122ea394385f58092c4c4b200ca9cbeb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 Comprehensive IHC Screening for Lynch Syndrome: What You Need to Know Andrea Lewis, MS, CGC January 14, 2010
Comprehensive IHC Screening for Lynch Syndrome: What You Need to Know Andrea Lewis, MS, CGC January 14, 2010
 Overview l Lynch syndrome review l Norton Comprehensive IHC Screening Program l Interpreting IHC results
Overview l Lynch syndrome review l Norton Comprehensive IHC Screening Program l Interpreting IHC results
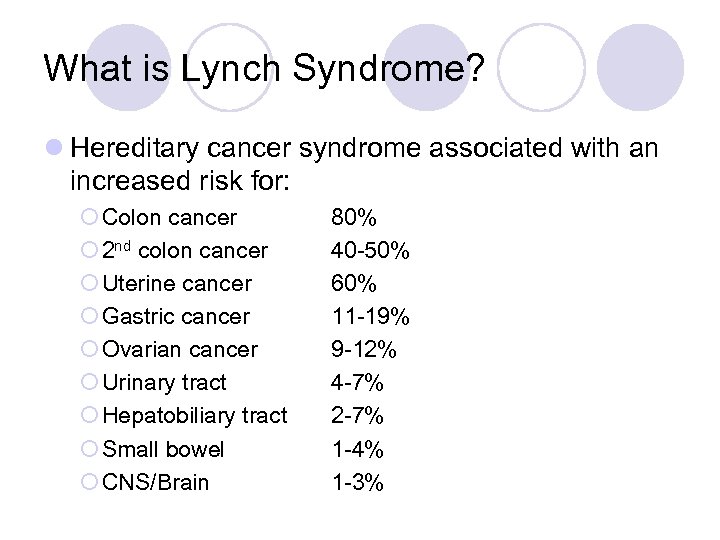 What is Lynch Syndrome? l Hereditary cancer syndrome associated with an increased risk for: ¡ Colon cancer ¡ 2 nd colon cancer ¡ Uterine cancer ¡ Gastric cancer ¡ Ovarian cancer ¡ Urinary tract ¡ Hepatobiliary tract ¡ Small bowel ¡ CNS/Brain 80% 40 -50% 60% 11 -19% 9 -12% 4 -7% 2 -7% 1 -4% 1 -3%
What is Lynch Syndrome? l Hereditary cancer syndrome associated with an increased risk for: ¡ Colon cancer ¡ 2 nd colon cancer ¡ Uterine cancer ¡ Gastric cancer ¡ Ovarian cancer ¡ Urinary tract ¡ Hepatobiliary tract ¡ Small bowel ¡ CNS/Brain 80% 40 -50% 60% 11 -19% 9 -12% 4 -7% 2 -7% 1 -4% 1 -3%
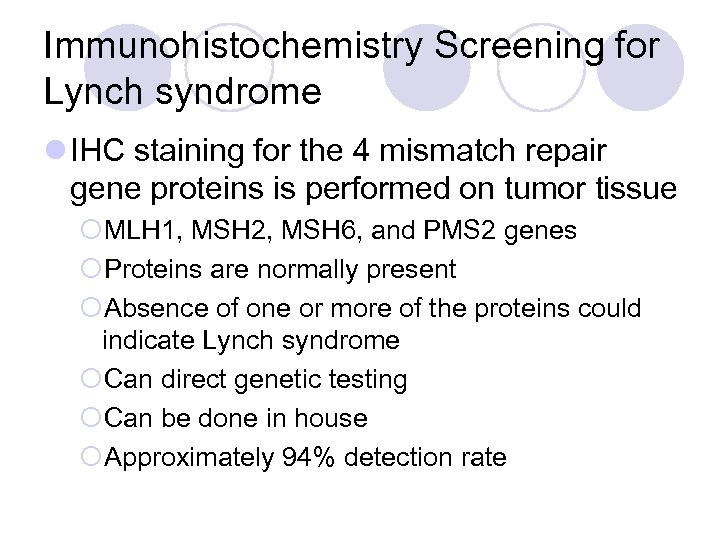 Immunohistochemistry Screening for Lynch syndrome l IHC staining for the 4 mismatch repair gene proteins is performed on tumor tissue ¡MLH 1, MSH 2, MSH 6, and PMS 2 genes ¡Proteins are normally present ¡Absence of one or more of the proteins could indicate Lynch syndrome ¡Can direct genetic testing ¡Can be done in house ¡Approximately 94% detection rate
Immunohistochemistry Screening for Lynch syndrome l IHC staining for the 4 mismatch repair gene proteins is performed on tumor tissue ¡MLH 1, MSH 2, MSH 6, and PMS 2 genes ¡Proteins are normally present ¡Absence of one or more of the proteins could indicate Lynch syndrome ¡Can direct genetic testing ¡Can be done in house ¡Approximately 94% detection rate
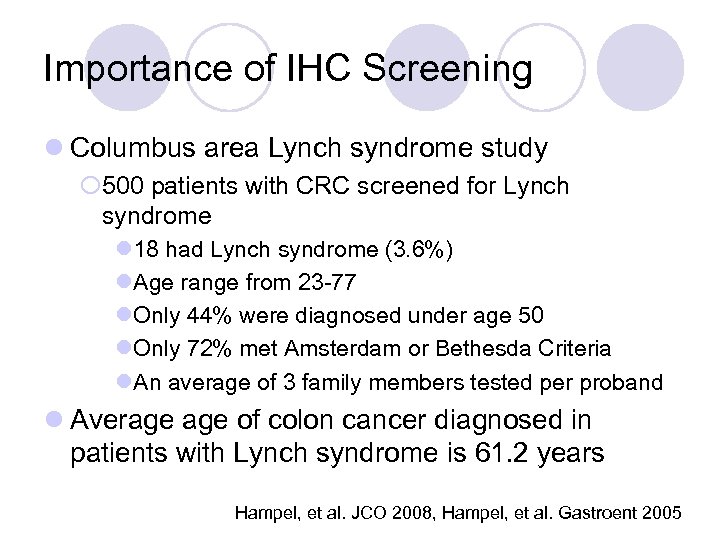 Importance of IHC Screening l Columbus area Lynch syndrome study ¡ 500 patients with CRC screened for Lynch syndrome l 18 had Lynch syndrome (3. 6%) l. Age range from 23 -77 l. Only 44% were diagnosed under age 50 l. Only 72% met Amsterdam or Bethesda Criteria l. An average of 3 family members tested per proband l Average of colon cancer diagnosed in patients with Lynch syndrome is 61. 2 years Hampel, et al. JCO 2008, Hampel, et al. Gastroent 2005
Importance of IHC Screening l Columbus area Lynch syndrome study ¡ 500 patients with CRC screened for Lynch syndrome l 18 had Lynch syndrome (3. 6%) l. Age range from 23 -77 l. Only 44% were diagnosed under age 50 l. Only 72% met Amsterdam or Bethesda Criteria l. An average of 3 family members tested per proband l Average of colon cancer diagnosed in patients with Lynch syndrome is 61. 2 years Hampel, et al. JCO 2008, Hampel, et al. Gastroent 2005
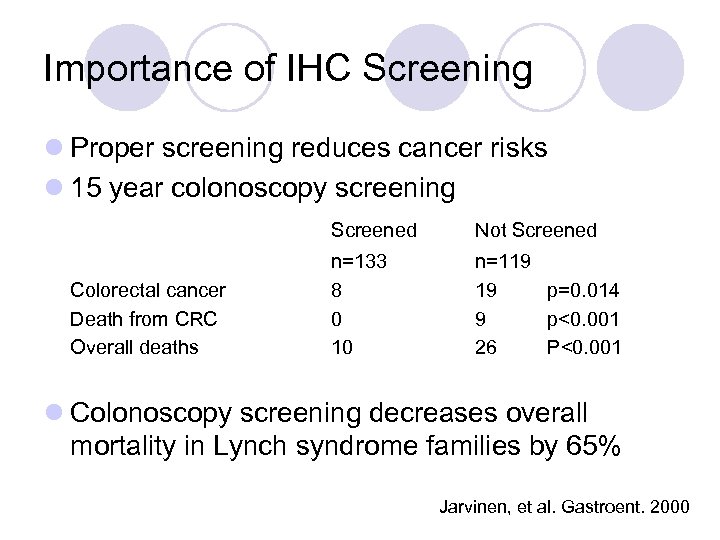 Importance of IHC Screening l Proper screening reduces cancer risks l 15 year colonoscopy screening Screened Colorectal cancer Death from CRC Overall deaths Not Screened n=133 8 0 10 n=119 19 p=0. 014 9 p<0. 001 26 P<0. 001 l Colonoscopy screening decreases overall mortality in Lynch syndrome families by 65% Jarvinen, et al. Gastroent. 2000
Importance of IHC Screening l Proper screening reduces cancer risks l 15 year colonoscopy screening Screened Colorectal cancer Death from CRC Overall deaths Not Screened n=133 8 0 10 n=119 19 p=0. 014 9 p<0. 001 26 P<0. 001 l Colonoscopy screening decreases overall mortality in Lynch syndrome families by 65% Jarvinen, et al. Gastroent. 2000
 Norton Comprehensive IHC Program l Launched October 1, 2009 l IHC for Lynch sx performed on all colorectal cancers resected at Norton Healthcare l All results sent to Genetic Counseling Service l Process for abnormal results ¡Surgeon is contacted to discuss follow-up plan ¡Patient is offered genetic counseling appointment ¡Gene specific testing for Lynch syndrome performed
Norton Comprehensive IHC Program l Launched October 1, 2009 l IHC for Lynch sx performed on all colorectal cancers resected at Norton Healthcare l All results sent to Genetic Counseling Service l Process for abnormal results ¡Surgeon is contacted to discuss follow-up plan ¡Patient is offered genetic counseling appointment ¡Gene specific testing for Lynch syndrome performed
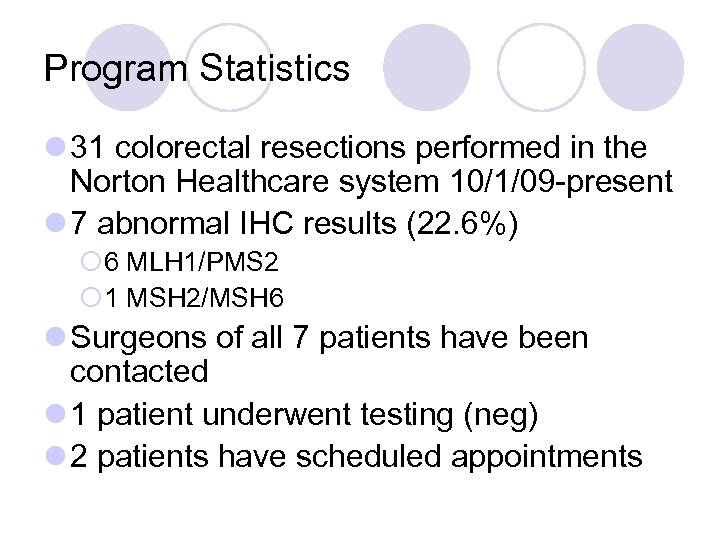 Program Statistics l 31 colorectal resections performed in the Norton Healthcare system 10/1/09 -present l 7 abnormal IHC results (22. 6%) ¡ 6 MLH 1/PMS 2 ¡ 1 MSH 2/MSH 6 l Surgeons of all 7 patients have been contacted l 1 patient underwent testing (neg) l 2 patients have scheduled appointments
Program Statistics l 31 colorectal resections performed in the Norton Healthcare system 10/1/09 -present l 7 abnormal IHC results (22. 6%) ¡ 6 MLH 1/PMS 2 ¡ 1 MSH 2/MSH 6 l Surgeons of all 7 patients have been contacted l 1 patient underwent testing (neg) l 2 patients have scheduled appointments
 Interpreting IHC Results
Interpreting IHC Results
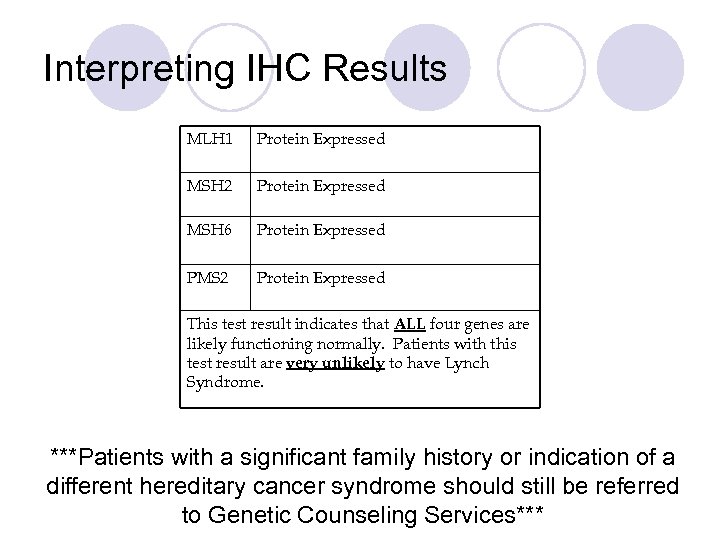 Interpreting IHC Results MLH 1 Protein Expressed MSH 2 Protein Expressed MSH 6 Protein Expressed PMS 2 Protein Expressed This test result indicates that ALL four genes are likely functioning normally. Patients with this test result are very unlikely to have Lynch Syndrome. ***Patients with a significant family history or indication of a different hereditary cancer syndrome should still be referred to Genetic Counseling Services***
Interpreting IHC Results MLH 1 Protein Expressed MSH 2 Protein Expressed MSH 6 Protein Expressed PMS 2 Protein Expressed This test result indicates that ALL four genes are likely functioning normally. Patients with this test result are very unlikely to have Lynch Syndrome. ***Patients with a significant family history or indication of a different hereditary cancer syndrome should still be referred to Genetic Counseling Services***
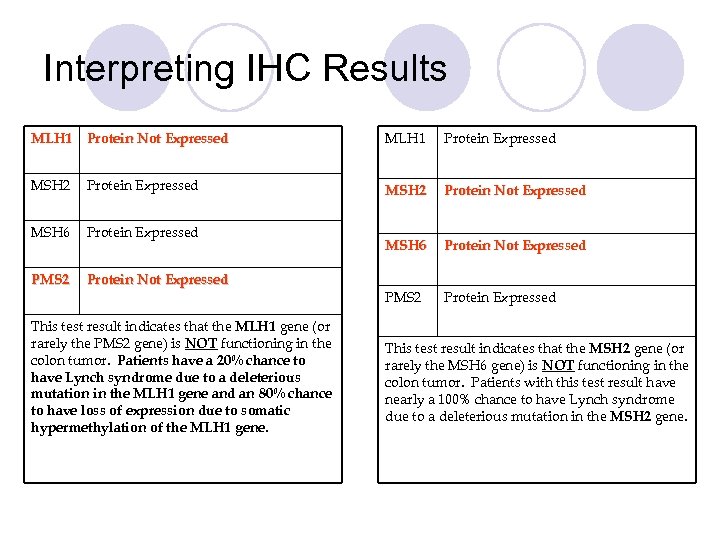 Interpreting IHC Results MLH 1 Protein Not Expressed MLH 1 Protein Expressed MSH 2 Protein Not Expressed MSH 6 Protein Not Expressed PMS 2 Protein Expressed This test result indicates that the MLH 1 gene (or rarely the PMS 2 gene) is NOT functioning in the colon tumor. Patients have a 20% chance to have Lynch syndrome due to a deleterious mutation in the MLH 1 gene and an 80% chance to have loss of expression due to somatic hypermethylation of the MLH 1 gene. This test result indicates that the MSH 2 gene (or rarely the MSH 6 gene) is NOT functioning in the colon tumor. Patients with this test result have nearly a 100% chance to have Lynch syndrome due to a deleterious mutation in the MSH 2 gene.
Interpreting IHC Results MLH 1 Protein Not Expressed MLH 1 Protein Expressed MSH 2 Protein Not Expressed MSH 6 Protein Not Expressed PMS 2 Protein Expressed This test result indicates that the MLH 1 gene (or rarely the PMS 2 gene) is NOT functioning in the colon tumor. Patients have a 20% chance to have Lynch syndrome due to a deleterious mutation in the MLH 1 gene and an 80% chance to have loss of expression due to somatic hypermethylation of the MLH 1 gene. This test result indicates that the MSH 2 gene (or rarely the MSH 6 gene) is NOT functioning in the colon tumor. Patients with this test result have nearly a 100% chance to have Lynch syndrome due to a deleterious mutation in the MSH 2 gene.
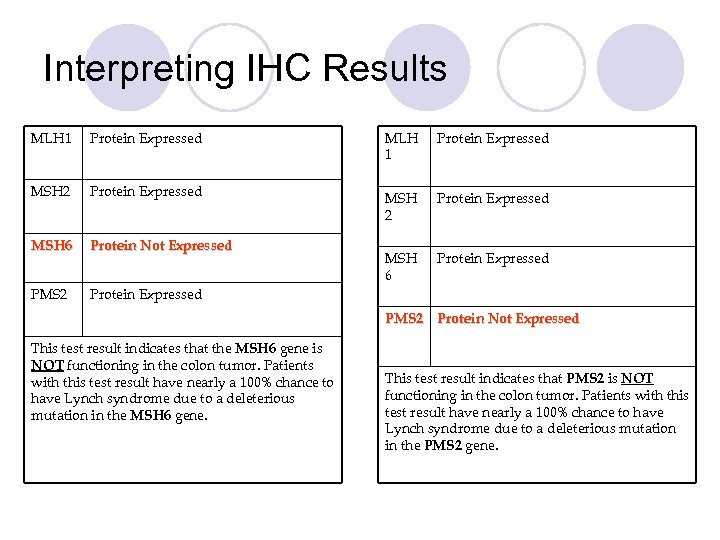 Interpreting IHC Results MLH 1 Protein Expressed MSH 2 Protein Expressed MSH 6 Protein Not Expressed MSH 6 Protein Expressed PMS 2 Protein Not Expressed This test result indicates that the MSH 6 gene is NOT functioning in the colon tumor. Patients with this test result have nearly a 100% chance to have Lynch syndrome due to a deleterious mutation in the MSH 6 gene. This test result indicates that PMS 2 is NOT functioning in the colon tumor. Patients with this test result have nearly a 100% chance to have Lynch syndrome due to a deleterious mutation in the PMS 2 gene.
Interpreting IHC Results MLH 1 Protein Expressed MSH 2 Protein Expressed MSH 6 Protein Not Expressed MSH 6 Protein Expressed PMS 2 Protein Not Expressed This test result indicates that the MSH 6 gene is NOT functioning in the colon tumor. Patients with this test result have nearly a 100% chance to have Lynch syndrome due to a deleterious mutation in the MSH 6 gene. This test result indicates that PMS 2 is NOT functioning in the colon tumor. Patients with this test result have nearly a 100% chance to have Lynch syndrome due to a deleterious mutation in the PMS 2 gene.
 Questions?
Questions?


