43ba1ef99d7363e4957b32665a0f592c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

COMP 5331 Knowledge Discovery in Databases Overview Prepared by Raymond Wong Presented by Raymond Wong raywong@cse COMP 5331 1

Course Details n Reference books/materials: n n n Papers Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques. Jiawei Han and Micheline Kamber. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers (3 rd edition) Introduction to Data Mining. Pang-Ning Tan, Michael Steinbach, Vipin Kumar Boston : Pearson Addison Wesley (2006) COMP 5331 2

Area n n DB or AI This course can count towards one of the areas ONLY and cannot be double counted towards the required credits COMP 5331 3
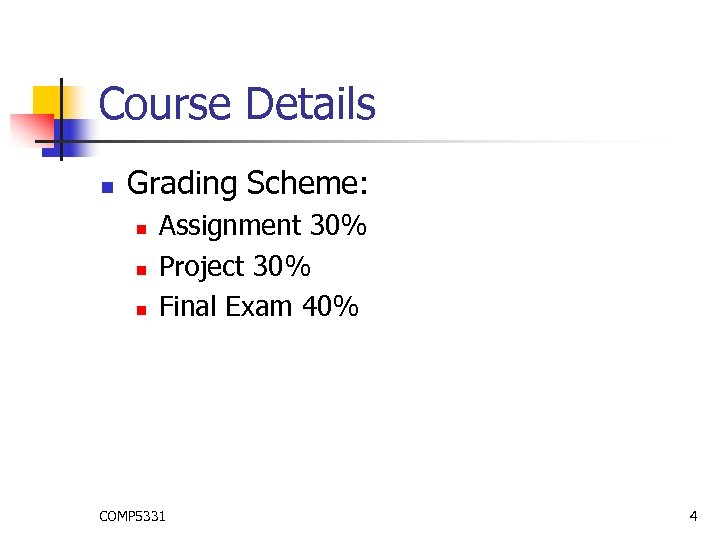
Course Details n Grading Scheme: n n n Assignment 30% Project 30% Final Exam 40% COMP 5331 4

Assignment n If the students can answer the selected questions in class correctly, n n n for each corrected answer, I will give him/her a coupon This coupon can be used to waive one question in an assignment which means that s/he can get full marks for this question without answering this question COMP 5331 5

Assignment n Guideline n For each assignment, each student can waive at most one question only. n n n s/he can waive any question he wants and obtain full marks for this question (no matter whether s/he answer this question or not) s/he may also answer this question. But, we will also mark it but will give full marks to this question. When the student submits the assignment, n n please staple the coupon to the submitted assignment please write down the question no. s/he wants to waive on the coupon COMP 5331 6

Project n n Each project is completed by a group. The number of students in a group depends on the class size. The duration of each presentation depends on the class size. It will be announced soon. COMP 5331 7
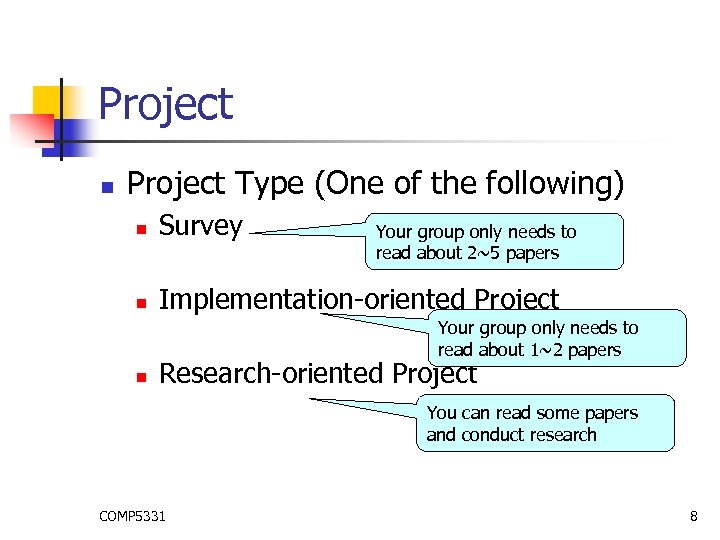
Project n Project Type (One of the following) n Survey n Implementation-oriented Project Your group only needs to read about 2~5 papers Your group only needs to read about 1~2 papers n Research-oriented Project You can read some papers and conduct research COMP 5331 8
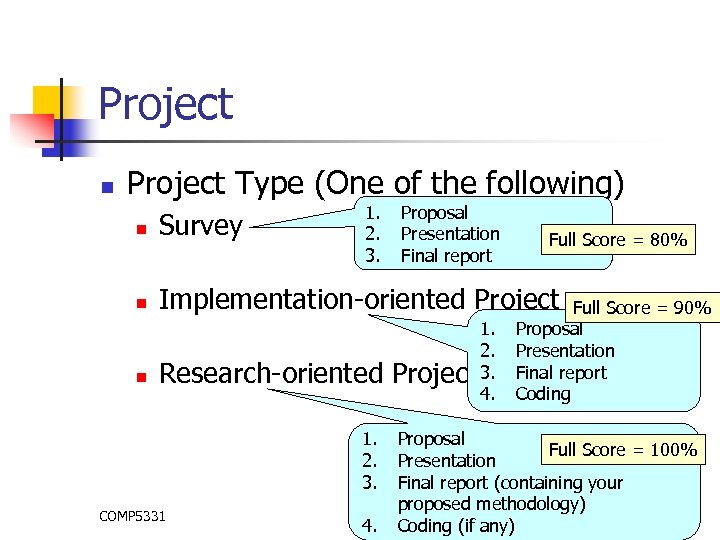
Project n Project Type (One of the following) 1. 2. 3. Proposal Presentation Final report n Survey n Implementation-oriented Project n Research-oriented 1. 2. 3. COMP 5331 4. 1. 2. Project 3. 4. Full Score = 80% Full Score = 90% Proposal Presentation Final report Coding Proposal Full Score = 100% Presentation Final report (containing your proposed methodology) 9 Coding (if any)

Project n Project Topic n n n Some pre-selected topics/papers Your own choice For fairness, please do not choose the topic which is closely related to your own research COMP 5331 10

Exam n n You are allowed to bring a calculator with you. Please remember to prepare a calculator for the exam COMP 5331 11

Major Topics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Association Clustering Classification Data Warehouse Data Mining over Data Streams Web Databases Multi-criteria Decision Making COMP 5331 12
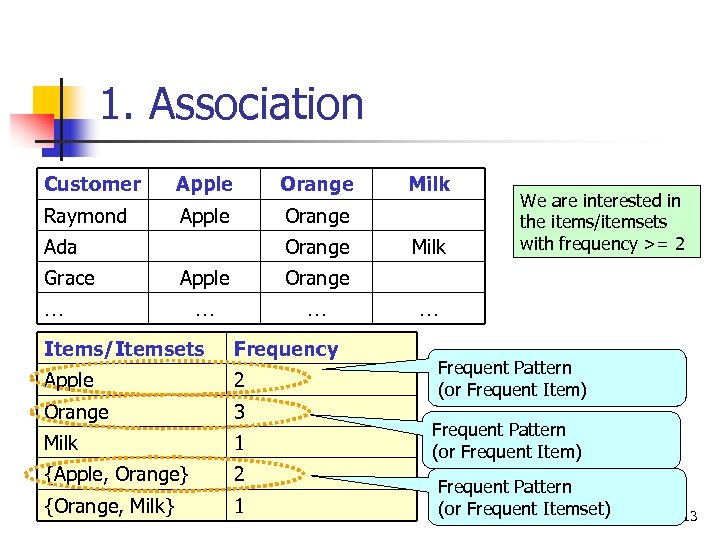
1. Association Customer Apple Orange Raymond Apple Orange Ada Grace Orange Apple … Milk We are interested in the items/itemsets with frequency >= 2 Orange … Milk … Items/Itemsets Frequency Apple 2 Orange 3 Milk 1 {Apple, Orange} 2 {Orange, Milk} COMP 5331 1 … Frequent Pattern (or Frequent Item) Frequent Pattern (or Frequent Itemset) 13
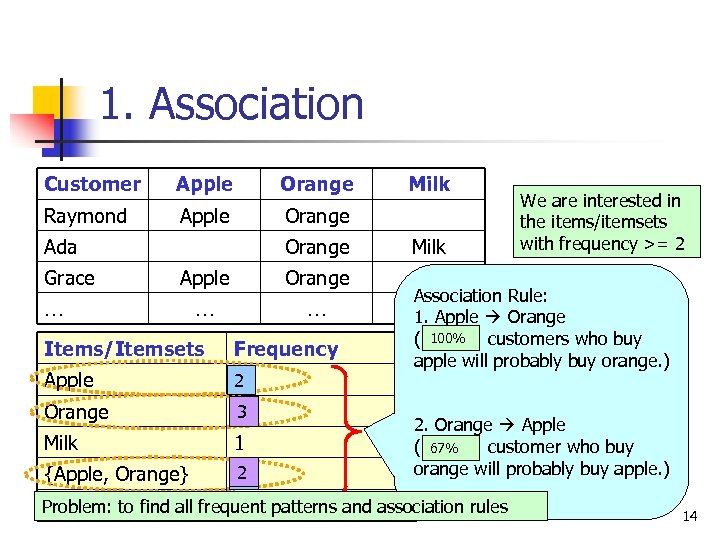
1. Association Customer Apple Orange Raymond Apple Orange Ada Grace Orange Apple Orange … … … Items/Itemsets Frequency Apple 2 Orange 3 3 Milk 1 {Apple, Orange} 2 2 Milk We are interested in the items/itemsets with frequency >= 2 Association Rule: … 1. Apple Orange ( 100% customers who buy apple will probably buy orange. ) 2. Orange Apple ( 67% customer who buy orange will probably buy apple. ) Problem: to find all frequent patterns and association rules {Orange, Milk} 1 COMP 5331 14

Major Topics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Association Clustering Classification Data Warehouse Data Mining over Data Streams Web Databases Multi-criteria Decision Making COMP 5331 15
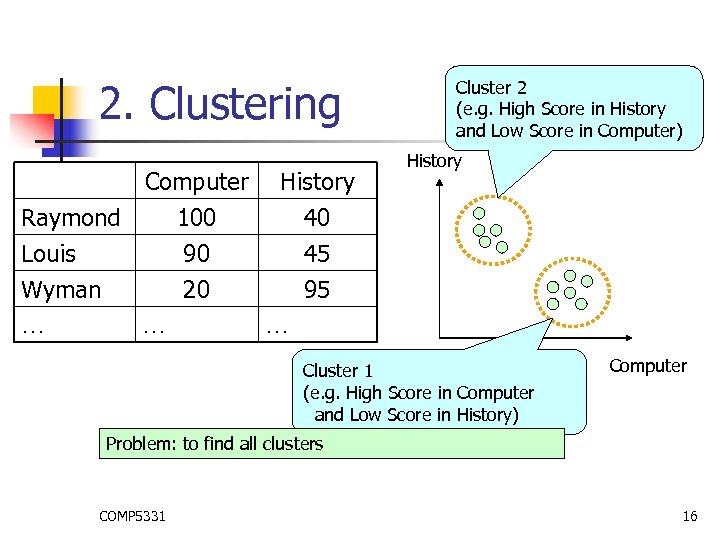
2. Clustering Computer History Raymond 100 40 Louis 90 45 Wyman 20 95 … … … Cluster 2 (e. g. High Score in History and Low Score in Computer) History Cluster 1 (e. g. High Score in Computer and Low Score in History) Computer Problem: to find all clusters COMP 5331 16

Major Topics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Association Clustering Classification Data Warehouse Data Mining over Data Streams Web Databases Multi-criteria Decision Making COMP 5331 17
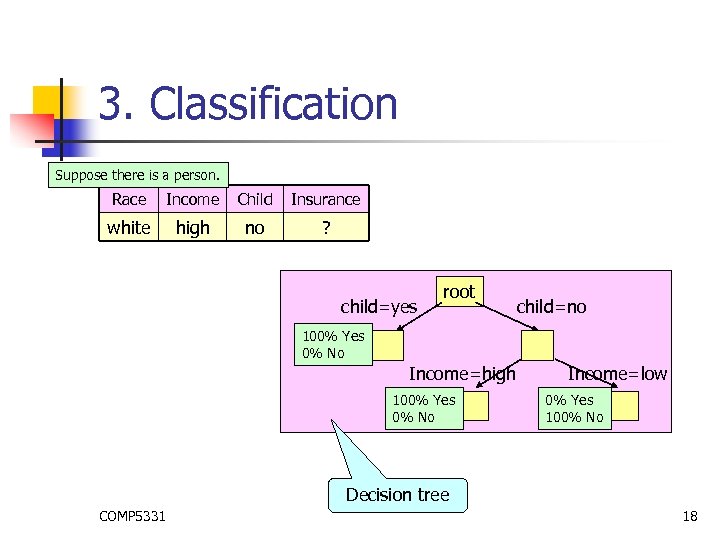
3. Classification Suppose there is a person. Race Income Child Insurance white high no ? child=yes root child=no 100% Yes 0% No Income=high 100% Yes 0% No Income=low 0% Yes 100% No Decision tree COMP 5331 18

Major Topics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Association Clustering Classification Data Warehouse Data Mining over Data Streams Web Databases Multi-criteria Decision Making COMP 5331 19
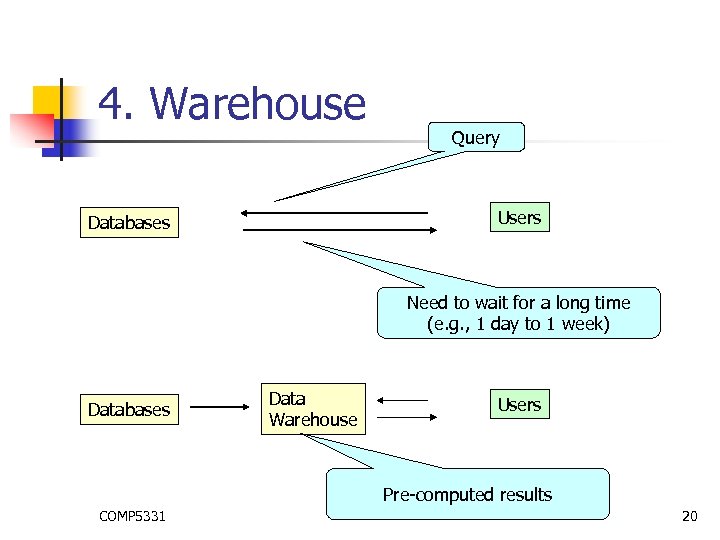
4. Warehouse Query Users Databases Need to wait for a long time (e. g. , 1 day to 1 week) Databases Data Warehouse Users Pre-computed results COMP 5331 20

Major Topics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Association Clustering Classification Data Warehouse Data Mining over Data Streams Web Databases Multi-criteria Decision Making COMP 5331 21
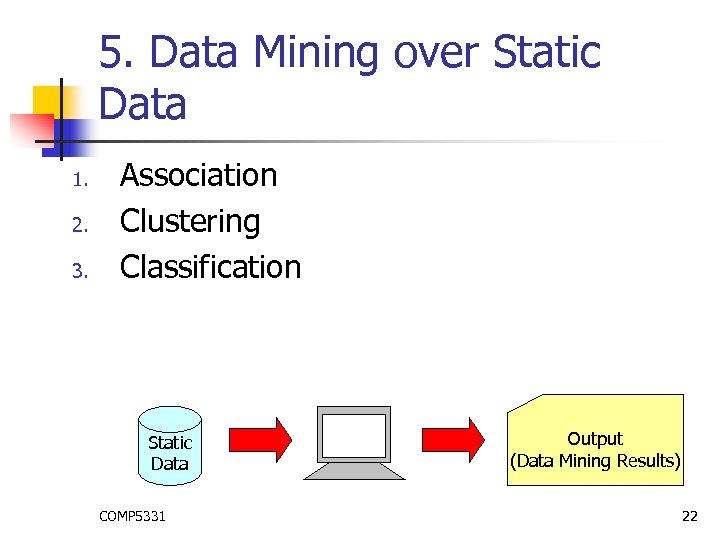
5. Data Mining over Static Data 1. 2. 3. Association Clustering Classification Static Data COMP 5331 Output (Data Mining Results) 22
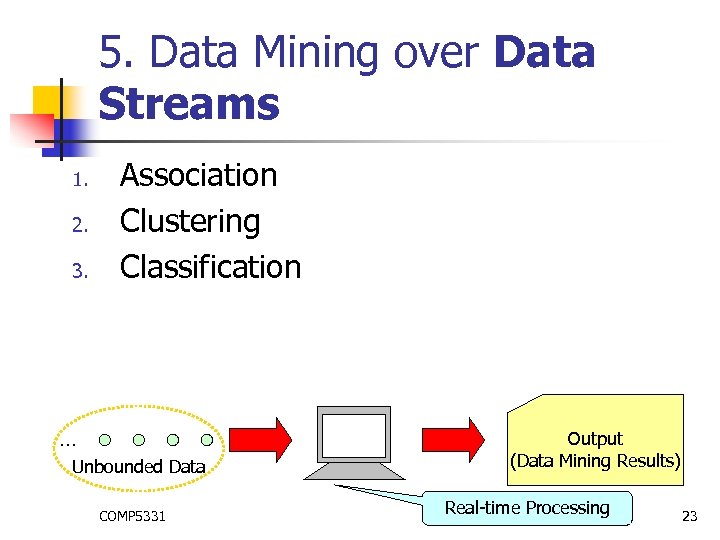
5. Data Mining over Data Streams 1. 2. 3. Association Clustering Classification … Unbounded Data COMP 5331 Output (Data Mining Results) Real-time Processing 23

Major Topics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Association Clustering Classification Data Warehouse Data Mining over Data Streams Web Databases Multi-criteria Decision Making COMP 5331 24

6. Web Databases Raymond Wong COMP 5331 25
How to rank the webpages? COMP 5331 26

Major Topics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Association Clustering Classification Data Warehouse Data Mining over Data Streams Web Databases Multi-criteria Decision Making COMP 5331 27
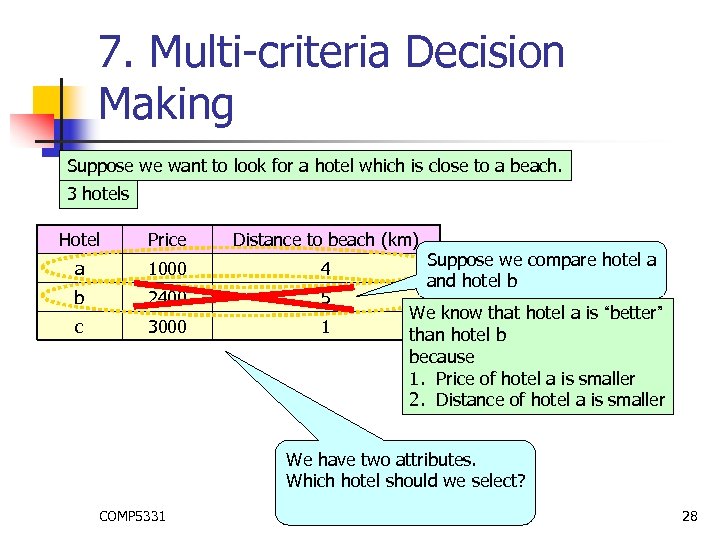
7. Multi-criteria Decision Making Suppose we want to look for a hotel which is close to a beach. 3 hotels Hotel Price Distance to beach (km) a 1000 4 b 2400 5 c 3000 1 Suppose we compare hotel a and hotel b We know that hotel a is “better” than hotel b because 1. Price of hotel a is smaller 2. Distance of hotel a is smaller We have two attributes. Which hotel should we select? COMP 5331 28
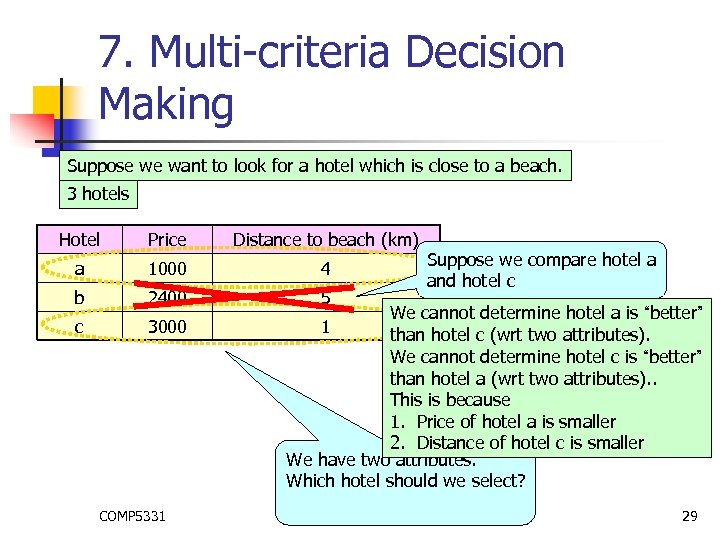
7. Multi-criteria Decision Making Suppose we want to look for a hotel which is close to a beach. 3 hotels Hotel Price Distance to beach (km) a 1000 4 b 2400 5 c 3000 COMP 5331 Suppose we compare hotel a and hotel c We cannot determine hotel a is “better” 1 than hotel c (wrt two attributes). We cannot determine hotel c is “better” than hotel a (wrt two attributes). . This is because 1. Price of hotel a is smaller 2. Distance of hotel c is smaller We have two attributes. Which hotel should we select? 29
43ba1ef99d7363e4957b32665a0f592c.ppt