4c70023bfb42002c256b76ca5e636532.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49

Computer Based Patient Records

Overview • Review the Computer Based Patient Record • Describe the UI CBPR Project • INFORMM Patient Record

Topics of Discussion • • • What is a Computer Based Patient Record? What are the Components? What are the Main Issues? Who are the Major Players? What is the Value?

What is a CBPR? • • • Documentation (e. g. , Medical Record) Workflow Clinical quality improvement Outcomes data http: //www. cpri. org/what. html http: //www. cpri. org/docs. html
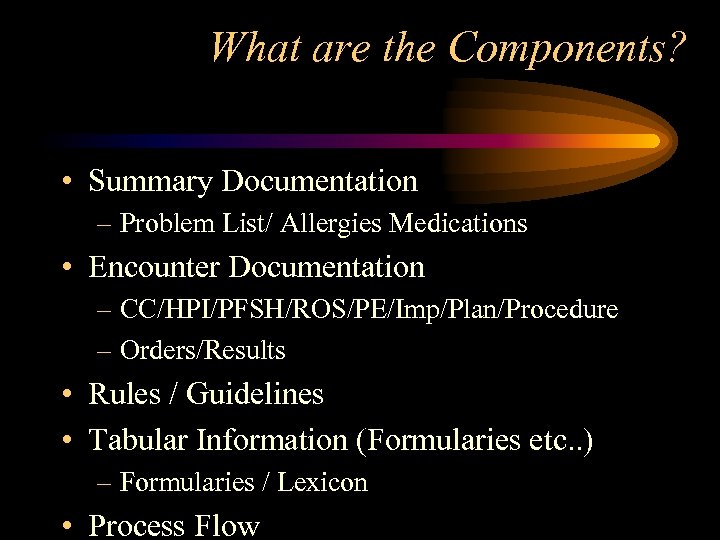
What are the Components? • Summary Documentation – Problem List/ Allergies Medications • Encounter Documentation – CC/HPI/PFSH/ROS/PE/Imp/Plan/Procedure – Orders/Results • Rules / Guidelines • Tabular Information (Formularies etc. . ) – Formularies / Lexicon • Process Flow

Components (cont’d) • Outcomes Tracking – Health Status Indicators – Problem Episode Tracking – Randomized Impact Studies

What are the Main Issues • • Text versus Structured & Coded Security versus Access Buy versus Build Human Interface – GUI / Voice / Wearable • Human Acceptance
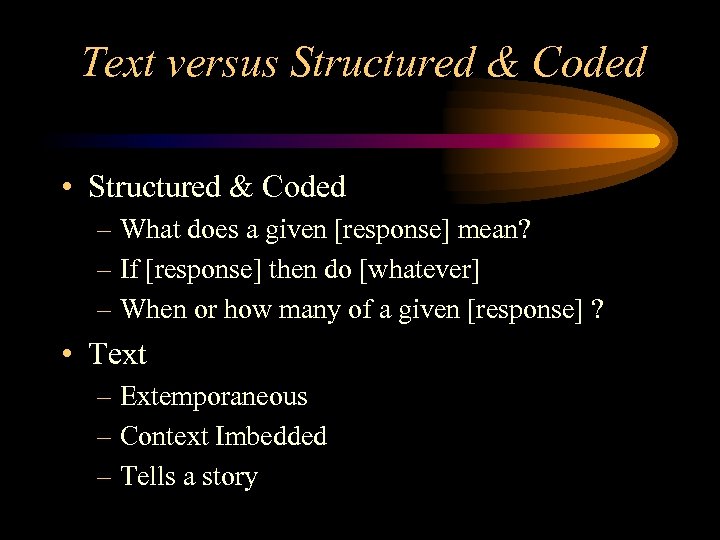
Text versus Structured & Coded • Structured & Coded – What does a given [response] mean? – If [response] then do [whatever] – When or how many of a given [response] ? • Text – Extemporaneous – Context Imbedded – Tells a story

Structured and Coded • Context – Validity • Question and Response – Lexicon – Metathesaurus

Transitioning: Text to Coded • Incomplete Vocabularies – In six defined vocabularies find only 60 -80% • Validity depends on context • Context may be implicit for the educated – nursing documentation – physical exam – test and therapy orders

In the Meanwhile: • Text is necessary • What can we do with it? – Categorize it • structured dictation – Encapsulate it • disallow it wherever possible – Extract from it • lexigraphical analyses have limited success

Security versus Access • Security – Who are you (authentication) – What are your information rights (authorization) – What did you do (audit trail) – How can we ensure integrity of communication • Access – Intuitive Design – Online Intelligent Assistance

Buy versus Build • Buy – Turn-key versus Customizable – Cost-sharing versus Cost-shifting – Support versus Holding-the-Bag • Build – Personal Relationship with the Customer – Talent Pool Stability

Human Interface • GUI – layout itself communicates information – pointing supported • Voice – ready for prime time? • Wearable • Virtual

Human Acceptance • Acceptable Interface • Workflow Makes Sense • Problems - More Solved than Created

Who Are the Major Players • Non-profit Organizations – Academies / Societies / CPRI • Government Institutions – NLM, ASTM • Academic & Medical Institutions – LDS/IMHC / Brigham / Columbia / Stanford – http: //ucsub. colorado. edu/~gorman/thesis/EMR. html • Commercial Product Vendors
http: \www. telemedical. com/ Telemedical/Products/emr. html

Processes • Macro – Birth to Death – Induction to Discharge • Micro – Check-in to Check-out – Chief Complaint to Episode Resolution
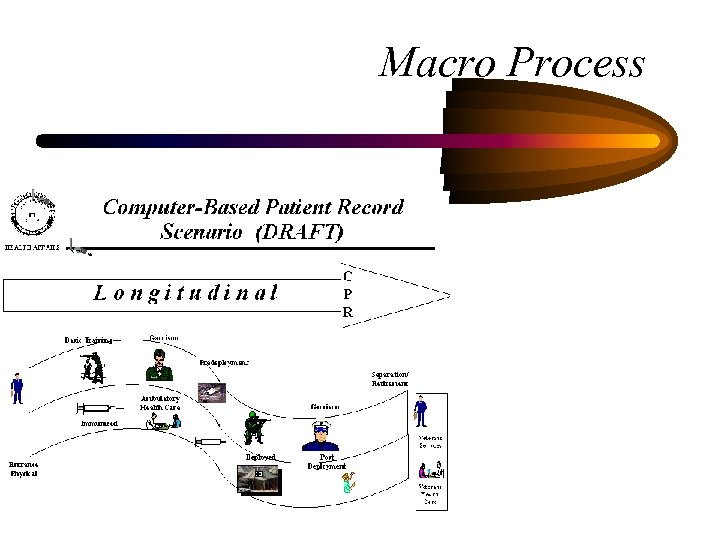
Macro Process

Birth to Death Record • • • Universal Identifier Data Model Vocabulary Data Exchange Security Policy

Micro Process • • • Patient Seeks Attention Patient Responds to Questions Provider Examines Impression and Plan Formed Plan Executed Outcome Assessed

Patient Seeks Attention • Now – Patient Calls or Drops In • Some Enhancements in Progress – System Proactively Advises Patient – Patient Seeks Online Information

Patient Responds to Questions • Now – Provider Assisted – Mostly Text, Some Coded • Some Enhancements in Progress – Coded Questions and Responses – Context-sensitive Branching – Automated Capture of Information – Automated Intelligent Assessment

Provider Examines • Now – Provider Documents After the Fact – Mostly Text, Some Coded • Some Enhancements in Progress – Coded Questions and Responses – Context-sensitive Branching – Automated Capture of Information

Impression and Plan Formed • Now – Information Reviewed (Hx, PE, Results) – Mostly Narrative • Some Enhancements in Progress – Assisted Differential Diagnosis – Guidelines • Evidence Based Medicine – Critical Path

Plan Executed • Now – Orders Written – Procedures Performed – Tests Done • Some Enhancements in Progress – Orders Captured Online with Problem – Plan Process Tracked

Outcome Assessed • Now – Follow Up Visit Narrative – A Few Objective Outcomes are Tracked • Some Enhancements in Progress – Episode Tracking • CC to Assessment to Treatment to Resolution • Beyond the Single Encounter – Outcome Classification • Health Status per Patient Report

Rules Span the Entire Process • If Event Detected – Demographics – History – Result – Order • Then Response – Communicate to Patient / Provider – Execute a Plan

University of Iowa CBPR Project • Phase I • Health Resume and Guidelines • Document System • Phase II • Outpatient Contact Summary – Templates, Coding, Ordering • Phase III • Inpatient Contact Summary – Templates, Coding, Ordering, Guidelines • Images
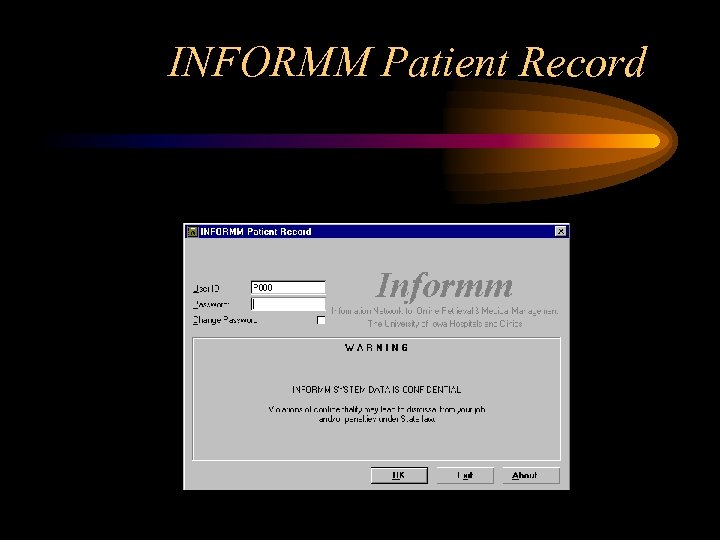
INFORMM Patient Record
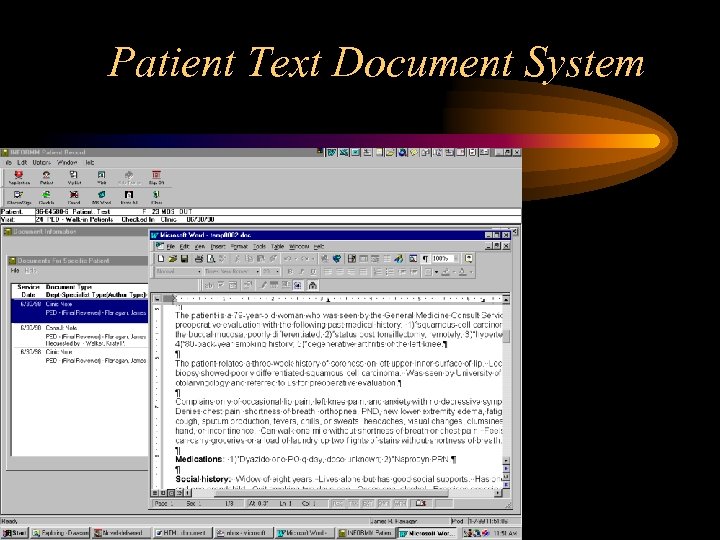
Patient Text Document System
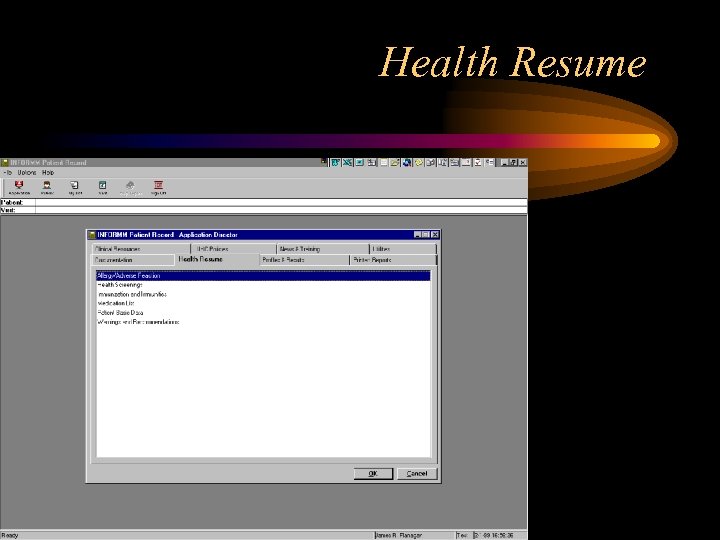
Health Resume
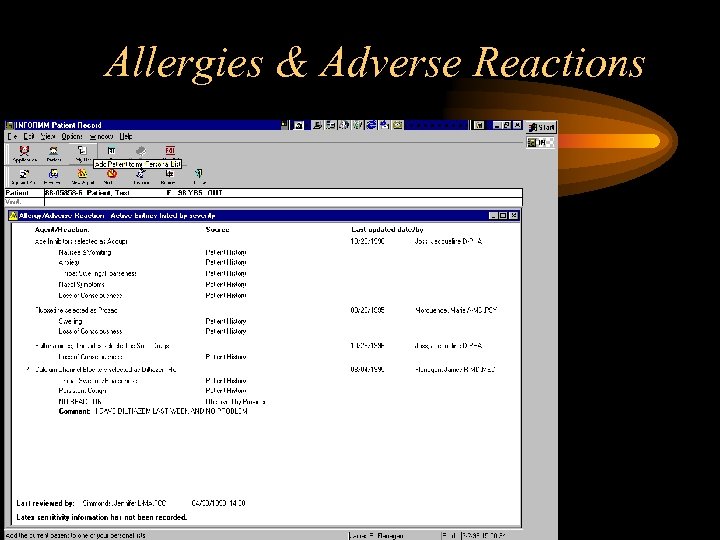
Allergies & Adverse Reactions
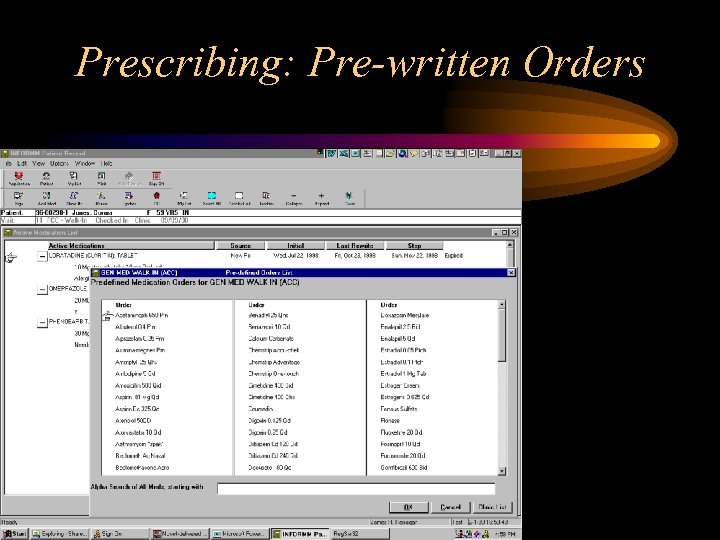
Prescribing: Pre-written Orders
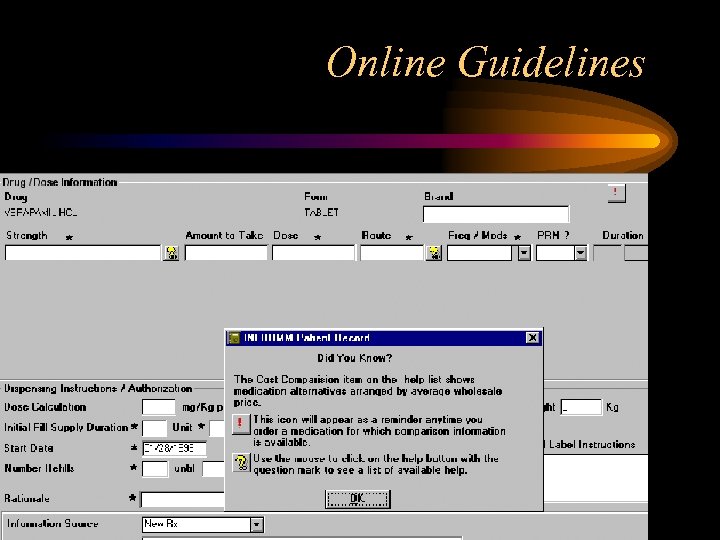
Online Guidelines
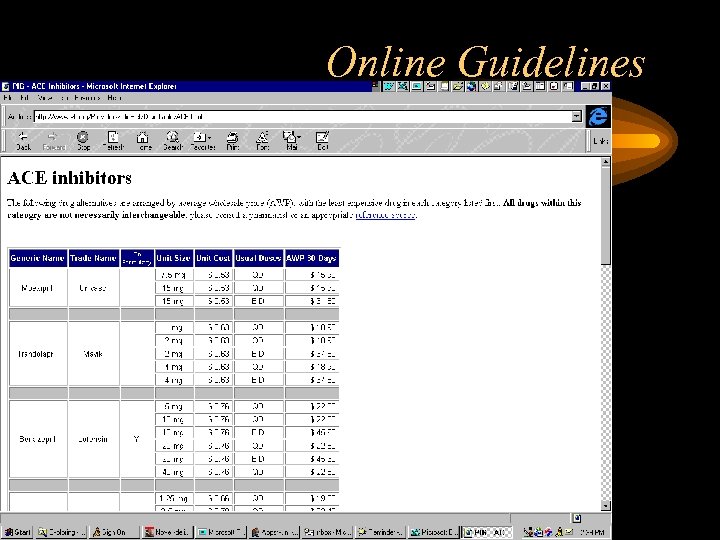
Online Guidelines
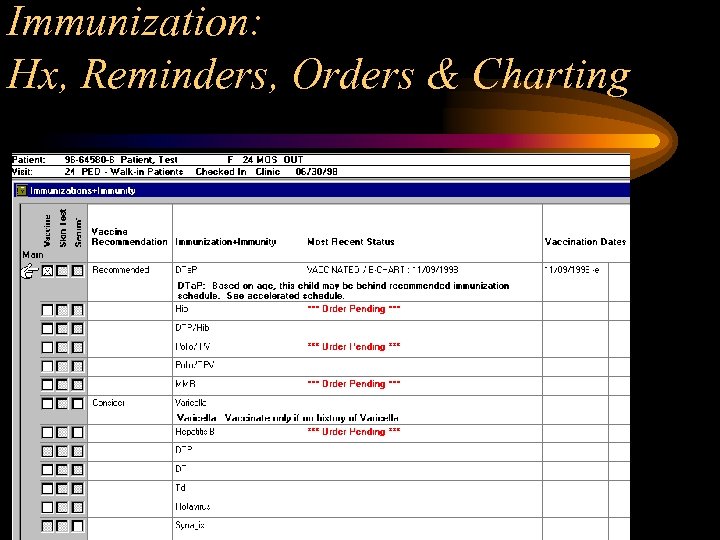
Immunization: Hx, Reminders, Orders & Charting
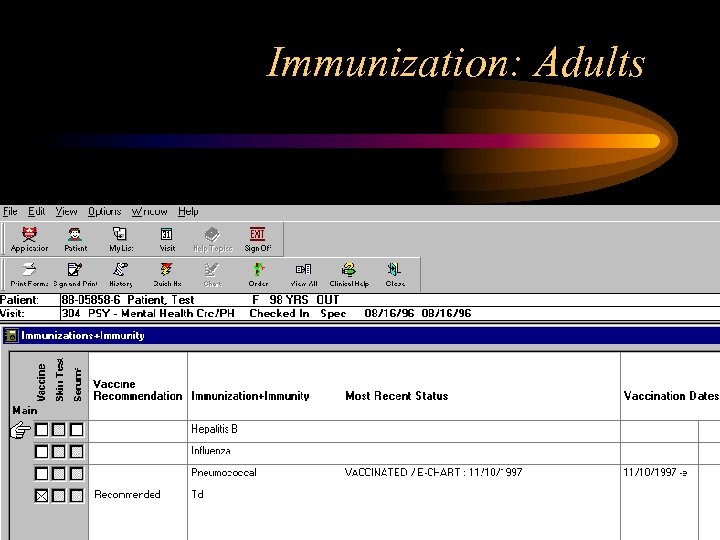
Immunization: Adults
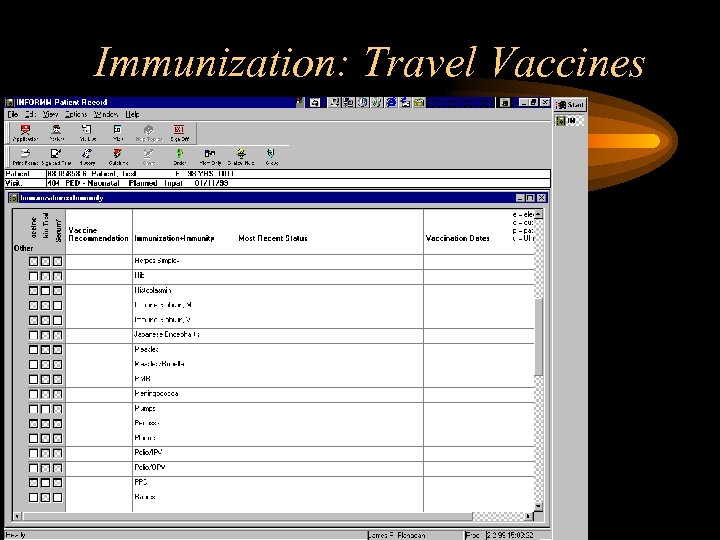
Immunization: Travel Vaccines
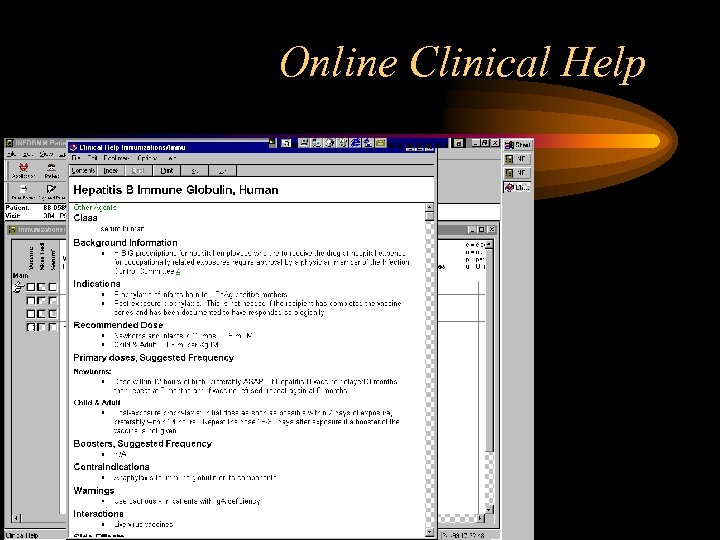
Online Clinical Help
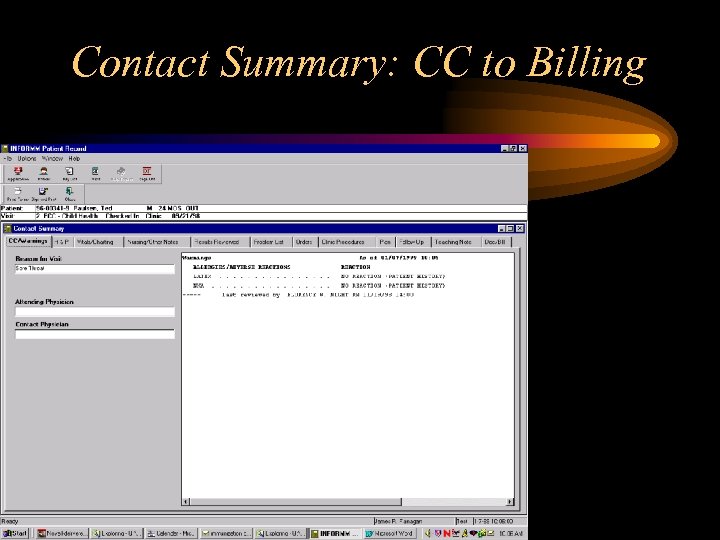
Contact Summary: CC to Billing
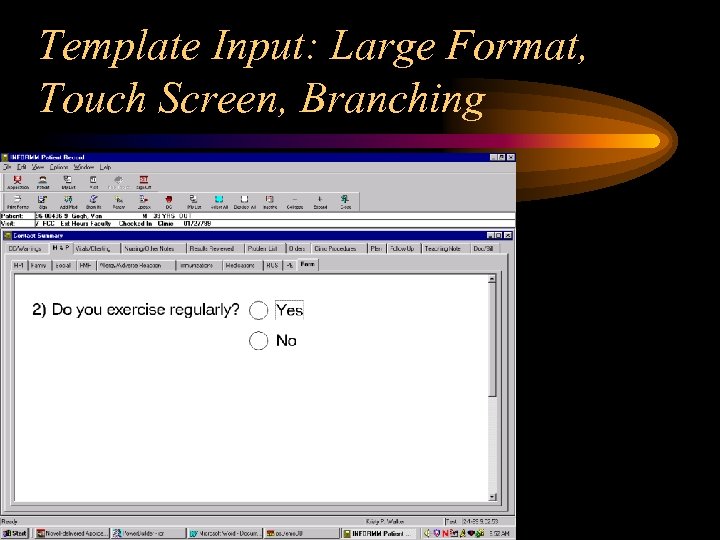
Template Input: Large Format, Touch Screen, Branching
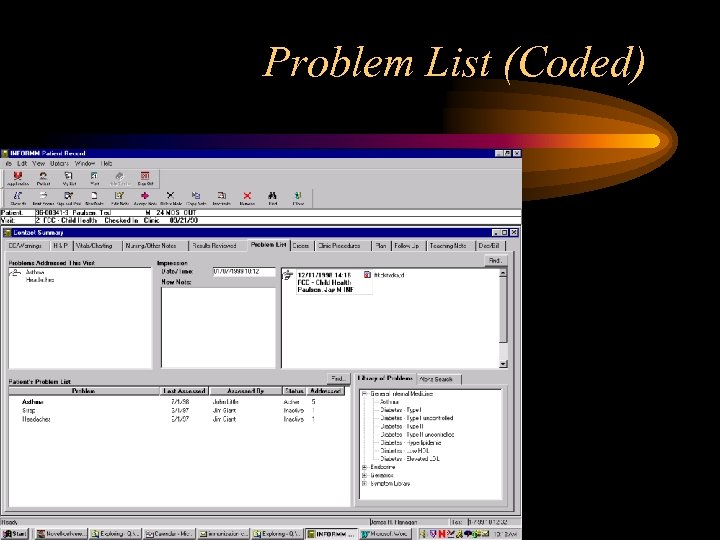
Problem List (Coded)
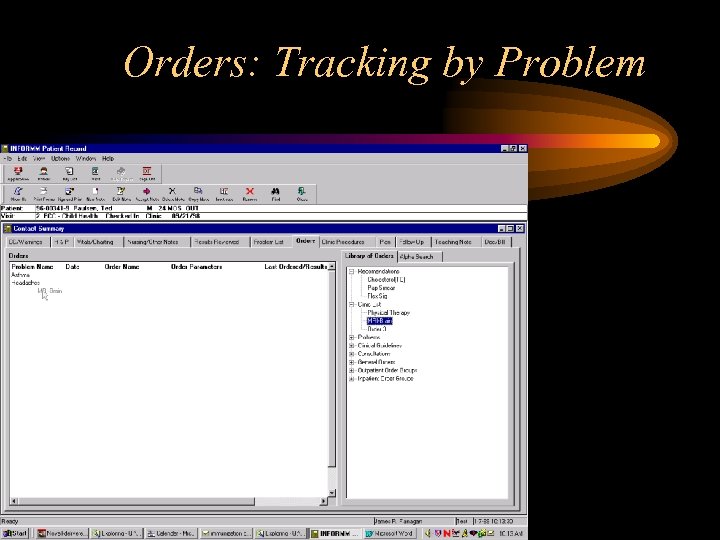
Orders: Tracking by Problem
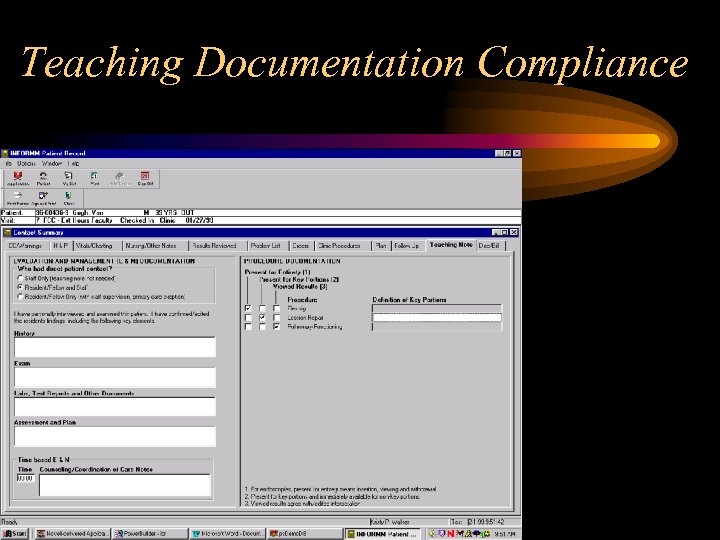
Teaching Documentation Compliance
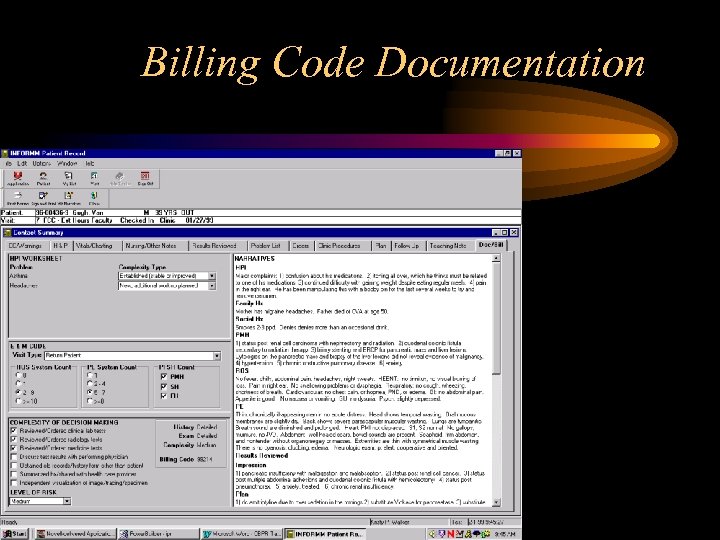
Billing Code Documentation

Online Impact Assessment

Lessons Learned from Experiments • Passive Information Increases Utilization • In-your-face Information Decreases It • If Seen, Information Changes Outcome – second-vaccine ordering – no vaccine ordering – prescription drug ordering

University of Iowa CBPR Project INFORMM Patient Record
4c70023bfb42002c256b76ca5e636532.ppt