6542a324b8959c9c284b9959b66f06cc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Comparison of Positioning Systems (GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo) Raga Yerva. Veera Ajay Jadhav DV Fernando Mendoza
Comparison of Positioning Systems (GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo) Raga Yerva. Veera Ajay Jadhav DV Fernando Mendoza
 Click to edit Master title style Contents Introduction NAVSTAR GPS GLONASS GALILEO Comparison Receivers (GPS + GLONASS and GPS + GALILEO) GNSS Other & Upcoming Positioning Systems Conclusions
Click to edit Master title style Contents Introduction NAVSTAR GPS GLONASS GALILEO Comparison Receivers (GPS + GLONASS and GPS + GALILEO) GNSS Other & Upcoming Positioning Systems Conclusions
 Click to edit Master title style Introduction Global positioning systems (GPS) have dramatically impacted GIS. These systems are providing high accuracy positioning and navigational functionality in the transportation, natural resources, oil and gas, emergency, agricultural and urban planning sectors amongst many others. There are various Global Positioning Systems. Each of these systems is suitable for use by GIS professionals and collectively could result in major benefits, design of new equipment and new applications that will affect GIS users. A debate has ongoing with respect to GALILEO for some time, questioning the need for another GPS system. The NAVSTAR GPS is owned by the United States and Managed by the Department of Defense. The Russian Federation’s GLONASS is a GPS system being proposed by a consortium in European. The GALILEO GPS system would be owned and operated by Europeans and was recently supported by the European Parliament.
Click to edit Master title style Introduction Global positioning systems (GPS) have dramatically impacted GIS. These systems are providing high accuracy positioning and navigational functionality in the transportation, natural resources, oil and gas, emergency, agricultural and urban planning sectors amongst many others. There are various Global Positioning Systems. Each of these systems is suitable for use by GIS professionals and collectively could result in major benefits, design of new equipment and new applications that will affect GIS users. A debate has ongoing with respect to GALILEO for some time, questioning the need for another GPS system. The NAVSTAR GPS is owned by the United States and Managed by the Department of Defense. The Russian Federation’s GLONASS is a GPS system being proposed by a consortium in European. The GALILEO GPS system would be owned and operated by Europeans and was recently supported by the European Parliament.
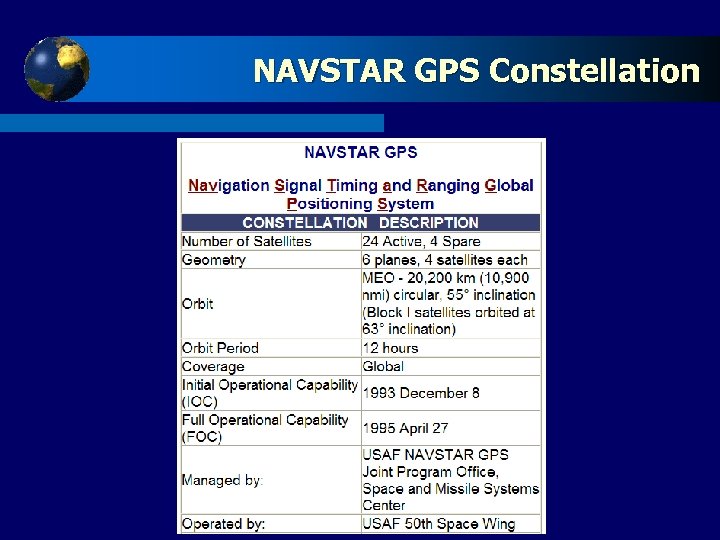
 Click to edit Master title style NAVSTAR GPS t t t Navigation Signal Timing and Ranging Global Positioning System. This is the only fully operational GNSS system currently available to users. Three Segments: Space, Control, and User. GPS has been completely operational since July 1995 and consists of 24 satellites in 6 orbital planes (As of February 2007, 30 operational Satellites) Sept, 2007, the White House said that President Bush has agreed with the U. S. Department of Defense recommendation to permanently do away with Selective Availability, the intentional degradation
Click to edit Master title style NAVSTAR GPS t t t Navigation Signal Timing and Ranging Global Positioning System. This is the only fully operational GNSS system currently available to users. Three Segments: Space, Control, and User. GPS has been completely operational since July 1995 and consists of 24 satellites in 6 orbital planes (As of February 2007, 30 operational Satellites) Sept, 2007, the White House said that President Bush has agreed with the U. S. Department of Defense recommendation to permanently do away with Selective Availability, the intentional degradation
 Click to NAVSTAR GPS edit Master title style t t The full constellation of the GPS satellites will contain four satellites equally distributed in 6 orbital planes. A GPS satellite will reappear in the same part of the sky on each sidereal day but always 4 minutes earlier. GPS satellites transmit two carrier signals L 1 and L 2 in the L band of radio frequency. These signals are modulated by two binary codes, the CA and the P code and by data message. GPS receiver works by looking for the satellite’s unique code modulation, thereby rejecting all signals with a different code. This method of separating the total incoming signals in to components is called Code division multiple access (CDMA).
Click to NAVSTAR GPS edit Master title style t t The full constellation of the GPS satellites will contain four satellites equally distributed in 6 orbital planes. A GPS satellite will reappear in the same part of the sky on each sidereal day but always 4 minutes earlier. GPS satellites transmit two carrier signals L 1 and L 2 in the L band of radio frequency. These signals are modulated by two binary codes, the CA and the P code and by data message. GPS receiver works by looking for the satellite’s unique code modulation, thereby rejecting all signals with a different code. This method of separating the total incoming signals in to components is called Code division multiple access (CDMA).
 Click to edit Master title style Three Different Type of Positioning 1. 2. 3. Single Point Positioning: Relies on a single Receiver. The positioning is corrupted by unmitigated errors inherent in satellite positioning. Differential (Code) Measurements (DGPS): Uses raw data or corrections from a reference receiver located at a known reference point. Carrier Phase Observations: Is the difference between the phase of the carrier signal generated at the receiver and the carrier receive from a satellite at the instant of the measurement.
Click to edit Master title style Three Different Type of Positioning 1. 2. 3. Single Point Positioning: Relies on a single Receiver. The positioning is corrupted by unmitigated errors inherent in satellite positioning. Differential (Code) Measurements (DGPS): Uses raw data or corrections from a reference receiver located at a known reference point. Carrier Phase Observations: Is the difference between the phase of the carrier signal generated at the receiver and the carrier receive from a satellite at the instant of the measurement.
 NAVSTAR Click to Constellation GPS edit Master title style
NAVSTAR Click to Constellation GPS edit Master title style
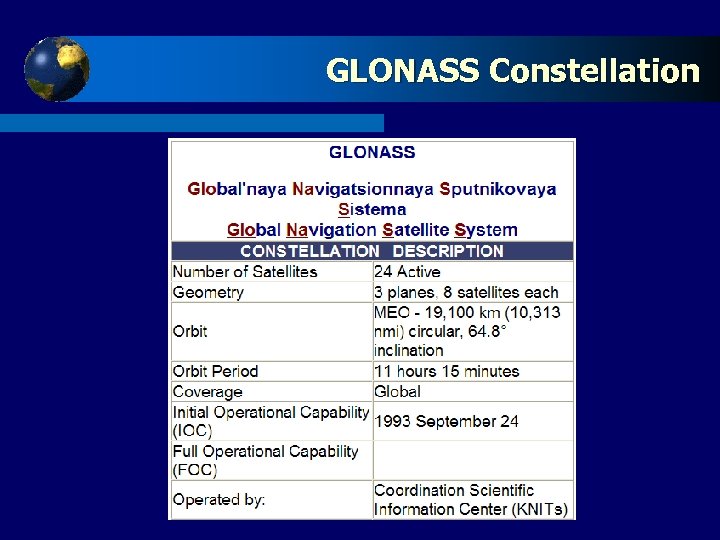
 Click to edit Master title style GLONASS t t t GLONASS – ГЛОбальная НАвигационная Спутниковая Система which is GLObal NAvigation Satellite System. The Russian Equivalent/Counterpart of NAVSTAR GPS. It was developed by the former Soviet Union and now operated by the Russian Federation. Development of GLONASS began in 1976, with a goal of global coverage by 1991. The constellation was completed in 1995. Following completion, the system rapidly fell into disrepair with the collapse of the Russian economy. By 2001, just 8 satellites remained in GLONASS. Beginning in 2001, Russia committed to restoring the system, and in recent years has diversified, introducing the Indian government as a partner, and accelerated the program with a goal of restoring global coverage by 2009
Click to edit Master title style GLONASS t t t GLONASS – ГЛОбальная НАвигационная Спутниковая Система which is GLObal NAvigation Satellite System. The Russian Equivalent/Counterpart of NAVSTAR GPS. It was developed by the former Soviet Union and now operated by the Russian Federation. Development of GLONASS began in 1976, with a goal of global coverage by 1991. The constellation was completed in 1995. Following completion, the system rapidly fell into disrepair with the collapse of the Russian economy. By 2001, just 8 satellites remained in GLONASS. Beginning in 2001, Russia committed to restoring the system, and in recent years has diversified, introducing the Indian government as a partner, and accelerated the program with a goal of restoring global coverage by 2009
 GLONASS Click to edit Master title style t t A fully operational GLONASS constellation consists of 24 satellites, with 21 used for transmitting signals and three for on-orbit spares, deployed in three orbital planes. However, as each orbit plane contains eight satellites, a satellite will pass the same place every 8 th sidereal day (the time needed for Earth to complete one rotation around its axis, relative to the stars). For comparison, each GPS satellite passes over the same spot once every sidereal day. GLONASS satellites transmit two types of signal: a Standard Precision (SP) signal and a High Precision (HP) signal. . All satellites transmit the same code as their SP signal, however each transmits on a different frequency using a 25 -
GLONASS Click to edit Master title style t t A fully operational GLONASS constellation consists of 24 satellites, with 21 used for transmitting signals and three for on-orbit spares, deployed in three orbital planes. However, as each orbit plane contains eight satellites, a satellite will pass the same place every 8 th sidereal day (the time needed for Earth to complete one rotation around its axis, relative to the stars). For comparison, each GPS satellite passes over the same spot once every sidereal day. GLONASS satellites transmit two types of signal: a Standard Precision (SP) signal and a High Precision (HP) signal. . All satellites transmit the same code as their SP signal, however each transmits on a different frequency using a 25 -
 Click to edit Master title style GLONASS Constellation
Click to edit Master title style GLONASS Constellation
 Click to edit Master title style GALILEO t t t GALILEO is a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) which is being developed by Europe. It is a next generation GNSS in the initial deployment phase, scheduled to be operational in 2010 In September 2003 China has joined with the EU in the development of the satellite navigational system. The system will provide a highly accurate, guaranteed global positioning service under civilian control, as opposed to military control as all other systems. This system includes “Public-Private-Partnership” (PPP). Main funding: Germany (20. 9%), France (17. 0%), Great Britain (16. 0%), and Italy (15. 2%). GALILEO is more reliable as it includes the error correction,
Click to edit Master title style GALILEO t t t GALILEO is a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) which is being developed by Europe. It is a next generation GNSS in the initial deployment phase, scheduled to be operational in 2010 In September 2003 China has joined with the EU in the development of the satellite navigational system. The system will provide a highly accurate, guaranteed global positioning service under civilian control, as opposed to military control as all other systems. This system includes “Public-Private-Partnership” (PPP). Main funding: Germany (20. 9%), France (17. 0%), Great Britain (16. 0%), and Italy (15. 2%). GALILEO is more reliable as it includes the error correction,
 Click to edit Master title style Comparison
Click to edit Master title style Comparison
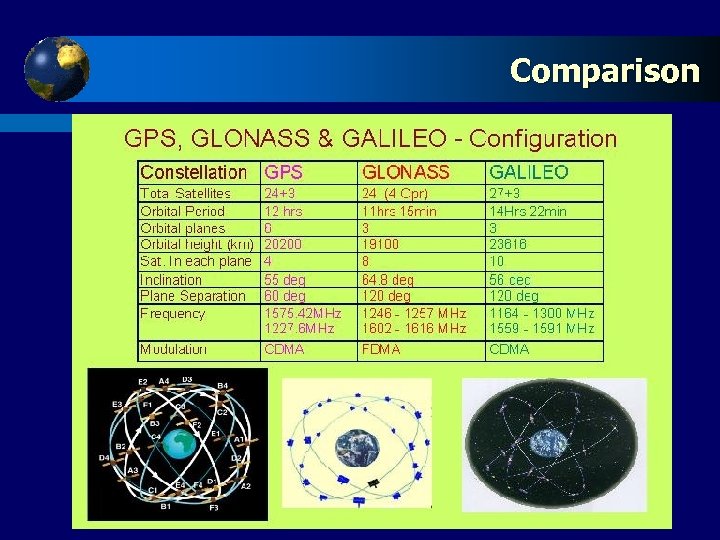
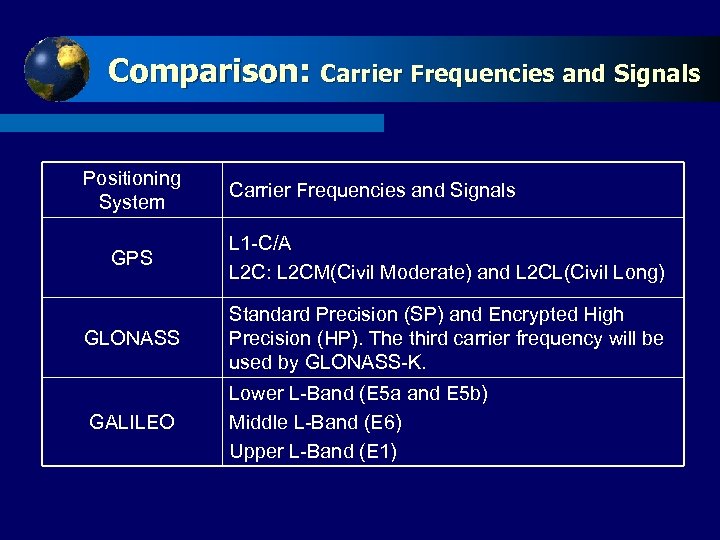 Comparison: Carrier Click to edit Master Signals Frequencies and title style Positioning System Carrier Frequencies and Signals GPS L 1 -C/A L 2 C: L 2 CM(Civil Moderate) and L 2 CL(Civil Long) GLONASS Standard Precision (SP) and Encrypted High Precision (HP). The third carrier frequency will be used by GLONASS-K. GALILEO Lower L-Band (E 5 a and E 5 b) Middle L-Band (E 6) Upper L-Band (E 1)
Comparison: Carrier Click to edit Master Signals Frequencies and title style Positioning System Carrier Frequencies and Signals GPS L 1 -C/A L 2 C: L 2 CM(Civil Moderate) and L 2 CL(Civil Long) GLONASS Standard Precision (SP) and Encrypted High Precision (HP). The third carrier frequency will be used by GLONASS-K. GALILEO Lower L-Band (E 5 a and E 5 b) Middle L-Band (E 6) Upper L-Band (E 1)
 Comparison: Click to and GLONASS GPS edit Master title style One of the major differences between the GPS and GLONASS satellite systems was the initial design life of their satellites. The latest GLONASS satellites have a design life of three years, but the new GLONASS-M satellites currently being launched incorporated advanced engineering and have a design life of seven years. The new GLONASS-K satellites will have a design life up 10 to 12 years. Users in higher latitude areas, such as Canada, obtain better GLONASS derived dilution of Precision (DOP) than users of NAVTARS GPS. This is due to the high inclination angle of GLONASS.
Comparison: Click to and GLONASS GPS edit Master title style One of the major differences between the GPS and GLONASS satellite systems was the initial design life of their satellites. The latest GLONASS satellites have a design life of three years, but the new GLONASS-M satellites currently being launched incorporated advanced engineering and have a design life of seven years. The new GLONASS-K satellites will have a design life up 10 to 12 years. Users in higher latitude areas, such as Canada, obtain better GLONASS derived dilution of Precision (DOP) than users of NAVTARS GPS. This is due to the high inclination angle of GLONASS.
 Click to and GALILEO Comparison: GPSedit Master title style t To reach the maximum precision of satellite based navigation, carrier phase observations are used to calculate the position and velocity of the antenna: Comparing Galileo and GPS, no tremendous increase of precision can be expected, however, Galileo offers some benefits with the introduction of more than two carrier phases which is known as Triple Carrier Ambiguity Resolution (TCAR) t Galileo will provide a highly accurate, guaranteed global positioning service under civilian control, as opposed to military control as NAVTARS GPS.
Click to and GALILEO Comparison: GPSedit Master title style t To reach the maximum precision of satellite based navigation, carrier phase observations are used to calculate the position and velocity of the antenna: Comparing Galileo and GPS, no tremendous increase of precision can be expected, however, Galileo offers some benefits with the introduction of more than two carrier phases which is known as Triple Carrier Ambiguity Resolution (TCAR) t Galileo will provide a highly accurate, guaranteed global positioning service under civilian control, as opposed to military control as NAVTARS GPS.
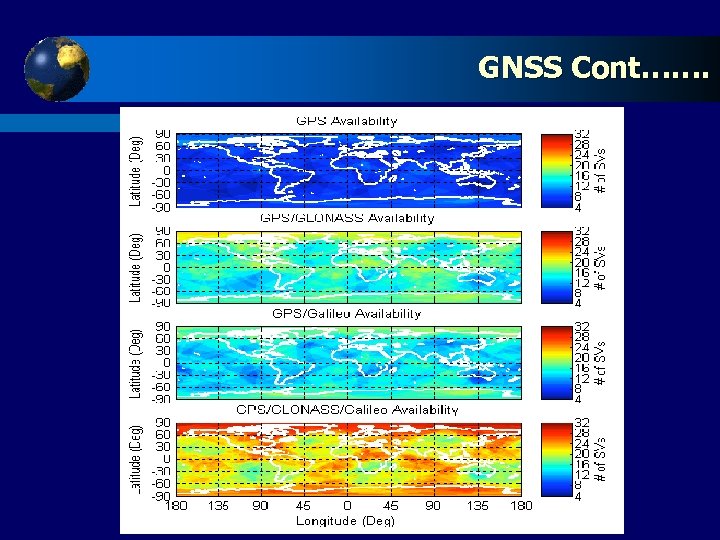
 Click System (GNSS) Global Navigation Satellite to edit Master title style t t With the future of Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) being almost certain to include the modernized U. S. GPS, the restored Russian GLONASS and the developing Galileo system of the European Commission (EC) it is prudent to investigate the levels of integrity that can be expected. Advantages of GNSS or Reasons for the formation of GNSS: t t t Improved satellite availability and hence improve accuracy in Positioning. Comparison between Satellite Availability for the standalone GPS, combined GPS/GLONASS, GPS/Galileo and GPS/GLONASS/Galileo constellations. The GPS/GLONASS and GPS/Galileo scenarios exhibit similar results, however, the GPS/Galileo system is slightly better due to 6 more satellites in the Galileo constellation in comparison with GLONASS.
Click System (GNSS) Global Navigation Satellite to edit Master title style t t With the future of Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) being almost certain to include the modernized U. S. GPS, the restored Russian GLONASS and the developing Galileo system of the European Commission (EC) it is prudent to investigate the levels of integrity that can be expected. Advantages of GNSS or Reasons for the formation of GNSS: t t t Improved satellite availability and hence improve accuracy in Positioning. Comparison between Satellite Availability for the standalone GPS, combined GPS/GLONASS, GPS/Galileo and GPS/GLONASS/Galileo constellations. The GPS/GLONASS and GPS/Galileo scenarios exhibit similar results, however, the GPS/Galileo system is slightly better due to 6 more satellites in the Galileo constellation in comparison with GLONASS.
 GNSS Cont……. Click to edit Master title style
GNSS Cont……. Click to edit Master title style
 GPS + Click to edit Master title style GLONASS receivers t Ashtech’s GG 24 receiver is the world’s first fully integrated GPS+GLONASS receiver. t LAIPAC System’s: TF 50 GPS + GLONASS receiver. t GPS/GLONASS Receiver(ARGO-16) t Javad Navigation Systems t Leica t Nov. Atel t Trimble t Topcon’s GMS-2
GPS + Click to edit Master title style GLONASS receivers t Ashtech’s GG 24 receiver is the world’s first fully integrated GPS+GLONASS receiver. t LAIPAC System’s: TF 50 GPS + GLONASS receiver. t GPS/GLONASS Receiver(ARGO-16) t Javad Navigation Systems t Leica t Nov. Atel t Trimble t Topcon’s GMS-2
 Click to edit Master title style GALILEO, GALILEO+GPS receivers t Whistler GPS 100 Galileo Global Positioning System (GPS 100, GPS 100) SKU: GPS 100 Brand: Whistler t t GSTB_V 2 Galileo Experimental Test Receiver (GETR) Available since 2004 Galileo TUR (Test User Receiver) Under Development (GPS
Click to edit Master title style GALILEO, GALILEO+GPS receivers t Whistler GPS 100 Galileo Global Positioning System (GPS 100, GPS 100) SKU: GPS 100 Brand: Whistler t t GSTB_V 2 Galileo Experimental Test Receiver (GETR) Available since 2004 Galileo TUR (Test User Receiver) Under Development (GPS
 GALILEO, GALILEO+GPS receivers Click to edit Master title style t t t GAMMA: Assisted Galileo/GPS/EGNOS Mass Market Receiver http: //www. gamma-project. info ARTUS: Advanced Receiver Terminal for User Services http: //www. artus-gju. org/ GR POSTER: Galileo Ready Positioning Terminal http: //www. st. com/stonline/galileo/index. htm GREAT: Galileo Receiver for mass market –Advanced technologies for Mass Market Receivers http: //www. greatproject. org SWIRLS: Development of a professional Galileo-GPS receiver http: //www. swirls-gju. com/index. htm
GALILEO, GALILEO+GPS receivers Click to edit Master title style t t t GAMMA: Assisted Galileo/GPS/EGNOS Mass Market Receiver http: //www. gamma-project. info ARTUS: Advanced Receiver Terminal for User Services http: //www. artus-gju. org/ GR POSTER: Galileo Ready Positioning Terminal http: //www. st. com/stonline/galileo/index. htm GREAT: Galileo Receiver for mass market –Advanced technologies for Mass Market Receivers http: //www. greatproject. org SWIRLS: Development of a professional Galileo-GPS receiver http: //www. swirls-gju. com/index. htm
 Click to edit Master title style Other & Upcoming Positioning Systems: t t t Beidou navigation system: China has planned to develop a truly global satellite navigation system consisting of 35 satellites (known as Compass or Beidou-2). GPS Aided Geo Augmented Navigation (GAGAN) is a planned implementation of a Satellite Based Augmentation System (SBAS) by the Indian government. (Gagan means sky. ) Indian Regional Navigational Satellite System (IRNSS): It is a developmental autonomous regional satellite navigation system that is being constructed with a constellation of 7 satellites. Expected to be functional by 2012. Doppler Orbitography and Radio-positioning Integrated by Satellite (DORIS): It is a French precision system developed for precise orbit determination and precise ground location. The Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS): It is a proposed three-satellite
Click to edit Master title style Other & Upcoming Positioning Systems: t t t Beidou navigation system: China has planned to develop a truly global satellite navigation system consisting of 35 satellites (known as Compass or Beidou-2). GPS Aided Geo Augmented Navigation (GAGAN) is a planned implementation of a Satellite Based Augmentation System (SBAS) by the Indian government. (Gagan means sky. ) Indian Regional Navigational Satellite System (IRNSS): It is a developmental autonomous regional satellite navigation system that is being constructed with a constellation of 7 satellites. Expected to be functional by 2012. Doppler Orbitography and Radio-positioning Integrated by Satellite (DORIS): It is a French precision system developed for precise orbit determination and precise ground location. The Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS): It is a proposed three-satellite
 Click to edit Master title style Conclusions t t Galileo is not yet available, but it has already influenced the accelerated modernization of GPS and GLONASS. Recent launches of new satellites in the GLONASS GPS system may lead to the establishment of a second fully functional GPS system in the near future. These developments have many potential advantages for not only the data collection aspects for GPS users, but also for the development of new applications using GIS worldwide. Potential areas of growth using these coupled systems will be associated with new applications, hardware and software, analysis techniques and will require additional training for GIS professionals.
Click to edit Master title style Conclusions t t Galileo is not yet available, but it has already influenced the accelerated modernization of GPS and GLONASS. Recent launches of new satellites in the GLONASS GPS system may lead to the establishment of a second fully functional GPS system in the near future. These developments have many potential advantages for not only the data collection aspects for GPS users, but also for the development of new applications using GIS worldwide. Potential areas of growth using these coupled systems will be associated with new applications, hardware and software, analysis techniques and will require additional training for GIS professionals.
 Click to edit References Master title style t t Eissfeller et al. , 2007. Performance of GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo. www. ifp. unistuttgart. de/publications/phowo 07/220 Eissfeller. pdf European Space Agency – ESA – Galileo Navigation http: //www. esa. int/esa. NA/galileo. html William Martin and Frank van Diggelen, “GPS+GLONASS Technology”, Geomatics Info Magazine, April 1997, pp. 73 -75 GPS +GALILEO receivers http: //galileo. cs. telespazio. it/metis/public/METIS%20 Morocco%20 Master%20 Training%20&%20 Seminar/Proceedings/8%20 EGNOS_GALILEO_Receivers%20 PS%20 VF. ppt t GPS World Magazine: Other GPS and GNSS Sites. http: //sidt. gpsworld. com/gpssidt/static. Html. jsp? id=4071 08
Click to edit References Master title style t t Eissfeller et al. , 2007. Performance of GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo. www. ifp. unistuttgart. de/publications/phowo 07/220 Eissfeller. pdf European Space Agency – ESA – Galileo Navigation http: //www. esa. int/esa. NA/galileo. html William Martin and Frank van Diggelen, “GPS+GLONASS Technology”, Geomatics Info Magazine, April 1997, pp. 73 -75 GPS +GALILEO receivers http: //galileo. cs. telespazio. it/metis/public/METIS%20 Morocco%20 Master%20 Training%20&%20 Seminar/Proceedings/8%20 EGNOS_GALILEO_Receivers%20 PS%20 VF. ppt t GPS World Magazine: Other GPS and GNSS Sites. http: //sidt. gpsworld. com/gpssidt/static. Html. jsp? id=4071 08
 Click to edit Master title style Any questions Thank You
Click to edit Master title style Any questions Thank You


