155ebb6961bd07ee9e2721f09f920039.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Computer and Information Security Jen-Chang Liu, 2005 http: //staffweb. ncnu. edu. tw/jcliu/course/security 05. html
Computer and Information Security Jen-Chang Liu, 2005 http: //staffweb. ncnu. edu. tw/jcliu/course/security 05. html
 Security Group in NCNU n n 2003/4, we have started a security study group in NCNU Members: n n n 黃育銘 陳彥錚(資管系) 阮夙姿 劉震昌 We have a security seminar on Friday morning
Security Group in NCNU n n 2003/4, we have started a security study group in NCNU Members: n n n 黃育銘 陳彥錚(資管系) 阮夙姿 劉震昌 We have a security seminar on Friday morning
 Class material n Textbook n n Reference: n n "Cryptography and Network Security", William Stallings , 3 rd Edition, Prentice Hall "Cryptography: Theory and Practice", Stinson, Chapman & Hall/CRC, 2002. Homepage n http: //staffweb. ncnu. edu. tw/jcliu/course/security 05. html
Class material n Textbook n n Reference: n n "Cryptography and Network Security", William Stallings , 3 rd Edition, Prentice Hall "Cryptography: Theory and Practice", Stinson, Chapman & Hall/CRC, 2002. Homepage n http: //staffweb. ncnu. edu. tw/jcliu/course/security 05. html
 Class schedule n Tuesday 2: 10~4: 00 p. m. n n lecture Tuesday 4: 10 -5: 00 p. m. n n n lecture Homework presentation Textbook presentation Quiz Cautious: If you think the load is too much for you, don’t take this course.
Class schedule n Tuesday 2: 10~4: 00 p. m. n n lecture Tuesday 4: 10 -5: 00 p. m. n n n lecture Homework presentation Textbook presentation Quiz Cautious: If you think the load is too much for you, don’t take this course.
 Aim of Course n Understand basic concept of cryptography ( 密碼學) system… n n Cover network security or applications if time is available Scoring n n n 50% homework, quiz, and class presentation 25% exam. for finite field, DES, and AES 25% final project
Aim of Course n Understand basic concept of cryptography ( 密碼學) system… n n Cover network security or applications if time is available Scoring n n n 50% homework, quiz, and class presentation 25% exam. for finite field, DES, and AES 25% final project
 Outline of this book n n Part I: Symmetric encryption Part II: Asymmetric encryption (public-key) Part III: Network security Part IV: System security
Outline of this book n n Part I: Symmetric encryption Part II: Asymmetric encryption (public-key) Part III: Network security Part IV: System security
 Chapter 1 – Introduction The art of war teaches us to rely not on the likelihood of the enemy's not coming, but on our own readiness to receive him; not on the chance of his not attacking, but rather on the fact that we have made our position unassailable. —The Art of War, Sun Tzu 無恃其不來, 恃吾有以待也; 無恃其不攻, 恃吾有所不可攻也。
Chapter 1 – Introduction The art of war teaches us to rely not on the likelihood of the enemy's not coming, but on our own readiness to receive him; not on the chance of his not attacking, but rather on the fact that we have made our position unassailable. —The Art of War, Sun Tzu 無恃其不來, 恃吾有以待也; 無恃其不攻, 恃吾有所不可攻也。
 Background n Information Security requirements have changed in recent times n n n traditionally provided by physical and administrative mechanisms Computer use requires automated tools to protect files and other stored information Use of networks and communications links requires measures to protect data during transmission
Background n Information Security requirements have changed in recent times n n n traditionally provided by physical and administrative mechanisms Computer use requires automated tools to protect files and other stored information Use of networks and communications links requires measures to protect data during transmission
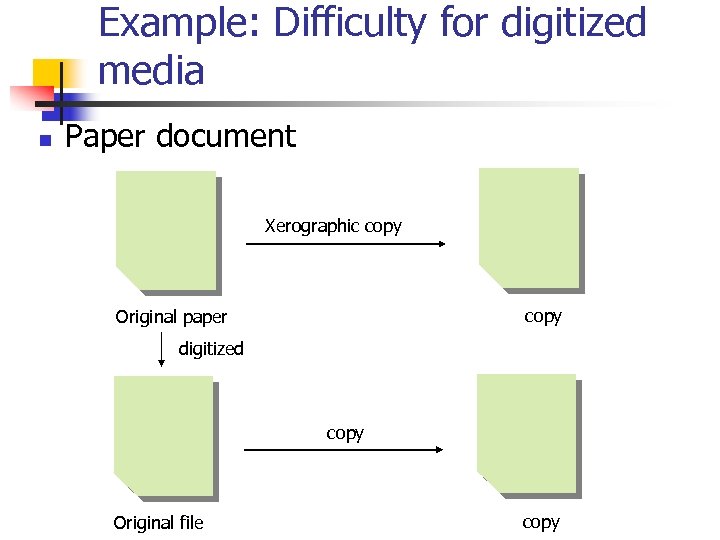 Example: Difficulty for digitized media n Paper document Xerographic copy Original paper digitized copy Original file copy
Example: Difficulty for digitized media n Paper document Xerographic copy Original paper digitized copy Original file copy
 Definitions n n n Computer Security - generic name for the collection of tools designed to protect data and to thwart hackers Network Security - measures to protect data during their transmission Internet Security - measures to protect data during their transmission over a collection of interconnected networks
Definitions n n n Computer Security - generic name for the collection of tools designed to protect data and to thwart hackers Network Security - measures to protect data during their transmission Internet Security - measures to protect data during their transmission over a collection of interconnected networks
 Model for Network Security
Model for Network Security
 Services, Mechanisms, Attacks n n need systematic way to define requirements consider three aspects of information security: n n security attack security mechanism security service X. 800 Security Architecture
Services, Mechanisms, Attacks n n need systematic way to define requirements consider three aspects of information security: n n security attack security mechanism security service X. 800 Security Architecture
 Security Service n n is something that enhances the security of the data processing systems and the information transfers of an organization intended to counter security attacks make use of one or more security mechanisms to provide the service replicate functions normally associated with physical documents n eg. Physical document have signatures, dates; need protection from disclosure, tampering, or destruction; be notarized(公證) or witnessed; be recorded or licensed
Security Service n n is something that enhances the security of the data processing systems and the information transfers of an organization intended to counter security attacks make use of one or more security mechanisms to provide the service replicate functions normally associated with physical documents n eg. Physical document have signatures, dates; need protection from disclosure, tampering, or destruction; be notarized(公證) or witnessed; be recorded or licensed
 Security Mechanism n n n a mechanism that is designed to detect, prevent, or recover from a security attack no single mechanism that will support all functions required however one particular element underlies many of the security mechanisms in use: cryptographic techniques
Security Mechanism n n n a mechanism that is designed to detect, prevent, or recover from a security attack no single mechanism that will support all functions required however one particular element underlies many of the security mechanisms in use: cryptographic techniques
 Security Attack n n any action that compromises the security of information owned by an organization note: often threat & attack mean same
Security Attack n n any action that compromises the security of information owned by an organization note: often threat & attack mean same
 OSI Security Architecture n ITU-T Recommendation X. 800 Security Architecture for OSI n defines a systematic way of defining and providing security requirements Security attacks Security mechanisms Security services
OSI Security Architecture n ITU-T Recommendation X. 800 Security Architecture for OSI n defines a systematic way of defining and providing security requirements Security attacks Security mechanisms Security services
 X. 800 Security Services n n n X. 800 defines it as: a service provided by a protocol layer of communicating open systems, which ensures adequate security of the systems or of data transfers RFC 2828 defines it as: a processing or communication service provided by a system to give a specific kind of protection to system resources X. 800 defines it in 5 major categories
X. 800 Security Services n n n X. 800 defines it as: a service provided by a protocol layer of communicating open systems, which ensures adequate security of the systems or of data transfers RFC 2828 defines it as: a processing or communication service provided by a system to give a specific kind of protection to system resources X. 800 defines it in 5 major categories
 Security Services (X. 800) n n n Authentication(認證) - assurance that the communicating entity is the one claimed Access Control - prevention of the unauthorized use of a resource Data Confidentiality –protection of data from unauthorized disclosure Data Integrity - assurance that data received is as sent by an authorized entity Non-Repudiation (不可拒絕) - protection against denial by one of the parties in a communication
Security Services (X. 800) n n n Authentication(認證) - assurance that the communicating entity is the one claimed Access Control - prevention of the unauthorized use of a resource Data Confidentiality –protection of data from unauthorized disclosure Data Integrity - assurance that data received is as sent by an authorized entity Non-Repudiation (不可拒絕) - protection against denial by one of the parties in a communication
 Security Mechanisms (X. 800) n Specific security mechanisms: n n encipherment, digital signatures, access controls, data integrity, authentication exchange, traffic padding, routing control, notarization Pervasive(普遍性) security mechanisms: n n trusted functionality, security labels, event detection, security audit trails, security recovery Check Table 1. 5 in textbook
Security Mechanisms (X. 800) n Specific security mechanisms: n n encipherment, digital signatures, access controls, data integrity, authentication exchange, traffic padding, routing control, notarization Pervasive(普遍性) security mechanisms: n n trusted functionality, security labels, event detection, security audit trails, security recovery Check Table 1. 5 in textbook
 Security Attacks (X. 800) n passive attacks – eavesdropping(偷聽) on, or monitoring of, transmissions to: n n n obtain message contents, or monitor traffic flows active attacks – modification of data stream to: n n masquerade(偽裝) of one entity as some other replay previous messages modify messages in transit denial of service
Security Attacks (X. 800) n passive attacks – eavesdropping(偷聽) on, or monitoring of, transmissions to: n n n obtain message contents, or monitor traffic flows active attacks – modification of data stream to: n n masquerade(偽裝) of one entity as some other replay previous messages modify messages in transit denial of service
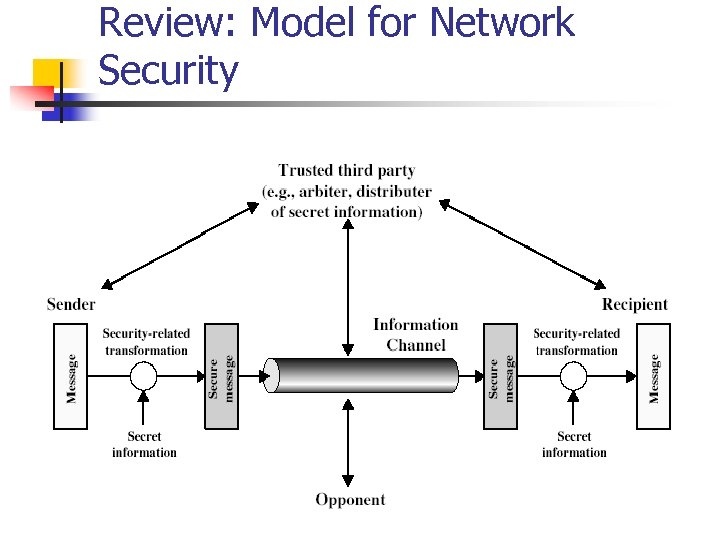 Review: Model for Network Security
Review: Model for Network Security
 Model for Network Security n using this model requires us to: n n design a suitable algorithm for the security transformation generate the secret information (keys) used by the algorithm develop methods to distribute and share the secret information specify a protocol enabling the principals to use the transformation and secret information for a security service
Model for Network Security n using this model requires us to: n n design a suitable algorithm for the security transformation generate the secret information (keys) used by the algorithm develop methods to distribute and share the secret information specify a protocol enabling the principals to use the transformation and secret information for a security service
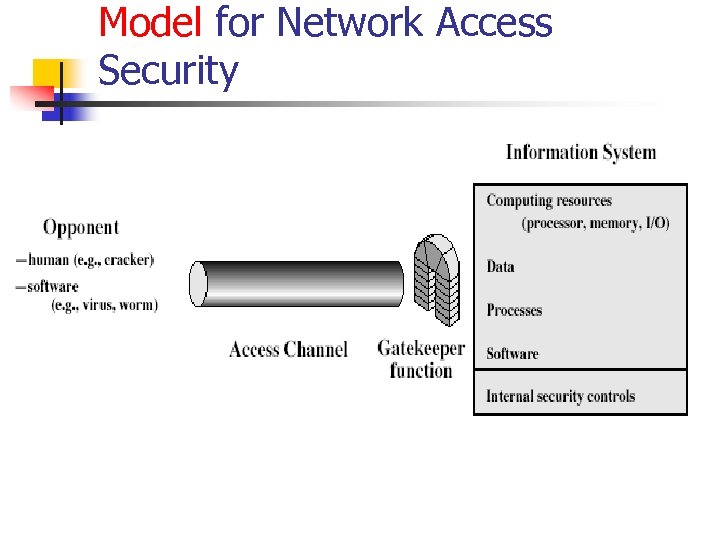 Model for Network Access Security
Model for Network Access Security
 Model for Network Access Security n using this model requires us to: n n select appropriate gatekeeper functions to identify users implement security controls to ensure only authorised users access designated information or resources
Model for Network Access Security n using this model requires us to: n n select appropriate gatekeeper functions to identify users implement security controls to ensure only authorised users access designated information or resources
 Summary n have considered: n n computer, network, internet security def’s security services, mechanisms, attacks X. 800 standard models for network (access) security
Summary n have considered: n n computer, network, internet security def’s security services, mechanisms, attacks X. 800 standard models for network (access) security


