fe8191aeed0b8ca898eac11cd192b41e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Computational grids and grids projects DSS, 4. 4. 2005 pesicka@kiv. zcu. cz
Computational grids and grids projects DSS, 4. 4. 2005 pesicka@kiv. zcu. cz
 Content § § Grid computing (terminology) EGEE grid elements, how it works Gilda testbed (example of simple job) Grid projects
Content § § Grid computing (terminology) EGEE grid elements, how it works Gilda testbed (example of simple job) Grid projects
 Grid computing § model for solving massive computational problems § use of unused resources (CPU cycles, disk storage, . . . ) § support computation across administrative domains – apart from traditional clusters § creates “virtual cluster” embedded in network infrastructure § multi-user environment § issue of authorization – allow remote users to control computing resources
Grid computing § model for solving massive computational problems § use of unused resources (CPU cycles, disk storage, . . . ) § support computation across administrative domains – apart from traditional clusters § creates “virtual cluster” embedded in network infrastructure § multi-user environment § issue of authorization – allow remote users to control computing resources
 Grid computing - resources § sharing heterogenous resources – – – different platforms hw / sw architectures computer languages § located in different places – different administrative domains – connected through the network § virtualizing computing resources
Grid computing - resources § sharing heterogenous resources – – – different platforms hw / sw architectures computer languages § located in different places – different administrative domains – connected through the network § virtualizing computing resources
 Grid x cluster § grids – heterogeneous – can use ordinary desktops as well § cluster – homogenous – located in data centres § Grids are build from Computational Elements (CE) § The cluster can act as an CE of the whole grid system
Grid x cluster § grids – heterogeneous – can use ordinary desktops as well § cluster – homogenous – located in data centres § Grids are build from Computational Elements (CE) § The cluster can act as an CE of the whole grid system
 Global Grid Forum § GGF – defines specification for grid computing § Globus Alliance – implements standards – GT § Globus Toolkit – middleware to build services based on GT; de facto standard; just part of the grid
Global Grid Forum § GGF – defines specification for grid computing § Globus Alliance – implements standards – GT § Globus Toolkit – middleware to build services based on GT; de facto standard; just part of the grid
 Globus – implemented services § Resource management – GRAM (Grid Resource Allocation Management) § Information services – MDS (Monitoring and Discovery Services) § Security Services – GSI (Grid Security Infrastructure) § Data Movement and Management – Grid. FTP, GASS (Global Access to Secondary Storage)
Globus – implemented services § Resource management – GRAM (Grid Resource Allocation Management) § Information services – MDS (Monitoring and Discovery Services) § Security Services – GSI (Grid Security Infrastructure) § Data Movement and Management – Grid. FTP, GASS (Global Access to Secondary Storage)
 EGEE grid components § UI (User Interface) – – user access to the computational grid logon, start jobs, info about state of jobs information about free resources management of user’s data § CE (Computing Element) – – – receive jobs for the given cluster, farm (homogenous) info about computational power and installed sw give the jobs to the local job management system (PBS, LFS, NQE, Load. Leveler, Condor), LJMS sends the job later to the working nodes
EGEE grid components § UI (User Interface) – – user access to the computational grid logon, start jobs, info about state of jobs information about free resources management of user’s data § CE (Computing Element) – – – receive jobs for the given cluster, farm (homogenous) info about computational power and installed sw give the jobs to the local job management system (PBS, LFS, NQE, Load. Leveler, Condor), LJMS sends the job later to the working nodes
 EGEE grid components II. § SE (Storage Element) – – interface how to store user data inside the grid access to the files replication of files file is registrated inside the grid with the internal name (independent of the name and the location) § RC (Replica Catalog) § RLS (Replica Location Server) – info about file replicas, selection of the appropriate replica
EGEE grid components II. § SE (Storage Element) – – interface how to store user data inside the grid access to the files replication of files file is registrated inside the grid with the internal name (independent of the name and the location) § RC (Replica Catalog) § RLS (Replica Location Server) – info about file replicas, selection of the appropriate replica
 EGEE grid components III. § WN (Worker Nodes) – – computation nodes, place where the computation is running have access to the application software (mount from server) capable of manipulation with data stored on SE they are accessible only from CE, not from the whole environment
EGEE grid components III. § WN (Worker Nodes) – – computation nodes, place where the computation is running have access to the application software (mount from server) capable of manipulation with data stored on SE they are accessible only from CE, not from the whole environment
 EGEE grid components IV. § IS (Information Service) – state information about elements of grids (CE, SE, . . . ) – monitoring of the state of the jobs § RB (Resource Broker) – – – scheduler, find the proper resources for the job requirements divide jobs to the CE, sending JDL (Job Description Language) use IS for its decisions
EGEE grid components IV. § IS (Information Service) – state information about elements of grids (CE, SE, . . . ) – monitoring of the state of the jobs § RB (Resource Broker) – – – scheduler, find the proper resources for the job requirements divide jobs to the CE, sending JDL (Job Description Language) use IS for its decisions
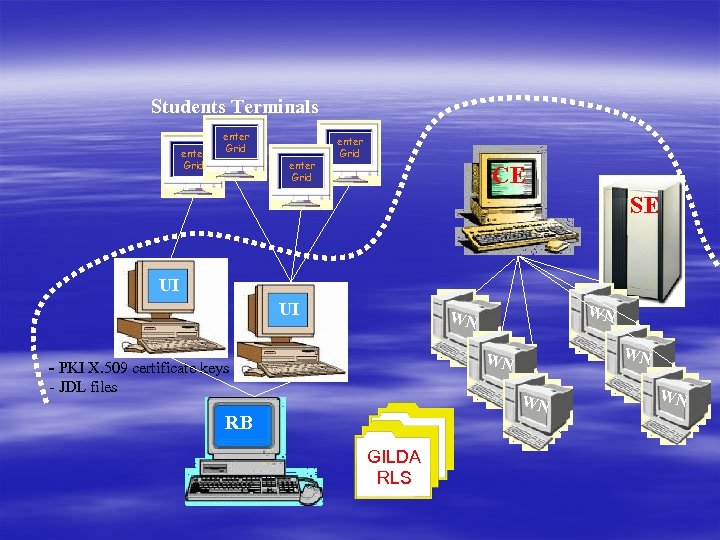 Students Terminals enter Grid CE SE UI UI WN WN - PKI X. 509 certificate keys - JDL files WN RB GILDA RLS WN
Students Terminals enter Grid CE SE UI UI WN WN - PKI X. 509 certificate keys - JDL files WN RB GILDA RLS WN
 How it all works together – step by step § User connects to the UI – time limited proxy certificate is created § User defines the computational job and tell it to the resource broker – by the means of JDL file – JDL file may contain some input data (more datasets – SE) § Resource broker talks to IS, finds proper CE § Resource broker creates job and sends it to the CE
How it all works together – step by step § User connects to the UI – time limited proxy certificate is created § User defines the computational job and tell it to the resource broker – by the means of JDL file – JDL file may contain some input data (more datasets – SE) § Resource broker talks to IS, finds proper CE § Resource broker creates job and sends it to the CE
 How it all works together II. § CE receives job and sends it to the local job management system § The job is running on the WN (working nodes) – using lager datasets – copy data from SE – new large output data – copy to SE, registrated with RLS (Replica Location Server) § At the end of the job, output (stdout, stderr) copied back to the RB
How it all works together II. § CE receives job and sends it to the local job management system § The job is running on the WN (working nodes) – using lager datasets – copy data from SE – new large output data – copy to SE, registrated with RLS (Replica Location Server) § At the end of the job, output (stdout, stderr) copied back to the RB
 How to try it and participate § Genius portal – access to the grid § Gilda – demo applications – last versions of middleware sw § https: //grid-demo. ct. infn. it/
How to try it and participate § Genius portal – access to the grid § Gilda – demo applications – last versions of middleware sw § https: //grid-demo. ct. infn. it/
 Example – hostname. jdl Type = "Job"; Job. Type = "Normal"; Executable = "/bin/hostname"; Std. Output = "hostname. out"; Std. Error = "hostname. err"; Output. Sandbox = {"hostname. err", "hostname. out"}; Arguments = "-f"; Retry. Count = 7;
Example – hostname. jdl Type = "Job"; Job. Type = "Normal"; Executable = "/bin/hostname"; Std. Output = "hostname. out"; Std. Error = "hostname. err"; Output. Sandbox = {"hostname. err", "hostname. out"}; Arguments = "-f"; Retry. Count = 7;
 Example – log after job submission Let the GILDA Resource Broker choose Selected Virtual Organisation name (from UI conf file): gilda Connecting to host grid 004. ct. infn. it, port 7772 Logging to host grid 004. ct. infn. it, port 9002 ================ edg-job-submit Success =================== The job has been successfully submitted to the Network Server. Use edg-job-status command to check job current status. Your job identifier (edg_job. Id) is: https: //grid 004. ct. infn. it: 9000/YWw. Yrw. Iirc. Pajba_1 p. Adeg The edg_job. Id has been saved in the following file: /home/demo 03/. genius/. tmp_submittedjob_demo 03 =========================
Example – log after job submission Let the GILDA Resource Broker choose Selected Virtual Organisation name (from UI conf file): gilda Connecting to host grid 004. ct. infn. it, port 7772 Logging to host grid 004. ct. infn. it, port 9002 ================ edg-job-submit Success =================== The job has been successfully submitted to the Network Server. Use edg-job-status command to check job current status. Your job identifier (edg_job. Id) is: https: //grid 004. ct. infn. it: 9000/YWw. Yrw. Iirc. Pajba_1 p. Adeg The edg_job. Id has been saved in the following file: /home/demo 03/. genius/. tmp_submittedjob_demo 03 =========================
 Example – job queue § Status of the job can be checked in job queue – – – ready scheduled running done – Get Output cleared (after Get. Output) § Output – hostname. err 0 – hostname. out. txt 24 § Hostname. out. txt – testbed 010. cnaf. infn. it {Heureka! We got it!}
Example – job queue § Status of the job can be checked in job queue – – – ready scheduled running done – Get Output cleared (after Get. Output) § Output – hostname. err 0 – hostname. out. txt 24 § Hostname. out. txt – testbed 010. cnaf. infn. it {Heureka! We got it!}
 Grid Projects § EGEE (Enabling Grid for E-scienc. E) – – – connect Europian grids, create production grid starten on 1. April 2004 70 partners (EU, USA, Russia) 7 federations (CE federation – Czech Rep. ) CERN – one federation itself CESNET – scheduling and state monitoring part of the middleware
Grid Projects § EGEE (Enabling Grid for E-scienc. E) – – – connect Europian grids, create production grid starten on 1. April 2004 70 partners (EU, USA, Russia) 7 federations (CE federation – Czech Rep. ) CERN – one federation itself CESNET – scheduling and state monitoring part of the middleware
 Project Geneva § § Core. Grid, Akogrimo, Data. Mining. Grid. Coord, HPC 4 U, Intelli. Grid K-WF Grid, Next. Grid, Onto. Grid Provenance, SIMDAT, Uni. Grid. S
Project Geneva § § Core. Grid, Akogrimo, Data. Mining. Grid. Coord, HPC 4 U, Intelli. Grid K-WF Grid, Next. Grid, Onto. Grid Provenance, SIMDAT, Uni. Grid. S
 Literature, Materials § Wikipedia § http: //egee. cesnet. cz § http: //www. globus. org
Literature, Materials § Wikipedia § http: //egee. cesnet. cz § http: //www. globus. org


