7f2fe12add422653bce9a53222c04118.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Computer Interfacing Via the Parallel Port Carlos M. Oppus ECCE Program, Ad. MU . 16/03/2018 1
Computer Interfacing Via the Parallel Port Carlos M. Oppus ECCE Program, Ad. MU . 16/03/2018 1
 Objectives This lecture aims : 1) to give an overview of computer interfacing. 2) to give the basics of interfacing via the parallel port 16/03/2018 2
Objectives This lecture aims : 1) to give an overview of computer interfacing. 2) to give the basics of interfacing via the parallel port 16/03/2018 2
 Introduction Computer Interfacing means connecting different devices to the computer and being able to control or read the status of these devices. There are many ways to achieve computer interfacing. (1) Interfacing by making your own computer interface card. (2) Interfacing via the existing ports in your computers. 16/03/2018 3
Introduction Computer Interfacing means connecting different devices to the computer and being able to control or read the status of these devices. There are many ways to achieve computer interfacing. (1) Interfacing by making your own computer interface card. (2) Interfacing via the existing ports in your computers. 16/03/2018 3
 Introduction (cont …) namely (a) modem (b) internet (c) serial port (d) game port (e) parallel port (f) USB etc. 16/03/2018 4
Introduction (cont …) namely (a) modem (b) internet (c) serial port (d) game port (e) parallel port (f) USB etc. 16/03/2018 4
 Parallel Port 16/03/2018 Computers are equipped with at least one parallel printer port card. This parallel port can be used as a general input-output device used for manipulating interfaced hardware. The printer port is designated as LPT 1, LPT 2 & LPT 3 5
Parallel Port 16/03/2018 Computers are equipped with at least one parallel printer port card. This parallel port can be used as a general input-output device used for manipulating interfaced hardware. The printer port is designated as LPT 1, LPT 2 & LPT 3 5
 Printer Port Parallel (printer) port as a general-purpose set of digital input and output port for interfacing devices. 8 -bit digital input/output (I/O) register if an enhanced parallel port is being used otherwise it is just an output register 4 -bit input register (actually 5 inputs) 16/03/2018 6
Printer Port Parallel (printer) port as a general-purpose set of digital input and output port for interfacing devices. 8 -bit digital input/output (I/O) register if an enhanced parallel port is being used otherwise it is just an output register 4 -bit input register (actually 5 inputs) 16/03/2018 6
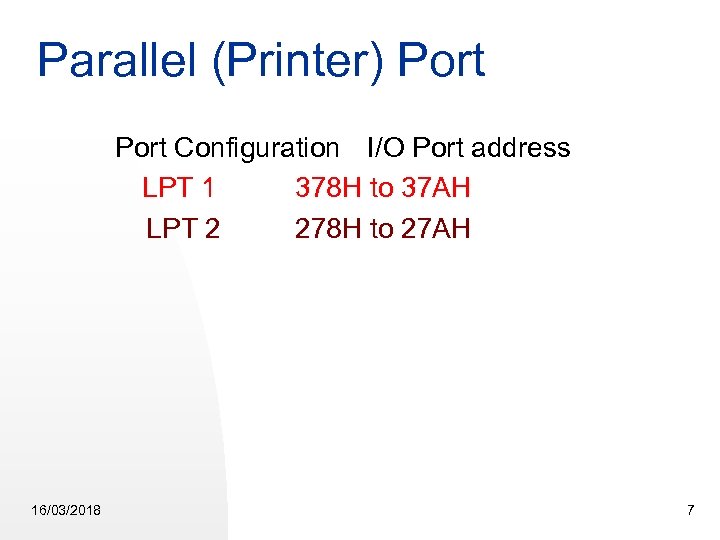 Parallel (Printer) Port Configuration I/O Port address LPT 1 378 H to 37 AH LPT 2 278 H to 27 AH 16/03/2018 7
Parallel (Printer) Port Configuration I/O Port address LPT 1 378 H to 37 AH LPT 2 278 H to 27 AH 16/03/2018 7
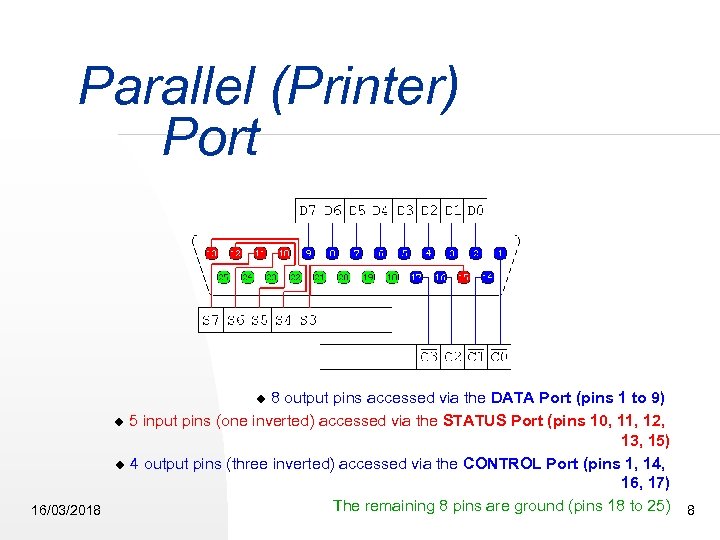 Parallel (Printer) Port 8 output pins accessed via the DATA Port (pins 1 to 9) 5 input pins (one inverted) accessed via the STATUS Port (pins 10, 11, 12, 13, 15) 4 output pins (three inverted) accessed via the CONTROL Port (pins 1, 14, 16, 17) The remaining 8 pins are ground (pins 18 to 25) 8 16/03/2018
Parallel (Printer) Port 8 output pins accessed via the DATA Port (pins 1 to 9) 5 input pins (one inverted) accessed via the STATUS Port (pins 10, 11, 12, 13, 15) 4 output pins (three inverted) accessed via the CONTROL Port (pins 1, 14, 16, 17) The remaining 8 pins are ground (pins 18 to 25) 8 16/03/2018
 Parallel (Printer) Port note: high TTL level = 2. 4 V to 5 V low TTL level = 0 V to 0. 8 V (normally 0 V) An OUT instruction to port address 378 H (278 H) and 37 A (27 A) can write the data directly to the connector pins. An IN instruction to port address 378 H (278 H) [if an enhanced parallel port is in use] and 379 H (279 H) can read the data directly from the connector pins. 16/03/2018 9
Parallel (Printer) Port note: high TTL level = 2. 4 V to 5 V low TTL level = 0 V to 0. 8 V (normally 0 V) An OUT instruction to port address 378 H (278 H) and 37 A (27 A) can write the data directly to the connector pins. An IN instruction to port address 378 H (278 H) [if an enhanced parallel port is in use] and 379 H (279 H) can read the data directly from the connector pins. 16/03/2018 9
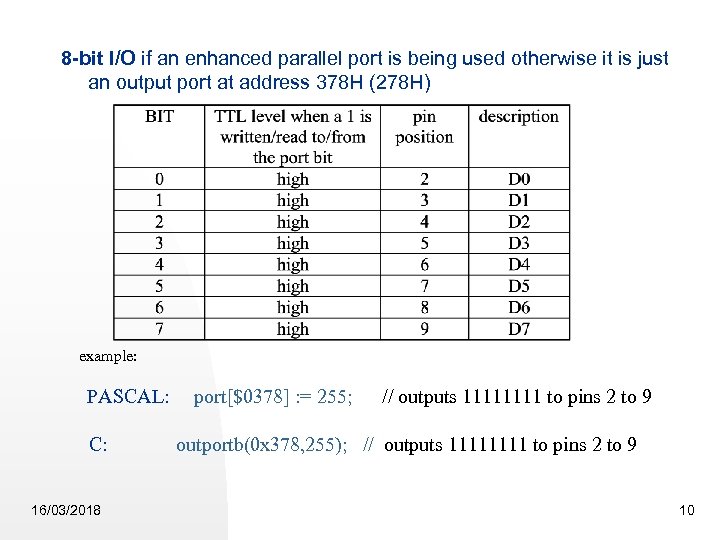 8 -bit I/O if an enhanced parallel port is being used otherwise it is just an output port at address 378 H (278 H) example: PASCAL: port[$0378] : = 255; // outputs 1111 to pins 2 to 9 C: 16/03/2018 outportb(0 x 378, 255); // outputs 1111 to pins 2 to 9 10
8 -bit I/O if an enhanced parallel port is being used otherwise it is just an output port at address 378 H (278 H) example: PASCAL: port[$0378] : = 255; // outputs 1111 to pins 2 to 9 C: 16/03/2018 outportb(0 x 378, 255); // outputs 1111 to pins 2 to 9 10
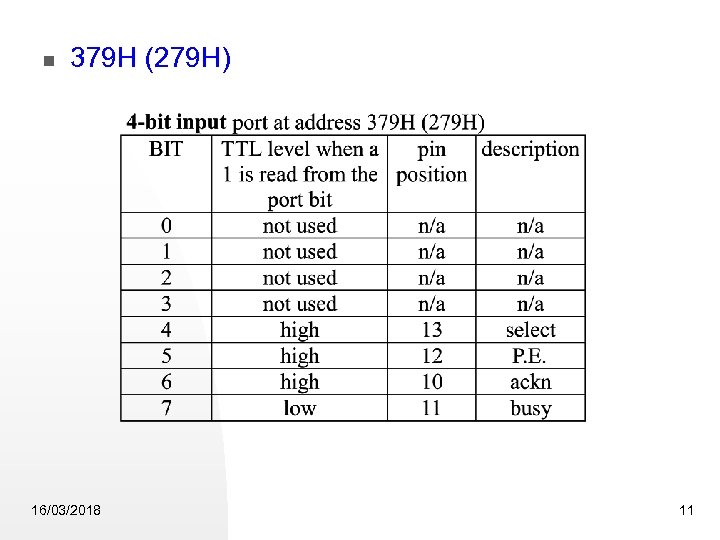 379 H (279 H) 16/03/2018 11
379 H (279 H) 16/03/2018 11
![Example PASCAL: data : = port[$037 A] ; reads port 37 AH i. e. Example PASCAL: data : = port[$037 A] ; reads port 37 AH i. e.](https://present5.com/presentation/7f2fe12add422653bce9a53222c04118/image-12.jpg) Example PASCAL: data : = port[$037 A] ; reads port 37 AH i. e. reads the TTL levels of pins 13, 12, 10 & 11 respectively and places the corresponding values at the higher nibble of variable “data”. C: data = inportb(0 x 37 A); reads port 37 AH i. e. reads the TTL levels of pins 13, 12, 10 & 11 respectively and places the corresponding values at the higher nibble of variable “data”. 16/03/2018 12
Example PASCAL: data : = port[$037 A] ; reads port 37 AH i. e. reads the TTL levels of pins 13, 12, 10 & 11 respectively and places the corresponding values at the higher nibble of variable “data”. C: data = inportb(0 x 37 A); reads port 37 AH i. e. reads the TTL levels of pins 13, 12, 10 & 11 respectively and places the corresponding values at the higher nibble of variable “data”. 16/03/2018 12
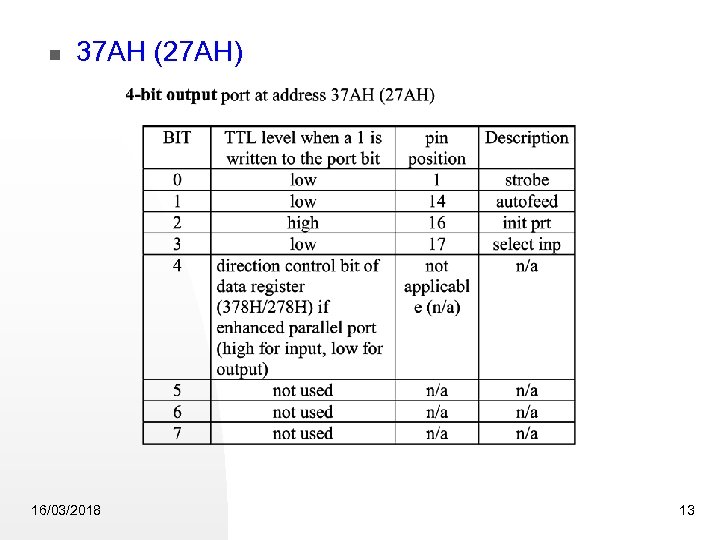 37 AH (27 AH) 16/03/2018 13
37 AH (27 AH) 16/03/2018 13
![Example PASCAL: Port[$037 A] : = 4; outputs 0100 to pins 17, 16, 14 Example PASCAL: Port[$037 A] : = 4; outputs 0100 to pins 17, 16, 14](https://present5.com/presentation/7f2fe12add422653bce9a53222c04118/image-14.jpg) Example PASCAL: Port[$037 A] : = 4; outputs 0100 to pins 17, 16, 14 & 1 respectively i. e. pin 17 is high, pin 16 is high, pin 14 is high and pin 1 is high. C: outportb(x 037 A, 4); outputs 0100 to pins 17, 16, 14 & 1 respectively i. e. pin 17 is high, pin 16 is high, pin 14 is high and pin 1 is high. 16/03/2018 14
Example PASCAL: Port[$037 A] : = 4; outputs 0100 to pins 17, 16, 14 & 1 respectively i. e. pin 17 is high, pin 16 is high, pin 14 is high and pin 1 is high. C: outportb(x 037 A, 4); outputs 0100 to pins 17, 16, 14 & 1 respectively i. e. pin 17 is high, pin 16 is high, pin 14 is high and pin 1 is high. 16/03/2018 14
 For 32 bit VB (WIN 95 IO. DLL), use: Declare Sub vb. Out Lib "WIN 95 IO. DLL" (By. Val n. Port As Integer, By. Val n. Data As Integer) Declare Sub vb. Outw Lib "WIN 95 IO. DLL" (By. Val n. Port As Integer, By. Val n. Data As Integer) Declare Function vb. Inp Lib "WIN 95 IO. DLL" (By. Val n. Port As Integer) As Integer Declare Function vb. Inpw Lib "WIN 95 IO. DLL" (By. Val n. Port As Integer) As Integer vb. Out [port], [number] example: 'set port to 00001011 378 H = 888 vb. Out 888, 11 [variable]=vb. Inp([port]) example: ‘input from 379 H = 889 Port. Num%=vb. Inp(889) 16/03/2018 15
For 32 bit VB (WIN 95 IO. DLL), use: Declare Sub vb. Out Lib "WIN 95 IO. DLL" (By. Val n. Port As Integer, By. Val n. Data As Integer) Declare Sub vb. Outw Lib "WIN 95 IO. DLL" (By. Val n. Port As Integer, By. Val n. Data As Integer) Declare Function vb. Inp Lib "WIN 95 IO. DLL" (By. Val n. Port As Integer) As Integer Declare Function vb. Inpw Lib "WIN 95 IO. DLL" (By. Val n. Port As Integer) As Integer vb. Out [port], [number] example: 'set port to 00001011 378 H = 888 vb. Out 888, 11 [variable]=vb. Inp([port]) example: ‘input from 379 H = 889 Port. Num%=vb. Inp(889) 16/03/2018 15
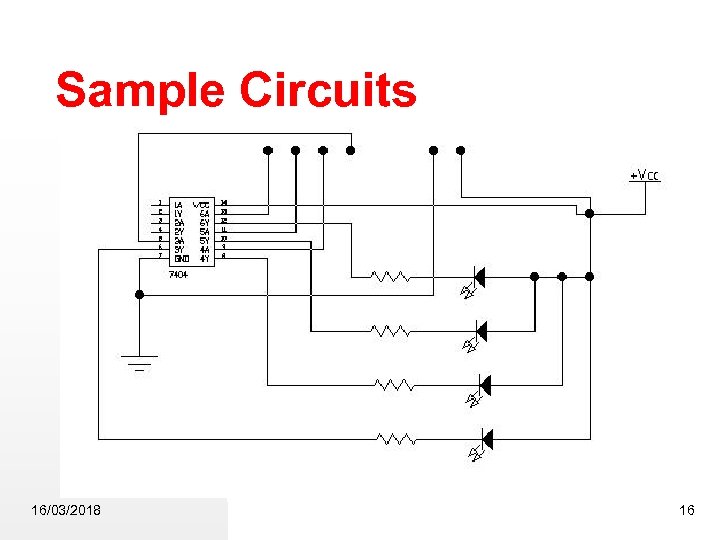 Sample Circuits 16/03/2018 16
Sample Circuits 16/03/2018 16
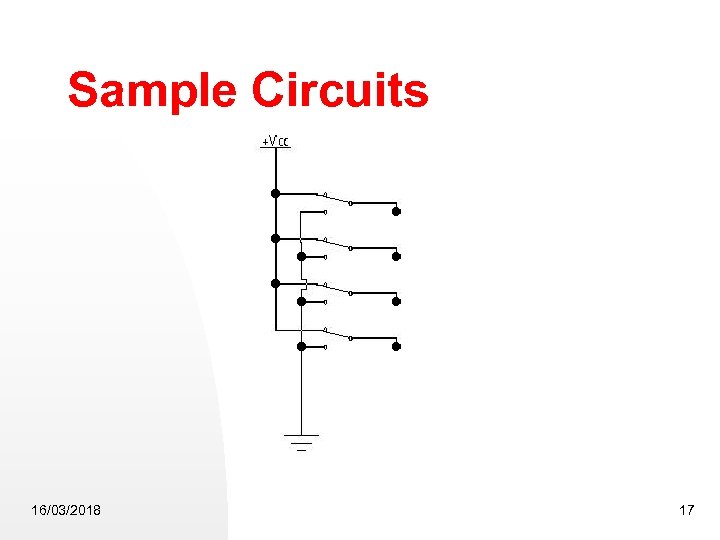 Sample Circuits 16/03/2018 17
Sample Circuits 16/03/2018 17
 Demonstration Appliance controller … 16/03/2018 18
Demonstration Appliance controller … 16/03/2018 18
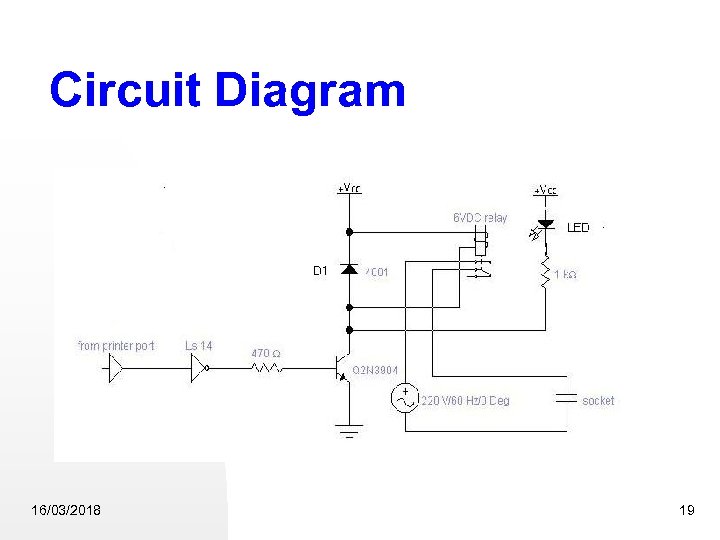 Circuit Diagram 16/03/2018 19
Circuit Diagram 16/03/2018 19
![Sample Program uses crt; var ch : char; begin clrscr; repeat port[$37 A] : Sample Program uses crt; var ch : char; begin clrscr; repeat port[$37 A] :](https://present5.com/presentation/7f2fe12add422653bce9a53222c04118/image-20.jpg) Sample Program uses crt; var ch : char; begin clrscr; repeat port[$37 A] : = $0 B; gotoxy(20, 20); write('off'); ch : = readkey; port[$37 A] : = $04; gotoxy(20, 20); write('on '); ch : = upcase(readkey); until ch = 'Q'; port[$37 A] : = $0 B; end 16/03/2018 20
Sample Program uses crt; var ch : char; begin clrscr; repeat port[$37 A] : = $0 B; gotoxy(20, 20); write('off'); ch : = readkey; port[$37 A] : = $04; gotoxy(20, 20); write('on '); ch : = upcase(readkey); until ch = 'Q'; port[$37 A] : = $0 B; end 16/03/2018 20


