caa6643c61ae524d54d959f8de3953c5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Compromise at the Constitutional Convention
Compromise at the Constitutional Convention
 Areas of Agreement • Need for a stronger central government • Three Branch Government – Legislative Branch – Executive Branch – Judicial Branch
Areas of Agreement • Need for a stronger central government • Three Branch Government – Legislative Branch – Executive Branch – Judicial Branch
 Areas of Debate • Representation of the states • Slavery • Declaration of war • Executive branch – structure and power • National vs state governments • Election of lower house Articles vs. Constitution
Areas of Debate • Representation of the states • Slavery • Declaration of war • Executive branch – structure and power • National vs state governments • Election of lower house Articles vs. Constitution
 Federal vs. State Authority • Necessary & Proper Clause (Art. I, Sec. 8) – “To make all laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into execution the foregoing powers, and all other powers vested by this Constitution in the government of the United States, or in any department or officer thereof. • 10 th Amendment – “The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people. ”
Federal vs. State Authority • Necessary & Proper Clause (Art. I, Sec. 8) – “To make all laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into execution the foregoing powers, and all other powers vested by this Constitution in the government of the United States, or in any department or officer thereof. • 10 th Amendment – “The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people. ”
 Great Compromise • Bicameral Legislature (2 Houses) • Upper House – Senate – Elected by the States’ legislatures and represent the issues of the state – 2 Senators per State – 6 year terms – Foreign policy focus • Lower House – House of Representatives – Elected by the people of the states to represent the issues of the people – Number of Representatives determined by the state population – 2 years terms – All tax bills MUST start in the House
Great Compromise • Bicameral Legislature (2 Houses) • Upper House – Senate – Elected by the States’ legislatures and represent the issues of the state – 2 Senators per State – 6 year terms – Foreign policy focus • Lower House – House of Representatives – Elected by the people of the states to represent the issues of the people – Number of Representatives determined by the state population – 2 years terms – All tax bills MUST start in the House
 3/5 th Compromise • Slaves and slavery were never directly addressed by name in the Constitution – “all other persons” • Taxation – 3/5 th of the value of a slave counts as property for the purpose of taxation • Representation – 3/5 th of the number of slaves in a state count towards the state’s population for the purpose of representation in the House of Representatives
3/5 th Compromise • Slaves and slavery were never directly addressed by name in the Constitution – “all other persons” • Taxation – 3/5 th of the value of a slave counts as property for the purpose of taxation • Representation – 3/5 th of the number of slaves in a state count towards the state’s population for the purpose of representation in the House of Representatives
 Executive Compromise • • Single Executive – President Elected by Electoral College Term of 4 years Commander in Chief but the Congress declares war and controls the money
Executive Compromise • • Single Executive – President Elected by Electoral College Term of 4 years Commander in Chief but the Congress declares war and controls the money
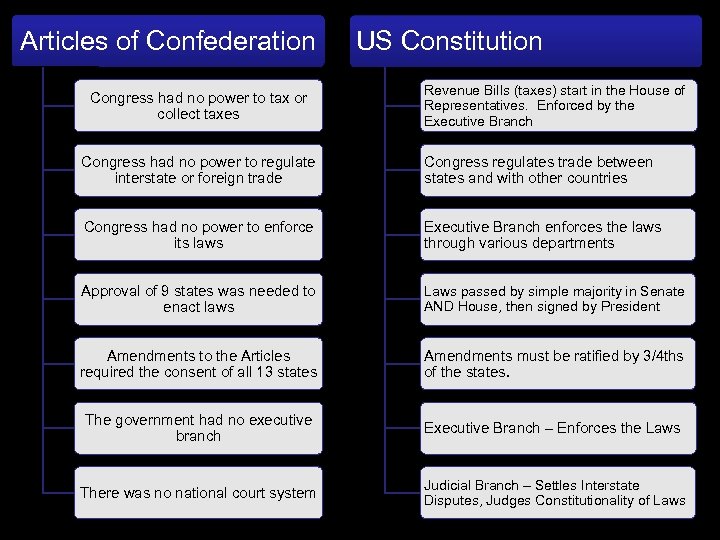 Articles of Confederation Congress had no power to tax or collect taxes US Constitution Revenue Bills (taxes) start in the House of Representatives. Enforced by the Executive Branch Congress had no power to regulate interstate or foreign trade Congress regulates trade between states and with other countries Congress had no power to enforce its laws Executive Branch enforces the laws through various departments Approval of 9 states was needed to enact laws Laws passed by simple majority in Senate AND House, then signed by President Amendments to the Articles required the consent of all 13 states Amendments must be ratified by 3/4 ths of the states. The government had no executive branch Executive Branch – Enforces the Laws There was no national court system Judicial Branch – Settles Interstate Disputes, Judges Constitutionality of Laws
Articles of Confederation Congress had no power to tax or collect taxes US Constitution Revenue Bills (taxes) start in the House of Representatives. Enforced by the Executive Branch Congress had no power to regulate interstate or foreign trade Congress regulates trade between states and with other countries Congress had no power to enforce its laws Executive Branch enforces the laws through various departments Approval of 9 states was needed to enact laws Laws passed by simple majority in Senate AND House, then signed by President Amendments to the Articles required the consent of all 13 states Amendments must be ratified by 3/4 ths of the states. The government had no executive branch Executive Branch – Enforces the Laws There was no national court system Judicial Branch – Settles Interstate Disputes, Judges Constitutionality of Laws
 Ratification of the Constitution
Ratification of the Constitution
 Federalists & Antifederalists • Antifederalists—people who opposed the Constitution – Complaints • Had gone too far • Central government too powerful • No bill of rights – Most were small farmers and debtors
Federalists & Antifederalists • Antifederalists—people who opposed the Constitution – Complaints • Had gone too far • Central government too powerful • No bill of rights – Most were small farmers and debtors
 Federalists & Antifederalists • Federalists—people who supported the Constitution • Reason for support: – US needed a stronger government – Careful compromise – Good balance of state and national power
Federalists & Antifederalists • Federalists—people who supported the Constitution • Reason for support: – US needed a stronger government – Careful compromise – Good balance of state and national power
 The Ratification Debate • The process: – Required approval of nine states – All states except RI held conventions – Antifederalists participated • The Federalist Papers – 85 essays written in support of the Constitution – Written by “Publius” (Hamilton, Madison, Jay)
The Ratification Debate • The process: – Required approval of nine states – All states except RI held conventions – Antifederalists participated • The Federalist Papers – 85 essays written in support of the Constitution – Written by “Publius” (Hamilton, Madison, Jay)
 The Ratification Debate • December 7, 1787: Delaware becomes the first state to ratify Constitution • June 1788: With the ratification of 9 states, Constitution goes into effect • NY, NC, RI, & VA hold out – NY: important trade center – VA: largest population • May 1790: RI becomes last state to ratify
The Ratification Debate • December 7, 1787: Delaware becomes the first state to ratify Constitution • June 1788: With the ratification of 9 states, Constitution goes into effect • NY, NC, RI, & VA hold out – NY: important trade center – VA: largest population • May 1790: RI becomes last state to ratify
 Demanding the Bill of Rights • Antifederalists: – Did not believe Constitution would protect personal freedoms – Demand bill of rights • Federalists: – State constitutions promised rights – Document written to protect rights • Madison understood bill of rights needed for ratification – September 1789: Congress proposes 12 amendments – December 1791: 10 of 12 amendments ratified
Demanding the Bill of Rights • Antifederalists: – Did not believe Constitution would protect personal freedoms – Demand bill of rights • Federalists: – State constitutions promised rights – Document written to protect rights • Madison understood bill of rights needed for ratification – September 1789: Congress proposes 12 amendments – December 1791: 10 of 12 amendments ratified
 Bill of Rights Preamble • Congress of the United States begun and held at the City of New-York, on Wednesday the fourth of March, one thousand seven hundred and eighty nine • THE Conventions of a number of the States, having at the time of their adopting the Constitution, expressed a desire, in order to prevent misconstruction or abuse of its powers, that further declaratory and restrictive clauses should be added: And as extending the ground of public confidence in the Government, will best ensure the beneficent ends of its institution. • • RESOLVED by the Senate and House of Representatives of the United States of America, in Congress assembled, two thirds of both Houses concurring, that the following Articles be proposed to the Legislatures of the several States, as amendments to the Constitution of the United States, all, or any of which Articles, when ratified by three fourths of the said Legislatures, to be valid to all intents and purposes, as part of the said Constitution; viz. ARTICLES in addition to, and Amendment of the Constitution of the United States of America, proposed by Congress, and ratified by the Legislatures of the several States, pursuant to the fifth Article of the original Constitution
Bill of Rights Preamble • Congress of the United States begun and held at the City of New-York, on Wednesday the fourth of March, one thousand seven hundred and eighty nine • THE Conventions of a number of the States, having at the time of their adopting the Constitution, expressed a desire, in order to prevent misconstruction or abuse of its powers, that further declaratory and restrictive clauses should be added: And as extending the ground of public confidence in the Government, will best ensure the beneficent ends of its institution. • • RESOLVED by the Senate and House of Representatives of the United States of America, in Congress assembled, two thirds of both Houses concurring, that the following Articles be proposed to the Legislatures of the several States, as amendments to the Constitution of the United States, all, or any of which Articles, when ratified by three fourths of the said Legislatures, to be valid to all intents and purposes, as part of the said Constitution; viz. ARTICLES in addition to, and Amendment of the Constitution of the United States of America, proposed by Congress, and ratified by the Legislatures of the several States, pursuant to the fifth Article of the original Constitution


