8492b117f2483b0277fa68160c05b19f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Computational Methods and Imaging in Medicine HEALTH INFORMATICS MODULE INTRODUCTION Dr Jeremy Rogers MD MRCGP Senior Clinical Fellow in Health Informatics Northwest Institute of Bio-Health Informatics
Computational Methods and Imaging in Medicine HEALTH INFORMATICS MODULE INTRODUCTION Dr Jeremy Rogers MD MRCGP Senior Clinical Fellow in Health Informatics Northwest Institute of Bio-Health Informatics
 Outline ►What Health Informatics is ►Who wants Health Informatics ►A history of Health Informatics
Outline ►What Health Informatics is ►Who wants Health Informatics ►A history of Health Informatics
 What Health Informatics is
What Health Informatics is
 What is health informatics ? Informatics, as applied to healthcare, of course!
What is health informatics ? Informatics, as applied to healthcare, of course!
 What’s Informatics, then? ► Jargon term, even in 2005 ► Some dictionaries x. Refer to ‘Information Science’ ► = librarianship ‘The creation, recognition, representation, collection, organization, transformation, communication, evaluation and control of information in a system… The art, science and human dimensions of information technologies. ’ Indiana University School of Journalism 2002
What’s Informatics, then? ► Jargon term, even in 2005 ► Some dictionaries x. Refer to ‘Information Science’ ► = librarianship ‘The creation, recognition, representation, collection, organization, transformation, communication, evaluation and control of information in a system… The art, science and human dimensions of information technologies. ’ Indiana University School of Journalism 2002
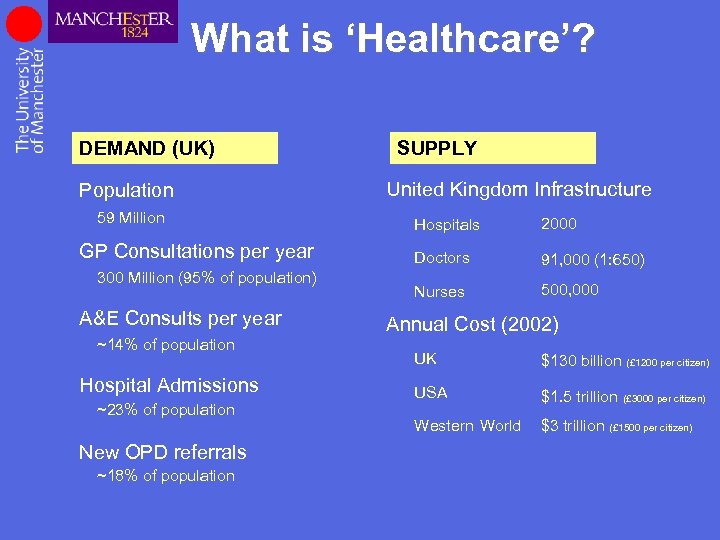 What is ‘Healthcare’? DEMAND (UK) Population 59 Million GP Consultations per year 300 Million (95% of population) A&E Consults per year ~14% of population Hospital Admissions ~23% of population New OPD referrals ~18% of population SUPPLY United Kingdom Infrastructure Hospitals 2000 Doctors 91, 000 (1: 650) Nurses 500, 000 Annual Cost (2002) UK $130 billion (£ 1200 per citizen) USA $1. 5 trillion (£ 3000 per citizen) Western World $3 trillion (£ 1500 per citizen)
What is ‘Healthcare’? DEMAND (UK) Population 59 Million GP Consultations per year 300 Million (95% of population) A&E Consults per year ~14% of population Hospital Admissions ~23% of population New OPD referrals ~18% of population SUPPLY United Kingdom Infrastructure Hospitals 2000 Doctors 91, 000 (1: 650) Nurses 500, 000 Annual Cost (2002) UK $130 billion (£ 1200 per citizen) USA $1. 5 trillion (£ 3000 per citizen) Western World $3 trillion (£ 1500 per citizen)
 What health informatics is #1 The understanding, skills and tools that enable the sharing and use of information to deliver healthcare and promote health. British Health Informatics Society
What health informatics is #1 The understanding, skills and tools that enable the sharing and use of information to deliver healthcare and promote health. British Health Informatics Society
 What health informatics is #2 The knowledge, skills and tools which enable information to be collected, managed, used and shared to support the delivery of healthcare and promote health (qv BMIS) Lead, promote and manage use of resources to improve health care delivery Identify, collect, analyse, disseminate and maintain data and information to improve health care delivery Enable, develop and manage knowledge to improve health care delivery Plan, implement, sustain and review the provision of ICT to support and improve health care delivery NHS National Occupational Standards for Health Informatics 2004
What health informatics is #2 The knowledge, skills and tools which enable information to be collected, managed, used and shared to support the delivery of healthcare and promote health (qv BMIS) Lead, promote and manage use of resources to improve health care delivery Identify, collect, analyse, disseminate and maintain data and information to improve health care delivery Enable, develop and manage knowledge to improve health care delivery Plan, implement, sustain and review the provision of ICT to support and improve health care delivery NHS National Occupational Standards for Health Informatics 2004
 What health informatics is #3 It is the rational study of the way we think about patients, and the way that treatments are defined, selected and evolved. It is the study of how clinical knowledge is created, shaped, shared and applied. Ultimately, it is the study of how we organise ourselves to create and run healthcare organisations. Enrico Coiera, U New South Wales Guide to Health Informatics 2 nd Edition
What health informatics is #3 It is the rational study of the way we think about patients, and the way that treatments are defined, selected and evolved. It is the study of how clinical knowledge is created, shaped, shared and applied. Ultimately, it is the study of how we organise ourselves to create and run healthcare organisations. Enrico Coiera, U New South Wales Guide to Health Informatics 2 nd Edition
 What health informatics is #4 The scientific field that deals with the storage, retrieval, sharing, and optimal use of biomedical information, data, and knowledge for problem solving and decision making. It touches on all basic and applied fields in biomedical science and is closely tied to modern information technologies, notably in the areas of computing and communication. The emergence of medical informatics as a new discipline is due in large part to rapid advances in computing and communications technology, to an increasing awareness that the knowledge base of biomedicine is essentially unmanageable by traditional paper-based methods, and to a growing conviction that the process of informed decision making is as important to modern biomedicine as is the collection of facts on which clinical decisions or research plans are made. Ted Shortliffe, Columbia University
What health informatics is #4 The scientific field that deals with the storage, retrieval, sharing, and optimal use of biomedical information, data, and knowledge for problem solving and decision making. It touches on all basic and applied fields in biomedical science and is closely tied to modern information technologies, notably in the areas of computing and communication. The emergence of medical informatics as a new discipline is due in large part to rapid advances in computing and communications technology, to an increasing awareness that the knowledge base of biomedicine is essentially unmanageable by traditional paper-based methods, and to a growing conviction that the process of informed decision making is as important to modern biomedicine as is the collection of facts on which clinical decisions or research plans are made. Ted Shortliffe, Columbia University
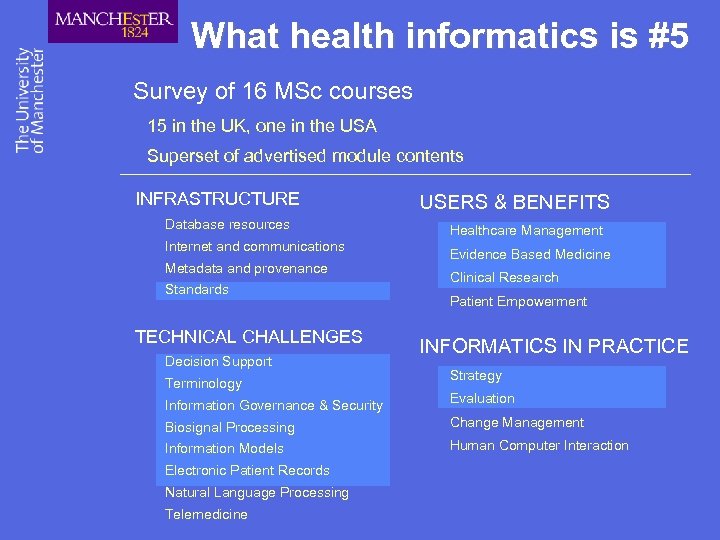 What health informatics is #5 Survey of 16 MSc courses 15 in the UK, one in the USA Superset of advertised module contents INFRASTRUCTURE Database resources Internet and communications Metadata and provenance Standards TECHNICAL CHALLENGES Decision Support Terminology USERS & BENEFITS Healthcare Management Evidence Based Medicine Clinical Research Patient Empowerment INFORMATICS IN PRACTICE Strategy Information Governance & Security Evaluation Biosignal Processing Change Management Information Models Human Computer Interaction Electronic Patient Records Natural Language Processing Telemedicine
What health informatics is #5 Survey of 16 MSc courses 15 in the UK, one in the USA Superset of advertised module contents INFRASTRUCTURE Database resources Internet and communications Metadata and provenance Standards TECHNICAL CHALLENGES Decision Support Terminology USERS & BENEFITS Healthcare Management Evidence Based Medicine Clinical Research Patient Empowerment INFORMATICS IN PRACTICE Strategy Information Governance & Security Evaluation Biosignal Processing Change Management Information Models Human Computer Interaction Electronic Patient Records Natural Language Processing Telemedicine
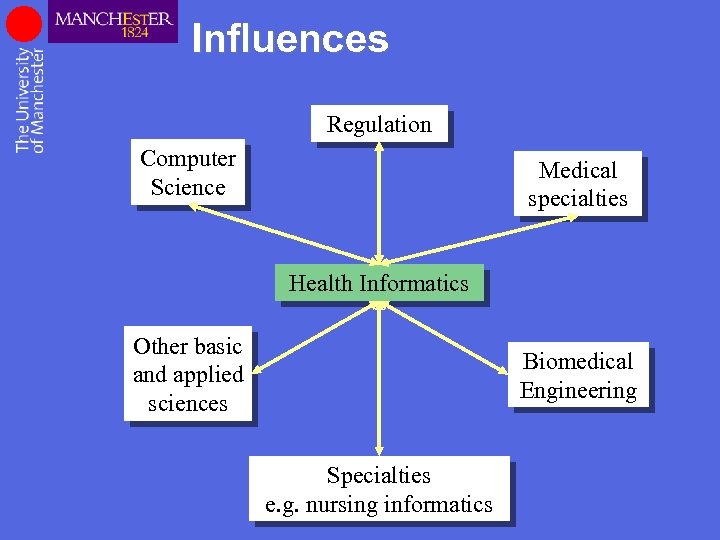 Influences Regulation Computer Science Medical specialties Health Informatics Other basic and applied sciences Biomedical Engineering Specialties e. g. nursing informatics
Influences Regulation Computer Science Medical specialties Health Informatics Other basic and applied sciences Biomedical Engineering Specialties e. g. nursing informatics
 Health Informatics: Broad Themes Complexity – systems (Coiera) Human factors Standards Ownership of data Data entry Integration Ethics Evaluation
Health Informatics: Broad Themes Complexity – systems (Coiera) Human factors Standards Ownership of data Data entry Integration Ethics Evaluation
 Who wants Health Informatics?
Who wants Health Informatics?
 Who wants health informatics? The Clinicians’ Story ► 11% of lab tests repeated ► Because result is lost ► 30% of treatment orders are undocumented ► 70% of acutely ill patients get right treatment ► 30% get contraindicated treatment ► 500% growth in number of new drugs in a decade
Who wants health informatics? The Clinicians’ Story ► 11% of lab tests repeated ► Because result is lost ► 30% of treatment orders are undocumented ► 70% of acutely ill patients get right treatment ► 30% get contraindicated treatment ► 500% growth in number of new drugs in a decade
 One doctor’s clinic…. …one patient’s notes
One doctor’s clinic…. …one patient’s notes
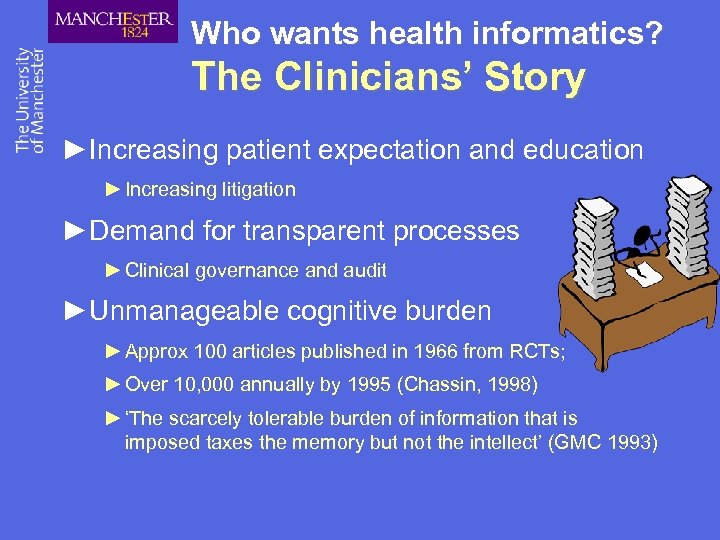 Who wants health informatics? The Clinicians’ Story ►Increasing patient expectation and education ► Increasing litigation ►Demand for transparent processes ► Clinical governance and audit ►Unmanageable cognitive burden ► Approx 100 articles published in 1966 from RCTs; ► Over 10, 000 annually by 1995 (Chassin, 1998) ► ‘The scarcely tolerable burden of information that is imposed taxes the memory but not the intellect’ (GMC 1993)
Who wants health informatics? The Clinicians’ Story ►Increasing patient expectation and education ► Increasing litigation ►Demand for transparent processes ► Clinical governance and audit ►Unmanageable cognitive burden ► Approx 100 articles published in 1966 from RCTs; ► Over 10, 000 annually by 1995 (Chassin, 1998) ► ‘The scarcely tolerable burden of information that is imposed taxes the memory but not the intellect’ (GMC 1993)
 Who wants health informatics? The Accountants’ Story ►Spiralling health care costs ►Developed world in 2002: USD $3 Trillion on 1. 2 billion people ► 11% of GDP ►e. g. $5. 5 M in 37 Days on one patient (Duke University) ►Per capita health cost inflation: 8% per year ►Population expansion ►Demographic shift ►New advances ►No visible means of control
Who wants health informatics? The Accountants’ Story ►Spiralling health care costs ►Developed world in 2002: USD $3 Trillion on 1. 2 billion people ► 11% of GDP ►e. g. $5. 5 M in 37 Days on one patient (Duke University) ►Per capita health cost inflation: 8% per year ►Population expansion ►Demographic shift ►New advances ►No visible means of control
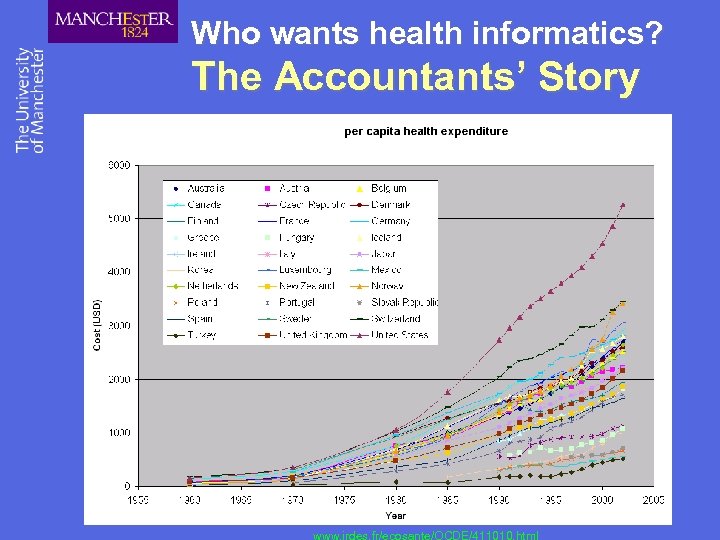 Who wants health informatics? The Accountants’ Story www. irdes. fr/ecosante/OCDE/411010. html
Who wants health informatics? The Accountants’ Story www. irdes. fr/ecosante/OCDE/411010. html
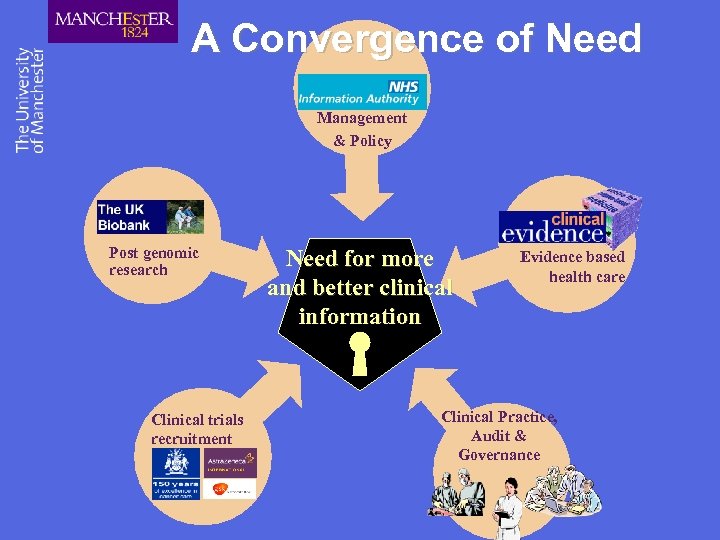 A Convergence of Need Management & Policy Post genomic research Clinical trials recruitment Need for more and better clinical information Evidence based health care Clinical Practice, Audit & Governance
A Convergence of Need Management & Policy Post genomic research Clinical trials recruitment Need for more and better clinical information Evidence based health care Clinical Practice, Audit & Governance
 Who wants health informatics? Stakeholders ►Health professionals ► Doctors (Primary / secondary care) ► Nurses ► Allied professions ►Administrators / Government ►Researchers ►Pharmaceutical Companies ►IT professionals ►Patients ? ? ? ? ?
Who wants health informatics? Stakeholders ►Health professionals ► Doctors (Primary / secondary care) ► Nurses ► Allied professions ►Administrators / Government ►Researchers ►Pharmaceutical Companies ►IT professionals ►Patients ? ? ? ? ?
 Health Informatics: A History
Health Informatics: A History
 Computers 1950 Prototypes 1960 Transistors 1970 Integrated circuits 1980 Microcomputer; Windows. 1990 Internet; Web 2000 Google
Computers 1950 Prototypes 1960 Transistors 1970 Integrated circuits 1980 Microcomputer; Windows. 1990 Internet; Web 2000 Google
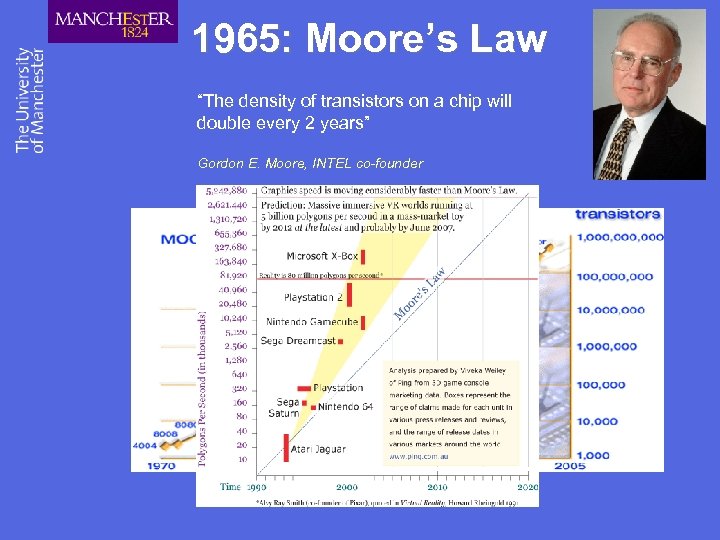 1965: Moore’s Law “The density of transistors on a chip will double every 2 years” Gordon E. Moore, INTEL co-founder
1965: Moore’s Law “The density of transistors on a chip will double every 2 years” Gordon E. Moore, INTEL co-founder
 Health informatics A History: The 50 s & 60 s 1959 Ledley “Reasoning foundations of medical diagnosis” 1960’s onward – Barnett “Mumps” 1961 Methods Inf Medicine Vol 1 1964 NLM adopts Medlars / Index Medicus 1969 Weed “Problem-oriented medical record” 1969 World’s first EPR First version had 4 k core and 1 k for each of 4 users. Everything stored on tape (1 per patient). ‘Great day’ when got first hard disk, storing 30 k Nursing system, Kings College London Systems predominantly for payroll, or pathology High volume Repetitious Rule-based processing (of numerical data)
Health informatics A History: The 50 s & 60 s 1959 Ledley “Reasoning foundations of medical diagnosis” 1960’s onward – Barnett “Mumps” 1961 Methods Inf Medicine Vol 1 1964 NLM adopts Medlars / Index Medicus 1969 Weed “Problem-oriented medical record” 1969 World’s first EPR First version had 4 k core and 1 k for each of 4 users. Everything stored on tape (1 per patient). ‘Great day’ when got first hard disk, storing 30 k Nursing system, Kings College London Systems predominantly for payroll, or pathology High volume Repetitious Rule-based processing (of numerical data)
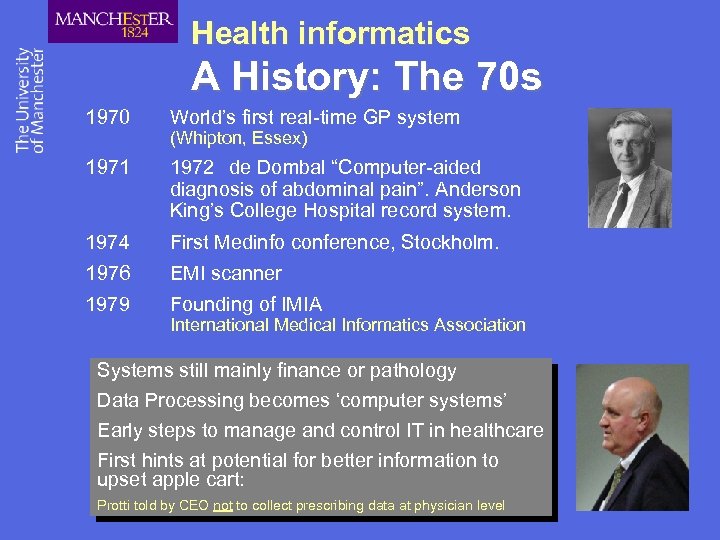 Health informatics A History: The 70 s 1970 World’s first real-time GP system 1971 1972 de Dombal “Computer-aided diagnosis of abdominal pain”. Anderson King’s College Hospital record system. 1974 First Medinfo conference, Stockholm. 1976 EMI scanner 1979 Founding of IMIA (Whipton, Essex) International Medical Informatics Association Systems still mainly finance or pathology Data Processing becomes ‘computer systems’ Early steps to manage and control IT in healthcare First hints at potential for better information to upset apple cart: Protti told by CEO not to collect prescribing data at physician level
Health informatics A History: The 70 s 1970 World’s first real-time GP system 1971 1972 de Dombal “Computer-aided diagnosis of abdominal pain”. Anderson King’s College Hospital record system. 1974 First Medinfo conference, Stockholm. 1976 EMI scanner 1979 Founding of IMIA (Whipton, Essex) International Medical Informatics Association Systems still mainly finance or pathology Data Processing becomes ‘computer systems’ Early steps to manage and control IT in healthcare First hints at potential for better information to upset apple cart: Protti told by CEO not to collect prescribing data at physician level
 1970: A moment in history… 1970 Delivery of fastran. II main backing store for 418/III at The London Hospital: Capacity 132 Mb.
1970: A moment in history… 1970 Delivery of fastran. II main backing store for 418/III at The London Hospital: Capacity 132 Mb.
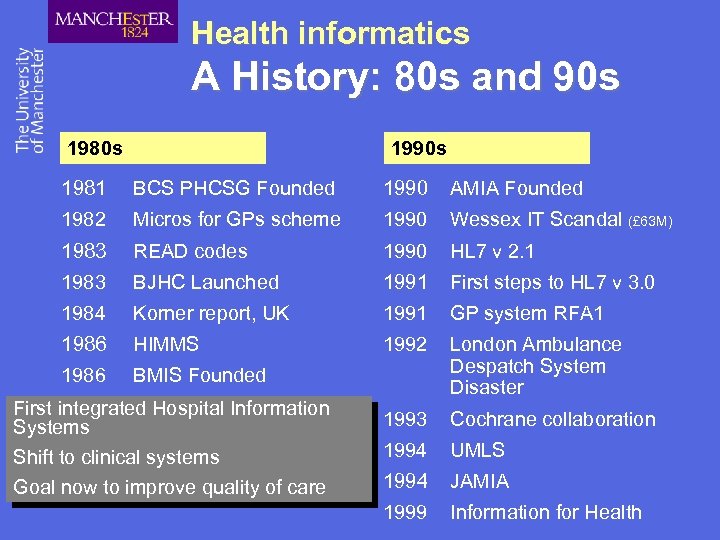 Health informatics A History: 80 s and 90 s 1980 s 1990 s 1981 BCS PHCSG Founded 1990 AMIA Founded 1982 Micros for GPs scheme 1990 Wessex IT Scandal (£ 63 M) 1983 READ codes 1990 HL 7 v 2. 1 1983 BJHC Launched 1991 First steps to HL 7 v 3. 0 1984 Korner report, UK 1991 GP system RFA 1 1986 HIMMS 1992 1986 BMIS Founded London Ambulance Despatch System Disaster 1993 Cochrane collaboration 1994 UMLS 1994 JAMIA 1999 Information for Health First integrated Hospital Information Systems Shift to clinical systems Goal now to improve quality of care
Health informatics A History: 80 s and 90 s 1980 s 1990 s 1981 BCS PHCSG Founded 1990 AMIA Founded 1982 Micros for GPs scheme 1990 Wessex IT Scandal (£ 63 M) 1983 READ codes 1990 HL 7 v 2. 1 1983 BJHC Launched 1991 First steps to HL 7 v 3. 0 1984 Korner report, UK 1991 GP system RFA 1 1986 HIMMS 1992 1986 BMIS Founded London Ambulance Despatch System Disaster 1993 Cochrane collaboration 1994 UMLS 1994 JAMIA 1999 Information for Health First integrated Hospital Information Systems Shift to clinical systems Goal now to improve quality of care
 Health informatics Recent History ► 2000 ► Electronic Record Development and Implementation Programme ► 2002 -2003 ► Wanless Report ► SNOMED CT ► National Programme for NHS IT (Cf. H) ► Integrated Care Record Service ► UK Council for Health Informatics Professionals (UKCHIP) ► 2005 ► NHS Faculty of Health Informatics
Health informatics Recent History ► 2000 ► Electronic Record Development and Implementation Programme ► 2002 -2003 ► Wanless Report ► SNOMED CT ► National Programme for NHS IT (Cf. H) ► Integrated Care Record Service ► UK Council for Health Informatics Professionals (UKCHIP) ► 2005 ► NHS Faculty of Health Informatics
 Health Informatics Best Practice in 2005 ► Denmark ► 85% of health sector integrated within single system ► 2 million messages a month ► Central database of all prescriptions and all lab tests ► New Zealand ► 75% of health sector integrated ► 3 million messages a month ► Veterans Administration ► $21 billion, covering 25 million servicemen & families ► Highest score in every category of quality assessment in 2003 ► Care based on VISTA, enabling Continuous Quality Control ► Cost per patient static over last decade (all other US providers 50%)
Health Informatics Best Practice in 2005 ► Denmark ► 85% of health sector integrated within single system ► 2 million messages a month ► Central database of all prescriptions and all lab tests ► New Zealand ► 75% of health sector integrated ► 3 million messages a month ► Veterans Administration ► $21 billion, covering 25 million servicemen & families ► Highest score in every category of quality assessment in 2003 ► Care based on VISTA, enabling Continuous Quality Control ► Cost per patient static over last decade (all other US providers 50%)
 Health Informatics Into the future ► New Focus ► Clinical Data Repositories ► Surrounded by rule-based alerts and DSS ► New Technologies ► Designer Drugs and Bioinformatics ► Wearable Computing and RFID ► Wireless Connectivity and New portable formats ► New Users ► Patient Empowerment and Intelligent Agents ► New Drivers ► Patient Safety ► Regulation and Accountability of Solutions
Health Informatics Into the future ► New Focus ► Clinical Data Repositories ► Surrounded by rule-based alerts and DSS ► New Technologies ► Designer Drugs and Bioinformatics ► Wearable Computing and RFID ► Wireless Connectivity and New portable formats ► New Users ► Patient Empowerment and Intelligent Agents ► New Drivers ► Patient Safety ► Regulation and Accountability of Solutions
 Recap ►Medicine is broken ►Medicine is expensive ►IT hasn’t helped yet despite 40 years ►But we live in hope
Recap ►Medicine is broken ►Medicine is expensive ►IT hasn’t helped yet despite 40 years ►But we live in hope


