022ac34b2131f5466bc1b90d478824cb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Computer Graphics chapter 1 Dr. Jehad Q. O. Alnihoud Email: jehad@aabu. edu. jo Phone: 3354 1
Computer Graphics chapter 1 Dr. Jehad Q. O. Alnihoud Email: jehad@aabu. edu. jo Phone: 3354 1
 Books • F. S. Hill, Computer Graphics Using Open. GL, Prentice-Hall (2001). • Mason Woo, Open. GL Programming Guide, Addison Wesley (2000). • Hearn and Baker, Computer Graphics, Prentice-Hall (1997). RM 2
Books • F. S. Hill, Computer Graphics Using Open. GL, Prentice-Hall (2001). • Mason Woo, Open. GL Programming Guide, Addison Wesley (2000). • Hearn and Baker, Computer Graphics, Prentice-Hall (1997). RM 2
 Books (Supplementary reference) n n RM Foley, V. Dam, Feiner, Hughes, Computer Graphics Principles and Practice, 2/e, Addison Wesley, 1997. Edward Angel, Interactive Computer Graphics, Addison Wesley, 1997. Zhigang Xiang, Schaum’s Outlines: Computer Graphics, Mc. Graw. Hill, 2001. Shreiner D, Open. GL Reference Manual, Addison-Wesley, 2000. 3
Books (Supplementary reference) n n RM Foley, V. Dam, Feiner, Hughes, Computer Graphics Principles and Practice, 2/e, Addison Wesley, 1997. Edward Angel, Interactive Computer Graphics, Addison Wesley, 1997. Zhigang Xiang, Schaum’s Outlines: Computer Graphics, Mc. Graw. Hill, 2001. Shreiner D, Open. GL Reference Manual, Addison-Wesley, 2000. 3
 Course Assessment n Coursework 50% First Exam u Second Exam u Group Project u Lab u n 15% 10% Final Exam 50% Attendance in both lecture and lab sessions is compulsory. RM 4
Course Assessment n Coursework 50% First Exam u Second Exam u Group Project u Lab u n 15% 10% Final Exam 50% Attendance in both lecture and lab sessions is compulsory. RM 4
 Graphics Applications n Art and Entertainment Animations u Movies u Commercials u Special Effects u RM 5
Graphics Applications n Art and Entertainment Animations u Movies u Commercials u Special Effects u RM 5
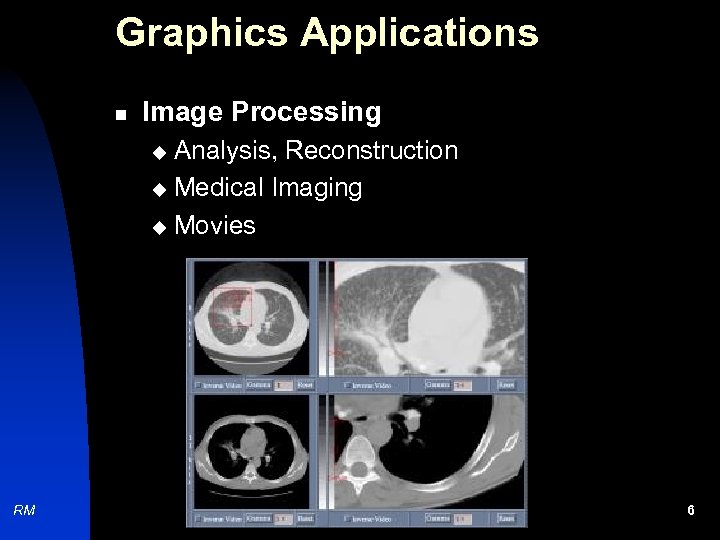 Graphics Applications n Image Processing Analysis, Reconstruction u Medical Imaging u Movies u RM 6
Graphics Applications n Image Processing Analysis, Reconstruction u Medical Imaging u Movies u RM 6
 Graphics Applications n Simulation Modeling and Analysis u Virtual Environments u RM 7
Graphics Applications n Simulation Modeling and Analysis u Virtual Environments u RM 7
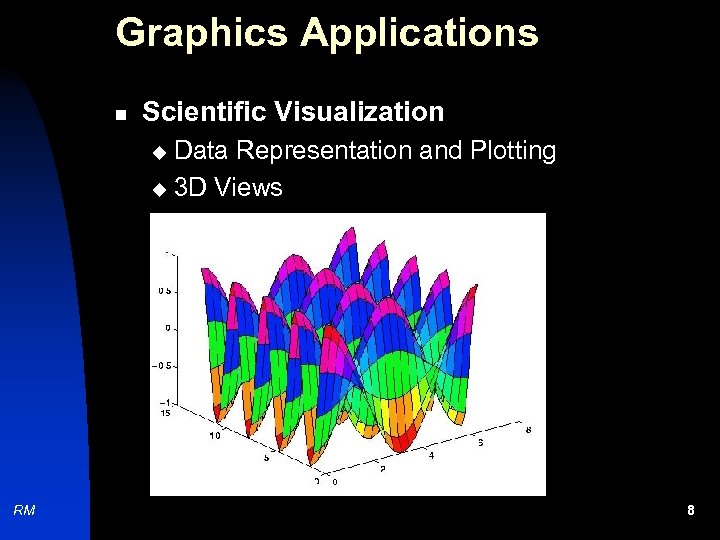 Graphics Applications n Scientific Visualization Data Representation and Plotting u 3 D Views u RM 8
Graphics Applications n Scientific Visualization Data Representation and Plotting u 3 D Views u RM 8
 Graphics Applications n CAD/CAM Industrial Design u Structural Design u Surface Modeling u RM 9
Graphics Applications n CAD/CAM Industrial Design u Structural Design u Surface Modeling u RM 9
 Graphics Software Packages n Early graphics libraries: u u GKS (Graphical Kernel System) PHIGS n n Java 2 D (Sun Microsystems) n Java 3 D (Sun Microsystems) n RM Open. GL (Silicon Graphics) VRML (Silicon Graphics) 10
Graphics Software Packages n Early graphics libraries: u u GKS (Graphical Kernel System) PHIGS n n Java 2 D (Sun Microsystems) n Java 3 D (Sun Microsystems) n RM Open. GL (Silicon Graphics) VRML (Silicon Graphics) 10
 Graphics: Main Components n Theory u u n Analytical Geometry Vectors and Matrices Algorithms u n Implementation u RM Eg: Line drawing, Filling etc. Programming (Open. GL) 11
Graphics: Main Components n Theory u u n Analytical Geometry Vectors and Matrices Algorithms u n Implementation u RM Eg: Line drawing, Filling etc. Programming (Open. GL) 11
 Graphics Hardware n Line Drawing Devices: Eg. Pen Plotters u Advantages: Perfect lines, Sharp Diagrams u Disadvantages: Not suitable for filled regions. u RM 12
Graphics Hardware n Line Drawing Devices: Eg. Pen Plotters u Advantages: Perfect lines, Sharp Diagrams u Disadvantages: Not suitable for filled regions. u RM 12
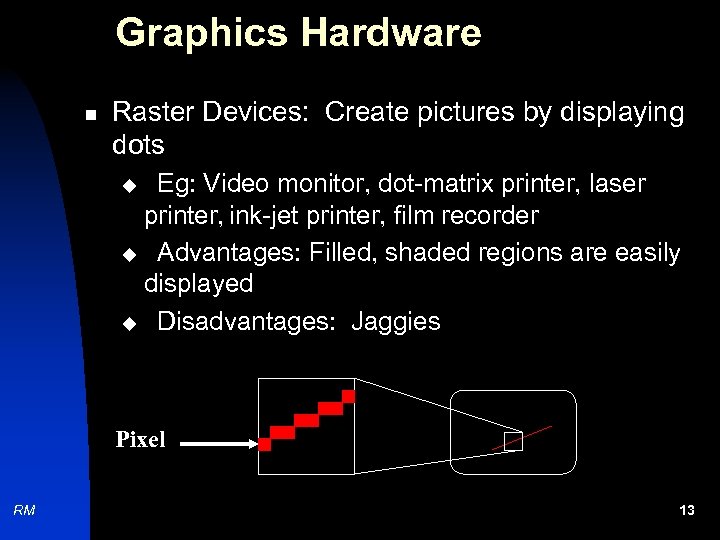 Graphics Hardware n Raster Devices: Create pictures by displaying dots Eg: Video monitor, dot-matrix printer, laser printer, ink-jet printer, film recorder u Advantages: Filled, shaded regions are easily displayed u Disadvantages: Jaggies u Pixel RM 13
Graphics Hardware n Raster Devices: Create pictures by displaying dots Eg: Video monitor, dot-matrix printer, laser printer, ink-jet printer, film recorder u Advantages: Filled, shaded regions are easily displayed u Disadvantages: Jaggies u Pixel RM 13
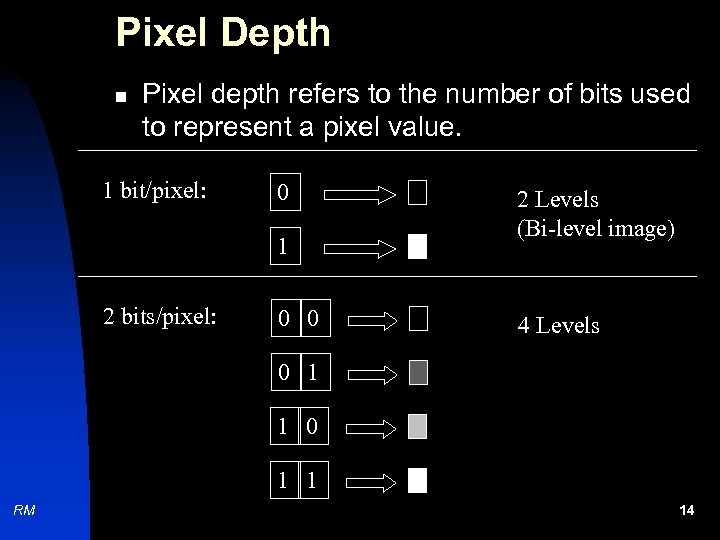 Pixel Depth n Pixel depth refers to the number of bits used to represent a pixel value. 1 bit/pixel: 0 1 2 bits/pixel: 0 0 2 Levels (Bi-level image) 4 Levels 0 1 1 RM 14
Pixel Depth n Pixel depth refers to the number of bits used to represent a pixel value. 1 bit/pixel: 0 1 2 bits/pixel: 0 0 2 Levels (Bi-level image) 4 Levels 0 1 1 RM 14
 Pixel Depth u 1 bit per pixel produce 2 levels (bilevel image). u 2 bits per pixel produce 4 levels. u 8 bits per pixel produce 256 levels. n RM In general, if the pixel depth is n, then it is possible to have 2 n levels. 15
Pixel Depth u 1 bit per pixel produce 2 levels (bilevel image). u 2 bits per pixel produce 4 levels. u 8 bits per pixel produce 256 levels. n RM In general, if the pixel depth is n, then it is possible to have 2 n levels. 15
 Raster Display n n n RM Most display used for computer graphics nowadays are raster displays. Image presented in display surface that contains certain number of pixels. Eg. 480 x 640 (r x c). Frame buffer is a region of memory sufficiently large to hold all the pixel values for display. 16
Raster Display n n n RM Most display used for computer graphics nowadays are raster displays. Image presented in display surface that contains certain number of pixels. Eg. 480 x 640 (r x c). Frame buffer is a region of memory sufficiently large to hold all the pixel values for display. 16
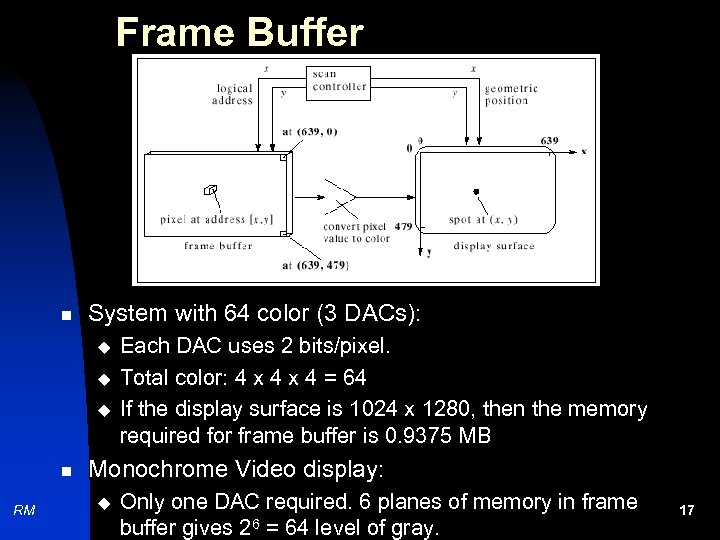 Frame Buffer n System with 64 color (3 DACs): u u u n RM Each DAC uses 2 bits/pixel. Total color: 4 x 4 = 64 If the display surface is 1024 x 1280, then the memory required for frame buffer is 0. 9375 MB Monochrome Video display: u Only one DAC required. 6 planes of memory in frame buffer gives 26 = 64 level of gray. 17
Frame Buffer n System with 64 color (3 DACs): u u u n RM Each DAC uses 2 bits/pixel. Total color: 4 x 4 = 64 If the display surface is 1024 x 1280, then the memory required for frame buffer is 0. 9375 MB Monochrome Video display: u Only one DAC required. 6 planes of memory in frame buffer gives 26 = 64 level of gray. 17
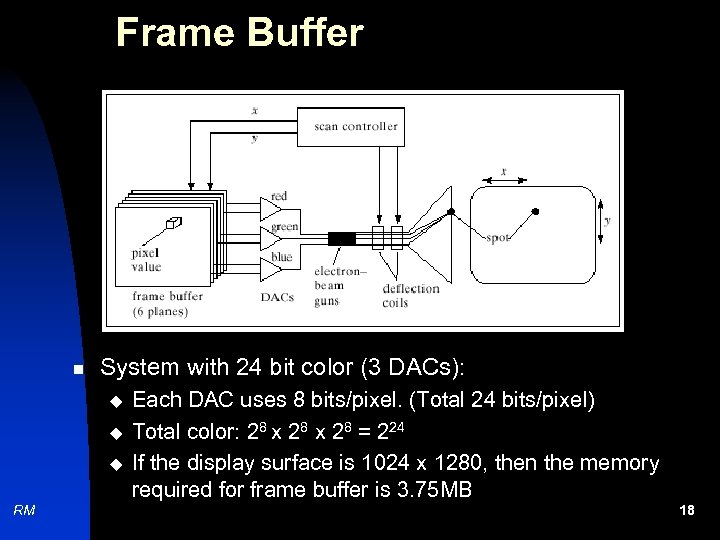 Frame Buffer n System with 24 bit color (3 DACs): u u u RM Each DAC uses 8 bits/pixel. (Total 24 bits/pixel) Total color: 28 x 28 = 224 If the display surface is 1024 x 1280, then the memory required for frame buffer is 3. 75 MB 18
Frame Buffer n System with 24 bit color (3 DACs): u u u RM Each DAC uses 8 bits/pixel. (Total 24 bits/pixel) Total color: 28 x 28 = 224 If the display surface is 1024 x 1280, then the memory required for frame buffer is 3. 75 MB 18
 Color Models: RGB Diagram • RGB Model is used for colored light sources • RGB Model is additive Basis colors: R, G, B R: Red=[1, 0, 0] G: Green=[0, 1, 0] B: Blue=[0, 0, 1] C: Cyan=[0, 1, 1] M: Magenta=[1, 0, 1] Y: Yellow=[1, 1, 0] W: White=[1, 1, 1] K: Black=[0, 0, 0]
Color Models: RGB Diagram • RGB Model is used for colored light sources • RGB Model is additive Basis colors: R, G, B R: Red=[1, 0, 0] G: Green=[0, 1, 0] B: Blue=[0, 0, 1] C: Cyan=[0, 1, 1] M: Magenta=[1, 0, 1] Y: Yellow=[1, 1, 0] W: White=[1, 1, 1] K: Black=[0, 0, 0]
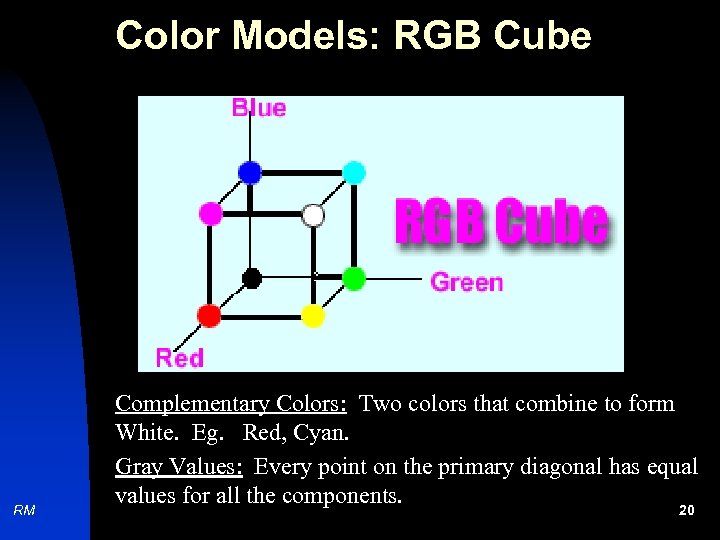 Color Models: RGB Cube RM Complementary Colors: Two colors that combine to form White. Eg. Red, Cyan. Gray Values: Every point on the primary diagonal has equal values for all the components. 20
Color Models: RGB Cube RM Complementary Colors: Two colors that combine to form White. Eg. Red, Cyan. Gray Values: Every point on the primary diagonal has equal values for all the components. 20
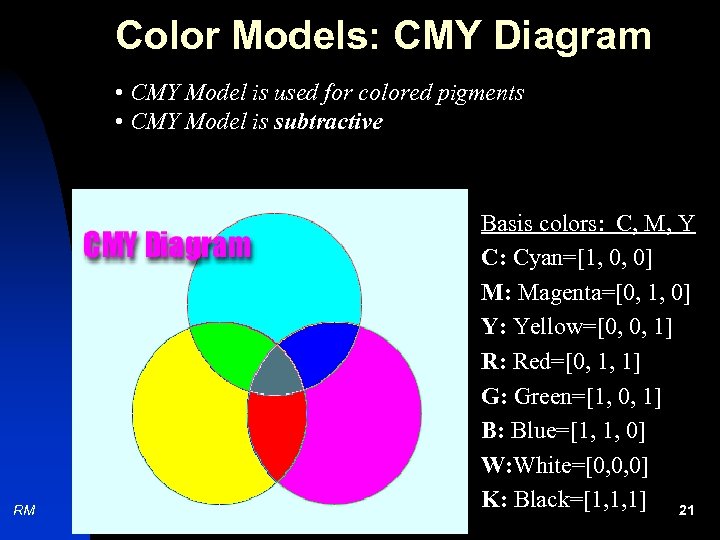 Color Models: CMY Diagram • CMY Model is used for colored pigments • CMY Model is subtractive RM Basis colors: C, M, Y C: Cyan=[1, 0, 0] M: Magenta=[0, 1, 0] Y: Yellow=[0, 0, 1] R: Red=[0, 1, 1] G: Green=[1, 0, 1] B: Blue=[1, 1, 0] W: White=[0, 0, 0] K: Black=[1, 1, 1] 21
Color Models: CMY Diagram • CMY Model is used for colored pigments • CMY Model is subtractive RM Basis colors: C, M, Y C: Cyan=[1, 0, 0] M: Magenta=[0, 1, 0] Y: Yellow=[0, 0, 1] R: Red=[0, 1, 1] G: Green=[1, 0, 1] B: Blue=[1, 1, 0] W: White=[0, 0, 0] K: Black=[1, 1, 1] 21
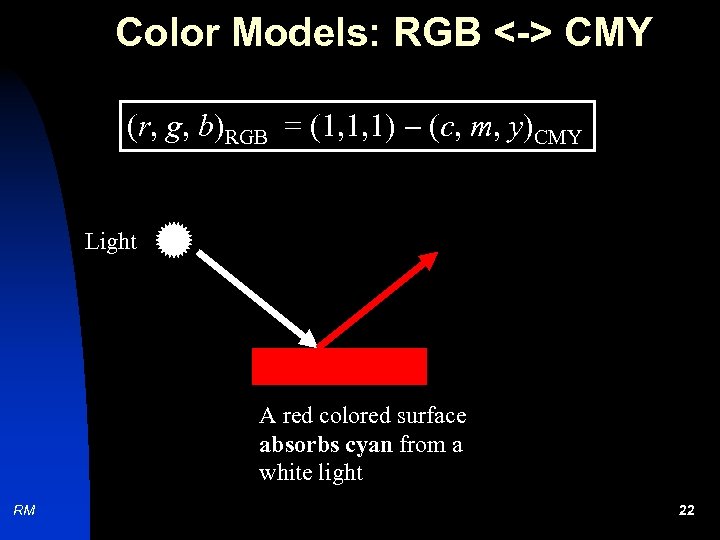 Color Models: RGB <-> CMY (r, g, b)RGB = (1, 1, 1) (c, m, y)CMY Light A red colored surface absorbs cyan from a white light RM 22
Color Models: RGB <-> CMY (r, g, b)RGB = (1, 1, 1) (c, m, y)CMY Light A red colored surface absorbs cyan from a white light RM 22
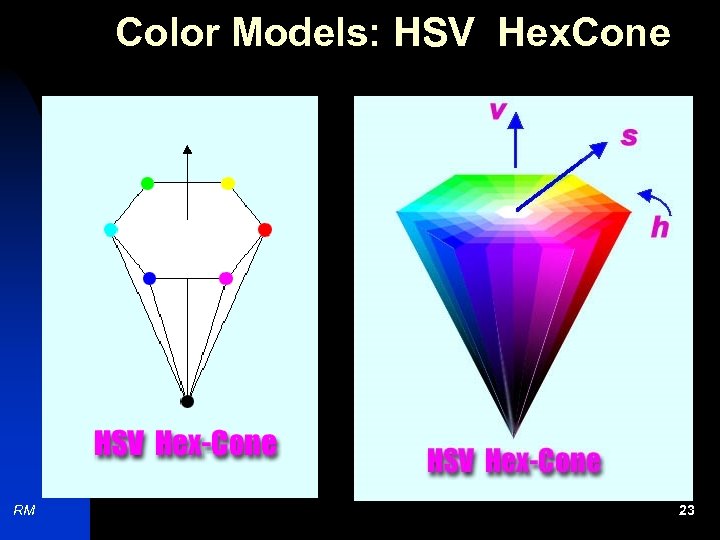 Color Models: HSV Hex. Cone RM 23
Color Models: HSV Hex. Cone RM 23
 Color Models: HSV H (Hue): 0 to 360 degrees S (Saturation): 0 to 1 V (Value): 0 to 1 Examples: Eg. RM 0: Red, 60: Yellow …. 0: Axis, 1: Boundary 0: Vertex, 1: Base Yellow: [60, 1. 0] Black: [ -, -, 0. 0] White: [-, 0. 0, 1. 0] 24
Color Models: HSV H (Hue): 0 to 360 degrees S (Saturation): 0 to 1 V (Value): 0 to 1 Examples: Eg. RM 0: Red, 60: Yellow …. 0: Axis, 1: Boundary 0: Vertex, 1: Base Yellow: [60, 1. 0] Black: [ -, -, 0. 0] White: [-, 0. 0, 1. 0] 24
 RGB Color Definition (Open. GL) RM 25
RGB Color Definition (Open. GL) RM 25


