af1eae133a634149eb69e95768578df9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49
 Compliance Road Maps Vipul Doshi Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Limited
Compliance Road Maps Vipul Doshi Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Limited
 Preamble • The Pharmaceutical Industry is constantly being challenged to comply with rigorous regulatory requirements. • Satisfying regulatory agencies that a company’s processes are being operated at a level of control that will ensure that their products will meet predetermined safety, efficacy and quality specifications. • Compliance is evolving from an isolated departmental initiative to an enterprise level risk management challenge. • However, compliance is not a one-time event and organizations are redesigning their compliance programs to make them repeatable processes that could be sustained.
Preamble • The Pharmaceutical Industry is constantly being challenged to comply with rigorous regulatory requirements. • Satisfying regulatory agencies that a company’s processes are being operated at a level of control that will ensure that their products will meet predetermined safety, efficacy and quality specifications. • Compliance is evolving from an isolated departmental initiative to an enterprise level risk management challenge. • However, compliance is not a one-time event and organizations are redesigning their compliance programs to make them repeatable processes that could be sustained.
 Cost of Non – Compliance Regulators Act ! Non Compliance Observations Warning Letter (WL) Import Alerts Withheld Approvals Cancellation Of Government Contracts Product Recalls Seizures A Consent Decree Of Permanent Injunction Civil Money Penalties Suspension / Revocation Prosecution
Cost of Non – Compliance Regulators Act ! Non Compliance Observations Warning Letter (WL) Import Alerts Withheld Approvals Cancellation Of Government Contracts Product Recalls Seizures A Consent Decree Of Permanent Injunction Civil Money Penalties Suspension / Revocation Prosecution
 Who Governs
Who Governs
 Challenges • Rising Standards of Quality • Rising Regulatory requirements and reporting mandates • International Regulatory Requirement Harmonization Compliance is not one time requirement, it’s required Round the Clock
Challenges • Rising Standards of Quality • Rising Regulatory requirements and reporting mandates • International Regulatory Requirement Harmonization Compliance is not one time requirement, it’s required Round the Clock
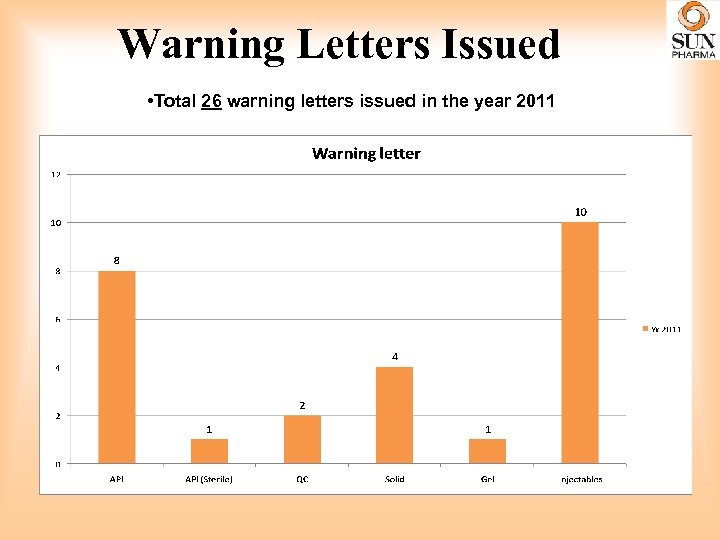 Warning Letters Issued • Total 26 warning letters issued in the year 2011
Warning Letters Issued • Total 26 warning letters issued in the year 2011
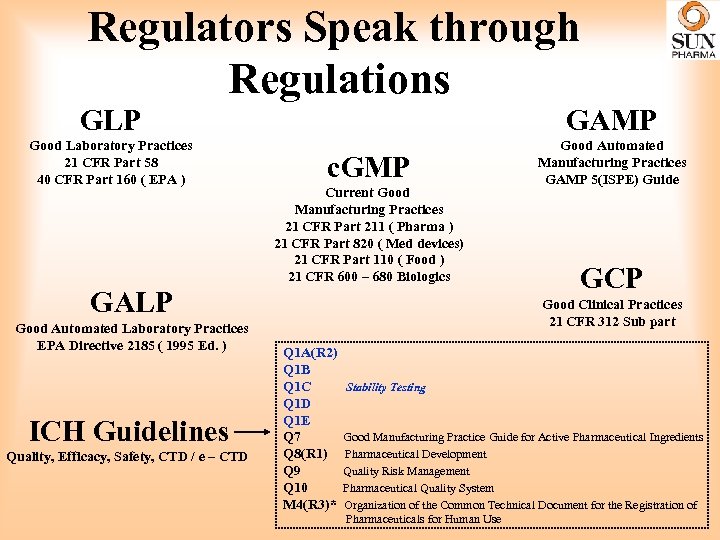 Regulators Speak through Regulations GLP GAMP Good Laboratory Practices 21 CFR Part 58 40 CFR Part 160 ( EPA ) Good Automated Manufacturing Practices GAMP 5(ISPE) Guide c. GMP Current Good Manufacturing Practices 21 CFR Part 211 ( Pharma ) 21 CFR Part 820 ( Med devices) 21 CFR Part 110 ( Food ) 21 CFR 600 – 680 Biologics GALP Good Automated Laboratory Practices EPA Directive 2185 ( 1995 Ed. ) ICH Guidelines Quality, Efficacy, Safety, CTD / e – CTD GCP Good Clinical Practices 21 CFR 312 Sub part Q 1 A(R 2) Q 1 B Q 1 C Q 1 D Q 1 E Q 7 Q 8(R 1) Q 9 Q 10 M 4(R 3)* Stability Testing Good Manufacturing Practice Guide for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Pharmaceutical Development Quality Risk Management Pharmaceutical Quality System Organization of the Common Technical Document for the Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use
Regulators Speak through Regulations GLP GAMP Good Laboratory Practices 21 CFR Part 58 40 CFR Part 160 ( EPA ) Good Automated Manufacturing Practices GAMP 5(ISPE) Guide c. GMP Current Good Manufacturing Practices 21 CFR Part 211 ( Pharma ) 21 CFR Part 820 ( Med devices) 21 CFR Part 110 ( Food ) 21 CFR 600 – 680 Biologics GALP Good Automated Laboratory Practices EPA Directive 2185 ( 1995 Ed. ) ICH Guidelines Quality, Efficacy, Safety, CTD / e – CTD GCP Good Clinical Practices 21 CFR 312 Sub part Q 1 A(R 2) Q 1 B Q 1 C Q 1 D Q 1 E Q 7 Q 8(R 1) Q 9 Q 10 M 4(R 3)* Stability Testing Good Manufacturing Practice Guide for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Pharmaceutical Development Quality Risk Management Pharmaceutical Quality System Organization of the Common Technical Document for the Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use
 Regulators Speak through Regulations • GMP guidelines comprise strong recommendation on Quality Management, Personnel Production, Facility and Equipment, Documentation and Records, Product and inprocess Control, Packaging and Identification, Labeling, Storage and Distribution, Laboratory Controls, Validation, Complaint and Recalls, and Contract Manufacturers. • The WHO version of GMPs was prepared in 2004 (20 th World Assembly) from then, there are several amendments and extensions of the guidelines. • Schedule M (1987): Good Manufacturing Practices and requirements of Premises , Plant and Equipment for Pharmaceutical Products were regulated. • Schedule M (2001) : Stringent norms to match with Global requirements were devised.
Regulators Speak through Regulations • GMP guidelines comprise strong recommendation on Quality Management, Personnel Production, Facility and Equipment, Documentation and Records, Product and inprocess Control, Packaging and Identification, Labeling, Storage and Distribution, Laboratory Controls, Validation, Complaint and Recalls, and Contract Manufacturers. • The WHO version of GMPs was prepared in 2004 (20 th World Assembly) from then, there are several amendments and extensions of the guidelines. • Schedule M (1987): Good Manufacturing Practices and requirements of Premises , Plant and Equipment for Pharmaceutical Products were regulated. • Schedule M (2001) : Stringent norms to match with Global requirements were devised.
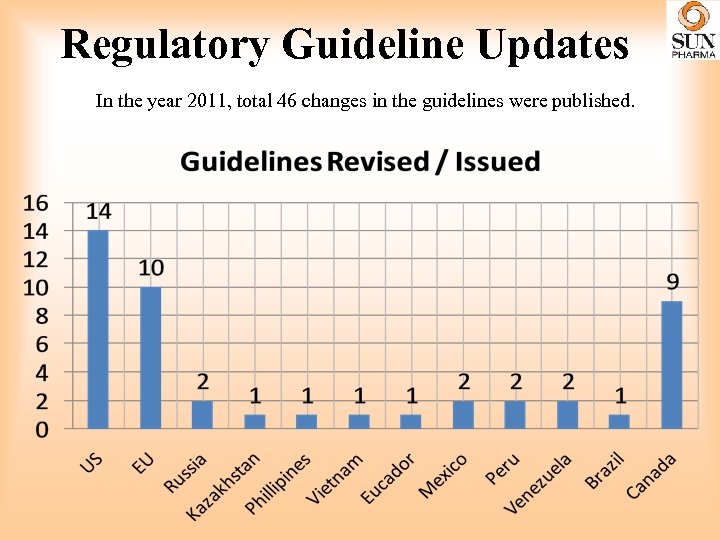 Regulatory Guideline Updates In the year 2011, total 46 changes in the guidelines were published.
Regulatory Guideline Updates In the year 2011, total 46 changes in the guidelines were published.
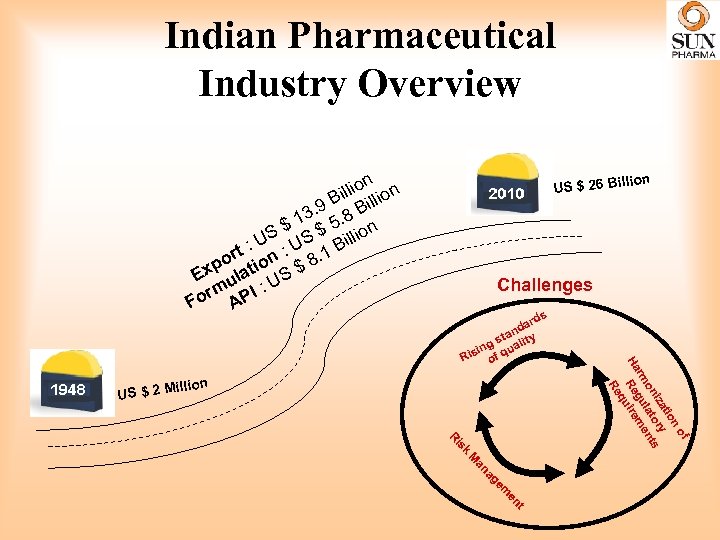 Indian Pharmaceutical Industry Overview n illion B i 3. 9. 8 B $ 1 $ 5 ion S : US 1 Bill rt po ation $ 8. Ex ul S m PI : U r Fo A lion US $ 26 Bil Challenges illion US $ 2 M s k is R of n tio iza ory s on lat nt rm gu me Ha Re uire q Re ard nd ta y g s ualit in q Ris of t en em ag an M
Indian Pharmaceutical Industry Overview n illion B i 3. 9. 8 B $ 1 $ 5 ion S : US 1 Bill rt po ation $ 8. Ex ul S m PI : U r Fo A lion US $ 26 Bil Challenges illion US $ 2 M s k is R of n tio iza ory s on lat nt rm gu me Ha Re uire q Re ard nd ta y g s ualit in q Ris of t en em ag an M
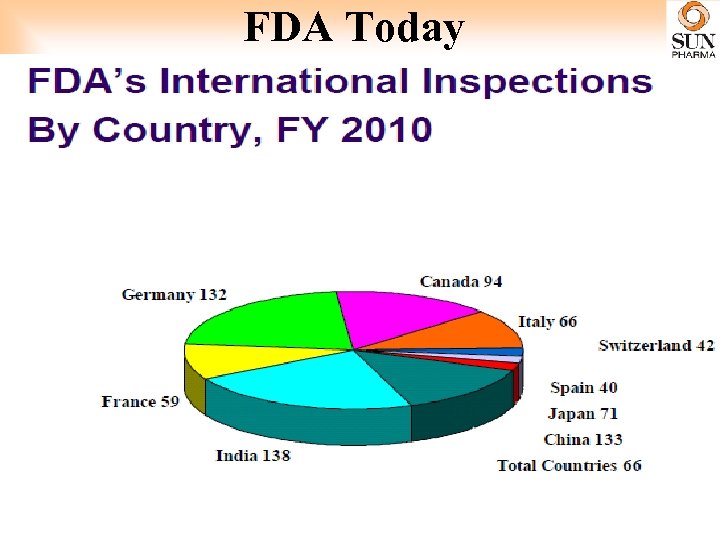 FDA Today
FDA Today
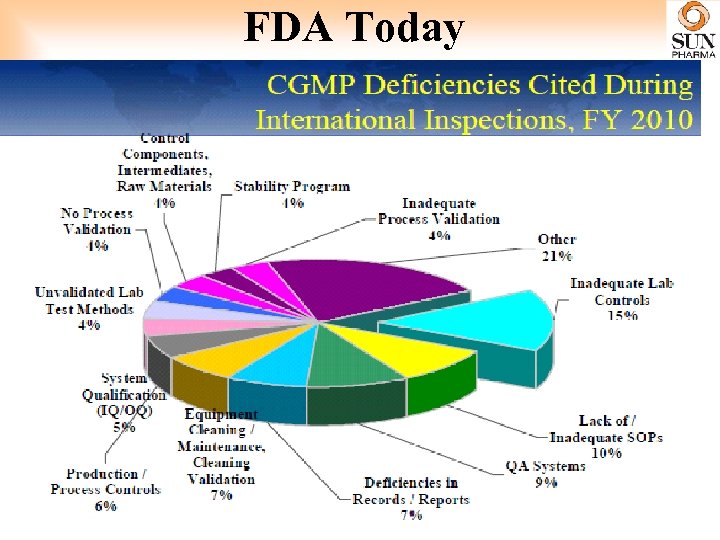 FDA Today
FDA Today
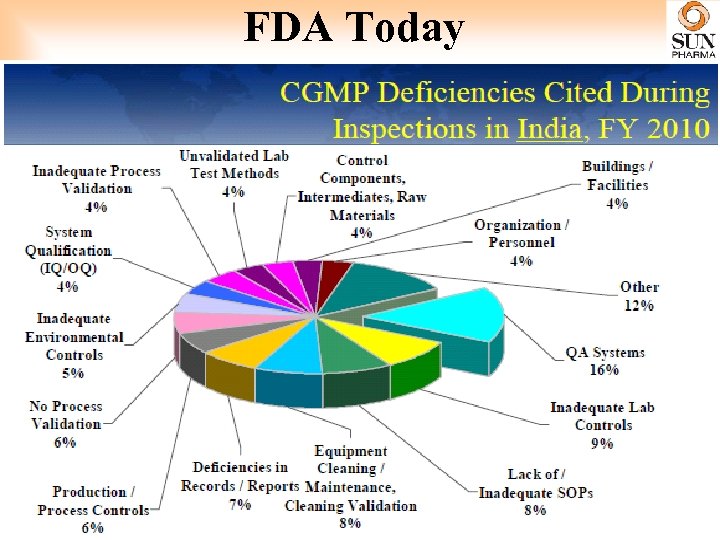 FDA Today
FDA Today
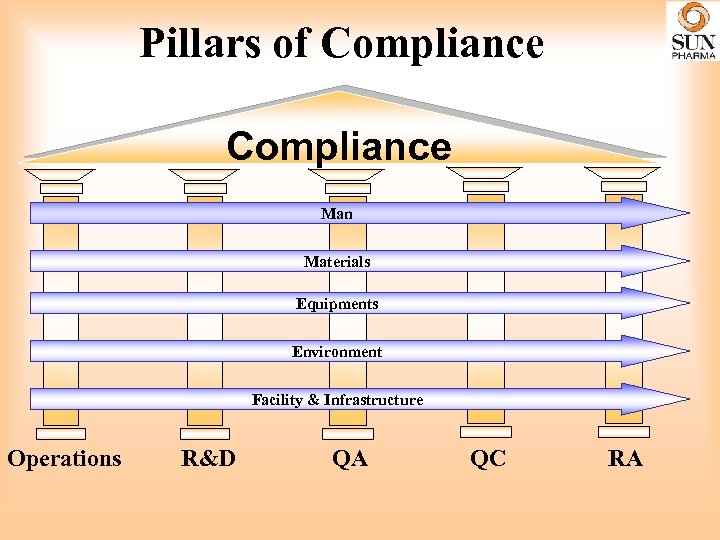 Pillars of Compliance Man Materials Equipments Environment Facility & Infrastructure Operations R&D QA QC RA
Pillars of Compliance Man Materials Equipments Environment Facility & Infrastructure Operations R&D QA QC RA
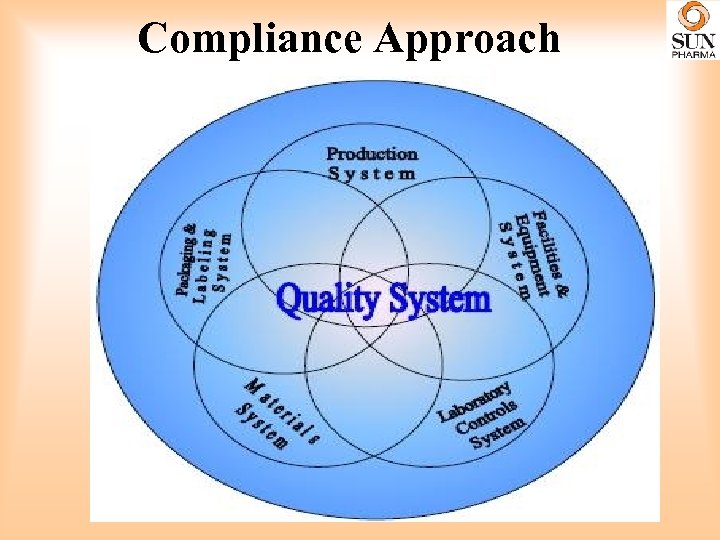 Compliance Approach
Compliance Approach
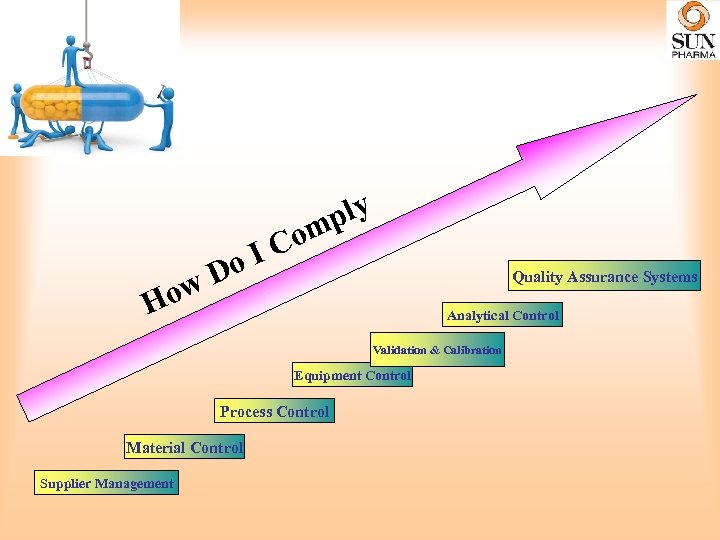 Do w ply m Co I Quality Assurance Systems Ho Analytical Control Validation & Calibration Equipment Control Process Control Material Control Supplier Management
Do w ply m Co I Quality Assurance Systems Ho Analytical Control Validation & Calibration Equipment Control Process Control Material Control Supplier Management
 Supplier Management Importance of Knowing the supply chain “Using a pharmaceutical ingredient without knowing the manufacturing location, where it’s been, and how it got to you is like using a toothbrush found lying in a public restroom. ”
Supplier Management Importance of Knowing the supply chain “Using a pharmaceutical ingredient without knowing the manufacturing location, where it’s been, and how it got to you is like using a toothbrush found lying in a public restroom. ”
 Supplier Management Gold Sheet May 2012 “FDA inspections last year identified more problems in the global supply chain, of the 52 warning letters issued in FY 2011, 17 went to active pharmaceutical Ingredient manufacturers up from 8 in FY 2010”
Supplier Management Gold Sheet May 2012 “FDA inspections last year identified more problems in the global supply chain, of the 52 warning letters issued in FY 2011, 17 went to active pharmaceutical Ingredient manufacturers up from 8 in FY 2010”
 Excerpts of Non-Compliance • “Your vendor qualification has not provided adequate evidence that the manufacturer can consistently supply raw materials that meet appropriate quality attributes • You did not specify how you intend to document and implement such audits • Your firm accepts suppliers certificates of analysis (COA) without having qualified the vendor • Your firm has not conducted at least one specific identity test and has not established the reliability of the supplier's analyses through appropriate validation of the supplier's test results at appropriate intervals" • In addition, you failed to appropriately validate your suppliers' test results (as furnished to you on the suppliers certificates of analysis) at appropriate intervals”
Excerpts of Non-Compliance • “Your vendor qualification has not provided adequate evidence that the manufacturer can consistently supply raw materials that meet appropriate quality attributes • You did not specify how you intend to document and implement such audits • Your firm accepts suppliers certificates of analysis (COA) without having qualified the vendor • Your firm has not conducted at least one specific identity test and has not established the reliability of the supplier's analyses through appropriate validation of the supplier's test results at appropriate intervals" • In addition, you failed to appropriately validate your suppliers' test results (as furnished to you on the suppliers certificates of analysis) at appropriate intervals”
 Challenges in Assuring Supply Chain – Quality System Vulnerabilities § Often vendor audits restricted to the evaluation questionnaire and obtaining TSE/BSE certifications § Certificates of analysis (COAs) – Over reliance on COAs – Original manufacturer’s COA not always obtained – COA often altered to remove true identity of manufacturer – Reported test results may be unreliable or falsified § Supplier qualification programs, quality agreements, and lifecycle monitoring are often deficient § Distant manufacturing sites
Challenges in Assuring Supply Chain – Quality System Vulnerabilities § Often vendor audits restricted to the evaluation questionnaire and obtaining TSE/BSE certifications § Certificates of analysis (COAs) – Over reliance on COAs – Original manufacturer’s COA not always obtained – COA often altered to remove true identity of manufacturer – Reported test results may be unreliable or falsified § Supplier qualification programs, quality agreements, and lifecycle monitoring are often deficient § Distant manufacturing sites
 Pharmaceutical Ingredient Supply Chain – A Shared Responsibility! Manufacturers & Distributors Are responsible for assuring that ingredients they supply comply GMP, are not misbranded or contaminated, are packaged/stored appropriately, and adhere to contract End Users Are ultimately responsible for the use of appropriate ingredients and assuring ingredient quality at every stage of the supply chain
Pharmaceutical Ingredient Supply Chain – A Shared Responsibility! Manufacturers & Distributors Are responsible for assuring that ingredients they supply comply GMP, are not misbranded or contaminated, are packaged/stored appropriately, and adhere to contract End Users Are ultimately responsible for the use of appropriate ingredients and assuring ingredient quality at every stage of the supply chain
 Incoming Material Control v Purchasing – important operation v From approved suppliers – if possible, direct from the manufacturer v Specifications for materials v Consignment checks v Integrity of package v Seal intact v Corresponds with the purchase order v Delivery note v Supplier’s labels
Incoming Material Control v Purchasing – important operation v From approved suppliers – if possible, direct from the manufacturer v Specifications for materials v Consignment checks v Integrity of package v Seal intact v Corresponds with the purchase order v Delivery note v Supplier’s labels
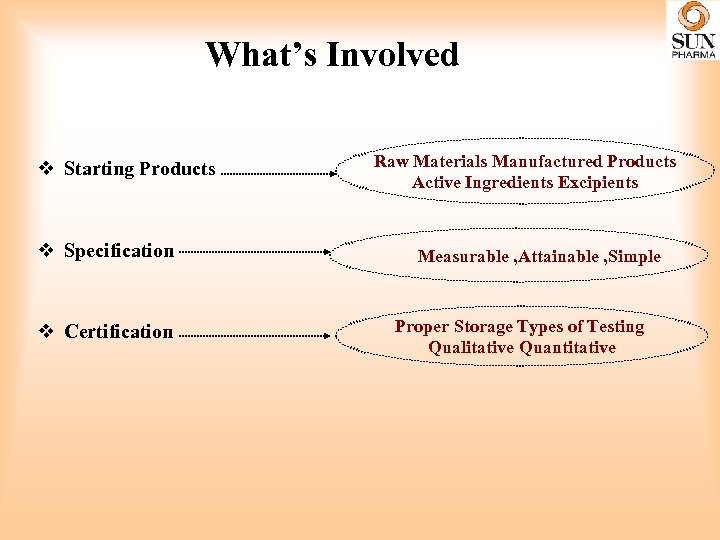 What’s Involved v Starting Products v Specification v Certification Raw Materials Manufactured Products Active Ingredients Excipients Measurable , Attainable , Simple Proper Storage Types of Testing Qualitative Quantitative
What’s Involved v Starting Products v Specification v Certification Raw Materials Manufactured Products Active Ingredients Excipients Measurable , Attainable , Simple Proper Storage Types of Testing Qualitative Quantitative
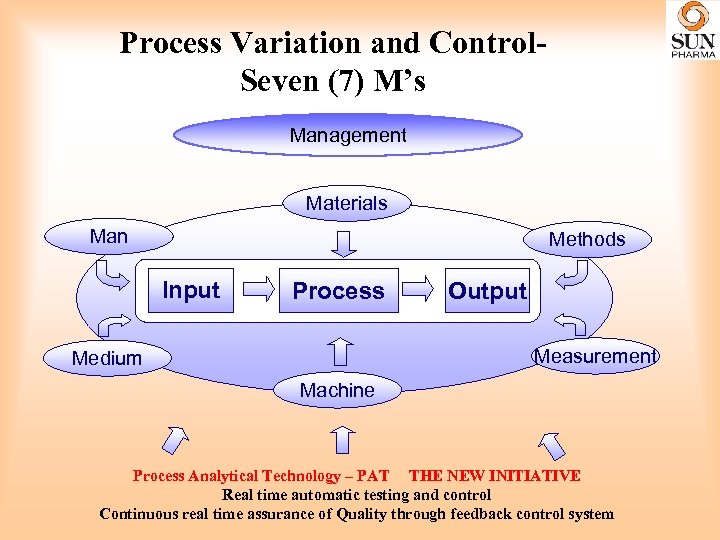 Process Variation and Control. Seven (7) M’s Management Materials Man Methods Input Process Output Measurement Medium Machine Process Analytical Technology – PAT THE NEW INITIATIVE Real time automatic testing and control Continuous real time assurance of Quality through feedback control system
Process Variation and Control. Seven (7) M’s Management Materials Man Methods Input Process Output Measurement Medium Machine Process Analytical Technology – PAT THE NEW INITIATIVE Real time automatic testing and control Continuous real time assurance of Quality through feedback control system
 Process Control Process control by Trending of applicable data and its analysis to determine the performance of the product quality , over a period of time and provides an opportunity to take appropriate decisions. The methodology and techniques of computation of data, preparation of control charts and knowing the process capability are simple tools which can be used successfully to identify potential problem areas to facilitate corrective and preventive measures which will go a long way in improving product consistency, quality, its performance in the market within compliance framework as per regulatory agencies.
Process Control Process control by Trending of applicable data and its analysis to determine the performance of the product quality , over a period of time and provides an opportunity to take appropriate decisions. The methodology and techniques of computation of data, preparation of control charts and knowing the process capability are simple tools which can be used successfully to identify potential problem areas to facilitate corrective and preventive measures which will go a long way in improving product consistency, quality, its performance in the market within compliance framework as per regulatory agencies.
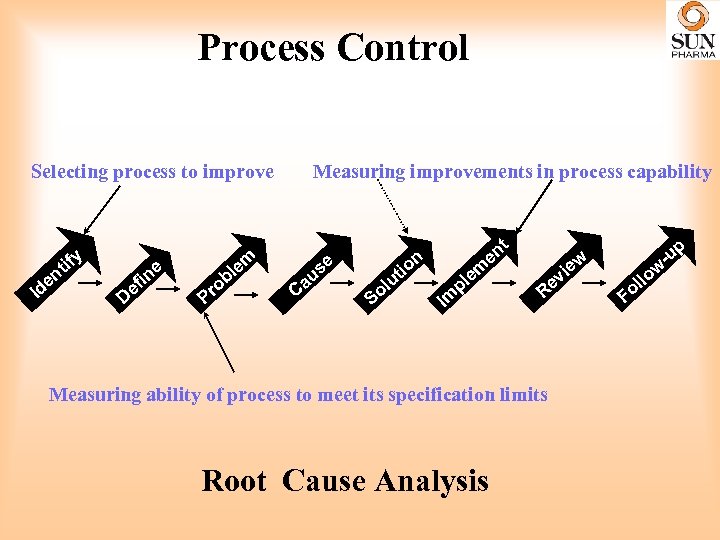 Process Control Selecting process to improve ify Id nt e De e in f bl ro P Measuring improvements in process capability em C e us a nt e i ut ol S on Im m le p i ev R Measuring ability of process to meet its specification limits Root Cause Analysis p ew Fo llo w -u
Process Control Selecting process to improve ify Id nt e De e in f bl ro P Measuring improvements in process capability em C e us a nt e i ut ol S on Im m le p i ev R Measuring ability of process to meet its specification limits Root Cause Analysis p ew Fo llo w -u
 Equipment Controls • Equipment must be located, designed, constructed, adapted and maintained to suit the operations to be carried out. • The layout and design of equipment must aim to minimize the risk of errors. • Permit effective cleaning and maintenance in order to avoid cross-contamination, build-up of dust or dirt, and, in general, any adverse effect on the quality of products.
Equipment Controls • Equipment must be located, designed, constructed, adapted and maintained to suit the operations to be carried out. • The layout and design of equipment must aim to minimize the risk of errors. • Permit effective cleaning and maintenance in order to avoid cross-contamination, build-up of dust or dirt, and, in general, any adverse effect on the quality of products.
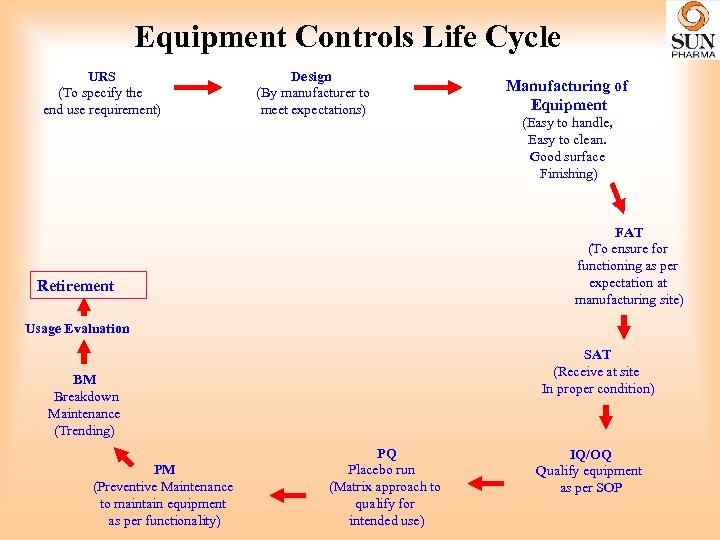 Equipment Controls Life Cycle URS (To specify the end use requirement) Design (By manufacturer to meet expectations) Manufacturing of Equipment (Easy to handle, Easy to clean. Good surface Finishing) FAT (To ensure for functioning as per expectation at manufacturing site) Retirement Usage Evaluation SAT (Receive at site In proper condition) BM Breakdown Maintenance (Trending) PM (Preventive Maintenance to maintain equipment as per functionality) PQ Placebo run (Matrix approach to qualify for intended use) IQ/OQ Qualify equipment as per SOP
Equipment Controls Life Cycle URS (To specify the end use requirement) Design (By manufacturer to meet expectations) Manufacturing of Equipment (Easy to handle, Easy to clean. Good surface Finishing) FAT (To ensure for functioning as per expectation at manufacturing site) Retirement Usage Evaluation SAT (Receive at site In proper condition) BM Breakdown Maintenance (Trending) PM (Preventive Maintenance to maintain equipment as per functionality) PQ Placebo run (Matrix approach to qualify for intended use) IQ/OQ Qualify equipment as per SOP
 Calibration What ? • A set of operations that establish, under specified conditions, the relationship between the values of quantities indicated by a measuring instrument or measuring system, or values represented by a material measure or a reference material, and the corresponding values realized by its standards. Why ? • When process measuring instruments age and experience physical stress or temperature variations, critical performance gradually declines. This is called drift. • The slow variation with time of metro logical characteristics of the measuring instruments. As a result of this, the measurement results become unreliable and ultimately the production quality can suffer. • Drift cannot be eliminated, but it can be discovered through calibration.
Calibration What ? • A set of operations that establish, under specified conditions, the relationship between the values of quantities indicated by a measuring instrument or measuring system, or values represented by a material measure or a reference material, and the corresponding values realized by its standards. Why ? • When process measuring instruments age and experience physical stress or temperature variations, critical performance gradually declines. This is called drift. • The slow variation with time of metro logical characteristics of the measuring instruments. As a result of this, the measurement results become unreliable and ultimately the production quality can suffer. • Drift cannot be eliminated, but it can be discovered through calibration.
 Calibration BENEFITS • Calibrated equipment provides confidence that products/services meet their specifications. • Calibration: • Increases production yields, • Optimizes resources, • Assures consistency and • Ensures measurements (and perhaps products) are compatible with those made elsewhere. By making sure that measurements are based on international standards, promote customer acceptance of the products around the world. • “Neglecting calibration can lead to unscheduled production downtime, quality problems and product recalls. Risking employee safety. Risking customer/consumer safety. Loosing license to operate due to not meeting regulatory requirements. ”
Calibration BENEFITS • Calibrated equipment provides confidence that products/services meet their specifications. • Calibration: • Increases production yields, • Optimizes resources, • Assures consistency and • Ensures measurements (and perhaps products) are compatible with those made elsewhere. By making sure that measurements are based on international standards, promote customer acceptance of the products around the world. • “Neglecting calibration can lead to unscheduled production downtime, quality problems and product recalls. Risking employee safety. Risking customer/consumer safety. Loosing license to operate due to not meeting regulatory requirements. ”
 Validation General Validation Comments • Results MUST be repeatable • Validation must be standardized • Validation must meet industry standards
Validation General Validation Comments • Results MUST be repeatable • Validation must be standardized • Validation must meet industry standards
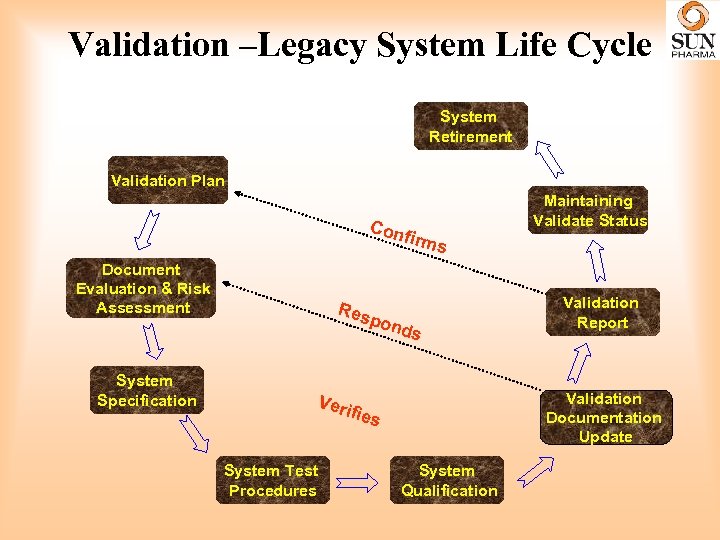 Validation –Legacy System Life Cycle System Retirement Validation Plan Con Document Evaluation & Risk Assessment System Specification Res firm s pon ds Validation Report Validation Documentation Update Veri fi es System Test Procedures Maintaining Validate Status System Qualification
Validation –Legacy System Life Cycle System Retirement Validation Plan Con Document Evaluation & Risk Assessment System Specification Res firm s pon ds Validation Report Validation Documentation Update Veri fi es System Test Procedures Maintaining Validate Status System Qualification
 Validation - Challenges • Risk-based approach. – Conduct appropriate levels of Gx. P impact and criticality risk assessment of systems and system functionality early in the planning stage and then throughout the validation life cycle as required. • Computer System Validation – Map the stages and terminology of “Information systems”, e. g. , enterprise resource planning (ERP) and Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) with the recognized validation life cycle model. • Cleaning Validation – Appropriate and sensitive method to determine low level to meet MACO
Validation - Challenges • Risk-based approach. – Conduct appropriate levels of Gx. P impact and criticality risk assessment of systems and system functionality early in the planning stage and then throughout the validation life cycle as required. • Computer System Validation – Map the stages and terminology of “Information systems”, e. g. , enterprise resource planning (ERP) and Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) with the recognized validation life cycle model. • Cleaning Validation – Appropriate and sensitive method to determine low level to meet MACO
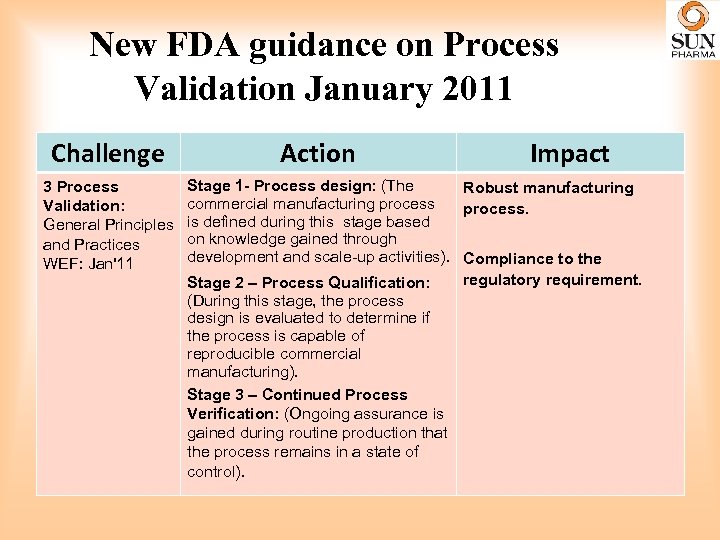 New FDA guidance on Process Validation January 2011 Challenge 3 Process Validation: General Principles and Practices WEF: Jan'11 Action Impact Stage 1 - Process design: (The Robust manufacturing commercial manufacturing process. is defined during this stage based on knowledge gained through development and scale-up activities). Compliance to the regulatory requirement. Stage 2 – Process Qualification: (During this stage, the process design is evaluated to determine if the process is capable of reproducible commercial manufacturing). Stage 3 – Continued Process Verification: (Ongoing assurance is gained during routine production that the process remains in a state of control).
New FDA guidance on Process Validation January 2011 Challenge 3 Process Validation: General Principles and Practices WEF: Jan'11 Action Impact Stage 1 - Process design: (The Robust manufacturing commercial manufacturing process. is defined during this stage based on knowledge gained through development and scale-up activities). Compliance to the regulatory requirement. Stage 2 – Process Qualification: (During this stage, the process design is evaluated to determine if the process is capable of reproducible commercial manufacturing). Stage 3 – Continued Process Verification: (Ongoing assurance is gained during routine production that the process remains in a state of control).
 Analytical • Good Quality Control Practices- Personnel, Premises and Equipment in Laboratories should be appropriate as per the tasks. - Laboratory Controls – Documentation , Sampling , Testing “ A management system to assure the quality and integrity of data underlying a study” “All records to be retained”
Analytical • Good Quality Control Practices- Personnel, Premises and Equipment in Laboratories should be appropriate as per the tasks. - Laboratory Controls – Documentation , Sampling , Testing “ A management system to assure the quality and integrity of data underlying a study” “All records to be retained”
 Analytical • • • Effective specification and method Appropriate instruments Effective calibration program Effective preventive maintenance program Qualified personnel Effective standard management Effective and usable SOP for OOS and OOT Trending of laboratory failure and CAPA Effective sample management Glassware Controls
Analytical • • • Effective specification and method Appropriate instruments Effective calibration program Effective preventive maintenance program Qualified personnel Effective standard management Effective and usable SOP for OOS and OOT Trending of laboratory failure and CAPA Effective sample management Glassware Controls
 Analytical Current Issues • OOS • Investigation is too brief and “templated” before Retesting begins. • Checklist of possible causes not used, used incorrectly or incompletely. • Equipment not Qualified or not within Calibration window. PM not performed per SOP or recently. • • • Standard (solid, stock solution and dilution expired). Spreadsheet Application for calculation(s) not Qualified and incorrect. Method version changed and not accessible to analyst or analyst has not checked (“going from memory”) • Wrong or expired Reagents, Solvents, Titrants, etc. , used.
Analytical Current Issues • OOS • Investigation is too brief and “templated” before Retesting begins. • Checklist of possible causes not used, used incorrectly or incompletely. • Equipment not Qualified or not within Calibration window. PM not performed per SOP or recently. • • • Standard (solid, stock solution and dilution expired). Spreadsheet Application for calculation(s) not Qualified and incorrect. Method version changed and not accessible to analyst or analyst has not checked (“going from memory”) • Wrong or expired Reagents, Solvents, Titrants, etc. , used.
 Analytical Current Issues • Wrong or damaged volumetric glassware used. • System results have changed significantly (I. e. , System Suitability parameters). • Analytical method not followed correctly. • Results yield much higher variability than found in original method validation. • Sample preparation error made (e. g. , weighing, sampling, dilutions). • Environmental room conditions changed (e. g. , room temperature or light excursion). • Reagent or solvent contamination present. • Sample identification transcribed incorrectly.
Analytical Current Issues • Wrong or damaged volumetric glassware used. • System results have changed significantly (I. e. , System Suitability parameters). • Analytical method not followed correctly. • Results yield much higher variability than found in original method validation. • Sample preparation error made (e. g. , weighing, sampling, dilutions). • Environmental room conditions changed (e. g. , room temperature or light excursion). • Reagent or solvent contamination present. • Sample identification transcribed incorrectly.
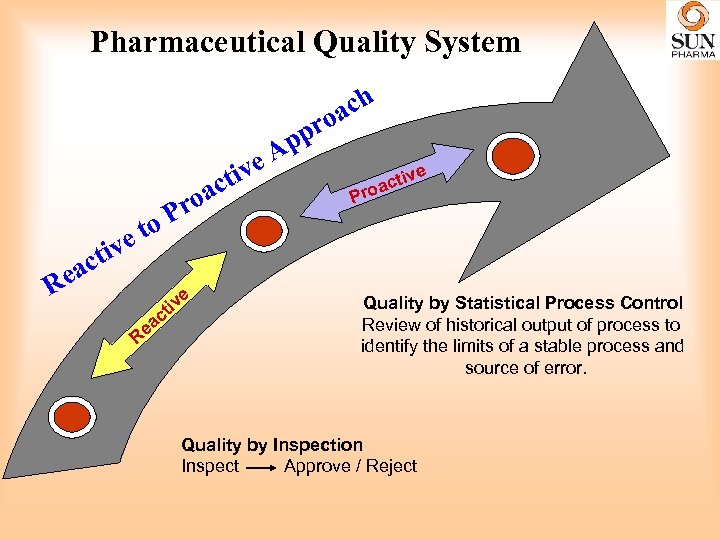 Pharmaceutical Quality System e. A tiv et iv R act e ac o Pr o iv ct ea R e ach o pr p e ctiv oa Pr Quality by Statistical Process Control Review of historical output of process to identify the limits of a stable process and source of error. Quality by Inspection Inspect Approve / Reject
Pharmaceutical Quality System e. A tiv et iv R act e ac o Pr o iv ct ea R e ach o pr p e ctiv oa Pr Quality by Statistical Process Control Review of historical output of process to identify the limits of a stable process and source of error. Quality by Inspection Inspect Approve / Reject
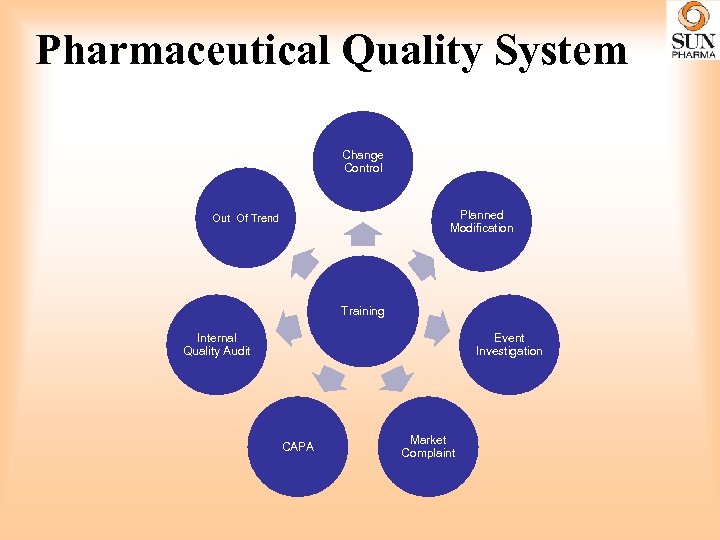 Pharmaceutical Quality System Change Control Planned Modification Out Of Trend Training Internal Quality Audit Event Investigation CAPA Market Complaint
Pharmaceutical Quality System Change Control Planned Modification Out Of Trend Training Internal Quality Audit Event Investigation CAPA Market Complaint
 Effective Tools for Compliance Current Expectation of Regulators CAPA is much more than just “corrective actions” and “preventive actions”. Any opportunity to improve quality in the organization is a CAPA! Risk Management : Systematic application of management policies, procedures, and practices towards analyzing, evaluating, and controlling risk.
Effective Tools for Compliance Current Expectation of Regulators CAPA is much more than just “corrective actions” and “preventive actions”. Any opportunity to improve quality in the organization is a CAPA! Risk Management : Systematic application of management policies, procedures, and practices towards analyzing, evaluating, and controlling risk.
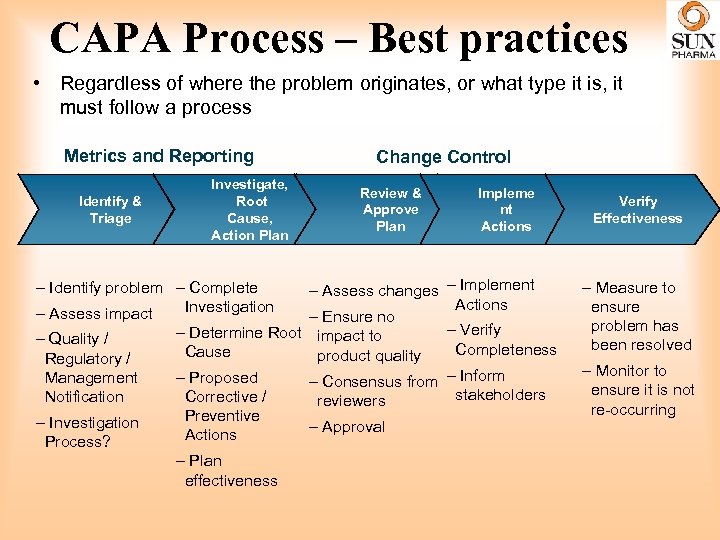 CAPA Process – Best practices • Regardless of where the problem originates, or what type it is, it must follow a process Metrics and Reporting Identify & Triage Investigate, Root Cause, Action Plan - Investigation Process? Review & Approve Plan Impleme nt Actions - Assess changes - Implement Actions - Ensure no - Verify - Determine Root impact to Completeness Cause product quality - Proposed - Consensus from - Inform stakeholders Corrective / reviewers Preventive - Approval Actions - Identify problem - Complete Investigation - Assess impact - Quality / Regulatory / Management Notification Change Control - Plan effectiveness Verify Effectiveness - Measure to ensure problem has been resolved - Monitor to ensure it is not re-occurring
CAPA Process – Best practices • Regardless of where the problem originates, or what type it is, it must follow a process Metrics and Reporting Identify & Triage Investigate, Root Cause, Action Plan - Investigation Process? Review & Approve Plan Impleme nt Actions - Assess changes - Implement Actions - Ensure no - Verify - Determine Root impact to Completeness Cause product quality - Proposed - Consensus from - Inform stakeholders Corrective / reviewers Preventive - Approval Actions - Identify problem - Complete Investigation - Assess impact - Quality / Regulatory / Management Notification Change Control - Plan effectiveness Verify Effectiveness - Measure to ensure problem has been resolved - Monitor to ensure it is not re-occurring
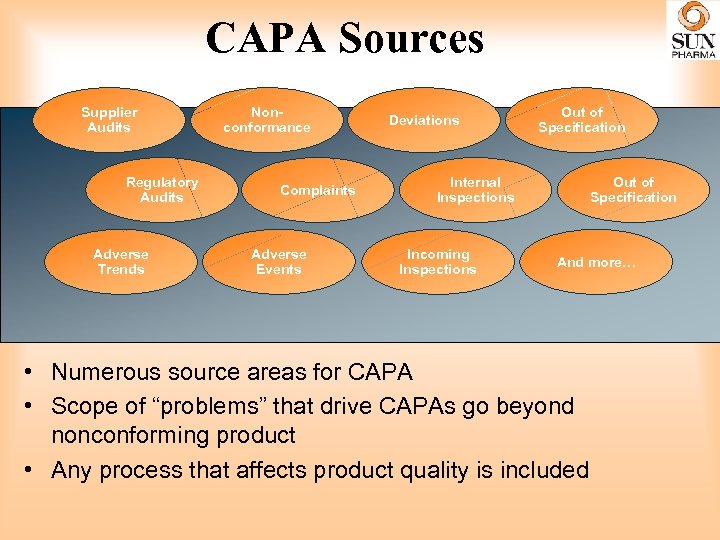 CAPA Sources Supplier Audits Regulatory Audits Adverse Trends Nonconformance Complaints Adverse Events Deviations Out of Specification Internal Inspections Incoming Inspections Out of Specification And more… • Numerous source areas for CAPA • Scope of “problems” that drive CAPAs go beyond nonconforming product • Any process that affects product quality is included
CAPA Sources Supplier Audits Regulatory Audits Adverse Trends Nonconformance Complaints Adverse Events Deviations Out of Specification Internal Inspections Incoming Inspections Out of Specification And more… • Numerous source areas for CAPA • Scope of “problems” that drive CAPAs go beyond nonconforming product • Any process that affects product quality is included
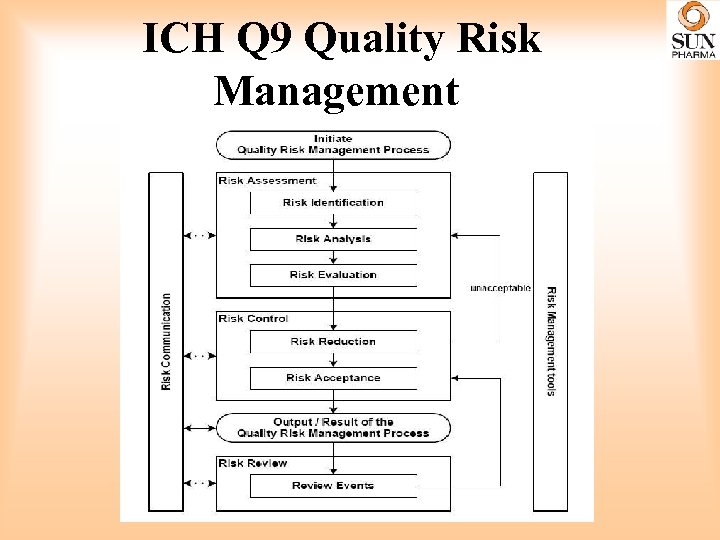 ICH Q 9 Quality Risk Management
ICH Q 9 Quality Risk Management
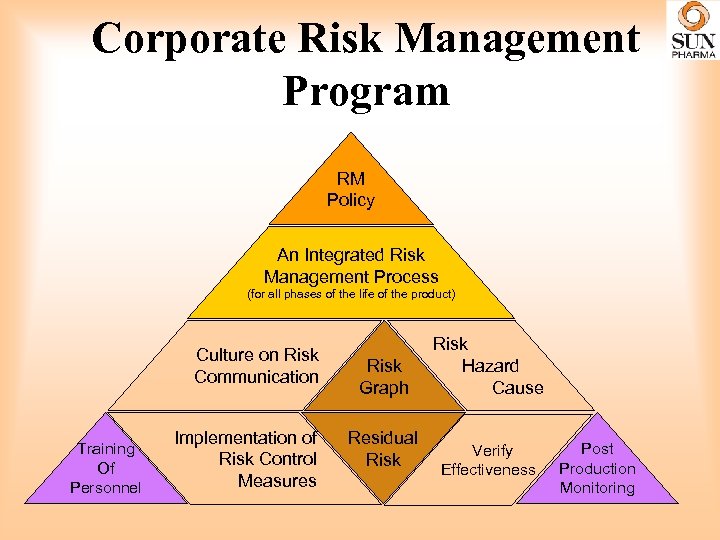 Corporate Risk Management Program RM Policy An Integrated Risk Management Process (for all phases of the life of the product) Culture on Risk Communication Training Of Personnel Implementation of Risk Control Measures Risk Graph Residual Risk Hazard Cause Verify Effectiveness Post Production Monitoring
Corporate Risk Management Program RM Policy An Integrated Risk Management Process (for all phases of the life of the product) Culture on Risk Communication Training Of Personnel Implementation of Risk Control Measures Risk Graph Residual Risk Hazard Cause Verify Effectiveness Post Production Monitoring
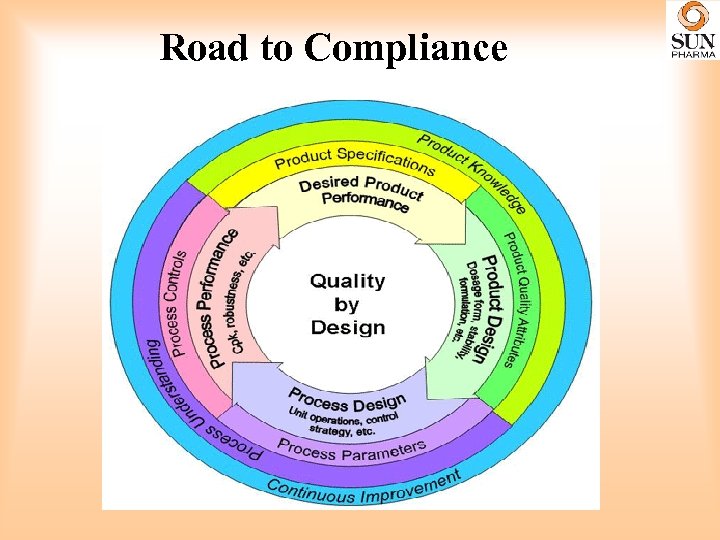 Road to Compliance
Road to Compliance
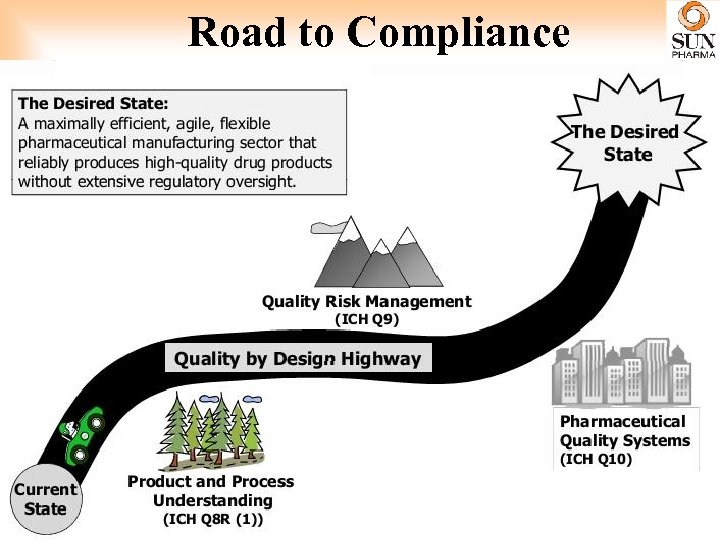 Road to Compliance
Road to Compliance
 When it comes to ensuring drug product quality and ultimately Consumer/Patient Safety. . . We need to think and act globally!
When it comes to ensuring drug product quality and ultimately Consumer/Patient Safety. . . We need to think and act globally!



