80d14251e8904cc861894c6c6f3587d3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Comparison Of Wide Area Wireless Data Networks -Selling The GPRS Standard -By Pranav S. Vaidya
Comparison Of Wide Area Wireless Data Networks -Selling The GPRS Standard -By Pranav S. Vaidya
 Sales Scenario n n Client has USD 100 M to invest Client is considering the following wireless data standards. Hence client is interested in wireless data networks more than wireless voice networks. n n n ARDIS … The Oldest One (1 G) MOBITEX … The Most Widely Used (1, 2 G) CDPD …The Smart One GPRS … The New One Not considering other broadband standards such as Metri. Comm Richochet.
Sales Scenario n n Client has USD 100 M to invest Client is considering the following wireless data standards. Hence client is interested in wireless data networks more than wireless voice networks. n n n ARDIS … The Oldest One (1 G) MOBITEX … The Most Widely Used (1, 2 G) CDPD …The Smart One GPRS … The New One Not considering other broadband standards such as Metri. Comm Richochet.
 Evaluation Criterion Of Technologies Data transmission Characteristics. Transmission Costs. Throughput – Faster Throughput Cost Of Service 1. 2. 3. 4. n n Customer Satisfaction – Roaming. Interoperability with the Internet (WAP and IP). Security Concerns Application Domains 5. 6. Money Reaps Money V/S Too Many Pieces to the Pie n n n Mobile Office. Financial Critical Communications. Remote Control or Monitoring.
Evaluation Criterion Of Technologies Data transmission Characteristics. Transmission Costs. Throughput – Faster Throughput Cost Of Service 1. 2. 3. 4. n n Customer Satisfaction – Roaming. Interoperability with the Internet (WAP and IP). Security Concerns Application Domains 5. 6. Money Reaps Money V/S Too Many Pieces to the Pie n n n Mobile Office. Financial Critical Communications. Remote Control or Monitoring.
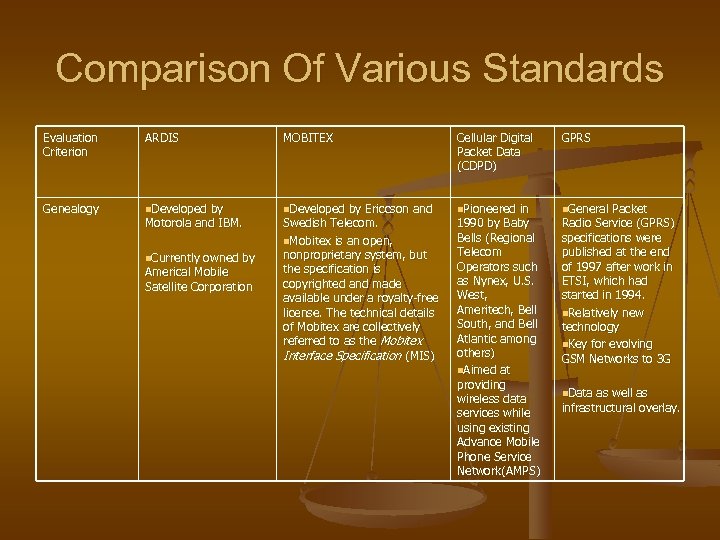 Comparison Of Various Standards Evaluation Criterion ARDIS MOBITEX Cellular Digital Packet Data (CDPD) GPRS Genealogy n. Developed by Ericcson and n. Pioneered in n. General Packet Motorola and IBM. n. Currently owned by Americal Mobile Satellite Corporation Swedish Telecom. n. Mobitex is an open, nonproprietary system, but the specification is copyrighted and made available under a royalty-free license. The technical details of Mobitex are collectively referred to as the Mobitex Interface Specification (MIS) 1990 by Baby Bells (Regional Telecom Operators such as Nynex, U. S. West, Ameritech, Bell South, and Bell Atlantic among others) n. Aimed at providing wireless data services while using existing Advance Mobile Phone Service Network(AMPS) Radio Service (GPRS) specifications were published at the end of 1997 after work in ETSI, which had started in 1994. n. Relatively new technology n. Key for evolving GSM Networks to 3 G n. Data as well as infrastructural overlay.
Comparison Of Various Standards Evaluation Criterion ARDIS MOBITEX Cellular Digital Packet Data (CDPD) GPRS Genealogy n. Developed by Ericcson and n. Pioneered in n. General Packet Motorola and IBM. n. Currently owned by Americal Mobile Satellite Corporation Swedish Telecom. n. Mobitex is an open, nonproprietary system, but the specification is copyrighted and made available under a royalty-free license. The technical details of Mobitex are collectively referred to as the Mobitex Interface Specification (MIS) 1990 by Baby Bells (Regional Telecom Operators such as Nynex, U. S. West, Ameritech, Bell South, and Bell Atlantic among others) n. Aimed at providing wireless data services while using existing Advance Mobile Phone Service Network(AMPS) Radio Service (GPRS) specifications were published at the end of 1997 after work in ETSI, which had started in 1994. n. Relatively new technology n. Key for evolving GSM Networks to 3 G n. Data as well as infrastructural overlay.
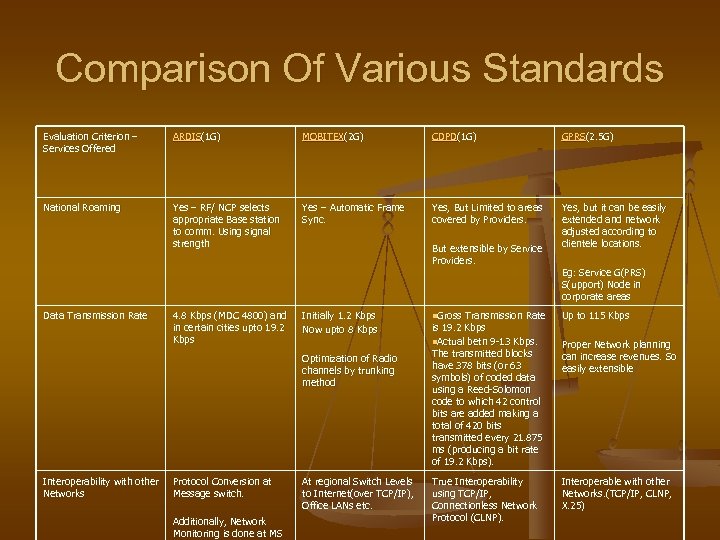 Comparison Of Various Standards Evaluation Criterion – Services Offered ARDIS(1 G) MOBITEX(2 G) CDPD(1 G) GPRS(2. 5 G) National Roaming Yes – RF/ NCP selects appropriate Base station to comm. Using signal strength Yes – Automatic Frame Sync. Yes, But Limited to areas covered by Providers. Yes, but it can be easily extended and network adjusted according to clientele locations. Data Transmission Rate 4. 8 Kbps (MDC 4800) and in certain cities upto 19. 2 Kbps But extensible by Service Providers. Initially 1. 2 Kbps Now upto 8 Kbps Optimization of Radio channels by trunking method Interoperability with other Networks Protocol Conversion at Message switch. Additionally, Network Monitoring is done at MS At regional Switch Levels to Internet(over TCP/IP), Office LANs etc. n. Gross Transmission Rate is 19. 2 Kbps n. Actual betn 9 -13 Kbps. The transmitted blocks have 378 bits (or 63 symbols) of coded data using a Reed-Solomon code to which 42 control bits are added making a total of 420 bits transmitted every 21. 875 ms (producing a bit rate of 19. 2 Kbps). True Interoperability using TCP/IP, Connectionless Network Protocol (CLNP). Eg: Service G(PRS) S(upport) Node in corporate areas Up to 115 Kbps Proper Network planning can increase revenues. So easily extensible Interoperable with other Networks. (TCP/IP, CLNP, X. 25)
Comparison Of Various Standards Evaluation Criterion – Services Offered ARDIS(1 G) MOBITEX(2 G) CDPD(1 G) GPRS(2. 5 G) National Roaming Yes – RF/ NCP selects appropriate Base station to comm. Using signal strength Yes – Automatic Frame Sync. Yes, But Limited to areas covered by Providers. Yes, but it can be easily extended and network adjusted according to clientele locations. Data Transmission Rate 4. 8 Kbps (MDC 4800) and in certain cities upto 19. 2 Kbps But extensible by Service Providers. Initially 1. 2 Kbps Now upto 8 Kbps Optimization of Radio channels by trunking method Interoperability with other Networks Protocol Conversion at Message switch. Additionally, Network Monitoring is done at MS At regional Switch Levels to Internet(over TCP/IP), Office LANs etc. n. Gross Transmission Rate is 19. 2 Kbps n. Actual betn 9 -13 Kbps. The transmitted blocks have 378 bits (or 63 symbols) of coded data using a Reed-Solomon code to which 42 control bits are added making a total of 420 bits transmitted every 21. 875 ms (producing a bit rate of 19. 2 Kbps). True Interoperability using TCP/IP, Connectionless Network Protocol (CLNP). Eg: Service G(PRS) S(upport) Node in corporate areas Up to 115 Kbps Proper Network planning can increase revenues. So easily extensible Interoperable with other Networks. (TCP/IP, CLNP, X. 25)
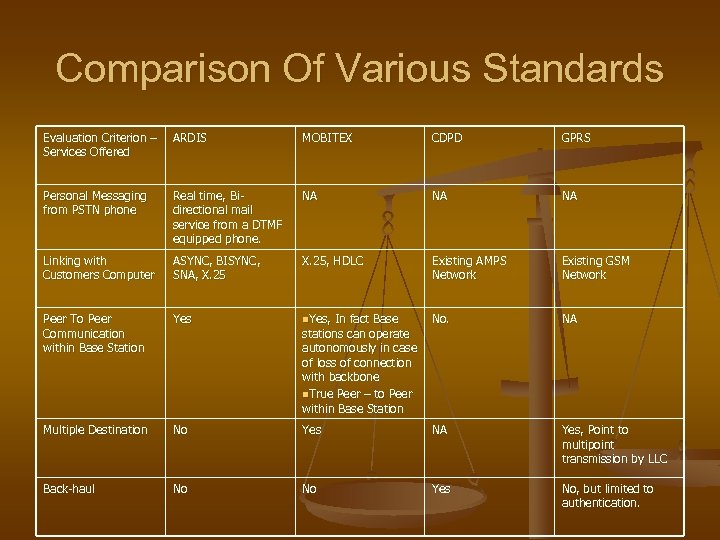 Comparison Of Various Standards Evaluation Criterion – ARDIS Services Offered MOBITEX CDPD GPRS Personal Messaging from PSTN phone Real time, Bidirectional mail service from a DTMF equipped phone. NA NA NA Linking with Customers Computer ASYNC, BISYNC, SNA, X. 25, HDLC Existing AMPS Network Existing GSM Network Peer To Peer Communication within Base Station Yes n. Yes, In fact Base No. NA Multiple Destination No Yes NA Yes, Point to multipoint transmission by LLC Back-haul No No Yes No, but limited to authentication. stations can operate autonomously in case of loss of connection with backbone n. True Peer – to Peer within Base Station
Comparison Of Various Standards Evaluation Criterion – ARDIS Services Offered MOBITEX CDPD GPRS Personal Messaging from PSTN phone Real time, Bidirectional mail service from a DTMF equipped phone. NA NA NA Linking with Customers Computer ASYNC, BISYNC, SNA, X. 25, HDLC Existing AMPS Network Existing GSM Network Peer To Peer Communication within Base Station Yes n. Yes, In fact Base No. NA Multiple Destination No Yes NA Yes, Point to multipoint transmission by LLC Back-haul No No Yes No, but limited to authentication. stations can operate autonomously in case of loss of connection with backbone n. True Peer – to Peer within Base Station
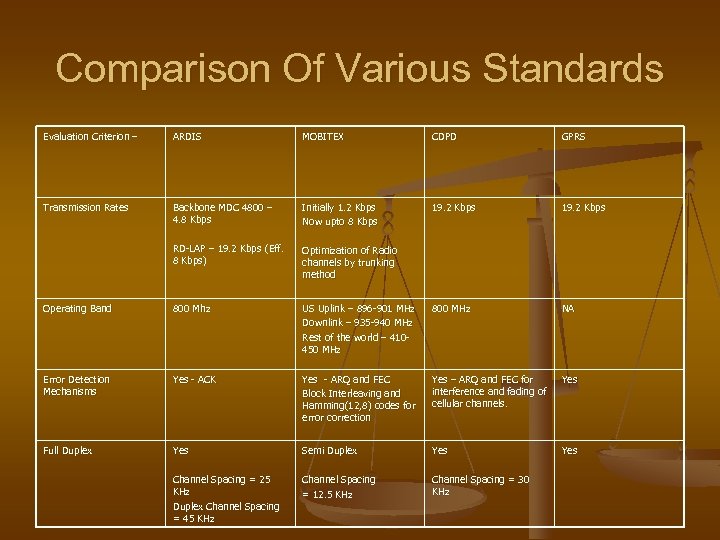 Comparison Of Various Standards Evaluation Criterion – ARDIS MOBITEX CDPD GPRS Transmission Rates Backbone MDC 4800 – 4. 8 Kbps Initially 1. 2 Kbps Now upto 8 Kbps 19. 2 Kbps RD-LAP – 19. 2 Kbps (Eff. 8 Kbps) Optimization of Radio channels by trunking method Operating Band 800 Mhz US Uplink – 896 -901 MHz Downlink – 935 -940 MHz Rest of the world – 410450 MHz 800 MHz NA Error Detection Mechanisms Yes - ACK Yes - ARQ and FEC Block Interleaving and Hamming(12, 8) codes for error correction Yes – ARQ and FEC for interference and fading of cellular channels. Yes Full Duplex Yes Semi Duplex Yes Channel Spacing = 25 KHz Duplex Channel Spacing = 45 KHz Channel Spacing = 12. 5 KHz Channel Spacing = 30 KHz
Comparison Of Various Standards Evaluation Criterion – ARDIS MOBITEX CDPD GPRS Transmission Rates Backbone MDC 4800 – 4. 8 Kbps Initially 1. 2 Kbps Now upto 8 Kbps 19. 2 Kbps RD-LAP – 19. 2 Kbps (Eff. 8 Kbps) Optimization of Radio channels by trunking method Operating Band 800 Mhz US Uplink – 896 -901 MHz Downlink – 935 -940 MHz Rest of the world – 410450 MHz 800 MHz NA Error Detection Mechanisms Yes - ACK Yes - ARQ and FEC Block Interleaving and Hamming(12, 8) codes for error correction Yes – ARQ and FEC for interference and fading of cellular channels. Yes Full Duplex Yes Semi Duplex Yes Channel Spacing = 25 KHz Duplex Channel Spacing = 45 KHz Channel Spacing = 12. 5 KHz Channel Spacing = 30 KHz
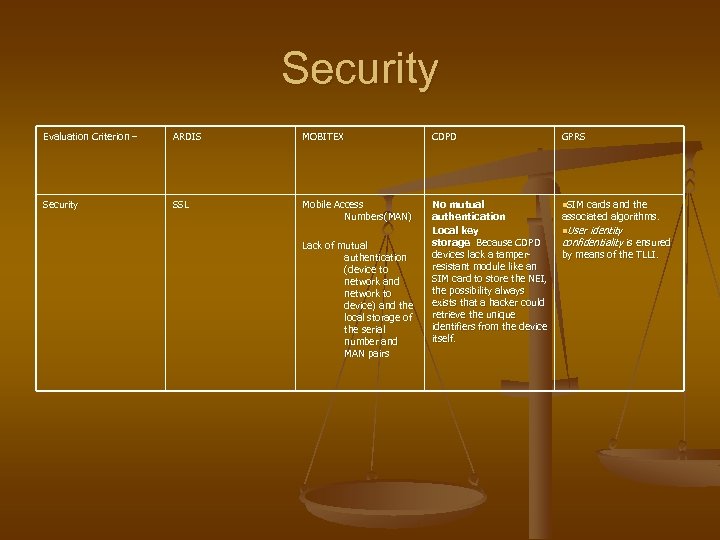 Security Evaluation Criterion – ARDIS MOBITEX CDPD GPRS Security SSL Mobile Access Numbers(MAN) No mutual authentication Local key storage Because CDPD devices lack a tamperresistant module like an SIM card to store the NEI, the possibility always exists that a hacker could retrieve the unique identifiers from the device itself. n. SIM cards and the Lack of mutual authentication (device to network and network to device) and the local storage of the serial number and MAN pairs associated algorithms. n. User identity confidentiality is ensured by means of the TLLI.
Security Evaluation Criterion – ARDIS MOBITEX CDPD GPRS Security SSL Mobile Access Numbers(MAN) No mutual authentication Local key storage Because CDPD devices lack a tamperresistant module like an SIM card to store the NEI, the possibility always exists that a hacker could retrieve the unique identifiers from the device itself. n. SIM cards and the Lack of mutual authentication (device to network and network to device) and the local storage of the serial number and MAN pairs associated algorithms. n. User identity confidentiality is ensured by means of the TLLI.
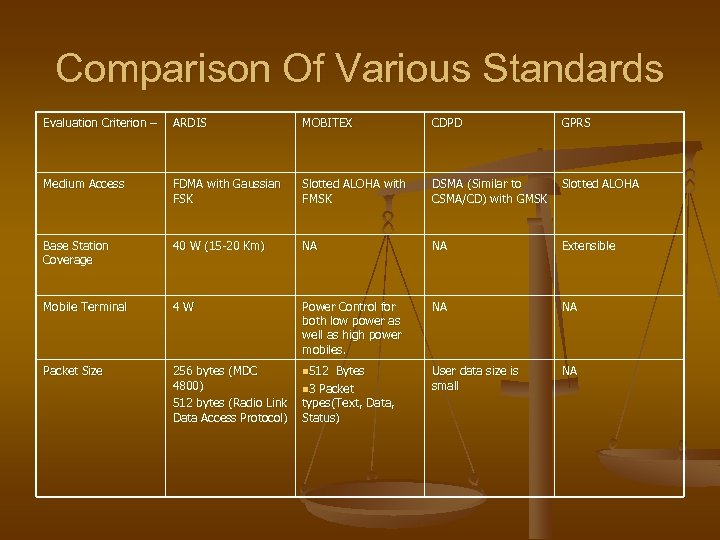 Comparison Of Various Standards Evaluation Criterion – ARDIS MOBITEX CDPD GPRS Medium Access FDMA with Gaussian FSK Slotted ALOHA with FMSK DSMA (Similar to CSMA/CD) with GMSK Slotted ALOHA Base Station Coverage 40 W (15 -20 Km) NA NA Extensible Mobile Terminal 4 W Power Control for both low power as well as high power mobiles. NA NA Packet Size 256 bytes (MDC n 512 Bytes 4800) n 3 Packet 512 bytes (Radio Link types(Text, Data, Data Access Protocol) Status) User data size is small NA
Comparison Of Various Standards Evaluation Criterion – ARDIS MOBITEX CDPD GPRS Medium Access FDMA with Gaussian FSK Slotted ALOHA with FMSK DSMA (Similar to CSMA/CD) with GMSK Slotted ALOHA Base Station Coverage 40 W (15 -20 Km) NA NA Extensible Mobile Terminal 4 W Power Control for both low power as well as high power mobiles. NA NA Packet Size 256 bytes (MDC n 512 Bytes 4800) n 3 Packet 512 bytes (Radio Link types(Text, Data, Data Access Protocol) Status) User data size is small NA
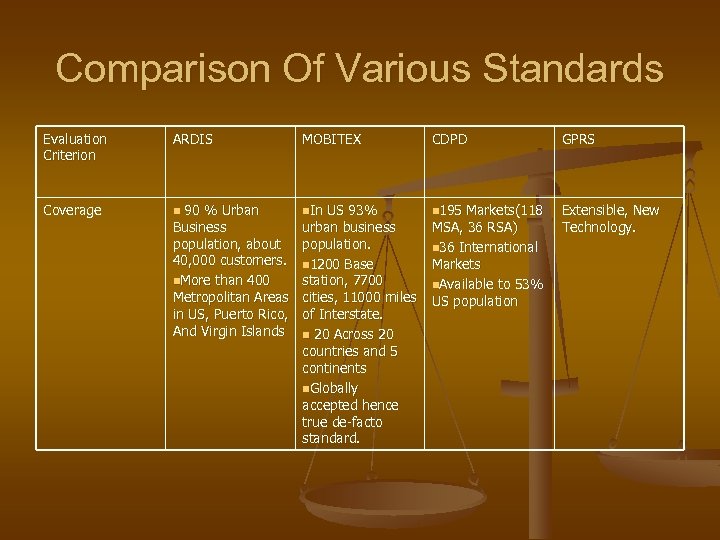 Comparison Of Various Standards Evaluation Criterion ARDIS MOBITEX CDPD GPRS Coverage n 90 % Urban n. In US 93% n 195 Markets(118 Extensible, New Technology. Business population, about 40, 000 customers. n. More than 400 Metropolitan Areas in US, Puerto Rico, And Virgin Islands urban business population. n 1200 Base station, 7700 cities, 11000 miles of Interstate. n 20 Across 20 countries and 5 continents n. Globally accepted hence true de-facto standard. MSA, 36 RSA) n 36 International Markets n. Available to 53% US population
Comparison Of Various Standards Evaluation Criterion ARDIS MOBITEX CDPD GPRS Coverage n 90 % Urban n. In US 93% n 195 Markets(118 Extensible, New Technology. Business population, about 40, 000 customers. n. More than 400 Metropolitan Areas in US, Puerto Rico, And Virgin Islands urban business population. n 1200 Base station, 7700 cities, 11000 miles of Interstate. n 20 Across 20 countries and 5 continents n. Globally accepted hence true de-facto standard. MSA, 36 RSA) n 36 International Markets n. Available to 53% US population
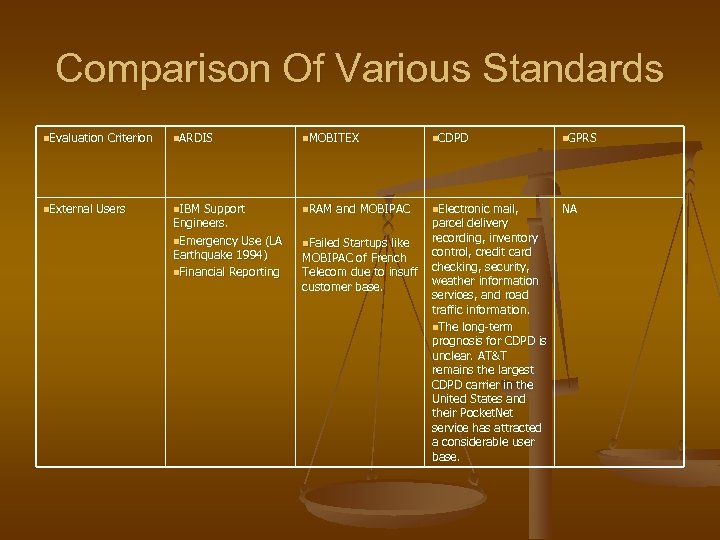 Comparison Of Various Standards n. Evaluation Criterion n. ARDIS n. MOBITEX n. CDPD n. GPRS n. External Users n. IBM Support n. RAM and MOBIPAC n. Electronic mail, NA Engineers. n. Emergency Use (LA Earthquake 1994) n. Financial Reporting n. Failed Startups like MOBIPAC of French Telecom due to insuff customer base. parcel delivery recording, inventory control, credit card checking, security, weather information services, and road traffic information. n. The long-term prognosis for CDPD is unclear. AT&T remains the largest CDPD carrier in the United States and their Pocket. Net service has attracted a considerable user base.
Comparison Of Various Standards n. Evaluation Criterion n. ARDIS n. MOBITEX n. CDPD n. GPRS n. External Users n. IBM Support n. RAM and MOBIPAC n. Electronic mail, NA Engineers. n. Emergency Use (LA Earthquake 1994) n. Financial Reporting n. Failed Startups like MOBIPAC of French Telecom due to insuff customer base. parcel delivery recording, inventory control, credit card checking, security, weather information services, and road traffic information. n. The long-term prognosis for CDPD is unclear. AT&T remains the largest CDPD carrier in the United States and their Pocket. Net service has attracted a considerable user base.
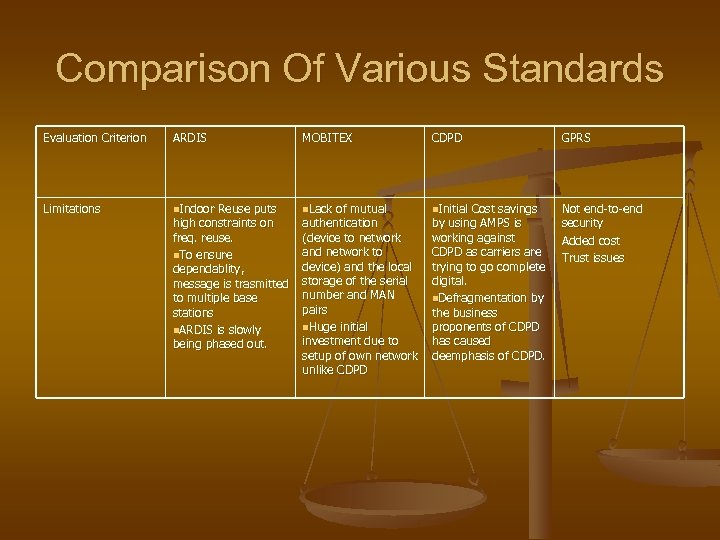 Comparison Of Various Standards Evaluation Criterion ARDIS MOBITEX CDPD GPRS Limitations n. Indoor Reuse puts n. Lack of mutual n. Initial Cost savings Not end-to-end security Added cost Trust issues high constraints on freq. reuse. n. To ensure dependablity, message is trasmitted to multiple base stations n. ARDIS is slowly being phased out. authentication (device to network and network to device) and the local storage of the serial number and MAN pairs n. Huge initial investment due to setup of own network unlike CDPD by using AMPS is working against CDPD as carriers are trying to go complete digital. n. Defragmentation by the business proponents of CDPD has caused deemphasis of CDPD.
Comparison Of Various Standards Evaluation Criterion ARDIS MOBITEX CDPD GPRS Limitations n. Indoor Reuse puts n. Lack of mutual n. Initial Cost savings Not end-to-end security Added cost Trust issues high constraints on freq. reuse. n. To ensure dependablity, message is trasmitted to multiple base stations n. ARDIS is slowly being phased out. authentication (device to network and network to device) and the local storage of the serial number and MAN pairs n. Huge initial investment due to setup of own network unlike CDPD by using AMPS is working against CDPD as carriers are trying to go complete digital. n. Defragmentation by the business proponents of CDPD has caused deemphasis of CDPD.
 Why GPRS n n n Compatibility with the Internet Because the Internet is a packet-based network utilizing the IP, GPRS provides an easy connection with Internet-based data. This makes GPRS ideally suited for wireless data and applications. Always-on connection Packet switching does not require that a physical link (such as a circuit) be opened for data transfer. This enables GPRS users to receive information only when they need to, but more importantly, it does not require that a circuit-switched connection be established for every individual call. Efficient networks Packet switching enables data packets to be redirected over the optimal network path and bypass potential network bottlenecks. Furthermore, packet switching means that the radio spectrum is only used during the transmit or receive mode. This enables multiple users to share the same spectrum in a given area. In circuit switching, a dedicated circuit must be opened for each call, preventing multiple users from using the same frequency in a cell site. n From Handbook of Wireless Networks
Why GPRS n n n Compatibility with the Internet Because the Internet is a packet-based network utilizing the IP, GPRS provides an easy connection with Internet-based data. This makes GPRS ideally suited for wireless data and applications. Always-on connection Packet switching does not require that a physical link (such as a circuit) be opened for data transfer. This enables GPRS users to receive information only when they need to, but more importantly, it does not require that a circuit-switched connection be established for every individual call. Efficient networks Packet switching enables data packets to be redirected over the optimal network path and bypass potential network bottlenecks. Furthermore, packet switching means that the radio spectrum is only used during the transmit or receive mode. This enables multiple users to share the same spectrum in a given area. In circuit switching, a dedicated circuit must be opened for each call, preventing multiple users from using the same frequency in a cell site. n From Handbook of Wireless Networks
 Upgrade to GPRS Over 3 G • Because these networks did not require additional radio spectrum, the cost of building GPRS-capable wireless networks was relatively minor. This contrasted sharply with the emerging third-generation (3 G) networks, which required new spectrum and a large infrastructure upgrade. Above figureprovides a sense of the infrastructure requirements for deploying a GPRS network. • As another example, in December 2001, AT&T Wireless stated that the network upgrade cost for GPRS was $300 to $400 million, whereas the 3 G upgrade cost was at least $1 billion. • From Wireless Security
Upgrade to GPRS Over 3 G • Because these networks did not require additional radio spectrum, the cost of building GPRS-capable wireless networks was relatively minor. This contrasted sharply with the emerging third-generation (3 G) networks, which required new spectrum and a large infrastructure upgrade. Above figureprovides a sense of the infrastructure requirements for deploying a GPRS network. • As another example, in December 2001, AT&T Wireless stated that the network upgrade cost for GPRS was $300 to $400 million, whereas the 3 G upgrade cost was at least $1 billion. • From Wireless Security
 GPRS – Good for the Customer and Good for the operator. n n In Europe, many GSM operators started promoting GPRS to build awareness around the capabilities of these faster networks. Furthermore, because the network upgrade costs were relatively low, the operators could charge relatively modest tariffs for GPRS and still generate a positive return on the investment. In order to utilize GPRS, subscribers only needed to purchase a new GPRSenabled handset. Monthly fees were usually based on the amount of data sent to an individual’s phone. GPRS subscribers could then utilize significantly higher data throughput for accessing the Internet, and for receiving and sending e-mail. In most cases, subscription fees are based on the amount of data received.
GPRS – Good for the Customer and Good for the operator. n n In Europe, many GSM operators started promoting GPRS to build awareness around the capabilities of these faster networks. Furthermore, because the network upgrade costs were relatively low, the operators could charge relatively modest tariffs for GPRS and still generate a positive return on the investment. In order to utilize GPRS, subscribers only needed to purchase a new GPRSenabled handset. Monthly fees were usually based on the amount of data sent to an individual’s phone. GPRS subscribers could then utilize significantly higher data throughput for accessing the Internet, and for receiving and sending e-mail. In most cases, subscription fees are based on the amount of data received.
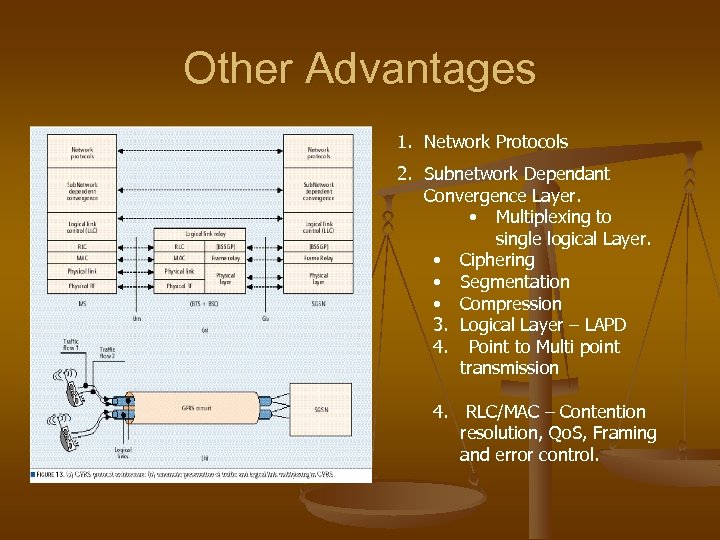 Other Advantages 1. Network Protocols 2. Subnetwork Dependant Convergence Layer. • Multiplexing to single logical Layer. • Ciphering • Segmentation • Compression 3. Logical Layer – LAPD 4. Point to Multi point transmission 4. RLC/MAC – Contention resolution, Qo. S, Framing and error control.
Other Advantages 1. Network Protocols 2. Subnetwork Dependant Convergence Layer. • Multiplexing to single logical Layer. • Ciphering • Segmentation • Compression 3. Logical Layer – LAPD 4. Point to Multi point transmission 4. RLC/MAC – Contention resolution, Qo. S, Framing and error control.
 Questions ?
Questions ?


