63cc5fb2906310349988709a6969c9ab.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 COMP 136: Introduction to Computer Graphics Hardware and Graphics in Video Games
COMP 136: Introduction to Computer Graphics Hardware and Graphics in Video Games
 Outline History of PC graphics cards n Current PC graphics cards n Where things are going n Games, how do they do that? n
Outline History of PC graphics cards n Current PC graphics cards n Where things are going n Games, how do they do that? n
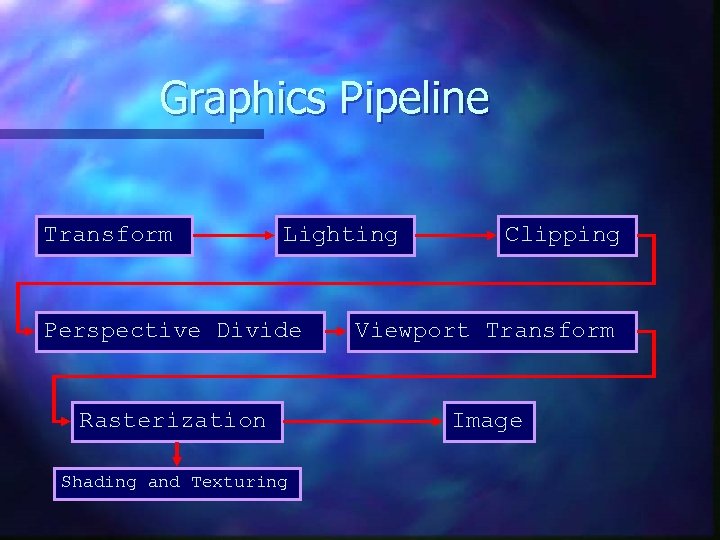 Graphics Pipeline Transform Lighting Clipping Perspective Divide Viewport Transform Rasterization Image Shading and Texturing
Graphics Pipeline Transform Lighting Clipping Perspective Divide Viewport Transform Rasterization Image Shading and Texturing
 n n n n n 2005 – Madden 06 2004 – Doom 3 2003 – Sim. City 4 2002 – Madden 2003 2000 – Madden 2001 1999 – Quake 3 1998 – Soul Calibur 1997 – Wing Commander Prophecy 1996 – Quake 1995 – Wing Commander IV 1994 – Doom 2 1993 – Doom 1992 – Wolfenstein 3 D 1991 – Wing Commander 2 1985 – Super Mario Bros 1983 – Star Wars arcade 1981 – Pac man 1978 – Space Invaders 1972 – Pong
n n n n n 2005 – Madden 06 2004 – Doom 3 2003 – Sim. City 4 2002 – Madden 2003 2000 – Madden 2001 1999 – Quake 3 1998 – Soul Calibur 1997 – Wing Commander Prophecy 1996 – Quake 1995 – Wing Commander IV 1994 – Doom 2 1993 – Doom 1992 – Wolfenstein 3 D 1991 – Wing Commander 2 1985 – Super Mario Bros 1983 – Star Wars arcade 1981 – Pac man 1978 – Space Invaders 1972 – Pong
 ‘ 72
‘ 72
 ‘ 72
‘ 72
 ‘ 81
‘ 81
 ‘ 83
‘ 83
 ‘ 85
‘ 85
 ‘ 90
‘ 90
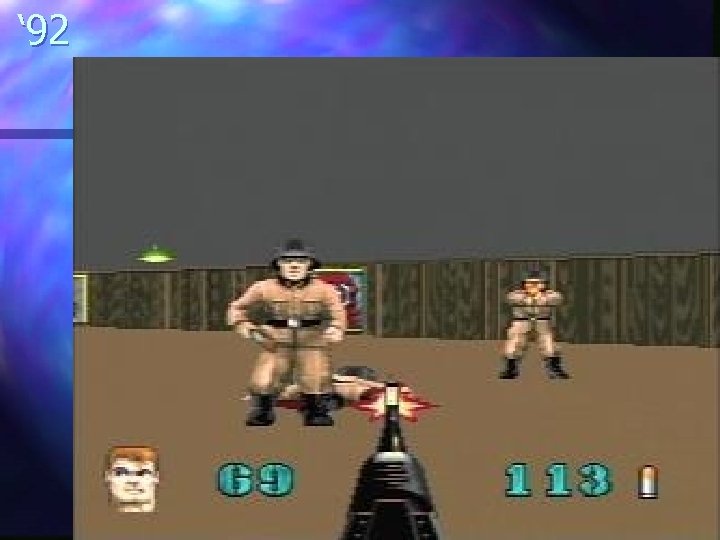 ‘ 92
‘ 92
 ‘ 93
‘ 93
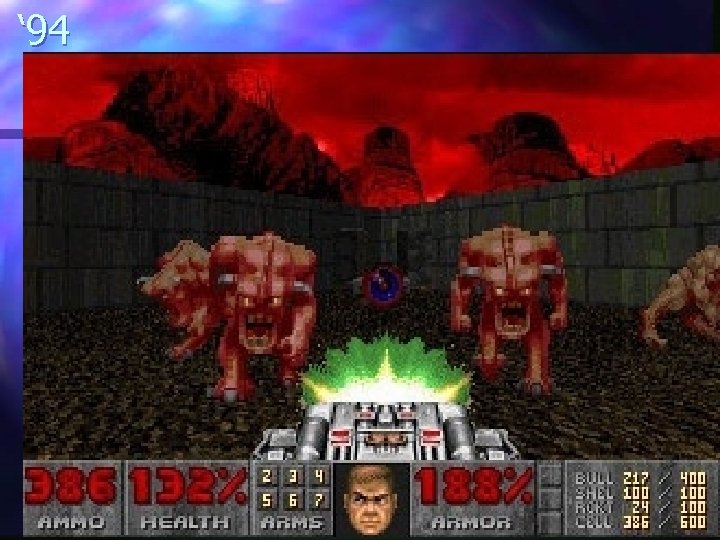 ‘ 94
‘ 94
 ‘ 95
‘ 95
 ‘ 96
‘ 96
 ‘ 97
‘ 97
 ‘ 98
‘ 98
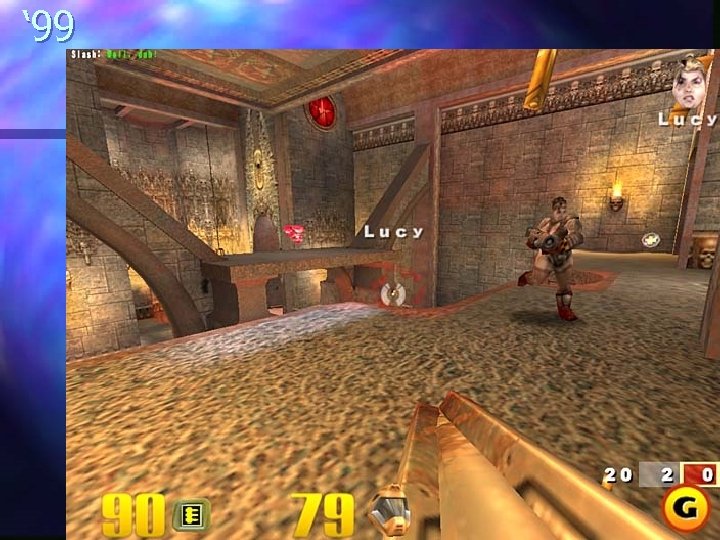 ‘ 99
‘ 99
 ‘ 00
‘ 00
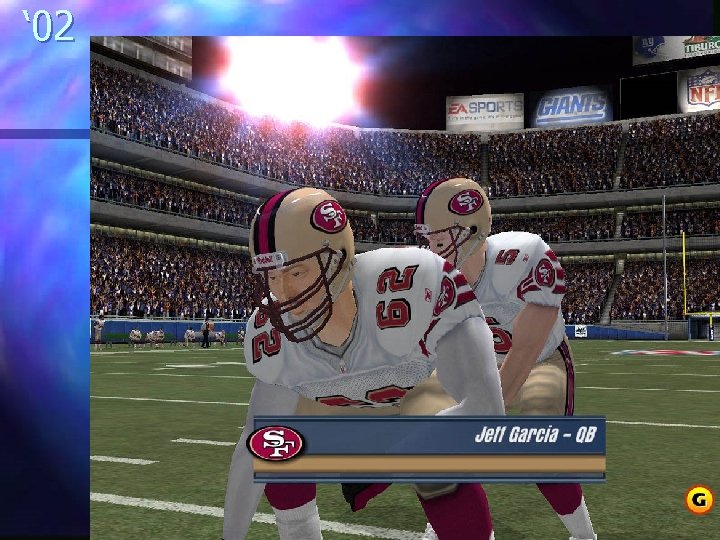 ‘ 02
‘ 02
 ‘ 03
‘ 03
 ‘ 04
‘ 04
 ‘ 05
‘ 05
 2006
2006
 ‘ 08
‘ 08
 n n n n n 2005 – Madden 06 2004 – Doom 3 2003 – Sim. City 4 2002 – Madden 2003 2000 – Madden 2001 1999 – Quake 3 1998 – Soul Calibur 1997 – Wing Commander Prophecy 1996 – Quake 1995 – Wing Commander IV 1994 – Doom 2 1993 – Doom 1992 – Wolfenstein 3 D 1991 – Wing Commander 2 1985 – Super Mario Bros 1983 – Star Wars arcade 1981 – Pac man 1978 – Space Invaders 1972 – Pong
n n n n n 2005 – Madden 06 2004 – Doom 3 2003 – Sim. City 4 2002 – Madden 2003 2000 – Madden 2001 1999 – Quake 3 1998 – Soul Calibur 1997 – Wing Commander Prophecy 1996 – Quake 1995 – Wing Commander IV 1994 – Doom 2 1993 – Doom 1992 – Wolfenstein 3 D 1991 – Wing Commander 2 1985 – Super Mario Bros 1983 – Star Wars arcade 1981 – Pac man 1978 – Space Invaders 1972 – Pong
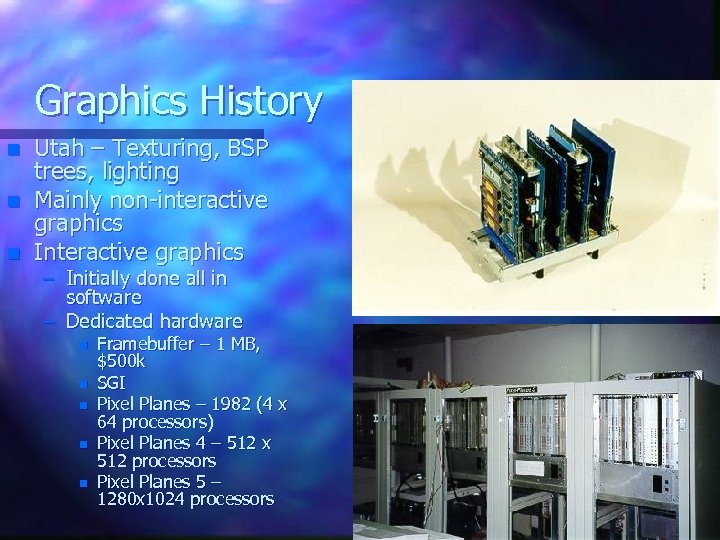 Graphics History n n n Utah – Texturing, BSP trees, lighting Mainly non-interactive graphics Interactive graphics – Initially done all in software – Dedicated hardware n n n Framebuffer – 1 MB, $500 k SGI Pixel Planes – 1982 (4 x 64 processors) Pixel Planes 4 – 512 x 512 processors Pixel Planes 5 – 1280 x 1024 processors
Graphics History n n n Utah – Texturing, BSP trees, lighting Mainly non-interactive graphics Interactive graphics – Initially done all in software – Dedicated hardware n n n Framebuffer – 1 MB, $500 k SGI Pixel Planes – 1982 (4 x 64 processors) Pixel Planes 4 – 512 x 512 processors Pixel Planes 5 – 1280 x 1024 processors
 PC History n n Software Renderer Graphics APIs – DOS – Windows - Direct. X n v 1 -3 were pretty unused for 3 D n v 5 - people started using it for 3 D n currently v 10 – Open. GL n Currently 2. 0 UNIX workstation n Migrated to the PC, mainly because of Quake. GL n
PC History n n Software Renderer Graphics APIs – DOS – Windows - Direct. X n v 1 -3 were pretty unused for 3 D n v 5 - people started using it for 3 D n currently v 10 – Open. GL n Currently 2. 0 UNIX workstation n Migrated to the PC, mainly because of Quake. GL n
 Direct. X vs. Open. GL Evolution time n Multiplatform n
Direct. X vs. Open. GL Evolution time n Multiplatform n
 PC Graphics History n n till 1994 (ATI, Matrox, etc) – accelerated 2 D – some 3 D acceleration, though non-standard 1995 – 3 dfx released the Voodoo chip (~1 million triangles per second). – Graphics “co-processor” (you still had a 2 d card) – Hardware accelerated rasterization – Textures, shading, etc. – Increased texture filtering, resolution, textures, models – GLIDE API – 16 bit color and framebuffer (how does this affect things? )
PC Graphics History n n till 1994 (ATI, Matrox, etc) – accelerated 2 D – some 3 D acceleration, though non-standard 1995 – 3 dfx released the Voodoo chip (~1 million triangles per second). – Graphics “co-processor” (you still had a 2 d card) – Hardware accelerated rasterization – Textures, shading, etc. – Increased texture filtering, resolution, textures, models – GLIDE API – 16 bit color and framebuffer (how does this affect things? )
 PC Graphics History n 1996 – Quake was released – Brought Open. GL to the masses! (How? ) – n. Vidia, ATI, 3 DLabs, 3 dfx, Intel – How could each one of these companies compete? – Direct. X 5. 0!
PC Graphics History n 1996 – Quake was released – Brought Open. GL to the masses! (How? ) – n. Vidia, ATI, 3 DLabs, 3 dfx, Intel – How could each one of these companies compete? – Direct. X 5. 0!
 PC Graphics History n 1998 – 3 dfx releases Voodoo 2 (3 million triangles per second) – Two texture units. Why? Single pass multitextures! – Three major APIs: Open. GL, Direct. X, GLIDE – All games now are hardware accelerated – Quake 2 released – n. Vidia releases TNT, ATI focuses on retail, Matrox – single card solutions – 32 bit color for everything (except voodoo 2)
PC Graphics History n 1998 – 3 dfx releases Voodoo 2 (3 million triangles per second) – Two texture units. Why? Single pass multitextures! – Three major APIs: Open. GL, Direct. X, GLIDE – All games now are hardware accelerated – Quake 2 released – n. Vidia releases TNT, ATI focuses on retail, Matrox – single card solutions – 32 bit color for everything (except voodoo 2)
 PC Graphics History n 1999: – 3 dfx Voodoo 3000 (they buy out STB) – n. Vidia TNT 2 (300 Mpixels, 5? Million triangles) – Matrox G 400 (bump mapping, etc). – How do you add features to a standard? – Late 1999: Quake 3 is released – APIs standardize: Open. GL and Direct. X – Pros and Cons of each
PC Graphics History n 1999: – 3 dfx Voodoo 3000 (they buy out STB) – n. Vidia TNT 2 (300 Mpixels, 5? Million triangles) – Matrox G 400 (bump mapping, etc). – How do you add features to a standard? – Late 1999: Quake 3 is released – APIs standardize: Open. GL and Direct. X – Pros and Cons of each
 2000 n 2000: – n. Vidia releases Ge. Force and Ge. Force 2 cards (25 million triangles per second) 4 texture units n Hardware Transform, Clipping, and Lighting! n Per vertex shading n – ATI releases Radeon n adds additional features like bump mapping, vertex skinning, 3 texture units – 3 dfx releases Voodoo 5500 n Full Screen Antialiasing
2000 n 2000: – n. Vidia releases Ge. Force and Ge. Force 2 cards (25 million triangles per second) 4 texture units n Hardware Transform, Clipping, and Lighting! n Per vertex shading n – ATI releases Radeon n adds additional features like bump mapping, vertex skinning, 3 texture units – 3 dfx releases Voodoo 5500 n Full Screen Antialiasing
 2006 n Remaining Companies: – ATI – n. Vidia n Scientific Viz (High-end) – – n 3 d. Labs SGI Consumer Market: – Billion $$$ industry – $500 -600 top end card n n ATI Radeon X 1900 XT Ge. Force 7900 GTX, SLI – $200 -300 highest margins – Direct. X 9. 0
2006 n Remaining Companies: – ATI – n. Vidia n Scientific Viz (High-end) – – n 3 d. Labs SGI Consumer Market: – Billion $$$ industry – $500 -600 top end card n n ATI Radeon X 1900 XT Ge. Force 7900 GTX, SLI – $200 -300 highest margins – Direct. X 9. 0
 What happens on a gl. Vertex? n n n Your code calls a gl. Vertex opengl 32. dll (vendor specific) takes the command communicates it to the card via the graphics bus Is there hardware T, L, and C? – Yes: the vertex data is sent across the bus and the hardware pushes the vertex through the graphics pipeline – No: the CPU transforms, lights, and clips the data and THEN sends it to the card via the bus. Why only now do we have hardware T&L&C? What are the bottlenecks for an application? – How can we alleviate some of the bandwidth concerns? – Store vertices ON the card (or in compiled form) – Different data types like triangle fans and strips
What happens on a gl. Vertex? n n n Your code calls a gl. Vertex opengl 32. dll (vendor specific) takes the command communicates it to the card via the graphics bus Is there hardware T, L, and C? – Yes: the vertex data is sent across the bus and the hardware pushes the vertex through the graphics pipeline – No: the CPU transforms, lights, and clips the data and THEN sends it to the card via the bus. Why only now do we have hardware T&L&C? What are the bottlenecks for an application? – How can we alleviate some of the bandwidth concerns? – Store vertices ON the card (or in compiled form) – Different data types like triangle fans and strips
 Vertex and Pixel Shaders n What is limitation how the quality of CG? – Speed n What’s the fix? – Realism n n n What do we mean by that? Solution? What if we could change the functions being executed in the graphics pipeline?
Vertex and Pixel Shaders n What is limitation how the quality of CG? – Speed n What’s the fix? – Realism n n n What do we mean by that? Solution? What if we could change the functions being executed in the graphics pipeline?
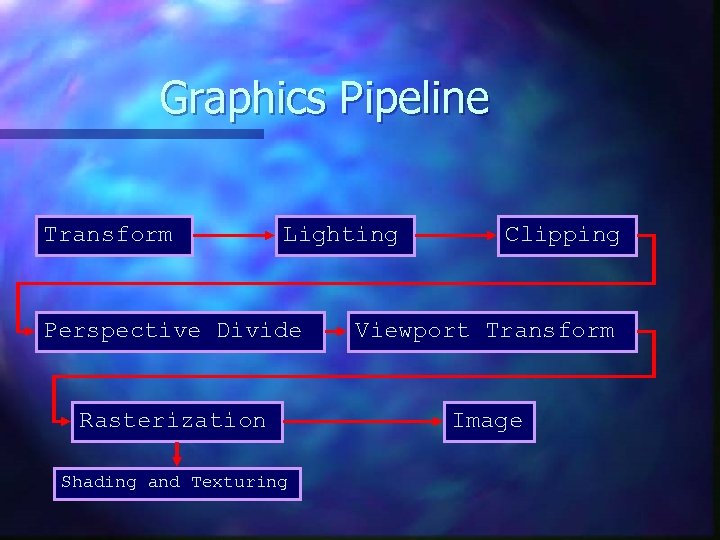 Graphics Pipeline Transform Lighting Clipping Perspective Divide Viewport Transform Rasterization Image Shading and Texturing
Graphics Pipeline Transform Lighting Clipping Perspective Divide Viewport Transform Rasterization Image Shading and Texturing
 n Vertex Shader – A graphics processing function, which manipulates vertex data values on an X (length), Y (height) and Z (depth) 3 D plane through mathematical operations on an object. n Written in assembly-like language (ex. Cg)
n Vertex Shader – A graphics processing function, which manipulates vertex data values on an X (length), Y (height) and Z (depth) 3 D plane through mathematical operations on an object. n Written in assembly-like language (ex. Cg)
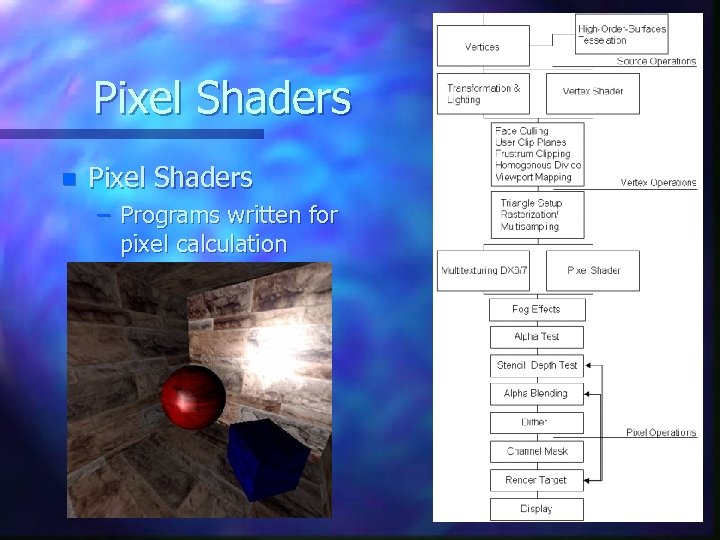 Pixel Shaders n Pixel Shaders – Programs written for pixel calculation
Pixel Shaders n Pixel Shaders – Programs written for pixel calculation
 Vertex and Pixel Shaders
Vertex and Pixel Shaders
 Things to consider n n n n Memory bandwidth and speed Framebuffer memory type AGP, PCI-Express bus mobile 3 d graphics Loading models and textures Designing “family” of cards How can we get more out of a current design? – Increase memory speed – Increase core clock speed – Driver improvements
Things to consider n n n n Memory bandwidth and speed Framebuffer memory type AGP, PCI-Express bus mobile 3 d graphics Loading models and textures Designing “family” of cards How can we get more out of a current design? – Increase memory speed – Increase core clock speed – Driver improvements
 Looking Forward n n n n n Per Pixel Shaders Full screen antialiasing Parallel Processing Animation assistance – Skinning – Interpolation Curved Surfaces Collision Detection Level of Detail Culling More texture units Higher bit depths! Why would we want this?
Looking Forward n n n n n Per Pixel Shaders Full screen antialiasing Parallel Processing Animation assistance – Skinning – Interpolation Curved Surfaces Collision Detection Level of Detail Culling More texture units Higher bit depths! Why would we want this?
 Benchmarks n n n Triangles Fill Rate Refresh rate color depths buffer bit depth – framebuffer – z buffer – stencil buffer Resolution capabilities – How does high refresh rate and resolutions affect the chip and memory design?
Benchmarks n n n Triangles Fill Rate Refresh rate color depths buffer bit depth – framebuffer – z buffer – stencil buffer Resolution capabilities – How does high refresh rate and resolutions affect the chip and memory design?
 Cycle of development n Single Purpose n Multi-purpose
Cycle of development n Single Purpose n Multi-purpose
 Tricks! How would you do: n n n n n Shafts of light Blood Sparks Many lights Trees Forest Flashlights Movie projectors Bullet holes Rain/Snow n n n n n Motion Blur Depth of focus Cue Ball reflections Airplane damage Lens flares Water Skin Clothes Faces Shadows
Tricks! How would you do: n n n n n Shafts of light Blood Sparks Many lights Trees Forest Flashlights Movie projectors Bullet holes Rain/Snow n n n n n Motion Blur Depth of focus Cue Ball reflections Airplane damage Lens flares Water Skin Clothes Faces Shadows
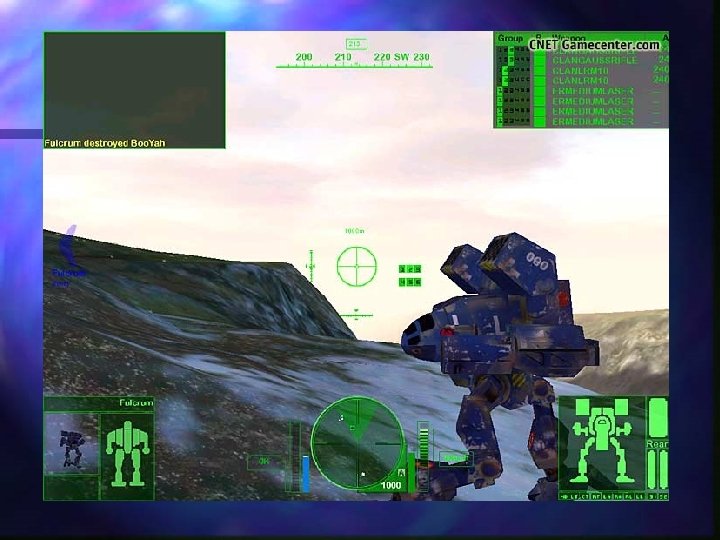
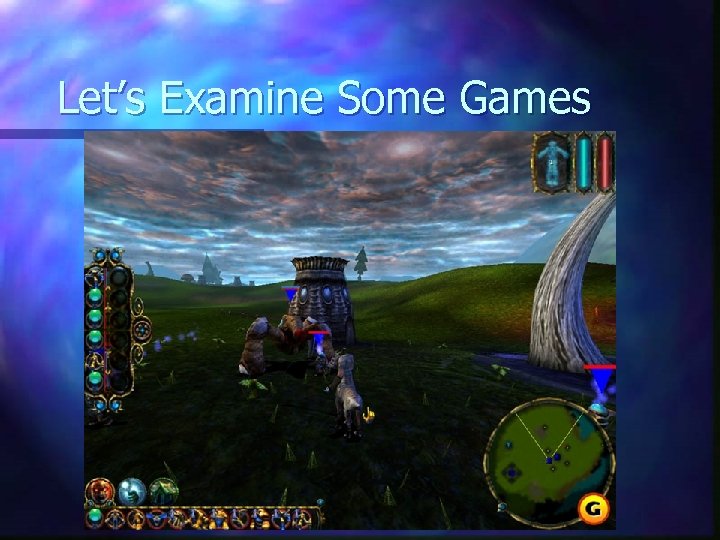 Let’s Examine Some Games
Let’s Examine Some Games
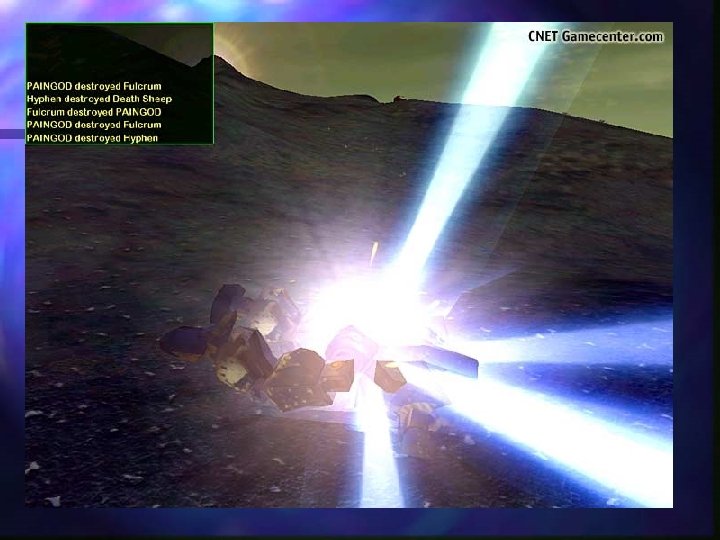
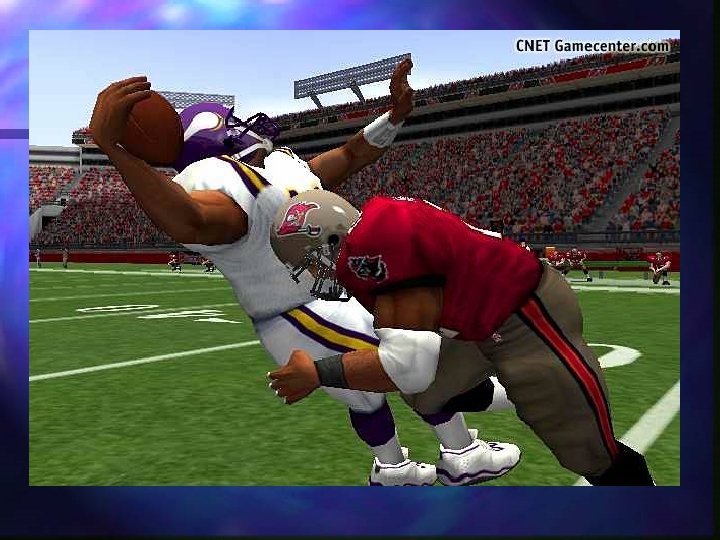



 Shadows
Shadows
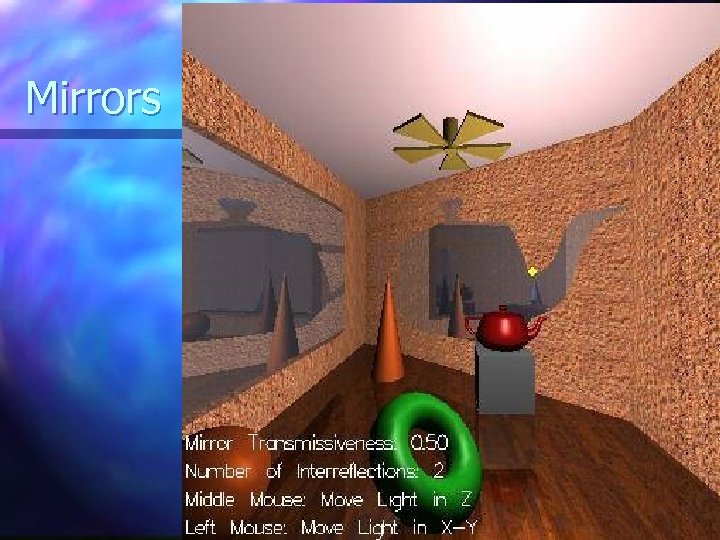 Mirrors
Mirrors


