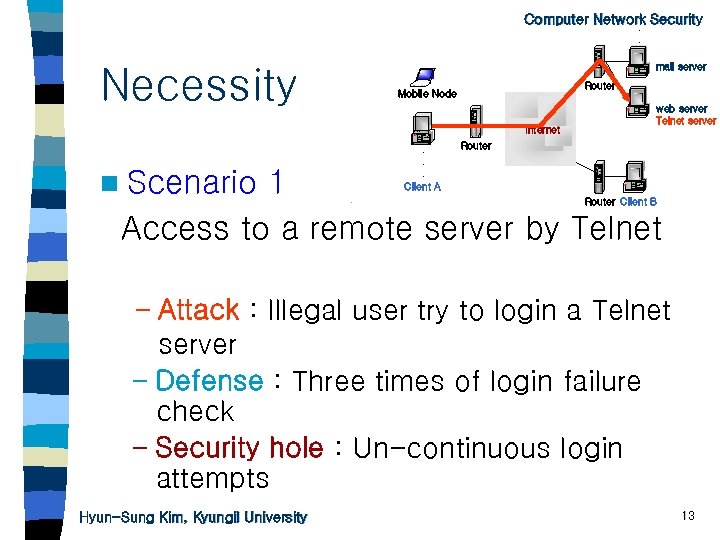 . Computer Network Security. . Necessity mail server Router Mobile Node Internet n Scenario . . . Client A web server Telnet server Router 1 Access to a remote server by Telnet Router Client B – Attack : Illegal user try to login a Telnet server – Defense : Three times of login failure check – Security hole : Un-continuous login attempts Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 13
. Computer Network Security. . Necessity mail server Router Mobile Node Internet n Scenario . . . Client A web server Telnet server Router 1 Access to a remote server by Telnet Router Client B – Attack : Illegal user try to login a Telnet server – Defense : Three times of login failure check – Security hole : Un-continuous login attempts Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 13
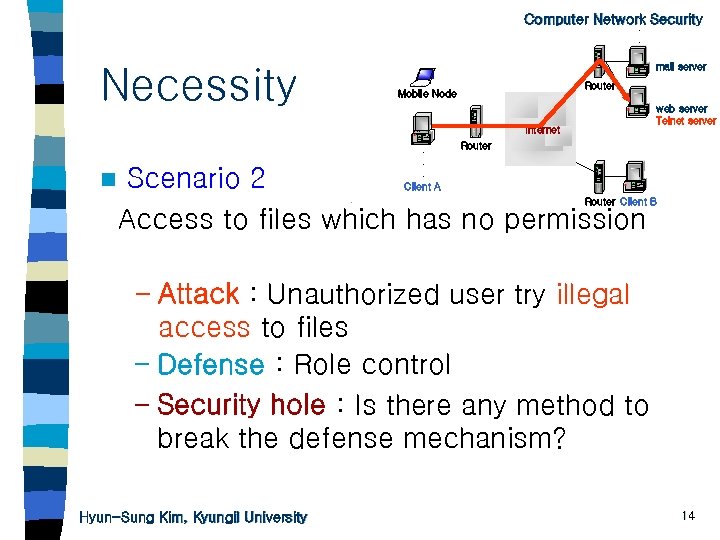 . Computer Network Security. . Necessity mail server Router Mobile Node web server Telnet server Internet n . . . Client A Router Scenario 2 Access to files which has no permission Router Client B – Attack : Unauthorized user try illegal access to files – Defense : Role control – Security hole : Is there any method to break the defense mechanism? Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 14
. Computer Network Security. . Necessity mail server Router Mobile Node web server Telnet server Internet n . . . Client A Router Scenario 2 Access to files which has no permission Router Client B – Attack : Unauthorized user try illegal access to files – Defense : Role control – Security hole : Is there any method to break the defense mechanism? Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 14
 . Computer Network Security. . Necessity mail server Mobile Node Router 3510 2211… Internet n Scenario . . . Client A web server Telnet server Router 3 Sending a very important information over Internet Router Client B – Attack : Illegal user try to listen the information – Defense : Encoding & decoding – Security hole : Is there any method to break the defense mechanism? Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 15
. Computer Network Security. . Necessity mail server Mobile Node Router 3510 2211… Internet n Scenario . . . Client A web server Telnet server Router 3 Sending a very important information over Internet Router Client B – Attack : Illegal user try to listen the information – Defense : Encoding & decoding – Security hole : Is there any method to break the defense mechanism? Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 15
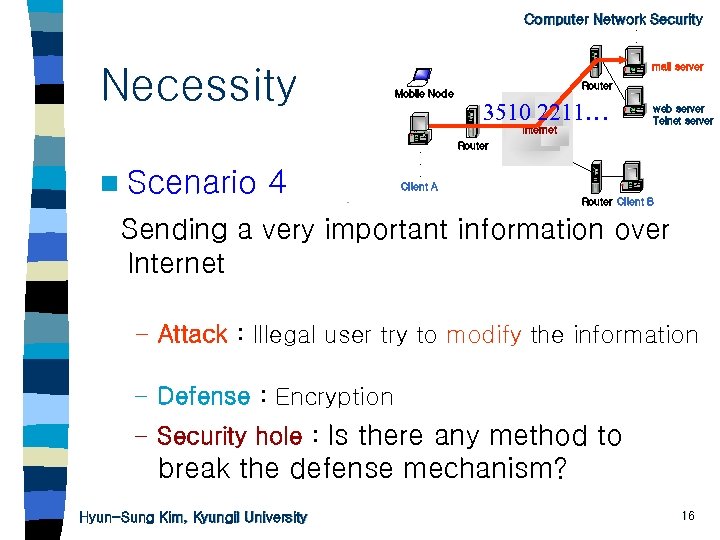 . Computer Network Security. . Necessity mail server Mobile Node Router 3510 2211… Internet n Scenario 4 . . . Client A web server Telnet server Router Client B Sending a very important information over Internet – Attack : Illegal user try to modify the information – Defense : Encryption – Security hole : Is there any method to break the defense mechanism? Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 16
. Computer Network Security. . Necessity mail server Mobile Node Router 3510 2211… Internet n Scenario 4 . . . Client A web server Telnet server Router Client B Sending a very important information over Internet – Attack : Illegal user try to modify the information – Defense : Encryption – Security hole : Is there any method to break the defense mechanism? Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 16
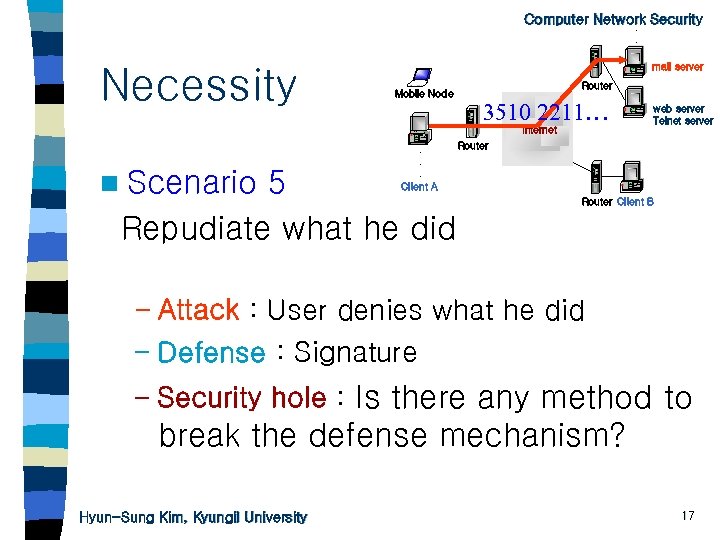 . Computer Network Security. . Necessity mail server Mobile Node Router 3510 2211… Internet n Scenario . . . Client A 5 Repudiate what he did web server Telnet server Router Client B – Attack : User denies what he did – Defense : Signature – Security hole : Is there any method to break the defense mechanism? Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 17
. Computer Network Security. . Necessity mail server Mobile Node Router 3510 2211… Internet n Scenario . . . Client A 5 Repudiate what he did web server Telnet server Router Client B – Attack : User denies what he did – Defense : Signature – Security hole : Is there any method to break the defense mechanism? Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 17
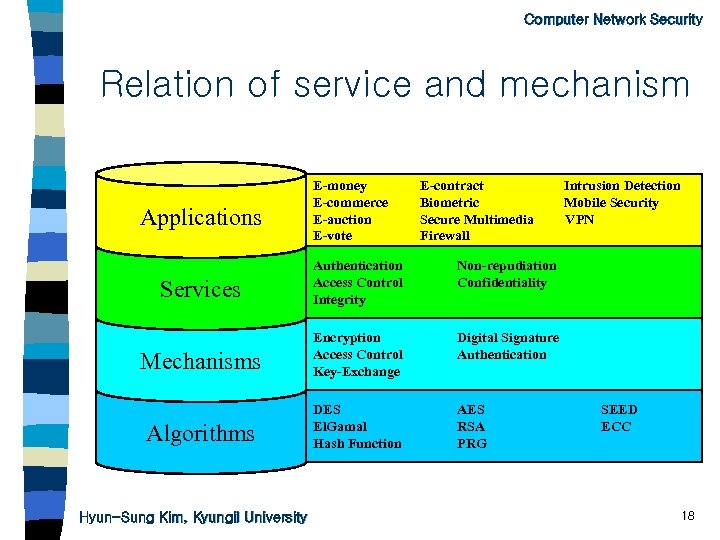 Computer Network Security Relation of service and mechanism Applications E-money E-commerce E-auction E-vote E-contract Biometric Secure Multimedia Firewall Services Authentication Access Control Integrity Non-repudiation Confidentiality Mechanisms Encryption Access Control Key-Exchange Digital Signature Authentication Algorithms DES El. Gamal Hash Function AES RSA PRG Intrusion Detection Mobile Security VPN Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University SEED ECC 18
Computer Network Security Relation of service and mechanism Applications E-money E-commerce E-auction E-vote E-contract Biometric Secure Multimedia Firewall Services Authentication Access Control Integrity Non-repudiation Confidentiality Mechanisms Encryption Access Control Key-Exchange Digital Signature Authentication Algorithms DES El. Gamal Hash Function AES RSA PRG Intrusion Detection Mobile Security VPN Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University SEED ECC 18
 Computer Network Security services n Authentication -> Scenario 1 n Access control -> Scenario 2 n Confidentiality -> Scenario 3 n Integrity -> Scenario 4 n Non-repudiation -> Scenario 5 Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 19
Computer Network Security services n Authentication -> Scenario 1 n Access control -> Scenario 2 n Confidentiality -> Scenario 3 n Integrity -> Scenario 4 n Non-repudiation -> Scenario 5 Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 19
 Computer Network Security services n Authentication – An assurance that the identity is not false – Ensures that the origin is correctly identified n Non-repudiation – Requires that neither the sender nor the receiver of a message be able to deny the transmission Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 20
Computer Network Security services n Authentication – An assurance that the identity is not false – Ensures that the origin is correctly identified n Non-repudiation – Requires that neither the sender nor the receiver of a message be able to deny the transmission Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 20
 Computer Network Security services n Confidentiality – Ensures that the information are accessible only by authorized parties n Integrity – Ensures that the only authorized parties are able to modify information Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 21
Computer Network Security services n Confidentiality – Ensures that the information are accessible only by authorized parties n Integrity – Ensures that the only authorized parties are able to modify information Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 21
 Computer Network Security Mechanisms n Encryption n Digital signature n Authentication n Key-exchange Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 22
Computer Network Security Mechanisms n Encryption n Digital signature n Authentication n Key-exchange Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 22
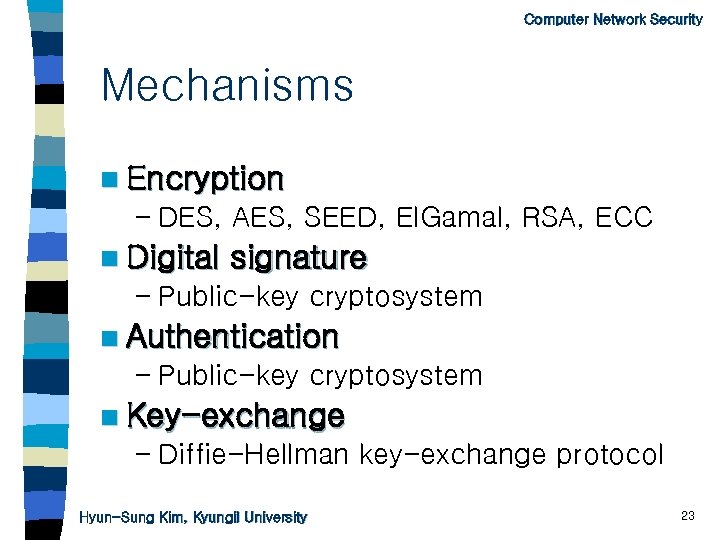 Computer Network Security Mechanisms n Encryption – DES, AES, SEED, El. Gamal, RSA, ECC n Digital signature – Public-key cryptosystem n Authentication – Public-key cryptosystem n Key-exchange – Diffie-Hellman key-exchange protocol Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 23
Computer Network Security Mechanisms n Encryption – DES, AES, SEED, El. Gamal, RSA, ECC n Digital signature – Public-key cryptosystem n Authentication – Public-key cryptosystem n Key-exchange – Diffie-Hellman key-exchange protocol Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 23
 Cryptography Confidentiality Integrity
Cryptography Confidentiality Integrity
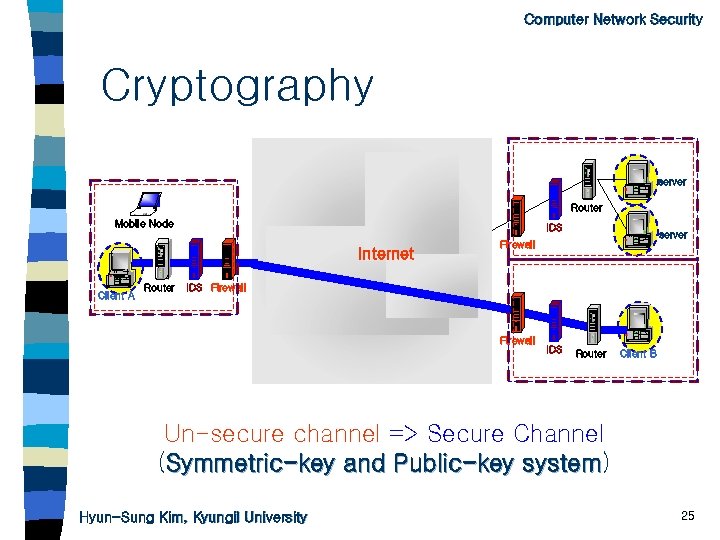 Computer Network Security Cryptography server Router Mobile Node IDS Internet Client A Router server Firewall IDS Router Client B Un-secure channel => Secure Channel (Symmetric-key and Public-key system) system Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 25
Computer Network Security Cryptography server Router Mobile Node IDS Internet Client A Router server Firewall IDS Router Client B Un-secure channel => Secure Channel (Symmetric-key and Public-key system) system Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 25
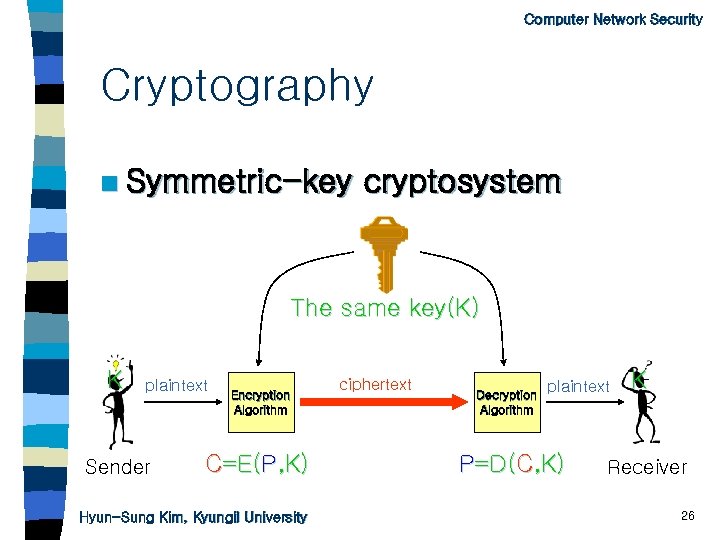 Computer Network Security Cryptography n Symmetric-key cryptosystem The same key(K) K plaintext Sender Encryption Algorithm C=E(P, K) Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University ciphertext Decryption Algorithm plaintext P=D(C, K) K Receiver 26
Computer Network Security Cryptography n Symmetric-key cryptosystem The same key(K) K plaintext Sender Encryption Algorithm C=E(P, K) Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University ciphertext Decryption Algorithm plaintext P=D(C, K) K Receiver 26
 Computer Network Security Cryptography n Symmetric-key cryptosystem – Caesar Cipher(Basic scheme) Key => 3 Plain text : meet me after the party Cipher text : phhw ph diwhu wkh sduwb Encryption algorithm : Addition Decryption algorithm : Subtraction Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 27
Computer Network Security Cryptography n Symmetric-key cryptosystem – Caesar Cipher(Basic scheme) Key => 3 Plain text : meet me after the party Cipher text : phhw ph diwhu wkh sduwb Encryption algorithm : Addition Decryption algorithm : Subtraction Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 27
 Computer Network Security Cryptography n Symmetric-key cryptosystem – Problems in Caesar Cipher • The key size is so small : -25 ~ 25 (about 50 keys) • Weak at the brute force attack – Solutions • Enlarge the key size • Apply more complex operations Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 28
Computer Network Security Cryptography n Symmetric-key cryptosystem – Problems in Caesar Cipher • The key size is so small : -25 ~ 25 (about 50 keys) • Weak at the brute force attack – Solutions • Enlarge the key size • Apply more complex operations Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 28
 Computer Network Security Cryptography n Symmetric-key cryptosystem – DES(Data Encryption Standard) • Key size : 56 bits • Basic operations – – Transposition Substitution XOR Shift • USA standard – DES : from 1977 to 1998 – AES : 2001 draft Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 29
Computer Network Security Cryptography n Symmetric-key cryptosystem – DES(Data Encryption Standard) • Key size : 56 bits • Basic operations – – Transposition Substitution XOR Shift • USA standard – DES : from 1977 to 1998 – AES : 2001 draft Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 29
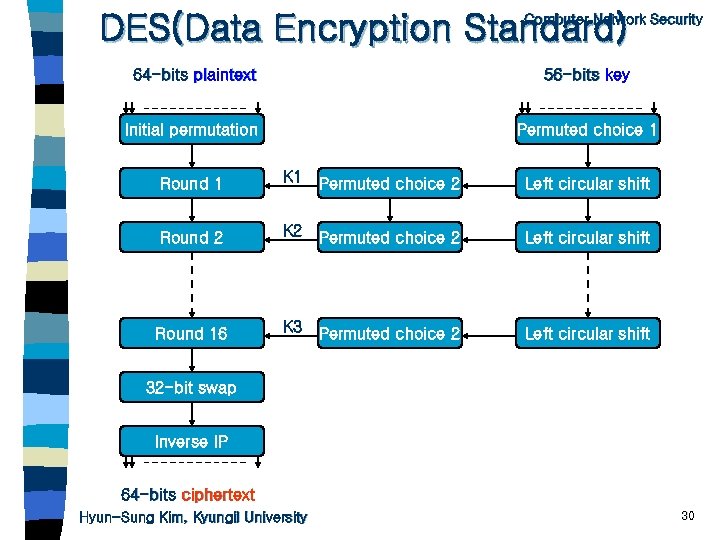 DES(Data Encryption Standard) Computer Network Security 64 -bits plaintext 56 -bits key Initial permutation Permuted choice 1 Round 1 K 1 Permuted choice 2 Left circular shift Round 2 K 2 Permuted choice 2 Left circular shift Round 16 K 3 Permuted choice 2 Left circular shift 32 -bit swap Inverse IP 64 -bits ciphertext Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 30
DES(Data Encryption Standard) Computer Network Security 64 -bits plaintext 56 -bits key Initial permutation Permuted choice 1 Round 1 K 1 Permuted choice 2 Left circular shift Round 2 K 2 Permuted choice 2 Left circular shift Round 16 K 3 Permuted choice 2 Left circular shift 32 -bit swap Inverse IP 64 -bits ciphertext Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 30
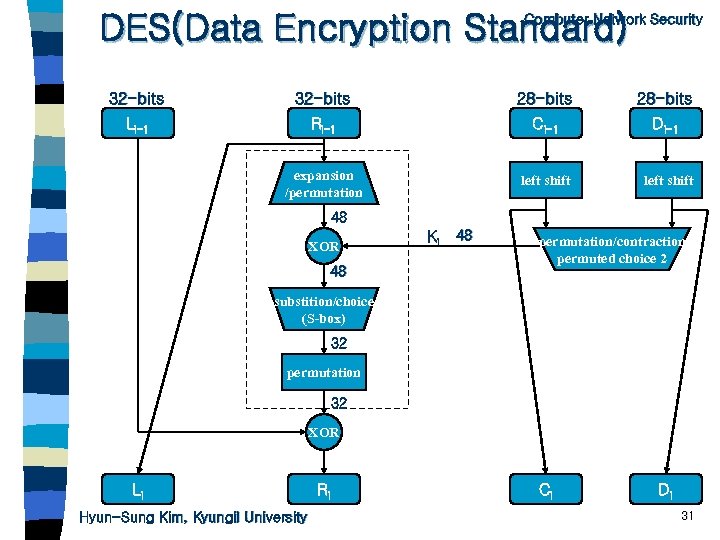 DES(Data Encryption Standard) Computer Network Security 32 -bits 28 -bits Li-1 Ri-1 Ci-1 Di-1 expansion /permutation left shift 48 XOR 48 Ki 48 permutation/contraction permuted choice 2 substition/choice (S-box) 32 permutation 32 XOR Li Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University Ri Ci Di 31
DES(Data Encryption Standard) Computer Network Security 32 -bits 28 -bits Li-1 Ri-1 Ci-1 Di-1 expansion /permutation left shift 48 XOR 48 Ki 48 permutation/contraction permuted choice 2 substition/choice (S-box) 32 permutation 32 XOR Li Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University Ri Ci Di 31
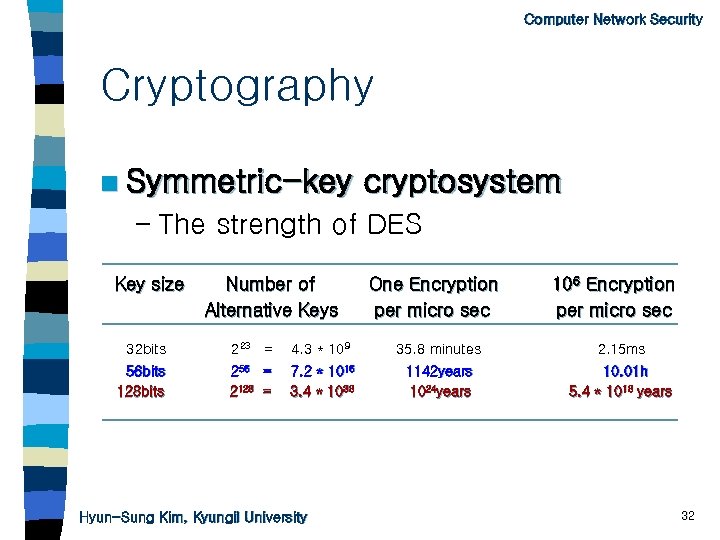 Computer Network Security Cryptography n Symmetric-key cryptosystem – The strength of DES Key size Number of Alternative Keys One Encryption per micro sec 106 Encryption per micro sec 32 bits 223 = 4. 3 * 109 35. 8 minutes 2. 15 ms 56 bits 128 bits 256 = 2128 = 7. 2 * 1016 3. 4 * 1038 1142 years 1024 years 10. 01 h 5. 4 * 1018 years Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 32
Computer Network Security Cryptography n Symmetric-key cryptosystem – The strength of DES Key size Number of Alternative Keys One Encryption per micro sec 106 Encryption per micro sec 32 bits 223 = 4. 3 * 109 35. 8 minutes 2. 15 ms 56 bits 128 bits 256 = 2128 = 7. 2 * 1016 3. 4 * 1038 1142 years 1024 years 10. 01 h 5. 4 * 1018 years Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 32
 Computer Network Security Cryptography n Is DES secure enough? enough – No! • There are potential weaknesses • Key size is not secure enough n Is there any alternative? alternative – Yes! • Enlarge key size from 56 to 128 => Triple DES • AES Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 33
Computer Network Security Cryptography n Is DES secure enough? enough – No! • There are potential weaknesses • Key size is not secure enough n Is there any alternative? alternative – Yes! • Enlarge key size from 56 to 128 => Triple DES • AES Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 33
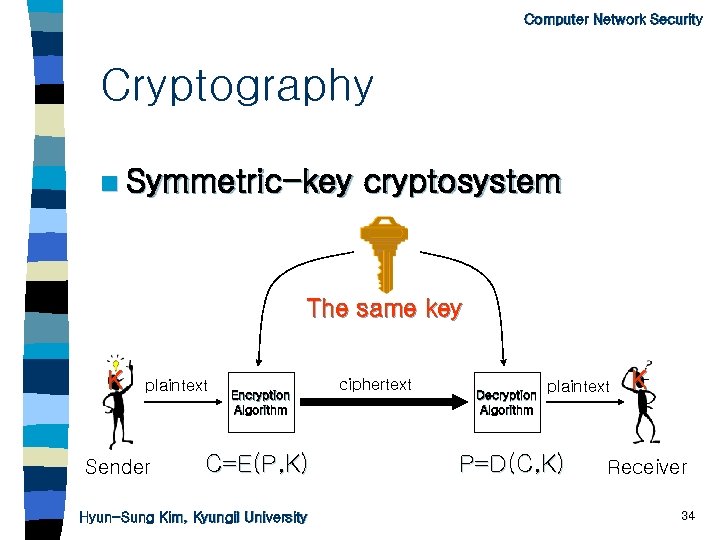 Computer Network Security Cryptography n Symmetric-key cryptosystem The same key K plaintext Sender Encryption Algorithm C=E(P, K) Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University ciphertext Decryption Algorithm plaintext P=D(C, K) K Receiver 34
Computer Network Security Cryptography n Symmetric-key cryptosystem The same key K plaintext Sender Encryption Algorithm C=E(P, K) Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University ciphertext Decryption Algorithm plaintext P=D(C, K) K Receiver 34
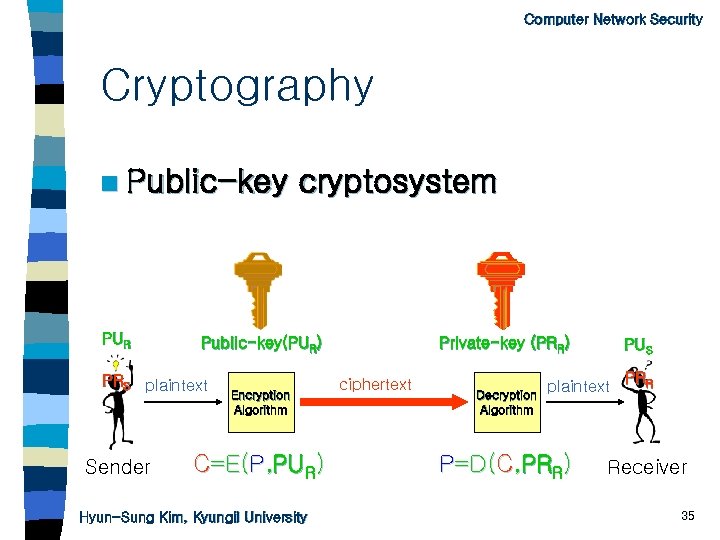 Computer Network Security Cryptography n Public-key PUR Public-key(PUR) PRS plaintext Sender cryptosystem Encryption Algorithm C=E(P, PUR) Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University Private-key (PRR) ciphertext Decryption Algorithm PUS plaintext P=D(C, PRR) PRR Receiver 35
Computer Network Security Cryptography n Public-key PUR Public-key(PUR) PRS plaintext Sender cryptosystem Encryption Algorithm C=E(P, PUR) Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University Private-key (PRR) ciphertext Decryption Algorithm PUS plaintext P=D(C, PRR) PRR Receiver 35
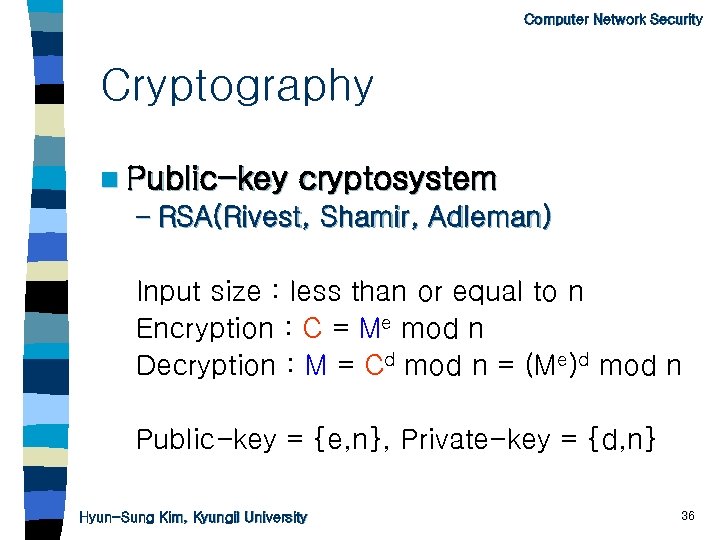 Computer Network Security Cryptography n Public-key cryptosystem – RSA(Rivest, Shamir, Adleman) Input size : less than or equal to n Encryption : C = Me mod n Decryption : M = Cd mod n = (Me)d mod n Public-key = {e, n}, Private-key = {d, n} Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 36
Computer Network Security Cryptography n Public-key cryptosystem – RSA(Rivest, Shamir, Adleman) Input size : less than or equal to n Encryption : C = Me mod n Decryption : M = Cd mod n = (Me)d mod n Public-key = {e, n}, Private-key = {d, n} Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 36
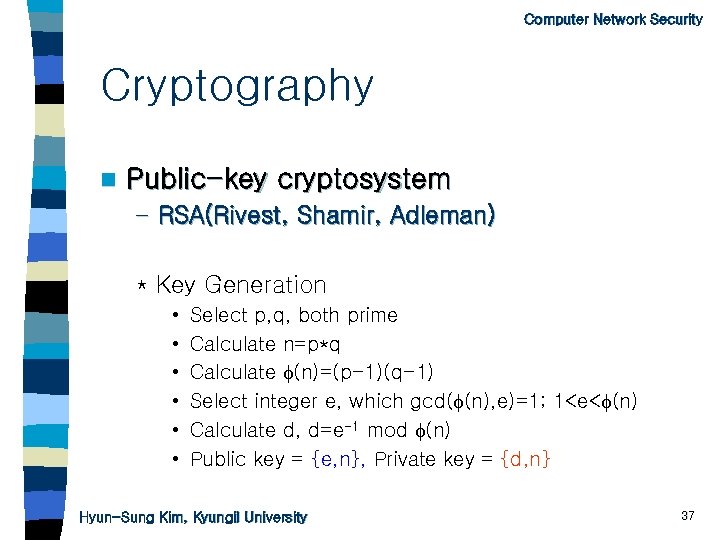 Computer Network Security Cryptography n Public-key cryptosystem – RSA(Rivest, Shamir, Adleman) * Key Generation • • • Select p, q, both prime Calculate n=p*q Calculate (n)=(p-1)(q-1) Select integer e, which gcd( (n), e)=1; 1
Computer Network Security Cryptography n Public-key cryptosystem – RSA(Rivest, Shamir, Adleman) * Key Generation • • • Select p, q, both prime Calculate n=p*q Calculate (n)=(p-1)(q-1) Select integer e, which gcd( (n), e)=1; 1
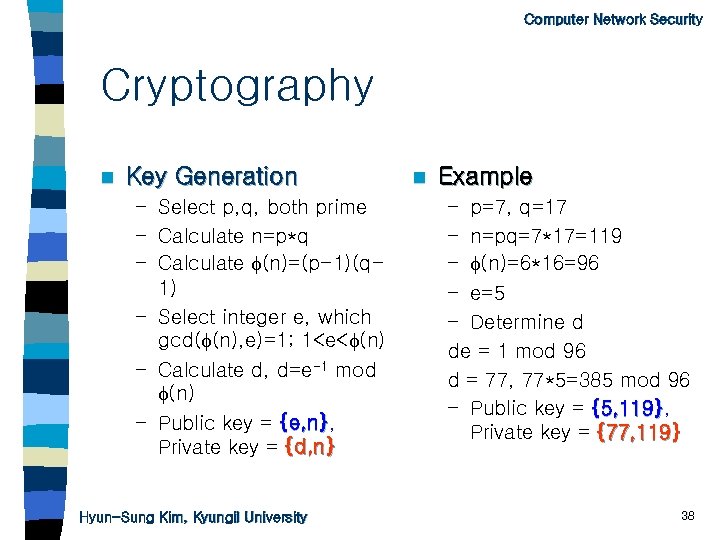 Computer Network Security Cryptography n Key Generation – Select p, q, both prime – Calculate n=p*q – Calculate (n)=(p-1)(q 1) – Select integer e, which gcd( (n), e)=1; 1
Computer Network Security Cryptography n Key Generation – Select p, q, both prime – Calculate n=p*q – Calculate (n)=(p-1)(q 1) – Select integer e, which gcd( (n), e)=1; 1
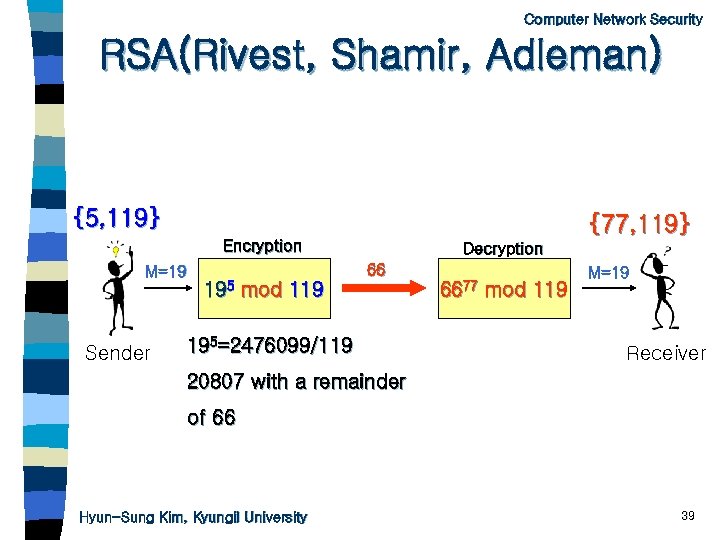 Computer Network Security RSA(Rivest, Shamir, Adleman) {5, 119} {77, 119} Encryption M=19 Sender Decryption 66 195 mod 119 195=2476099/119 6677 mod 119 M=19 Receiver 20807 with a remainder of 66 Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 39
Computer Network Security RSA(Rivest, Shamir, Adleman) {5, 119} {77, 119} Encryption M=19 Sender Decryption 66 195 mod 119 195=2476099/119 6677 mod 119 M=19 Receiver 20807 with a remainder of 66 Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 39
 Computer Network Security Cryptography n Public-key cryptosystem – The security of RSA • Brute force • Mathematical attacks – The factoring problem, finding large two primes from p and q • Timing attacks Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 40
Computer Network Security Cryptography n Public-key cryptosystem – The security of RSA • Brute force • Mathematical attacks – The factoring problem, finding large two primes from p and q • Timing attacks Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 40
 Computer Network Security Cryptography n Is RSA secure enough? enough – Yes! • But, requires the large key size, 1024 n Is there any alternative? alternative – Yes! • ECC with much less key size, 160 bits Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 41
Computer Network Security Cryptography n Is RSA secure enough? enough – Yes! • But, requires the large key size, 1024 n Is there any alternative? alternative – Yes! • ECC with much less key size, 160 bits Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 41
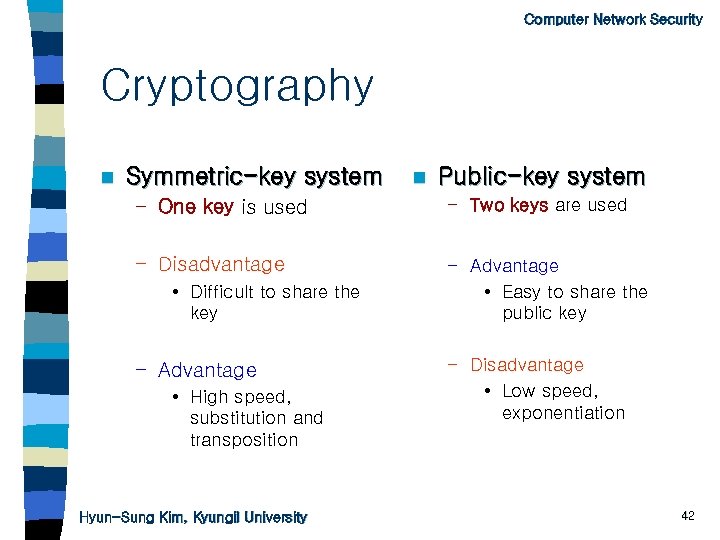 Computer Network Security Cryptography n Symmetric-key system n Public-key system – One key is used – Two keys are used – Disadvantage – Advantage • Easy to share the public key • Difficult to share the key – Advantage • High speed, substitution and transposition Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University – Disadvantage • Low speed, exponentiation 42
Computer Network Security Cryptography n Symmetric-key system n Public-key system – One key is used – Two keys are used – Disadvantage – Advantage • Easy to share the public key • Difficult to share the key – Advantage • High speed, substitution and transposition Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University – Disadvantage • Low speed, exponentiation 42
 Cryptography Digital signature Authentication
Cryptography Digital signature Authentication
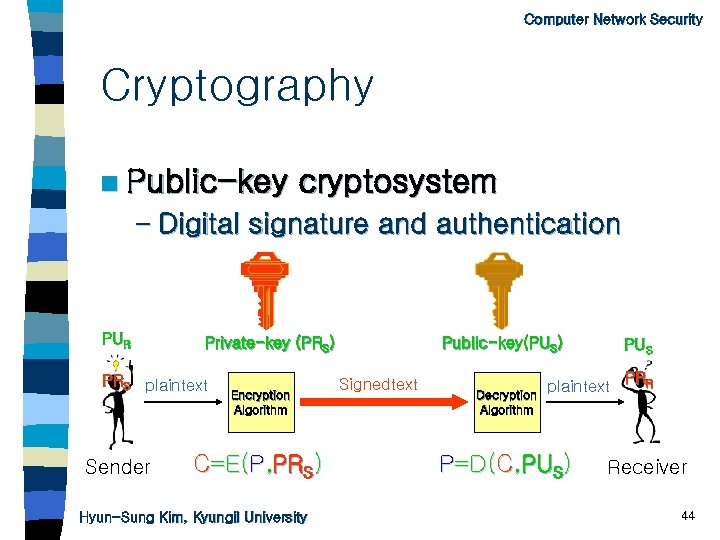 Computer Network Security Cryptography n Public-key cryptosystem – Digital signature and authentication PUR Private-key (PRS) PRS plaintext Sender Encryption Algorithm C=E(P, PRS) Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University Public-key(PUS) Signedtext Decryption Algorithm PUS plaintext P=D(C, PUS) PRR Receiver 44
Computer Network Security Cryptography n Public-key cryptosystem – Digital signature and authentication PUR Private-key (PRS) PRS plaintext Sender Encryption Algorithm C=E(P, PRS) Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University Public-key(PUS) Signedtext Decryption Algorithm PUS plaintext P=D(C, PUS) PRR Receiver 44
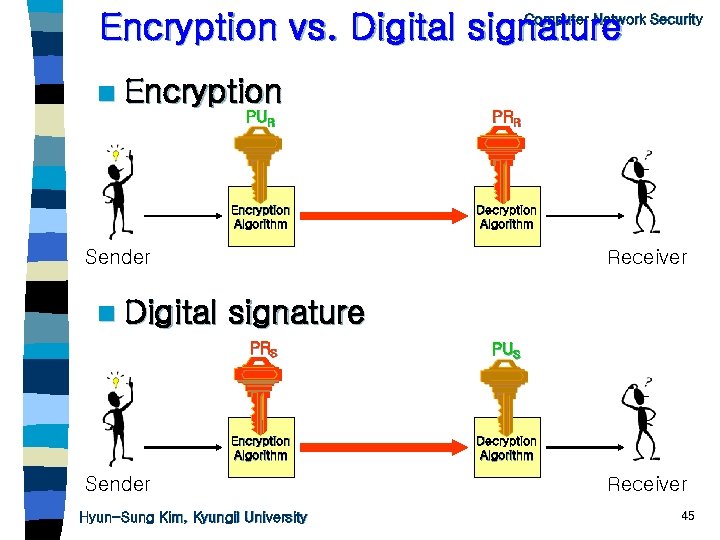 Encryption vs. Digital signature Computer Network Security n Encryption PUR PRR Encryption Algorithm Decryption Algorithm Sender n Digital Receiver signature PRS PUS Encryption Algorithm Decryption Algorithm Sender Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University Receiver 45
Encryption vs. Digital signature Computer Network Security n Encryption PUR PRR Encryption Algorithm Decryption Algorithm Sender n Digital Receiver signature PRS PUS Encryption Algorithm Decryption Algorithm Sender Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University Receiver 45
 Cryptography Confidentiality with Digital signature
Cryptography Confidentiality with Digital signature
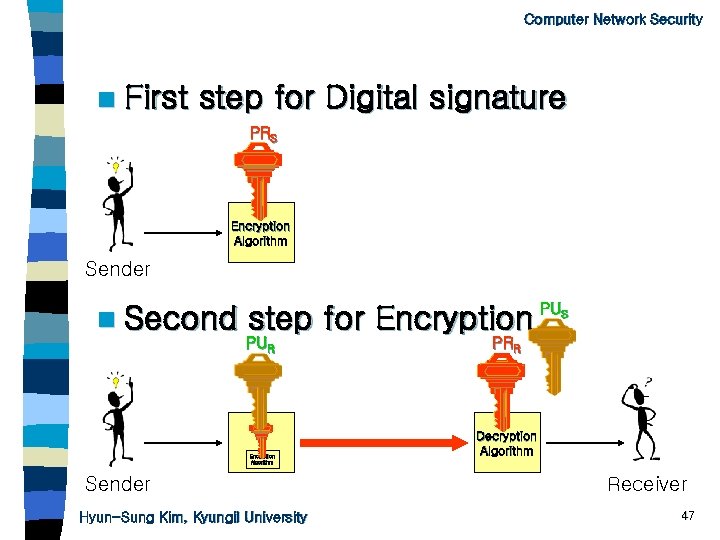 Computer Network Security n First step for Digital signature PRS Encryption Algorithm Sender n Second step for Encryption PUR Encryption Algorithm Sender Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University PUS PRR Decryption Algorithm Receiver 47
Computer Network Security n First step for Digital signature PRS Encryption Algorithm Sender n Second step for Encryption PUR Encryption Algorithm Sender Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University PUS PRR Decryption Algorithm Receiver 47
 Cryptography Non-repudiation
Cryptography Non-repudiation
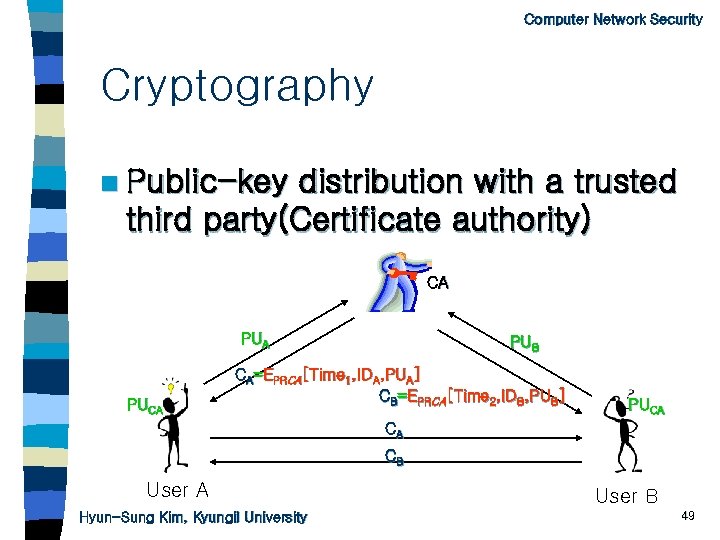 Computer Network Security Cryptography n Public-key distribution with a trusted third party(Certificate authority) CA PUCA PUB CA=EPRCA[Time 1, IDA, PUA] CB=EPRCA[Time 2, IDB, PUB] PUCA CA CB User A Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University User B 49
Computer Network Security Cryptography n Public-key distribution with a trusted third party(Certificate authority) CA PUCA PUB CA=EPRCA[Time 1, IDA, PUA] CB=EPRCA[Time 2, IDB, PUB] PUCA CA CB User A Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University User B 49
 Cryptography Key exchange
Cryptography Key exchange
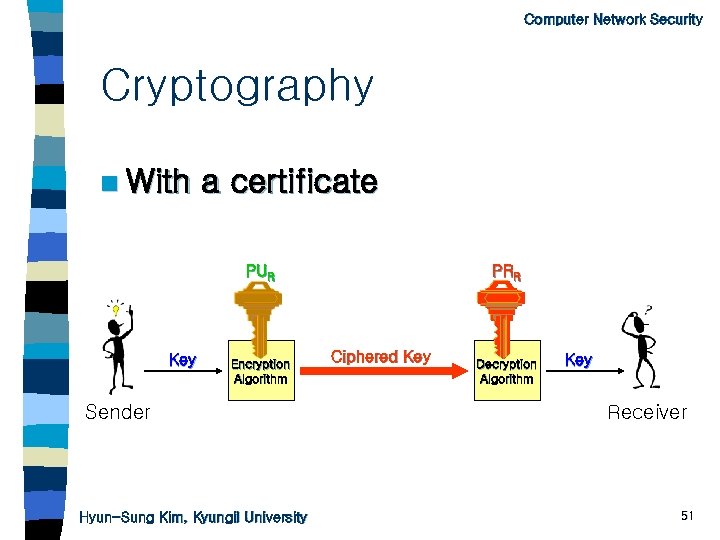 Computer Network Security Cryptography n With a certificate PUR Key Encryption Algorithm Sender Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University PRR Ciphered Key Decryption Algorithm Key Receiver 51
Computer Network Security Cryptography n With a certificate PUR Key Encryption Algorithm Sender Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University PRR Ciphered Key Decryption Algorithm Key Receiver 51
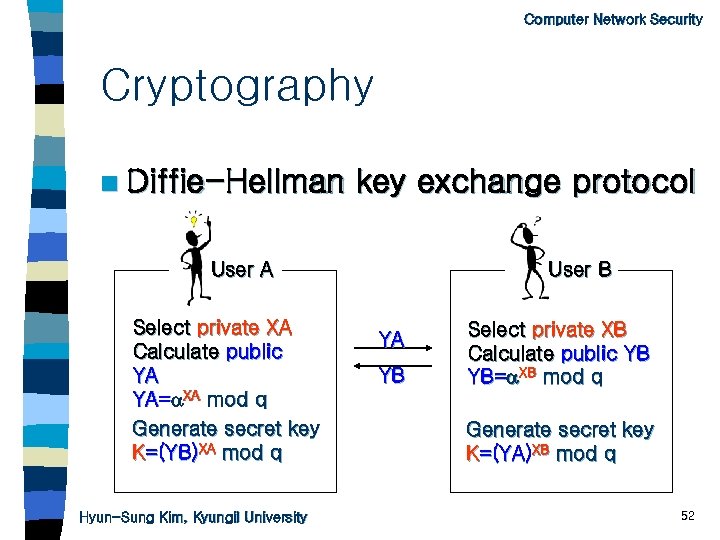 Computer Network Security Cryptography n Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol User A Select private XA Calculate public YA YA= XA mod q Generate secret key K=(YB)XA mod q Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University User B YA YB Select private XB Calculate public YB YB= XB mod q Generate secret key K=(YA)XB mod q 52
Computer Network Security Cryptography n Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol User A Select private XA Calculate public YA YA= XA mod q Generate secret key K=(YB)XA mod q Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University User B YA YB Select private XB Calculate public YB YB= XB mod q Generate secret key K=(YA)XB mod q 52
 Secure Internet Banking
Secure Internet Banking
 Computer Network Security Secure Internet Banking n User authentication n Issue a certificate n Key-exchange n Transaction n Additional security with a secret card Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 54
Computer Network Security Secure Internet Banking n User authentication n Issue a certificate n Key-exchange n Transaction n Additional security with a secret card Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 54
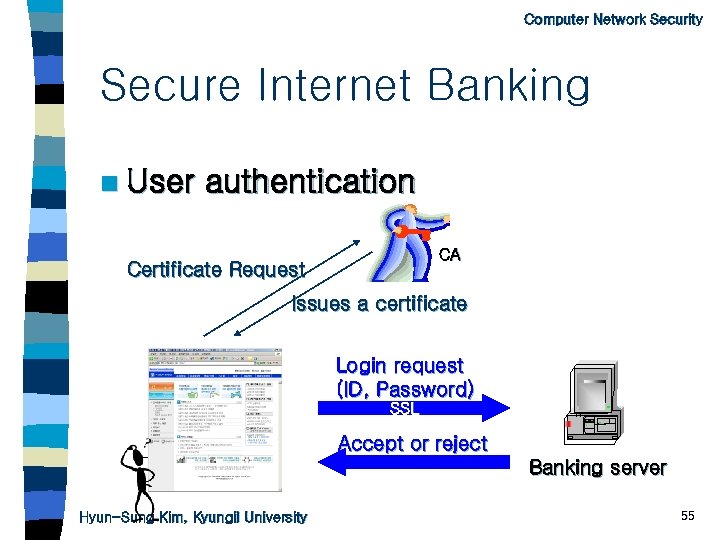 Computer Network Security Secure Internet Banking n User authentication CA Certificate Request Issues a certificate Login request (ID, Password) SSL Accept or reject Banking server Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 55
Computer Network Security Secure Internet Banking n User authentication CA Certificate Request Issues a certificate Login request (ID, Password) SSL Accept or reject Banking server Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 55
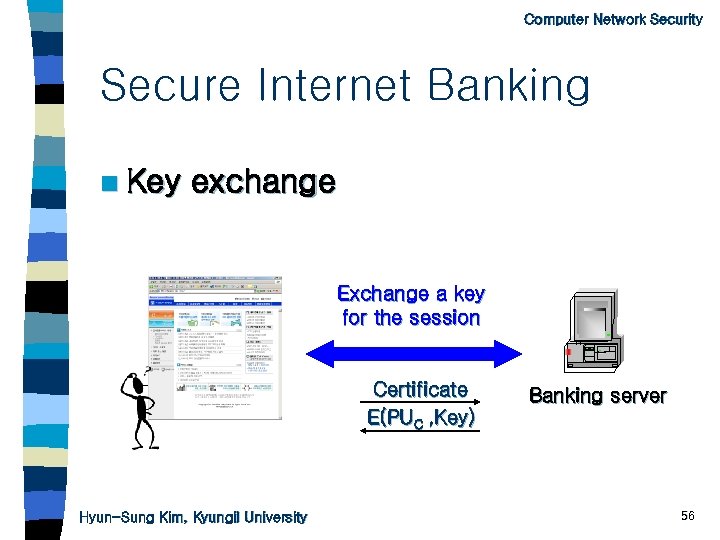 Computer Network Security Secure Internet Banking n Key exchange Exchange a key for the session Certificate E(PUC , Key) Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University Banking server 56
Computer Network Security Secure Internet Banking n Key exchange Exchange a key for the session Certificate E(PUC , Key) Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University Banking server 56
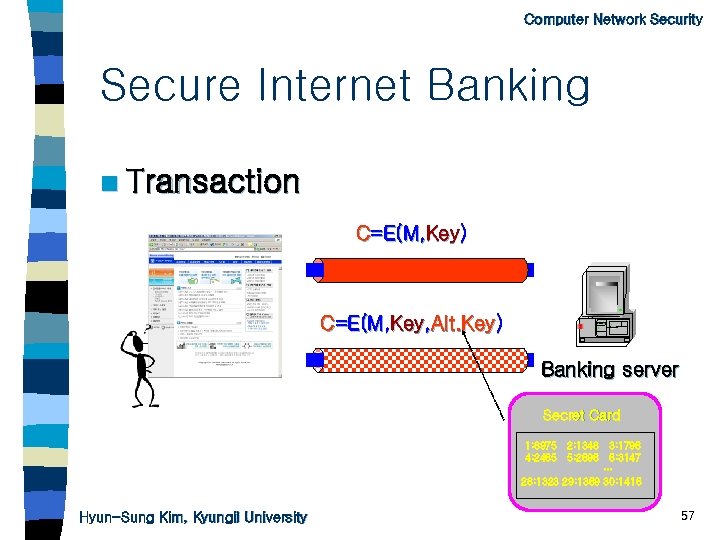 Computer Network Security Secure Internet Banking n Transaction C=E(M, Key) C=E(M, Key, Alt. Key) Banking server Secret Card 1: 8975 2: 1348 3: 1796 4: 2465 5: 2696 6: 3147 … 28: 1323 29: 1369 30: 1416 Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 57
Computer Network Security Secure Internet Banking n Transaction C=E(M, Key) C=E(M, Key, Alt. Key) Banking server Secret Card 1: 8975 2: 1348 3: 1796 4: 2465 5: 2696 6: 3147 … 28: 1323 29: 1369 30: 1416 Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University 57
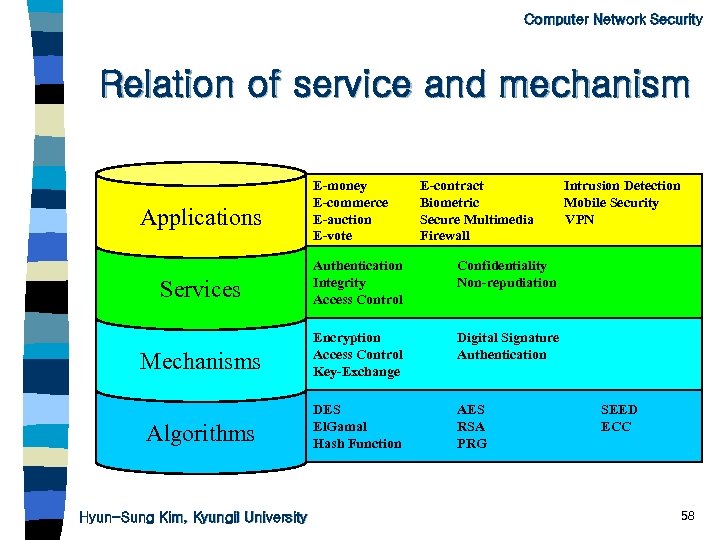 Computer Network Security Relation of service and mechanism Applications E-money E-commerce E-auction E-vote E-contract Biometric Secure Multimedia Firewall Services Authentication Integrity Access Control Confidentiality Non-repudiation Mechanisms Encryption Access Control Key-Exchange Digital Signature Authentication Algorithms DES El. Gamal Hash Function AES RSA PRG Intrusion Detection Mobile Security VPN Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University SEED ECC 58
Computer Network Security Relation of service and mechanism Applications E-money E-commerce E-auction E-vote E-contract Biometric Secure Multimedia Firewall Services Authentication Integrity Access Control Confidentiality Non-repudiation Mechanisms Encryption Access Control Key-Exchange Digital Signature Authentication Algorithms DES El. Gamal Hash Function AES RSA PRG Intrusion Detection Mobile Security VPN Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University SEED ECC 58
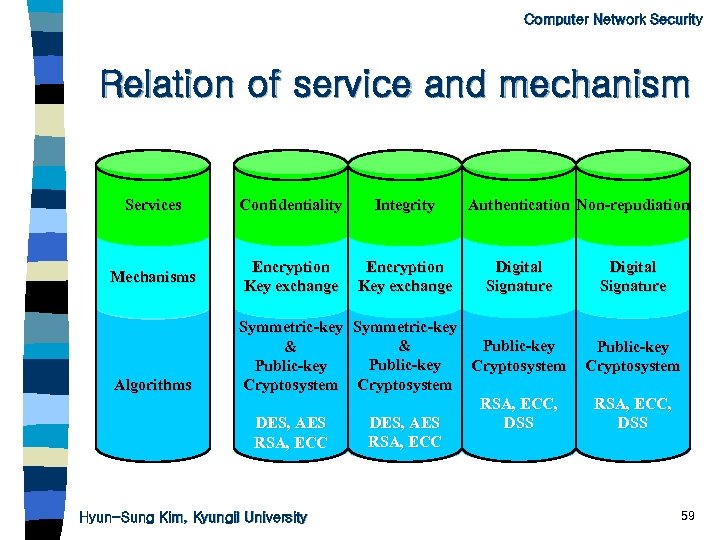 Computer Network Security Relation of service and mechanism Services Confidentiality Integrity Mechanisms Encryption Key exchange Algorithms Symmetric-key & Public-key Cryptosystem RSA, ECC, DES, AES DSS DES, AES RSA, ECC Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University Authentication Non-repudiation Digital Signature Public-key Cryptosystem RSA, ECC, DSS 59
Computer Network Security Relation of service and mechanism Services Confidentiality Integrity Mechanisms Encryption Key exchange Algorithms Symmetric-key & Public-key Cryptosystem RSA, ECC, DES, AES DSS DES, AES RSA, ECC Hyun-Sung Kim, Kyungil University Authentication Non-repudiation Digital Signature Public-key Cryptosystem RSA, ECC, DSS 59
 Thank you ! Hyun-Sung Kim kim@kiu. ac. kr
Thank you ! Hyun-Sung Kim kim@kiu. ac. kr


