45652c0f9acdf6615819317c8d5586a9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

Competence development between motivational structures and working relationships Dr. Martin Kröll Institute for Applied Work Science, Ruhr University Bochum ----4 th International Network on innovative Apprenticeship Conference May 26 th to 28 th 2011, in Beijing China Human Resource Management & Qualification

Human Resource Management & Qualification Outline 1. Challenges 2. Theoretical Framework 3. Method 4. Results 5. Impacts on conceiving further education 6. Conclusion Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion

Ruhr-University Bochum Institute for Applied Work Science (IAW) Study fields and specialization Master of Organizational Management (MOM) Modern Administration Management (Mo. Ve) and Single Modules (certificate)

Guiding priciples of MOM The MOM is committed to the following principles: § § § Holistic, interdisciplinary management education (Including knowledge from economics, sociology, applied computer science as well as administrative sciences and law) Application orientation (problem-oriented didactics, close cooperation with companies, practical weeks and advanced projects) Support of the development of students‘ individual profiles (in connection to their practice and focal points of interest while ensuring uniform academic standards) Interactive, mutual learning (learning in small groups of different professional origin, inclusion of know-how) Service orientation concerning the coordination of studies, working life and family (Block and weekend seminars, prepared readers, addressability) Ensurance of employability (thematically inspired by the challenges of the working environment)

Level of the Qualification and Contents LEVEL OF THE QUALIFICATION § Access Requirements - first degree (with a minimum result of “good”) - two years of relevant professional experience § Level Master’s degree, second degree, further education, practice-based § official Length of the Programme 4 semesters, 120 ECTS-Credit Points CONTENTS AND RESULTS GAINED § Mode of Study postgraduate program of study § Qualification Profile of the Graduate After their graduation, students shall: - be able to evaluate change management problems and to develop coping strategies - develop an interdisciplinary understanding of work processes and to integrate results form different disciplines - take responsibility in leadership and management issue

Modules and Courses Human Resources and Work Process Management Strategic Corporate Management Performance Management Change Management (engl. ) Human Resources Management Information and Technology Management Promotion of Creativity in Organizations Innovation through Process Management Corporate Communications Management Knowledge Management Offers across all chairs Project Management Work Organization and Work Structuring Diversity Management Process consultancy – Basics & Tools Leadership and personnel development (engl. ) Communication, Participation, Trust Human Resource Management and Qualification Organization of quality-oriented Human Resource Management Human Resource Development between Further Education and Competence Development

Academic Team Prof. Herrmann Prof. Minssen Work Organization and Work Structuring Information and Technology Management Dean Scientific further education at the Institute of Applied Work Science: “Design of changes, management of organization, technology and human resources" Dr. Kröll Prof. Wilkens Human Resource Management and Qualification Human Resources and Work Process Management (member of vice-president from the ruhr-university)

Human Resource Management & Qualification Challenges: Development of further education • During the last years: an increase of further education proposals (Wolter 2007) • Universities should perceive themselves as an „education service provider“ (further education as the third column of universities) • Claim: competence development´s provider should consider motives and aims as well as professional and private life situation Central question: How could such a market orientation look like? Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion

Human Resource Management & Qualification Development of further education • demand: potential member of the organizaition or organizations (e. g. company specific master program) • Quality of further education depends on the trainee´s specific situation • Research questions: - Are there differences between motives and behaviour concerning further education attempts? - Which points are important (e. g. employment biography, life and business situation etc. )? Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion

Human Resource Management & Qualification Reasons: Why… Why is it important to consider motives and the situation of the professional? • competence need to outdated faster and faster demography problematic lifelong learning demand for continuing education rises • 34 % of all employees: resistant to futher • self-organisation is a crucial point regarding competence development (which itself depends on motives and aims) • competence transfer: key factor of further education (depends on professional situation) • there is a research gap: (so far: entrance requirements, arrangement in regard to content, quality management and marketing (Seufert, 2008; Hanft/Knust 2007) Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion

Human Resource Management & Qualification Theoretical Framework Theoretical approaches concerning… • • process-oriented further education (Baegthe-Kinsky u. a. 2004) lifelong learning (Heyse 2003; Erpenbeck 2005) transfer-oriented further education (Winkler/Mandl 2009, Festner/ Gruber 2008) employability (Blancke 2000, Rump 2006) biographical competence development (Wittwer 2003) graduate research (Willich/Minks 2004) evaluation research (Stockmann/Meyer 2010) Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion

Human Resource Management & Qualification Comparison of two studies (1) graduate survey of Higher Education Information System (HIS) Gmb. H (HIS, 2005; N = 8117) (after 5 years/ 2 nd wave) (HIS-Study I) (representative survey in Germany) (2) first-year students (qualified employees and executives) of a non consecutive master program (Master of Organizational Management) at the Institute for Applied Work Science (IAW-Study) of Ruhr-Universität Bochum (2005 – 2010; N=158) (Pre-Test, IAW) Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion

Human Resource Management & Qualification Method • survey first-year students: 37 cohesive questions (IAW-Study) • on the basis of HIS (66 cohesive questions) Øopportunities: classification and reflection of IAW -results based on HIS-survey Øsimulation of control groups: external further education and no further education Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion
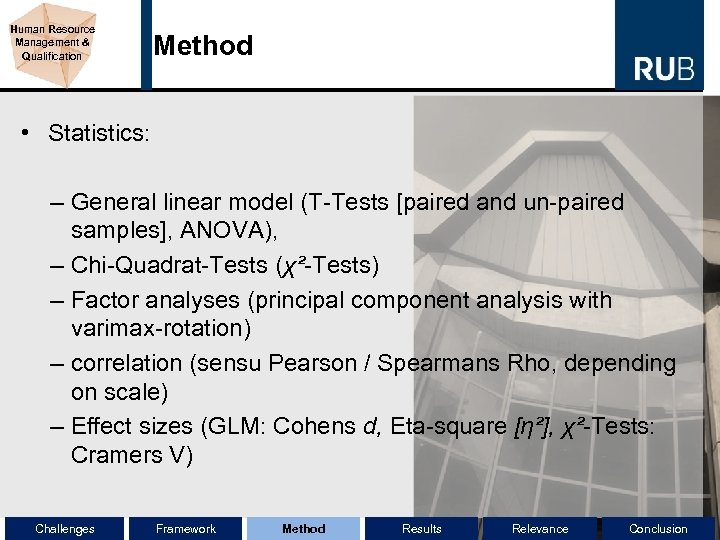
Human Resource Management & Qualification Method • Statistics: – General linear model (T-Tests [paired and un-paired samples], ANOVA), – Chi-Quadrat-Tests (χ²-Tests) – Factor analyses (principal component analysis with varimax-rotation) – correlation (sensu Pearson / Spearmans Rho, depending on scale) – Effect sizes (GLM: Cohens d, Eta-square [η²], χ²-Tests: Cramers V) Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion
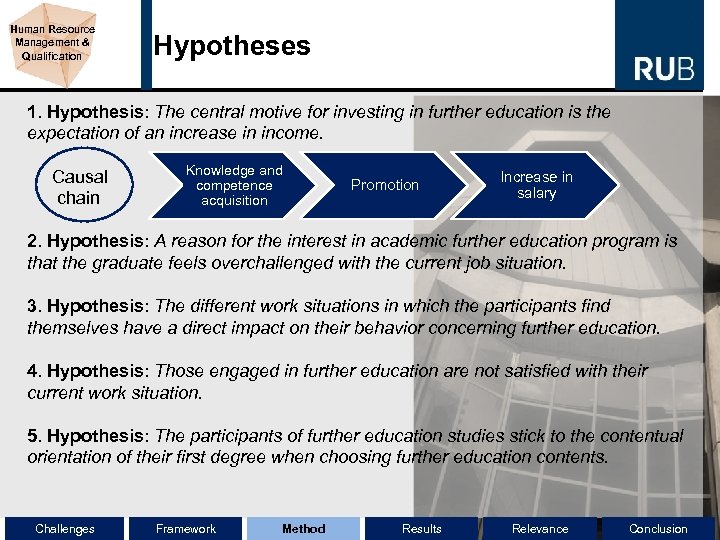
Human Resource Management & Qualification Hypotheses 1. Hypothesis: The central motive for investing in further education is the expectation of an increase in income. Causal chain Knowledge and competence acquisition Promotion Increase in salary 2. Hypothesis: A reason for the interest in academic further education program is that the graduate feels overchallenged with the current job situation. 3. Hypothesis: The different work situations in which the participants find themselves have a direct impact on their behavior concerning further education. 4. Hypothesis: Those engaged in further education are not satisfied with their current work situation. 5. Hypothesis: The participants of further education studies stick to the contentual orientation of their first degree when choosing further education contents. Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion

Human Resource Management & Qualification Sociodemographic data IAW-Study: (economics, humanities, natur sciences or engineering), • N=158 • averaged 33, 27 years old (SD=7, 595 years) • 55 % female and 45 % male 2 nd wave of HIS-Study I (economics, humanities, natur sciences or engineering + e. g. medicine, philosophie, politic, law, music …): • N=8117 • averaged 31, 51 years old (SD=3, 51) • 59 % female and 41 % male Data chosen from HIS-Study II (economics, humanities, natur sciences or engineerin): • N=1061 • averaged 31, 82 years old (SD=3, 77) • 64 % female and 36 % male Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion

Human Resource Management & Qualification Bundles of Motives and Aims • Factor analysis: search for relevant motives and aims with regard to further education – Quality criteria are fullfilled (suitability of sample: Kaiser. Meyer-Olkin = , 640; Bartlett-Test Sphärizität χ² 45=185, 202, p<, 000) (IAW-Study) Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion

Human Resource Management & Qualification Nr. Example Welche Motive bzw. Ziele (motives and Sehr goals) waren bei Ihrem Entschluss, ein wichtig postgraduiertes Studium aufzunehmen, (absol utely) wichtig 1 …. fachlichen/beruflichen Neigungen (leaning) eher nachkommen zu können …. . 17 Erhöhung des Einkommens (income) Challenges Framework Method unwichtig (not at all) 1 2 3 4 5 … … … 1 2 3 4 5 Results Relevance Conclusion
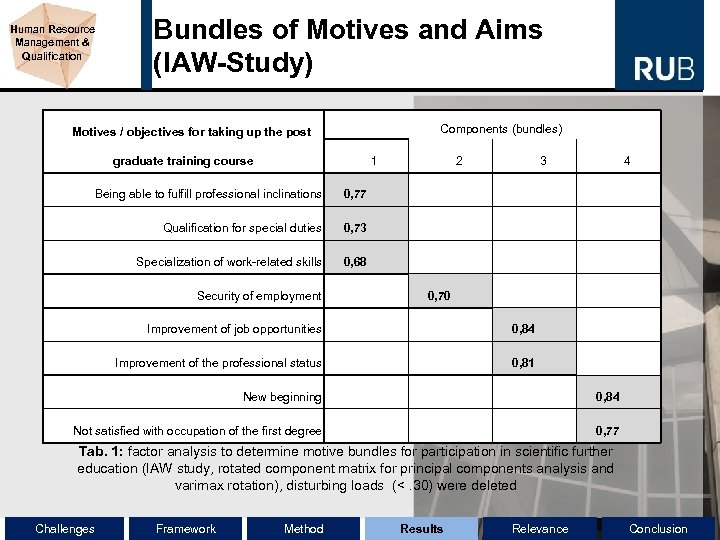
Human Resource Management & Qualification Bundles of Motives and Aims (IAW-Study) Components (bundles) Motives / objectives for taking up the post 1 graduate training course Being able to fulfill professional inclinations 2 3 4 0, 77 Qualification for special duties 0, 73 Specialization of work-related skills 0, 68 Security of employment 0, 70 Improvement of job opportunities 0, 84 Improvement of the professional status 0, 81 New beginning 0, 84 Not satisfied with occupation of the first degree 0, 77 Tab. 1: factor analysis to determine motive bundles for participation in scientific further education (IAW study, rotated component matrix for principal components analysis and varimax rotation), disturbing loads (<. 30) were deleted Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion

Human Resource Management & Qualification Bundles of Motives and Aims Based on 17 various motives and aims, we summarized… 4 motive dimensions: • (I) Reorientation, • (II) job security, • (III) improved business opportunities • (IV) orientation to consolidation • income does not play an important role • Similar to HIS-Study´s results Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion

Human Resource Management & Qualification Motives of further education (HIS -Study II) (1= „absolutely“ to 5= “not at all“) Motive: FE within university Improvement of professional competences (M=1, 66; SD=0, 975) Motive: FE beyond university Improvement of professional competences (M=1, 34; SD=0, 730) 3. Improvement of career opportunities (M=1, 91; SD=1, 316) More interesting/challenging job (M=2, 24; SD=1, 216) Personality development (M=2, 43; SD=1, 303) Acquirement of social competences (M=2, 52; SD=1, 319) 4. Personality developmnt (M=2, 51; SD=1, 228) More interesting/challenging job (M=2, 52; SD=1, 285) 5. Reach a higher position (M=2, 64; SD=1, 283) Improvement of career opportunities (M=2, 58; SD=1, 457) … 1. 2. … 9. … Reach a higher income (M=3, 11; SD=1, 32). 10. … Challenges Framework Method … Reach a higher income (M=3, 40; SD=1, 32) Tab. 2 Results Relevance Conclusion

Human Resource Management & Qualification Reasons for being interested in further education… • Results of IAW-Study: – excessive demands at work: 98, 8 % „no“, 1, 2 % „yes“ – underchallenged at work: 54, 3 % „no“, 45, 7 % „yes“ – no sex differences • HIS- Study II: counterbalancing of deficits is not important: further education at universities (M=3, 33; SD=1, 41), further education beyond universities (M=2, 95; SD=1, 45) Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion

Human Resource Management & Qualification Example Characteristics of job situation Nr. 5. 6 Wie würden Sie Ihren derzeitigen (bzw. letzten) Arbeitsplatz, Ihre Arbeitsbedingungen und Ihre Arbeitsumgebung beschreiben? (charaterization of the work situation) 1 …. Es wird Wert auf Eigeninitiative (value of initiative of one`s own) gelegt . …. . 29 Meine Arbeit ist weitgehend vordefiniert (predefinded work) …. . Challenges Framework Method trifft gar nicht zu no, absolutly not trifft sehr stark zu yes, absolutly 1 2 3 4 5 …. …. …. 1 2 3 4 5 Results Relevance Conclusion
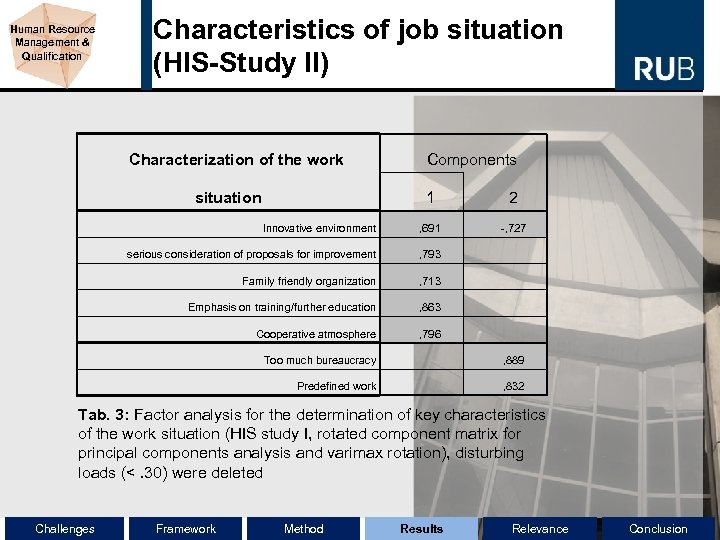
Human Resource Management & Qualification Characteristics of job situation (HIS-Study II) Characterization of the work Components 1 2 Innovative environment , 691 -, 727 serious consideration of proposals for improvement , 793 Family friendly organization , 713 Emphasis on training/further education , 863 Cooperative atmosphere , 796 situation Too much bureaucracy , 889 Predefined work , 832 Tab. 3: Factor analysis for the determination of key characteristics of the work situation (HIS study I, rotated component matrix for principal components analysis and varimax rotation), disturbing loads (<. 30) were deleted Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion

Human Resource Management & Qualification Job situation and further education (HIS-Study II) Results of one-way ANOVA: - Source: 31 Items - persons of first group (innovative job situation) engage more often in further education than persons of the second group - F(2, 1245)=4, 244; p<, 033; η²=, 097 - Explanation: Transfer of competences is easier in the first group Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion

Human Resource Management & Qualification • Satisfaction and further education High internal consistency (Source: 15 Items) … – entire HIS-Study I (Cronbachs Alpha = , 831) – HIS-Study II(selected participants) (Cronbachs Alpha = , 814) – IAW-Study (Cronbachs Alpha = , 761) reflection of these satisfaction-values for different groups (further education: yes; further education: no but planned; further education: no) (HIS-Study II) • the more satisfied the more further education – One-way ANOVA: high significant effects (F(2, 4686)=14, 440; p<, 001) – post-hoc-t-test (Bonferroni-Correction): Differences are especially based on a comparison between persons who engage in further education and persons who don´t (T (4567)=5, 056, p<, 000 ) Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion

Human Resource Management & Qualification Influence of employment market: choice and configuration of undergraduate degree Does the natural scientific graduate group choose courses in engineering terms and the graduate group from economic science choose courses in economic science? Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion
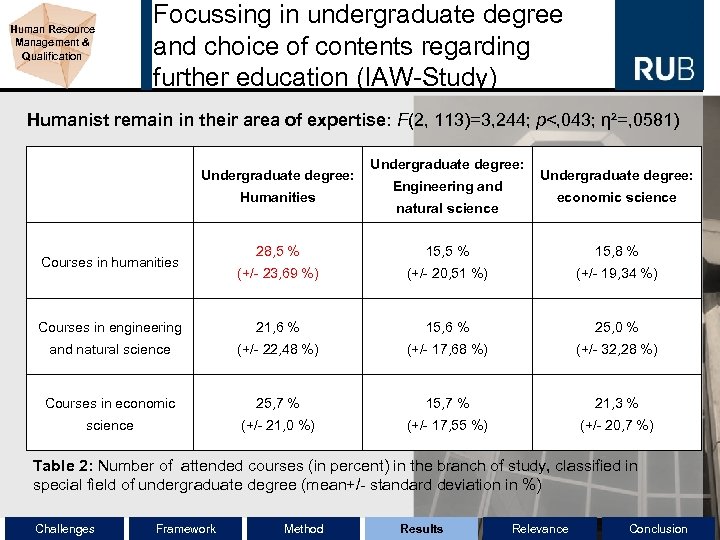
Human Resource Management & Qualification Focussing in undergraduate degree and choice of contents regarding further education (IAW-Study) Humanist remain in their area of expertise: F(2, 113)=3, 244; p<, 043; η²=, 0581) Undergraduate degree: Humanities Undergraduate degree: Engineering and natural science Undergraduate degree: economic science 28, 5 % 15, 8 % (+/- 23, 69 %) (+/- 20, 51 %) (+/- 19, 34 %) Courses in engineering 21, 6 % 15, 6 % 25, 0 % and natural science (+/- 22, 48 %) (+/- 17, 68 %) (+/- 32, 28 %) Courses in economic 25, 7 % 15, 7 % 21, 3 % science (+/- 21, 0 %) (+/- 17, 55 %) (+/- 20, 7 %) Courses in humanities Table 2: Number of attended courses (in percent) in the branch of study, classified in special field of undergraduate degree (mean+/- standard deviation in %) Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion
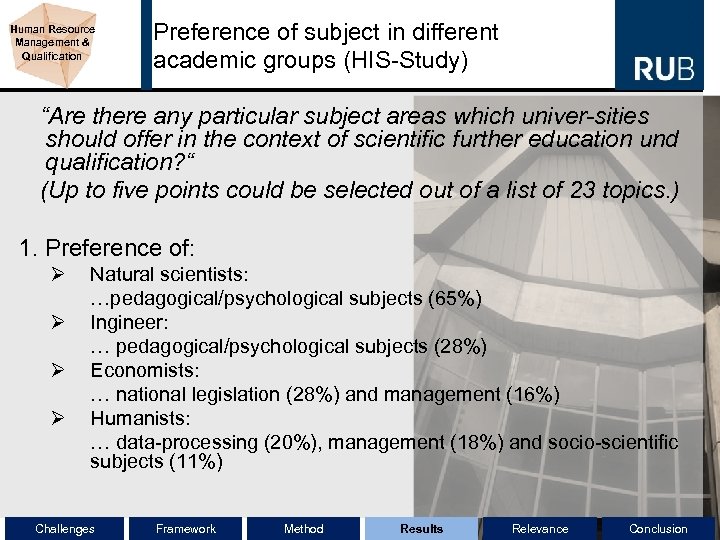
Human Resource Management & Qualification Preference of subject in different academic groups (HIS-Study) “Are there any particular subject areas which univer-sities should offer in the context of scientific further education und qualification? “ (Up to five points could be selected out of a list of 23 topics. ) 1. Preference of: Ø Ø Natural scientists: …pedagogical/psychological subjects (65%) Ingineer: … pedagogical/psychological subjects (28%) Economists: … national legislation (28%) and management (16%) Humanists: … data-processing (20%), management (18%) and socio-scientific subjects (11%) Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion

Human Resource Management & Qualification • Verification of hypotheses 1. Hypothesis: The central motive for investing in further education is the expectation of an increase in income. The results indicate the following: The causal chain, which is based on thesis motivational structure, is limited. Causal Knowledge and competence acquisition chain • Promotion Increase in salary 2. Hypothesis: A reason for the interest in academic further education program is that the graduate feels overchallenged with the current job situation. Almost no participant is overchallenged, instead most of the participants are feeling underchallenged; potentials should be the initial point and not deficits change of perspectives Problem: Heterogeneity – How to analyse the potentials? Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion

Human Resource Management & Qualification Verification of hypotheses • 3. Hypothesis: The different work situations in which the participants find themselves have a direct impact on their behavior concerning further education. Confirmed: cooperative and innovative vs. bureaucratic working situation Further research needed: consequences for competence transfer and further education programs • 4. Hypothesis: Those engaged in further education are not satisfied with their current work situation. not confirmed, dissatisfaction is not a central driver for further education; further research needed • 5. Hypothesis: The participants of further education studies stick to the contentual orientation of their first degree when choosing further education contents. only partly confirmed, further research needed challenge for universities: „home faculties“ not sufficient for further scientific education Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion
Human Resource Management & Qualification Conclusion • demand orientation is more complex • methodical and didactical organization of further education, content of further education consideration of different motives (specialization, reorientation, job security, improvement of job-related opportunities) • results are very important professionalization of further education at universities should be the focus of didactical efforts Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion

Human Resource Management & Qualification Thanks for your kind attention! Contact: martin. kroell@rub. de Institute for Applied Work Science Ruhr University Bochum, NB 1/174 44780 Bochum, Germany Phone: +49 (0)234 – 32 23 293 Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion

Human Resource Management & Qualification Role of job market and sexes • Whereas men focus on specialisation and consolidation (t 137 = -. 30, p <. 004) • Women do more place emphasis on addiction and affinity (t 138 = 2, 529, p <. 013) • Selection of undergraduate degree: job market situation influences men more than women (t 145 = -2. 67, p <. 01) • Structure of undergraduate degree: no differences in regard to role of job market (t 137 = -. 30, p >. 05) A job market-oriented view concerning undergraduate degree does also influence postgraduate degree! Challenges Framework Method Results Relevance Conclusion
45652c0f9acdf6615819317c8d5586a9.ppt