c43952e38f14bfe5b22de2288932c15d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 72
 Computer Hardware How to Choose a Multimedia Computer Plymouth State University
Computer Hardware How to Choose a Multimedia Computer Plymouth State University
 ENIAC - The First Electronic Digital Computer Plymouth State University
ENIAC - The First Electronic Digital Computer Plymouth State University
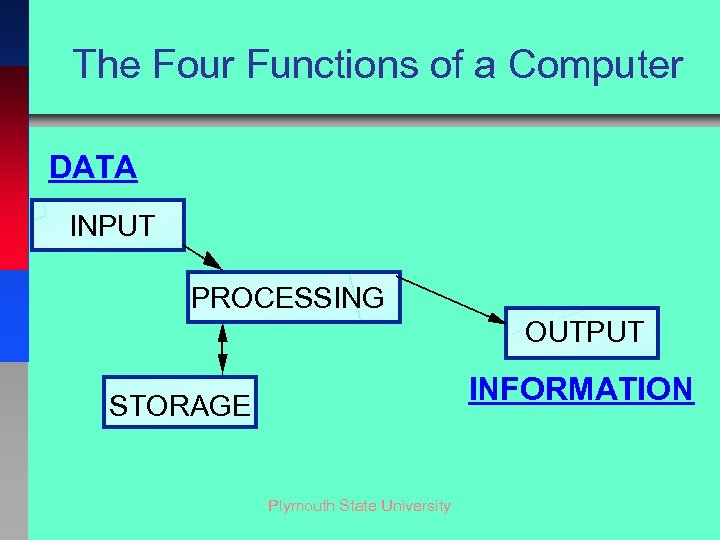 The Four Functions of a Computer DATA INPUT PROCESSING OUTPUT INFORMATION STORAGE Plymouth State University
The Four Functions of a Computer DATA INPUT PROCESSING OUTPUT INFORMATION STORAGE Plymouth State University
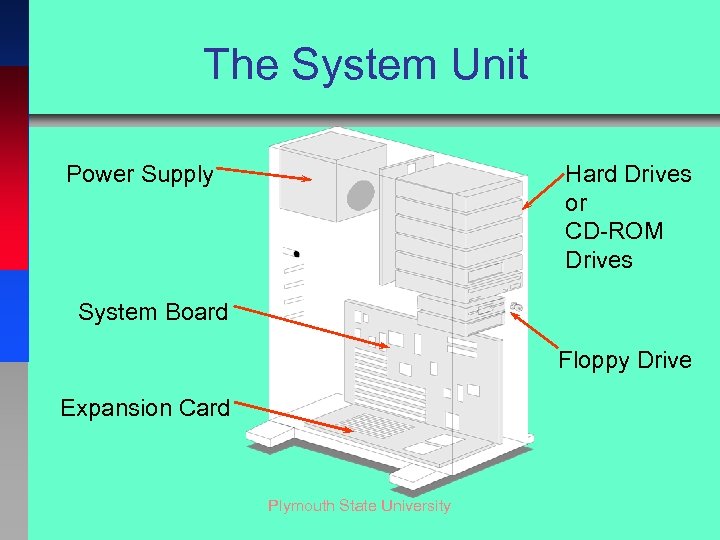 The System Unit Hard Drives or CD-ROM Drives Power Supply System Board Floppy Drive Expansion Card Plymouth State University
The System Unit Hard Drives or CD-ROM Drives Power Supply System Board Floppy Drive Expansion Card Plymouth State University
 Directions of Computer Development • Miniaturization – Transistors – Integrated circuits • Solid state • Semiconductor • Chip Plymouth State University
Directions of Computer Development • Miniaturization – Transistors – Integrated circuits • Solid state • Semiconductor • Chip Plymouth State University
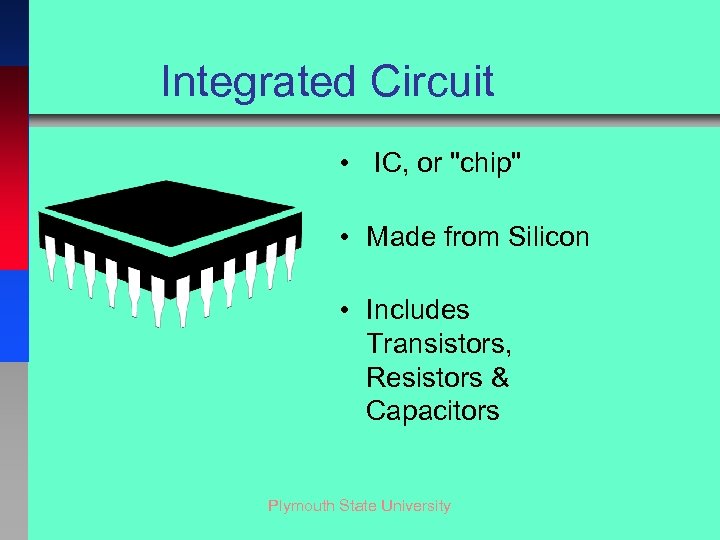 Integrated Circuit • IC, or "chip" • Made from Silicon • Includes Transistors, Resistors & Capacitors Plymouth State University
Integrated Circuit • IC, or "chip" • Made from Silicon • Includes Transistors, Resistors & Capacitors Plymouth State University
 Steps in Manufacture of a Microchip 1 Make large drawing. Reduce drawing hundreds of times to microscopic size. 2 Duplicate reduced photo many times on sheet. Plymouth State University
Steps in Manufacture of a Microchip 1 Make large drawing. Reduce drawing hundreds of times to microscopic size. 2 Duplicate reduced photo many times on sheet. Plymouth State University
 Etched Silicon Wafer Plymouth State University
Etched Silicon Wafer Plymouth State University
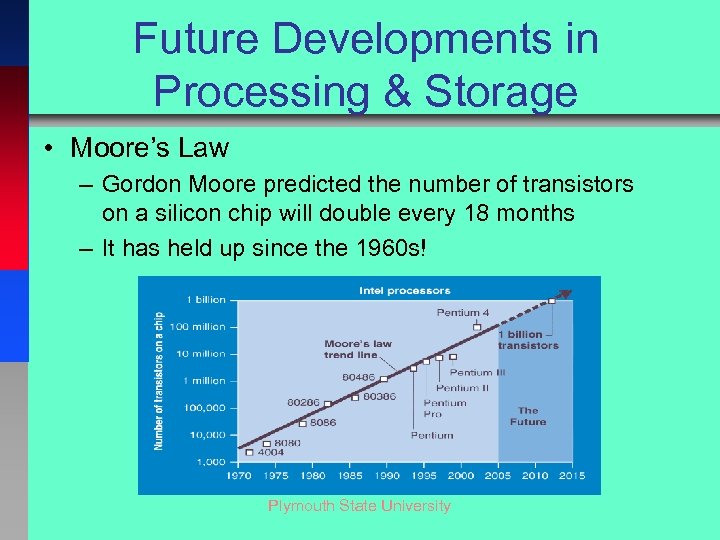 Future Developments in Processing & Storage • Moore’s Law – Gordon Moore predicted the number of transistors on a silicon chip will double every 18 months – It has held up since the 1960 s! Plymouth State University
Future Developments in Processing & Storage • Moore’s Law – Gordon Moore predicted the number of transistors on a silicon chip will double every 18 months – It has held up since the 1960 s! Plymouth State University
 The System Unit: The Basics • The CPU – Older CPUs processing speeds are in Mega. Hertz • 1 MHz = 1 Million ticks per second – Current CPUs processing speeds are in Giga. Hertz • 1 GHz = 1 Billion ticks per second – The faster a CPU runs, the more power it consumes, and the more heat it generates Plymouth State University
The System Unit: The Basics • The CPU – Older CPUs processing speeds are in Mega. Hertz • 1 MHz = 1 Million ticks per second – Current CPUs processing speeds are in Giga. Hertz • 1 GHz = 1 Billion ticks per second – The faster a CPU runs, the more power it consumes, and the more heat it generates Plymouth State University
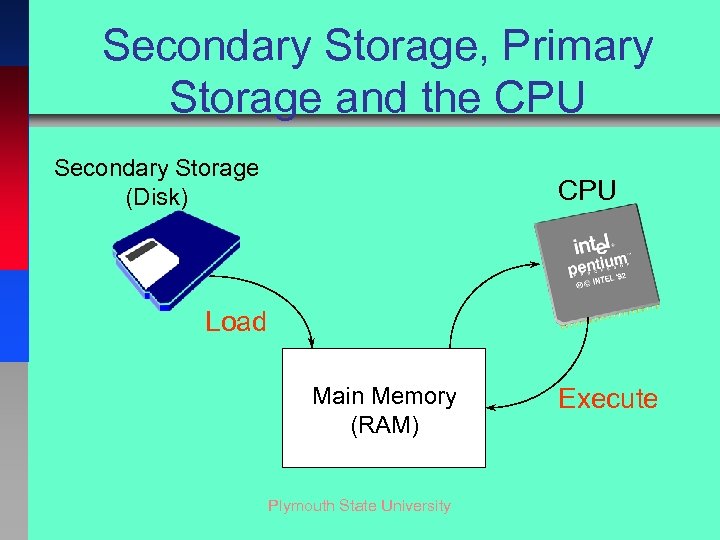 Secondary Storage, Primary Storage and the CPU Secondary Storage (Disk) CPU Load Main Memory (RAM) Plymouth State University Execute
Secondary Storage, Primary Storage and the CPU Secondary Storage (Disk) CPU Load Main Memory (RAM) Plymouth State University Execute
 How Memory Works: RAM, ROM, & Flash • Types of memory chips: 1. RAM - Random Access Memory, used to temporarily hold software instructions and data 2. ROM 3. Flash Plymouth State University
How Memory Works: RAM, ROM, & Flash • Types of memory chips: 1. RAM - Random Access Memory, used to temporarily hold software instructions and data 2. ROM 3. Flash Plymouth State University
 How Memory Works: RAM, ROM, & Flash • Types of memory chips: 1. RAM 2. ROM - Read-Only Memory, which cannot be written on or erased by the computer user. Contains fixed start-up instructions 3. Flash Plymouth State University
How Memory Works: RAM, ROM, & Flash • Types of memory chips: 1. RAM 2. ROM - Read-Only Memory, which cannot be written on or erased by the computer user. Contains fixed start-up instructions 3. Flash Plymouth State University
 How Memory Works: RAM, ROM, CMOS, & Flash • Types of memory chips: 1. RAM 2. ROM 3. Flash - can be erased and reprogrammed more than once Plymouth State University
How Memory Works: RAM, ROM, CMOS, & Flash • Types of memory chips: 1. RAM 2. ROM 3. Flash - can be erased and reprogrammed more than once Plymouth State University
 Bits & Bytes • • • Kilobyte Megabyte Gigabyte Terabyte Petabyte Plymouth State University
Bits & Bytes • • • Kilobyte Megabyte Gigabyte Terabyte Petabyte Plymouth State University
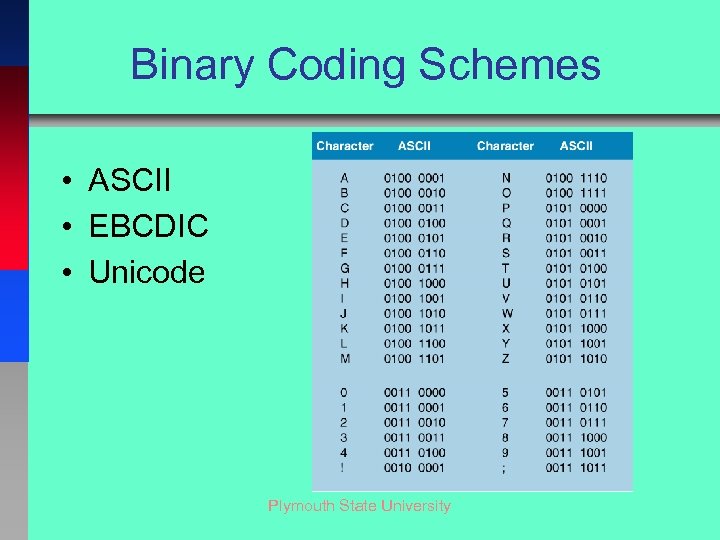 Binary Coding Schemes • ASCII • EBCDIC • Unicode Plymouth State University
Binary Coding Schemes • ASCII • EBCDIC • Unicode Plymouth State University
 Microchips • • • Microprocessors Memory Logic Communications Graphics Plymouth State University
Microchips • • • Microprocessors Memory Logic Communications Graphics Plymouth State University
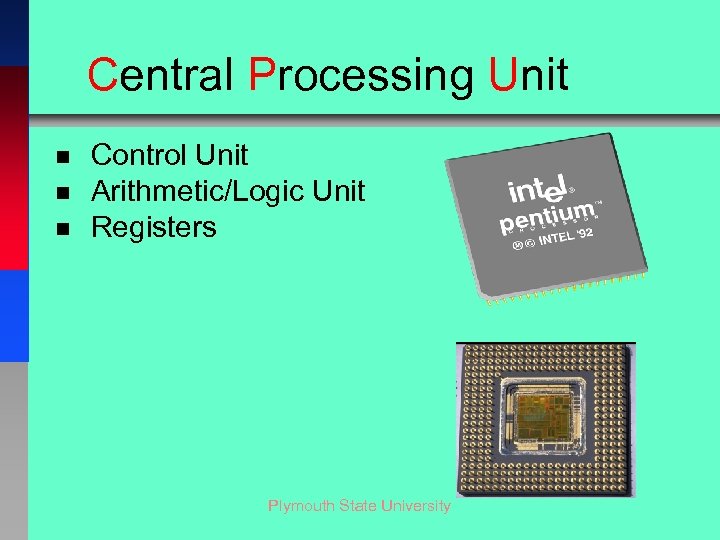 Central Processing Unit n n n Control Unit Arithmetic/Logic Unit Registers Plymouth State University
Central Processing Unit n n n Control Unit Arithmetic/Logic Unit Registers Plymouth State University
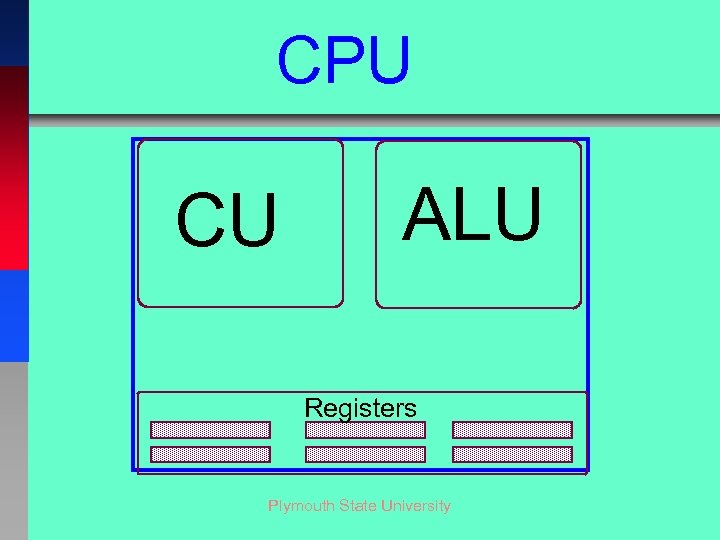 CPU CU ALU Registers Plymouth State University
CPU CU ALU Registers Plymouth State University
 Control Unit n. Controls step-by-step operation of computer Plymouth State University
Control Unit n. Controls step-by-step operation of computer Plymouth State University
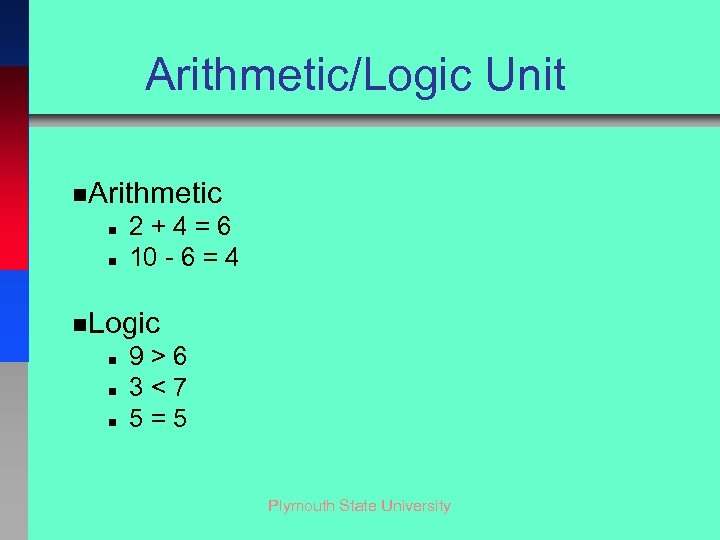 Arithmetic/Logic Unit n. Arithmetic n n 2+4=6 10 - 6 = 4 n. Logic n n n 9>6 3<7 5=5 Plymouth State University
Arithmetic/Logic Unit n. Arithmetic n n 2+4=6 10 - 6 = 4 n. Logic n n n 9>6 3<7 5=5 Plymouth State University
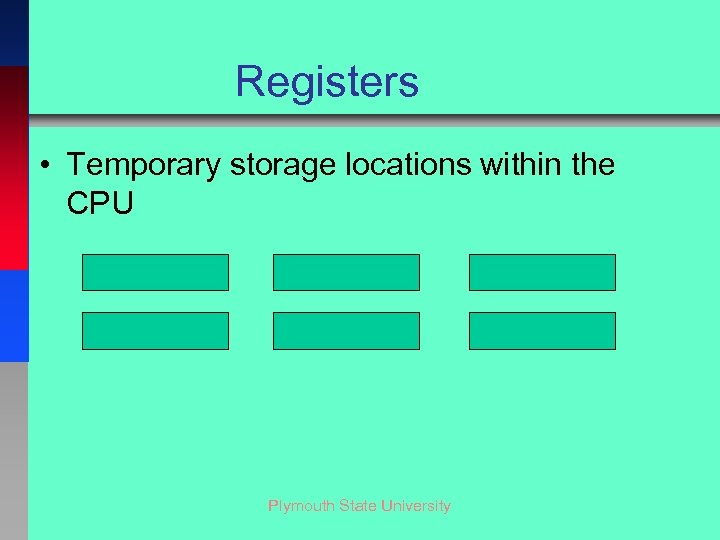 Registers • Temporary storage locations within the CPU Plymouth State University
Registers • Temporary storage locations within the CPU Plymouth State University
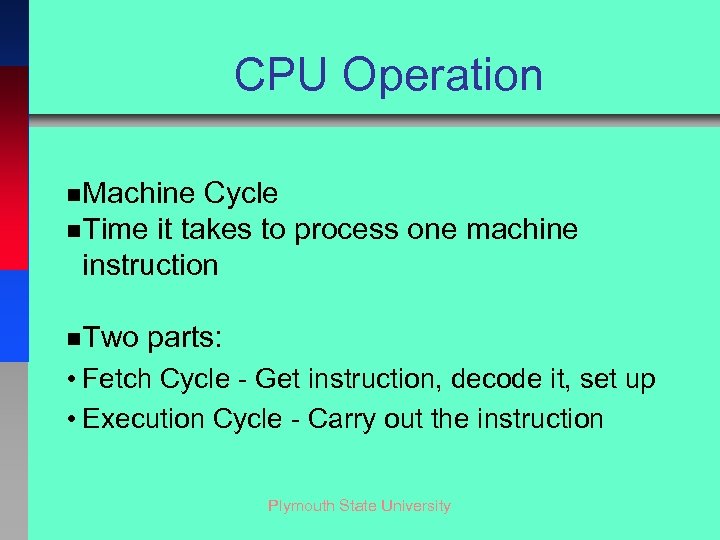 CPU Operation n. Machine Cycle n. Time it takes to process one machine instruction n. Two parts: • Fetch Cycle - Get instruction, decode it, set up • Execution Cycle - Carry out the instruction Plymouth State University
CPU Operation n. Machine Cycle n. Time it takes to process one machine instruction n. Two parts: • Fetch Cycle - Get instruction, decode it, set up • Execution Cycle - Carry out the instruction Plymouth State University
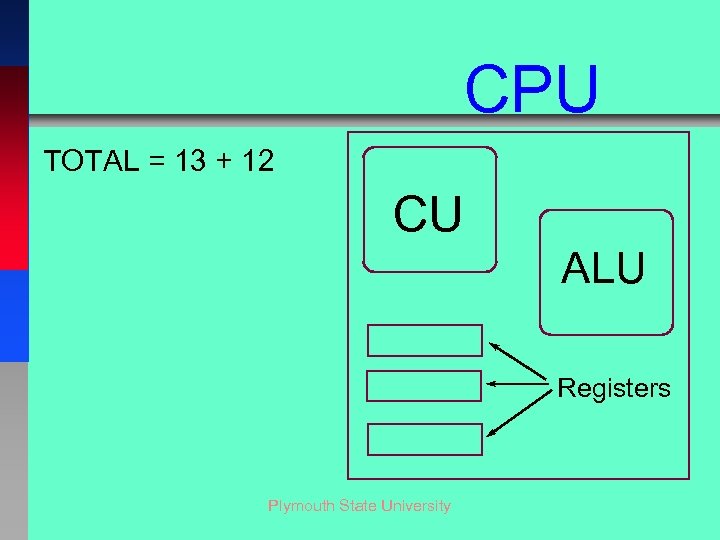 CPU TOTAL = 13 + 12 CU ALU Registers Plymouth State University
CPU TOTAL = 13 + 12 CU ALU Registers Plymouth State University
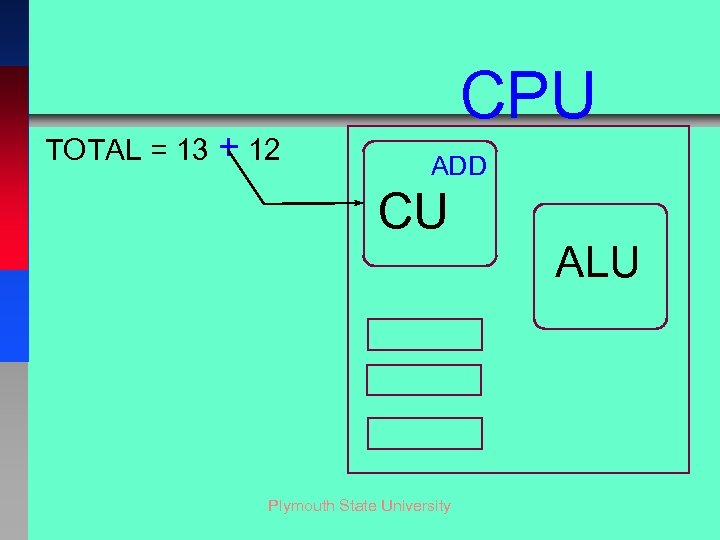 TOTAL = 13 + 12 CPU ADD CU Plymouth State University ALU
TOTAL = 13 + 12 CPU ADD CU Plymouth State University ALU
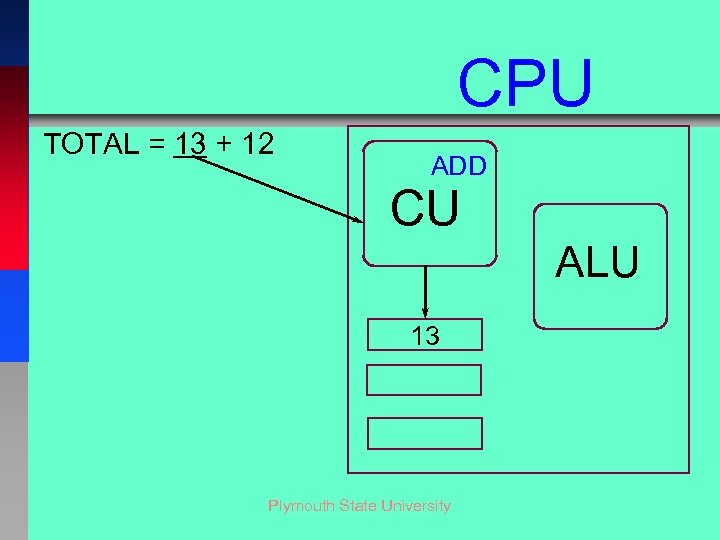 CPU TOTAL = 13 + 12 ADD CU ALU 13 Plymouth State University
CPU TOTAL = 13 + 12 ADD CU ALU 13 Plymouth State University
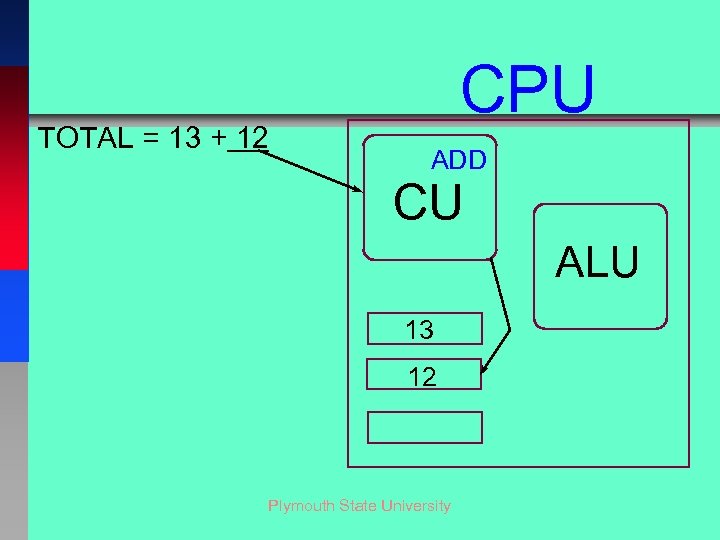 TOTAL = 13 + 12 CPU ADD CU ALU 13 12 Plymouth State University
TOTAL = 13 + 12 CPU ADD CU ALU 13 12 Plymouth State University
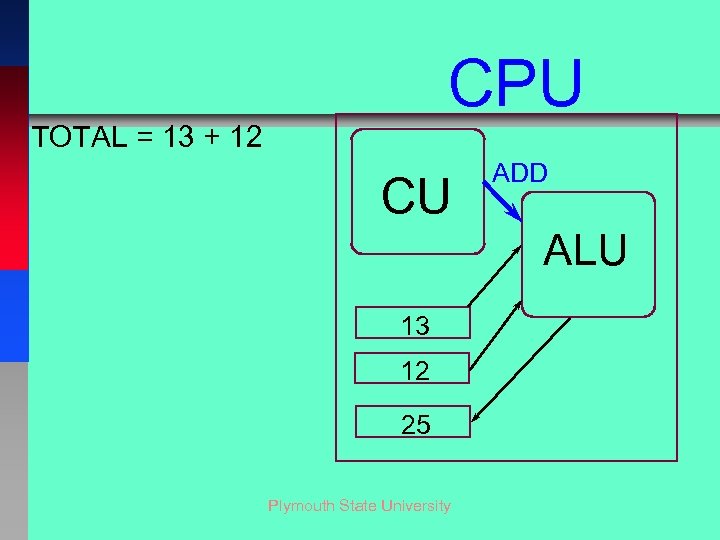 CPU TOTAL = 13 + 12 CU ADD ALU 13 12 25 Plymouth State University
CPU TOTAL = 13 + 12 CU ADD ALU 13 12 25 Plymouth State University
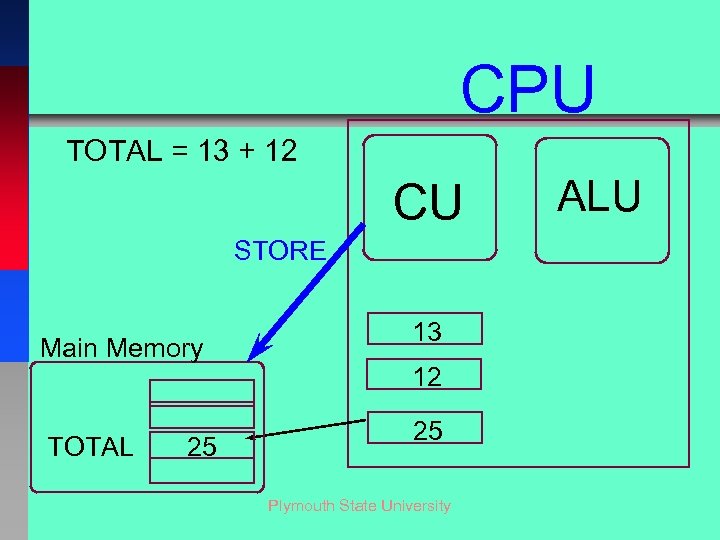 CPU TOTAL = 13 + 12 CU STORE Main Memory TOTAL 25 13 12 25 Plymouth State University ALU
CPU TOTAL = 13 + 12 CU STORE Main Memory TOTAL 25 13 12 25 Plymouth State University ALU
 Two Types of Storage • PRIMARY Storage - Main memory or RAM • SECONDARY Storage - Auxiliary Storage (disks, Flash etc. ) Plymouth State University
Two Types of Storage • PRIMARY Storage - Main memory or RAM • SECONDARY Storage - Auxiliary Storage (disks, Flash etc. ) Plymouth State University
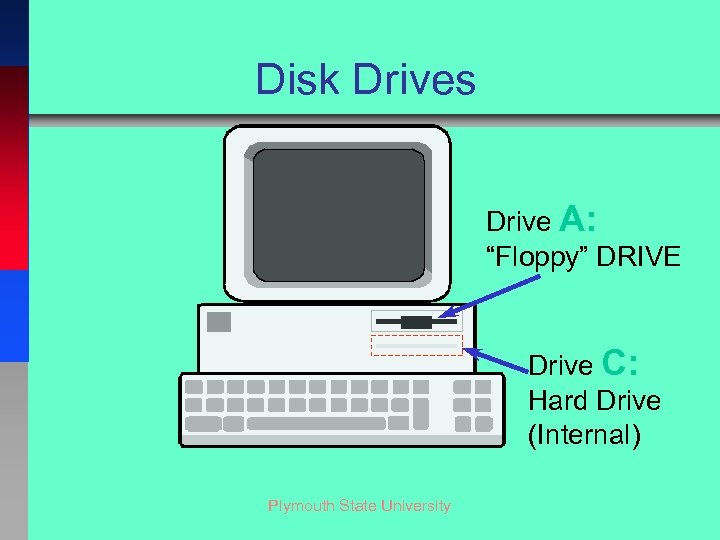 Disk Drives Drive A: “Floppy” DRIVE Drive C: Hard Drive (Internal) Plymouth State University
Disk Drives Drive A: “Floppy” DRIVE Drive C: Hard Drive (Internal) Plymouth State University
 Secondary Storage Devices Hard Disks • Nonremovable disks – Known as a fixed disk – Capacity up to 1 terabyte + – Consists of 4 - 3. 5 inch metallic platters Plymouth State University
Secondary Storage Devices Hard Disks • Nonremovable disks – Known as a fixed disk – Capacity up to 1 terabyte + – Consists of 4 - 3. 5 inch metallic platters Plymouth State University
 Hard Disk Drive Plymouth State University
Hard Disk Drive Plymouth State University
 Magnetic Disk Uses Direct Access 1 5 6 3 2 4 7 Plymouth State University
Magnetic Disk Uses Direct Access 1 5 6 3 2 4 7 Plymouth State University
 Magnetic Disk Storage Rotational Delay Seek Time Plymouth State University
Magnetic Disk Storage Rotational Delay Seek Time Plymouth State University
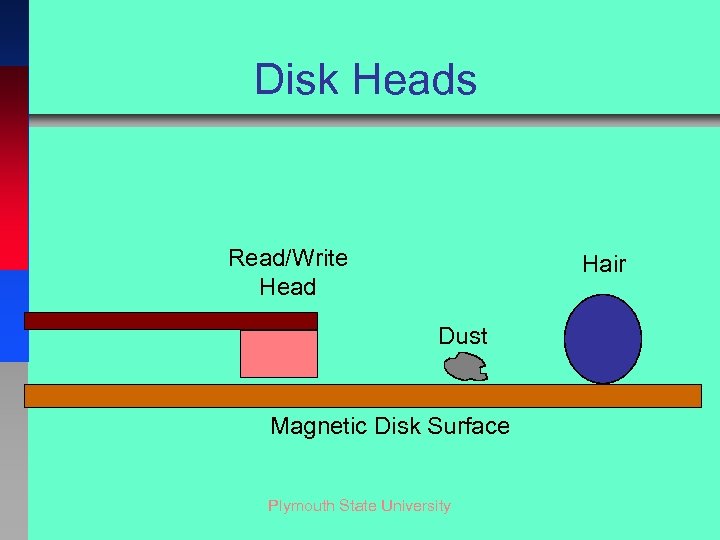 Disk Heads Read/Write Head Hair Dust Magnetic Disk Surface Plymouth State University
Disk Heads Read/Write Head Hair Dust Magnetic Disk Surface Plymouth State University
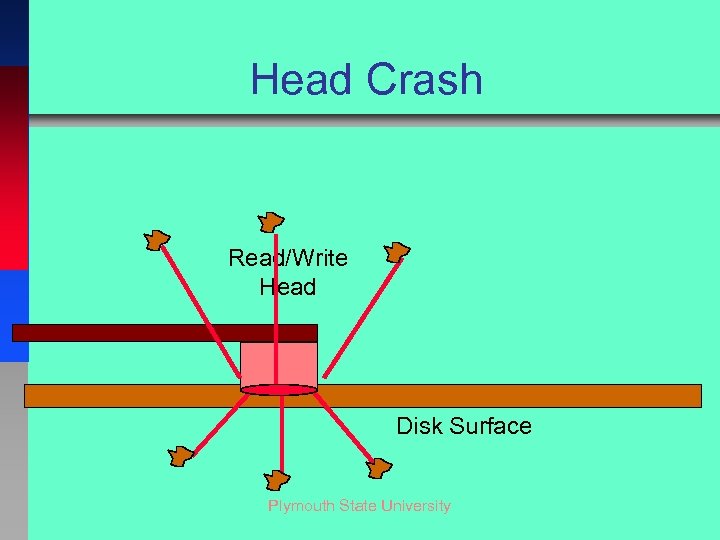 Head Crash Read/Write Head Disk Surface Plymouth State University
Head Crash Read/Write Head Disk Surface Plymouth State University
 Compact Disk (CD) Plymouth State University
Compact Disk (CD) Plymouth State University
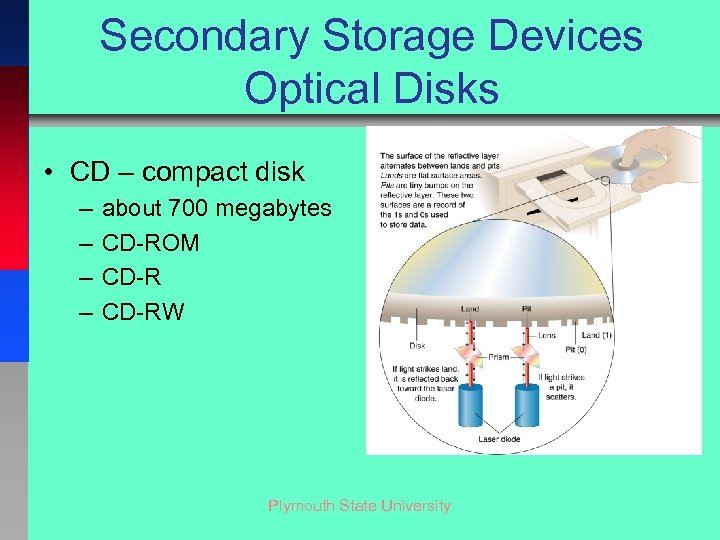 Secondary Storage Devices Optical Disks • CD – compact disk – – about 700 megabytes CD-ROM CD-RW Plymouth State University
Secondary Storage Devices Optical Disks • CD – compact disk – – about 700 megabytes CD-ROM CD-RW Plymouth State University
 Secondary Storage Devices Optical Disks • DVD – digital video disk – 4. 7 – 17 gigabytes – DVD-ROM – read-only – DVD-R – rewritable one time – Reusable types • DVD-RW • DVD-RAM Plymouth State University
Secondary Storage Devices Optical Disks • DVD – digital video disk – 4. 7 – 17 gigabytes – DVD-ROM – read-only – DVD-R – rewritable one time – Reusable types • DVD-RW • DVD-RAM Plymouth State University
 Flash Memory Flash memory is nonvolatile Plymouth State University
Flash Memory Flash memory is nonvolatile Plymouth State University
 Input and Output n INPUT - We provide the DATA to be processed n OUTPUT - We use the INFORMATION produced Plymouth State University
Input and Output n INPUT - We provide the DATA to be processed n OUTPUT - We use the INFORMATION produced Plymouth State University
 Input & Output Hardware Ø Input hardware ØTranslates words, numbers, sounds, and pictures into numbers Ø Output hardware ØTranslates numbers back into words, numbers, sounds, and pictures Plymouth State University
Input & Output Hardware Ø Input hardware ØTranslates words, numbers, sounds, and pictures into numbers Ø Output hardware ØTranslates numbers back into words, numbers, sounds, and pictures Plymouth State University
 Some Input Devices • Keyboards • Pointing devices • • Mouse Trackball • Touch screen • Pen input • Source data-entry devices • • • Scanner Text (OCR) Voice Video MICR FAX Plymouth State University
Some Input Devices • Keyboards • Pointing devices • • Mouse Trackball • Touch screen • Pen input • Source data-entry devices • • • Scanner Text (OCR) Voice Video MICR FAX Plymouth State University
 Input Hardware • Keyboards: convert letters, numbers, and characters into electrical signals – English keyboards differ from foreign language keyboards German Keyboard Plymouth State University
Input Hardware • Keyboards: convert letters, numbers, and characters into electrical signals – English keyboards differ from foreign language keyboards German Keyboard Plymouth State University
 Input Hardware Webcams and Video-input Cards • Webcams – Video cameras attached to a computer to record live moving images then post them to a website in real time – Require special software, usually included with the camera Plymouth State University
Input Hardware Webcams and Video-input Cards • Webcams – Video cameras attached to a computer to record live moving images then post them to a website in real time – Require special software, usually included with the camera Plymouth State University
 Input Hardware Camera Phones • Digital cameras are now on cell phones – Convenience of being able to take photos, then instantly email or message them to someone else Plymouth State University
Input Hardware Camera Phones • Digital cameras are now on cell phones – Convenience of being able to take photos, then instantly email or message them to someone else Plymouth State University
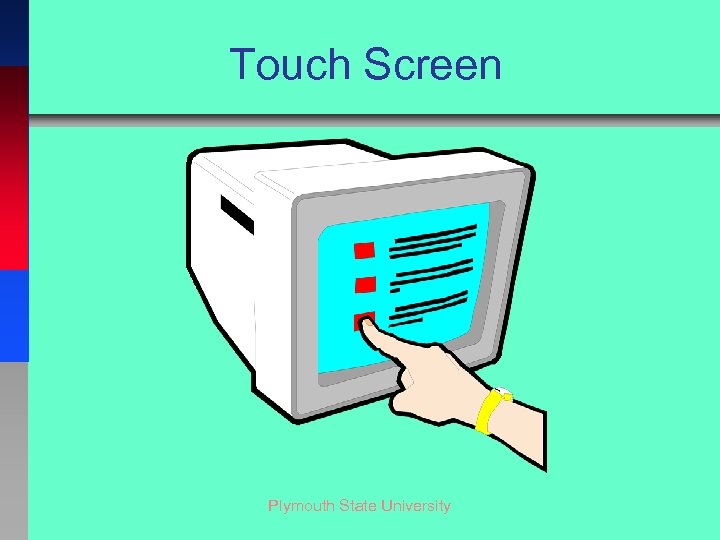 Touch Screen Plymouth State University
Touch Screen Plymouth State University
 Input Hardware Source Data-Entry Devices • Scanning devices – imaging systems • Scanning devices – bar code readers – Magnetic-ink character recognition (MICR) – Optical-mark recognition (OMR) – Optical character recognition (OCR) • Scanning devices – fax machines Plymouth State University
Input Hardware Source Data-Entry Devices • Scanning devices – imaging systems • Scanning devices – bar code readers – Magnetic-ink character recognition (MICR) – Optical-mark recognition (OMR) – Optical character recognition (OCR) • Scanning devices – fax machines Plymouth State University
 Check Processing 9999999 12345687 Plymouth State University
Check Processing 9999999 12345687 Plymouth State University
 Source Data-Entry Device Plymouth State University
Source Data-Entry Device Plymouth State University
 Bar Code Plymouth State University
Bar Code Plymouth State University
 Smart Cards Similar to credit cards Contain a microprocessor Plymouth State University
Smart Cards Similar to credit cards Contain a microprocessor Plymouth State University
 Digital Camera Plymouth State University
Digital Camera Plymouth State University
 GPS Plymouth State University
GPS Plymouth State University
 Biometrics • Fingerprints • Retina Scanning • Face Recognition Plymouth State University
Biometrics • Fingerprints • Retina Scanning • Face Recognition Plymouth State University
 Output Hardware • Softcopy – Data that is shown on a display screen or is in audio or voice form; exists electronically – Output that is ephemeral in nature • Hardcopy – Printed and film output – Output that is more permanent in nature Plymouth State University
Output Hardware • Softcopy – Data that is shown on a display screen or is in audio or voice form; exists electronically – Output that is ephemeral in nature • Hardcopy – Printed and film output – Output that is more permanent in nature Plymouth State University
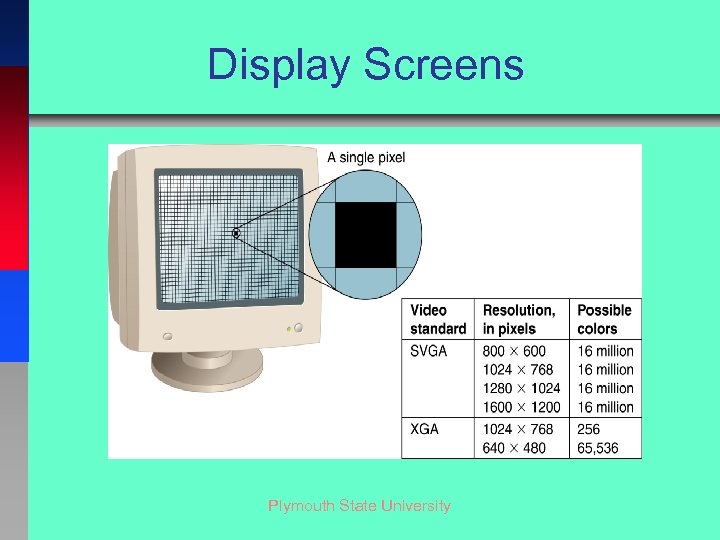 Display Screens Plymouth State University
Display Screens Plymouth State University
 Resolution. . . . Resolution = TOTAL PIXELS = # dots across by # dots down Example: 1024 X 768 Plymouth State University
Resolution. . . . Resolution = TOTAL PIXELS = # dots across by # dots down Example: 1024 X 768 Plymouth State University
 Types of Terminals • Dumb Terminals • Intelligent Terminals Plymouth State University
Types of Terminals • Dumb Terminals • Intelligent Terminals Plymouth State University
 Specialized Terminals n ATM’s n POS’s Plymouth State University
Specialized Terminals n ATM’s n POS’s Plymouth State University
 MIDI Music Plymouth State University
MIDI Music Plymouth State University
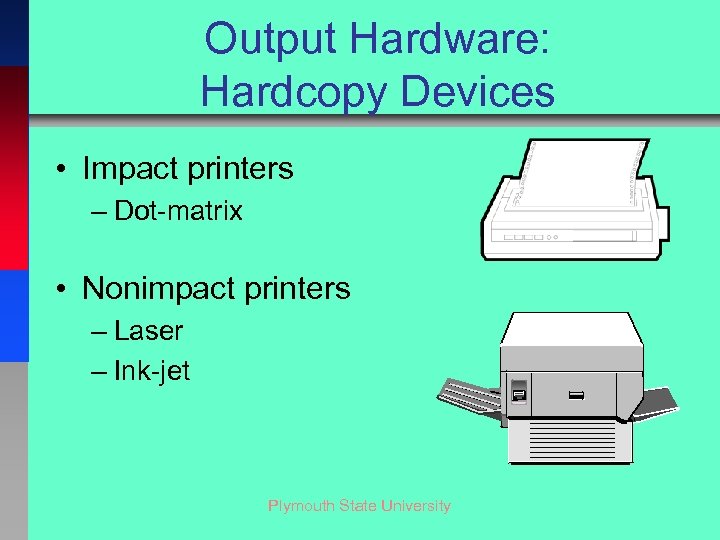 Output Hardware: Hardcopy Devices • Impact printers – Dot-matrix • Nonimpact printers – Laser – Ink-jet Plymouth State University
Output Hardware: Hardcopy Devices • Impact printers – Dot-matrix • Nonimpact printers – Laser – Ink-jet Plymouth State University
 Other Types of Output • • • Projectors COM Machine Control Voice House Control Center Plymouth State University
Other Types of Output • • • Projectors COM Machine Control Voice House Control Center Plymouth State University
 Machine Control Plymouth State University
Machine Control Plymouth State University
 Health Matters • Repetitive stress injuries – Carpal tunnel syndrome • • Eyestrain & headaches Back & neck pains Electromagnetic fields Noise Plymouth State University
Health Matters • Repetitive stress injuries – Carpal tunnel syndrome • • Eyestrain & headaches Back & neck pains Electromagnetic fields Noise Plymouth State University
 Ergonomics • Fitting the job environment to the worker • Purpose – make working conditions and equipment safer and more efficient Plymouth State University
Ergonomics • Fitting the job environment to the worker • Purpose – make working conditions and equipment safer and more efficient Plymouth State University
 Ergonomic Considerations • • • Chair Keyboard Height Wrist Rest Monitor Height Lighting Noise Plymouth State University
Ergonomic Considerations • • • Chair Keyboard Height Wrist Rest Monitor Height Lighting Noise Plymouth State University
 Ergonomic Keyboard Plymouth State University
Ergonomic Keyboard Plymouth State University
 Ergonomics • Eye strain • Radiation • Glare Plymouth State University
Ergonomics • Eye strain • Radiation • Glare Plymouth State University
 Ethics • Theft • Counterfeiting Plymouth State University
Ethics • Theft • Counterfeiting Plymouth State University
 Craig’s List 72 Web Expressions
Craig’s List 72 Web Expressions


