99dadb0204e521255bb9ae0643534b51.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 Computational Geometry and Geometric Shape Matching
Computational Geometry and Geometric Shape Matching
 What is Computational Geometry? · Algorithms for geometric objects
What is Computational Geometry? · Algorithms for geometric objects
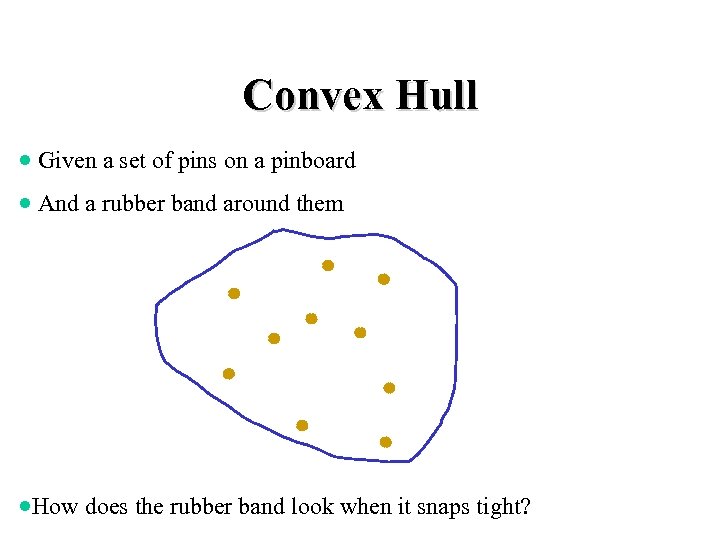 Convex Hull · Given a set of pins on a pinboard · And a rubber band around them ·How does the rubber band look when it snaps tight?
Convex Hull · Given a set of pins on a pinboard · And a rubber band around them ·How does the rubber band look when it snaps tight?
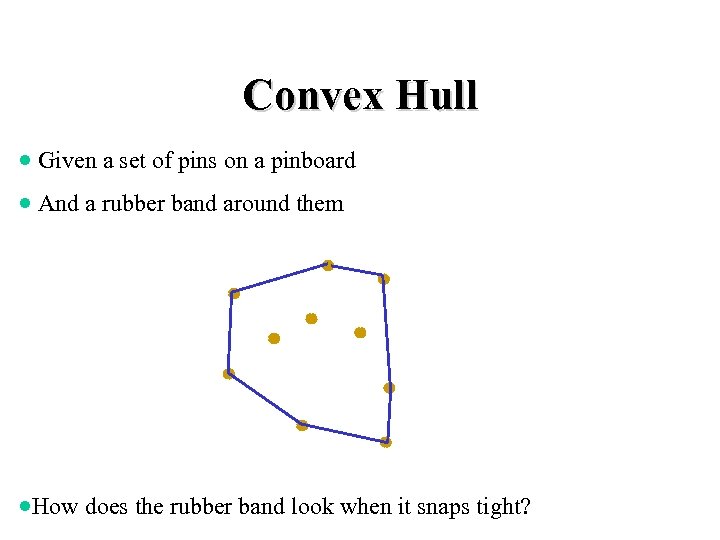 Convex Hull · Given a set of pins on a pinboard · And a rubber band around them ·How does the rubber band look when it snaps tight?
Convex Hull · Given a set of pins on a pinboard · And a rubber band around them ·How does the rubber band look when it snaps tight?
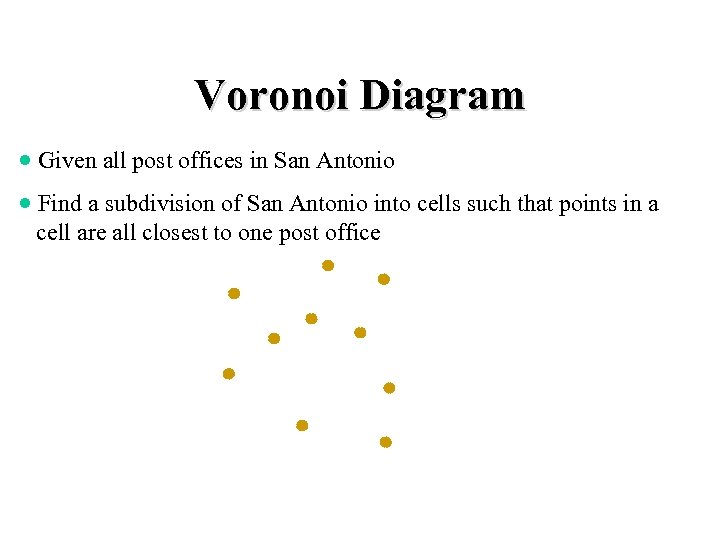 Voronoi Diagram · Given all post offices in San Antonio · Find a subdivision of San Antonio into cells such that points in a cell are all closest to one post office
Voronoi Diagram · Given all post offices in San Antonio · Find a subdivision of San Antonio into cells such that points in a cell are all closest to one post office
 Voronoi Diagram · Given all post offices in San Antonio · Find a subdivision of San Antonio into cells such that points in a cell are all closest to one post office
Voronoi Diagram · Given all post offices in San Antonio · Find a subdivision of San Antonio into cells such that points in a cell are all closest to one post office
 Security: Art Gallery · Given an art gallery · How many guards do you need to guard the whole gallery? Where should they be located?
Security: Art Gallery · Given an art gallery · How many guards do you need to guard the whole gallery? Where should they be located?
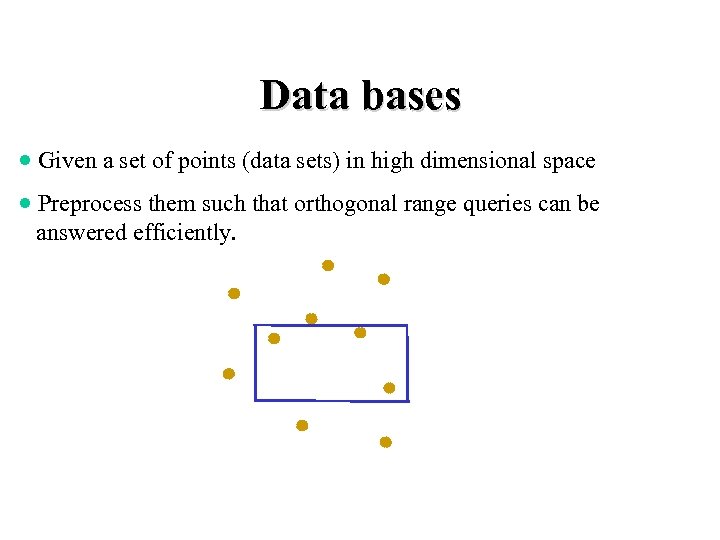 Data bases · Given a set of points (data sets) in high dimensional space · Preprocess them such that orthogonal range queries can be answered efficiently.
Data bases · Given a set of points (data sets) in high dimensional space · Preprocess them such that orthogonal range queries can be answered efficiently.
 Geometric Shape Matching · Consider geometric shapes to be composed of a number of basic objects
Geometric Shape Matching · Consider geometric shapes to be composed of a number of basic objects
 Geometric Shape Matching · Consider geometric shapes to be composed of a number of basic objects such as points
Geometric Shape Matching · Consider geometric shapes to be composed of a number of basic objects such as points
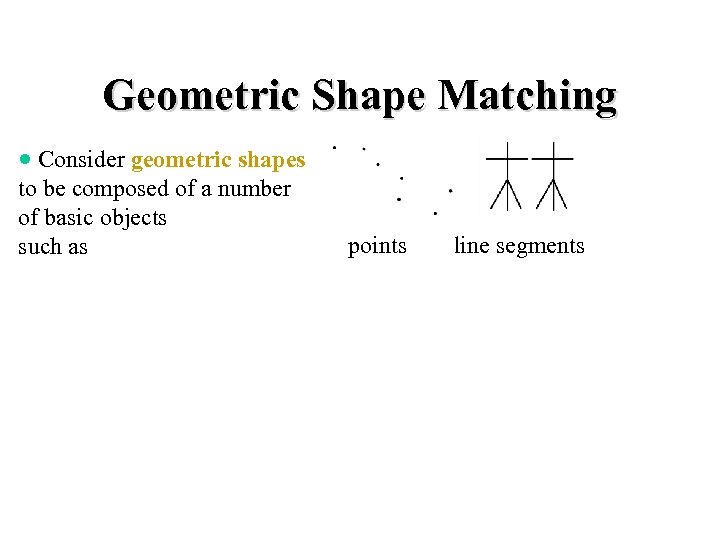 Geometric Shape Matching · Consider geometric shapes to be composed of a number of basic objects such as points line segments
Geometric Shape Matching · Consider geometric shapes to be composed of a number of basic objects such as points line segments
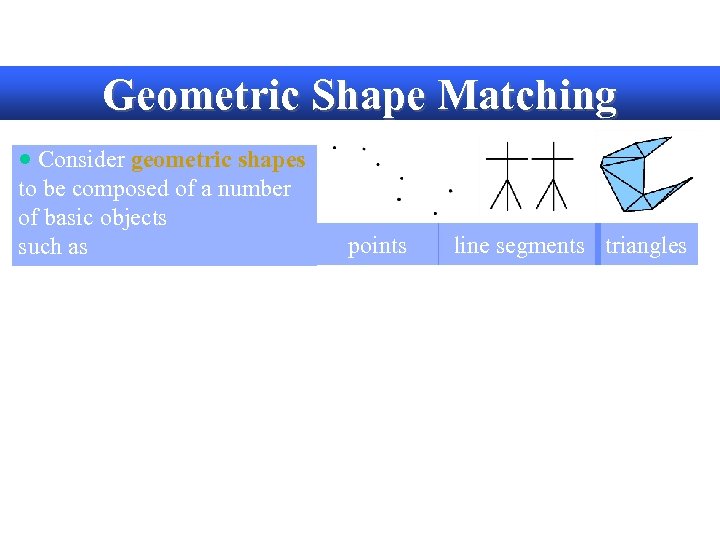 Geometric Shape Matching · Consider geometric shapes to be composed of a number of basic objects such as points line segments triangles
Geometric Shape Matching · Consider geometric shapes to be composed of a number of basic objects such as points line segments triangles
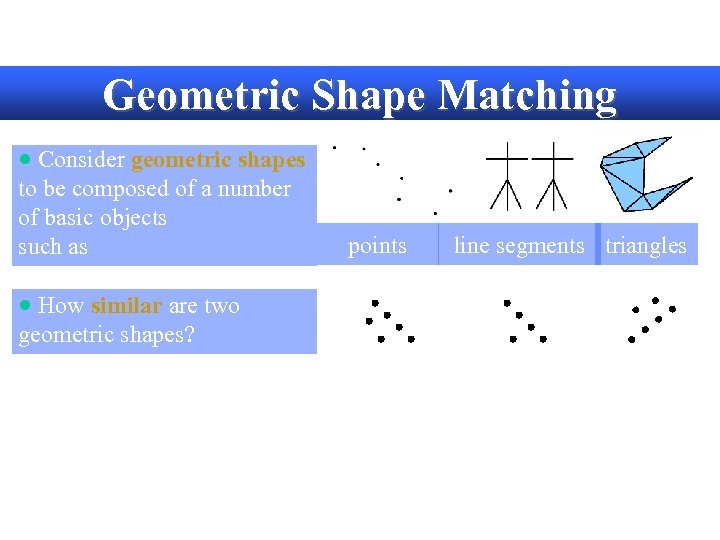 Geometric Shape Matching · Consider geometric shapes to be composed of a number of basic objects such as · How similar are two geometric shapes? points line segments triangles
Geometric Shape Matching · Consider geometric shapes to be composed of a number of basic objects such as · How similar are two geometric shapes? points line segments triangles
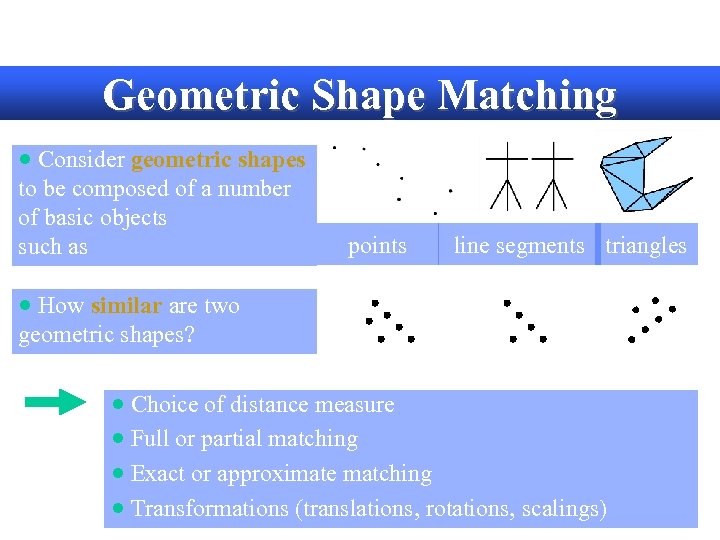 Geometric Shape Matching · Consider geometric shapes to be composed of a number of basic objects such as points line segments triangles · How similar are two geometric shapes? · Choice of distance measure · Full or partial matching · Exact or approximate matching · Transformations (translations, rotations, scalings)
Geometric Shape Matching · Consider geometric shapes to be composed of a number of basic objects such as points line segments triangles · How similar are two geometric shapes? · Choice of distance measure · Full or partial matching · Exact or approximate matching · Transformations (translations, rotations, scalings)
 Computer-Aided Neurosurgery FU Berlin, Functional Imaging Technologies Gmb. H and the medical school ‘Benjamin Franklin’ at FU Berlin
Computer-Aided Neurosurgery FU Berlin, Functional Imaging Technologies Gmb. H and the medical school ‘Benjamin Franklin’ at FU Berlin
 Background · Computer assisted neuro surgery (esp. brain tumor surgery)
Background · Computer assisted neuro surgery (esp. brain tumor surgery)
 Background · Computer assisted neuro surgery (esp. brain tumor surgery) Before Surgery: · Functional MR scan of the brain · 3 D model of the brain
Background · Computer assisted neuro surgery (esp. brain tumor surgery) Before Surgery: · Functional MR scan of the brain · 3 D model of the brain
 Background · Computer assisted neuro surgery (esp. brain tumor surgery) Before Surgery: · Functional MR scan of the brain · 3 D model of the brain During Surgery:
Background · Computer assisted neuro surgery (esp. brain tumor surgery) Before Surgery: · Functional MR scan of the brain · 3 D model of the brain During Surgery:
 Background · Computer assisted neuro surgery (esp. brain tumor surgery) Before Surgery: During Surgery: · Functional MR scan of · Electromagnetic pointing the brain device · 3 D model of the brain · Display positions in 3 D model
Background · Computer assisted neuro surgery (esp. brain tumor surgery) Before Surgery: During Surgery: · Functional MR scan of · Electromagnetic pointing the brain device · 3 D model of the brain · Display positions in 3 D model
 Background · Computer assisted neuro surgery (esp. brain tumor surgery) Before Surgery: During Surgery: · Functional MR scan of · Electromagnetic pointing the brain device · 3 D model of the brain · Display positions in 3 D model Navigation aid mapping positions in the brain to a prerecorded 3 D MR image of the brain
Background · Computer assisted neuro surgery (esp. brain tumor surgery) Before Surgery: During Surgery: · Functional MR scan of · Electromagnetic pointing the brain device · 3 D model of the brain · Display positions in 3 D model Navigation aid mapping positions in the brain to a prerecorded 3 D MR image of the brain
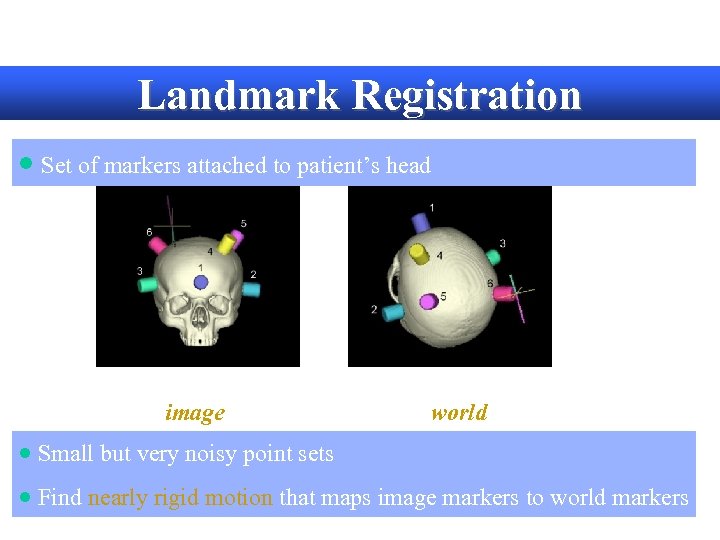 Landmark Registration · Set of markers attached to patient’s head 3 D model image during surgery world · Small but very noisy point sets · Find nearly rigid motion that maps image markers to world markers
Landmark Registration · Set of markers attached to patient’s head 3 D model image during surgery world · Small but very noisy point sets · Find nearly rigid motion that maps image markers to world markers
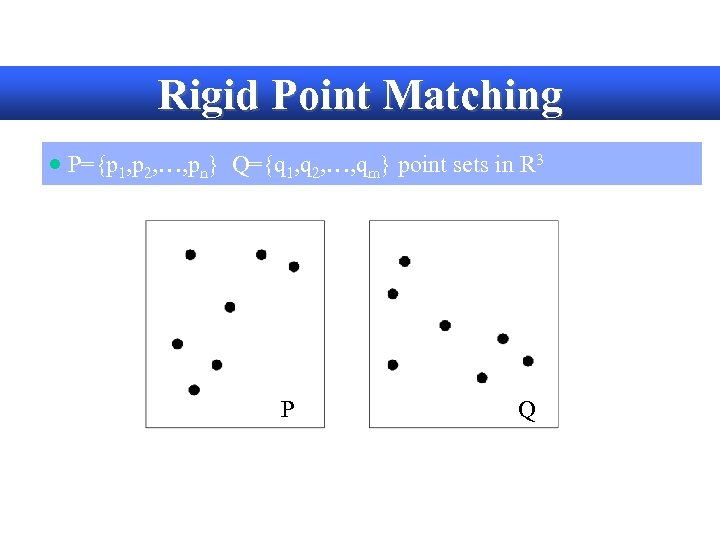 Rigid Point Matching · P={p 1, p 2, …, pn} Q={q 1, q 2, …, qm} point sets in R 3 P Q
Rigid Point Matching · P={p 1, p 2, …, pn} Q={q 1, q 2, …, qm} point sets in R 3 P Q
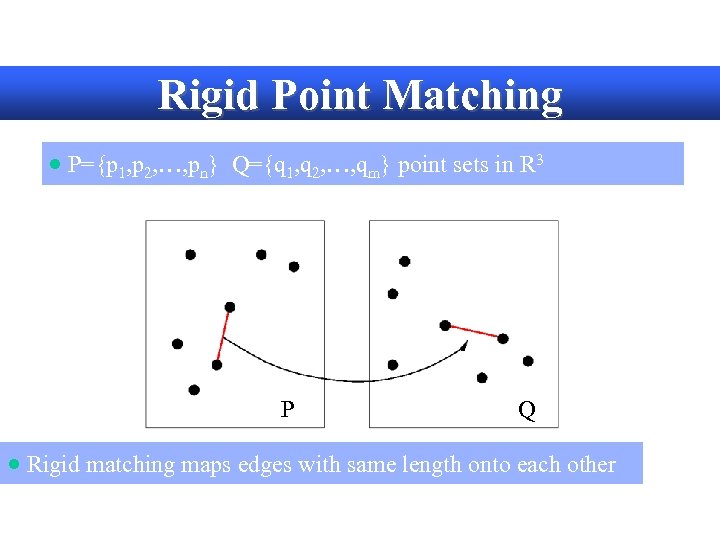 Rigid Point Matching · P={p 1, p 2, …, pn} Q={q 1, q 2, …, qm} point sets in R 3 P Q · Rigid matching maps edges with same length onto each other
Rigid Point Matching · P={p 1, p 2, …, pn} Q={q 1, q 2, …, qm} point sets in R 3 P Q · Rigid matching maps edges with same length onto each other
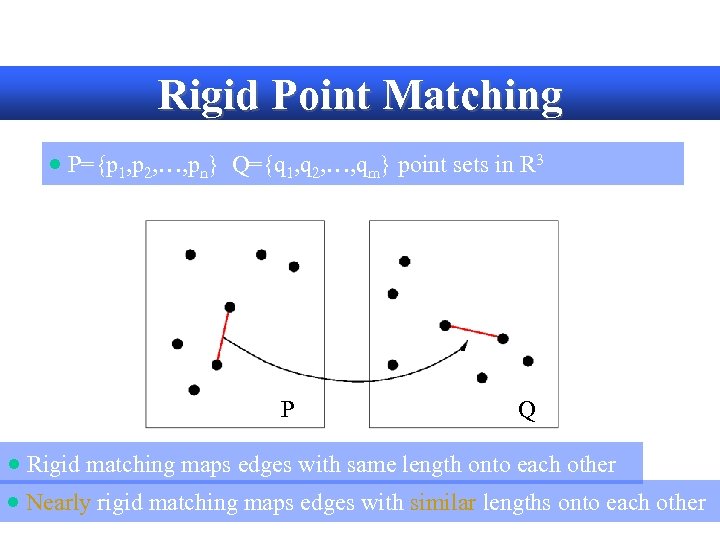 Rigid Point Matching · P={p 1, p 2, …, pn} Q={q 1, q 2, …, qm} point sets in R 3 P Q · Rigid matching maps edges with same length onto each other · Nearly rigid matching maps edges with similar lengths onto each other
Rigid Point Matching · P={p 1, p 2, …, pn} Q={q 1, q 2, …, qm} point sets in R 3 P Q · Rigid matching maps edges with same length onto each other · Nearly rigid matching maps edges with similar lengths onto each other
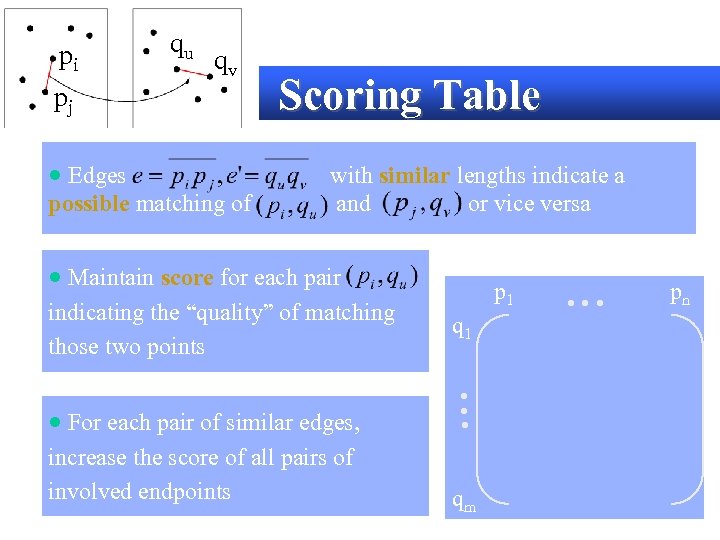 pi qu qv pj · Edges possible matching of Scoring Table with similar lengths indicate a and or vice versa · Maintain score for each pair indicating the “quality” of matching those two points q 1 · For each pair of similar edges, • • • p 1 increase the score of all pairs of involved endpoints qm • • • pn
pi qu qv pj · Edges possible matching of Scoring Table with similar lengths indicate a and or vice versa · Maintain score for each pair indicating the “quality” of matching those two points q 1 · For each pair of similar edges, • • • p 1 increase the score of all pairs of involved endpoints qm • • • pn
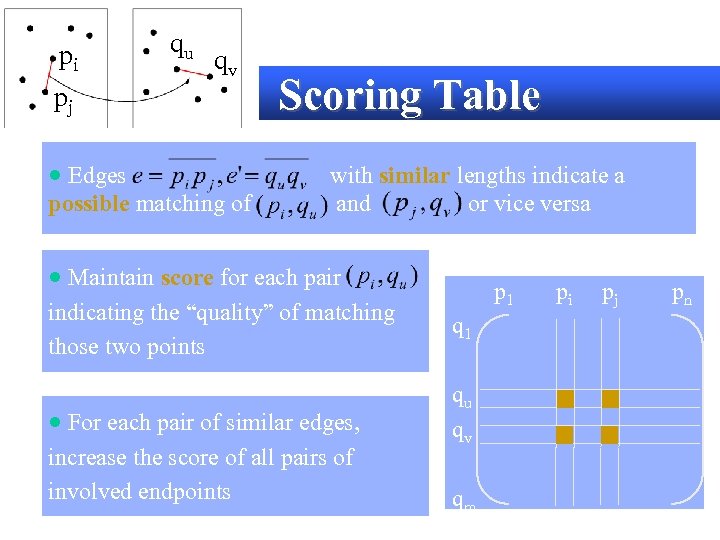 pi qu qv pj · Edges possible matching of Scoring Table with similar lengths indicate a and or vice versa · Maintain score for each pair p 1 indicating the “quality” of matching those two points q 1 · For each pair of similar edges, qu qv increase the score of all pairs of involved endpoints qm pi pj pn
pi qu qv pj · Edges possible matching of Scoring Table with similar lengths indicate a and or vice versa · Maintain score for each pair p 1 indicating the “quality” of matching those two points q 1 · For each pair of similar edges, qu qv increase the score of all pairs of involved endpoints qm pi pj pn
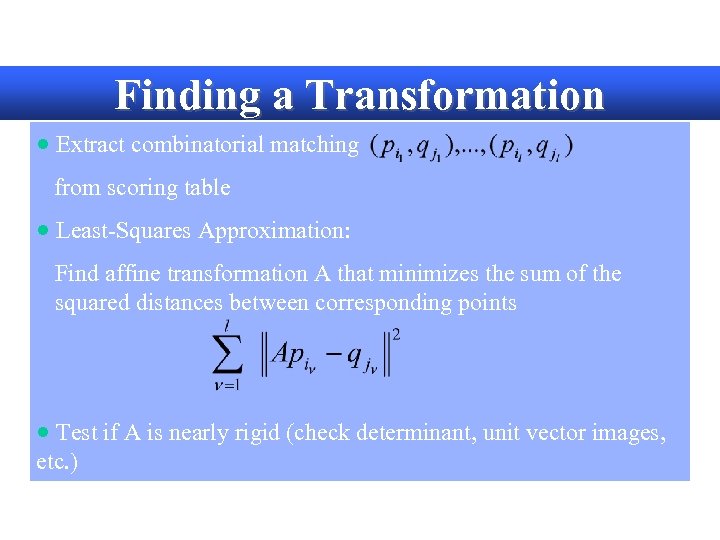 Finding a Transformation · Extract combinatorial matching from scoring table · Least-Squares Approximation: Find affine transformation A that minimizes the sum of the squared distances between corresponding points · Test if A is nearly rigid (check determinant, unit vector images, etc. )
Finding a Transformation · Extract combinatorial matching from scoring table · Least-Squares Approximation: Find affine transformation A that minimizes the sum of the squared distances between corresponding points · Test if A is nearly rigid (check determinant, unit vector images, etc. )
 Computer-Aided Neurosurgery: Summary · Direct linear algebra approaches were numerically very unstable · Geometric approach of splitting the problem into - finding the combinatorial matching and then - computing the nearly rigid transformation is very easy to implement and proved to be very robust. · The algorithm is integrated into a commercial product and used in practice.
Computer-Aided Neurosurgery: Summary · Direct linear algebra approaches were numerically very unstable · Geometric approach of splitting the problem into - finding the combinatorial matching and then - computing the nearly rigid transformation is very easy to implement and proved to be very robust. · The algorithm is integrated into a commercial product and used in practice.
 Protein Gel Matching FU Berlin, Uof. A, German Heart Center Berlin
Protein Gel Matching FU Berlin, Uof. A, German Heart Center Berlin
 2 D Gel Electrophoresis Two-dimensional Gel Electrophoresis (2 DE) is · an important method in proteome research · a high resolution technique which is capable to separate thousands of proteins from a tissue sample
2 D Gel Electrophoresis Two-dimensional Gel Electrophoresis (2 DE) is · an important method in proteome research · a high resolution technique which is capable to separate thousands of proteins from a tissue sample
 2 D Gel Electrophoresis
2 D Gel Electrophoresis
 2 D Gel Electrophoresis · Proteins are concentrated in so called spots of (axisparallel) elliptic shape
2 D Gel Electrophoresis · Proteins are concentrated in so called spots of (axisparallel) elliptic shape
 2 D Gel Electrophoresis · Proteins are concentrated in so called spots of (axisparallel) elliptic shape · Protein analysis by mass spectrometry (expensive)
2 D Gel Electrophoresis · Proteins are concentrated in so called spots of (axisparallel) elliptic shape · Protein analysis by mass spectrometry (expensive)
 2 D Gel Electrophoresis
2 D Gel Electrophoresis
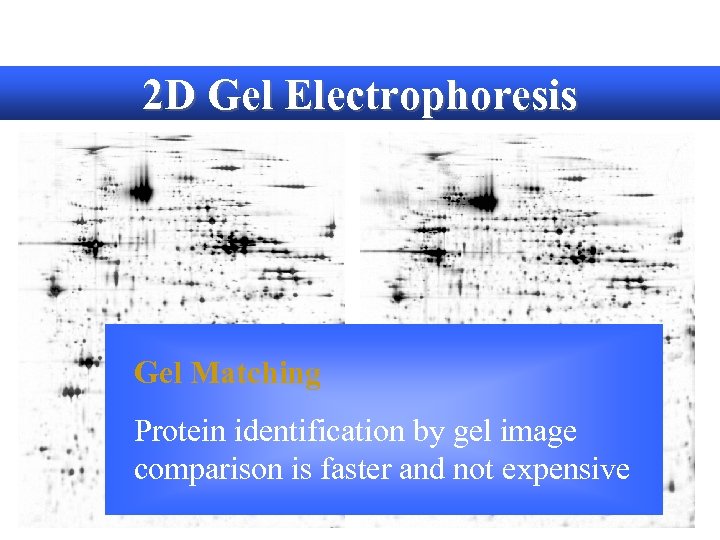 2 D Gel Electrophoresis Gel Matching Protein identification by gel image comparison is faster and not expensive
2 D Gel Electrophoresis Gel Matching Protein identification by gel image comparison is faster and not expensive
 The Algorithmic Approach Make use of ideas and methods from Computational Geometry: · Spot detection Assign to each spot the coordinates of its center point and its intensity · Point pattern matching Consider a gel as a point pattern. Then the problem reduces to a partial approximate point pattern matching.
The Algorithmic Approach Make use of ideas and methods from Computational Geometry: · Spot detection Assign to each spot the coordinates of its center point and its intensity · Point pattern matching Consider a gel as a point pattern. Then the problem reduces to a partial approximate point pattern matching.
 GPS Curve Location FU Berlin and Uof. A and UTSA
GPS Curve Location FU Berlin and Uof. A and UTSA
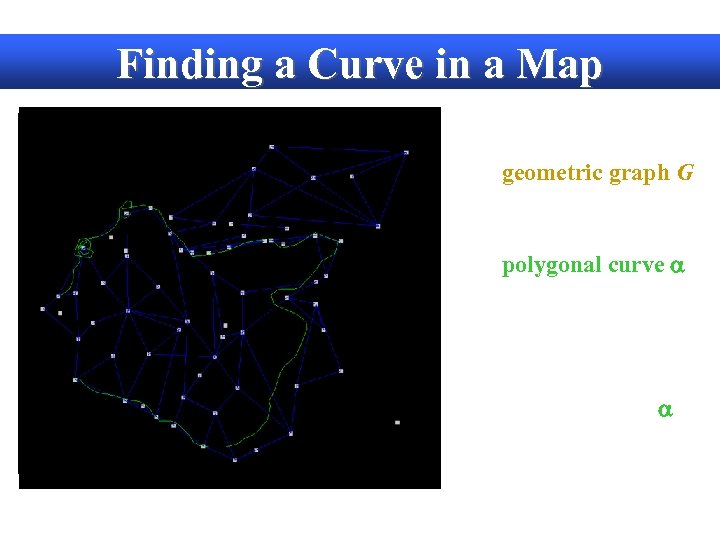 Finding a Curve in a Map Given: • A geometric graph G (embedded in R 2 with line segments) • A polygonal curve a Task: Find a path p in G that is the most similar to a
Finding a Curve in a Map Given: • A geometric graph G (embedded in R 2 with line segments) • A polygonal curve a Task: Find a path p in G that is the most similar to a
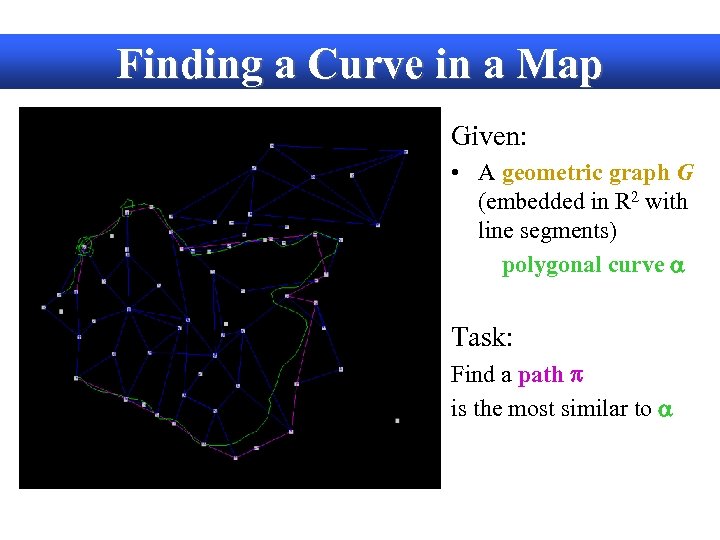 Finding a Curve in a Map Given: • A geometric graph G (embedded in R 2 with line segments) • A polygonal curve a Task: Find a path p in G that is the most similar to a
Finding a Curve in a Map Given: • A geometric graph G (embedded in R 2 with line segments) • A polygonal curve a Task: Find a path p in G that is the most similar to a
 Application: Map Construction • Consider : – A given roadmap, and – a sequence of GPS positions obtained from a person travelling on some of the roads while recording her positioning information using a GPS receiver polygonal curve • Problem: – The noise of the GPS receiver distorts the polygonal curve inherently • Task: – Find the roads in the roadmap that have been traveled
Application: Map Construction • Consider : – A given roadmap, and – a sequence of GPS positions obtained from a person travelling on some of the roads while recording her positioning information using a GPS receiver polygonal curve • Problem: – The noise of the GPS receiver distorts the polygonal curve inherently • Task: – Find the roads in the roadmap that have been traveled


