231a5182e589b7a1cc743eac9c2d8f8a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49

Computational Anatomy and Neuropsychiatric Disease Probabilistic Assessment of Variation and Statistical Inference of Group Difference, Hemispheric Asymmetry, and Time-Dependent Change John G. Csernansky, M. D. Washington University School of Medicine

Rationale for Assessing Neuroanatomy as a Disease Biomarker • Neuroanatomical changes are characteristic of neuropsychiatric diseases and may be discoverable before clinical symptoms occur (preclinical diagnosis) • Ongoing changes in neuroanatomy may occur during the disease process and may be modified by treatment (monitoring of treatment response)

Challenges in Assessing Neuroanatomy as a Disease Biomarkers • Small sample sizes • Normative variability (age, gender, etc. ) • Disease heterogeneity • Abnormalities may be specific a particular stages of illness

Approaches to Hypothesis Testing: Using a ROI Approach • Group comparisons of individual structures - volumes and shapes • Group comparisons of the relationship between structures - hemispheric asymmetries • Group comparisons of the rate of change in the volume and shape of structures over time

Rationale for Using a ROI Approach • Problems encountered in structural analysis may be region specific • Different regions may have different tissue characteristics and be susceptible to different sources of measurement error • Hypothesis generation versus hypothesis testing - taking advantage of prior knowledge about a disease
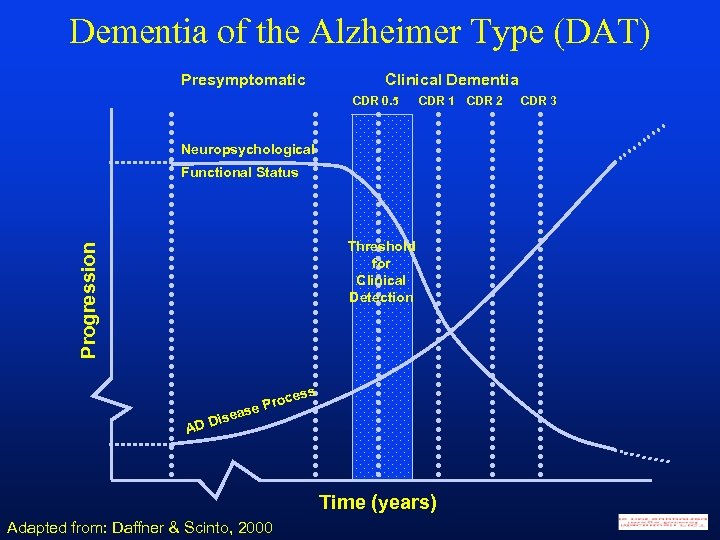
Dementia of the Alzheimer Type (DAT) Presymptomatic Clinical Dementia CDR 0. 5 CDR 1 Neuropsychological Functional Status Progression Threshold for Clinical Detection ess AD roc se P sea Di Time (years) Adapted from: Daffner & Scinto, 2000 CDR 2 CDR 3
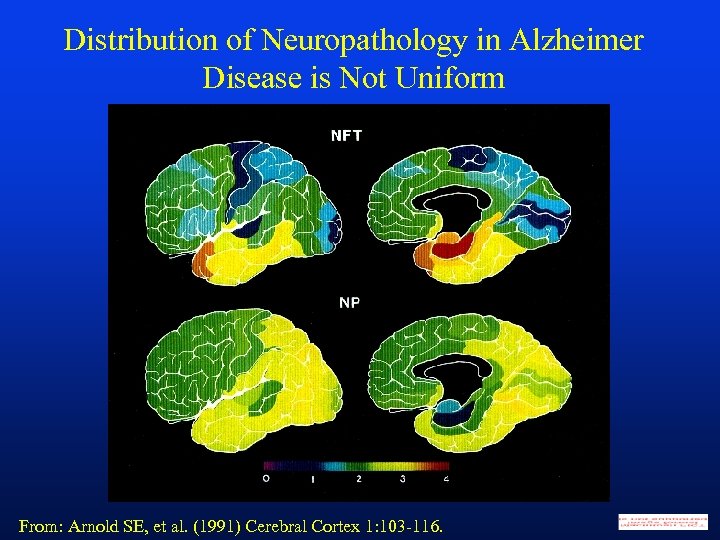
Distribution of Neuropathology in Alzheimer Disease is Not Uniform From: Arnold SE, et al. (1991) Cerebral Cortex 1: 103 -116.
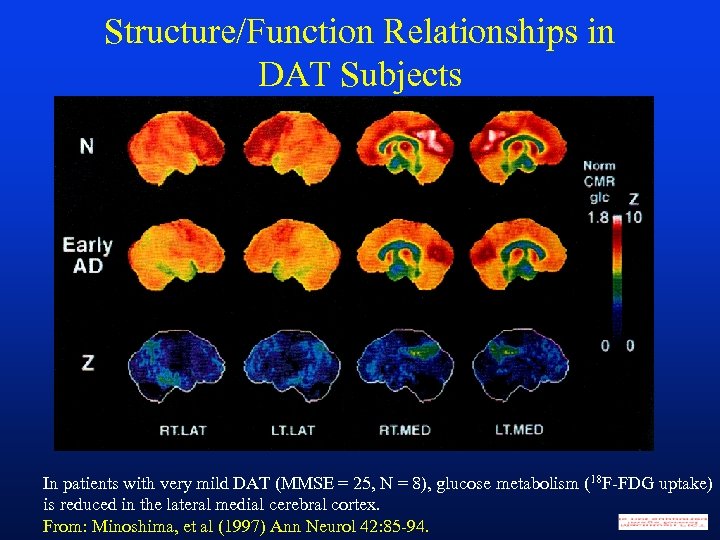
Structure/Function Relationships in DAT Subjects In patients with very mild DAT (MMSE = 25, N = 8), glucose metabolism (18 F-FDG uptake) is reduced in the lateral medial cerebral cortex. From: Minoshima, et al (1997) Ann Neurol 42: 85 -94.
Group Comparisons of Individual Structures in DAT Subjects • Hippocampus (subcortical gray matter structure volume enclosed by a single surface) • Cingulate gyrus (cortical mantle structure subregion of gray matter layered between CSF and white matter)
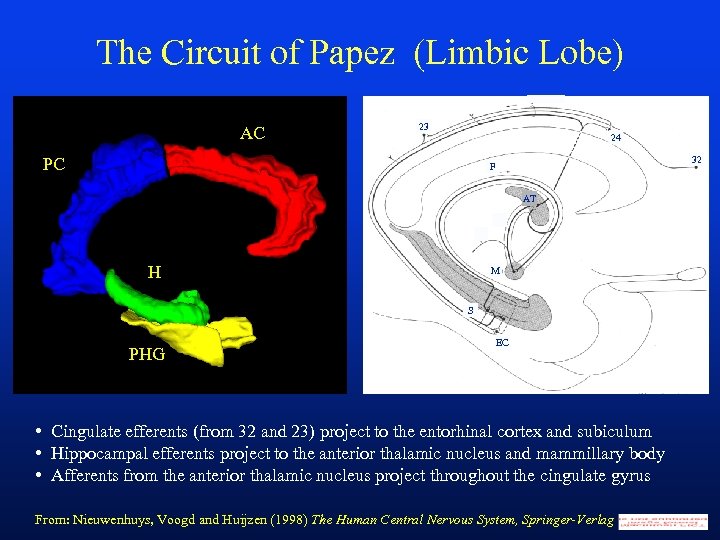
The Circuit of Papez (Limbic Lobe) AC 23 24 PC 32 F AT Picture of limbic lobe here H M S PHG EC • Cingulate efferents (from 32 and 23) project to the entorhinal cortex and subiculum • Hippocampal efferents project to the anterior thalamic nucleus and mammillary body • Afferents from the anterior thalamic nucleus project throughout the cingulate gyrus From: Nieuwenhuys, Voogd and Huijzen (1998) The Human Central Nervous System, Springer-Verlag
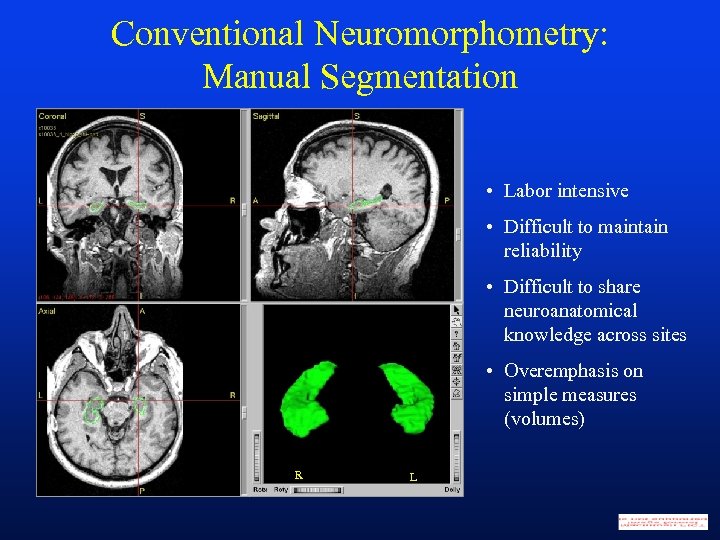
Conventional Neuromorphometry: Manual Segmentation • Labor intensive • Difficult to maintain reliability • Difficult to share neuroanatomical knowledge across sites • Overemphasis on simple measures (volumes) R L
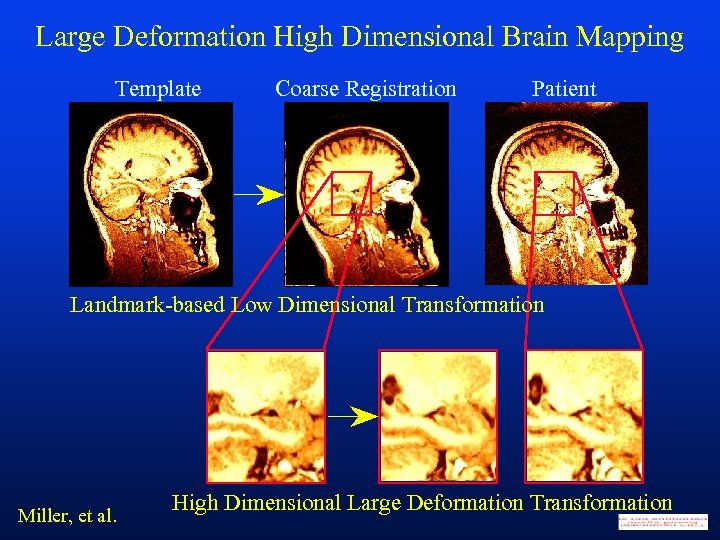
Large Deformation High Dimensional Brain Mapping Template Coarse Registration Patient Landmark-based Low Dimensional Transformation Miller, et al. High Dimensional Large Deformation Transformation
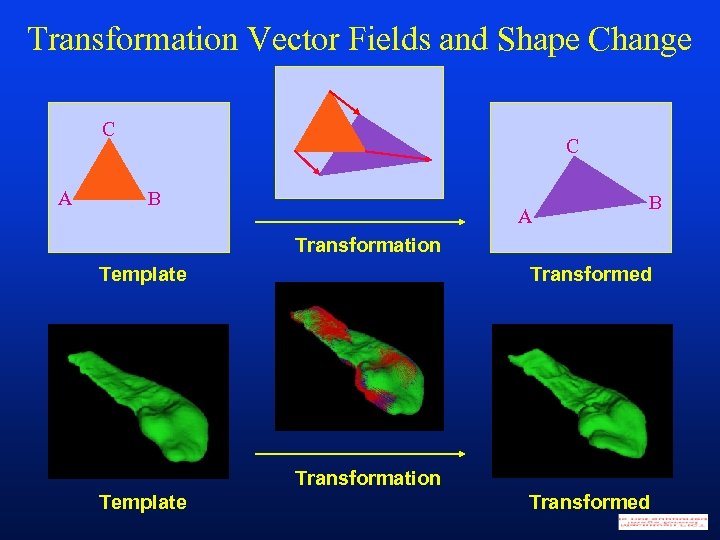
Transformation Vector Fields and Shape Change C A C B A B Transformation Template Transformed
Eigenvectors Derived from Vector Fields Using Singular Value Decomposition • Latent variables representing dimensions of shape variation within a population • Use first n eigenvectors and MANOVA to test basic “shape” hypothesis • Logistic regression is used to select most informative eigenvectors, and a leave-one-out analysis to test power of classification
Selecting Brain Regions to Look for Early Changes in Alzheimer Disease • Hippocampus (CA 1 and subiculum) • Cingulate gyrus (posterior > anterior)
Hippocampal Volume Changes in Early AD From: Csernansky, et al (2000) Neurology 55: 1636 -1643.
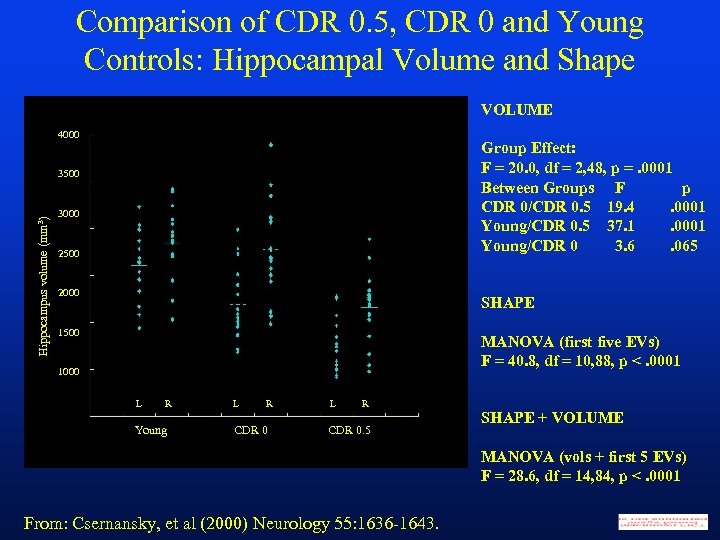
Comparison of CDR 0. 5, CDR 0 and Young Controls: Hippocampal Volume and Shape VOLUME 4000 Group Effect: F = 20. 0, df = 2, 48, p =. 0001 Between Groups F p CDR 0/CDR 0. 5 19. 4. 0001 Young/CDR 0. 5 37. 1. 0001 Young/CDR 0 3. 6. 065 Hippocampus volume (mm 3) 3500 3000 2500 2000 SHAPE 1500 MANOVA (first five EVs) F = 40. 8, df = 10, 88, p <. 0001 1000 L R Young L R CDR 0. 5 SHAPE + VOLUME MANOVA (vols + first 5 EVs) F = 28. 6, df = 14, 84, p <. 0001 From: Csernansky, et al (2000) Neurology 55: 1636 -1643.
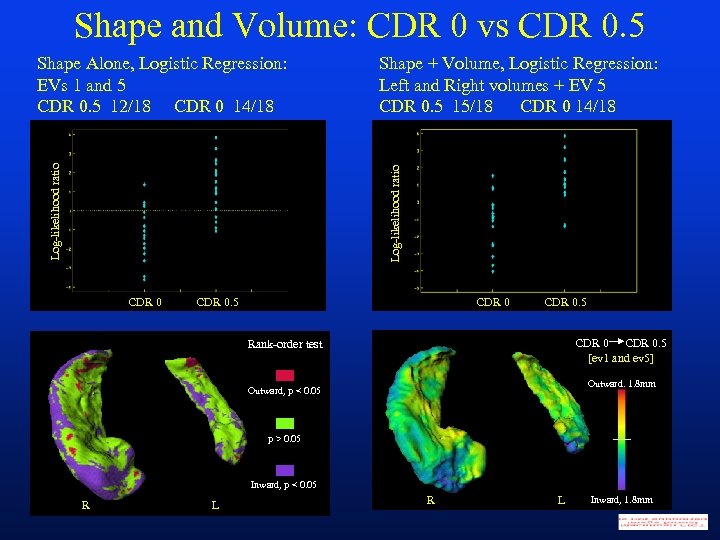
Shape and Volume: CDR 0 vs CDR 0. 5 Shape + Volume, Logistic Regression: Left and Right volumes + EV 5 CDR 0. 5 15/18 CDR 0 14/18 Log-likelihood ratio Shape Alone, Logistic Regression: EVs 1 and 5 CDR 0. 5 12/18 CDR 0 14/18 CDR 0. 5 CDR 0. 5 [ev 1 and ev 5] Rank-order test Outward, 1. 8 mm Outward, p < 0. 05 p > 0. 05 Inward, p < 0. 05 R L Inward, 1. 8 mm
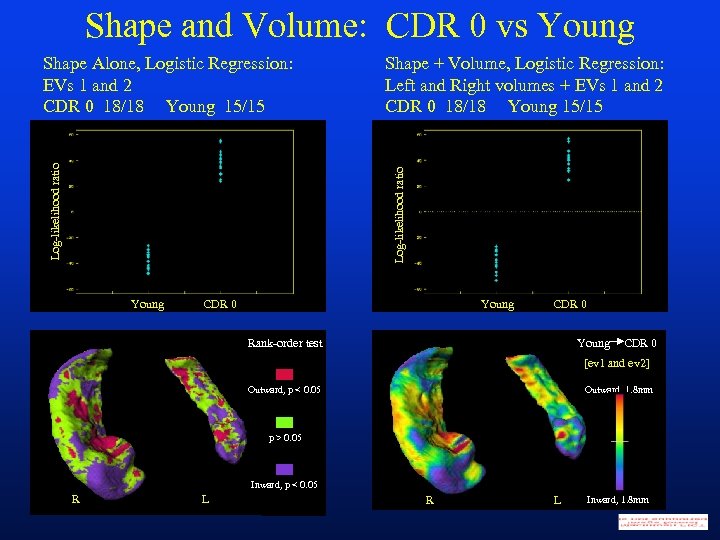
Shape and Volume: CDR 0 vs Young Shape + Volume, Logistic Regression: Left and Right volumes + EVs 1 and 2 CDR 0 18/18 Young 15/15 Log-likelihood ratio Shape Alone, Logistic Regression: EVs 1 and 2 CDR 0 18/18 Young 15/15 Young CDR 0 Young Rank-order test CDR 0 [ev 1 and ev 2] Outward, 1. 8 mm Outward, p < 0. 05 p > 0. 05 Inward, p < 0. 05 R L Inward, 1. 8 mm
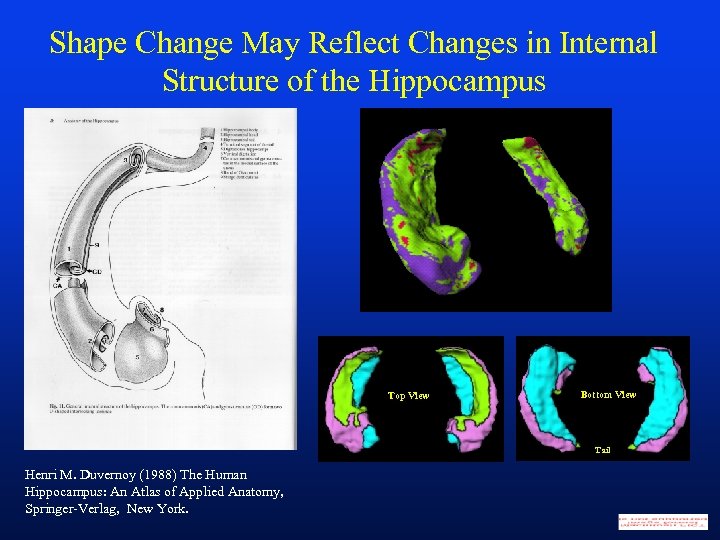
Shape Change May Reflect Changes in Internal Structure of the Hippocampus Top View Bottom View Tail Henri M. Duvernoy (1988) The Human Hippocampus: An Atlas of Applied Anatomy, Springer-Verlag, New York.

Group Comparison of Rate of Change in Hippocampal Volume and Shape From: Wang, et al (2003) Neuro. Image 20: 667 -682.
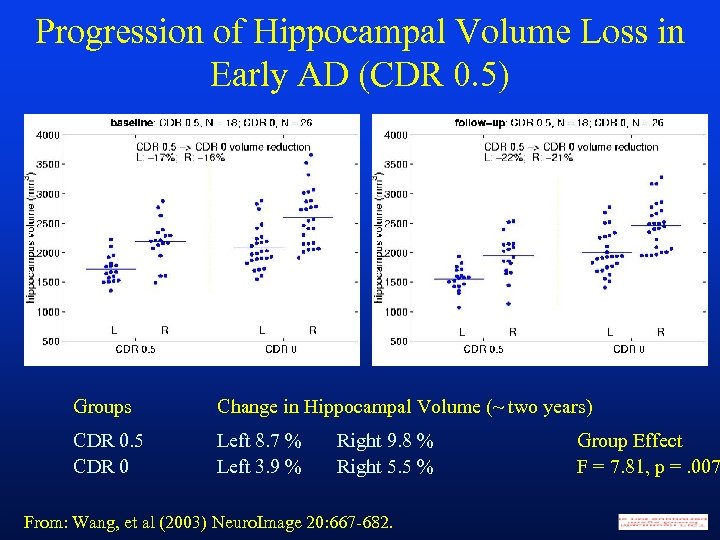
Progression of Hippocampal Volume Loss in Early AD (CDR 0. 5) Groups Change in Hippocampal Volume (~ two years) CDR 0. 5 CDR 0 Left 8. 7 % Left 3. 9 % Right 9. 8 % Right 5. 5 % From: Wang, et al (2003) Neuro. Image 20: 667 -682. Group Effect F = 7. 81, p =. 007
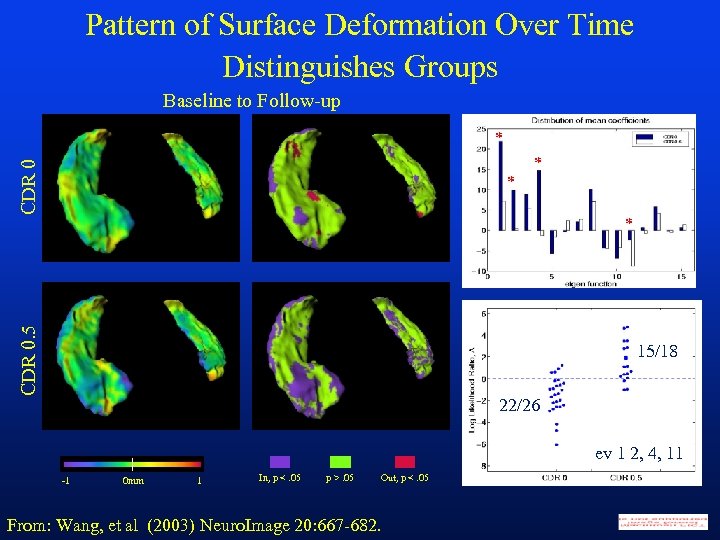
Pattern of Surface Deformation Over Time Distinguishes Groups Baseline to Follow-up * CDR 0 * * CDR 0. 5 * 15/18 22/26 ev 1 2, 4, 11 -1 0 mm 1 In, p <. 05 p >. 05 Out, p <. 05 From: Wang, et al (2003) Neuro. Image 20: 667 -682.
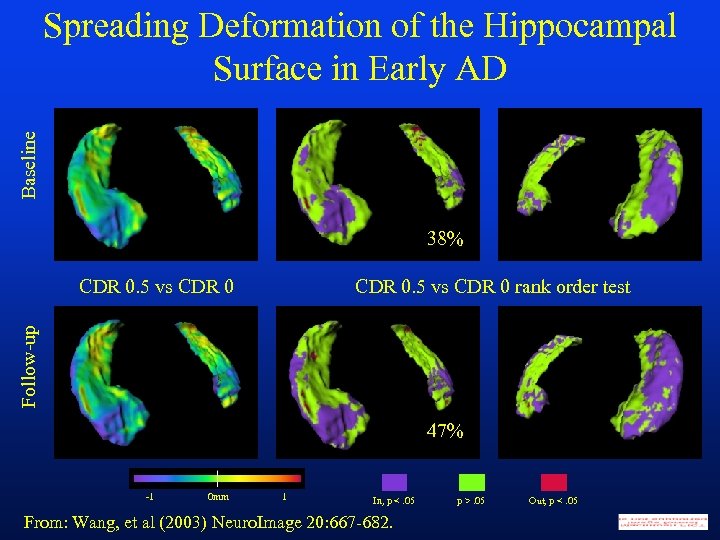
Baseline Spreading Deformation of the Hippocampal Surface in Early AD 38% CDR 0. 5 vs CDR 0 rank order test Follow-up CDR 0. 5 vs CDR 0 47% -1 0 mm 1 In, p <. 05 From: Wang, et al (2003) Neuro. Image 20: 667 -682. p >. 05 Out, p <. 05
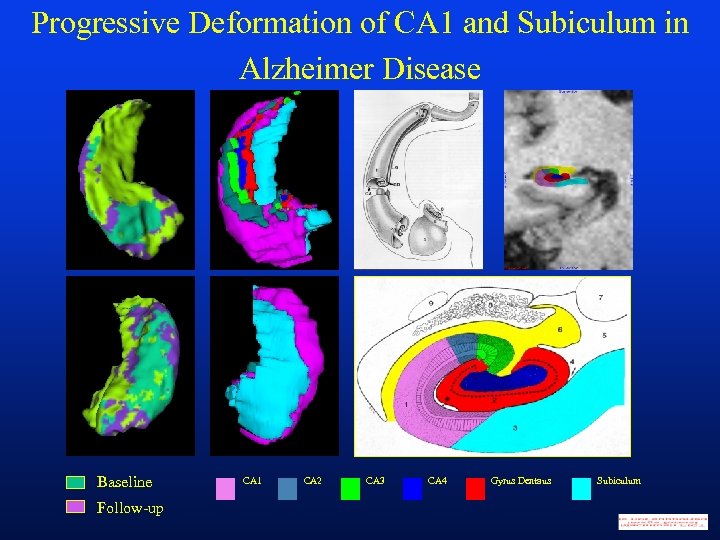
Progressive Deformation of CA 1 and Subiculum in Alzheimer Disease Baseline Follow-up CA 1 CA 2 CA 3 CA 4 Gyrus Dentaus Subiculum
Selecting Brain Regions to Look for Early Changes in Alzheimer Disease • Hippocampus (CA 1 and subiculum) • Cingulate gyrus (posterior > anterior)

Methodological Challenges in the Assessment of Cortical Structures • Segmentation of tissue subtypes (gray, white and mixed) • Definition of a reference surface (gray/CSF vs gray/white) • Definition of boundaries with neighboring cortical regions (gross anatomy, histology, function) • Definition and calculation of distinct metrics (volume, thickness, surface area)
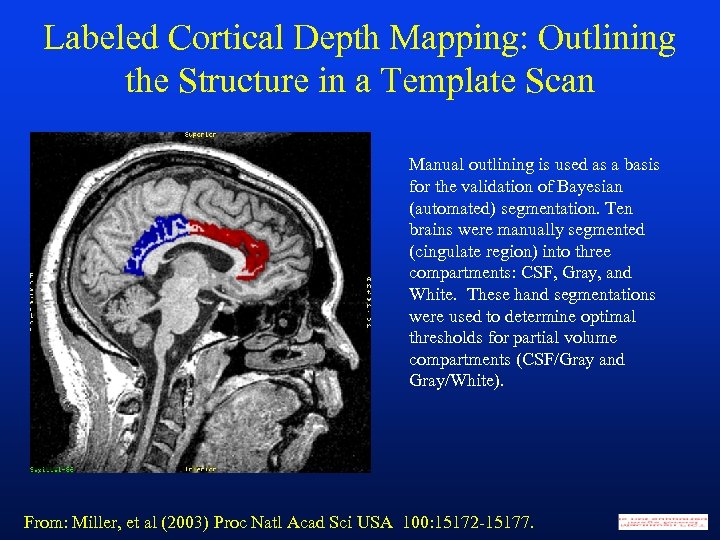
Labeled Cortical Depth Mapping: Outlining the Structure in a Template Scan Manual outlining is used as a basis for the validation of Bayesian (automated) segmentation. Ten brains were manually segmented (cingulate region) into three compartments: CSF, Gray, and White. These hand segmentations were used to determine optimal thresholds for partial volume compartments (CSF/Gray and Gray/White). From: Miller, et al (2003) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 15172 -15177.
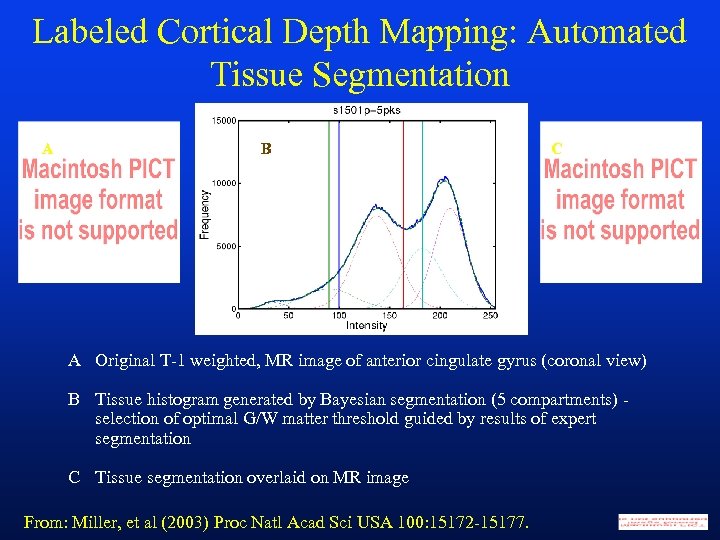
Labeled Cortical Depth Mapping: Automated Tissue Segmentation A B C A Original T-1 weighted, MR image of anterior cingulate gyrus (coronal view) B Tissue histogram generated by Bayesian segmentation (5 compartments) selection of optimal G/W matter threshold guided by results of expert segmentation C Tissue segmentation overlaid on MR image From: Miller, et al (2003) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 15172 -15177.
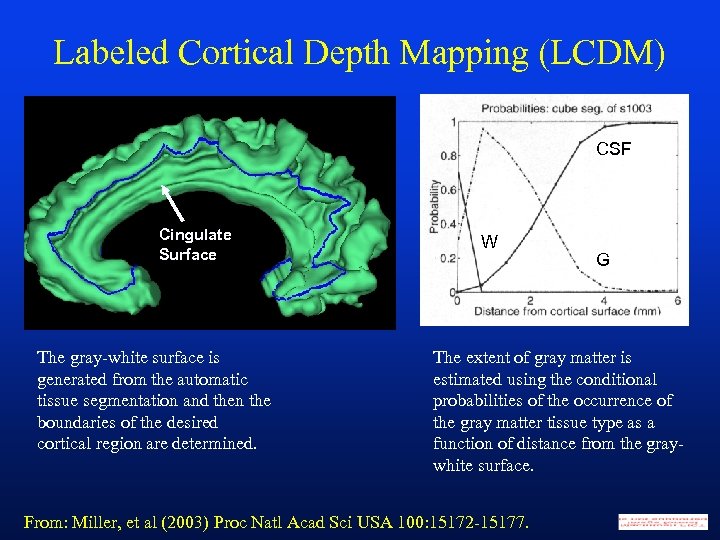
Labeled Cortical Depth Mapping (LCDM) CSF Cingulate Surface The gray-white surface is generated from the automatic tissue segmentation and then the boundaries of the desired cortical region are determined. W G The extent of gray matter is estimated using the conditional probabilities of the occurrence of the gray matter tissue type as a function of distance from the graywhite surface. From: Miller, et al (2003) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 15172 -15177.
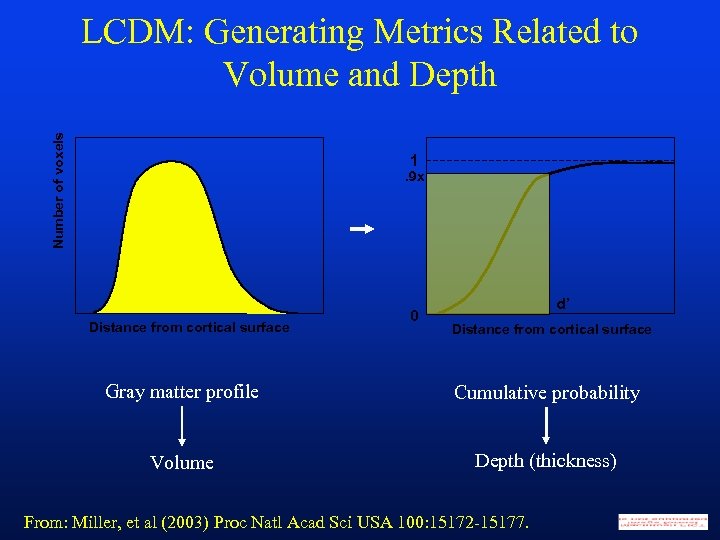
Number of voxels LCDM: Generating Metrics Related to Volume and Depth 1 . 9 x Distance from cortical surface 0 d’ Distance from cortical surface Gray matter profile Cumulative probability Volume Depth (thickness) From: Miller, et al (2003) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 15172 -15177.
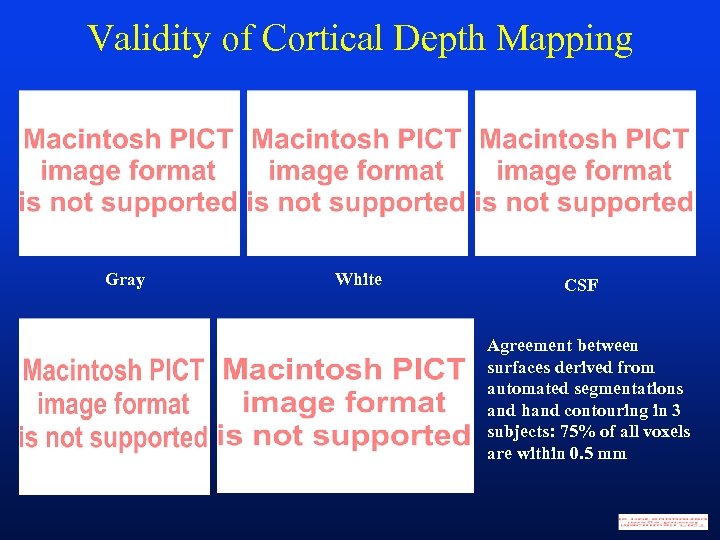
Validity of Cortical Depth Mapping Gray White CSF Agreement between surfaces derived from automated segmentations and hand contouring in 3 subjects: 75% of all voxels are within 0. 5 mm
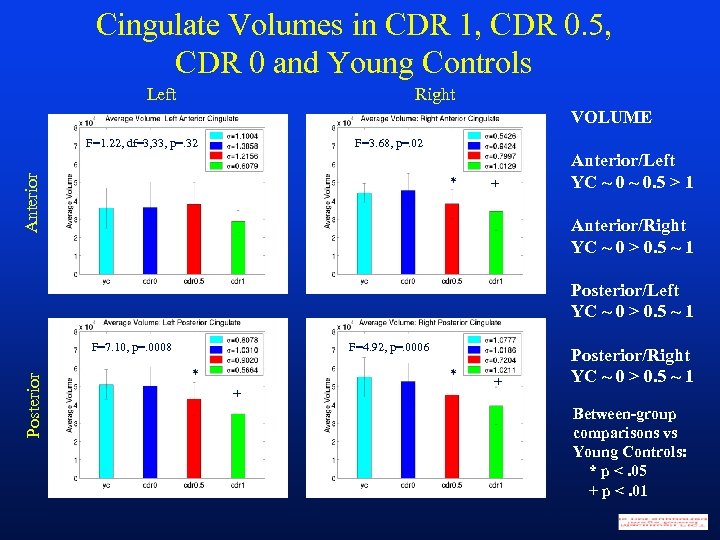
Cingulate Volumes in CDR 1, CDR 0. 5, CDR 0 and Young Controls Left Right VOLUME F=3. 68, p=. 02 Anterior F=1. 22, df=3, 33, p=. 32 * + Anterior/Left YC ~ 0. 5 > 1 Anterior/Right YC ~ 0 > 0. 5 ~ 1 Posterior/Left YC ~ 0 > 0. 5 ~ 1 Posterior F=7. 10, p=. 0008 F=4. 92, p=. 0006 * * + + Posterior/Right YC ~ 0 > 0. 5 ~ 1 Between-group comparisons vs Young Controls: * p <. 05 + p <. 01
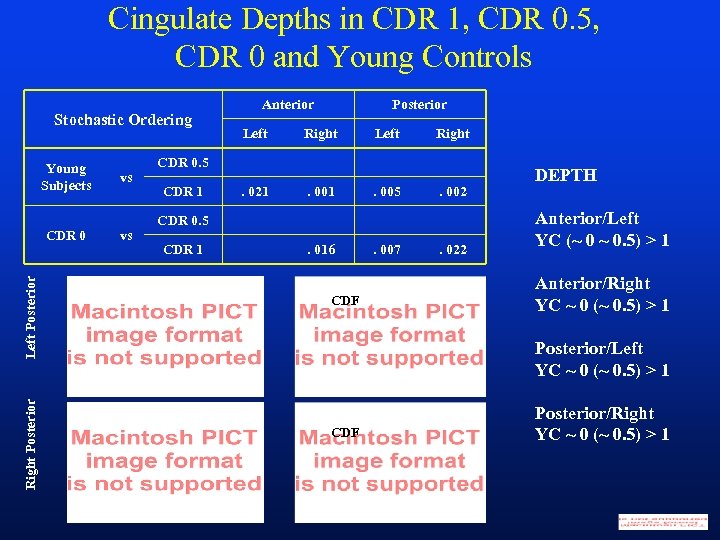
Cingulate Depths in CDR 1, CDR 0. 5, CDR 0 and Young Controls Stochastic Ordering Right Posterior vs CDR 0 Left Posterior Young Subjects vs Anterior Posterior Left Right . 021 . 005 . 002 CDR 0. 5 CDR 1 . 016 CDF . 007 . 022 DEPTH Anterior/Left YC (~ 0 ~ 0. 5) > 1 Anterior/Right YC ~ 0 (~ 0. 5) > 1 Posterior/Left YC ~ 0 (~ 0. 5) > 1 CDF Posterior/Right YC ~ 0 (~ 0. 5) > 1

Summary of Findings in AD • Hippocampus - Smaller volumes and patterns of shape deformation consistent with damage to the CA 1 subfield are present in very mildly demented subjects and progress in parallel with the worsening of dementia. Little change with healthy aging. • Cingulate gyrus (posterior/anterior) - Smaller volumes and thinning are present in mildly demented subjects. Little change with healthy aging. Volume loss may precede thinning (shrinkage of surface area? )
Analysis of Neuroanatomical Structure in Schizophrenia • Group comparisons of individual structures • Analysis of structural asymmetries • Combining information from more than one brain structure
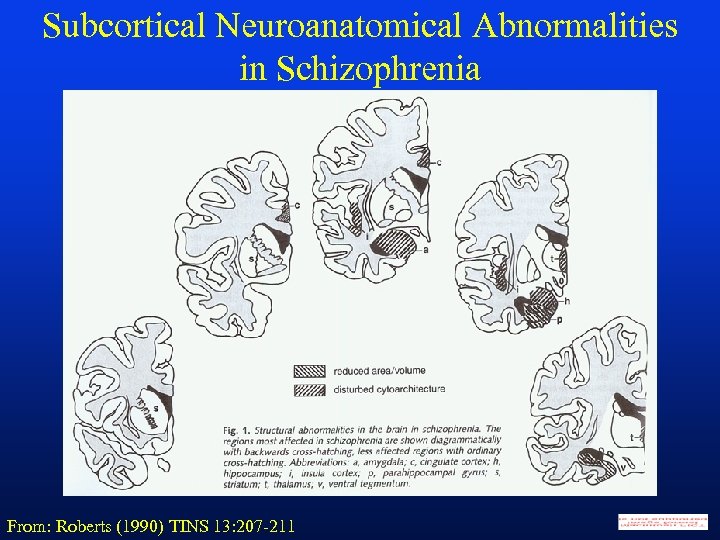
Subcortical Neuroanatomical Abnormalities in Schizophrenia From: Roberts (1990) TINS 13: 207 -211
![Hippocampal Deformities in Schizophrenia Variables (mean +/- SEM [range]) Schizophrenia Subjects Healthy Controls N Hippocampal Deformities in Schizophrenia Variables (mean +/- SEM [range]) Schizophrenia Subjects Healthy Controls N](https://present5.com/presentation/231a5182e589b7a1cc743eac9c2d8f8a/image-38.jpg)
Hippocampal Deformities in Schizophrenia Variables (mean +/- SEM [range]) Schizophrenia Subjects Healthy Controls N Age Gender (M/F) Race (Cau/Afr-Amer/Other) Parental SES Age of Illness Onset Total SAPS Score Total SANS Score 52 38. 0 (1. 74 [20 -63]) 30/22 22/30/2 4. 1 (0. 12 [2 -5]) 22. 8 (1. 18 [13 -54]) 19. 7 (2. 41 [0 -67]) 19. 7 (1. 76 [0 -52]) 65 40. 0 (1. 78 [20 -67]) 33/32 34/18/0 3. 6 (0. 13 [1. 5 -5]) ------- From: Csernansky, et al (2002) Am J Psychiatry 159: 2000 -2006
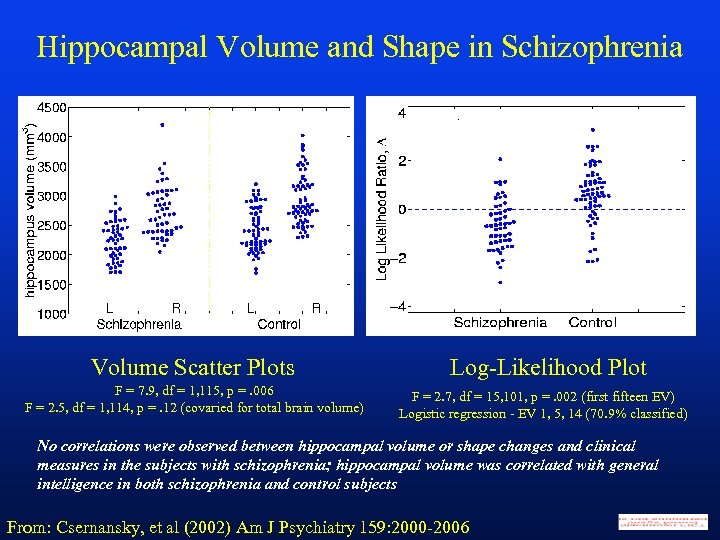
Hippocampal Volume and Shape in Schizophrenia Volume Scatter Plots F = 7. 9, df = 1, 115, p =. 006 F = 2. 5, df = 1, 114, p =. 12 (covaried for total brain volume) Log-Likelihood Plot F = 2. 7, df = 15, 101, p =. 002 (first fifteen EV) Logistic regression - EV 1, 5, 14 (70. 9% classified) No correlations were observed between hippocampal volume or shape changes and clinical measures in the subjects with schizophrenia; hippocampal volume was correlated with general intelligence in both schizophrenia and control subjects From: Csernansky, et al (2002) Am J Psychiatry 159: 2000 -2006
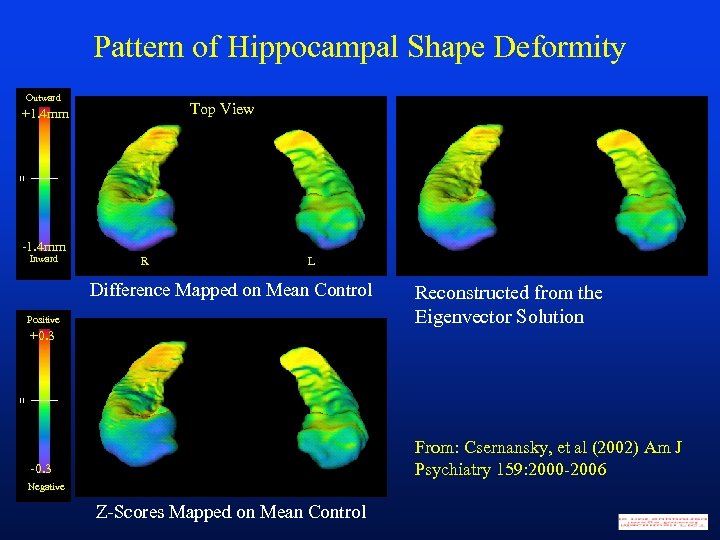
Pattern of Hippocampal Shape Deformity Outward Top View +1. 4 mm -1. 4 mm Inward R L Difference Mapped on Mean Control Positive Reconstructed from the Eigenvector Solution +0. 3 From: Csernansky, et al (2002) Am J Psychiatry 159: 2000 -2006 -0. 3 Negative Z-Scores Mapped on Mean Control
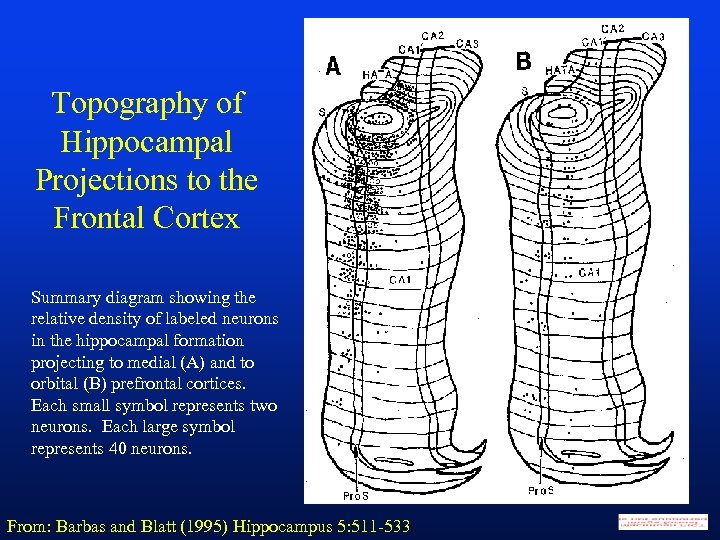
Topography of Hippocampal Projections to the Frontal Cortex Summary diagram showing the relative density of labeled neurons in the hippocampal formation projecting to medial (A) and to orbital (B) prefrontal cortices. Each small symbol represents two neurons. Each large symbol represents 40 neurons. From: Barbas and Blatt (1995) Hippocampus 5: 511 -533
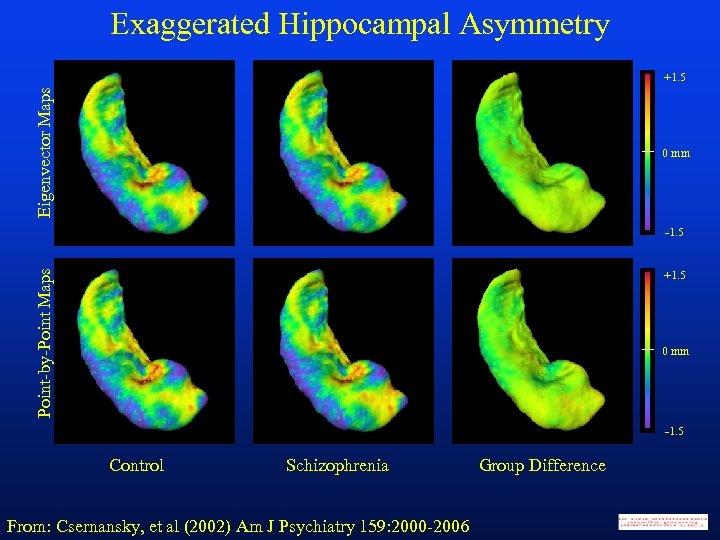
Exaggerated Hippocampal Asymmetry Eigenvector Maps +1. 5 0 mm Point-by-Point Maps -1. 5 +1. 5 0 mm -1. 5 Control Schizophrenia From: Csernansky, et al (2002) Am J Psychiatry 159: 2000 -2006 Group Difference
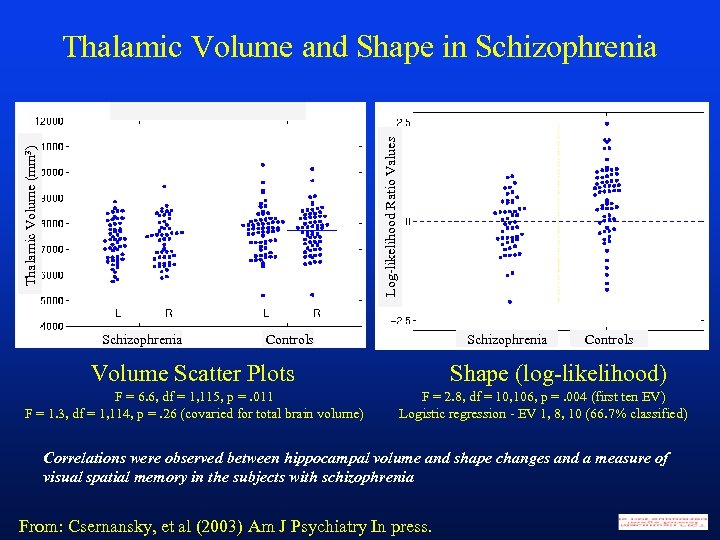
Thalamic Volume (mm 3) Log-likelihood Ratio Values Thalamic Volume and Shape in Schizophrenia Controls Schizophrenia Shape (log-likelihood) Volume Scatter Plots F = 6. 6, df = 1, 115, p =. 011 F = 1. 3, df = 1, 114, p =. 26 (covaried for total brain volume) Controls F = 2. 8, df = 10, 106, p =. 004 (first ten EV) Logistic regression - EV 1, 8, 10 (66. 7% classified) Correlations were observed between hippocampal volume and shape changes and a measure of visual spatial memory in the subjects with schizophrenia From: Csernansky, et al (2003) Am J Psychiatry In press.
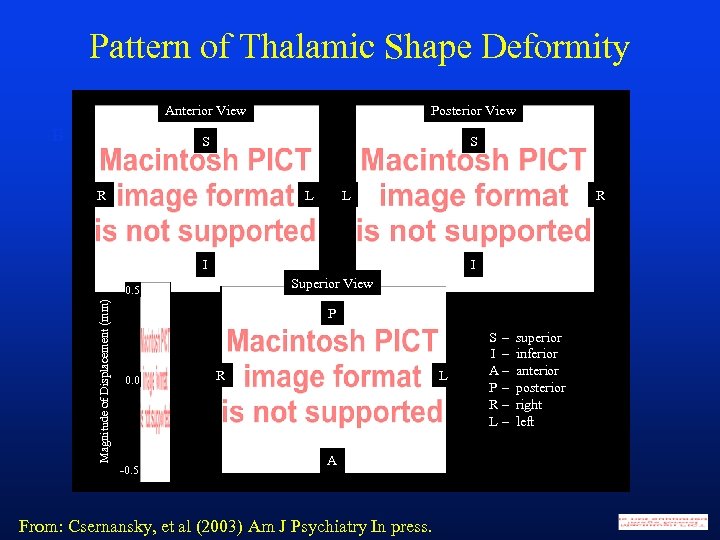
Pattern of Thalamic Shape Deformity Anterior View S B Posterior View S R L L R I I Superior View Magnitude of Displacement (mm) 0. 5 P 0. 0 -0. 5 R L A From: Csernansky, et al (2003) Am J Psychiatry In press. S– I – A– P– R– L– superior inferior anterior posterior right left
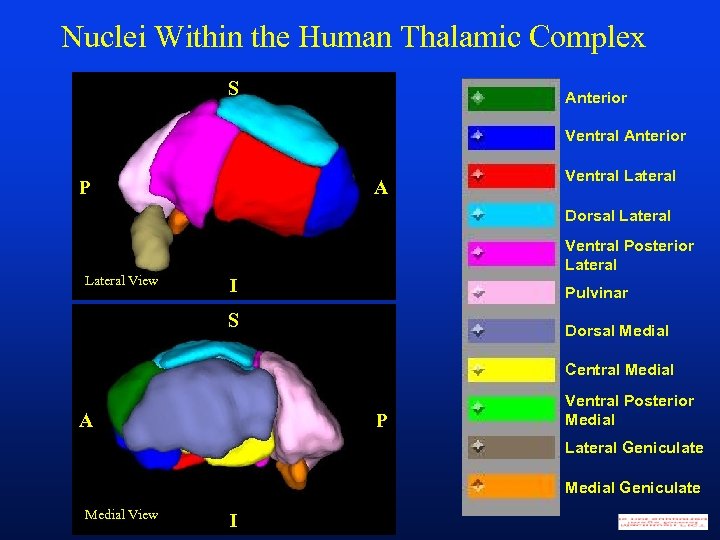
Nuclei Within the Human Thalamic Complex S Anterior Ventral Anterior P A Ventral Lateral Dorsal Lateral View Ventral Posterior Lateral I Pulvinar S Dorsal Medial Central Medial A P Ventral Posterior Medial Lateral Geniculate Medial View I
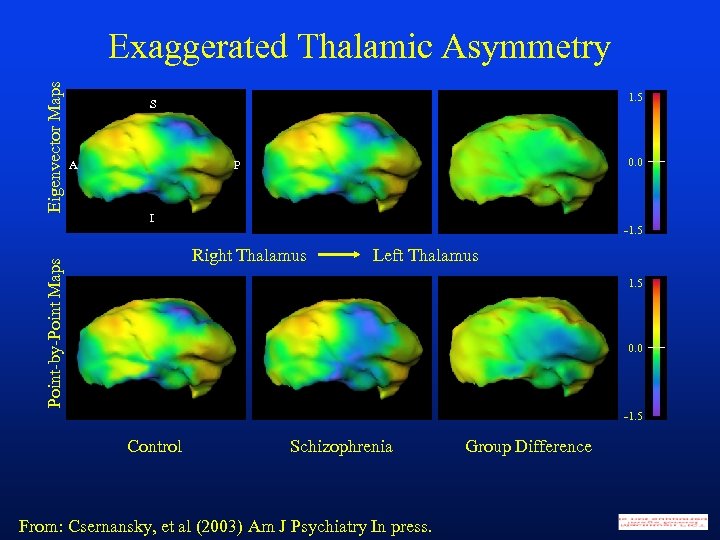
1. 5 S A 0. 0 P I -1. 5 Right Thalamus Point-by-Point Maps Eigenvector Maps Exaggerated Thalamic Asymmetry Left Thalamus 1. 5 0. 0 -1. 5 Control Schizophrenia From: Csernansky, et al (2003) Am J Psychiatry In press. Group Difference
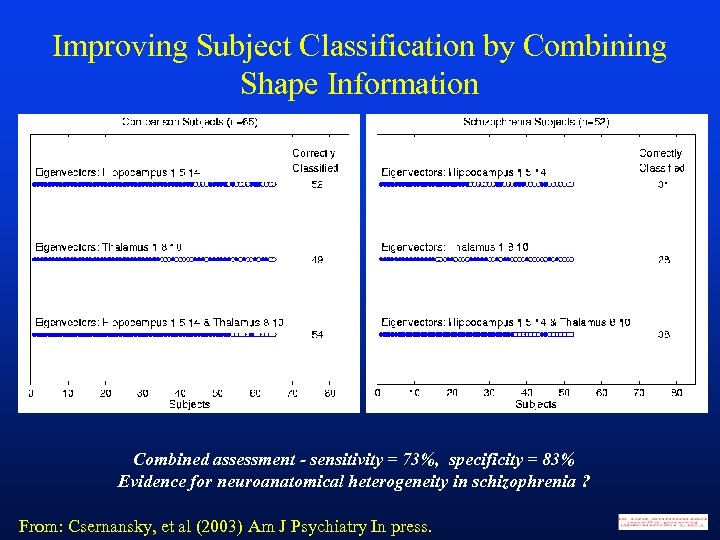
Improving Subject Classification by Combining Shape Information Combined assessment - sensitivity = 73%, specificity = 83% Evidence for neuroanatomical heterogeneity in schizophrenia ? From: Csernansky, et al (2003) Am J Psychiatry In press.

Acknowledgments Collaborators Support Deanna Barch, Ph. D. C. Robert Cloninger, M. D. J. Philip Miller Paul A. Thompson, Ph. D. John C. Morris, M. D. Lei Wang, Ph. D. Thomas Conturo, M. D. Mokhtar Gado, M. D. MH 62130/071616 (Conte) MH 56584 MH 60883 NARSAD AHAF AG 05681 (ADRC) AG 03991 Michael I. Miller, Ph. D. (JHU) Tilak Ratnanather, Ph. D. (JHU) Sarang Joshi, D. Sc. (UNC)
Computational Neuroanatomy Ashburner J, Csernansky JG, Davatzikos C, Fox NC, Frisoni G, Thompson PM. Computer-assisted imaging to assess brain structure in healthy and diseased brains. Lancet: Neurology 2: 79 -88, 2003.
231a5182e589b7a1cc743eac9c2d8f8a.ppt