1ccfc0ad8fdbc19aff8aa9b336da2dcf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
Competing in Global Markets Key Ideas Absolute Advantage Comparative Advantage Free Trade Measuring Trade Economic Institutions Macro Factors Multi-domestic and Global (Competition/Strategy) Entry Strategies Partnerships

Why Trade? No country is self-sufficient Countries need products that other countries produce. Natural Resources, technological skills and other factors of production are not distributed evenly or “efficiently” around the world.

Example: Weekly Business Project Pretend that Each Week the Following Activities Need to be Completed for a Business Project: Gathering Data through Interviews Statistical Analysis Report Writing Report Editing Putting together a Power. Point Presentation Standing up before the audience and presenting the report How many hours would it take you to complete each task? How do you value your time?

Absolute Advantage Exists when a country can produce a product more efficiently than any other country.

Theory of Comparative Advantage Countries should sell to other countries those products that it produces most efficiently and buy from countries those products it cannot produce as effectively or efficiently. In other words, comparative advantage is the ability of a country to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another country.

Free Trade The movement of good and services among nations without political or economic trade barriers. Examples of Barriers: Tariffs, Quotas, Embargo, Exchange Controls

Measuring Global Trade Balance of Payments Balance of Trade Deficit Exchange Rates

Important Economic Institutions World Trade Organization World Bank International Monetary Fund
International Macro Environment Factors Economic Social/Cultural Political/Legal Technological

Economic Factors Help us to measure the state of the macroeconomic environment and determine the general health and well being of an economy. Examples: GDP trends, interest rates, money supply, inflation unemployment levels, wage/price controls, energy availability and costs, disposable and discretionary income, exchange rates.
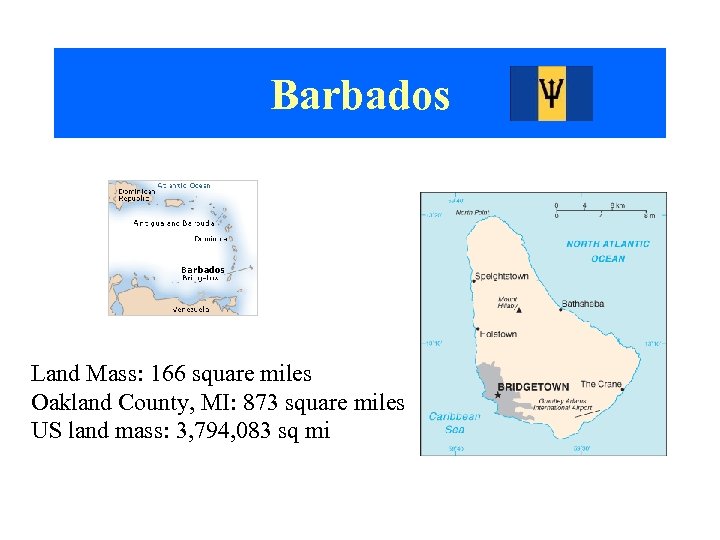
Barbados Land Mass: 166 square miles Oakland County, MI: 873 square miles US land mass: 3, 794, 083 sq mi
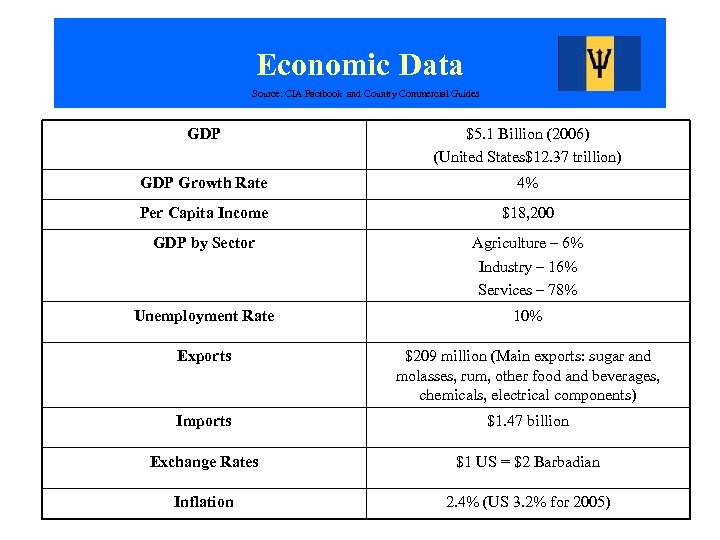
Economic Data Source: CIA Factbook and Country Commercial Guides GDP $5. 1 Billion (2006) (United States$12. 37 trillion) GDP Growth Rate 4% Per Capita Income $18, 200 GDP by Sector Agriculture – 6% Industry – 16% Services – 78% Unemployment Rate 10% Exports $209 million (Main exports: sugar and molasses, rum, other food and beverages, chemicals, electrical components) Imports $1. 47 billion Exchange Rates $1 US = $2 Barbadian Inflation 2. 4% (US 3. 2% for 2005)

Haiti Source: CIA Factbook Land mass: 10, 714 sq mi
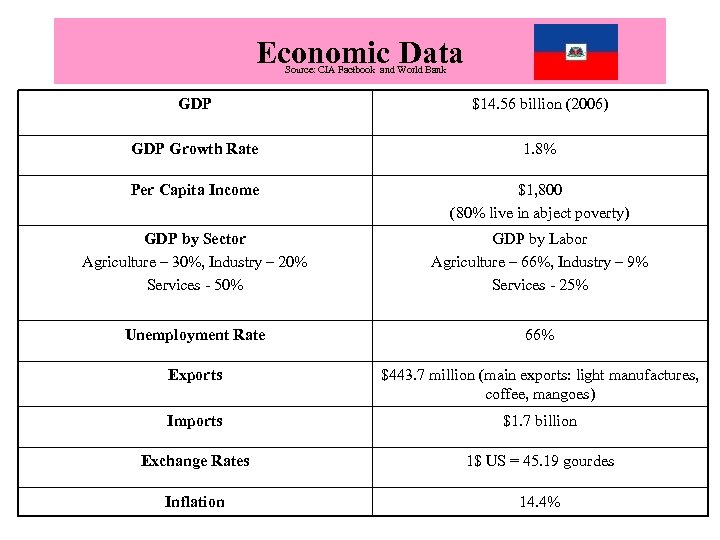
Economic Data Source: CIA Factbook and World Bank GDP $14. 56 billion (2006) GDP Growth Rate 1. 8% Per Capita Income $1, 800 (80% live in abject poverty) GDP by Sector Agriculture – 30%, Industry – 20% Services - 50% GDP by Labor Agriculture – 66%, Industry – 9% Services - 25% Unemployment Rate 66% Exports $443. 7 million (main exports: light manufactures, coffee, mangoes) Imports $1. 7 billion Exchange Rates 1$ US = 45. 19 gourdes Inflation 14. 4%

Social/Cultural Factors This category of factors describe the beliefs, values, attitudes, opinions, and lifestyles of persons in the firm’s external environment as developed from cultural, demographic, religious, educational and ethnic conditioning. Examples: Lifestyle changes, career expectations, age distribution, regional shifts in population, birth rates, life expectancies, growth rate in population, consumer activism, rate of family formation, literacy levels, language, social institutions, skill level of the workforce

Social/Cultural Factors Source: CIA Factbook Total Population: 279, 912 (Oakland County, MI: 1, 213, 339) Fertility rate: 1. 65 children/woman Ethnic Groups: Black (90%), White (4%), Asian and Mixed (6%) Language: English Years of Compulsory Schooling: 12 years Literacy Rates: 99% (United States: 97%) Religious Affiliations: Christian (71%), None (17%), Other (12%) Other Info: Life Expectancy = 71 (m) and 75 (f)

Social/Cultural Factors Source: CIA Factbook and World Bank Total Population: 8. 3 million (2006) Fertility rate: 4. 9 children/woman Ethic Groups: Black (95%), White and Mixed (5%) Language: French and Creole Years of Compulsory Schooling: 6 years Literacy Rates: 52. 9% Religious Affiliations: Christian (96%), None (1%), Other (3%) Other Info: Doctors per 100, 000 people = 25, Life expectancy = 53. 23 years

Political/Legal Factors These factors define the legal and regulatory parameters within which a firm must operate. Examples: Antitrust regulations, environmental protection, tax laws, employment laws, stability of government, foreign trade protection Form of government, political ideology, protectionist sentiment, terrorist activity, legal system, government’s attitude toward foreign firms, corruption.

Politics in Barbados CIA Factbook and http: //www. transparency. org Government Type: Parliamentary democracy; independent sovereign state within the Commonwealth Legislative Branch: Bicameral Parliament (Senate (appointed by the Governor General) and House of Assembly (elected by popular vote)) Political Parties: 2 Corruption: Ranked 21 in the world by Transparency International

Politics in Haiti CIA Factbook and http: //www. transparency. org Government Type: Bicameral National Assembly Legislative Branch: Senate and Chamber of Duties)/All elected by popular vote Political Parties: 24 Corruption: Ranked 145 by Transparency International
Technological Factors This factor deals with the general technological infrastructure, the rate of change in technology, and those things impacting the development and introduction of new technologies. Examples: Total government spending for R&D, Total industry spending for R&D, focus of technological efforts, patent protection, new developments in technology transfer, productivity improvements through automation, Regulations on technology transfer, information flow infrastructure, patent and trademark protection.

Barbados – Technological Factors Source: World Bank (2000, 2004) Haiti Technological Factors Source: World Bank (2000, 2004) See Handout

Balancing Macro Factors is Key Do low wages in developing countries translate into lower manufacturing costs? What about higher profitability?
Globalization in Competition Multi-domestic Competition Global Competition

Multidomestic Competition is essentially segmented from country to country. Competition in one country is independent of competition in other countries. Examples: Grocery, healthcare

Global Competition Global competition occurs when competition crosses national borders. A firm’s strategic moves in one country can be significantly affected by it’s competitive position in another country. Examples: Automobiles, Consumer electronics, Petroleum

How should firms position themselves to compete in the global marketplace?

Competing Pressures Pressure for Local Responsiveness Pressure for Cost Reductions Consumer’s Tastes and Preferences Commodity-type product Differences in Infrastructure or Traditional Practices Universal needs of customers Differences in Distribution Channels Demands of Host Governments Competitors use a low cost position

Multidomestic Strategy Focus: Local Responsiveness Customize the strategy to fit the circumstances of each host country Little to no coordination of strategy across countries Form subsidiary companies to handle operations in each host country; each subsidiary operates more or less autonomously

Global Strategy Focus: Cost Reduction Same basic strategy worldwide (minor variations where essential) Takes advantage of location economies Locate subunits near high-quality raw material Locate subunits near sources of high-quality or low cost labor Seek low cost financing anywhere in the world Much more worldwide coordination All major strategic decisions are closely coordinated at global headquarters. Structure is designed to unify subsidiaries.
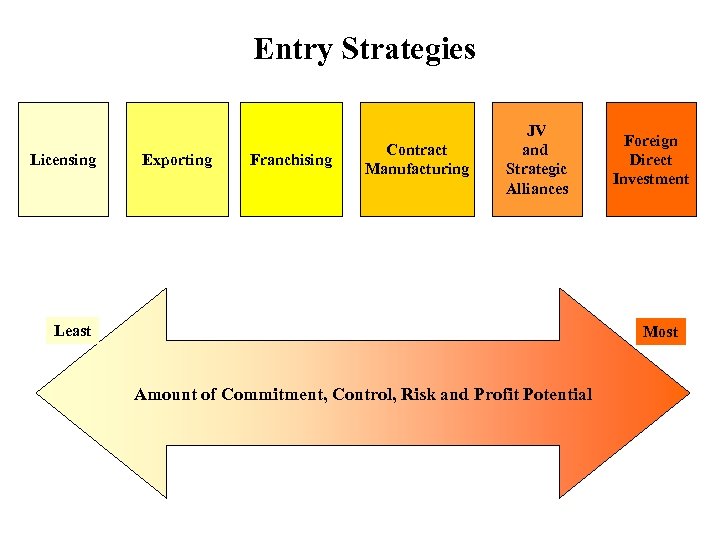
Entry Strategies Licensing Exporting Franchising Contract Manufacturing JV and Strategic Alliances Least Foreign Direct Investment Most Amount of Commitment, Control, Risk and Profit Potential
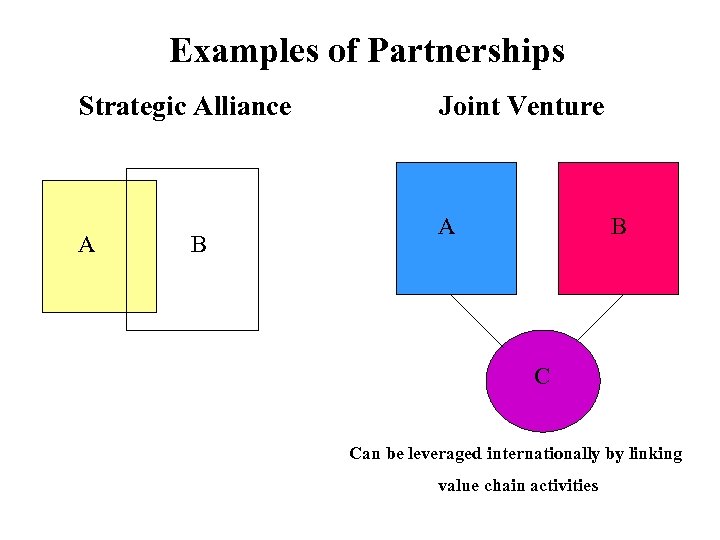
Examples of Partnerships Strategic Alliance A B Joint Venture A B C Can be leveraged internationally by linking value chain activities

Motivations for Partnerships 1. Generate scale economies: Toyota/GM joint venture (Toyota could spread fixed investment over more units) 2. Gain access to strategic markets: Japanese firm, JVC, provided design technology to partner in exchange for access to European market. 3. Overcoming trade barriers: Inland Steel and Nippon Steel built cold steel plant in Indiana (Nippon supplied technology, capital and access to Japanese firms in the US). 4. Use excess capacity: Toyota/GM joint venture used an idle GM plant 5. Gain access to low-cost manufacturing capabilities: GE sourcing microwaves from Korea.
1ccfc0ad8fdbc19aff8aa9b336da2dcf.ppt