19d7a677ddc355baeba242b490249449.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 75
 Computer Communication Networks Data Transmission, Media Signal Encoding Techniques Data Communication Techniques Local and Control, Spread Spectrum, ATM Multiplexing, Switching, Data Link Wide Area Networks Wireless Routing Networks Introductory Lecture
Computer Communication Networks Data Transmission, Media Signal Encoding Techniques Data Communication Techniques Local and Control, Spread Spectrum, ATM Multiplexing, Switching, Data Link Wide Area Networks Wireless Routing Networks Introductory Lecture
 Course Overview Data Communication Networks and Open System Standards Data Transmission Data Link Controls Technologies of Local Area Networks and Wide Area Networks Communication Architecture and Protocols
Course Overview Data Communication Networks and Open System Standards Data Transmission Data Link Controls Technologies of Local Area Networks and Wide Area Networks Communication Architecture and Protocols
 Course Objectives The aim of this course is to provide a unified overview in the basic principles of data communications and computer networks. The lectures emphasize basic principles and topics of fundamental importance concerning the technology and architecture of this field, as well as providing the state of the art topics.
Course Objectives The aim of this course is to provide a unified overview in the basic principles of data communications and computer networks. The lectures emphasize basic principles and topics of fundamental importance concerning the technology and architecture of this field, as well as providing the state of the art topics.
 Course Objectives Followings are the basic objectives : To provide a conceptual foundation for the study of data communications using the Open Systems Interconnect (OSI) model for layered architecture To develop an understanding in basic hardware and software environments for data communications and computer networks
Course Objectives Followings are the basic objectives : To provide a conceptual foundation for the study of data communications using the Open Systems Interconnect (OSI) model for layered architecture To develop an understanding in basic hardware and software environments for data communications and computer networks
 Text Books Data and Computer Communications, 7 th Edition, Prentice Hall, 2004 by William Stallings Data Communication and Networking, 3 rd Edition, Mc. Graw-Hill, 2004 by Behrouz A. Forouzan
Text Books Data and Computer Communications, 7 th Edition, Prentice Hall, 2004 by William Stallings Data Communication and Networking, 3 rd Edition, Mc. Graw-Hill, 2004 by Behrouz A. Forouzan
 Course Website http: //web. uettaxila. edu. pk/cms/te. CCNms. AU 09/
Course Website http: //web. uettaxila. edu. pk/cms/te. CCNms. AU 09/
![Class Schedule [Tuesdays 4~6 / 6~9] No. Lecture Topics Text's slides 1 Course Orientation, Class Schedule [Tuesdays 4~6 / 6~9] No. Lecture Topics Text's slides 1 Course Orientation,](https://present5.com/presentation/19d7a677ddc355baeba242b490249449/image-7.jpg) Class Schedule [Tuesdays 4~6 / 6~9] No. Lecture Topics Text's slides 1 Course Orientation, Overview chapter 1, chapter 2 2 Data Transmission, Media chapter 3, chapter 4 3 Signal Encoding Techniques chapter 5 4 Data Communication Techniques chapter 6 5 Data Link Control chapter 7 6 Multiplexing chapter 8 7 Spread Spectrum chapter 9 8 Circuit and Packet Switching, ATM chapter 10 9 Routing/Congestion Control in Switched Networks chapter 12, chapter 13 10 Cellular Wireless Networks chapter 14 11 LANs chapter 15 12 High Speed LANs chapter 16 13 Class Summary
Class Schedule [Tuesdays 4~6 / 6~9] No. Lecture Topics Text's slides 1 Course Orientation, Overview chapter 1, chapter 2 2 Data Transmission, Media chapter 3, chapter 4 3 Signal Encoding Techniques chapter 5 4 Data Communication Techniques chapter 6 5 Data Link Control chapter 7 6 Multiplexing chapter 8 7 Spread Spectrum chapter 9 8 Circuit and Packet Switching, ATM chapter 10 9 Routing/Congestion Control in Switched Networks chapter 12, chapter 13 10 Cellular Wireless Networks chapter 14 11 LANs chapter 15 12 High Speed LANs chapter 16 13 Class Summary
 Overview
Overview
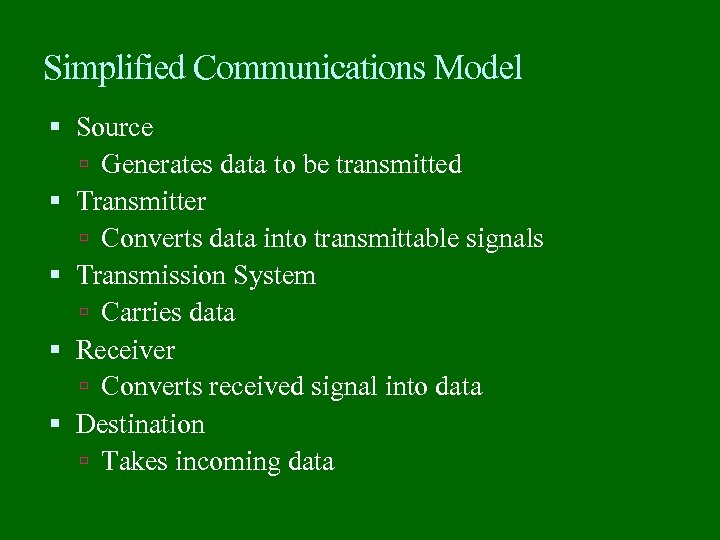 Simplified Communications Model Source Generates data to be transmitted Transmitter Converts data into transmittable signals Transmission System Carries data Receiver Converts received signal into data Destination Takes incoming data
Simplified Communications Model Source Generates data to be transmitted Transmitter Converts data into transmittable signals Transmission System Carries data Receiver Converts received signal into data Destination Takes incoming data
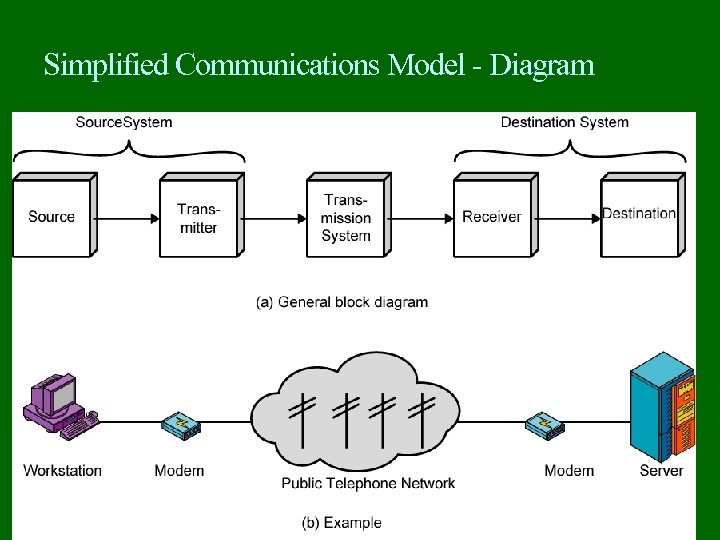 Simplified Communications Model - Diagram
Simplified Communications Model - Diagram
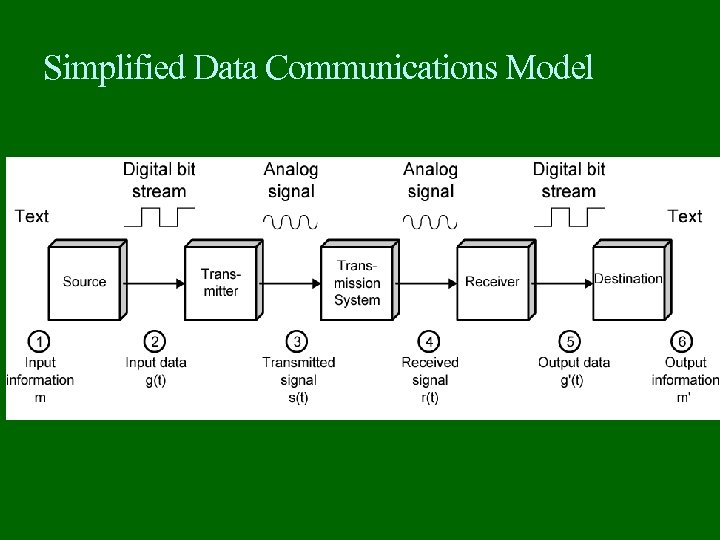 Simplified Data Communications Model
Simplified Data Communications Model
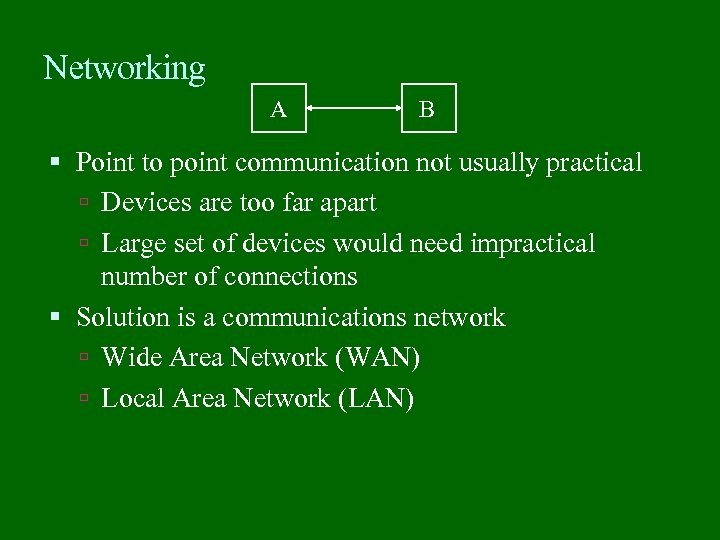 Networking A B Point to point communication not usually practical Devices are too far apart Large set of devices would need impractical number of connections Solution is a communications network Wide Area Network (WAN) Local Area Network (LAN)
Networking A B Point to point communication not usually practical Devices are too far apart Large set of devices would need impractical number of connections Solution is a communications network Wide Area Network (WAN) Local Area Network (LAN)
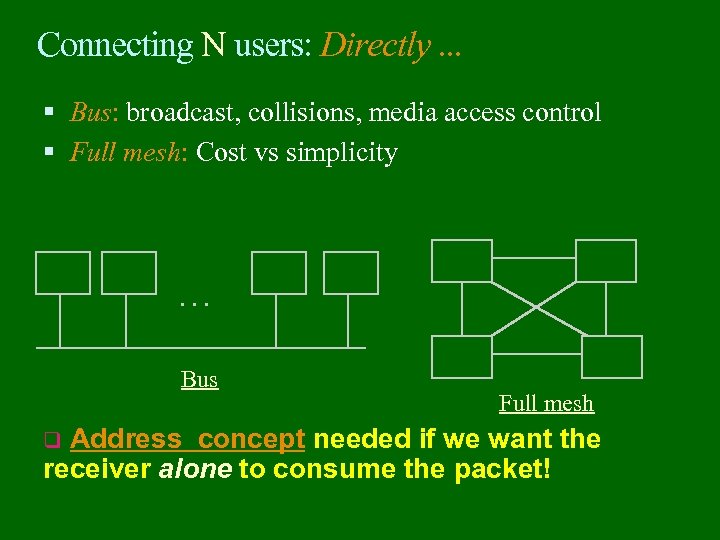 Connecting N users: Directly. . . Bus: broadcast, collisions, media access control Full mesh: Cost vs simplicity . . . Bus Full mesh Address concept needed if we want the receiver alone to consume the packet! q
Connecting N users: Directly. . . Bus: broadcast, collisions, media access control Full mesh: Cost vs simplicity . . . Bus Full mesh Address concept needed if we want the receiver alone to consume the packet! q
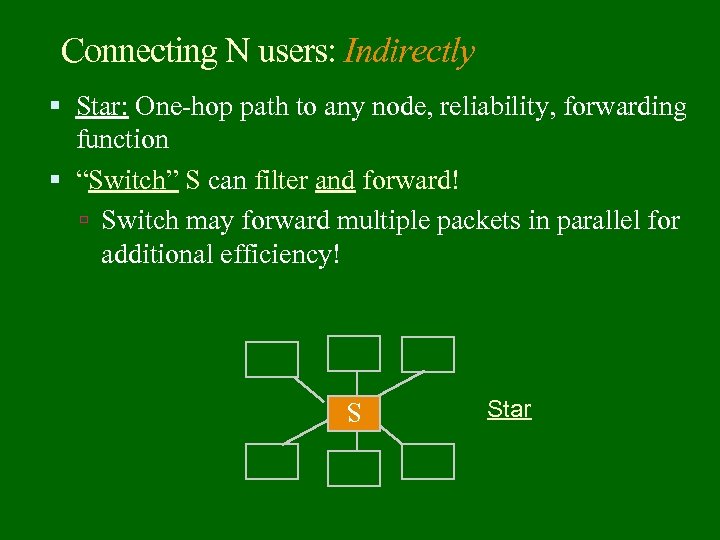 Connecting N users: Indirectly Star: One-hop path to any node, reliability, forwarding function “Switch” S can filter and forward! Switch may forward multiple packets in parallel for additional efficiency! Star S
Connecting N users: Indirectly Star: One-hop path to any node, reliability, forwarding function “Switch” S can filter and forward! Switch may forward multiple packets in parallel for additional efficiency! Star S
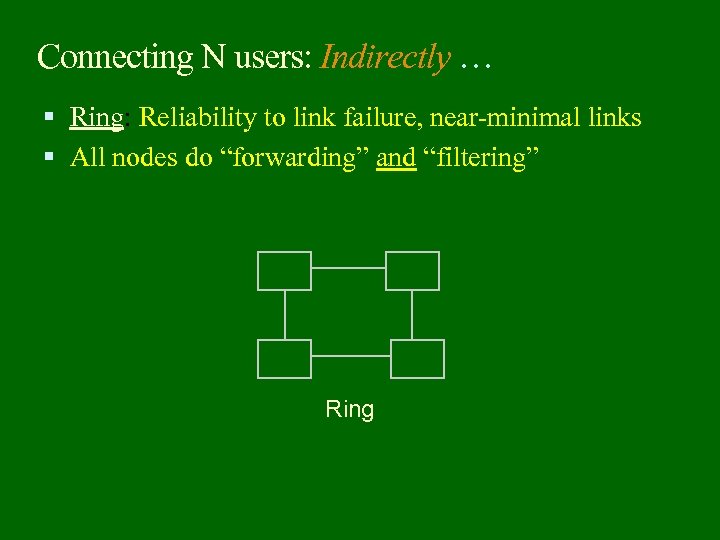 Connecting N users: Indirectly … Ring: Reliability to link failure, near-minimal links All nodes do “forwarding” and “filtering” Ring
Connecting N users: Indirectly … Ring: Reliability to link failure, near-minimal links All nodes do “forwarding” and “filtering” Ring
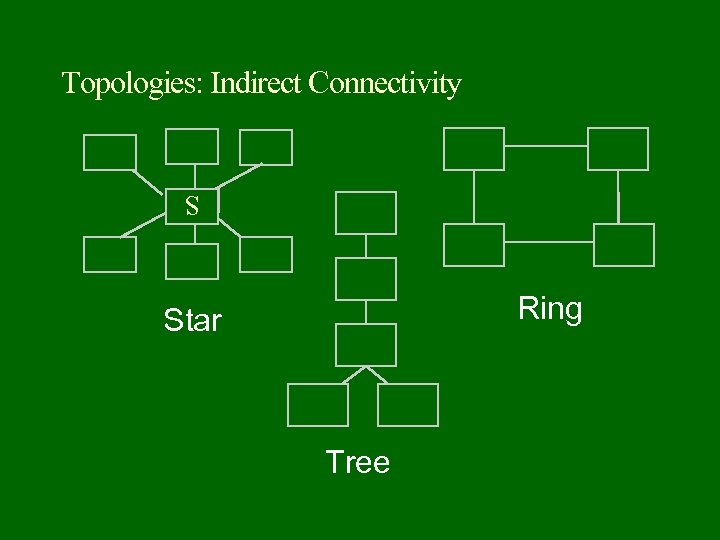 Topologies: Indirect Connectivity S Ring Star Tree
Topologies: Indirect Connectivity S Ring Star Tree
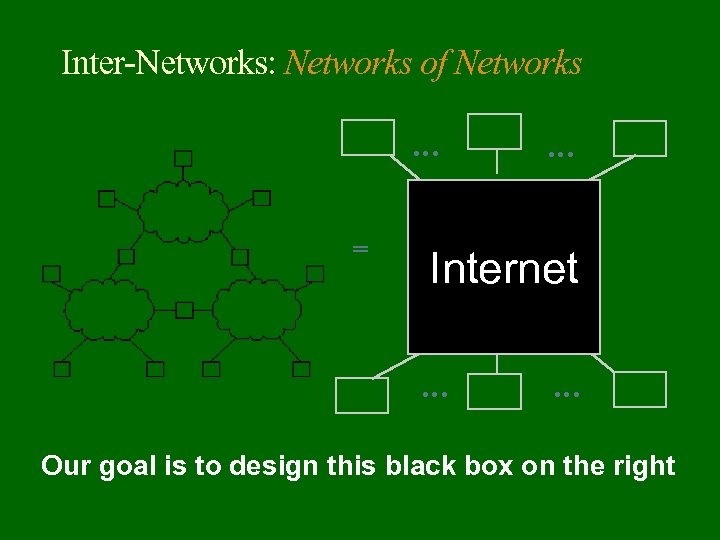 Inter-Networks: Networks of Networks … = … Internet … … Our goal is to design this black box on the right
Inter-Networks: Networks of Networks … = … Internet … … Our goal is to design this black box on the right
 Wide Area Networks Large geographical area Crossing public rights of way Rely in part on common carrier circuits Alternative technologies Circuit switching Packet switching Frame relay Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
Wide Area Networks Large geographical area Crossing public rights of way Rely in part on common carrier circuits Alternative technologies Circuit switching Packet switching Frame relay Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
 Circuit Switching Dedicated communications path established for the duration of the conversation e. g. telephone network
Circuit Switching Dedicated communications path established for the duration of the conversation e. g. telephone network
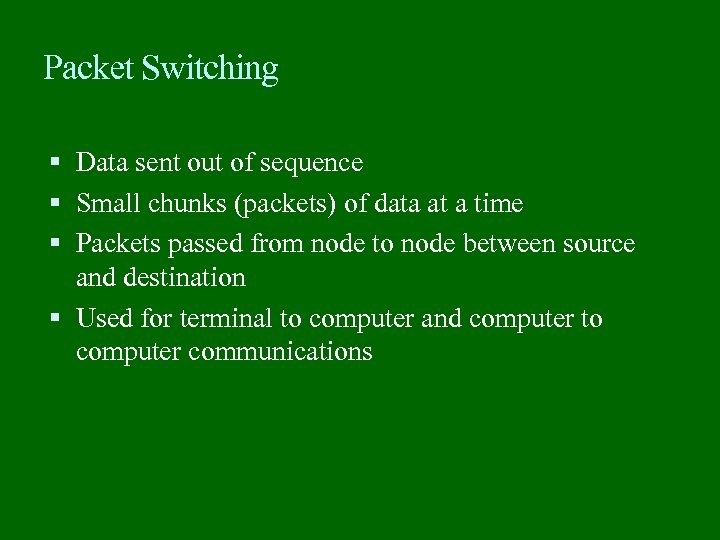 Packet Switching Data sent out of sequence Small chunks (packets) of data at a time Packets passed from node to node between source and destination Used for terminal to computer and computer to computer communications
Packet Switching Data sent out of sequence Small chunks (packets) of data at a time Packets passed from node to node between source and destination Used for terminal to computer and computer to computer communications
 Frame Relay Packet switching systems have large overheads to compensate for errors Modern systems are more reliable Errors can be caught in end system Most overhead for error control is stripped out
Frame Relay Packet switching systems have large overheads to compensate for errors Modern systems are more reliable Errors can be caught in end system Most overhead for error control is stripped out
 Asynchronous Transfer Mode ATM Evolution of frame relay Little overhead for error control Fixed packet (called cell) length Anything from 10 Mbps to many Gbps Constant data rate using packet switching technique
Asynchronous Transfer Mode ATM Evolution of frame relay Little overhead for error control Fixed packet (called cell) length Anything from 10 Mbps to many Gbps Constant data rate using packet switching technique
 Local Area Networks Smaller scope Building or small campus Usually owned by same organization as attached devices Data rates much higher Usually broadcast systems Now some switched systems and ATM are being introduced
Local Area Networks Smaller scope Building or small campus Usually owned by same organization as attached devices Data rates much higher Usually broadcast systems Now some switched systems and ATM are being introduced
 LAN Configurations Switched Ethernet May be single or multiple switches ATM LAN Fibre Channel Wireless Mobility Ease of installation
LAN Configurations Switched Ethernet May be single or multiple switches ATM LAN Fibre Channel Wireless Mobility Ease of installation
 Metropolitan Area Networks MAN Middle ground between LAN and WAN Private or public network High speed Large area
Metropolitan Area Networks MAN Middle ground between LAN and WAN Private or public network High speed Large area
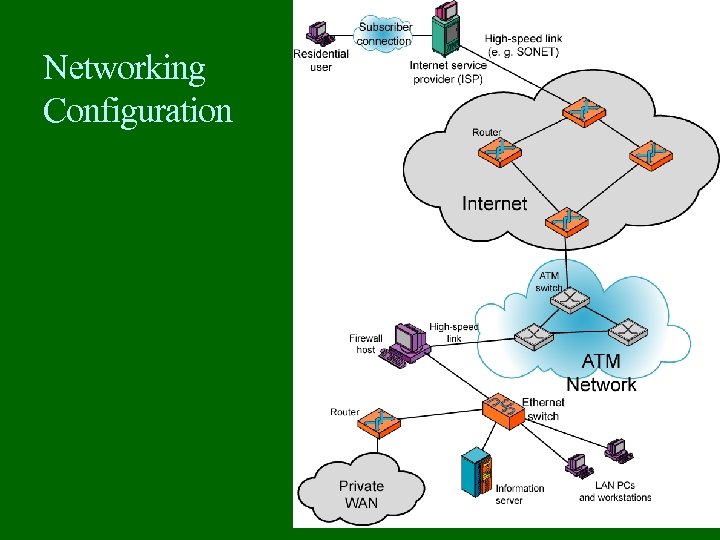 Networking Configuration
Networking Configuration
![Further Reading Stallings, W. [2003] Data and Computer Communications (7 th edition), Prentice Hall, Further Reading Stallings, W. [2003] Data and Computer Communications (7 th edition), Prentice Hall,](https://present5.com/presentation/19d7a677ddc355baeba242b490249449/image-27.jpg) Further Reading Stallings, W. [2003] Data and Computer Communications (7 th edition), Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River NJ, Chapter 1 Web site for Stallings book http: //williamstallings. com/DCC 7 e. html
Further Reading Stallings, W. [2003] Data and Computer Communications (7 th edition), Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River NJ, Chapter 1 Web site for Stallings book http: //williamstallings. com/DCC 7 e. html
 Protocols and Architecture
Protocols and Architecture
 Need For Protocol Architecture E. g. File transfer Source must initiate communications. Find Path or inform network of destination Source must check destination is prepared to receive File transfer application on source must check destination file management system will accept and store file for his user May need file format translation Task broken into subtasks Implemented separately in layers in stack Functions needed in both systems Peer layers communicate
Need For Protocol Architecture E. g. File transfer Source must initiate communications. Find Path or inform network of destination Source must check destination is prepared to receive File transfer application on source must check destination file management system will accept and store file for his user May need file format translation Task broken into subtasks Implemented separately in layers in stack Functions needed in both systems Peer layers communicate
 Key Elements of a Protocol Syntax Data formats Signal levels Semantics Control information Error handling Timing Speed matching Sequencing
Key Elements of a Protocol Syntax Data formats Signal levels Semantics Control information Error handling Timing Speed matching Sequencing
 Protocol Architecture Task of communication broken up into modules For example file transfer could use three modules File transfer application Communication service module Network access module
Protocol Architecture Task of communication broken up into modules For example file transfer could use three modules File transfer application Communication service module Network access module
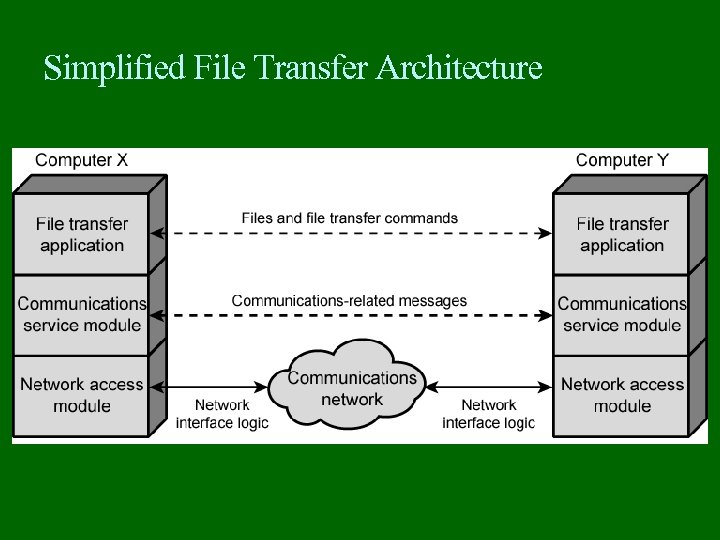 Simplified File Transfer Architecture
Simplified File Transfer Architecture
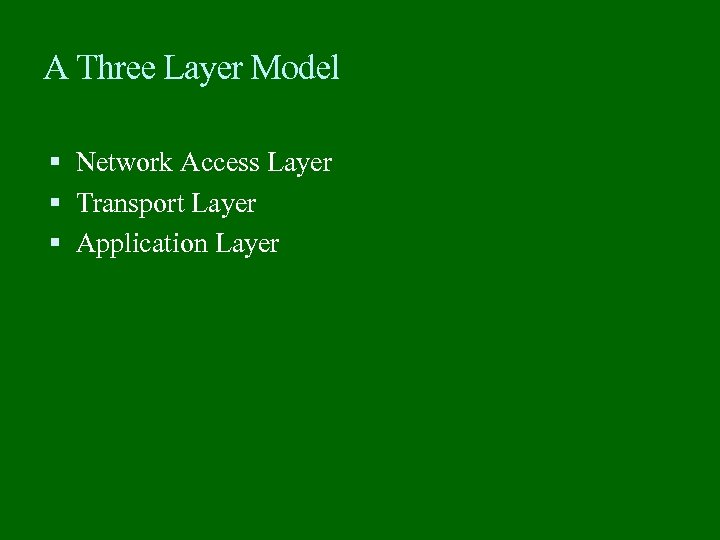 A Three Layer Model Network Access Layer Transport Layer Application Layer
A Three Layer Model Network Access Layer Transport Layer Application Layer
 Network Access Layer Exchange of data between the computer and the network Sending computer provides address of destination May invoke levels of service Dependent on type of network used (LAN, packet switched etc. )
Network Access Layer Exchange of data between the computer and the network Sending computer provides address of destination May invoke levels of service Dependent on type of network used (LAN, packet switched etc. )
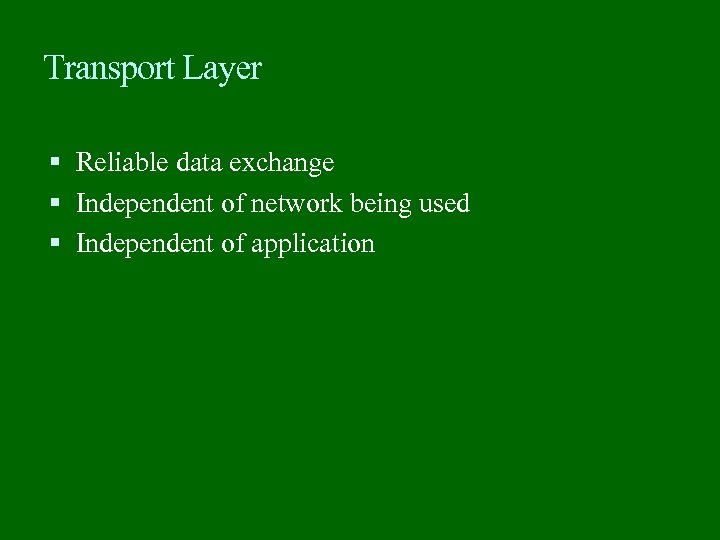 Transport Layer Reliable data exchange Independent of network being used Independent of application
Transport Layer Reliable data exchange Independent of network being used Independent of application
 Application Layer Support for different user applications e. g. e-mail, file transfer
Application Layer Support for different user applications e. g. e-mail, file transfer
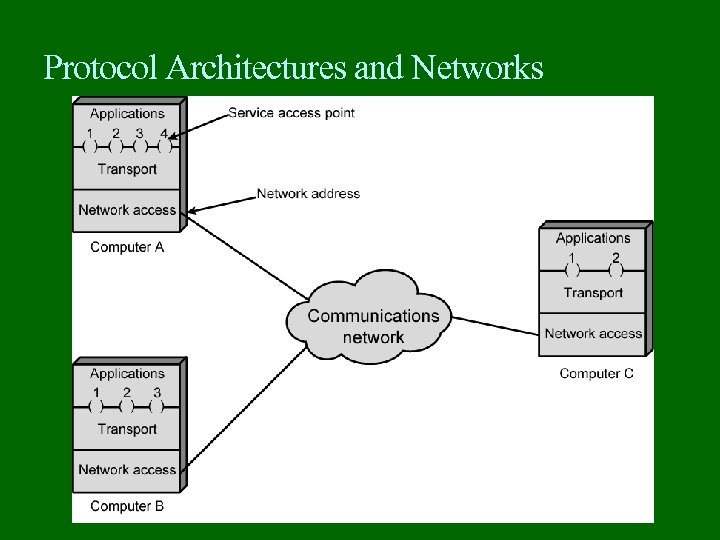 Protocol Architectures and Networks
Protocol Architectures and Networks
 Addressing Requirements Two levels of addressing required Each computer needs unique network address Each application on a (multi-tasking) computer needs a unique address within the computer The service access point or SAP The port on TCP/IP stacks
Addressing Requirements Two levels of addressing required Each computer needs unique network address Each application on a (multi-tasking) computer needs a unique address within the computer The service access point or SAP The port on TCP/IP stacks
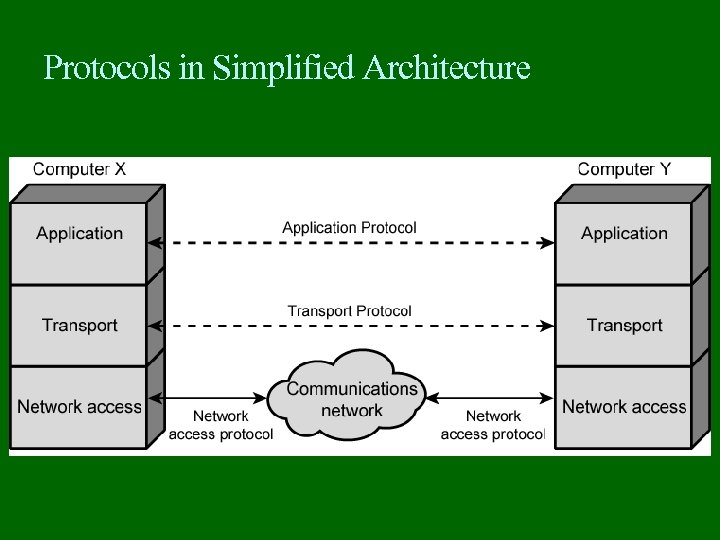 Protocols in Simplified Architecture
Protocols in Simplified Architecture
 Protocol Data Units (PDU) At each layer, protocols are used to communicate Control information is added to user data at each layer Transport layer may fragment user data Each fragment has a transport header added Destination SAP Sequence number Error detection code This gives a transport protocol data unit
Protocol Data Units (PDU) At each layer, protocols are used to communicate Control information is added to user data at each layer Transport layer may fragment user data Each fragment has a transport header added Destination SAP Sequence number Error detection code This gives a transport protocol data unit
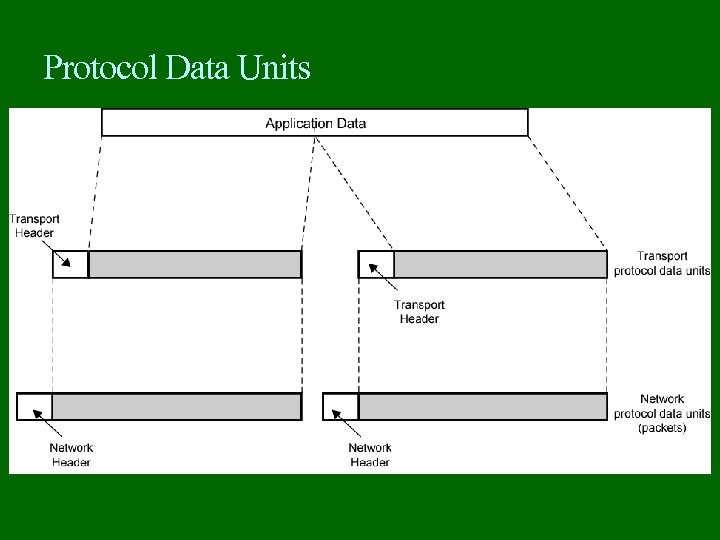 Protocol Data Units
Protocol Data Units
 Network PDU Adds network header network address for destination computer Facilities requests
Network PDU Adds network header network address for destination computer Facilities requests
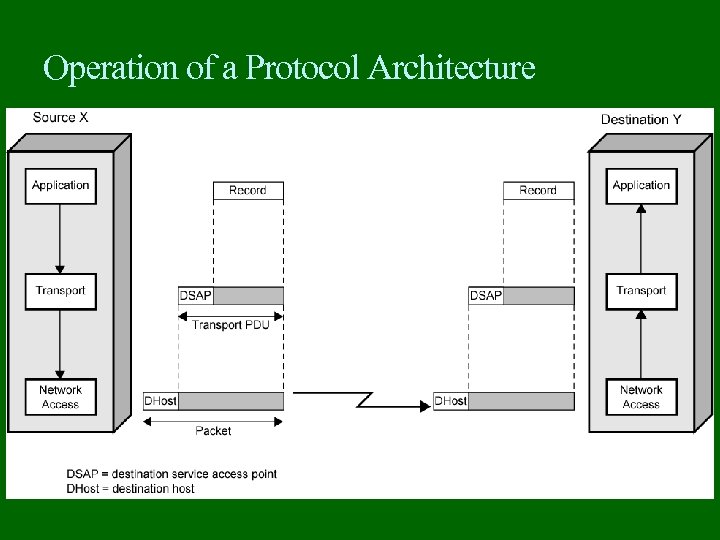 Operation of a Protocol Architecture
Operation of a Protocol Architecture
 Standardized Protocol Architectures Required for devices to communicate Vendors have more marketable products Customers can insist on standards based equipment Two standards: OSI Reference model Never lived up to early promises TCP/IP protocol suite Most widely used Also: IBM Systems Network Architecture (SNA)
Standardized Protocol Architectures Required for devices to communicate Vendors have more marketable products Customers can insist on standards based equipment Two standards: OSI Reference model Never lived up to early promises TCP/IP protocol suite Most widely used Also: IBM Systems Network Architecture (SNA)
 OSI Open Systems Interconnection Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Seven layers A theoretical system delivered too late! TCP/IP is the de facto standard
OSI Open Systems Interconnection Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Seven layers A theoretical system delivered too late! TCP/IP is the de facto standard
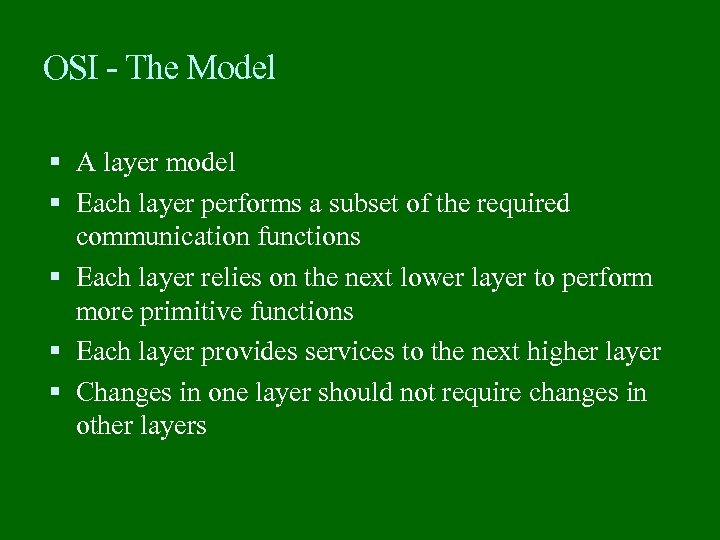 OSI - The Model A layer model Each layer performs a subset of the required communication functions Each layer relies on the next lower layer to perform more primitive functions Each layer provides services to the next higher layer Changes in one layer should not require changes in other layers
OSI - The Model A layer model Each layer performs a subset of the required communication functions Each layer relies on the next lower layer to perform more primitive functions Each layer provides services to the next higher layer Changes in one layer should not require changes in other layers
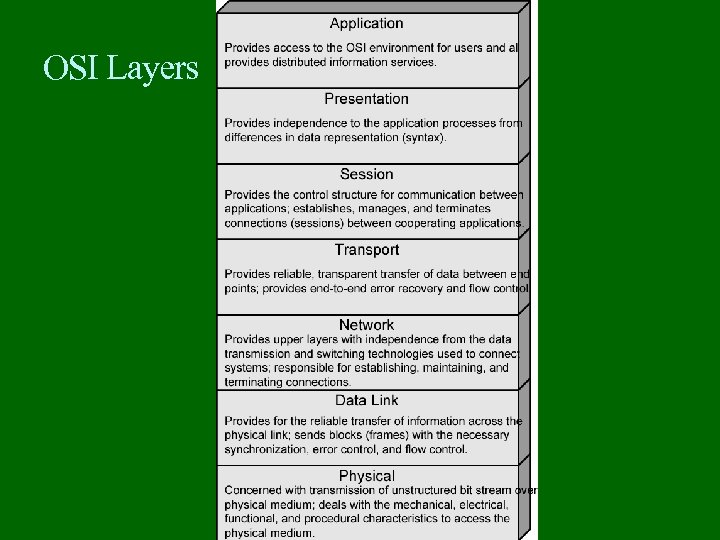 OSI Layers
OSI Layers
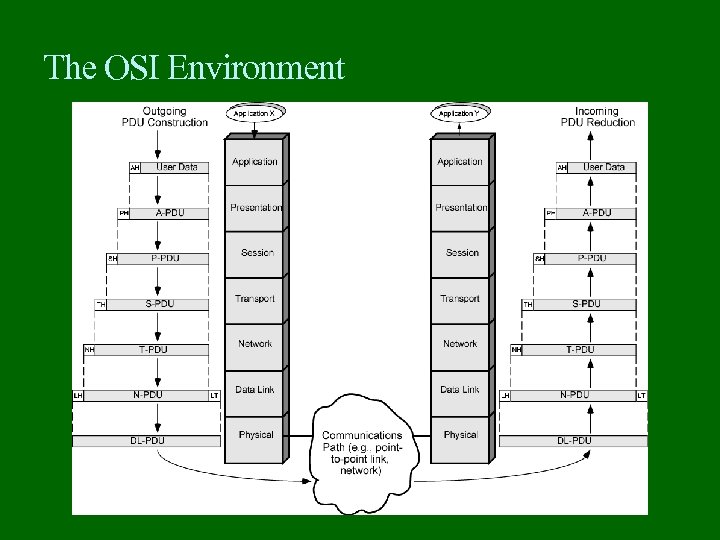 The OSI Environment
The OSI Environment
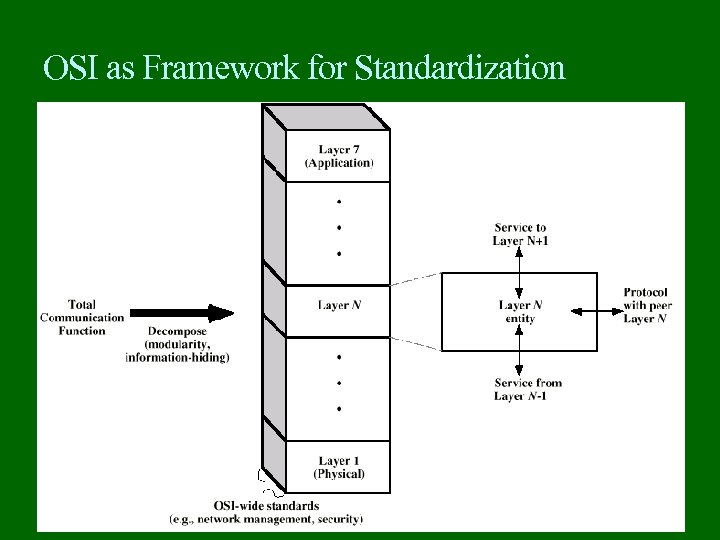 OSI as Framework for Standardization
OSI as Framework for Standardization
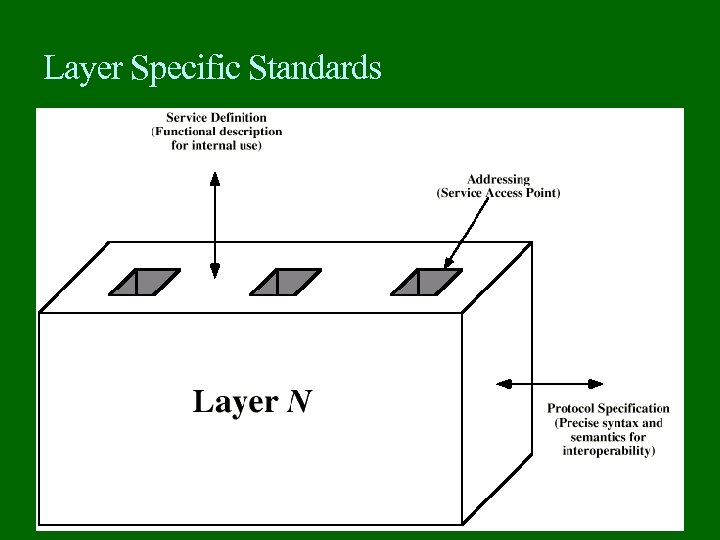 Layer Specific Standards
Layer Specific Standards
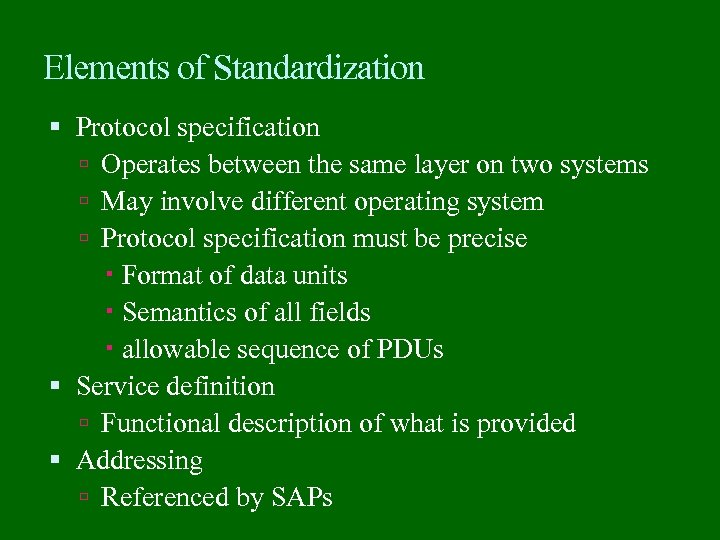 Elements of Standardization Protocol specification Operates between the same layer on two systems May involve different operating system Protocol specification must be precise Format of data units Semantics of all fields allowable sequence of PDUs Service definition Functional description of what is provided Addressing Referenced by SAPs
Elements of Standardization Protocol specification Operates between the same layer on two systems May involve different operating system Protocol specification must be precise Format of data units Semantics of all fields allowable sequence of PDUs Service definition Functional description of what is provided Addressing Referenced by SAPs
 Service Primitives and Parameters Services between adjacent layers expressed in terms of primitives and parameters Primitives specify function to be performed Parameters pass data and control info
Service Primitives and Parameters Services between adjacent layers expressed in terms of primitives and parameters Primitives specify function to be performed Parameters pass data and control info
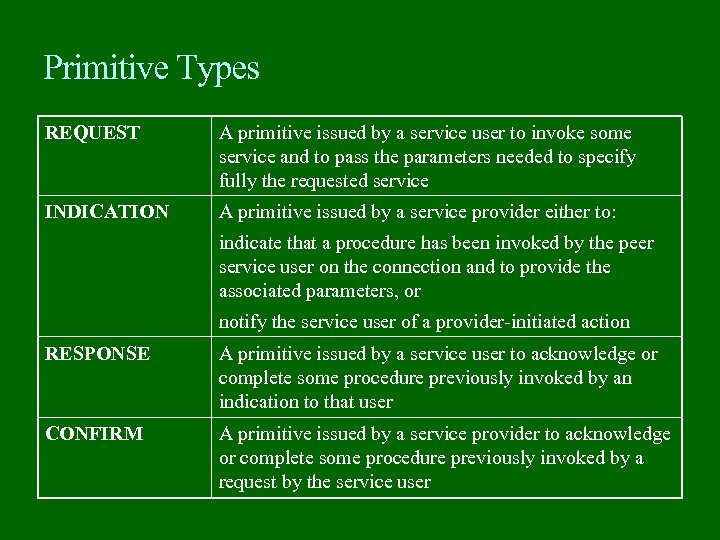 Primitive Types REQUEST A primitive issued by a service user to invoke some service and to pass the parameters needed to specify fully the requested service INDICATION A primitive issued by a service provider either to: indicate that a procedure has been invoked by the peer service user on the connection and to provide the associated parameters, or notify the service user of a provider-initiated action RESPONSE A primitive issued by a service user to acknowledge or complete some procedure previously invoked by an indication to that user CONFIRM A primitive issued by a service provider to acknowledge or complete some procedure previously invoked by a request by the service user
Primitive Types REQUEST A primitive issued by a service user to invoke some service and to pass the parameters needed to specify fully the requested service INDICATION A primitive issued by a service provider either to: indicate that a procedure has been invoked by the peer service user on the connection and to provide the associated parameters, or notify the service user of a provider-initiated action RESPONSE A primitive issued by a service user to acknowledge or complete some procedure previously invoked by an indication to that user CONFIRM A primitive issued by a service provider to acknowledge or complete some procedure previously invoked by a request by the service user
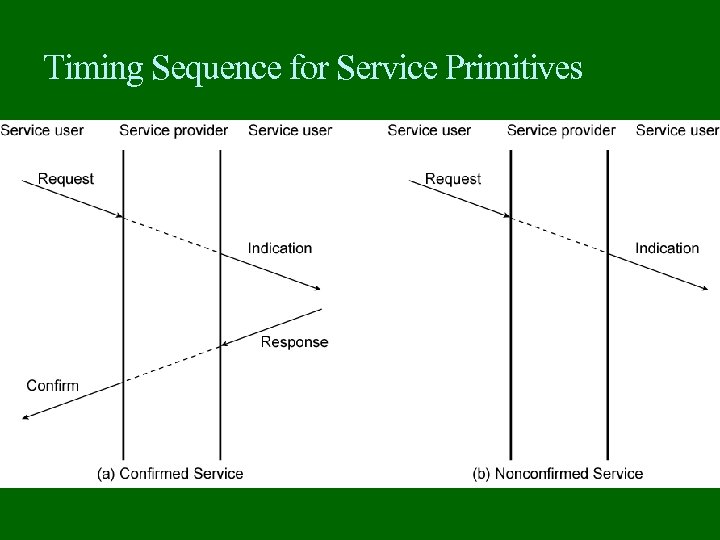 Timing Sequence for Service Primitives
Timing Sequence for Service Primitives
 OSI Layers (1) Physical interface between devices Mechanical Electrical Functional Procedural Data Link Means of activating, maintaining and deactivating a reliable link Error detection and control Higher layers may assume error free transmission
OSI Layers (1) Physical interface between devices Mechanical Electrical Functional Procedural Data Link Means of activating, maintaining and deactivating a reliable link Error detection and control Higher layers may assume error free transmission
 OSI Layers (2) Network Transport of information Higher layers do not need to know about underlying technology Not needed on direct links Transport Exchange of data between end systems Error free In sequence No losses No duplicates Quality of service
OSI Layers (2) Network Transport of information Higher layers do not need to know about underlying technology Not needed on direct links Transport Exchange of data between end systems Error free In sequence No losses No duplicates Quality of service
 OSI Layers (3) Session Control of dialogues between applications Dialogue discipline Grouping Recovery Presentation Data formats and coding Data compression Encryption Application Means for applications to access OSI environment
OSI Layers (3) Session Control of dialogues between applications Dialogue discipline Grouping Recovery Presentation Data formats and coding Data compression Encryption Application Means for applications to access OSI environment
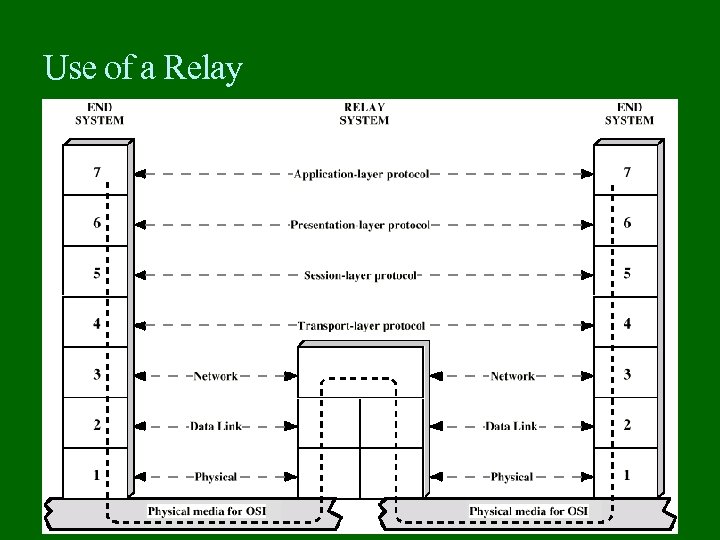 Use of a Relay
Use of a Relay
 TCP/IP Protocol Architecture Developed by the US Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) for its packet switched network (ARPANET) Used by the global Internet No official model but a working one. Application layer Host to host or transport layer Internet layer Network access layer Physical layer
TCP/IP Protocol Architecture Developed by the US Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) for its packet switched network (ARPANET) Used by the global Internet No official model but a working one. Application layer Host to host or transport layer Internet layer Network access layer Physical layer
 Physical Layer Physical interface between data transmission device (e. g. computer) and transmission medium or network Characteristics of transmission medium Signal levels Data rates etc.
Physical Layer Physical interface between data transmission device (e. g. computer) and transmission medium or network Characteristics of transmission medium Signal levels Data rates etc.
 Network Access Layer Exchange of data between end system and network Destination address provision Invoking services like priority
Network Access Layer Exchange of data between end system and network Destination address provision Invoking services like priority
 Internet Layer (IP) Systems may be attached to different networks Routing functions across multiple networks Implemented in end systems and routers
Internet Layer (IP) Systems may be attached to different networks Routing functions across multiple networks Implemented in end systems and routers
 Transport Layer (TCP) Reliable delivery of data Ordering of delivery
Transport Layer (TCP) Reliable delivery of data Ordering of delivery
 Application Layer Support for user applications e. g. http, SMTP
Application Layer Support for user applications e. g. http, SMTP
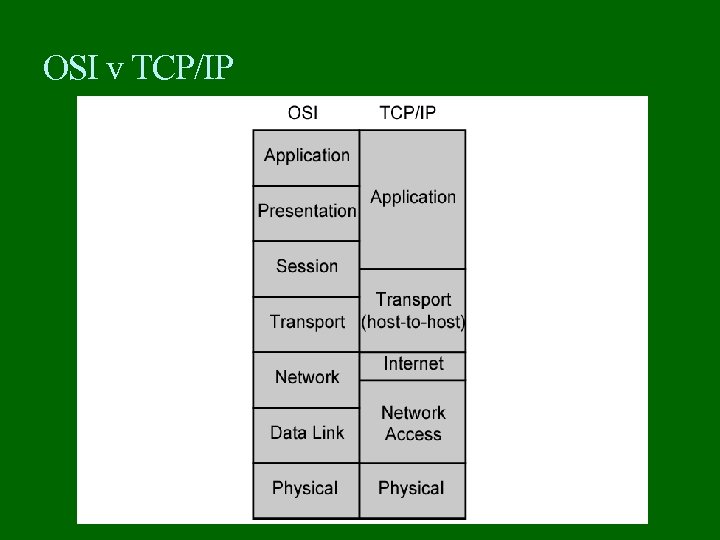 OSI v TCP/IP
OSI v TCP/IP
 TCP Usual transport layer is Transmission Control Protocol Reliable connection Connection Temporary logical association between entities in different systems TCP PDU Called TCP segment Includes source and destination port (c. f. SAP) Identify respective users (applications) Connection refers to pair of ports TCP tracks segments between entities on each connection
TCP Usual transport layer is Transmission Control Protocol Reliable connection Connection Temporary logical association between entities in different systems TCP PDU Called TCP segment Includes source and destination port (c. f. SAP) Identify respective users (applications) Connection refers to pair of ports TCP tracks segments between entities on each connection
 UDP Alternative to TCP is User Datagram Protocol Not guaranteed delivery No preservation of sequence No protection against duplication Minimum overhead Adds port addressing to IP
UDP Alternative to TCP is User Datagram Protocol Not guaranteed delivery No preservation of sequence No protection against duplication Minimum overhead Adds port addressing to IP
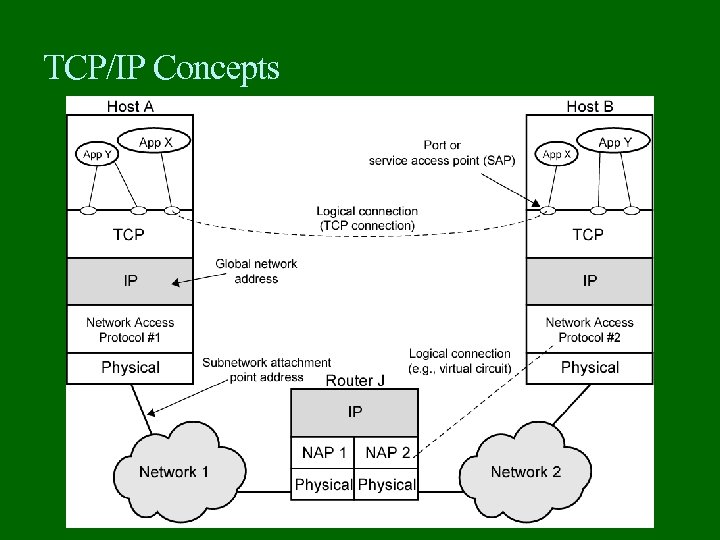 TCP/IP Concepts
TCP/IP Concepts
 Addressing level Level in architecture at which entity is named Unique address for each end system (computer) and router Network level address IP or internet address (TCP/IP) Network service access point or NSAP (OSI) Process within the system Port number (TCP/IP) Service access point or SAP (OSI)
Addressing level Level in architecture at which entity is named Unique address for each end system (computer) and router Network level address IP or internet address (TCP/IP) Network service access point or NSAP (OSI) Process within the system Port number (TCP/IP) Service access point or SAP (OSI)
 Trace of Simple Operation Process associated with port 1 in host A sends message to port 2 in host B Process at A hands down message to TCP to send to port 2 TCP hands down to IP to send to host B IP hands down to network layer (e. g. Ethernet) to send to router J Generates a set of encapsulated PDUs
Trace of Simple Operation Process associated with port 1 in host A sends message to port 2 in host B Process at A hands down message to TCP to send to port 2 TCP hands down to IP to send to host B IP hands down to network layer (e. g. Ethernet) to send to router J Generates a set of encapsulated PDUs
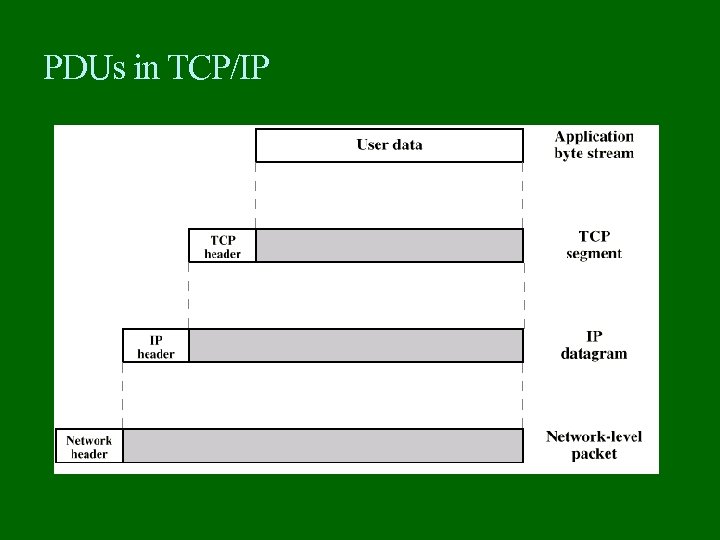 PDUs in TCP/IP
PDUs in TCP/IP
 Example Header Information Destination port Sequence number Checksum
Example Header Information Destination port Sequence number Checksum
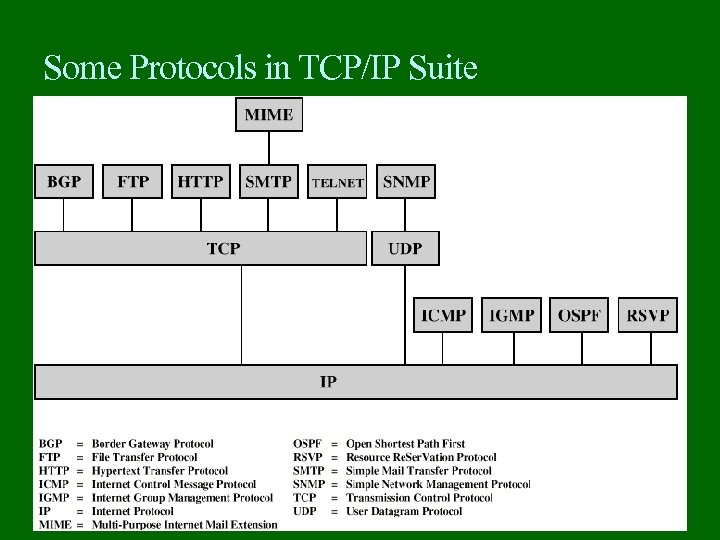 Some Protocols in TCP/IP Suite
Some Protocols in TCP/IP Suite
![Required Reading Stallings, W. [2003] Data and Computer Communications (7 th edition), Prentice Hall, Required Reading Stallings, W. [2003] Data and Computer Communications (7 th edition), Prentice Hall,](https://present5.com/presentation/19d7a677ddc355baeba242b490249449/image-74.jpg) Required Reading Stallings, W. [2003] Data and Computer Communications (7 th edition), Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River NJ, Chapter 2 Web site for Stallings book http: //williamstallings. com/DCC 7 e. html RFCs from Internet
Required Reading Stallings, W. [2003] Data and Computer Communications (7 th edition), Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River NJ, Chapter 2 Web site for Stallings book http: //williamstallings. com/DCC 7 e. html RFCs from Internet
 Q&A ?
Q&A ?


