d88153c963c2b00a000fa90bec65528b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 70
 Complaints of hand wrist Wim Willems HOVUmc, Amsterdam
Complaints of hand wrist Wim Willems HOVUmc, Amsterdam
 Program • Basic anatomy • Common complaints • Practice
Program • Basic anatomy • Common complaints • Practice
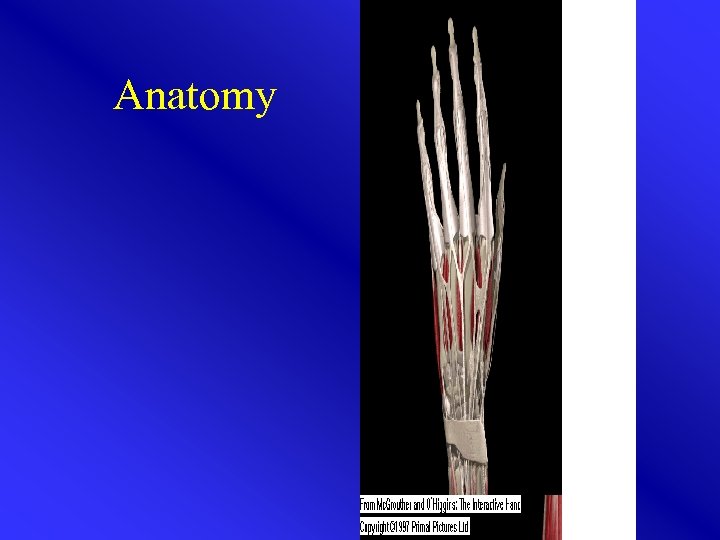 Anatomy
Anatomy
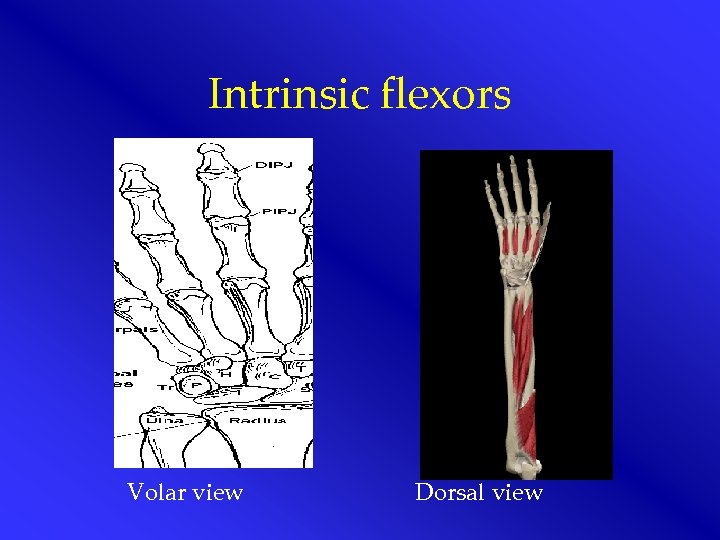 Intrinsic flexors Volar view Dorsal view
Intrinsic flexors Volar view Dorsal view
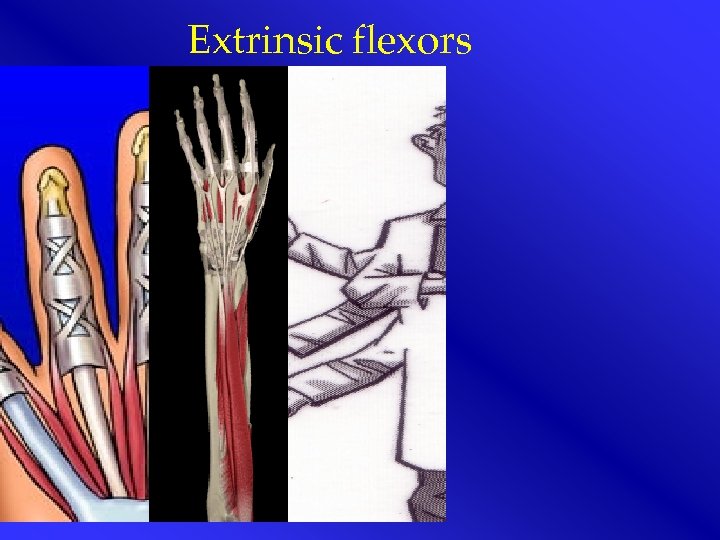 Extrinsic flexors
Extrinsic flexors
 Extensors
Extensors
 Nerves
Nerves
 “Elderly lady with a painful thumb” • Female, 78 years old • Pain thumb right hand • Difficulty with sewing / opening pots
“Elderly lady with a painful thumb” • Female, 78 years old • Pain thumb right hand • Difficulty with sewing / opening pots
 “Elderly lady with a painful thumb” • • Questions? Physical examination? Further examination? D. d. ?
“Elderly lady with a painful thumb” • • Questions? Physical examination? Further examination? D. d. ?
 Arthrosis • Start of arthrosis in DIP most common • Heberden’s nodules • CMC-1 (possibly afflicted relatively young) • Grind test
Arthrosis • Start of arthrosis in DIP most common • Heberden’s nodules • CMC-1 (possibly afflicted relatively young) • Grind test
 Grind test
Grind test
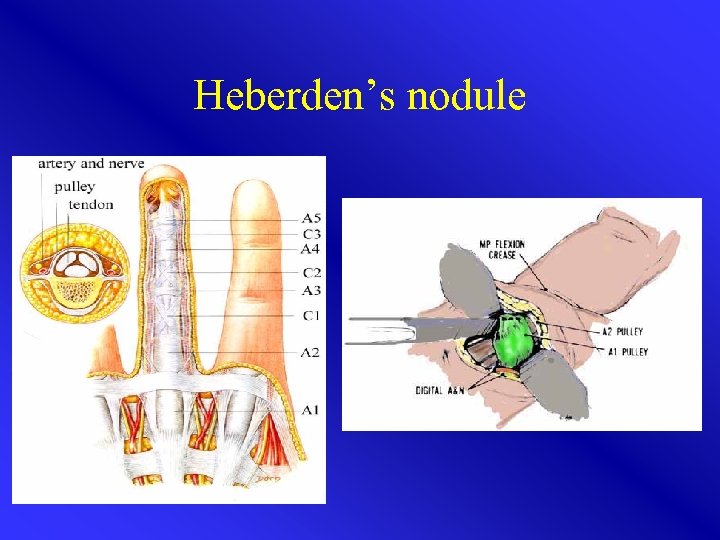 Heberden’s nodule
Heberden’s nodule
 Treatment
Treatment
 Arthrosis CMC I Injection Splint Avoid operation as long as possible
Arthrosis CMC I Injection Splint Avoid operation as long as possible
 Arthrosis CMC I
Arthrosis CMC I
 “Finger gets stuck” • • Female, 45 year Right hand Palmar pain/ middle finger Impossible to straighten finger
“Finger gets stuck” • • Female, 45 year Right hand Palmar pain/ middle finger Impossible to straighten finger
 “Finger gets stuck” • • Questions? Physical examination? Further examination? D. d. ?
“Finger gets stuck” • • Questions? Physical examination? Further examination? D. d. ?
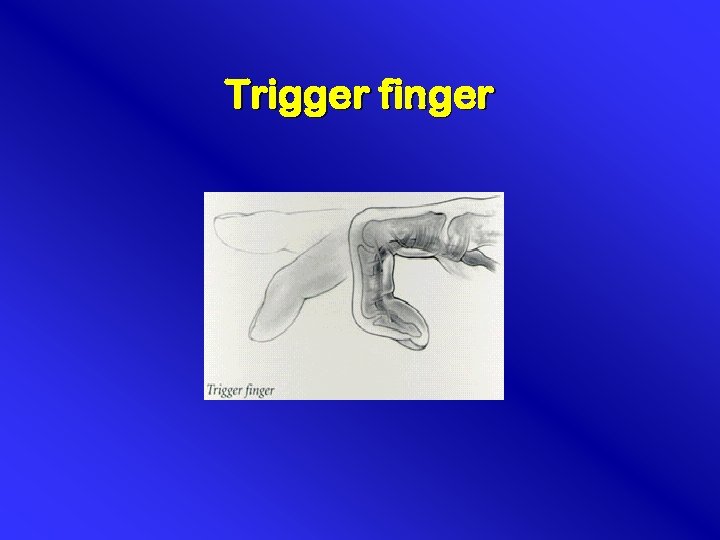 Trigger finger
Trigger finger
 Pathofysiology • Thickening of tendon / tenosynovitis of m. flexor digitorum communis • Finger triggers
Pathofysiology • Thickening of tendon / tenosynovitis of m. flexor digitorum communis • Finger triggers
 Epidemiology • Few data • life time prevalence, > 30 jr, no DM: 2. 2%. • Connected with DM, carpal tunnel syndrome, reumatic arthritis, hypothyreoidy.
Epidemiology • Few data • life time prevalence, > 30 jr, no DM: 2. 2%. • Connected with DM, carpal tunnel syndrome, reumatic arthritis, hypothyreoidy.
 Treatment
Treatment
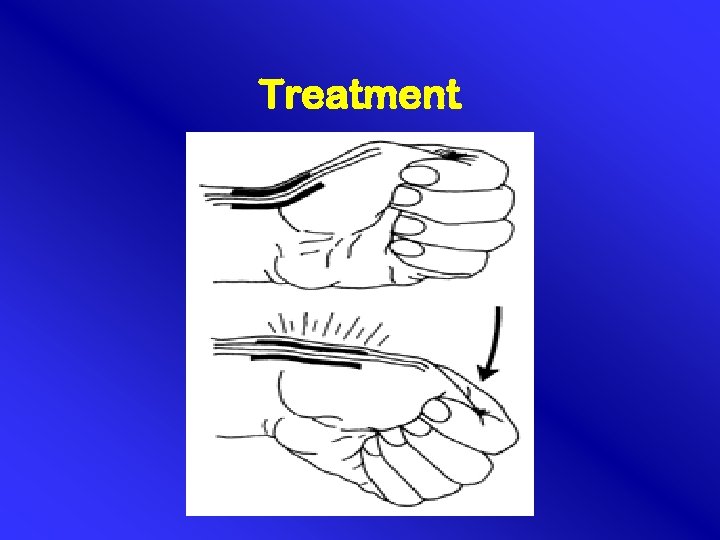
 Conservative therapy • Self limiting 10 -20% ? ? • NSAID • Splint. 6 - 8 weeks (MCP in 10 -15 degrees flexion). Effective 66% of the cases • Steroïd injection. Effectiveness 50% >90%
Conservative therapy • Self limiting 10 -20% ? ? • NSAID • Splint. 6 - 8 weeks (MCP in 10 -15 degrees flexion). Effective 66% of the cases • Steroïd injection. Effectiveness 50% >90%
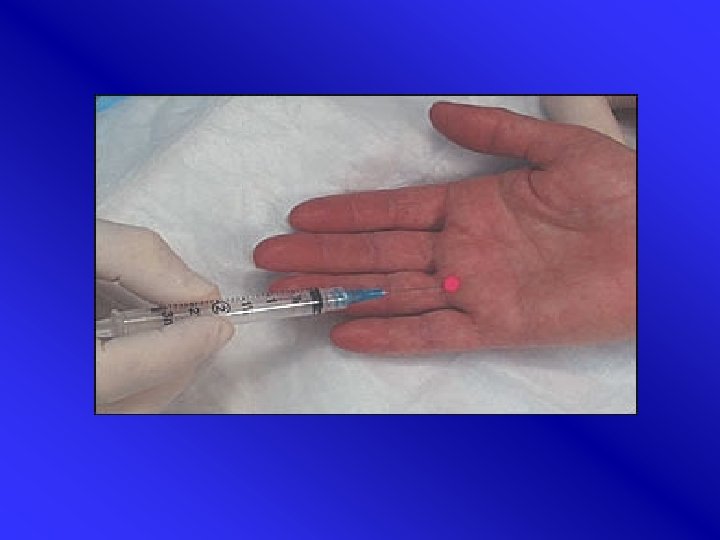
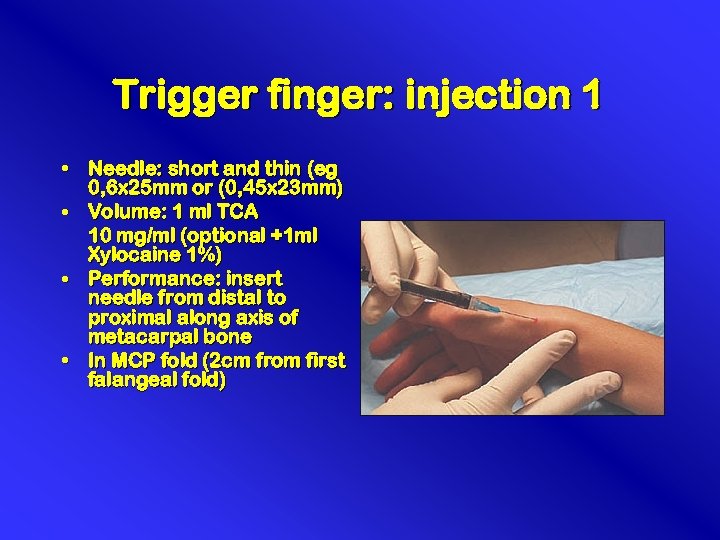 Trigger finger: injection 1 • Needle: short and thin (eg 0, 6 x 25 mm or (0, 45 x 23 mm) • Volume: 1 ml TCA 10 mg/ml (optional +1 ml Xylocaine 1%) • Performance: insert needle from distal to proximal along axis of metacarpal bone • In MCP fold (2 cm from first falangeal fold)
Trigger finger: injection 1 • Needle: short and thin (eg 0, 6 x 25 mm or (0, 45 x 23 mm) • Volume: 1 ml TCA 10 mg/ml (optional +1 ml Xylocaine 1%) • Performance: insert needle from distal to proximal along axis of metacarpal bone • In MCP fold (2 cm from first falangeal fold)
 Trigger finger: injection 2 • Preferred angle 45 degrees • Ca. 1 ml around tendon Subcutaneous injection is as effective as injection in tendon sheath • No pressure • Effectiveness: 70 -80% after 1 -3 injections
Trigger finger: injection 2 • Preferred angle 45 degrees • Ca. 1 ml around tendon Subcutaneous injection is as effective as injection in tendon sheath • No pressure • Effectiveness: 70 -80% after 1 -3 injections
 Operative treatment • Open or percutanous. • Success >90% • More complications (nerve damage, inflammation)
Operative treatment • Open or percutanous. • Success >90% • More complications (nerve damage, inflammation)
 “Painful thumb” • Man, 37 years • House painter • Pain radial side wrist
“Painful thumb” • Man, 37 years • House painter • Pain radial side wrist
 “Painful thumb” • • Questions? Physical examination? Further examination? D. d. ?
“Painful thumb” • • Questions? Physical examination? Further examination? D. d. ?
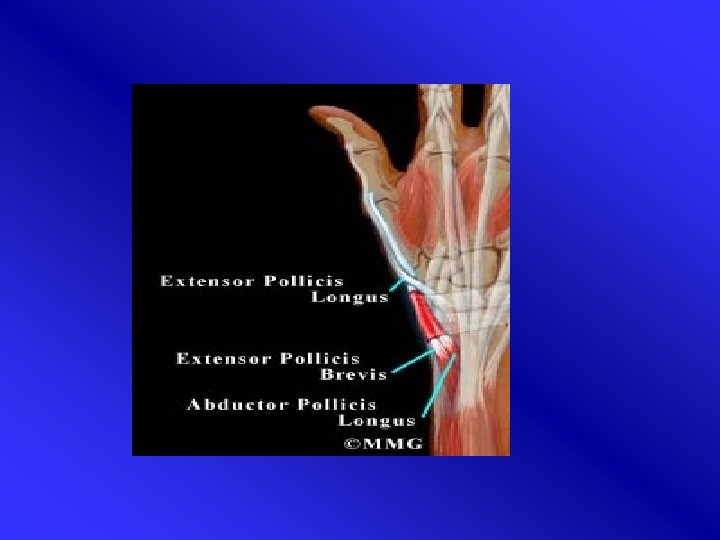
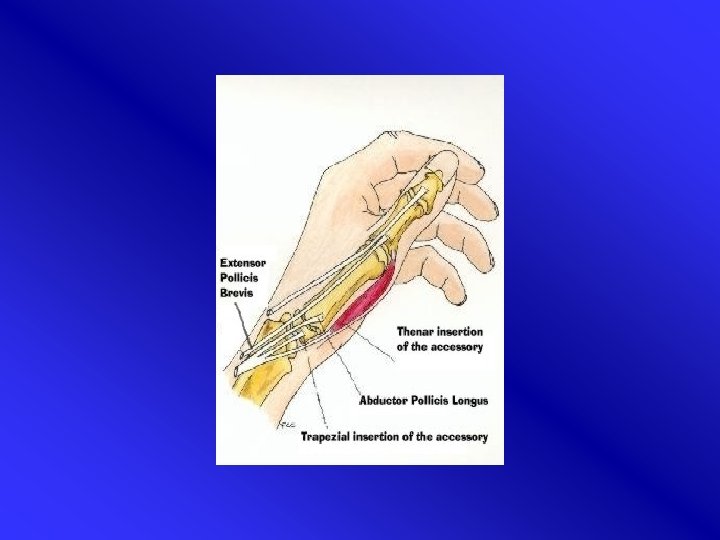
 De Quervain’s disease • Tenosynovitis of m. abductor pollicis longus and m. extensor pollicis brevis (APL & EPB) • distal end radius • Women > men, 35 -55 yr. • Presentation in general practice: 5, 6/1000 • Often recurrent esp. when crepitations
De Quervain’s disease • Tenosynovitis of m. abductor pollicis longus and m. extensor pollicis brevis (APL & EPB) • distal end radius • Women > men, 35 -55 yr. • Presentation in general practice: 5, 6/1000 • Often recurrent esp. when crepitations
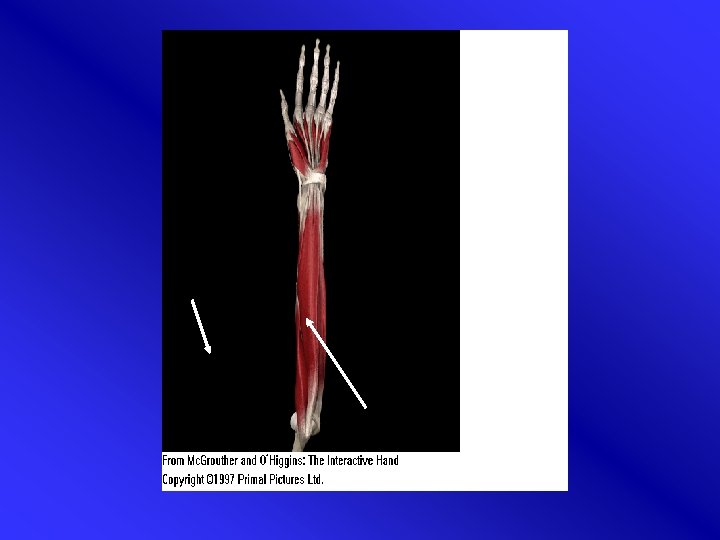
 Etiology • Tendons in common sheath APL & EPB irritation caused by frequent movements • Overuse (wringing, racket sports) • Pregnancy • Anatomic variations
Etiology • Tendons in common sheath APL & EPB irritation caused by frequent movements • Overuse (wringing, racket sports) • Pregnancy • Anatomic variations
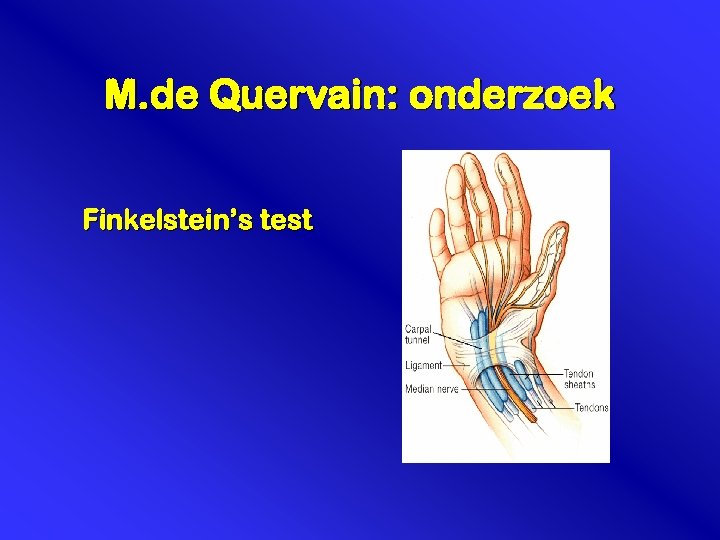 M. de Quervain: onderzoek Finkelstein’s test
M. de Quervain: onderzoek Finkelstein’s test
 Treatment • Corticosterod injection: success rate 2/3 of patients after 3 weeks. Sometimes 2 nd or 3 rd injection. • Splint : unhelpful • Operation (cutting tendon sheath): longstanding complaints or failure injections • Injection possible in pregnancy
Treatment • Corticosterod injection: success rate 2/3 of patients after 3 weeks. Sometimes 2 nd or 3 rd injection. • Splint : unhelpful • Operation (cutting tendon sheath): longstanding complaints or failure injections • Injection possible in pregnancy
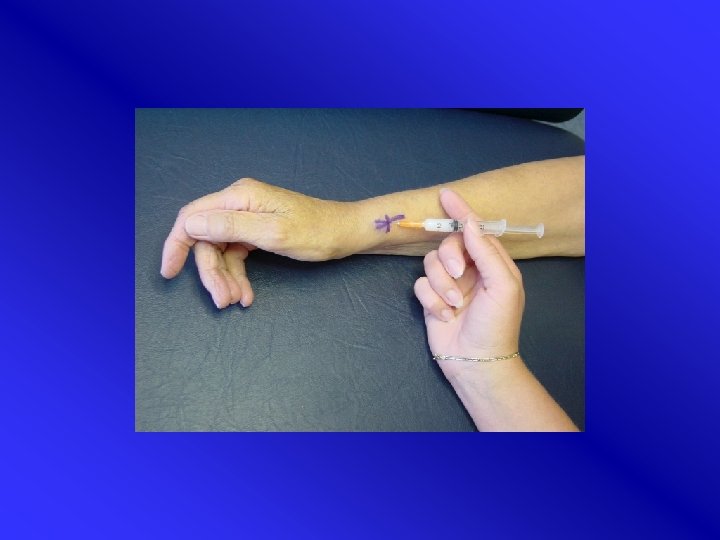
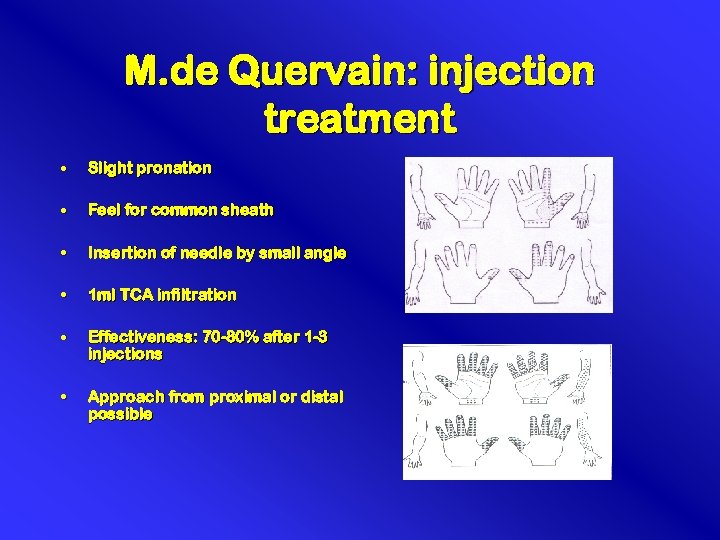 M. de Quervain: injection treatment • Slight pronation • Feel for common sheath • Insertion of needle by small angle • 1 ml TCA infiltration • Effectiveness: 70 -80% after 1 -3 injections • Approach from proximal or distal possible
M. de Quervain: injection treatment • Slight pronation • Feel for common sheath • Insertion of needle by small angle • 1 ml TCA infiltration • Effectiveness: 70 -80% after 1 -3 injections • Approach from proximal or distal possible
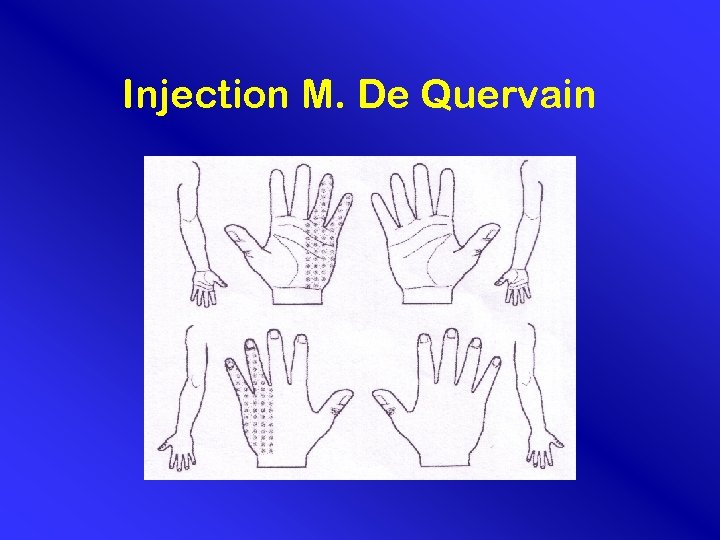 Injection M. De Quervain
Injection M. De Quervain
 “Painful nightly tingling” • Female, 52 years • Wakes up in the early morning with painful tingling in the hand (thumb / index) • Flapping of hand to ease complaints
“Painful nightly tingling” • Female, 52 years • Wakes up in the early morning with painful tingling in the hand (thumb / index) • Flapping of hand to ease complaints
 “Painful nightly tingling” • • Questions? Physical examination? Further examintion? D. d. ?
“Painful nightly tingling” • • Questions? Physical examination? Further examintion? D. d. ?
 Carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome
 Epidemiology • Open population (history + nerve conduction examination): – Female: 9 % – Male: 0, 6% – Peak between 40 -60 year
Epidemiology • Open population (history + nerve conduction examination): – Female: 9 % – Male: 0, 6% – Peak between 40 -60 year
 Risk factors Ø Weight Ø Pregnancy Ø Diabetes mellitus Ø Hypo/hyperthyreoidy Ø Ovariectomy Ø Anatomic deviation (traumatic / RA / congenital) Ø Work related
Risk factors Ø Weight Ø Pregnancy Ø Diabetes mellitus Ø Hypo/hyperthyreoidy Ø Ovariectomy Ø Anatomic deviation (traumatic / RA / congenital) Ø Work related
 Natural course • ¼ - 1/3 significant improvement > 1 year • After pregnancy 50% without complaints
Natural course • ¼ - 1/3 significant improvement > 1 year • After pregnancy 50% without complaints
 Pathofysiology • Narrow tunnel • compression n. medianus in carpal tunnel • 90% idiopatic
Pathofysiology • Narrow tunnel • compression n. medianus in carpal tunnel • 90% idiopatic
 Diagnosis: history Dutch consensus (CBO 2006): • Nightly tingling • Median nerve area • Sleep disturbance • Other tingling / pains • Flapping (Flick’s sign) • Advanced stages: tingling during the day
Diagnosis: history Dutch consensus (CBO 2006): • Nightly tingling • Median nerve area • Sleep disturbance • Other tingling / pains • Flapping (Flick’s sign) • Advanced stages: tingling during the day
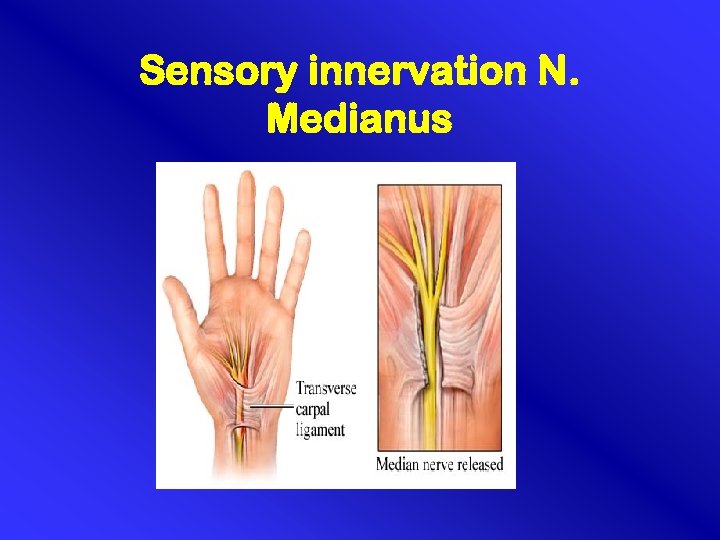 Sensory innervation N. Medianus
Sensory innervation N. Medianus
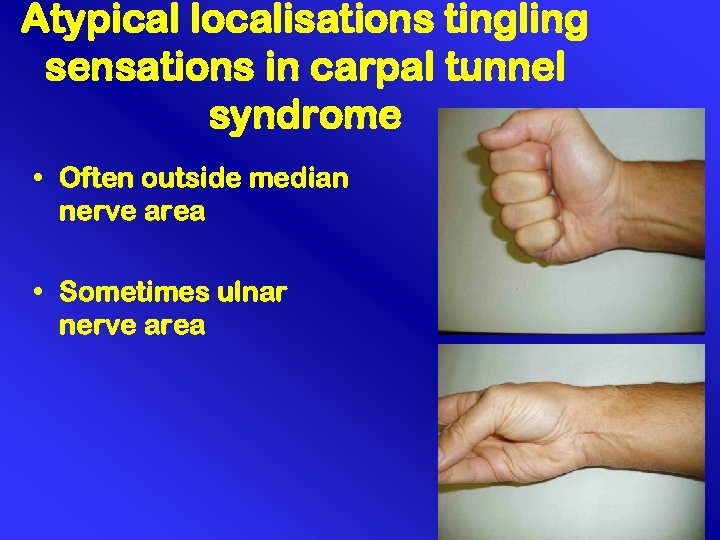 Atypical localisations tingling sensations in carpal tunnel syndrome • Often outside median nerve area • Sometimes ulnar nerve area
Atypical localisations tingling sensations in carpal tunnel syndrome • Often outside median nerve area • Sometimes ulnar nerve area
 Provocation tests: CBO 2006: Limited usefulness
Provocation tests: CBO 2006: Limited usefulness
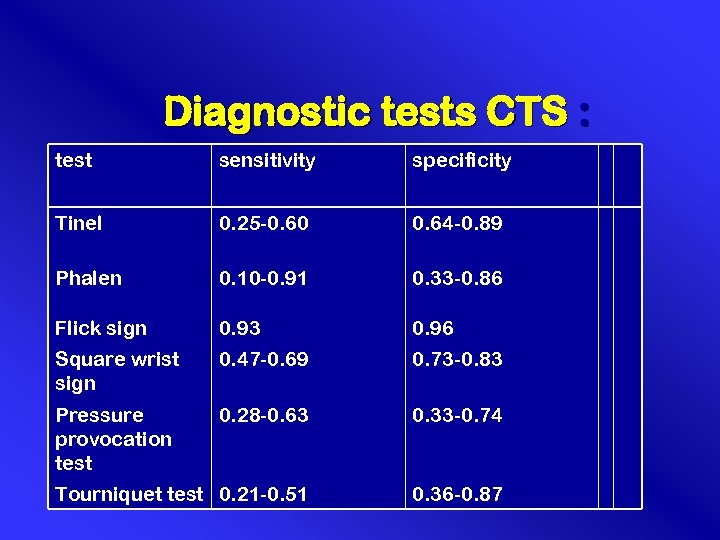 C. A. Diagnostic tests CTS : test sensitivity specificity Tinel 0. 25 -0. 60 0. 64 -0. 89 Phalen 0. 10 -0. 91 0. 33 -0. 86 Flick sign 0. 93 0. 96 Square wrist sign 0. 47 -0. 69 0. 73 -0. 83 Pressure provocation test 0. 28 -0. 63 0. 33 -0. 74 Tourniquet test 0. 21 -0. 51 0. 36 -0. 87
C. A. Diagnostic tests CTS : test sensitivity specificity Tinel 0. 25 -0. 60 0. 64 -0. 89 Phalen 0. 10 -0. 91 0. 33 -0. 86 Flick sign 0. 93 0. 96 Square wrist sign 0. 47 -0. 69 0. 73 -0. 83 Pressure provocation test 0. 28 -0. 63 0. 33 -0. 74 Tourniquet test 0. 21 -0. 51 0. 36 -0. 87
 Tests • Tinel percussion median nerve • Phalen: flexion during 60 seconds • Further: -sensory loss median nerve area -thenar dystrophy -dry skin (thumb / index / middle finger)
Tests • Tinel percussion median nerve • Phalen: flexion during 60 seconds • Further: -sensory loss median nerve area -thenar dystrophy -dry skin (thumb / index / middle finger)
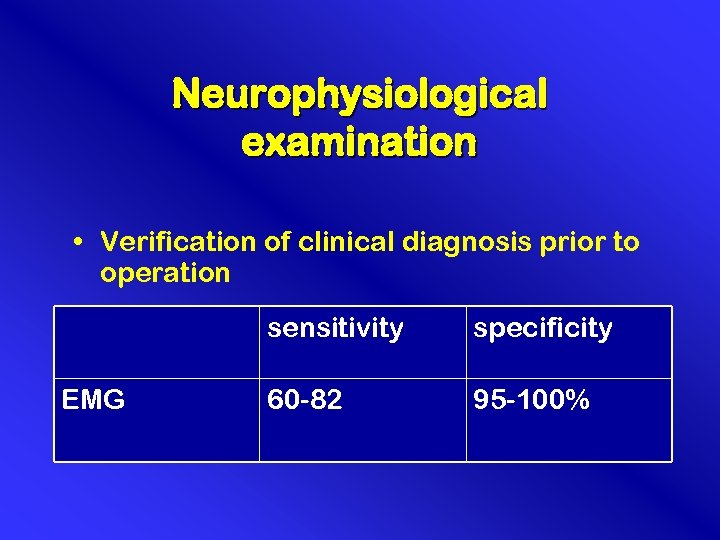 Neurophysiological examination • Verification of clinical diagnosis prior to operation sensitivity EMG specificity 60 -82 95 -100%
Neurophysiological examination • Verification of clinical diagnosis prior to operation sensitivity EMG specificity 60 -82 95 -100%
 Limitation EMG: • No golden standard • 10 -15% false negative • No relation between complaints and results • Results not predictive for therapy • Value unclear for primary health care
Limitation EMG: • No golden standard • 10 -15% false negative • No relation between complaints and results • Results not predictive for therapy • Value unclear for primary health care
 Treatment
Treatment
 Splint • Day and night • Short term effective • Minor complaints / recent onset
Splint • Day and night • Short term effective • Minor complaints / recent onset
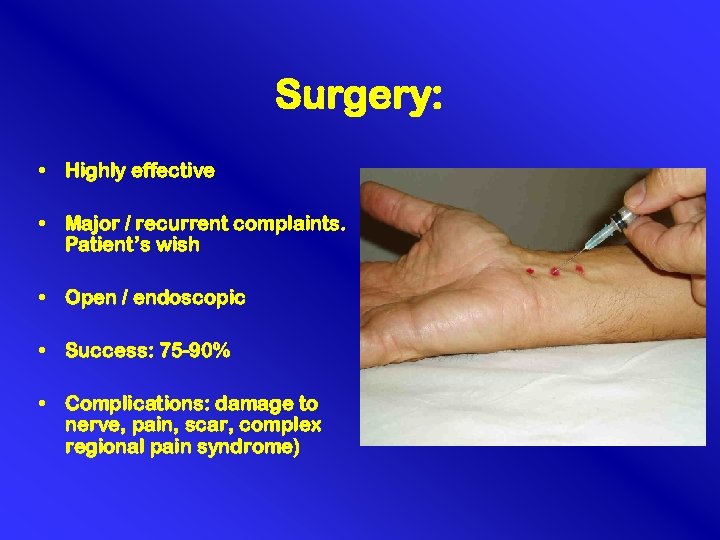 Surgery: • Highly effective • Major / recurrent complaints. Patient’s wish • Open / endoscopic • Success: 75 -90% • Complications: damage to nerve, pain, scar, complex regional pain syndrome)
Surgery: • Highly effective • Major / recurrent complaints. Patient’s wish • Open / endoscopic • Success: 75 -90% • Complications: damage to nerve, pain, scar, complex regional pain syndrome)
 Corticosteroid injection • Several techniques 1. Underneath retinaculum (most common technique) 2. Through retinaculum 3. In front of retinaculum (method by Dammers) • • • Safe Effective Tradition / experience / authority determines technique
Corticosteroid injection • Several techniques 1. Underneath retinaculum (most common technique) 2. Through retinaculum 3. In front of retinaculum (method by Dammers) • • • Safe Effective Tradition / experience / authority determines technique
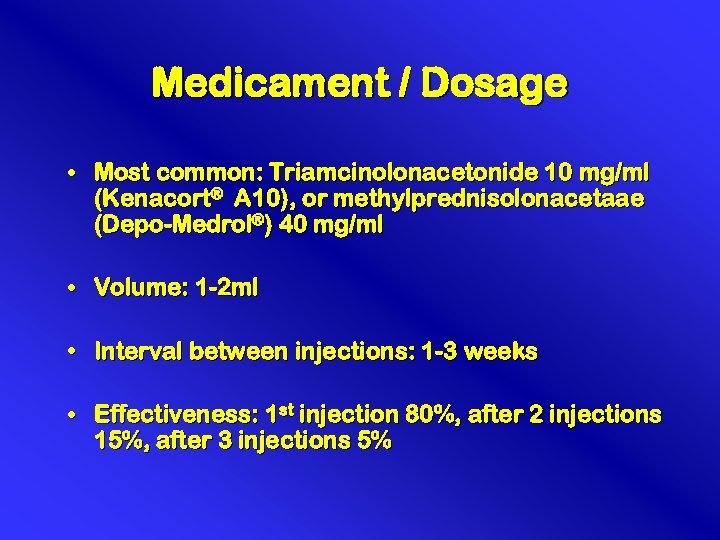 Medicament / Dosage • Most common: Triamcinolonacetonide 10 mg/ml (Kenacort® A 10), or methylprednisolonacetaae (Depo-Medrol®) 40 mg/ml • Volume: 1 -2 ml • Interval between injections: 1 -3 weeks • Effectiveness: 1 st injection 80%, after 2 injections 15%, after 3 injections 5%
Medicament / Dosage • Most common: Triamcinolonacetonide 10 mg/ml (Kenacort® A 10), or methylprednisolonacetaae (Depo-Medrol®) 40 mg/ml • Volume: 1 -2 ml • Interval between injections: 1 -3 weeks • Effectiveness: 1 st injection 80%, after 2 injections 15%, after 3 injections 5%
 Needle? -orange/ light brown (0, 45 x 23 mm) -light blue (0, 5 x 25 mm) -green (0, 8 x 40 mm)
Needle? -orange/ light brown (0, 45 x 23 mm) -light blue (0, 5 x 25 mm) -green (0, 8 x 40 mm)
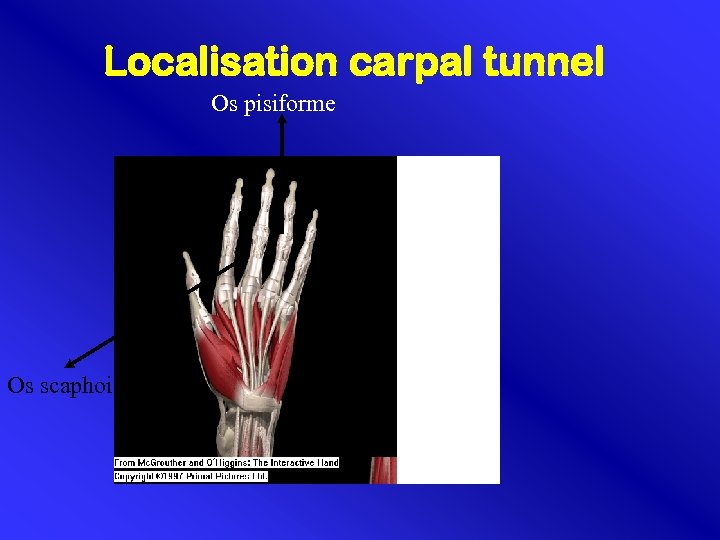 Localisation carpal tunnel Os pisiforme Os scaphoideum
Localisation carpal tunnel Os pisiforme Os scaphoideum
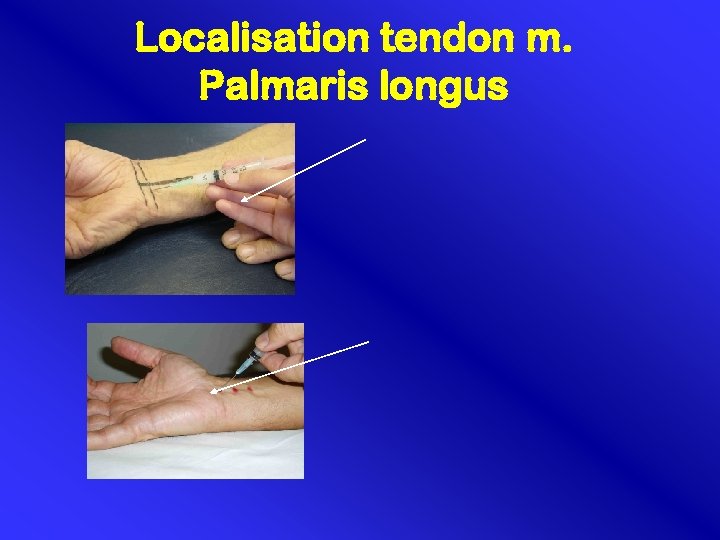 Localisation tendon m. Palmaris longus
Localisation tendon m. Palmaris longus
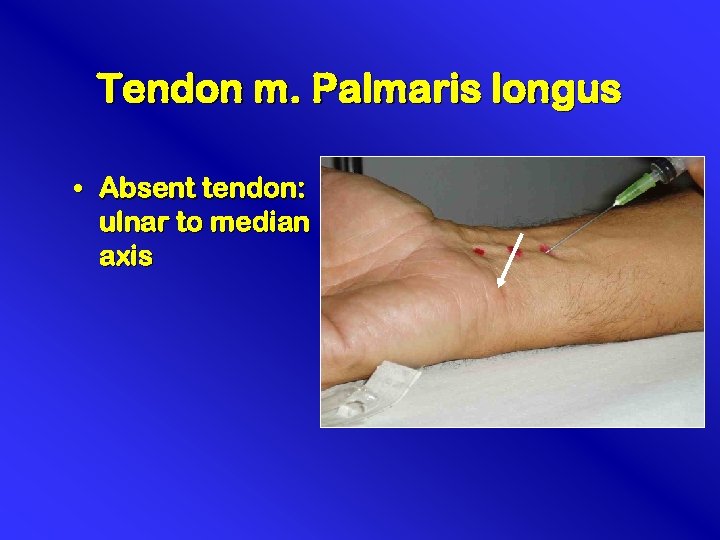 Tendon m. Palmaris longus • Absent tendon: ulnar to median axis
Tendon m. Palmaris longus • Absent tendon: ulnar to median axis
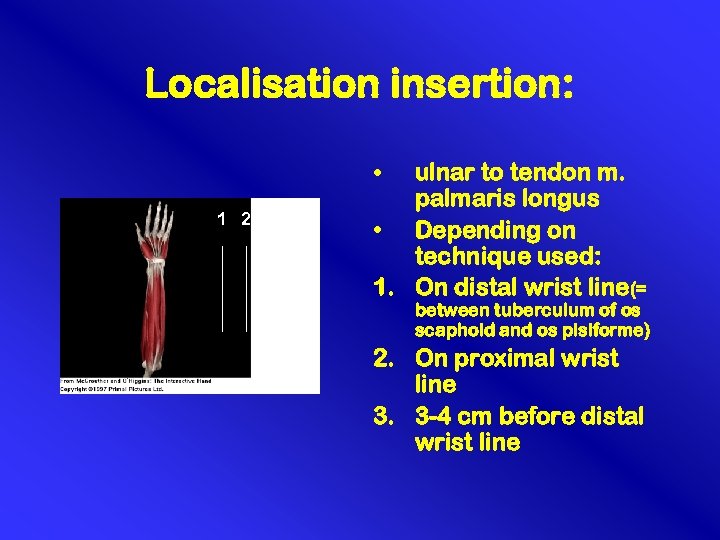 Localisation insertion: • 1 2 3 3 ulnar to tendon m. palmaris longus • Depending on technique used: 1. On distal wrist line(= between tuberculum of os scaphoid and os pisiforme) 2. On proximal wrist line 3. 3 -4 cm before distal wrist line
Localisation insertion: • 1 2 3 3 ulnar to tendon m. palmaris longus • Depending on technique used: 1. On distal wrist line(= between tuberculum of os scaphoid and os pisiforme) 2. On proximal wrist line 3. 3 -4 cm before distal wrist line
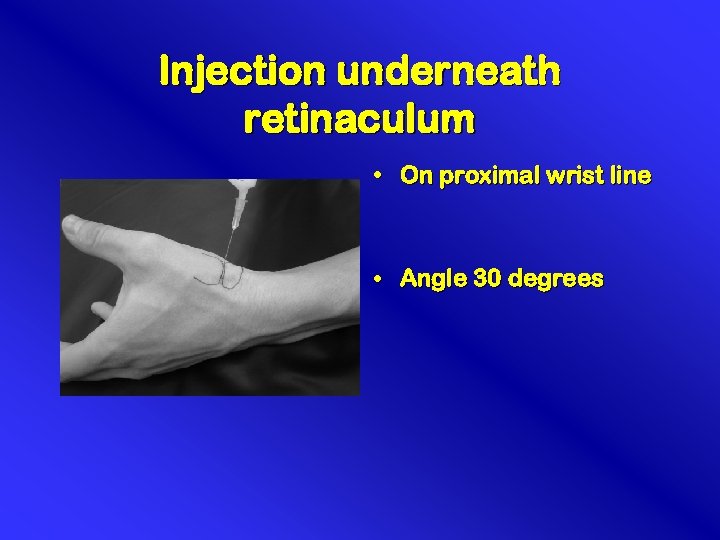 Injection underneath retinaculum • On proximal wrist line • Angle 30 degrees
Injection underneath retinaculum • On proximal wrist line • Angle 30 degrees
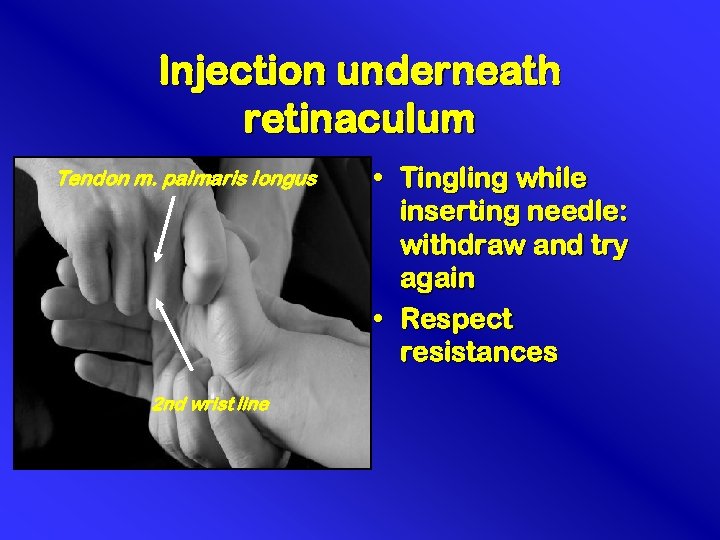 Injection underneath retinaculum Tendon m. palmaris longus 2 nd wrist line • Tingling while inserting needle: withdraw and try again • Respect resistances
Injection underneath retinaculum Tendon m. palmaris longus 2 nd wrist line • Tingling while inserting needle: withdraw and try again • Respect resistances
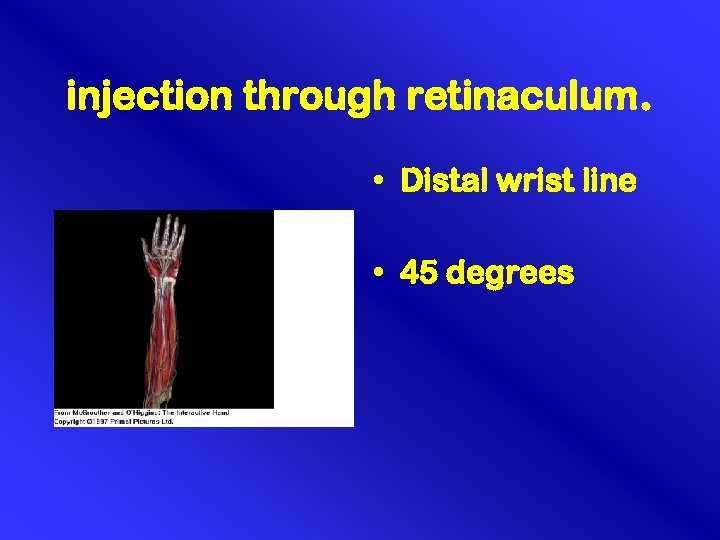 injection through retinaculum. • Distal wrist line • 45 degrees
injection through retinaculum. • Distal wrist line • 45 degrees
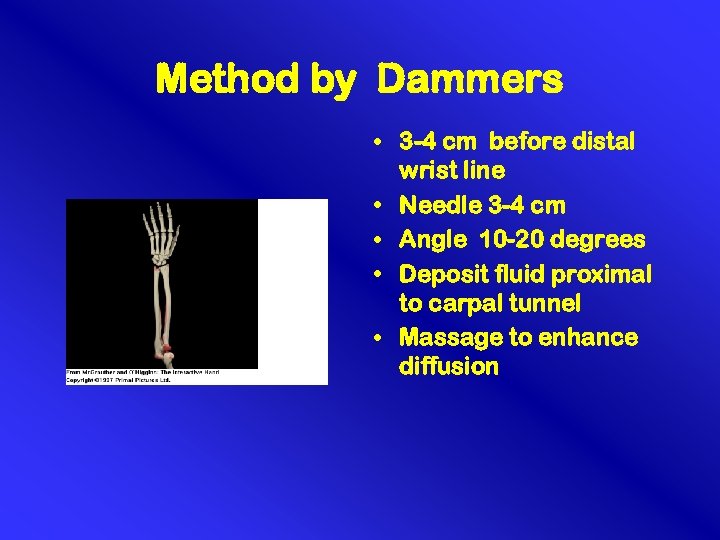 Method by Dammers • 3 -4 cm before distal wrist line • Needle 3 -4 cm • Angle 10 -20 degrees • Deposit fluid proximal to carpal tunnel • Massage to enhance diffusion
Method by Dammers • 3 -4 cm before distal wrist line • Needle 3 -4 cm • Angle 10 -20 degrees • Deposit fluid proximal to carpal tunnel • Massage to enhance diffusion
 Hygiene • Wash hands, wear gloves or disinfect fingers • Once-only ampoules • Change needles • Disinfect skin
Hygiene • Wash hands, wear gloves or disinfect fingers • Once-only ampoules • Change needles • Disinfect skin
 Side effects and complications • Side effects -flushing: 1 day after injection -steroid-flare 24 -48 hours -menstruation problems -hyperglycemia -locale effects: redness, atrophy fatty tissue, hypopigmentation • Complications -very rare, case-reports -tendon ruptures, median neuritis (CTS), local infection
Side effects and complications • Side effects -flushing: 1 day after injection -steroid-flare 24 -48 hours -menstruation problems -hyperglycemia -locale effects: redness, atrophy fatty tissue, hypopigmentation • Complications -very rare, case-reports -tendon ruptures, median neuritis (CTS), local infection
 Practice • Anatomy • Injection
Practice • Anatomy • Injection


