Comparing two means.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 20

Comparing two means Ksusha Steblovskaya

What we already know… Doing an experiment, we - manipulate the ID - observe, measure, record the DV - control confounds We can use: - between-group design - within-group design
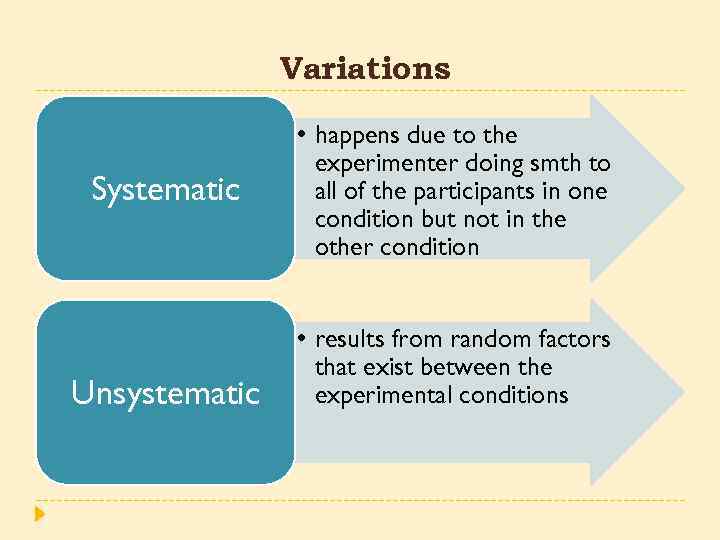
Variations Systematic Unsystematic • happens due to the experimenter doing smth to all of the participants in one condition but not in the other condition • results from random factors that exist between the experimental conditions
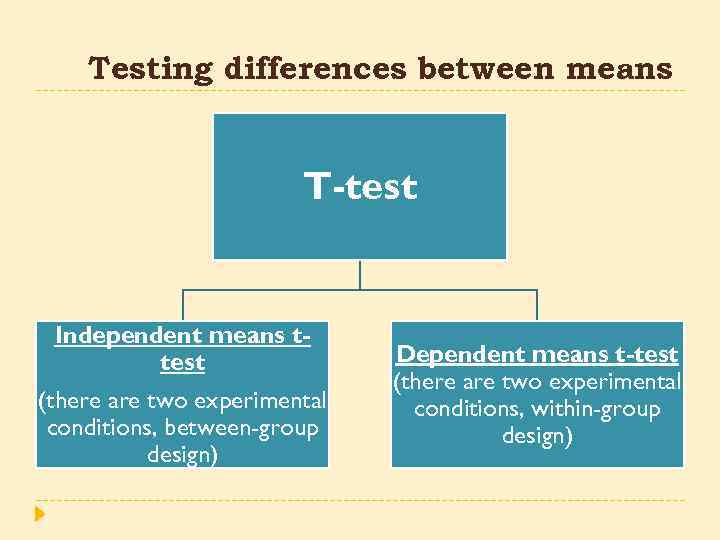
Testing differences between means T-test Independent means ttest (there are two experimental conditions, between-group design) Dependent means t-test (there are two experimental conditions, within-group design)

Rationale 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. Two samples of data are collected and the sample means calculated; If samples come from the same population, we expect the means to be roughly equal; H 0: experimental manipulation has no effect on the participants - the sample means are to be very similar; We compare the difference between the sample means that we collected to the difference between the sample means that we would expect to obtain; If the SE is large, two scenarios are possible: we collected two samples that are atypical of the population from which they came; these samples came from different populations - H 0 is incorrect; H 0 is rejected - H 1 (the experimental hypothesis): the two sample means differ because of the different experimental manipulations imposed on each sample.

Assumptions (for both t-tests): Data are from normally distributed populations; Data are measured at least at the interval level. + For independent t-test: § Variance in the populations are roughly equal § Scores are independent General formula
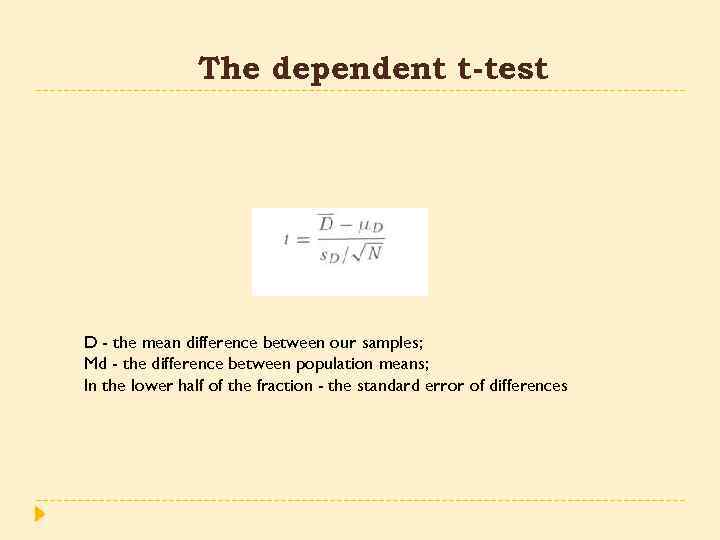
The dependent t-test D - the mean difference between our samples; Md - the difference between population means; In the lower half of the fraction - the standard error of differences
SPSS AND T-test
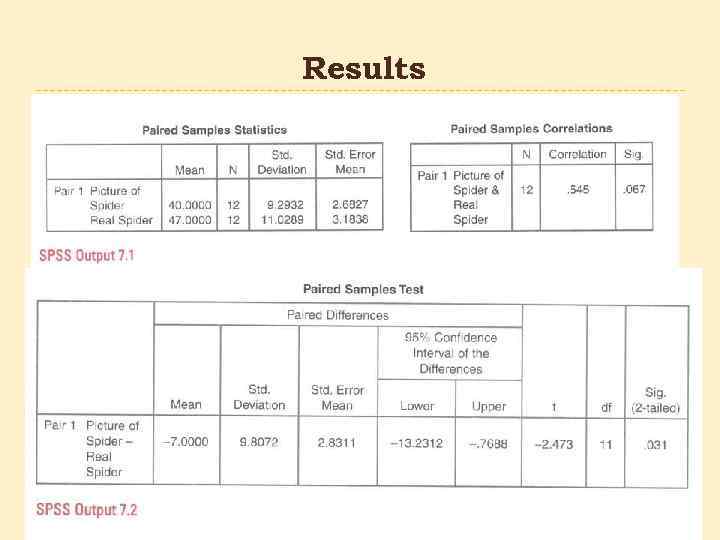
Results

How to report the results Effect size On average, participants experienced significantly greater anxiety to real spiders (M=47. 00, SE=3. 18), than to pictures of spiders (M=40. 00, SE=2. 68, t(11)=-2. 43, p<. 05, r=. 60).
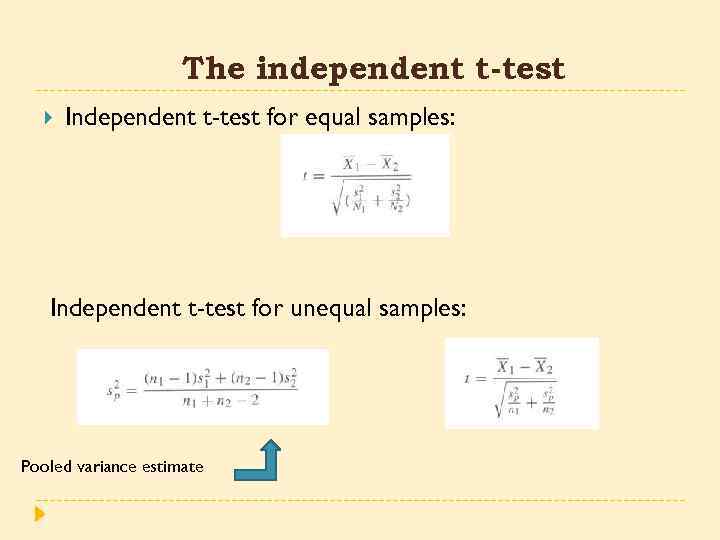
The independent t-test Independent t-test for equal samples: Independent t-test for unequal samples: Pooled variance estimate
The independent t-test and SPSS
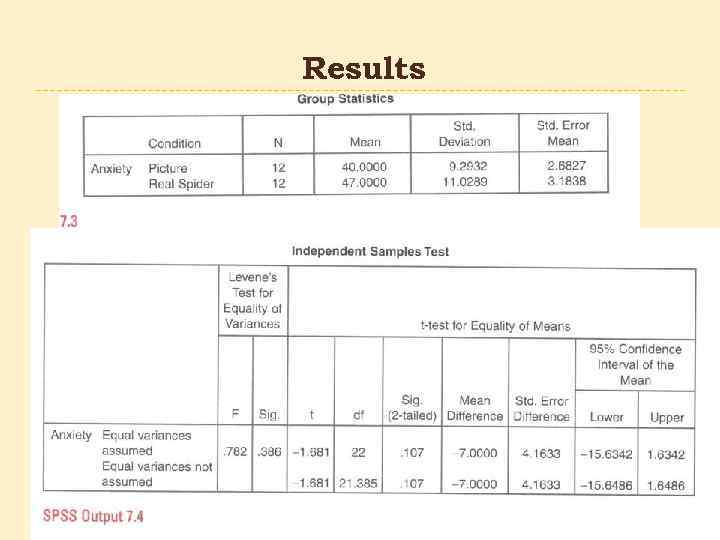
Results

Reporting the results On average, participants experienced greater anxiety to real spiders (M=47. 00, SE=3. 18), than to pictures of spiders (M=40. 00, SE=2, 68). This difference was not significant t(22)=-1. 68, p>. 05; however, it represented a medium size effect r=. 34.

Thank you for your attention and good luck!
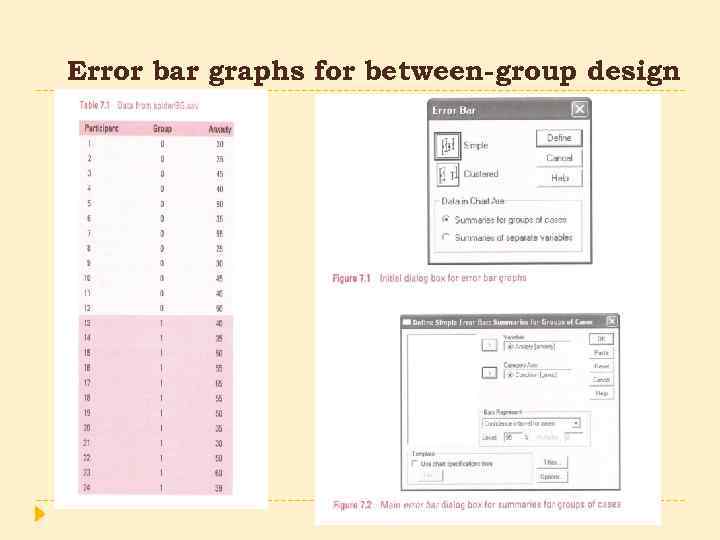
Error bar graphs for between-group design
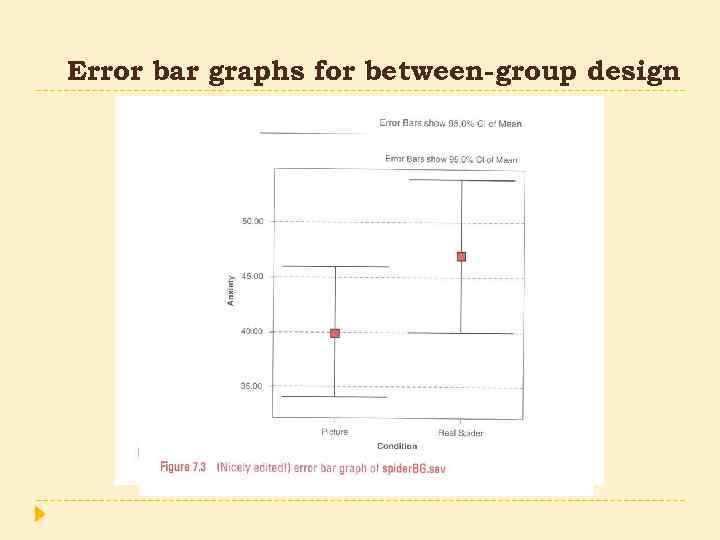
Error bar graphs for between-group design
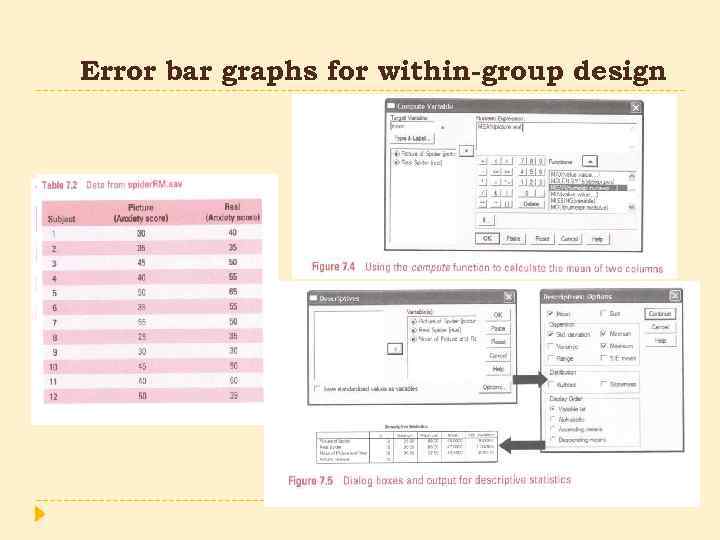
Error bar graphs for within-group design

Error bar graphs for within-group design
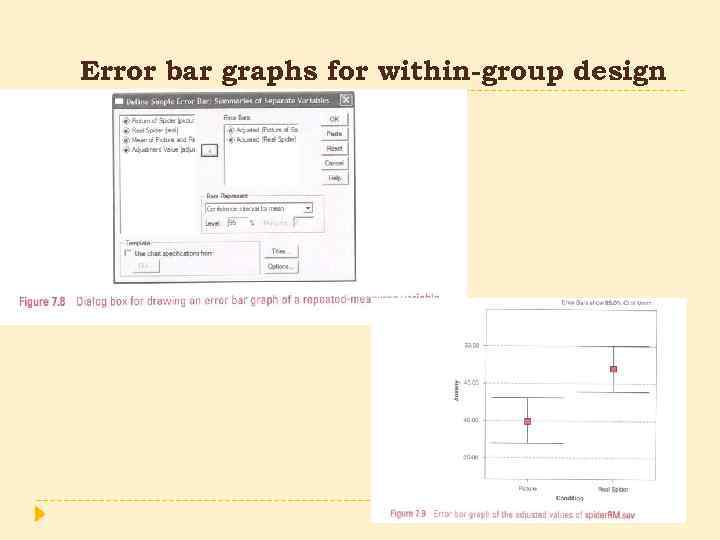
Error bar graphs for within-group design
Comparing two means.pptx