9733c5f391b2195610571f6e00d1b88c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 71

Compliance in an on demand environment ® IBM Software Group, Information Management Software Taking Control over the Wild, Wild West within your Organization Tom Reding, CRM, Executive Consultant: Risk, Governance, & Compliance Solutions © 2006 IBM Corporation

IBM Software Group | DB 2 Information Management Software Agenda (2. 0 Hours) § Define the Wild, Wild West of your enterprise § Managing Records on Network Drives § Impact of the “new” Federal Rules of Civil Procedure (FRCP) § Federated Records Management (FRM) for “all of the repositories in your enterprise § Handling Transactional Database Records § e-Records enabling Reports Management § Where and how does RM & FRM fit into an SOA Framework? § Phased Implementation Recommendation § What’s next for Master Policy Management? § Q&A 2

Compliance in an on demand environment ® IBM Software Group, Information Management Software “Corporations can not demonstrate compliance without Records Management” © 2006 IBM Corporation

IBM Software Group | DB 2 Information Management Software Defining the “Wild, Wild West of your enterprise § Desktops & Laptops § Network file shares § Various Corporate Archives § Data Warehouses § Report Management Systems (IDARS, COLD) 4

Compliance in an on demand environment ® IBM Software Group, Information Management Software Records Management Solutions should be capable of preserving your existing investments in business applications & repositories, while at the same time future proofing you regarding future application and repository investments. “Corporations can not demonstrate compliance without Records Management” © 2006 IBM Corporation

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software An e-Records Management Strategy Deliver electronic records management as an element of information technology infrastructure. Records Management technology should be used to “e-Records enable” all types of business processes, applications, repositories, storage management systems, and content integration solutions.

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software OK, I’ll Set Up Records Management Policies…zzz! Records Retention Policies are … well … rather boring, But consistent adherence to Policies helps to demonstrate Compliance

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Are you one of those in the Board Room or “middle management”?

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Examples of What NOT to do | Compliance Hall of Shame Bernie Ebbers Former CEO of World. Com Now Serving 25 Years Luke Duffy Formerly of Bank of Australia Now Serving Time, Took Down CEO Ken Lay Former CEO of Enron Faced 175 Years Gale Norton Secretary of the Interior Held in Contempt of Court Morgan Stanley Fined $1. 45 Billion Stock Price Down CEO Removed Liu Jinbao Former CEO of Bank of China Now on Death Row
® IBM Software Group

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Effective Records Management is the Goal for MOST Corporate Legal Departments….
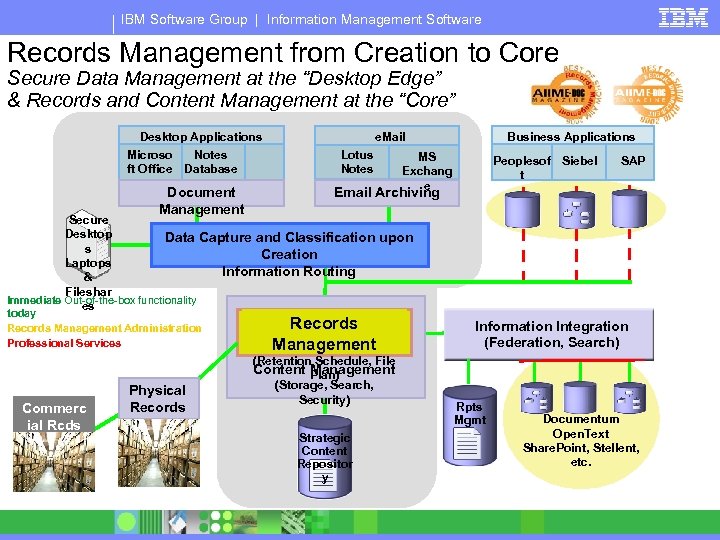
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Records Management from Creation to Core Secure Data Management at the “Desktop Edge” & Records and Content Management at the “Core” Desktop Applications Microso Notes ft Office Database Document Management e. Mail Lotus Notes Business Applications MS Exchang e Peoplesof Siebel t SAP Email Archiving Secure Desktop Data Capture and Classification upon s Creation Laptops Information Routing & Fileshar Immediate Out-of-the-box functionality es today Records Management Administration Professional Services Commerc ial Rcds Store Physical Records Management (Retention Schedule, File Content Plan) Management (Storage, Search, Security) Strategic Content Repositor y Information Integration (Federation, Search) Rpts Mgmt R Documentum Open. Text Share. Point, Stellent, etc.

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software e-Records Management: Past, Present, & Future § 1 st Generation – Paper & Microforms Retrieval System § § § (Computer Assisted Retrieval Systems [CARS]) 2 nd Generation - 1 st Generation Solutions upgraded to manage desktop documents, bring their own repository and search tool (Records Management Applications [RMA]) 3 rd Generation – New Paradigm introduced, e-Records Policy Engine used to embed RM features and functions into business applications (at server & / or desktop), w / repository independence, use existing customer search tools 4 th Generation – e-Records Policy Engine extended to embed RM features and functions via Enterprise Content Integration (Federated Records Management) 5 th Generation – To be determined 6 th Generation – Universal Virtual Computer
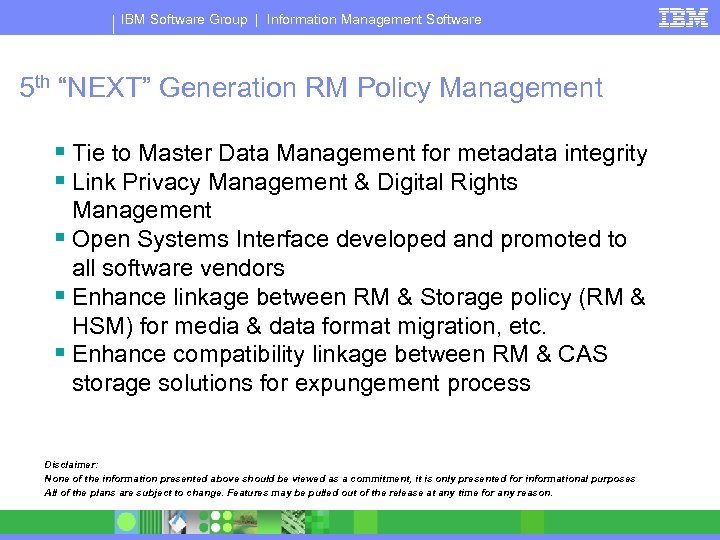
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software 5 th “NEXT” Generation RM Policy Management § Tie to Master Data Management for metadata integrity § Link Privacy Management & Digital Rights Management § Open Systems Interface developed and promoted to all software vendors § Enhance linkage between RM & Storage policy (RM & HSM) for media & data format migration, etc. § Enhance compatibility linkage between RM & CAS storage solutions for expungement process Disclaimer: None of the information presented above should be viewed as a commitment, it is only presented for informational purposes All of the plans are subject to change. Features may be pulled out of the release at any time for any reason.
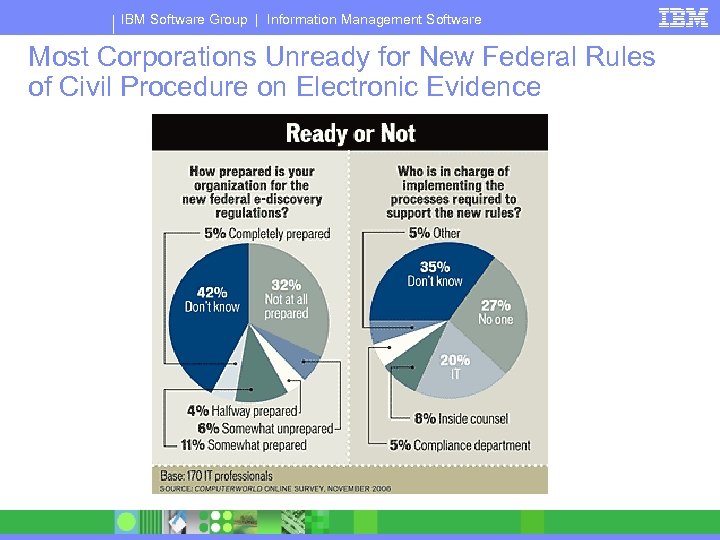
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Most Corporations Unready for New Federal Rules of Civil Procedure on Electronic Evidence

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software New FRCP: How Does This Impact You? § Your Organization faces a >95% § § chance of litigation in 2007 You MUST know where your documents live You MUST keep relevant documents with metadata FULL Records Management is INEVITABLE You MUST be able to search for and present documents intact regardless of location Evidence Discovery Legal • Search • Redact • Review • Present

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Summary of Rule Change / Clarification § An assessment of the organization’s information policies and procedures § § to ensure that the right records and information can be located, preserved and produced for discovery when necessary. The creation of an effective Legal Hold policy to stop the destruction of records and information due to routine business processes or other reasons. A process for disseminating a clear and effective Legal Hold notice to inform employees and others of their responsibility to preserve certain records / information for litigation. Assessment of the organization’s IT infrastructure to ensure it can effectively support the Legal Hold process and preserve all necessary records and “data compilations” without hindering business processes. Points of contact across the organization’s business units that possess a thorough knowledge of their areas’ records and information, as well as what form those records are in and where they are located.

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Summary of Rule Change / Clarification (continued) § Within 30 days of filing a discovery order opposition counsels must meet to decide how to handle electronic evidence discovery. § Firms must agree on what records are shared and in what format. § Gartner Analyst John Bace said, “… companies will need to act immediately to avoid the potential for sanctions and "negative inferences" in court battles; … organizations should quickly take steps to develop records retention policies and content management procedures to help protect the organization in case records are lost. ”
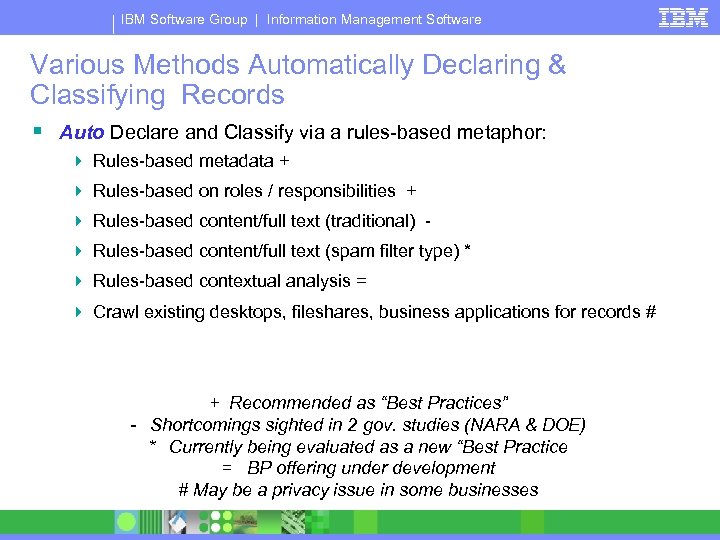
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Various Methods Automatically Declaring & Classifying Records § Auto Declare and Classify via a rules-based metaphor: 4 Rules-based metadata + 4 Rules-based on roles / responsibilities + 4 Rules-based content/full text (traditional) 4 Rules-based content/full text (spam filter type) * 4 Rules-based contextual analysis = 4 Crawl existing desktops, fileshares, business applications for records # + Recommended as “Best Practices” - Shortcomings sighted in 2 gov. studies (NARA & DOE) * Currently being evaluated as a new “Best Practice = BP offering under development # May be a privacy issue in some businesses
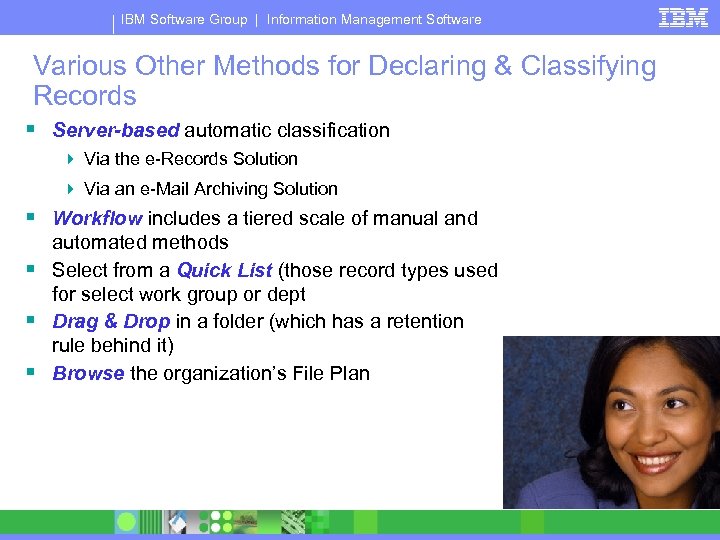
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Various Other Methods for Declaring & Classifying Records § Server-based automatic classification 4 Via the e-Records Solution 4 Via an e-Mail Archiving Solution § Workflow includes a tiered scale of manual and automated methods § Select from a Quick List (those record types used for select work group or dept § Drag & Drop in a folder (which has a retention rule behind it) § Browse the organization’s File Plan
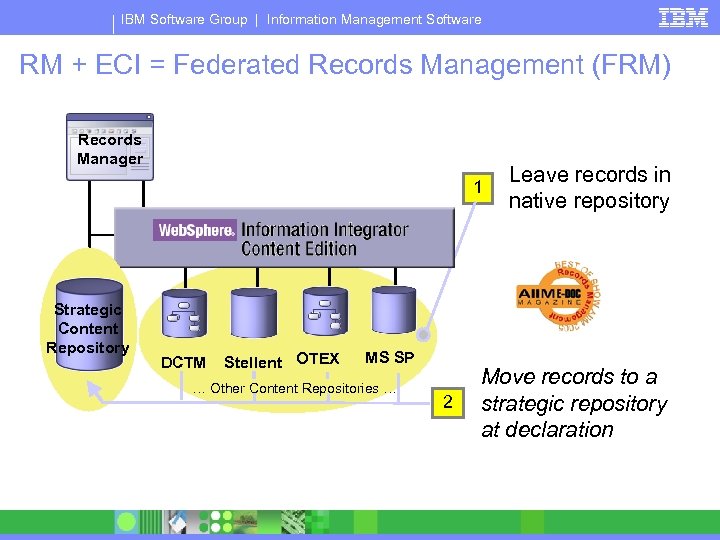
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software RM + ECI = Federated Records Management (FRM) Records Manager 1 Strategic Content Repository DCTM Stellent OTEX MS SP … Other Content Repositories … 2 Leave records in native repository Move records to a strategic repository at declaration
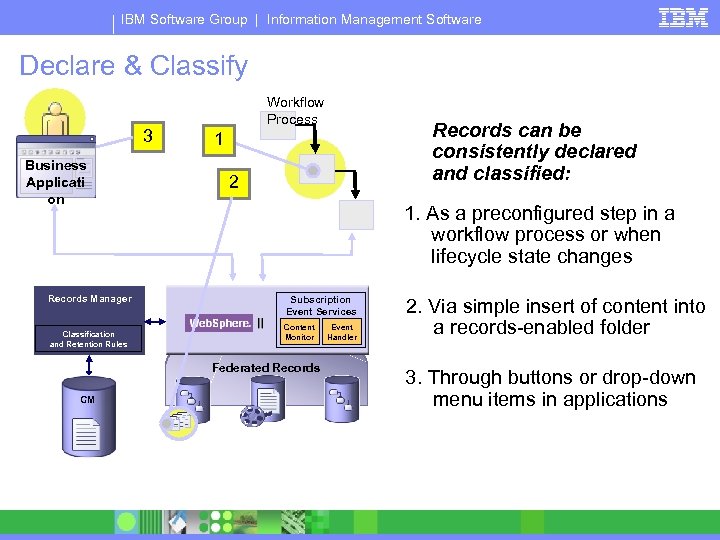
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Declare & Classify Workflow Process 3 Records can be consistently declared and classified: 1 Business Applicati on 2 1. As a preconfigured step in a workflow process or when lifecycle state changes Records Manager Subscription Event Services Content Monitor Classification and Retention Rules Federated Records CM R Event Handler 2. Via simple insert of content into a records-enabled folder 3. Through buttons or drop-down menu items in applications
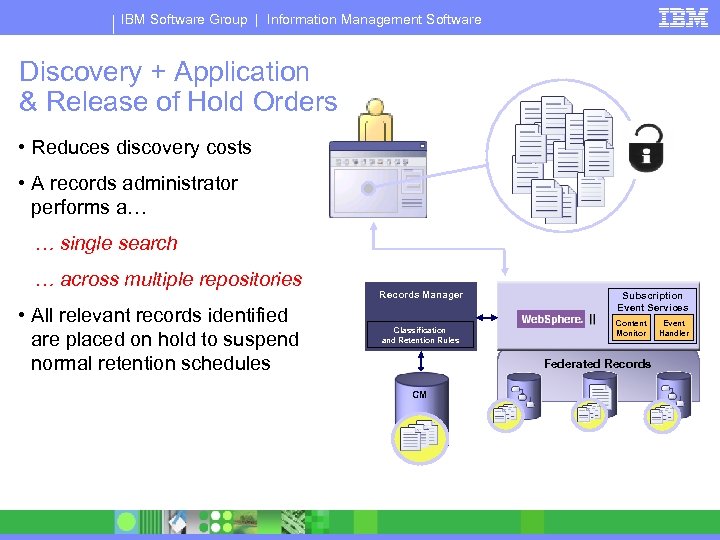
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Discovery + Application & Release of Hold Orders • Reduces discovery costs • A records administrator performs a… … single search … across multiple repositories • All relevant records identified are placed on hold to suspend normal retention schedules Records Manager Subscription Event Services Content Monitor Classification and Retention Rules Event Handler Federated Records CM R R
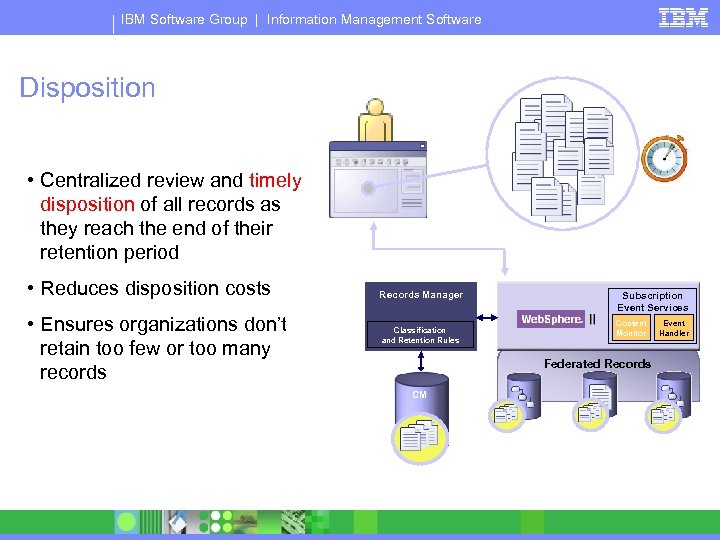
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Disposition • Centralized review and timely disposition of all records as they reach the end of their retention period • Reduces disposition costs • Ensures organizations don’t retain too few or too many records Records Manager Subscription Event Services Content Monitor Classification and Retention Rules Event Handler Federated Records CM R R

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Web. Sphere II Content Edition - Content Integration Platform Imaging/ Document Mgmt Report Mgmt Web Content/ Workflow/ Network Media Asset Business File Mgmt Process Mgmt Systems Custom Systems Lets you work with content from multiple, disparate content sources as if it were stored in one unified system § Single interface to multiple content sources and workflow systems § Rich, bi-directional content functionality § Exposes all underlying functionality and adds federation services § Development components and APIs for building custom applications § Requires an API at the application / repository level to enable federation
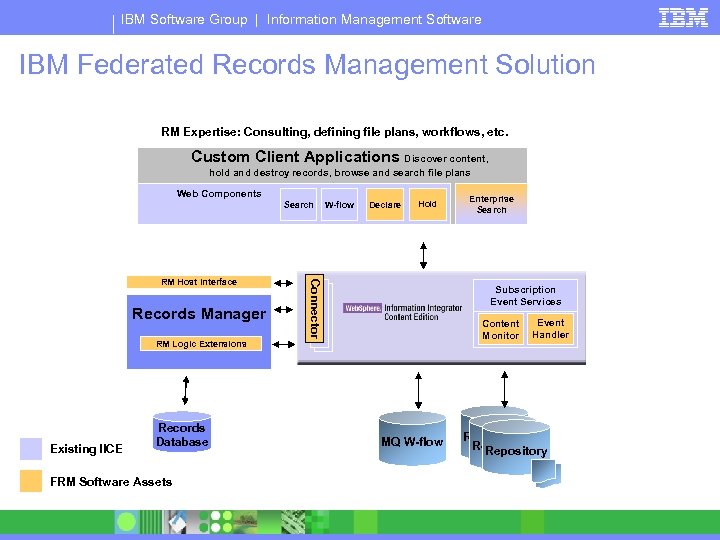
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software IBM Federated Records Management Solution RM Expertise: Consulting, defining file plans, workflows, etc. Custom Client Applications Discover content, hold and destroy records, browse and search file plans Web Components Search Records Manager Declare Hold Connector RM Host Interface W-flow Subscription Event Services Content Monitor RM Logic Extensions Existing IICE Records Database FRM Software Assets Enterprise Search MQ W-flow Event Handler Repository

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Federated Records Management for Reports Management § Reports data now consistent with other organizational records 4 Helps meet compliance objectives and supports litigation requirements § Declare and classify records 4 An entire load – or – individual documents within a load 4 Classify to the corporate records file plan 4 Time, event and event+time retention rules § Apply legal holds and manage the records lifecycle Jonathan Smith 123 -45 -6789 Records Ronald Smith 234 -56 -7890 William Smith 345 -67 -8901
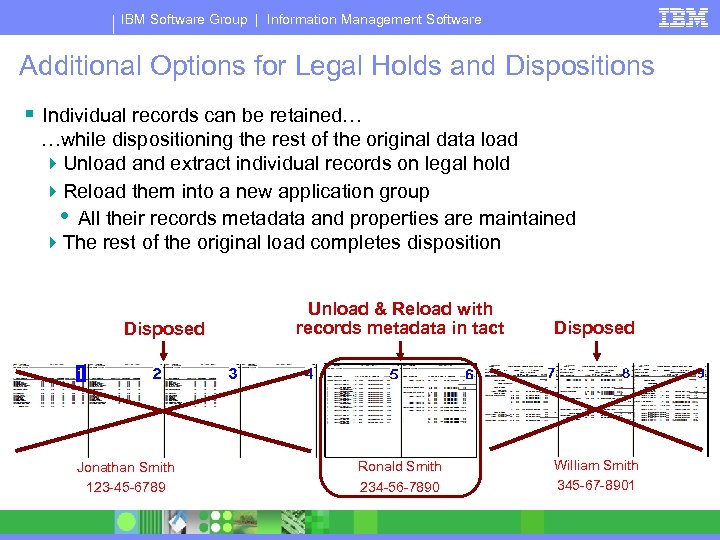
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Additional Options for Legal Holds and Dispositions § Individual records can be retained… …while dispositioning the rest of the original data load 4 Unload and extract individual records on legal hold 4 Reload them into a new application group • All their records metadata and properties are maintained 4 The rest of the original load completes disposition Disposed Jonathan Smith 123 -45 -6789 Unload & Reload with records metadata in tact Disposed Ronald Smith 234 -56 -7890 William Smith 345 -67 -8901
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software What, When, Where and How of Structured Data capture as “official” business records § What conclusions has your organization arrived at regarding 4 What, When, Where, and How § Keep it simple 4 Point of “authentication” vs. a draft § Reports Management System: Things to be aware of 4 LARGE BLOBS 4 Application and Release of Hold Orders 4 Unique disposition step-by-step processes § Example: Web Transactions at business records 4 Content, Structure, Context
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Structured Data as Business Records § Capturing the Input & Output is key § Manage in-place vs. capture and preserve in a secure repository (ECM) 4 In-place: no duplication, use production system when performing discovery 4 Move to a secure repository: use same user interface, helps ensure desired high performance of the transactional system

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Why Federated Records Management Matters § Content and records management have been departmental investments, creating many content silos § Reports Management data has typically not been brought under records control § Compliance requires complete access and control over records stored across many disparate systems § Consolidating all records to a single repository is typically not a viable alternative in the short-term § IBM Federated Records Management leverages legacy content / records investments Centralized records management helps ensure consistent application of recordkeeping policies… …regardless of where information is stored

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Benefits of IBM Federated Records Management § Reduce risk through automated, consistent application of the records program all content stores 4 Bring third-party content repositories under records control 4 Bring reports data under records control § Help meet compliance and litigation requirements § Accelerate enterprise records deployment § Reduce the initial and ongoing costs of recordkeeping § Provide a “future-proof” infrastructure 4 Add, remove, change repositories without disrupting records management and/or risking noncompliance
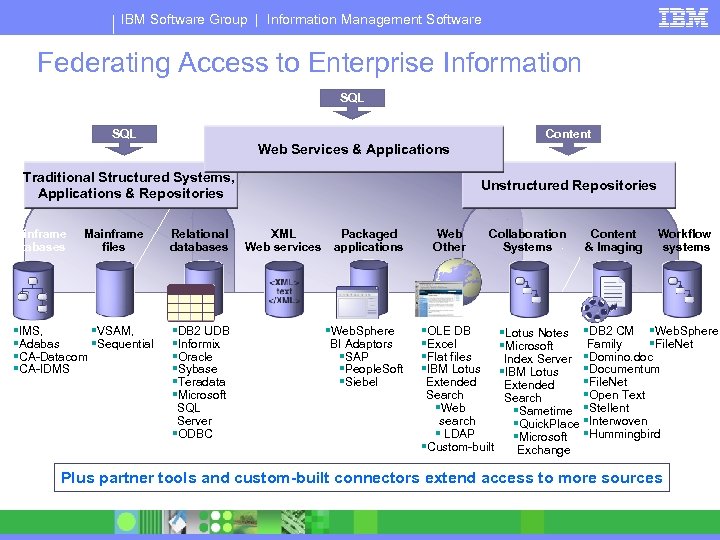
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Federating Access to Enterprise Information SQL Content Web Services & Applications Traditional Structured Systems, Applications & Repositories Mainframe databases Mainframe files §IMS, §VSAM, §Adabas §Sequential §CA-Datacom §CA-IDMS Relational databases §DB 2 UDB §Informix §Oracle §Sybase §Teradata §Microsoft SQL Server §ODBC Unstructured Repositories XML Web services Packaged applications §Web. Sphere BI Adaptors §SAP §People. Soft §Siebel Web Other Collaboration Systems §OLE DB §Excel §Flat files §IBM Lotus Extended Search §Web search § LDAP §Custom-built §Lotus Notes §Microsoft Index Server §IBM Lotus Extended Search §Sametime §Quick. Place §Microsoft Exchange Content & Imaging Workflow systems §DB 2 CM §Web. Sphere Family §File. Net §Domino. doc §Documentum §File. Net §Open Text §Stellent §Interwoven §Hummingbird Plus partner tools and custom-built connectors extend access to more sources

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Metadata is a key element in every electronic business record § Why is Metadata important? 4 It is often impossible to establish authenticity and relevancy of records w/o supporting metadata 4 Requesting parties are entitled to “all” metadata supporting records produced in discovery § Application Metadata vs. System Metadata 4 Application metadata is embedded within the file, it describes the file and moves with the file when it is copied 4 System metadata is an analogous to a library card catalog, it is stored and maintained external to the file • “Every” active file (no exception) in a computer system maintains system metadata used to track the file location & file demographics (i. e. , file name, size, creation, modification, and usage) § MS Windows and MS Word example: 4 Metadata supporting may be larger than the file itself, 80+ application & system metadata fields tracked for MS Word. doc files
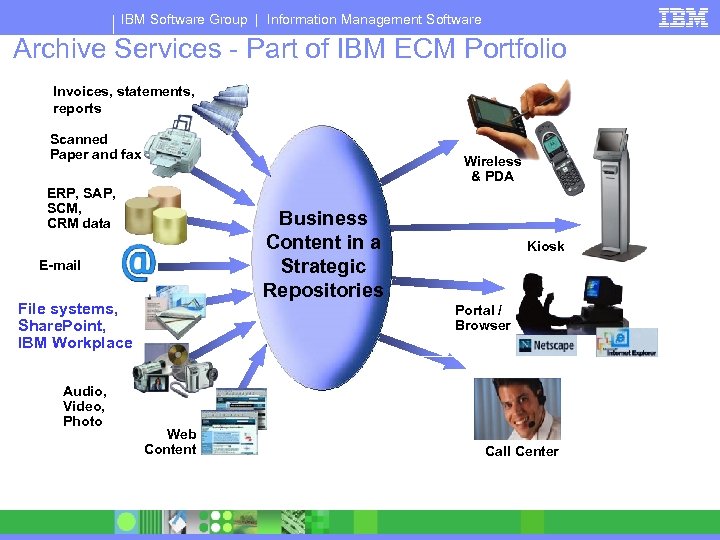
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Archive Services - Part of IBM ECM Portfolio Invoices, statements, reports Scanned Paper and fax Wireless & PDA ERP, SAP, SCM, CRM data Business Content in a Strategic Repositories E-mail File systems, Share. Point, IBM Workplace Audio, Video, Photo Kiosk Portal / Browser Web Content Call Center

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Control of the Wild, Wild West behind your firewall § What: Network File Shares, Desktops, Laptops § How: 4 File Systems Archive • Windows Explorer like capture, declaration / classification and move to a central repository 4 Records Crawler • Crawls Network File Shares, Desktops and Laptops looking for business records based on pre-defined business rules, declare / classify in place or move to central repository 4 Trusted Edge • Provides for end-user declaration and classification based on pre-defined business rules (leverages MS Office templates), declare / classify and secure in place or move to central repository allows for convenience copies and ensures their accountability and disposition

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Control of the Wild, Wild West behind your firewall § Who § When 4 File Systems Archive • Automated or End-users 4 Records Crawler • Automated 4 Trusted Edge • End-users 4 File Systems Archive • At project / case closure 4 Records Crawler • Anytime 4 Trusted Edge • Upon Creation / Receipt
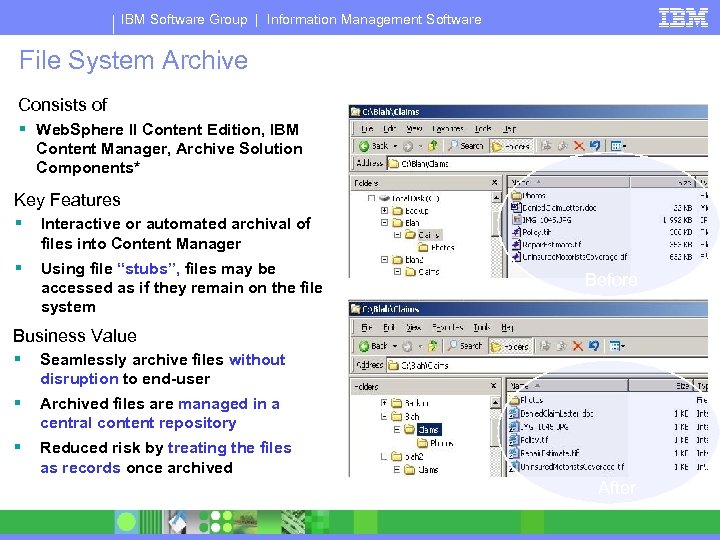
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software File System Archive Consists of § Web. Sphere II Content Edition, IBM File System Archive Example Content Manager, Archive Solution Components* Key Features § Interactive or automated archival of files into Content Manager § Using file “stubs”, files may be accessed as if they remain on the file system Before Business Value § Seamlessly archive files without disruption to end-user § Archived files are managed in a central content repository § Reduced risk by treating the files as records once archived *Services Offering After
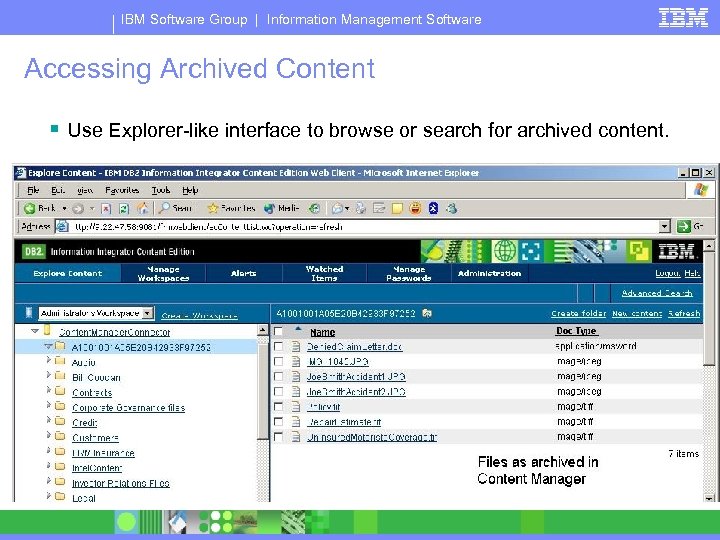
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Accessing Archived Content § Use Explorer-like interface to browse or search for archived content.
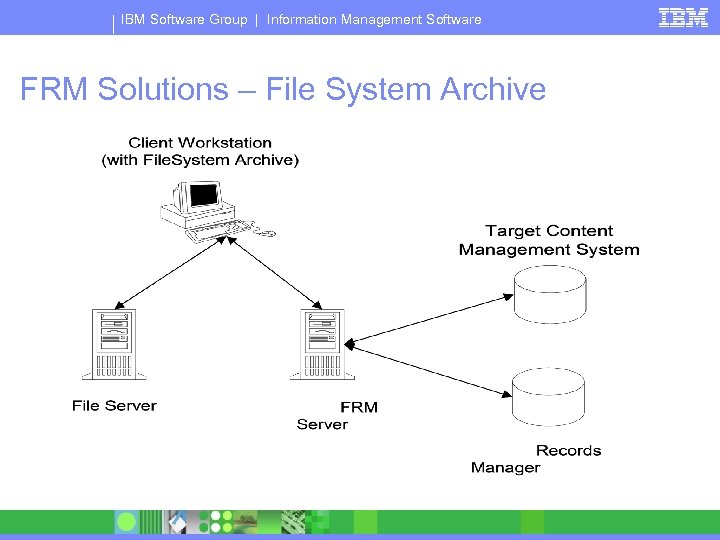
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software FRM Solutions – File System Archive

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software FRM Solutions – File System Archive § Ad-hoc archival of File System content to Content § § § Manager Select files individually from Windows Explorer or drag/drop them into a pre-configured folder to archive Configure the CM item class and folder where the content will be archived Prompts user to specify CM metadata for the content Formal Retention Rules applied via Records Manager Options to delete original File System content or leave a stub behind 4 Stub uses URL Addressability to open the content in CM
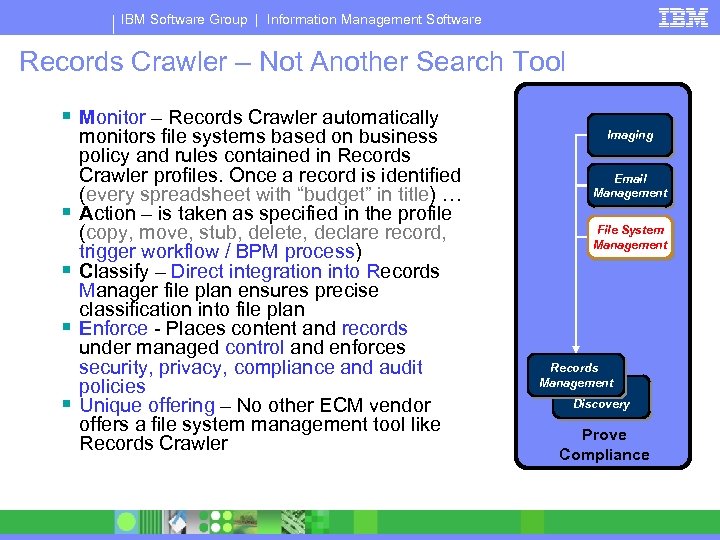
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Records Crawler – Not Another Search Tool § Monitor – Records Crawler automatically § § monitors file systems based on business policy and rules contained in Records Crawler profiles. Once a record is identified (every spreadsheet with “budget” in title) … Action – is taken as specified in the profile (copy, move, stub, delete, declare record, trigger workflow / BPM process) Classify – Direct integration into Records Manager file plan ensures precise classification into file plan Enforce - Places content and records under managed control and enforces security, privacy, compliance and audit policies Unique offering – No other ECM vendor offers a file system management tool like Records Crawler Imaging Email Management File System Management Records Management Content Discovery Prove Compliance
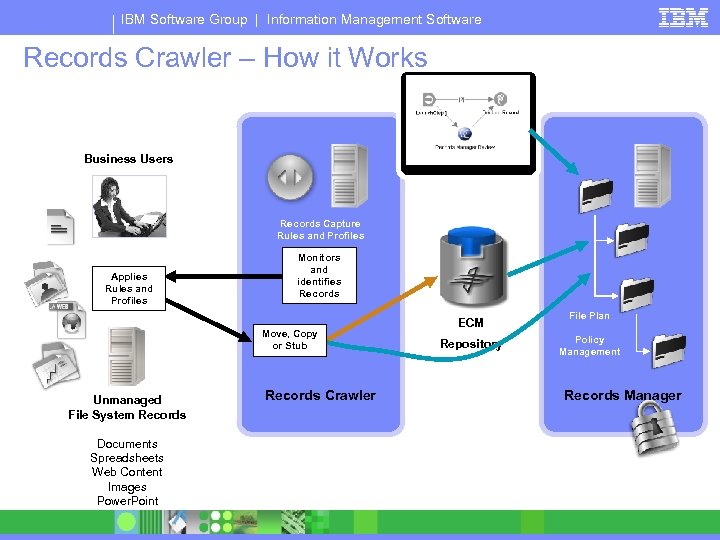
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Records Crawler – How it Works Business Users Records Capture Rules and Profiles Applies Rules and Profiles Monitors and identifies Records Move, Copy or Stub Unmanaged File System Records Documents Spreadsheets Web Content Images Power. Point Records Crawler ECM Repository File Plan Policy Management Records Manager
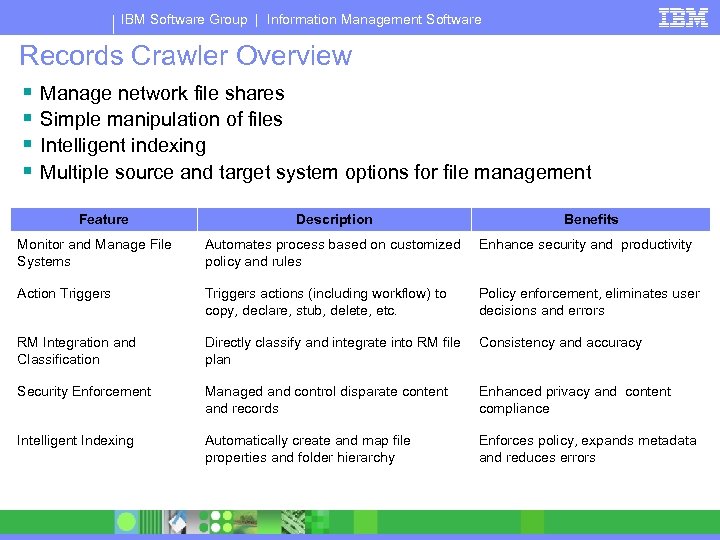
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Records Crawler Overview § § Manage network file shares Simple manipulation of files Intelligent indexing Multiple source and target system options for file management Feature Description Benefits Monitor and Manage File Systems Automates process based on customized policy and rules Enhance security and productivity Action Triggers actions (including workflow) to copy, declare, stub, delete, etc. Policy enforcement, eliminates user decisions and errors RM Integration and Classification Directly classify and integrate into RM file plan Consistency and accuracy Security Enforcement Managed and control disparate content and records Enhanced privacy and content compliance Intelligent Indexing Automatically create and map file properties and folder hierarchy Enforces policy, expands metadata and reduces errors
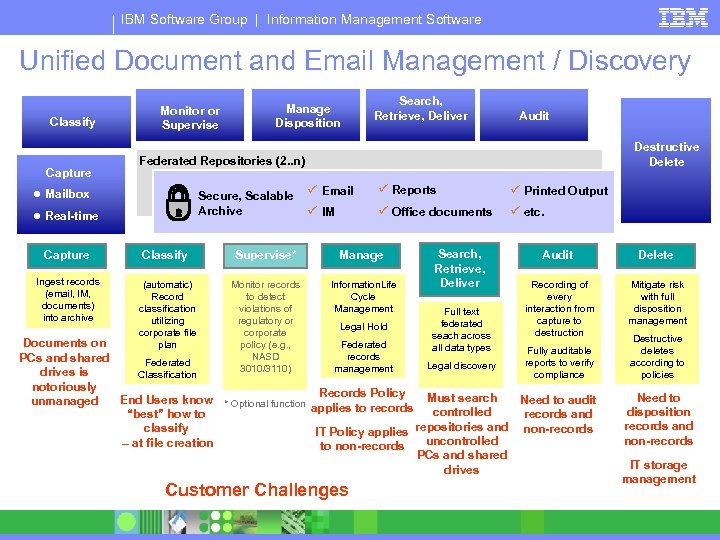
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Unified Document and Email Management / Discovery Classify Capture Monitor or Supervise Manage Disposition Search, Retrieve, Deliver Audit Destructive Delete Federated Repositories (2. . n) ● Mailbox Secure, Scalable Archive ● Real-time ü Email ü Reports ü Printed Output ü IM ü Office documents ü etc. Capture Classify Supervise* Manage Ingest records (email, IM, documents) into archive (automatic) Record classification utilizing corporate file plan Monitor records to detect violations of regulatory or corporate policy (e. g. , NASD 3010/3110) Information. Life Cycle Management Legal Hold Search, Retrieve, Deliver Full text federated seach across all data types Audit Delete Recording of every interaction from capture to destruction Mitigate risk with full disposition management Documents on Federated Fully auditable records PCs and shared Federated reports to verify Legal discovery management drives is Classification compliance notoriously Records Policy Must search End Users know * Optional function Need to audit unmanaged applies to records controlled “best” how to records and repositories and non-records classify IT Policy applies uncontrolled – at file creation to non-records PCs and shared drives Customer Challenges Destructive deletes according to policies Need to disposition records and non-records IT storage management
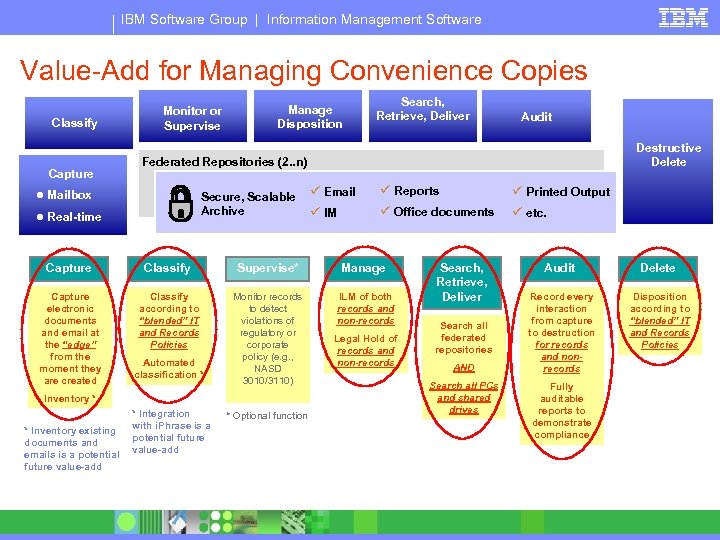
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Value-Add for Managing Convenience Copies Classify Capture Monitor or Supervise Manage Disposition Search, Retrieve, Deliver Destructive Delete Federated Repositories (2. . n) ● Mailbox Secure, Scalable Archive ● Real-time ü Email ü Reports ü Printed Output ü IM ü Office documents ü etc. Capture Classify Supervise* Manage Capture electronic documents and email at the “edge” from the moment they are created Classify according to “blended” IT and Records Policies Monitor records to detect violations of regulatory or corporate policy (e. g. , NASD 3010/3110) ILM of both records and non-records Automated classification * Inventory * * Inventory existing documents and emails is a potential future value-add Audit * Integration with i. Phrase is a potential future value-add * Optional function Legal Hold of records and non-records Search, Retrieve, Deliver Search all federated repositories AND Search all PCs and shared drives Audit Delete Record every interaction from capture to destruction for records and nonrecords Disposition according to “blended” IT and Records Policies Fully auditable reports to demonstrate compliance
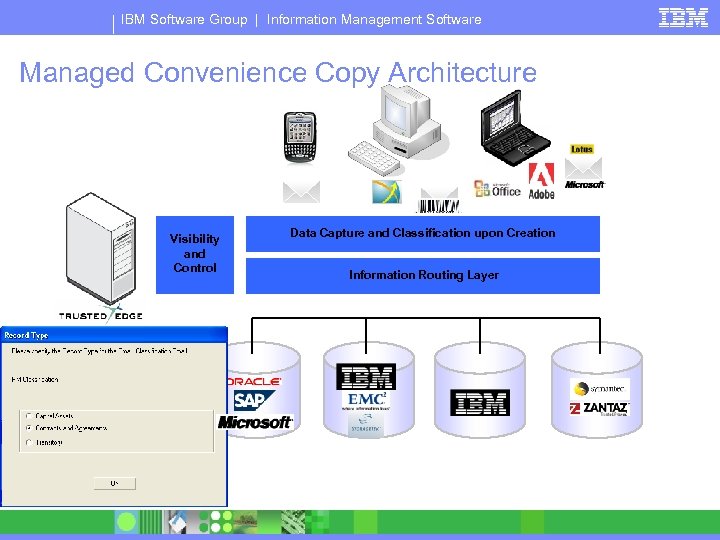
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Managed Convenience Copy Architecture XML Visibility and Control Applications Data Capture and Classification upon Creation Information Routing Layer Storage Content & Records Management Archiving

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Desktop Records Management §Capabilities: 4 Classification at Creation / Receipt 4 Document Branding 4 In-place and/or copy to Strategic Repository Records Management: Disposition and Litigation Holds of Desktop and File Server documents and files 4 Seamless Online / Offline operation 4 Fully integrated with IBM Records Manager and Content Manager 4 Future-proofing: Desktop management that anticipates ECM, Tivoli Storage Manager, etc.

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software How to Manage Desktop Information § Configure policies and actionable business rules 4 “Blended” Records and IT Policies 4 Flexible and robust policy configuration with location-sensitive retention rules § Classify documents and e-mails at creation / receipt 4 Acquire metadata (system, application, business context – policy and user specified) 4 Brand/Tag with metadata and a unique ASSET ID • Self-describing throughout its lifecycle 4 Classify 4 Store data and metadata to the designated location § Manage retention of all copies, regardless of location 4 4 4 Apply and release Legal Holds Reporting and Auditing Document and Email Forensics Discovery Disposition Official Records and all copies

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Benefits of Managing Desktop Documents § Desktop Information Management 4 Reduce enterprise risk at the desktop 4 Control all information and records from creation to destruction 4 Inventory files on desktops, laptops, shared drives (potential future FSA integration) 4 Automated contextual classification (potential future integration) § Bring information under policy control from the moment it is created in any desktop application 4 Manage retention of all copies according to policy • • • “In place” on desktops and shared drives In content management systems In email systems and archives 4 Reduce storage costs through intelligent storage management • Classification-driven tiered storage 4 Disposition official records and all copies and renditions • Eliminate “smoking guns” and rogue information
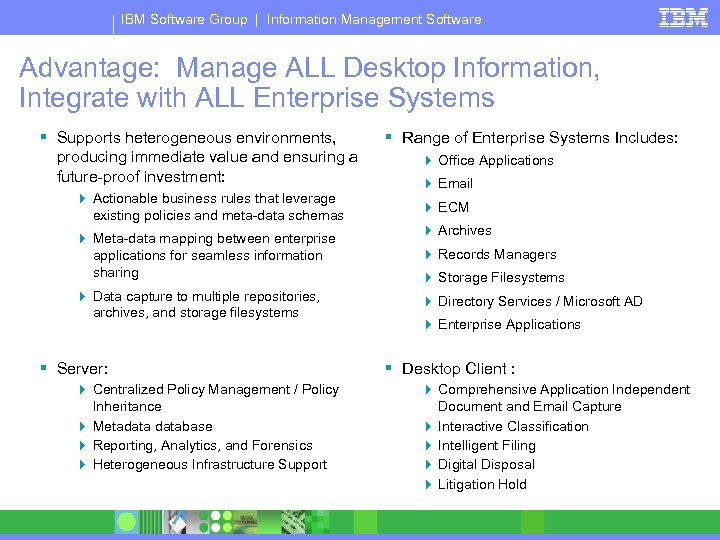
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Advantage: Manage ALL Desktop Information, Integrate with ALL Enterprise Systems § Supports heterogeneous environments, producing immediate value and ensuring a future-proof investment: 4 Actionable business rules that leverage existing policies and meta-data schemas 4 Meta-data mapping between enterprise applications for seamless information sharing 4 Data capture to multiple repositories, archives, and storage filesystems § Server: 4 Centralized Policy Management / Policy Inheritance 4 Metadatabase 4 Reporting, Analytics, and Forensics 4 Heterogeneous Infrastructure Support § Range of Enterprise Systems Includes: 4 Office Applications 4 Email 4 ECM 4 Archives 4 Records Managers 4 Storage Filesystems 4 Directory Services / Microsoft AD 4 Enterprise Applications § Desktop Client : 4 Comprehensive Application Independent Document and Email Capture 4 Interactive Classification 4 Intelligent Filing 4 Digital Disposal 4 Litigation Hold
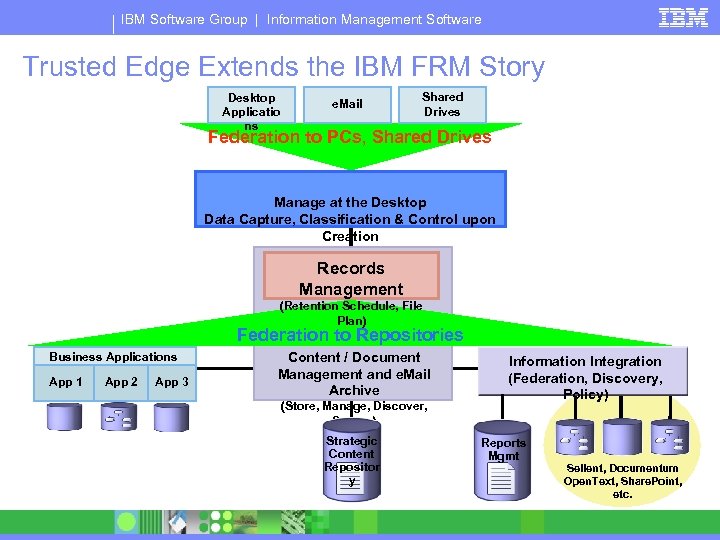
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Trusted Edge Extends the IBM FRM Story Desktop Applicatio ns e. Mail Shared Drives Federation to PCs, Shared Drives Manage at the Desktop Data Capture, Classification & Control upon Creation Records Management (Retention Schedule, File Plan) Federation to Repositories Business Applications App 1 App 2 App 3 Content / Document Management and e. Mail Archive Information Integration (Federation, Discovery, Policy) (Store, Manage, Discover, Secure) Strategic Content Repositor y Reports Mgmt R Sellent, Documentum Open. Text, Share. Point, etc.
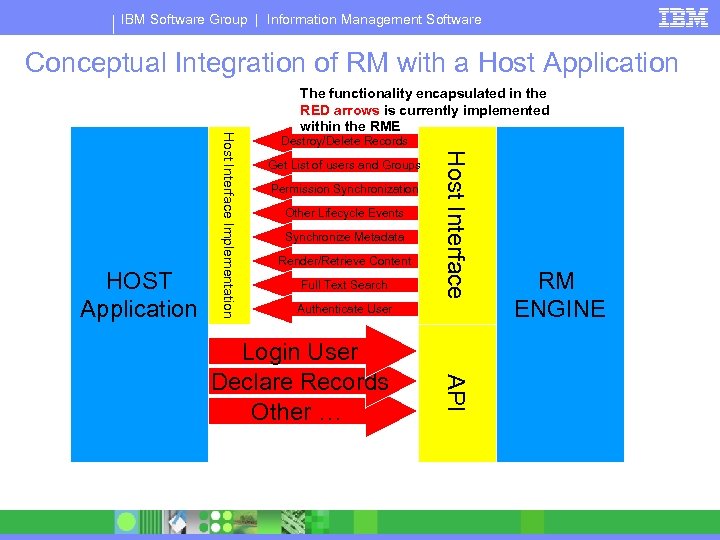
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Conceptual Integration of RM with a Host Application Destroy/Delete Records Get List of users and Groups Permission Synchronization Other Lifecycle Events Synchronize Metadata Render/Retrieve Content Full Text Search Host Interface Implementation HOST Application The functionality encapsulated in the RED arrows is currently implemented within the RME Authenticate User API Login User Declare Records Other … RM ENGINE
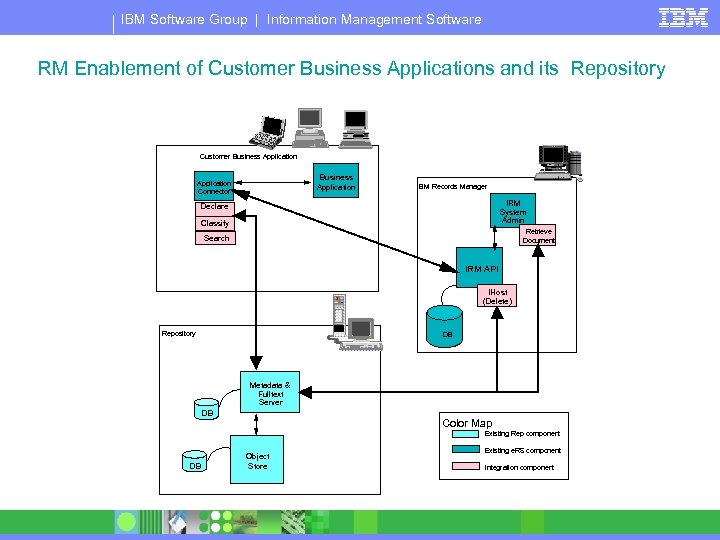
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software RM Enablement of Customer Business Applications and its Repository Customer Business Application Connector IBM Records Manager IRM System Admin Declare Classify Retrieve Document Search IRM API IHost (Delete) Repository DB Metadata & Fulltext Server DB Color Map Existing Rep component DB Object Store Existing e. RS component Integration component

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Philosophies Regarding Search / Discovery as a Function of Records Management § Records Management is about retention and disposition of business information assets § Records Management Solutions must offer easy, efficient, and effective retrieval / discovery solutions § The effectiveness of your Records Management Programs will likely be measured by how well it facilitates e-Evidence Discovery as well as traditional retention and disposition activities § This starts with selection of the tools, which can facilitate indexing, auto-classification as well as discovery

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Legacy of Discovery & Records Management Technology § For better than 50 years, people have been attempting to optimize search technology § Discovery technology has the potential to have a profound impact today upon the following business activities: advertising, marketing, and selling as well as auditing, litigation and regulatory enforcement § The “Goal of records management”: “provide the right information to the right people, in the right format, at the right time” can be achieved by providing enough of the right information, within the appropriate context, along with the right tools to filter / refine and abstract the information we will have the ideal intelligent discovery tool § Common problems: 4 To much information 4 To little relevancy

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Conclusions Regarding the Relationship Between the Two Technologies: § Too much information can significantly effect the speed, quality, efficiency, and effectiveness of discovery activities 4 The more information I have, the more I have to search through § Electronic Evidence Discovery involves more than discovery on “official business records” 4 It involves both declared and undeclared records § Based on the results of an e-discovery search, consider doing the following: 4 Declare all previously applicable undeclared records as “records” 4 Apply Hold Orders to all applicable records

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Consider the Benefits of the Following Technology When Defining / Building Your Organizations Discovery Infrastructure: § Federated Search: search one time with consistent criteria across all repositories, both structured and unstructured content § Contextual Analysis: minimize false positives § Information Accelerators: intelligently anticipate both industry and departmental use cases § Text Analytics: extraction of knowledge, meaning, and relevance from information sources

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Content Services Provide a comprehensive infrastructure to support a broad range of business processes that need unstructured data
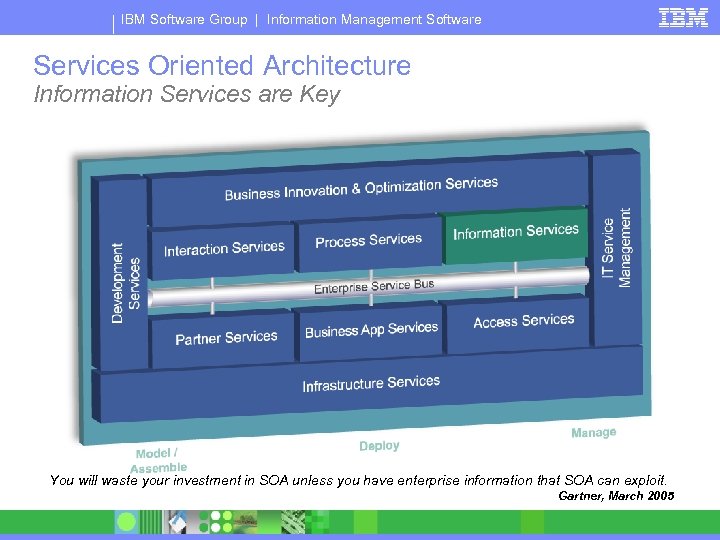
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Services Oriented Architecture Information Services are Key You will waste your investment in SOA unless you have enterprise information that SOA can exploit. Gartner, March 2005
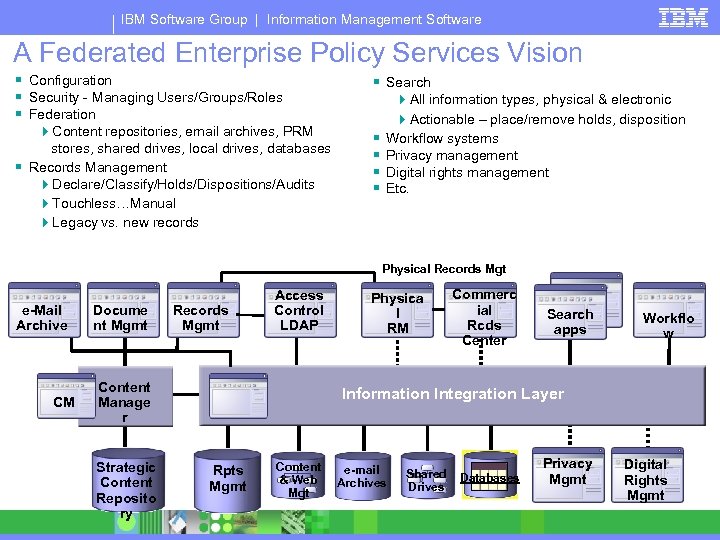
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software A Federated Enterprise Policy Services Vision § Configuration § Security - Managing Users/Groups/Roles § Federation § Search 4 Content repositories, email archives, PRM stores, shared drives, local drives, databases § Records Management 4 Declare/Classify/Holds/Dispositions/Audits 4 Touchless…Manual 4 Legacy vs. new records § § 4 All information types, physical & electronic 4 Actionable – place/remove holds, disposition Workflow systems Privacy management Digital rights management Etc. Physical Records Mgt e-Mail Archive CM Docume nt Mgmt Records Mgmt Access Control LDAP Content Manage r Strategic Content Reposito ry Physica l RM Commerc ial Rcds Center Search apps Workflo w Information Integration Layer Rpts Mgmt Content & Web Mgt e-mail Archives Shared Drives Databases Privacy Mgmt Digital Rights Mgmt
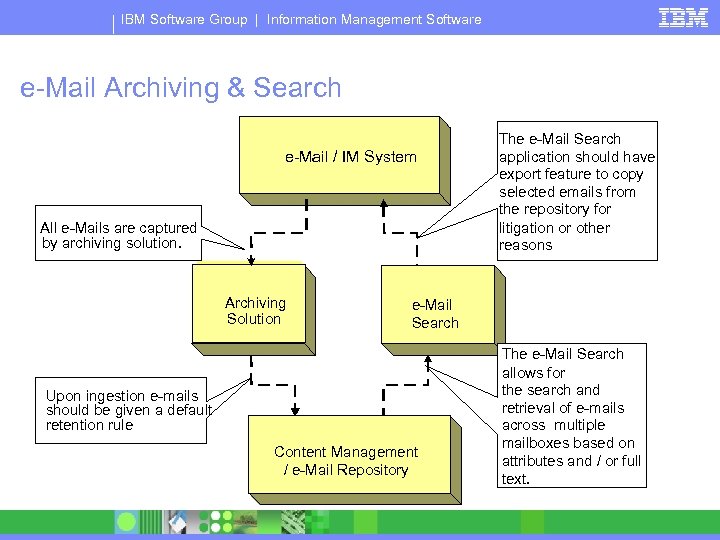
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software e-Mail Archiving & Search e-Mail / IM System All e-Mails are captured by archiving solution. e-Mail Archiving Solution Upon ingestion e-mails should be given a default retention rule e-Mail Search Content Management Repository / e-Mail Repository The e-Mail Search application should have export feature to copy selected emails from the repository for litigation or other reasons The e-Mail Search allows for the search and retrieval of e-mails across multiple mailboxes based on attributes and / or full text.
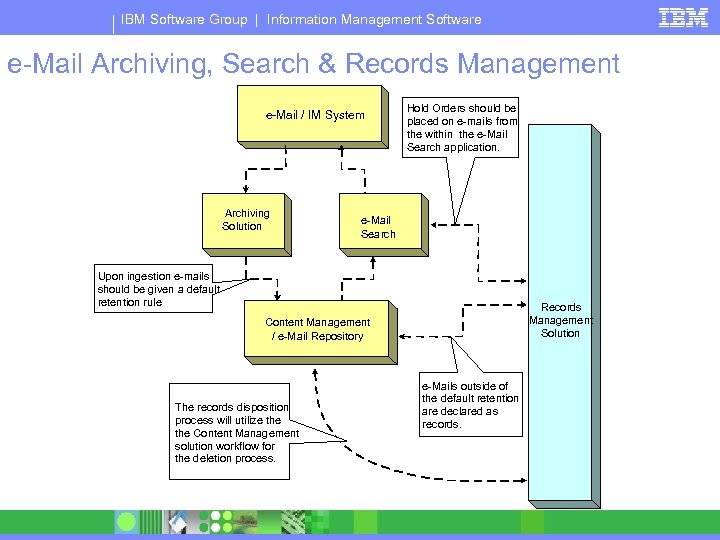
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software e-Mail Archiving, Search & Records Management e-Mail / IM System Archiving Solution Hold Orders should be placed on e-mails from the within the e-Mail Search application. e-Mail Search Upon ingestion e-mails should be given a default retention rule Records Management Solution Content Management / e-Mail Repository The records disposition process will utilize the Content Management solution workflow for the deletion process. e-Mails outside of the default retention are declared as records.
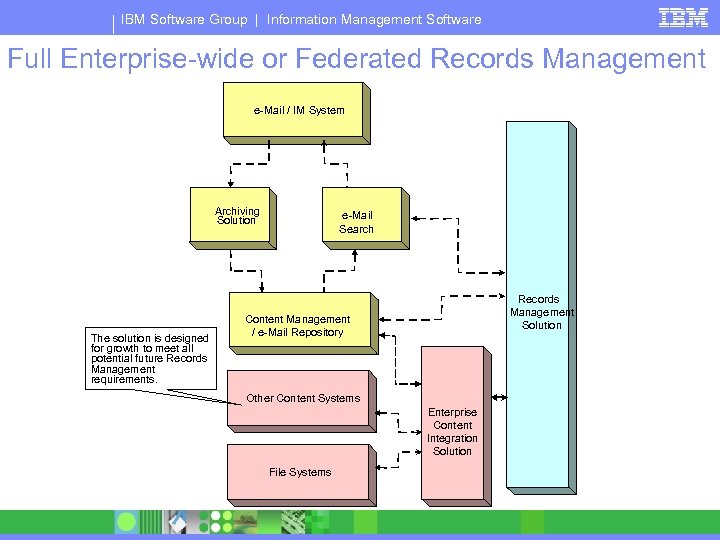
IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Full Enterprise-wide or Federated Records Management e-Mail / IM System Archiving Solution The solution is designed for growth to meet all potential future Records Management requirements. e-Mail Search Records Management Solution Content Management / e-Mail Repository Other Content Systems Enterprise Content Integration Solution File Systems

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Best Practices § Start small, but high profile, pick an advocate § Define and agree upon success criteria § Measure the success criteria § Minimize impact on end-users - “automate, automate” § Minimize impact on corporate culture change § Priority should be on the business process, not: Software, Media, or Data format § Use WORM / WORM-like technology ONLY when / where required to § Whiteboard your file plan prior to designing in the policy engine (similar to a database)

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Next Steps § Set expectations, define pilot & measure deliverables, don’t over commit § Know your Regulatory Requirement & Business Drives § Know your allies and their drivers § ECM vs. dedicated e-Mail Repository? § e-Discovery Solution? § Secure e-Mail at Storage Layer or with an Records Management Policy Engine?

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software What to look for in Discovery & Records Management Solution Provider § Deliver the appropriate mix of technologies required to meet your requirements § Efficiently integrate the various technologies into a seamless solution § Incorporate strong knowledge of the specific industry requirements into the required solution § Integrate the overall solution into our customer’s internal framework of policies and processes that reflect the requirements you have defined

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software What to look for in e-Mail Retention Solution Provider § Completeness of Solution (capture, supervision, discovery, storage, migration, retention, holds) § Track record for successful deployments § Platform independence § Scalability, Performance, Throughput § Support for Storage Solutions including CAS § Compression & Format § Hierarchal Storage Management in the solution § Support, Maintenance, Strategy

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software Predictions made three years ago § § Archiving Solutions and Data Warehouses Insurance Underwriters impact on Records Management Information Assets and Information as a Liability Challenge what we generate and keep and why Fast forward to today

IBM Software Group | Information Management Software How Many Times Do You Want to Pay for that Information that is NOT required? 1. 2. 3. 4. Generation Management (retain, preserve, and protect) Search and Retrieve (audit, litigation / discovery) Fines / Penalty / Settlement
Questions & Answers ® IBM Software Group “Risk mitigation can NOT be realized, nor good corporate governance, and compliance achieved without records management”. In the end, all that matters, is our integrity.
9733c5f391b2195610571f6e00d1b88c.ppt