366cfe79ce464d9e1d658b9949424745.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 Comparison of Clinical Parameters for Proton Therapy in the United States Paige Summers, MS
Comparison of Clinical Parameters for Proton Therapy in the United States Paige Summers, MS
 Disclosure • This project is supported by the Federal Share of program income earned by Massachusetts General Hospital on C 06 CA 059267, Proton Therapy Research and Treatment Center and by grants CA 10953 and CA 81647 (NCI, DHHS).
Disclosure • This project is supported by the Federal Share of program income earned by Massachusetts General Hospital on C 06 CA 059267, Proton Therapy Research and Treatment Center and by grants CA 10953 and CA 81647 (NCI, DHHS).
 RPC Background • Funded by the NCI, tasked with ensuring that radiotherapy institutions participating in clinical trials deliver clinically comparable and consistent doses • Asked to develop monitoring program for proton therapy facilities too
RPC Background • Funded by the NCI, tasked with ensuring that radiotherapy institutions participating in clinical trials deliver clinically comparable and consistent doses • Asked to develop monitoring program for proton therapy facilities too
 Proton Therapy Facilities • Monitored by RPC: • 10 clinical sites • 1 international site in Japan NJ 2012 • Forecast ~20 new centers • Will likely see increase in clinical trials with proton therapy, making comparability important Shizuoka 2003
Proton Therapy Facilities • Monitored by RPC: • 10 clinical sites • 1 international site in Japan NJ 2012 • Forecast ~20 new centers • Will likely see increase in clinical trials with proton therapy, making comparability important Shizuoka 2003
 Proton Approval Steps • Proton facility questionnaire • Annual monitoring of beam calibrations by the RPC • Ability to electronically transfer treatment plans • Irradiation of RPC’s baseline proton phantoms • On-site dosimetry review visit
Proton Approval Steps • Proton facility questionnaire • Annual monitoring of beam calibrations by the RPC • Ability to electronically transfer treatment plans • Irradiation of RPC’s baseline proton phantoms • On-site dosimetry review visit
 Information Collected by the RPC • Typical review components: • Dosimetry equipment calibration • CT scanner, CTN/RSP conversion • Patient immobilization • Treatment planning procedures • QA documentation
Information Collected by the RPC • Typical review components: • Dosimetry equipment calibration • CT scanner, CTN/RSP conversion • Patient immobilization • Treatment planning procedures • QA documentation
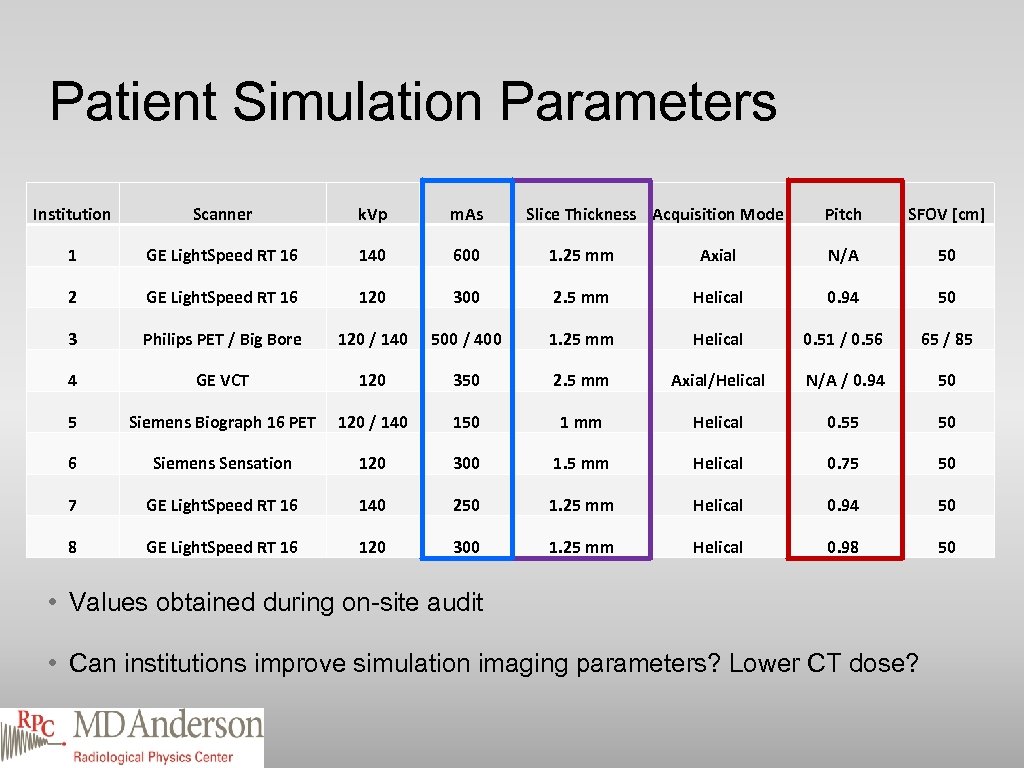 Patient Simulation Parameters Institution Scanner k. Vp m. As Slice Thickness Acquisition Mode Pitch SFOV [cm] 1 GE Light. Speed RT 16 140 600 1. 25 mm Axial N/A 50 2 GE Light. Speed RT 16 120 300 2. 5 mm Helical 0. 94 50 3 Philips PET / Big Bore 120 / 140 500 / 400 1. 25 mm Helical 0. 51 / 0. 56 65 / 85 4 GE VCT 120 350 2. 5 mm Axial/Helical N/A / 0. 94 50 5 Siemens Biograph 16 PET 120 / 140 150 1 mm Helical 0. 55 50 6 Siemens Sensation 120 300 1. 5 mm Helical 0. 75 50 7 GE Light. Speed RT 16 140 250 1. 25 mm Helical 0. 94 50 8 GE Light. Speed RT 16 120 300 1. 25 mm Helical 0. 98 50 • Values obtained during on-site audit • Can institutions improve simulation imaging parameters? Lower CT dose?
Patient Simulation Parameters Institution Scanner k. Vp m. As Slice Thickness Acquisition Mode Pitch SFOV [cm] 1 GE Light. Speed RT 16 140 600 1. 25 mm Axial N/A 50 2 GE Light. Speed RT 16 120 300 2. 5 mm Helical 0. 94 50 3 Philips PET / Big Bore 120 / 140 500 / 400 1. 25 mm Helical 0. 51 / 0. 56 65 / 85 4 GE VCT 120 350 2. 5 mm Axial/Helical N/A / 0. 94 50 5 Siemens Biograph 16 PET 120 / 140 150 1 mm Helical 0. 55 50 6 Siemens Sensation 120 300 1. 5 mm Helical 0. 75 50 7 GE Light. Speed RT 16 140 250 1. 25 mm Helical 0. 94 50 8 GE Light. Speed RT 16 120 300 1. 25 mm Helical 0. 98 50 • Values obtained during on-site audit • Can institutions improve simulation imaging parameters? Lower CT dose?
![Treatment Margins • Described by institution in facility questionnaire Site-Specific Lateral Margins [mm] Penetration Treatment Margins • Described by institution in facility questionnaire Site-Specific Lateral Margins [mm] Penetration](https://present5.com/presentation/366cfe79ce464d9e1d658b9949424745/image-8.jpg) Treatment Margins • Described by institution in facility questionnaire Site-Specific Lateral Margins [mm] Penetration Uncertainty Margins Brain H&N Abdomen Pelvis Institution 1 2. 5 3 5 5 Institution 1 3% Institution 2 3 3 5 5 Institution 2 3. 5% + 3 mm Institution 3 3 3 5 5 -8 Institution 3 1. 50% Institution 4 5 7 7 -9 7 Institution 4 3. 5% + 3 mm Institution 5 2 2 Institution 5 2 mm Institution 6 3 3 5 -7 5 - 10 Institution 6 3. 5% + 3 mm Institution 7 5 5 Institution 7 1% + 1 mm Institution 8 3 3 -5 5 - 10 3 -5 Institution 8 1. 5% + 1. 5 mm Institution 9 2 2 5 5 Institution 9 - Institution 10 3 5 5 5 Institution 10 1% + 1 mm Institution 11 5 5 10 10 Institution 11 3. 5% + 3 mm
Treatment Margins • Described by institution in facility questionnaire Site-Specific Lateral Margins [mm] Penetration Uncertainty Margins Brain H&N Abdomen Pelvis Institution 1 2. 5 3 5 5 Institution 1 3% Institution 2 3 3 5 5 Institution 2 3. 5% + 3 mm Institution 3 3 3 5 5 -8 Institution 3 1. 50% Institution 4 5 7 7 -9 7 Institution 4 3. 5% + 3 mm Institution 5 2 2 Institution 5 2 mm Institution 6 3 3 5 -7 5 - 10 Institution 6 3. 5% + 3 mm Institution 7 5 5 Institution 7 1% + 1 mm Institution 8 3 3 -5 5 - 10 3 -5 Institution 8 1. 5% + 1. 5 mm Institution 9 2 2 5 5 Institution 9 - Institution 10 3 5 5 5 Institution 10 1% + 1 mm Institution 11 5 5 10 10 Institution 11 3. 5% + 3 mm
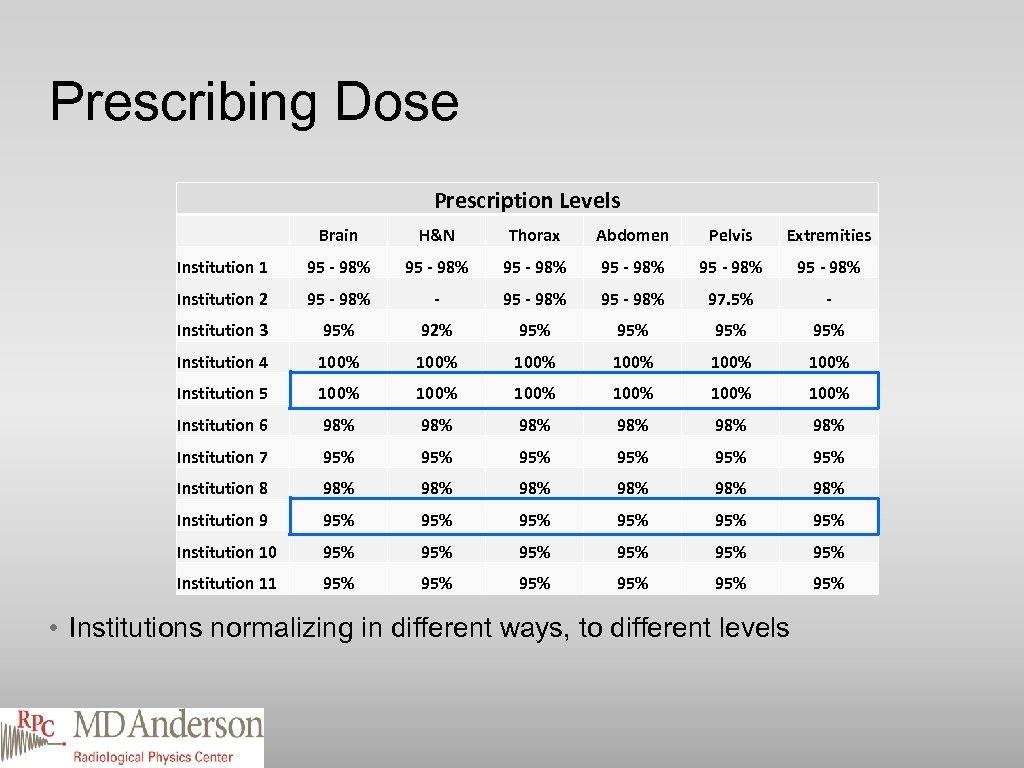 Prescribing Dose Prescription Levels Brain H&N Thorax Abdomen Pelvis Extremities Institution 1 95 - 98% 95 - 98% Institution 2 95 - 98% - 95 - 98% 97. 5% - Institution 3 95% 92% 95% 95% Institution 4 100% 100% Institution 5 100% 100% Institution 6 98% 98% 98% Institution 7 95% 95% 95% Institution 8 98% 98% 98% Institution 9 95% 95% 95% Institution 10 95% 95% 95% Institution 11 95% 95% 95% • Institutions normalizing in different ways, to different levels
Prescribing Dose Prescription Levels Brain H&N Thorax Abdomen Pelvis Extremities Institution 1 95 - 98% 95 - 98% Institution 2 95 - 98% - 95 - 98% 97. 5% - Institution 3 95% 92% 95% 95% Institution 4 100% 100% Institution 5 100% 100% Institution 6 98% 98% 98% Institution 7 95% 95% 95% Institution 8 98% 98% 98% Institution 9 95% 95% 95% Institution 10 95% 95% 95% Institution 11 95% 95% 95% • Institutions normalizing in different ways, to different levels
 Significance • Differences exits across centers • Task groups focusing on QA, papers on outcomes – not many recommendations about clinical parameters - could use more recommendations from experienced proton centers • Important to consider variation of dosimetric parameters in planning clinical trials – proton alone or mixed modality
Significance • Differences exits across centers • Task groups focusing on QA, papers on outcomes – not many recommendations about clinical parameters - could use more recommendations from experienced proton centers • Important to consider variation of dosimetric parameters in planning clinical trials – proton alone or mixed modality
 Questions? ? ?
Questions? ? ?
 Proton Approval Steps • Proton facility questionnaire • Annual monitoring of beam calibrations by the RPC • Ability to electronically transfer treatment plans • Successful irradiation of RPC’s baseline proton phantoms • Successful completion of on-site dosimetry review visit
Proton Approval Steps • Proton facility questionnaire • Annual monitoring of beam calibrations by the RPC • Ability to electronically transfer treatment plans • Successful irradiation of RPC’s baseline proton phantoms • Successful completion of on-site dosimetry review visit
 Facility Questionnaire • AAPM Proton Advisory group aids RPC & QARC in updating proton facility questionnaire • Submitted to QARC via email or paper – copy sent to RPC • Questions covered: • Experiences in the clinic • Dose calibration & verification • Proton beam production & delivery • Treatment Planning • Immobilization • Patient Alignment • QA
Facility Questionnaire • AAPM Proton Advisory group aids RPC & QARC in updating proton facility questionnaire • Submitted to QARC via email or paper – copy sent to RPC • Questions covered: • Experiences in the clinic • Dose calibration & verification • Proton beam production & delivery • Treatment Planning • Immobilization • Patient Alignment • QA
 RPC Proton Site Visits • Typical site visit measurements • Beam calibration comparison – RPC/Inst • CAX lateral and depth dose profiles for reference and patient fields • Scanning beam – less fields tested, more profiles obtained • X-ray system measurements • TLD measurements
RPC Proton Site Visits • Typical site visit measurements • Beam calibration comparison – RPC/Inst • CAX lateral and depth dose profiles for reference and patient fields • Scanning beam – less fields tested, more profiles obtained • X-ray system measurements • TLD measurements


