bac618515b02834431b7831b59e6126f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

COMP 7580: E-Transformation in Business 1. Introduction: From Net Commerce to e-Enterprise and e-Government Dickson K. W. Chiu Ph. D, SMIEEE (Thanks to Dr William Cheung) 1

Learning Objectives n n n To introduce e-Transformation in Business To clarify different views of e-Commerce / e-Business To understand the evolving aspects in different e-Transformation phases To overview e-Enterprise and business process reengineering To overview e-Government Dickson Chiu 2008 2

1. 1 e-Transformation in Business 3

Vending Machine On-line n n What are transformed? How are they transformed? Why do they need to be transformed? Who will be affected in what ways? Transforming a vending machine… Dickson Chiu 2008 4

e-Business – What are transformed? n Form of information and documents n n E. g. , invoice, customer information, contract, product catalog, company news, payment records, … Processes for managing, analyzing and using them n n Functional perspective: accounting, sales and marketing, production, design, human resource, … Organizational perspective: Operational, Knowledge, Management and Strategy Dickson Chiu 2008 5
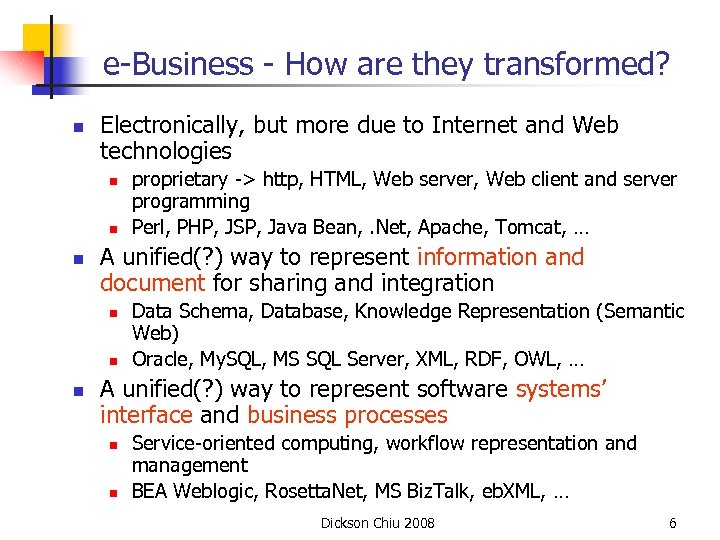
e-Business - How are they transformed? n Electronically, but more due to Internet and Web technologies n n n A unified(? ) way to represent information and document for sharing and integration n proprietary -> http, HTML, Web server, Web client and server programming Perl, PHP, JSP, Java Bean, . Net, Apache, Tomcat, … Data Schema, Database, Knowledge Representation (Semantic Web) Oracle, My. SQL, MS SQL Server, XML, RDF, OWL, … A unified(? ) way to represent software systems’ interface and business processes n n Service-oriented computing, workflow representation and management BEA Weblogic, Rosetta. Net, MS Biz. Talk, eb. XML, … Dickson Chiu 2008 6

e-Business – Who will be affected in what ways? n Clients/Customers (e. g. , personalized services) n n n Company staff (e. g. , decision support systems) n n n Cost: New experience (UI, security) Benefit: More competitive price, better services/products, better after-sales support -> better “customer experience” Cost: New experience and operation (UI, security) Benefit: higher productivity, fast decision & response Business partners (e. g. , SCM systems) n n Cost: New interface and operation (UI, security & trust) Benefit: more efficient communication, easier to establish business relationship dynamically, … Dickson Chiu 2008 7

e-Business – Why is the transformation needed n Stay competitive by value-adding … n n Operation Efficiency (for lowering the cost) Strategic Positioning (for raising the selling price) Dickson Chiu 2008 8

e-Transformation in Other Sectors n n What are transformed? How are they transformed? Why do they need to be transformed? Who will be affected in what ways? Can you repeat the same exercise for e-Government, e-Health? Dickson Chiu 2008 9

1. 2 Different Views 10

Limited Views on E-Commerce n Corporations n Electronic data interchange (EDI)? n n General public n n Electronic messages standard via a private network http: //www. pharogen. com/edi. asp#whatis http: //supplier. arvinmeritor. com/cvs_edi/ae/edi/TS 830_Exampl e_1. shtml (an example) Buying and selling on the Web? Association for Electronic Commerce n Doing business electronically? Call Centers? Dickson Chiu 2008 11
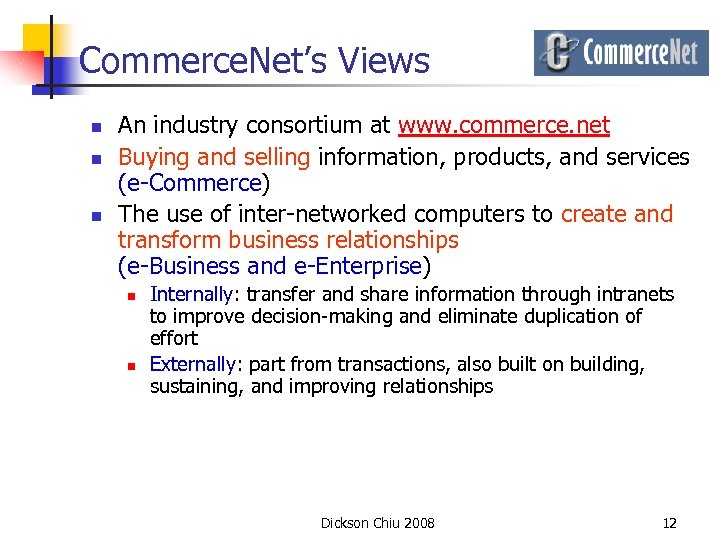
Commerce. Net’s Views n n n An industry consortium at www. commerce. net Buying and selling information, products, and services (e-Commerce) The use of inter-networked computers to create and transform business relationships (e-Business and e-Enterprise) n n Internally: transfer and share information through intranets to improve decision-making and eliminate duplication of effort Externally: part from transactions, also built on building, sustaining, and improving relationships Dickson Chiu 2008 12
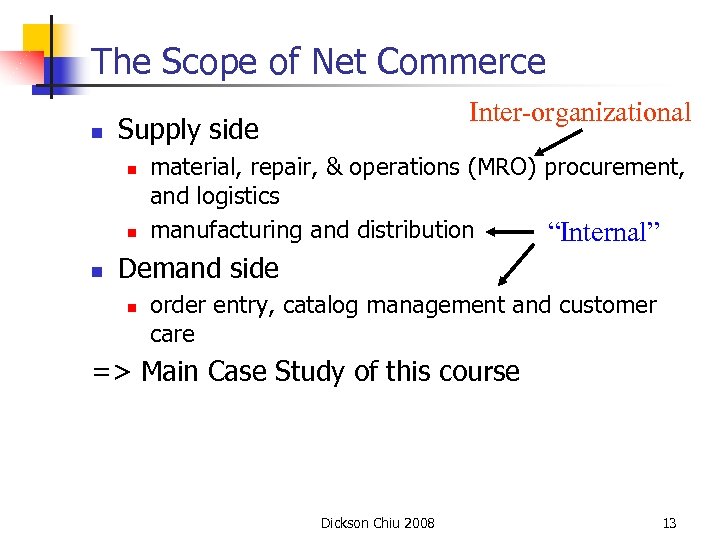
The Scope of Net Commerce n Supply side n n n Inter-organizational material, repair, & operations (MRO) procurement, and logistics manufacturing and distribution “Internal” Demand side n order entry, catalog management and customer care => Main Case Study of this course Dickson Chiu 2008 13

Vending Machine Again n n e-Commerce: Payment e-Business: n n n Machine -> Coca. Cola warehouse for refill CRM for where to put the machine and what to be sold Mobile payment solutions … Transforming a vending machine Dickson Chiu 2008 14

1. 3 Evolving aspects in different e -Transformation phases 15
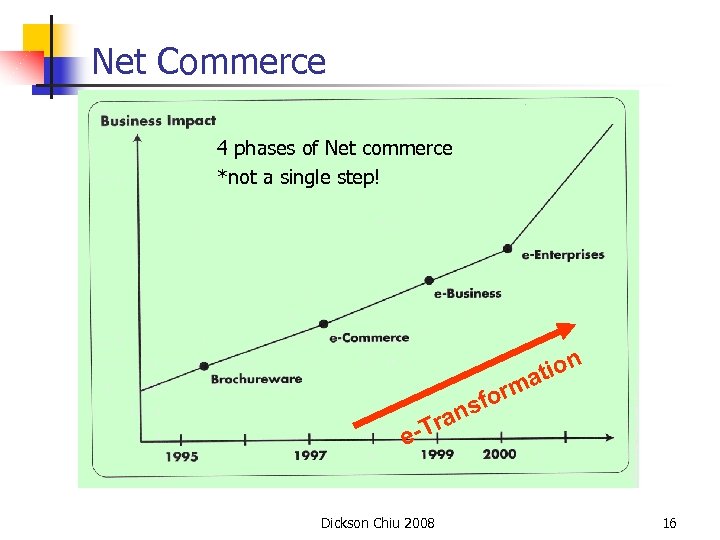
Net Commerce 4 phases of Net commerce *not a single step! atio n orm nsf Tra e- Dickson Chiu 2008 16

Evolving Aspects in e-Transformation n Business Models n n e-Application Categories n n How to accomplish… ? e-Application Functionalities n n What is to be accomplished? What is offered that helps to accomplish… ? To support the vision and strategy of the company n A Web-based system has no value by itself if it is not developed with a strategic plan Dickson Chiu 2008 17
Brochureware n Business Model (B 2 C) n Use the net as: n n n Customer interaction n n key medium for global marketing a low-cost repository of product and service information static documents and simple multimedia reading text view pictures Transactions are performed over traditional means Now, we still go the shops to buy most of our need… Dickson Chiu 2008 18

e-Commerce n n Focus on consumer transactions and interactions over the Internet Business Model n n Characterized by n n buying and selling to consumers online (B 2 C) the. com mania - lots of new companies operating online content-aggregation business model - focus on consumer founder and situation driven Some success factors n n Branding Marketing Personalization of service Creation of customer community Dickson Chiu 2008 19

e-Commerce Functionalities & Examples n e-Tailing and Consumer Portal (CDNOW): n n Bidding and Auctioning (e. Bay): n n online catalogs, bid boards, account management, and notification Consumer Care and Management (e-Trade): n n online catalogs, personalization, advertising, shopping carts, and online communities personalization, self-service, immediacy, and information Electronic Bill Payment (AT&T): n bill consolidation, analysis and reporting, payment processing, and integration Dickson Chiu 2008 20
e-Business n Business Model n n n Characterized by n n Focus on B 2 B applications over the Internet evolve from well-established brick-and-mortar companies seeking process improvement focus on an organization’s core competencies process aggregation oriented business model process-driven; also technology-driven Some success factors n n n create and integrate the right processes agile applications ability to integrate applications and data right organizational structure Means of overcoming political obstacles Dickson Chiu 2008 21

e-Business Functionalities & Examples n Virtual Marketplace (Dell) n n Procurement & Resource Management (Master. Card) n n Request for info, request for proposal, requisitioning, purchase orders, payment, and supplier management Extended Value Chain (Fed. Ex) n n Catalog, buying tools, integration, and payment option, . . Demand supply planning, logistics, and production planning Customer Relationship Management (HP) n Self-service, solution-center, personalization, and account management functionalities Dickson Chiu 2008 22
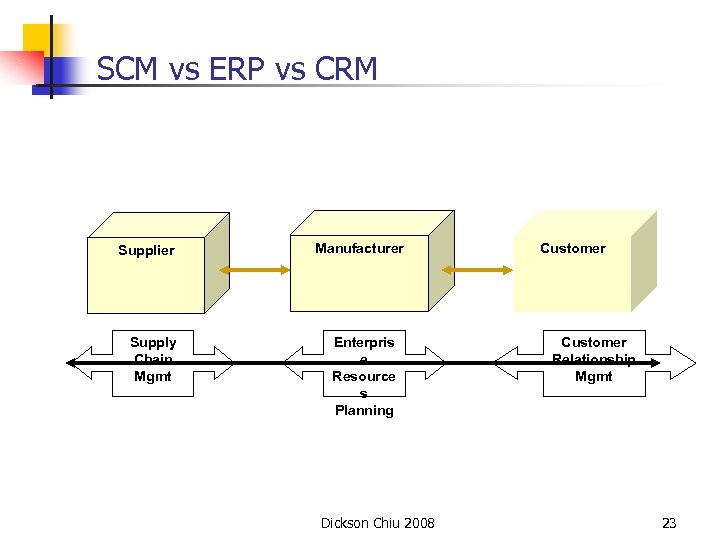
SCM vs ERP vs CRM Supplier Supply Chain Mgmt Manufacturer Enterpris e Resource s Planning Dickson Chiu 2008 Customer Relationship Mgmt 23
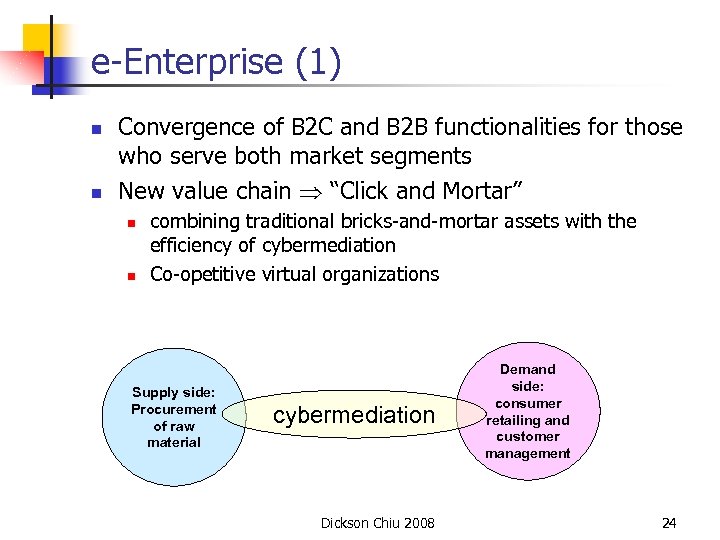
e-Enterprise (1) n n Convergence of B 2 C and B 2 B functionalities for those who serve both market segments New value chain “Click and Mortar” n n combining traditional bricks-and-mortar assets with the efficiency of cybermediation Co-opetitive virtual organizations Supply side: Procurement of raw material cybermediation Dickson Chiu 2008 Demand side: consumer retailing and customer management 24
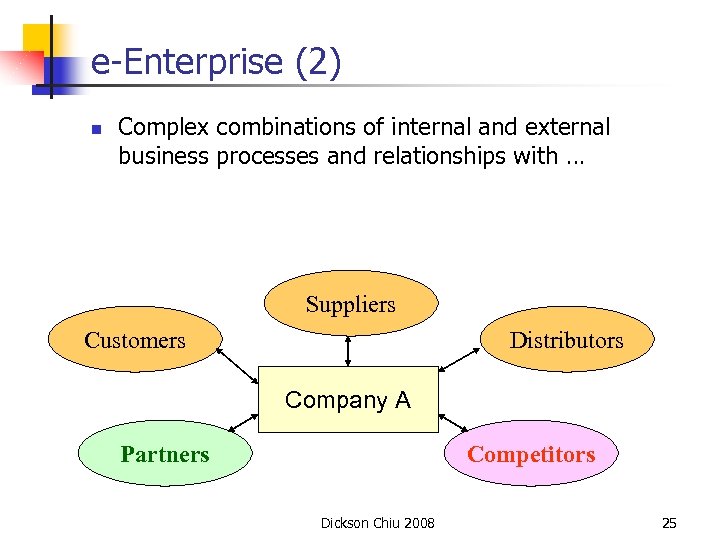
e-Enterprise (2) n Complex combinations of internal and external business processes and relationships with … Suppliers Customers Distributors Company A Partners Competitors Dickson Chiu 2008 25

e-Enterprise (3) n Business Model (B 2 C + B 2 B) n n Applications n n n Based on people (role) aggregation Focused on mission-critical, inter-organizational business processes CEO drives organizational changes Results come out via iterative and methodological efforts using technology (as an enabler and as a commodity ) Dickson Chiu 2008 26

e-Enterprise (4) n Value Proposition n n more than manufacturing techniques or prime location outlets Speed and Agility n n n Gained by leveraging existing asset base through the Net Example 1, Tim. Kin Corp. (bearings producer) n Self-service answers to customer about product availability and price (CRM) through linkage to the back-end inventory database -> 15 percent service reps moved to sales Example 2, Auto. Nation (automobile dealership network) n Use an on-line infrastructure to channel leads to its physical infrastructure of nationwise dealership. Dickson Chiu 2008 27

1. 4 e-Enterprise and Business Process Reengineering 28

Business Process Reengineering (BPR) n n A radical reinvention of how corporations do their work. Conventional BPR n n From business process automation to completely reengineering all the processes (NOT to follow the old way of doing things). Enabled by Web, XML, PKI, … n n n One can shift focus from internal to external process Dynamic, real-time information sharing become possible E. g. , How about from document exchange via emails (Push) to setting up VPN (Pull)? How about one-to-one marketing? Dickson Chiu 2008 29
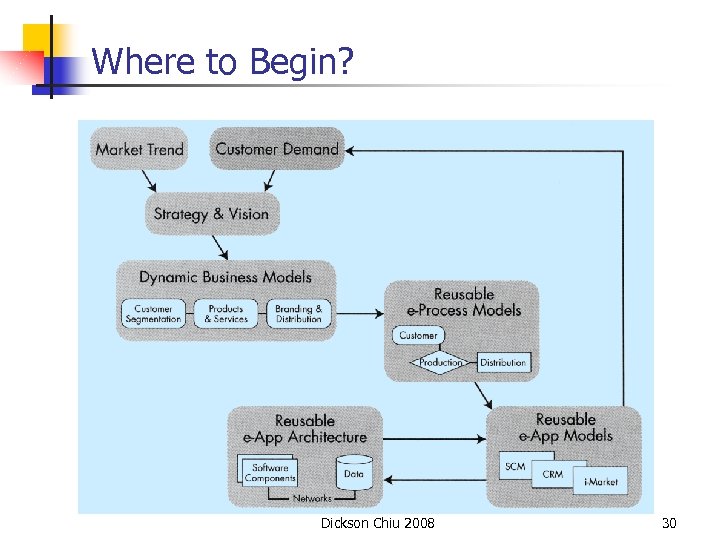
Where to Begin? Dickson Chiu 2008 30

References n Faisal Hoque, Business Models, Architecture, and Components, Chapter 1, Cambridge University Press, 2000 Dickson Chiu 2008 31

1. 5 e-Government 32

E-Government n n E-government: The use of IT and e-commerce to provide access to government information and delivery of public services to citizens and business partners Offers an opportunity to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the functions of government and to make governments more transparent to citizens and businesses by providing access to more of the information generated by government Dickson Chiu 2008 33

Government-to-citizens (G 2 C) n n E-government category that includes all the interactions between a government and its citizens Major features of government Web sites: n n phone and address information links to other sites publications databases Dickson Chiu 2008 34

G 2 C n Major areas of G 2 C activities: n n n n n (cont. ) tourism and recreation research and education downloadable forms discovery of government services information about public policy advice about health and safety issues Useful in solving constituents’ problems Netizen: A citizen surfing the Internet Electronic Benefits Transfer (EBT) n nationwide EBT system to deliver government benefits electronically deliver benefits to recipients’ bank accounts smart card system for those without bank accounts Dickson Chiu 2008 35

Government-to-business (G 2 B) n n E-government category that includes interactions between governments and businesses (government selling to businesses and providing them with services and businesses selling products and services to government) Group purchasing n n Forward e-auctions n n e. FAST service conducts reverse auctions for aggregated orders auction surplus or other goods Tax collection and management n electronic filing of taxes is now available in over 100 countries Dickson Chiu 2008 36

Other E-Government Modes n Government-to-government (G 2 G): e-Government category that includes activities within government units and those between governments n Government-to-employees (G 2 E): e-Government category that includes activities and services between government units and their employees Dickson Chiu 2008 37
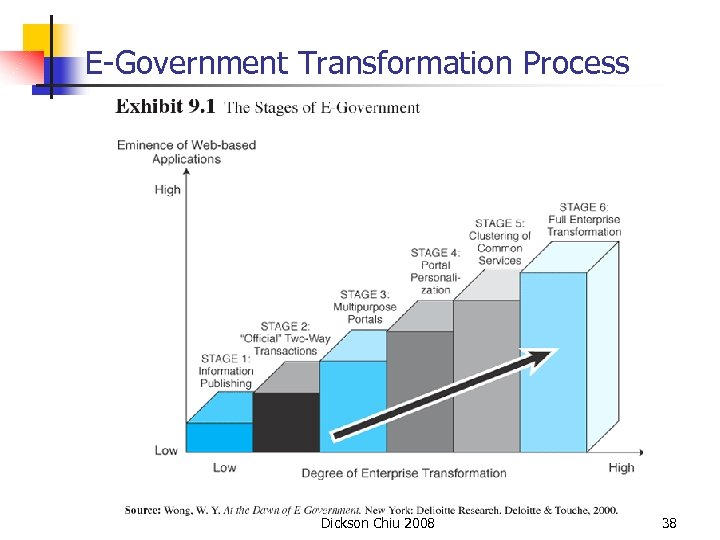
E-Government Transformation Process Dickson Chiu 2008 38

Implementing Issues of e-Government n n Transformation speed G 2 B implementation Security and privacy issues Wireless applications Dickson Chiu 2008 39
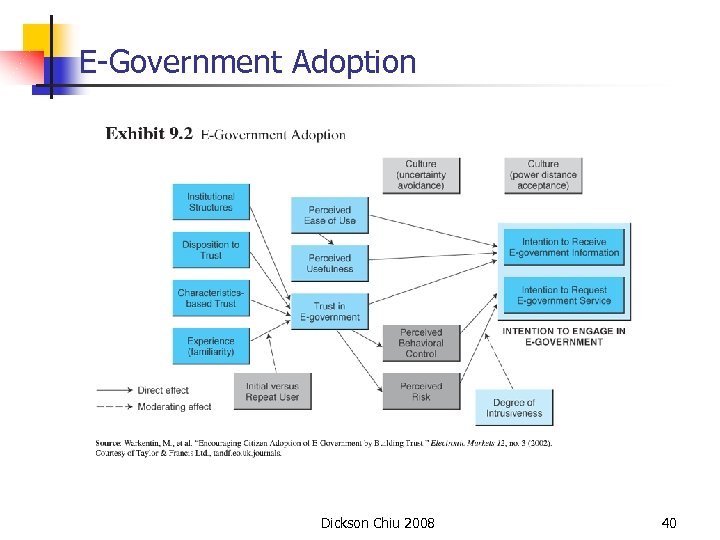
E-Government Adoption Dickson Chiu 2008 40

http: //www. comp. hkbu. edu. hk/~eee 05 Dickson Chiu 2008 41

http: //www. comp. hkbu. edu. hk/~ctr Dickson Chiu 2008 42
bac618515b02834431b7831b59e6126f.ppt