 Competitive advantages Like a G 9
Competitive advantages Like a G 9
 2 Competitive Factors Chapter learning objectives Introduction Competitive factors Competitive advantage Porter’s 5 forces Porter’s core values SWOT
2 Competitive Factors Chapter learning objectives Introduction Competitive factors Competitive advantage Porter’s 5 forces Porter’s core values SWOT
 Competitive Factors Competitive advantage Environmental analysis Key Issue The different ways a firm can achieve advantage Whether the firm has a sustainable competitive advantage The main competitive forces How different activities and departments within the firm contribute to its competitiveness Competitive Advantage Porter’s 5 Forces Porter’s Value Chain SWOT
Competitive Factors Competitive advantage Environmental analysis Key Issue The different ways a firm can achieve advantage Whether the firm has a sustainable competitive advantage The main competitive forces How different activities and departments within the firm contribute to its competitiveness Competitive Advantage Porter’s 5 Forces Porter’s Value Chain SWOT
 Competitive Factors Competitive advantage Competitive Advantage Choice one Competitive Advantage Generic Strategies Choice two Porter’s 5 Forces Porter’s Value Chain SWOT
Competitive Factors Competitive advantage Competitive Advantage Choice one Competitive Advantage Generic Strategies Choice two Porter’s 5 Forces Porter’s Value Chain SWOT
 Competitive Factors Basis of competition Environmental analysis Lower cost Broad target Competitive scope Narrow target Differentiation Cost leadership Differentiation Cost focus Differentiation focus Competitive Advantage Porter’s 5 Forces Porter’s Value Chain SWOT 5
Competitive Factors Basis of competition Environmental analysis Lower cost Broad target Competitive scope Narrow target Differentiation Cost leadership Differentiation Cost focus Differentiation focus Competitive Advantage Porter’s 5 Forces Porter’s Value Chain SWOT 5
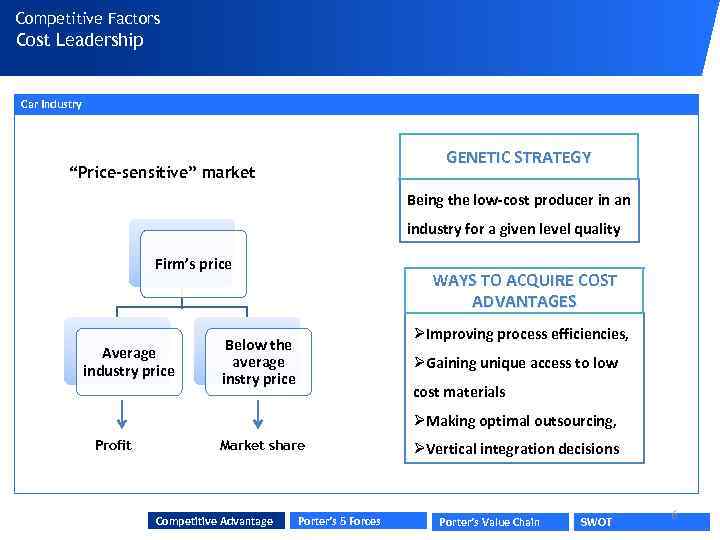 Competitive Factors Cost Leadership Car Industry GENETIC STRATEGY “Price-sensitive” market Being the low-cost producer in an industry for a given level quality Firm’s price Average industry price WAYS TO ACQUIRE COST ADVANTAGES ØImproving process efficiencies, Below the average instry price ØGaining unique access to low cost materials ØMaking optimal outsourcing, Profit Market share Competitive Advantage Porter’s 5 Forces ØVertical integration decisions Porter’s Value Chain SWOT 6
Competitive Factors Cost Leadership Car Industry GENETIC STRATEGY “Price-sensitive” market Being the low-cost producer in an industry for a given level quality Firm’s price Average industry price WAYS TO ACQUIRE COST ADVANTAGES ØImproving process efficiencies, Below the average instry price ØGaining unique access to low cost materials ØMaking optimal outsourcing, Profit Market share Competitive Advantage Porter’s 5 Forces ØVertical integration decisions Porter’s Value Chain SWOT 6
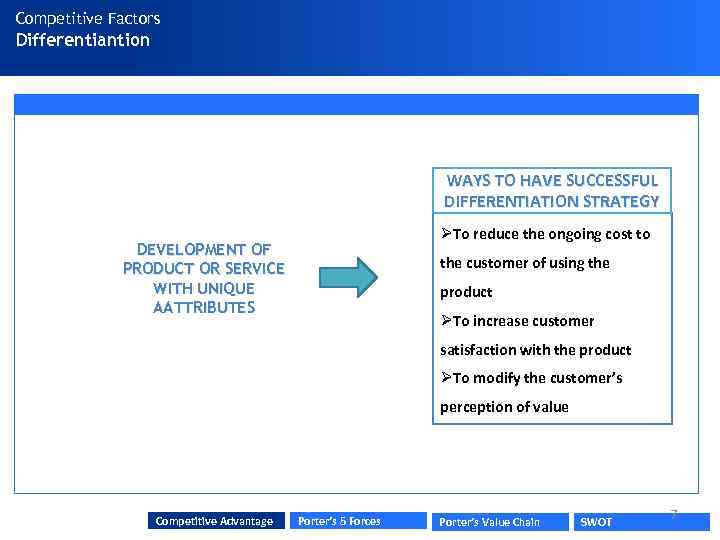 Competitive Factors Differentiantion WAYS TO HAVE SUCCESSFUL DIFFERENTIATION STRATEGY ØTo reduce the ongoing cost to DEVELOPMENT OF PRODUCT OR SERVICE WITH UNIQUE AATTRIBUTES the customer of using the product ØTo increase customer satisfaction with the product ØTo modify the customer’s perception of value Competitive Advantage Porter’s 5 Forces Porter’s Value Chain SWOT 7
Competitive Factors Differentiantion WAYS TO HAVE SUCCESSFUL DIFFERENTIATION STRATEGY ØTo reduce the ongoing cost to DEVELOPMENT OF PRODUCT OR SERVICE WITH UNIQUE AATTRIBUTES the customer of using the product ØTo increase customer satisfaction with the product ØTo modify the customer’s perception of value Competitive Advantage Porter’s 5 Forces Porter’s Value Chain SWOT 7
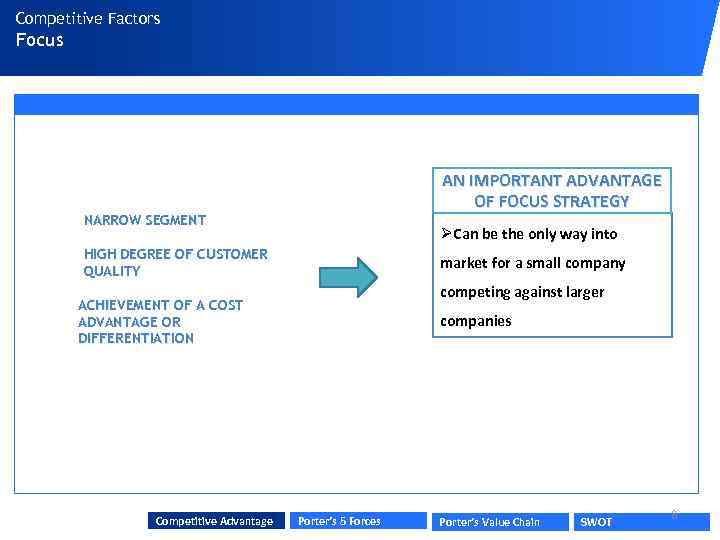 Competitive Factors Focus AN IMPORTANT ADVANTAGE OF FOCUS STRATEGY NARROW SEGMENT ØCan be the only way into HIGH DEGREE OF CUSTOMER QUALITY market for a small company competing against larger ACHIEVEMENT OF A COST ADVANTAGE OR DIFFERENTIATION Competitive Advantage companies Porter’s 5 Forces Porter’s Value Chain SWOT 8
Competitive Factors Focus AN IMPORTANT ADVANTAGE OF FOCUS STRATEGY NARROW SEGMENT ØCan be the only way into HIGH DEGREE OF CUSTOMER QUALITY market for a small company competing against larger ACHIEVEMENT OF A COST ADVANTAGE OR DIFFERENTIATION Competitive Advantage companies Porter’s 5 Forces Porter’s Value Chain SWOT 8
 Competitive Factors Competitive advantage / Illustration Car Industry Differentiation Cost Leadership Competitive Advantage Porter’s 5 Forces Focus Porter’s Value Chain SWOT
Competitive Factors Competitive advantage / Illustration Car Industry Differentiation Cost Leadership Competitive Advantage Porter’s 5 Forces Focus Porter’s Value Chain SWOT
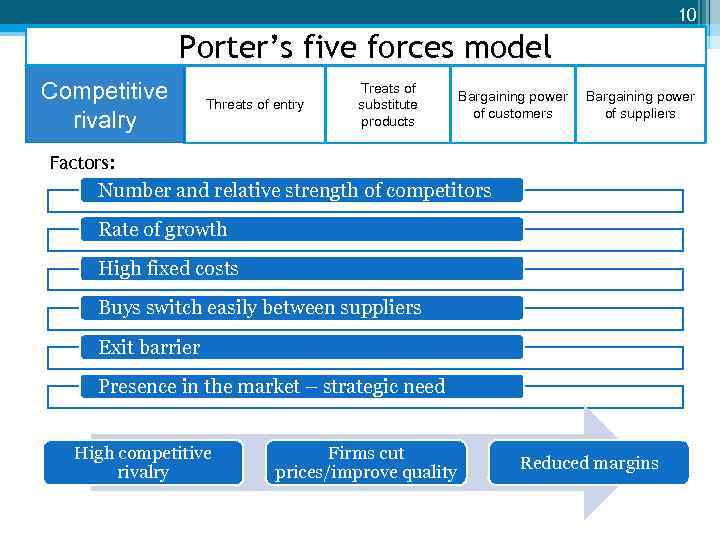 10 Porter’s five forces model Competitive rivalry Threats of entry Treats of substitute products Bargaining power of customers Bargaining power of suppliers Factors: Number and relative strength of competitors Rate of growth High fixed costs Buys switch easily between suppliers Exit barrier Presence in the market – strategic need High competitive rivalry Firms cut prices/improve quality Reduced margins
10 Porter’s five forces model Competitive rivalry Threats of entry Treats of substitute products Bargaining power of customers Bargaining power of suppliers Factors: Number and relative strength of competitors Rate of growth High fixed costs Buys switch easily between suppliers Exit barrier Presence in the market – strategic need High competitive rivalry Firms cut prices/improve quality Reduced margins
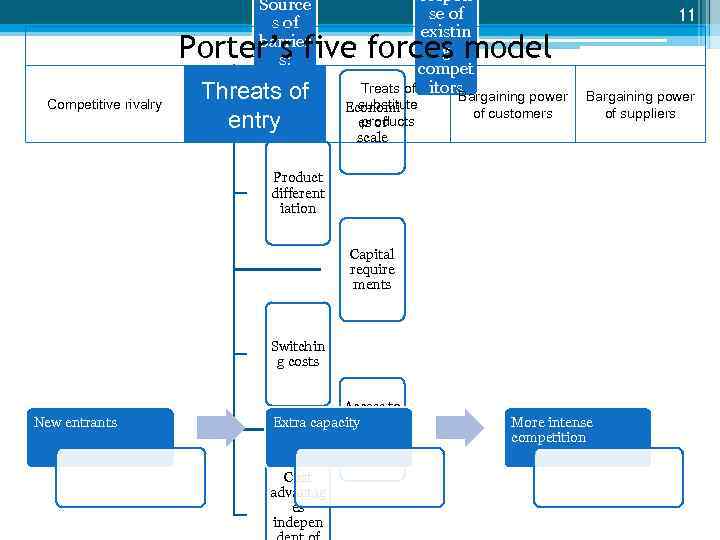 Source s of barrier s: respon se of existin g compet Treats of itors Bargaining power 11 Porter’s five forces model Competitive rivalry Threats of entry substitute Economi products es of scale of customers Bargaining power of suppliers Product different iation Capital require ments Switchin g costs New entrants Access to distribut Extra capacity ion channels Cost advantag es indepen More intense competition
Source s of barrier s: respon se of existin g compet Treats of itors Bargaining power 11 Porter’s five forces model Competitive rivalry Threats of entry substitute Economi products es of scale of customers Bargaining power of suppliers Product different iation Capital require ments Switchin g costs New entrants Access to distribut Extra capacity ion channels Cost advantag es indepen More intense competition
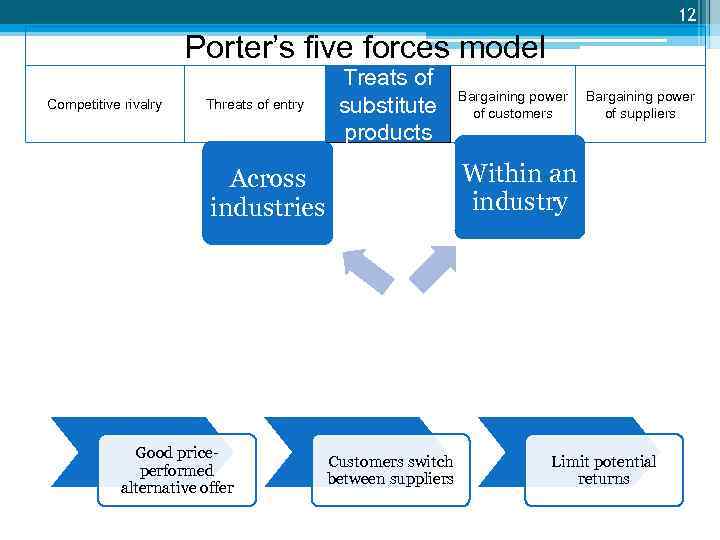 12 Porter’s five forces model Competitive rivalry Threats of entry Treats of substitute products Bargaining power of suppliers Within an industry Across industries Good priceperformed alternative offer Bargaining power of customers Customers switch between suppliers Limit potential returns
12 Porter’s five forces model Competitive rivalry Threats of entry Treats of substitute products Bargaining power of suppliers Within an industry Across industries Good priceperformed alternative offer Bargaining power of customers Customers switch between suppliers Limit potential returns
 13 Porter’s five forces model Competitive rivalry Threats of entry Treats of substitute products Bargaining power of customers Bargaining power of suppliers
13 Porter’s five forces model Competitive rivalry Threats of entry Treats of substitute products Bargaining power of customers Bargaining power of suppliers
 14 Porter’s five forces model Competitive rivalry Threats of entry Treats of substitute products Bargaining power of customers Bargaining power of suppliers
14 Porter’s five forces model Competitive rivalry Threats of entry Treats of substitute products Bargaining power of customers Bargaining power of suppliers
 15 Enterprise in economy Supplier Enterprise Customer
15 Enterprise in economy Supplier Enterprise Customer
 16 How do suppliers & customers influence on your margin? Customers bargaining power Customers try to buy your goods as cheap as possible Your margin (Depends on managing these two factors) Suppliers bargaining power Suppliers tend to raise prices on what they provide
16 How do suppliers & customers influence on your margin? Customers bargaining power Customers try to buy your goods as cheap as possible Your margin (Depends on managing these two factors) Suppliers bargaining power Suppliers tend to raise prices on what they provide
 17 High bargaining power of suppliers Lack of substitutes or high switching costs • (e. g. Transneft for Luk. Oil) Presence of dominant suppliers controlling prices • (e. g. Boing and Airbus for air transporters) Products of suppliers have a uniqueness of brand, technical performance or design • (e. g. Cosmetics producers for Specialised retailers)
17 High bargaining power of suppliers Lack of substitutes or high switching costs • (e. g. Transneft for Luk. Oil) Presence of dominant suppliers controlling prices • (e. g. Boing and Airbus for air transporters) Products of suppliers have a uniqueness of brand, technical performance or design • (e. g. Cosmetics producers for Specialised retailers)
 18 High bargaining power of customers • Where a buyer’s purchases are a high proportion of the suppliers business • (e. g. Cocoa producers for farmers) • Where a buyer makes a low profit • (e. g. Auchan for goods producers) • Where the quality of purchases is unimportant • (e. g. Discount stores for food producers)
18 High bargaining power of customers • Where a buyer’s purchases are a high proportion of the suppliers business • (e. g. Cocoa producers for farmers) • Where a buyer makes a low profit • (e. g. Auchan for goods producers) • Where the quality of purchases is unimportant • (e. g. Discount stores for food producers)
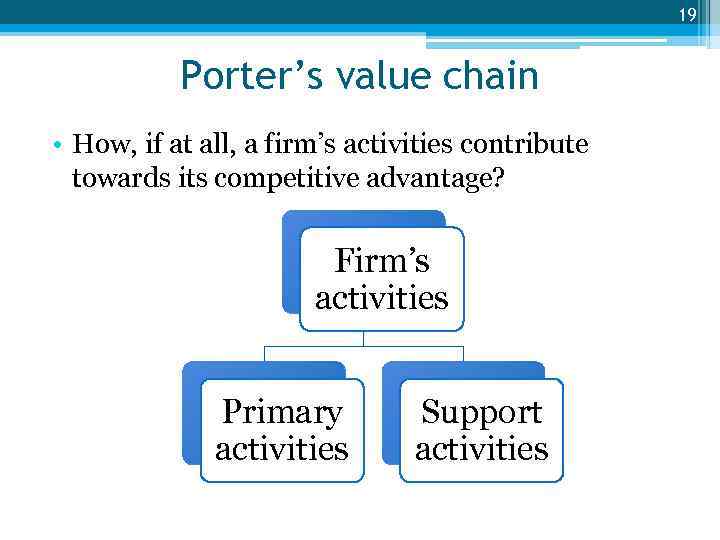 19 Porter’s value chain • How, if at all, a firm’s activities contribute towards its competitive advantage? Firm’s activities Primary activities Support activities
19 Porter’s value chain • How, if at all, a firm’s activities contribute towards its competitive advantage? Firm’s activities Primary activities Support activities
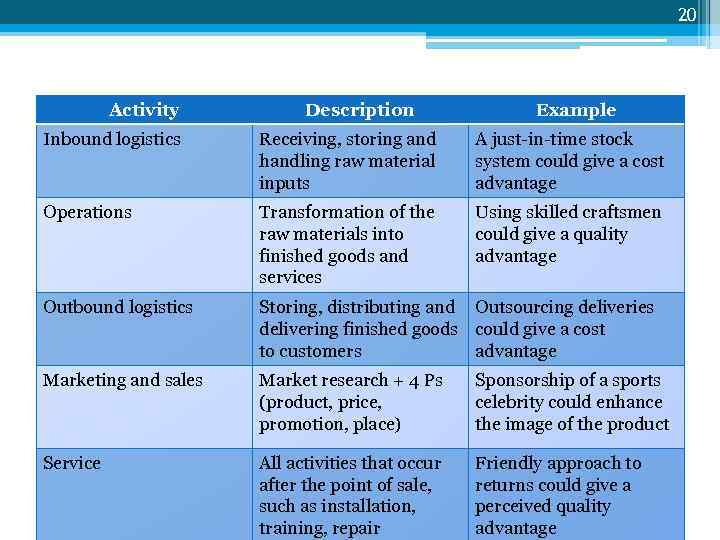 20 Activity Description Example Porter’s value chain: primary activities Receiving, storing and A just-in-time stock Inbound logistics handling raw material inputs system could give a cost advantage Operations Transformation of the raw materials into finished goods and services Using skilled craftsmen could give a quality advantage Outbound logistics Storing, distributing and Outsourcing deliveries delivering finished goods could give a cost to customers advantage Marketing and sales Market research + 4 Ps (product, price, promotion, place) Sponsorship of a sports celebrity could enhance the image of the product Service All activities that occur after the point of sale, such as installation, training, repair Friendly approach to returns could give a perceived quality advantage
20 Activity Description Example Porter’s value chain: primary activities Receiving, storing and A just-in-time stock Inbound logistics handling raw material inputs system could give a cost advantage Operations Transformation of the raw materials into finished goods and services Using skilled craftsmen could give a quality advantage Outbound logistics Storing, distributing and Outsourcing deliveries delivering finished goods could give a cost to customers advantage Marketing and sales Market research + 4 Ps (product, price, promotion, place) Sponsorship of a sports celebrity could enhance the image of the product Service All activities that occur after the point of sale, such as installation, training, repair Friendly approach to returns could give a perceived quality advantage
 21 Activity Description Example Porter’s value chain: support activities How the firm is Centralised buying could Firm infrastructure organised Technology development How the firm uses technology result in cost savings due to bulk discounts The latest computercontrolled machinery gives greater flexibility to tailor products to individual customer specifications Human resources development How people contribute to Employing expert buyers competitive advantage could enable a supermarket to purchase better wines than competitors Procurement Purchasing, but not just limited to materials Buying a building out of town could give a cost advantage over High Street Competitors
21 Activity Description Example Porter’s value chain: support activities How the firm is Centralised buying could Firm infrastructure organised Technology development How the firm uses technology result in cost savings due to bulk discounts The latest computercontrolled machinery gives greater flexibility to tailor products to individual customer specifications Human resources development How people contribute to Employing expert buyers competitive advantage could enable a supermarket to purchase better wines than competitors Procurement Purchasing, but not just limited to materials Buying a building out of town could give a cost advantage over High Street Competitors
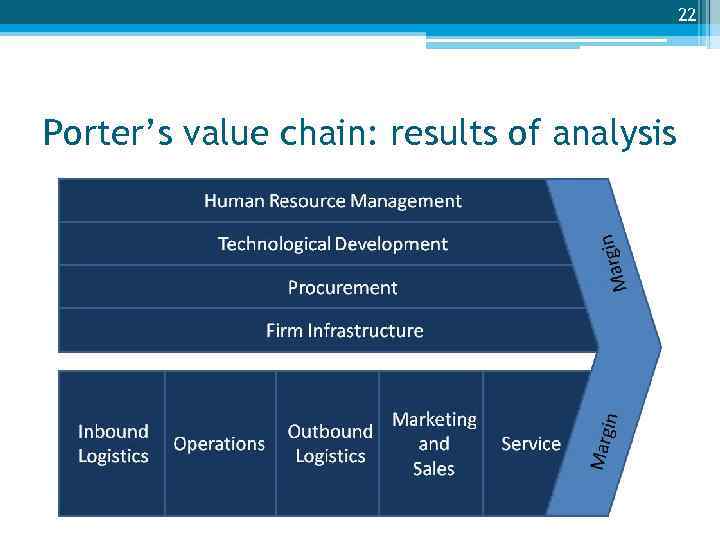 22 Porter’s value chain: results of analysis
22 Porter’s value chain: results of analysis
 How different departments contribute to competitive advantage?
How different departments contribute to competitive advantage?
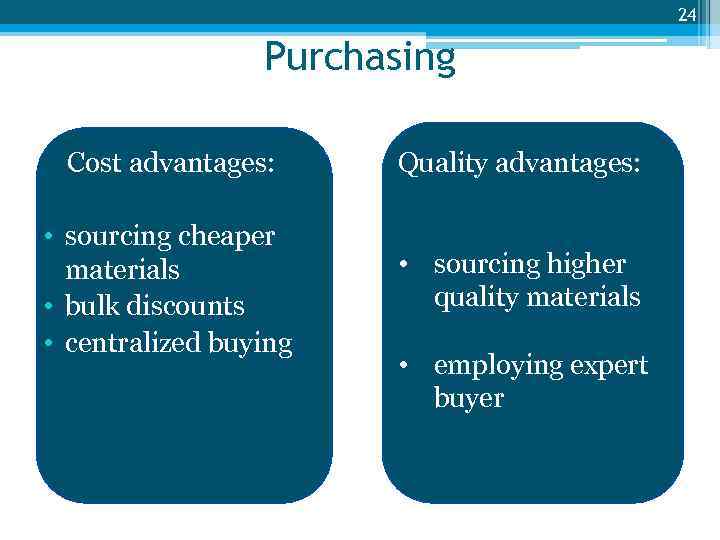 24 Purchasing Cost advantages: Quality advantages: • sourcing cheaper materials • bulk discounts • centralized buying • sourcing higher quality materials • employing expert buyer
24 Purchasing Cost advantages: Quality advantages: • sourcing cheaper materials • bulk discounts • centralized buying • sourcing higher quality materials • employing expert buyer
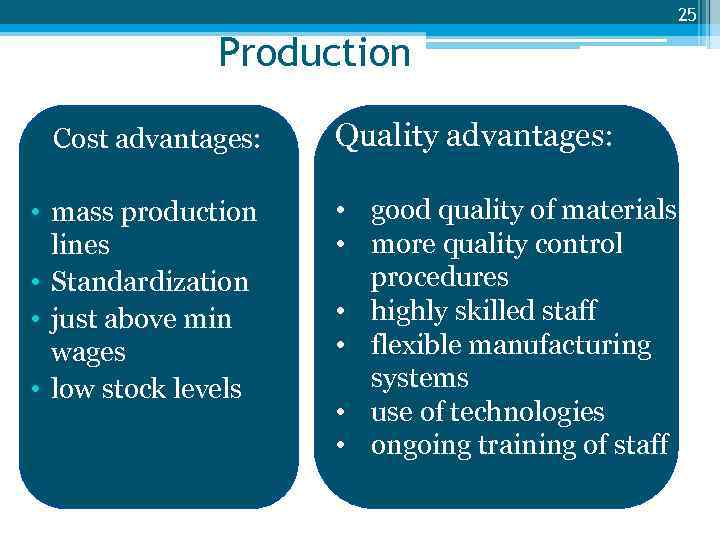 25 Production Cost advantages: • mass production lines • Standardization • just above min wages • low stock levels Quality advantages: • good quality of materials • more quality control procedures • highly skilled staff • flexible manufacturing systems • use of technologies • ongoing training of staff
25 Production Cost advantages: • mass production lines • Standardization • just above min wages • low stock levels Quality advantages: • good quality of materials • more quality control procedures • highly skilled staff • flexible manufacturing systems • use of technologies • ongoing training of staff
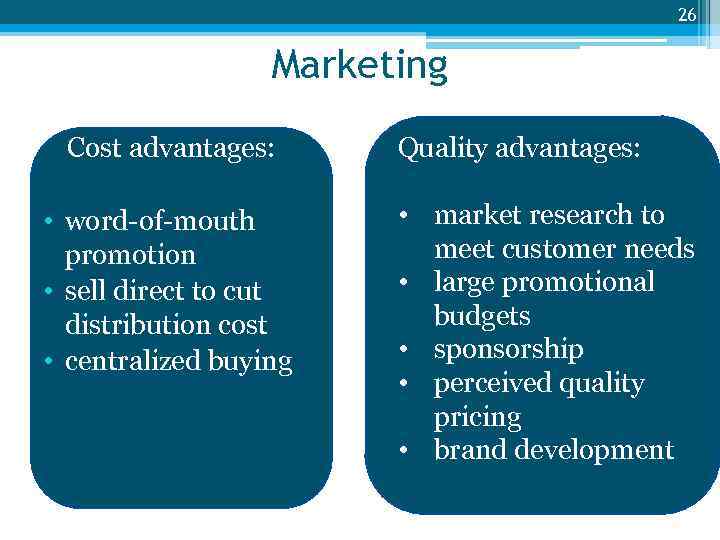 26 Marketing Cost advantages: • word-of-mouth promotion • sell direct to cut distribution cost • centralized buying Quality advantages: • market research to meet customer needs • large promotional budgets • sponsorship • perceived quality pricing • brand development
26 Marketing Cost advantages: • word-of-mouth promotion • sell direct to cut distribution cost • centralized buying Quality advantages: • market research to meet customer needs • large promotional budgets • sponsorship • perceived quality pricing • brand development
 27 Service Cost advantages: • outsourcing • not offering service provision • low paid staff Quality advantages: • outsourcing • highly skilled staff
27 Service Cost advantages: • outsourcing • not offering service provision • low paid staff Quality advantages: • outsourcing • highly skilled staff
 SWOT Description v One of the most effective tools in the analysis of environmental data and information v A SWOT analysis generates information that is helpful in matching an organization’s or a group’s goals, programs, and capacities to the social environment in which they operate
SWOT Description v One of the most effective tools in the analysis of environmental data and information v A SWOT analysis generates information that is helpful in matching an organization’s or a group’s goals, programs, and capacities to the social environment in which they operate
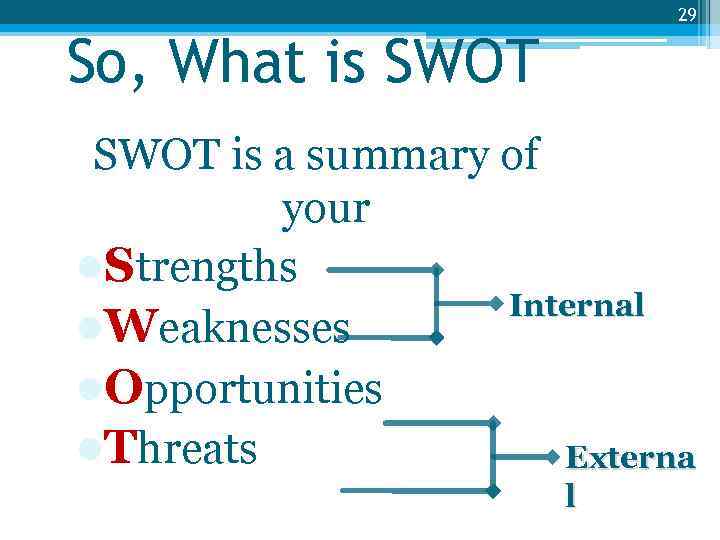 29 So, What is SWOT is a summary of your l. Strengths Internal l. Weaknesses l. Opportunities l. Threats Externa l
29 So, What is SWOT is a summary of your l. Strengths Internal l. Weaknesses l. Opportunities l. Threats Externa l
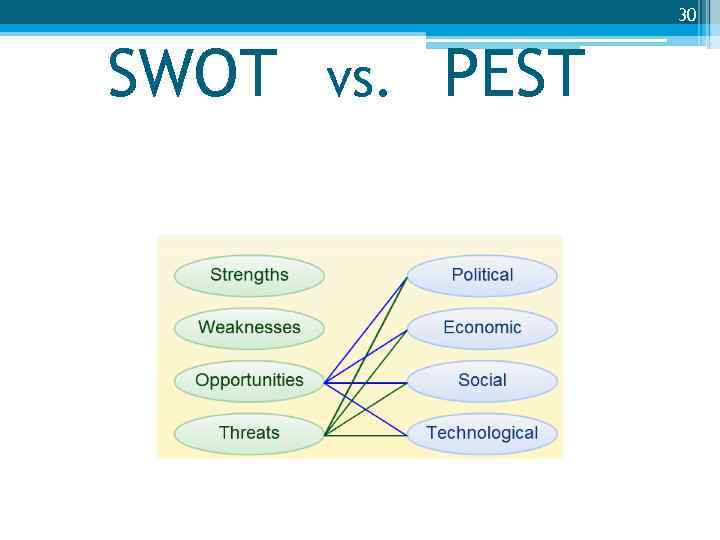 30 SWOT vs. PEST
30 SWOT vs. PEST
 Starbucks SWOT Strength • global coffee brand • 17, 000 stores in 49 countries • more than 6500 licenses shops • capture key locations Opportunities • Product diversification • Co-branding with other food manufactures • Entry into new markets Weaknesses • Higher prices compared to the competitors • Too focus on US domestic market • Protest against the company on different issues Threats • Competition • Substitute products 31
Starbucks SWOT Strength • global coffee brand • 17, 000 stores in 49 countries • more than 6500 licenses shops • capture key locations Opportunities • Product diversification • Co-branding with other food manufactures • Entry into new markets Weaknesses • Higher prices compared to the competitors • Too focus on US domestic market • Protest against the company on different issues Threats • Competition • Substitute products 31
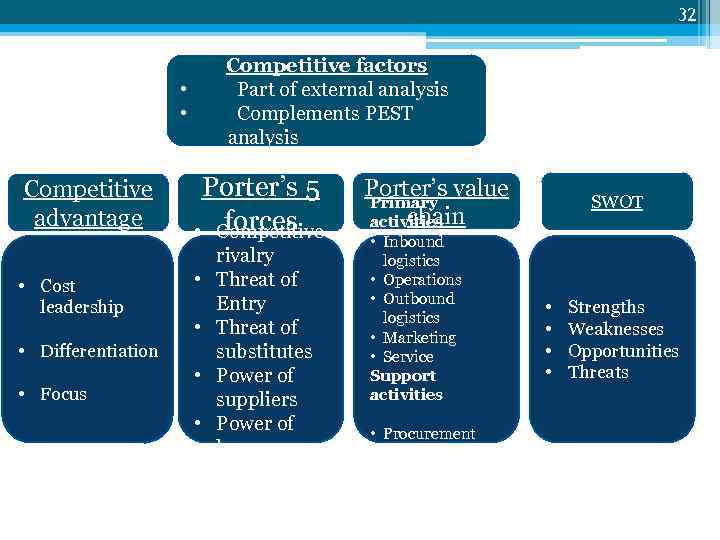 32 Competitive factors Part of external analysis Complements PEST analysis • • Competitive advantage • Cost leadership Porter’s 5 forces • Competitive • • • Differentiation • Focus • • rivalry Threat of Entry Threat of substitutes Power of suppliers Power of buyers Porter’s value Primary chain activities • Inbound logistics • Operations • Outbound logistics • Marketing • Service Support activities • Procurement • Infrastructure • Technology SWOT • • Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats
32 Competitive factors Part of external analysis Complements PEST analysis • • Competitive advantage • Cost leadership Porter’s 5 forces • Competitive • • • Differentiation • Focus • • rivalry Threat of Entry Threat of substitutes Power of suppliers Power of buyers Porter’s value Primary chain activities • Inbound logistics • Operations • Outbound logistics • Marketing • Service Support activities • Procurement • Infrastructure • Technology SWOT • • Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats
 33 Your questions are welcomed
33 Your questions are welcomed


