 Company grouping • Provides framework for understanding a firm • Insight about the firm’s potential growth, risks, competition, etc. • Identify industries that are undervalued or overvalued (in active management – industry rotation base on the current phase of the business cycle)
Company grouping • Provides framework for understanding a firm • Insight about the firm’s potential growth, risks, competition, etc. • Identify industries that are undervalued or overvalued (in active management – industry rotation base on the current phase of the business cycle)
 Company grouping • By products and services – principal business activity Examples: Global Industry Classification Standard (GICS), Russell Global Sectors (RGS) • Sensitivity to business cycles – cyclical & non-cyclical • Statistical methods
Company grouping • By products and services – principal business activity Examples: Global Industry Classification Standard (GICS), Russell Global Sectors (RGS) • Sensitivity to business cycles – cyclical & non-cyclical • Statistical methods
 Industry classification systems • Commercial classifications: • Basic materials and processing • Consumer discretionary • Consumer staples • Energy • Financial services • Health care • Industrial and producer durables • Technology • Telecom
Industry classification systems • Commercial classifications: • Basic materials and processing • Consumer discretionary • Consumer staples • Energy • Financial services • Health care • Industrial and producer durables • Technology • Telecom
 Government classifications • International Standard Industrial Classification of All Economic Activities • Statistical Classification of Economic Activities in the European Community • Australian and New Zealand Standard Industrial Classification • North American Industry Classification System
Government classifications • International Standard Industrial Classification of All Economic Activities • Statistical Classification of Economic Activities in the European Community • Australian and New Zealand Standard Industrial Classification • North American Industry Classification System
 Industry descriptors • Cyclical firm – earnings highly dependent on the stage of business cycle; high earnings volatility and high operating leverage. Basic materials and processing, consumer discretionary, energy, financial services, industrial and producer durables, technology • Non-cyclical – produces goods and services for which demand is relatively stable over the business cycle. Health care, utilities, telecoms, consumer staples
Industry descriptors • Cyclical firm – earnings highly dependent on the stage of business cycle; high earnings volatility and high operating leverage. Basic materials and processing, consumer discretionary, energy, financial services, industrial and producer durables, technology • Non-cyclical – produces goods and services for which demand is relatively stable over the business cycle. Health care, utilities, telecoms, consumer staples
 Industry descriptors (contd. ) • Defensive – least affected by the stage of the business cycle and include utilities, consumer staples (such as food producers) • Growth industries have demand so strong they are largelty unaffected by the stage of business cycle
Industry descriptors (contd. ) • Defensive – least affected by the stage of the business cycle and include utilities, consumer staples (such as food producers) • Growth industries have demand so strong they are largelty unaffected by the stage of business cycle
 Peer groups • A set of similar companies that can be used for valuation comparisons • Similar business activities, demand drivers, cost structure drivers, availability of capital
Peer groups • A set of similar companies that can be used for valuation comparisons • Similar business activities, demand drivers, cost structure drivers, availability of capital
 Thorough industry analysis • Evaluate the relationships between macroeconomic variables and industry trends • Estimate industry variables • Determine the relative valuation of different industries • Analyze industry prospects based on strategic groups • Classify industry by life-cycle stage • Position the industry on the experience curve (cost per unit relative to output) • Consider the forces that affect the industry • Examine the forces that determine competition
Thorough industry analysis • Evaluate the relationships between macroeconomic variables and industry trends • Estimate industry variables • Determine the relative valuation of different industries • Analyze industry prospects based on strategic groups • Classify industry by life-cycle stage • Position the industry on the experience curve (cost per unit relative to output) • Consider the forces that affect the industry • Examine the forces that determine competition
 Influences on industry • Macroeconomic factors • Technology • Demography • Governments • Social influences
Influences on industry • Macroeconomic factors • Technology • Demography • Governments • Social influences
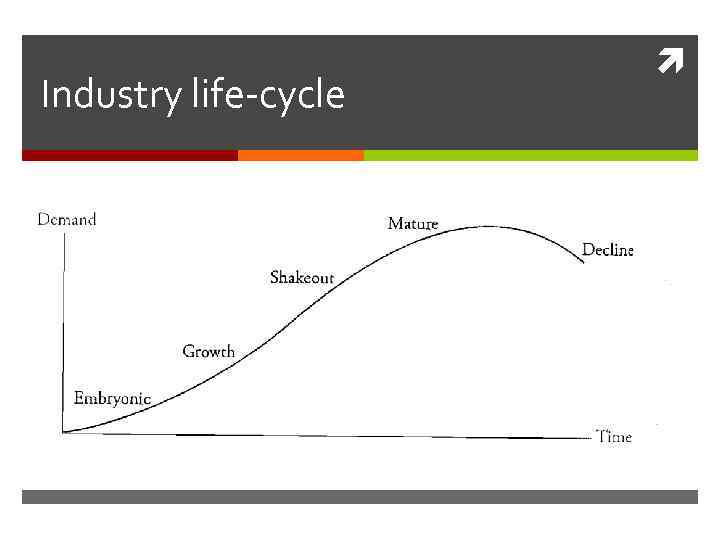 Industry life-cycle
Industry life-cycle
 Industry life-cycle (contd. ) • Embryonic stage – slow growth, high prices, large investment required, high risk of failure • Growth stage – rapid growth, limited competitive pressures, falling prices, increasing profitability • Shakeout stage - growth slowing, intense competition, increasing industry overcapacity, declining profitability, increased cost cutting, increased failures • Matured stage – slow growth, consolidation, high barriers to entry, stable pricing, superior firms gain market share • Decline stage – negative growth, declining prices, consolidation
Industry life-cycle (contd. ) • Embryonic stage – slow growth, high prices, large investment required, high risk of failure • Growth stage – rapid growth, limited competitive pressures, falling prices, increasing profitability • Shakeout stage - growth slowing, intense competition, increasing industry overcapacity, declining profitability, increased cost cutting, increased failures • Matured stage – slow growth, consolidation, high barriers to entry, stable pricing, superior firms gain market share • Decline stage – negative growth, declining prices, consolidation