 Compensation Stock Options 1
Compensation Stock Options 1
 Calls and Puts • A call option gives its owner the right, but not the obligation, to buy a stock at a specified exercise or strike price on or before a specified exercise date. • A put option gives you the right, but not the obligation, to sell a stock at a specified exercise price on or before a specified exercise date. 2
Calls and Puts • A call option gives its owner the right, but not the obligation, to buy a stock at a specified exercise or strike price on or before a specified exercise date. • A put option gives you the right, but not the obligation, to sell a stock at a specified exercise price on or before a specified exercise date. 2
 Employee Stock Options • When employees are granted “stock options, ” they are being granted call options on the company’s stock. • The value of the option increases with the firm’s stock price. • Note: volatility increases the value of an option. 3
Employee Stock Options • When employees are granted “stock options, ” they are being granted call options on the company’s stock. • The value of the option increases with the firm’s stock price. • Note: volatility increases the value of an option. 3
 Typical Features of Employee Stock Options • American call options (can exercise early) • Typical life = 10 years • Granted “at-the-money” (exercise price = share price at the time of the grant) • Rarely dividend protected • Cannot be sold (non-transferable) • Have vesting restrictions, i. e. , if you leave the firm before the option vests, option is forfeited 4
Typical Features of Employee Stock Options • American call options (can exercise early) • Typical life = 10 years • Granted “at-the-money” (exercise price = share price at the time of the grant) • Rarely dividend protected • Cannot be sold (non-transferable) • Have vesting restrictions, i. e. , if you leave the firm before the option vests, option is forfeited 4
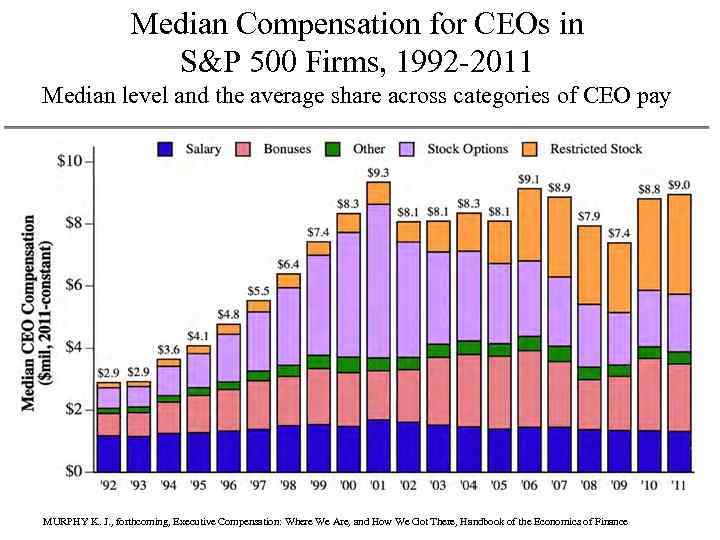 Median Compensation for CEOs in S&P 500 Firms, 1992 -2011 Median level and the average share across categories of CEO pay MURPHY K. J. , forthcoming, Executive Compensation: Where We Are, and How We Got There, Handbook of the Economics of Finance
Median Compensation for CEOs in S&P 500 Firms, 1992 -2011 Median level and the average share across categories of CEO pay MURPHY K. J. , forthcoming, Executive Compensation: Where We Are, and How We Got There, Handbook of the Economics of Finance
 Why Grant Options? • To align incentives in order to ameliorate principal -agent problems. (Employee is also a winner if the stock price goes up). • The agency problem usually refers to a conflict of interest between a company's management and the company's stockholders. • Accounting? 8
Why Grant Options? • To align incentives in order to ameliorate principal -agent problems. (Employee is also a winner if the stock price goes up). • The agency problem usually refers to a conflict of interest between a company's management and the company's stockholders. • Accounting? 8
 Accounting for Stock Options • Although the ultimate value of the stock option to the employee will not be known until exercised, the option has value when granted. • Some argue that just as cash wages are expensed from earnings, the value of options grants should be expensed. 9
Accounting for Stock Options • Although the ultimate value of the stock option to the employee will not be known until exercised, the option has value when granted. • Some argue that just as cash wages are expensed from earnings, the value of options grants should be expensed. 9
 Change in Accounting Rules • Pre-2006: As long as the exercise price of the option is >= current stock price at grant, the company never recognizes this compensation as an expense under current accounting standards. • Starting in 2006: Must expense value of option grants according to vesting schedule 10
Change in Accounting Rules • Pre-2006: As long as the exercise price of the option is >= current stock price at grant, the company never recognizes this compensation as an expense under current accounting standards. • Starting in 2006: Must expense value of option grants according to vesting schedule 10
 Effect of Stock Options on Firm • Evidence suggests that firms with options programs tend to repurchase more stock and pay fewer dividends. – Options are rarely dividend protected (if pay dividend, it reduces stock price and thus value of option). – Firms often repurchase stock to undo the dilution from option grants. 11
Effect of Stock Options on Firm • Evidence suggests that firms with options programs tend to repurchase more stock and pay fewer dividends. – Options are rarely dividend protected (if pay dividend, it reduces stock price and thus value of option). – Firms often repurchase stock to undo the dilution from option grants. 11
 Current Compensation Trends • Stock compensation gaining ground 2009 – 20% stock compensation types 2014 – 34. 7% • Combination of different policies 12
Current Compensation Trends • Stock compensation gaining ground 2009 – 20% stock compensation types 2014 – 34. 7% • Combination of different policies 12