d7e105849a756135470c2fdfc41ae4b4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Computer Hardware
Computer Hardware
 Focus Items Design systems that meet business needs ¡ Hardware industry trends ¡ Problems ¡ l l ¡ Legacy hardware (and software) Dealing with growth Improving fault tolerance
Focus Items Design systems that meet business needs ¡ Hardware industry trends ¡ Problems ¡ l l ¡ Legacy hardware (and software) Dealing with growth Improving fault tolerance
 Terms (CPU) (1) ¡ Central Processing Unit (CPU) l l l ¡ Many machines have multiple CPUs Servers scale from 1 -256 processors Many CPUs are designed to support virtualization Processor speed l l Measured in GHz. A measure of the internal clock
Terms (CPU) (1) ¡ Central Processing Unit (CPU) l l l ¡ Many machines have multiple CPUs Servers scale from 1 -256 processors Many CPUs are designed to support virtualization Processor speed l l Measured in GHz. A measure of the internal clock
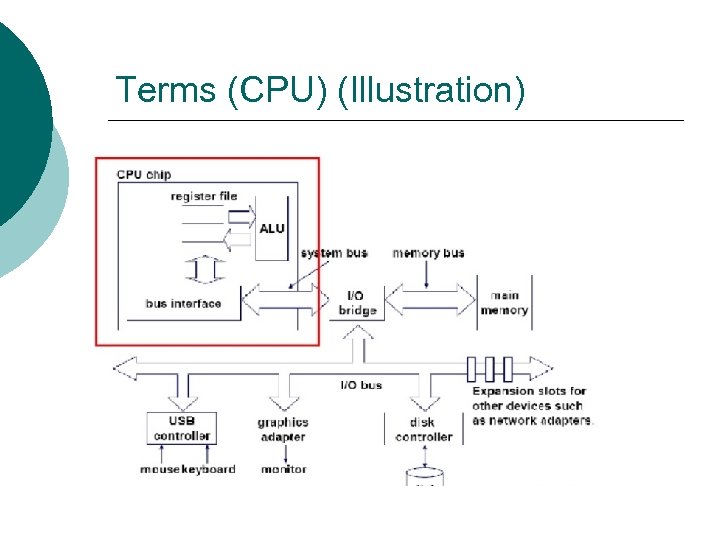 Terms (CPU) (Illustration)
Terms (CPU) (Illustration)
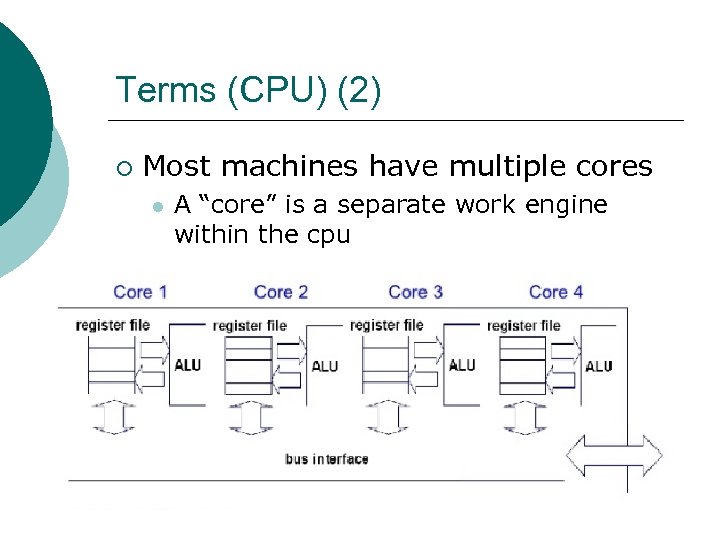 Terms (CPU) (2) ¡ Most machines have multiple cores l A “core” is a separate work engine within the cpu
Terms (CPU) (2) ¡ Most machines have multiple cores l A “core” is a separate work engine within the cpu
 Terms (Cache) (Memory) ¡ ¡ CACHE – Memory directly connected to the CPU l Fast Memory (Primary storage) l l Volatile storage to store data Not all memory is the same ¡ ¡ ¡ Some provides error correction Performance differences Density
Terms (Cache) (Memory) ¡ ¡ CACHE – Memory directly connected to the CPU l Fast Memory (Primary storage) l l Volatile storage to store data Not all memory is the same ¡ ¡ ¡ Some provides error correction Performance differences Density
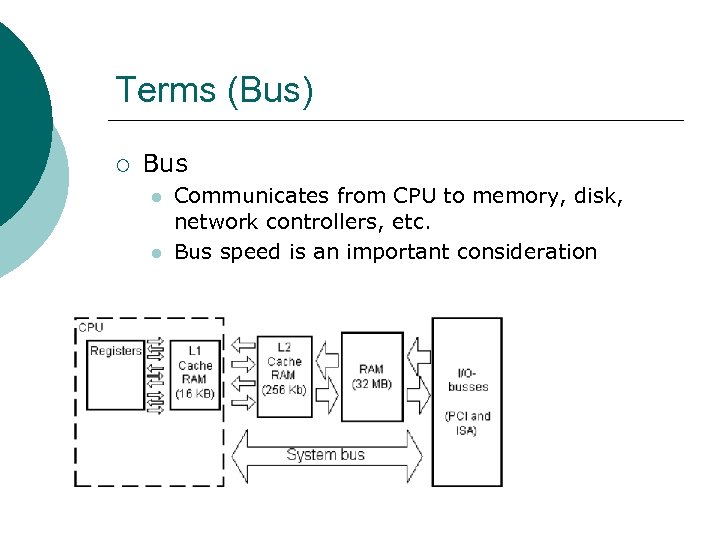 Terms (Bus) ¡ Bus l l Communicates from CPU to memory, disk, network controllers, etc. Bus speed is an important consideration
Terms (Bus) ¡ Bus l l Communicates from CPU to memory, disk, network controllers, etc. Bus speed is an important consideration
 Terms (Disk) ¡ Disk (Secondary storage) l Hard ¡ l l ATA, SCSI, Optical ¡ CD / DVD / Blu Ray Backup tape devices http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Hard_disk_drive
Terms (Disk) ¡ Disk (Secondary storage) l Hard ¡ l l ATA, SCSI, Optical ¡ CD / DVD / Blu Ray Backup tape devices http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Hard_disk_drive
 Categories of Computers (lightweight devices) ¡ “Lightweight devices” l l Network computers Special purpose transaction terminals ¡ l UPS / Fed. Ex Browser-only devices (kiosks) Phones ¡ Tablets ¡
Categories of Computers (lightweight devices) ¡ “Lightweight devices” l l Network computers Special purpose transaction terminals ¡ l UPS / Fed. Ex Browser-only devices (kiosks) Phones ¡ Tablets ¡
 Categories of Computers (Desktop) Market is shrinking because of tablet / phone horsepower ¡ These are the engineering workstations of yesterday ¡
Categories of Computers (Desktop) Market is shrinking because of tablet / phone horsepower ¡ These are the engineering workstations of yesterday ¡
 Categories of Computers (Servers) Oracle Sun / HP / IBM / Dell provide the lion’s share of todays servers ¡ Characterized by ¡ l Multiple CPUs with multiple cores
Categories of Computers (Servers) Oracle Sun / HP / IBM / Dell provide the lion’s share of todays servers ¡ Characterized by ¡ l Multiple CPUs with multiple cores
 Large Server (Example) ¡ SPARK Enterprise M 9000 l l l ¡ 64 processors / 4 cores per processor 4 TB memory Storage measure in the pedabytes (NAS) IBM Power 795 l l l Up to 256 processor cores book “book” and up to 8 books 16 TB memory All for about $1 million
Large Server (Example) ¡ SPARK Enterprise M 9000 l l l ¡ 64 processors / 4 cores per processor 4 TB memory Storage measure in the pedabytes (NAS) IBM Power 795 l l l Up to 256 processor cores book “book” and up to 8 books 16 TB memory All for about $1 million
 Larger Server (Illustration)
Larger Server (Illustration)
 Categories of Computers (Blade) A computer within a computer ¡ We buy a “blade chassis” containing ¡ l Power supplies / cooling / external media We buy blade computers that go into the chassis ¡ Blades: ¡ l Reduce power consumption and maintenance costs
Categories of Computers (Blade) A computer within a computer ¡ We buy a “blade chassis” containing ¡ l Power supplies / cooling / external media We buy blade computers that go into the chassis ¡ Blades: ¡ l Reduce power consumption and maintenance costs
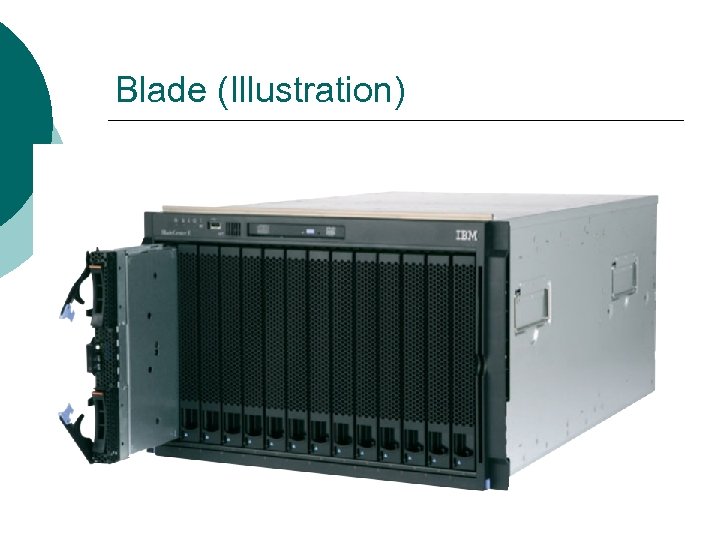 Blade (Illustration)
Blade (Illustration)
 Categories of Computers (Mainframe) ¡ These are really just the IBM Z series and a few special purpose devices
Categories of Computers (Mainframe) ¡ These are really just the IBM Z series and a few special purpose devices
 Categories of Computers (Distributed Computing) ¡ (Distributed computing) l l ¡ It’s really the software and not the hardware We just cluster multiple computers together Special purpose back ends l l l Tera. Data database servers Storage Tek disk and tape sub systems Storage Area Networks (SAN)
Categories of Computers (Distributed Computing) ¡ (Distributed computing) l l ¡ It’s really the software and not the hardware We just cluster multiple computers together Special purpose back ends l l l Tera. Data database servers Storage Tek disk and tape sub systems Storage Area Networks (SAN)
 Secondary Storage (Disk) ¡ Trends l They are cheap commodity items ¡ l Rated in mean time between failure (MTBF) ¡ l < $100. 00 per terabyte 100, 000 to 1. 5 M hours is common Multiple disks are connected to form disk subsystems
Secondary Storage (Disk) ¡ Trends l They are cheap commodity items ¡ l Rated in mean time between failure (MTBF) ¡ l < $100. 00 per terabyte 100, 000 to 1. 5 M hours is common Multiple disks are connected to form disk subsystems
 RAID ¡ ¡ Redundant disk arrays supply fault tolerance There are different types of RAID l l l ¡ Level 1 uses separate disks (mirroring) Level 2 uses striping There are others Example l HP 3 PAR Store. Serv 10000 storage ¡ Fault tolerant ¡ Up to 2. 2 PB of storage
RAID ¡ ¡ Redundant disk arrays supply fault tolerance There are different types of RAID l l l ¡ Level 1 uses separate disks (mirroring) Level 2 uses striping There are others Example l HP 3 PAR Store. Serv 10000 storage ¡ Fault tolerant ¡ Up to 2. 2 PB of storage
 Secondary Storage (Magnetic Tape) ¡ It’s still used for large archive sites l ¡ Phone records, credit card records, and other historical data Tapes are enclosed in tape robotic sub systems l l l We can store up to 75 -100 PB HP Store. Ever ESL G 3 Up to 12, 006 tape cartridges
Secondary Storage (Magnetic Tape) ¡ It’s still used for large archive sites l ¡ Phone records, credit card records, and other historical data Tapes are enclosed in tape robotic sub systems l l l We can store up to 75 -100 PB HP Store. Ever ESL G 3 Up to 12, 006 tape cartridges
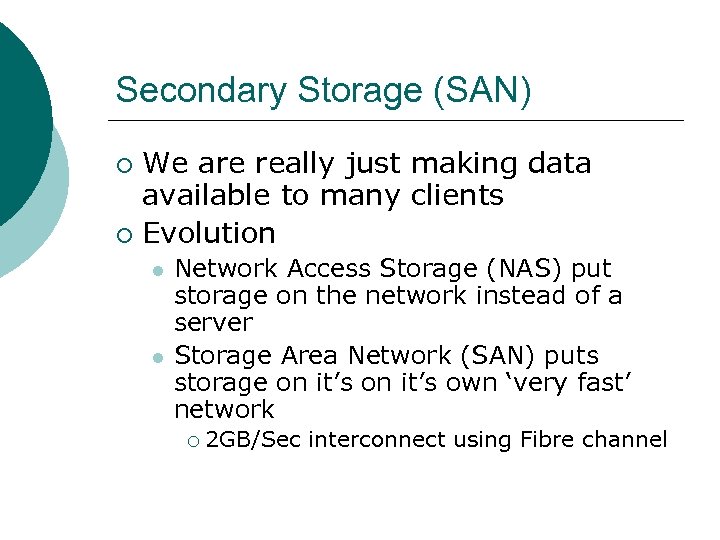 Secondary Storage (SAN) We are really just making data available to many clients ¡ Evolution ¡ l l Network Access Storage (NAS) put storage on the network instead of a server Storage Area Network (SAN) puts storage on it’s own ‘very fast’ network ¡ 2 GB/Sec interconnect using Fibre channel
Secondary Storage (SAN) We are really just making data available to many clients ¡ Evolution ¡ l l Network Access Storage (NAS) put storage on the network instead of a server Storage Area Network (SAN) puts storage on it’s own ‘very fast’ network ¡ 2 GB/Sec interconnect using Fibre channel
 Printer Technology Desktop laser printers offer low TCO ¡ High speed production printers ¡ l l These compete against traditional offset presses Continuous roll input Up to 2500 pages per minute www. delphax. com
Printer Technology Desktop laser printers offer low TCO ¡ High speed production printers ¡ l l These compete against traditional offset presses Continuous roll input Up to 2500 pages per minute www. delphax. com
 Printer Technology (2) ¡ ¡ ¡ Kodak example system: About 75 ft long and 15 ft tall Will print both sides at 2 up(2 different documents side by side) Ink jet printer - 12 print heads -- 8 nine inch heads and 4 four inch heads. Running at 1000 ft per minute Ink feeds from 275 gal tanks
Printer Technology (2) ¡ ¡ ¡ Kodak example system: About 75 ft long and 15 ft tall Will print both sides at 2 up(2 different documents side by side) Ink jet printer - 12 print heads -- 8 nine inch heads and 4 four inch heads. Running at 1000 ft per minute Ink feeds from 275 gal tanks
 Printer Technology (3)
Printer Technology (3)
 Printer Technology (4)
Printer Technology (4)
 Balance in Systems The issue in configuring large systems is balance ¡ Choosing the right system for the job ¡ l l Disk (IO) is often the bottleneck Bus Speed Memory shortfalls Network bandwith
Balance in Systems The issue in configuring large systems is balance ¡ Choosing the right system for the job ¡ l l Disk (IO) is often the bottleneck Bus Speed Memory shortfalls Network bandwith
 Scalability in Systems must be able to grow with a business ¡ Expansion of an existing system by adding memory, disk or other components ¡ Expansion by adding additional servers to a cluster or server farm ¡
Scalability in Systems must be able to grow with a business ¡ Expansion of an existing system by adding memory, disk or other components ¡ Expansion by adding additional servers to a cluster or server farm ¡
 Server Farms ¡ Many servers interconnected together
Server Farms ¡ Many servers interconnected together
 Server Farms (Load Balancing) ¡ Load balancing servers l l l Dispatch request to the actual servers Monitor the health of the servers Monitor the load on the various servers
Server Farms (Load Balancing) ¡ Load balancing servers l l l Dispatch request to the actual servers Monitor the health of the servers Monitor the load on the various servers
 Titan ¡ Oak Ridge National Labs houses the “fastest” computer in the world
Titan ¡ Oak Ridge National Labs houses the “fastest” computer in the world
 Titan 27, 000 trillion calculations / second (27 petaflops) ¡ 299, 008 CPU cores ¡ l l 18, 688 AMD Opteron 18, 688 K 20 x GPUs 710 TB of memory ¡ Cost of 97 million ¡
Titan 27, 000 trillion calculations / second (27 petaflops) ¡ 299, 008 CPU cores ¡ l l 18, 688 AMD Opteron 18, 688 K 20 x GPUs 710 TB of memory ¡ Cost of 97 million ¡
 Fault Tolerance in Systems One server in a farm can fail leaving the others running ¡ Fault tolerant servers have multiple CPUs ¡ Failed memory will not cause a system to fail ¡ RAID allows disk failures without causing system failures ¡
Fault Tolerance in Systems One server in a farm can fail leaving the others running ¡ Fault tolerant servers have multiple CPUs ¡ Failed memory will not cause a system to fail ¡ RAID allows disk failures without causing system failures ¡
 Economic Decisions Single vendor solutions vs. multivendor solutions ¡ Lease VS. buy decisions ¡
Economic Decisions Single vendor solutions vs. multivendor solutions ¡ Lease VS. buy decisions ¡
 Terms (Speed) Microsecond - 1/1000 second ¡ Millisecond – 1/1, 000 second ¡ Nanosecond – 1/1, 000, 000 second ¡ Picosecond – 1/1, 000, 000 second ¡ ¡ Teraflop – Trillion (1, 000, 000) floating point operations per second
Terms (Speed) Microsecond - 1/1000 second ¡ Millisecond – 1/1, 000 second ¡ Nanosecond – 1/1, 000, 000 second ¡ Picosecond – 1/1, 000, 000 second ¡ ¡ Teraflop – Trillion (1, 000, 000) floating point operations per second
 Terms (Storage) 1, 000 bytes – Kilobyte ¡ 1, 000 bytes – Megabyte ¡ 1, 000, 000 bytes – Gigabyte ¡ 1, 000, 000 bytes – Terabtye ¡ 1, 000, 000 bytes = Petabyte ¡
Terms (Storage) 1, 000 bytes – Kilobyte ¡ 1, 000 bytes – Megabyte ¡ 1, 000, 000 bytes – Gigabyte ¡ 1, 000, 000 bytes – Terabtye ¡ 1, 000, 000 bytes = Petabyte ¡


