communism & capitalism.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Communism & Capitalism
Communism & Capitalism
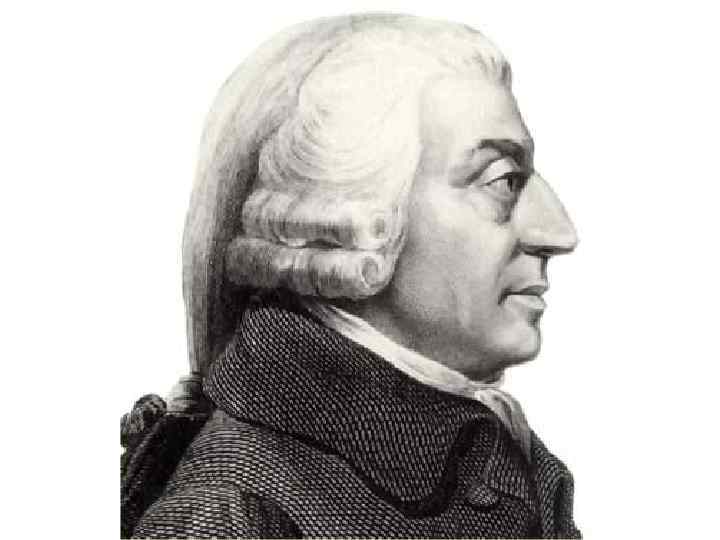
 What is capitalism? • Economic system. • Believes in individual ownership and competition. • The theory is that when everyone is selfish, it benefits everyone. • Adam Smith is “the” capitalist.
What is capitalism? • Economic system. • Believes in individual ownership and competition. • The theory is that when everyone is selfish, it benefits everyone. • Adam Smith is “the” capitalist.

 What’s good about capitalism? • Freedom, choice. • You can work wherever, buy whatever, and pretty much do whatever. • If you’re successful, you can be very successful. Think Bill Gates.
What’s good about capitalism? • Freedom, choice. • You can work wherever, buy whatever, and pretty much do whatever. • If you’re successful, you can be very successful. Think Bill Gates.
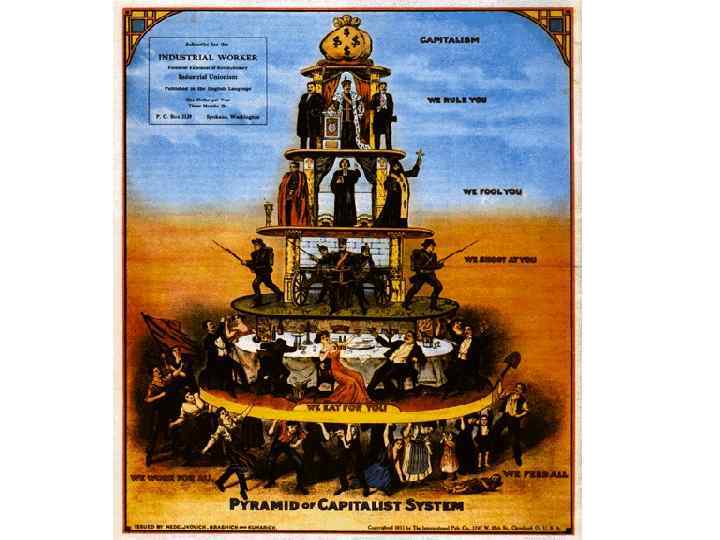
 What’s bad about capitalism? • No “safety net. ” • If you’re unsuccessful, you can be very unsuccessful. Think about the poor. • Big gap between rich and poor.
What’s bad about capitalism? • No “safety net. ” • If you’re unsuccessful, you can be very unsuccessful. Think about the poor. • Big gap between rich and poor.
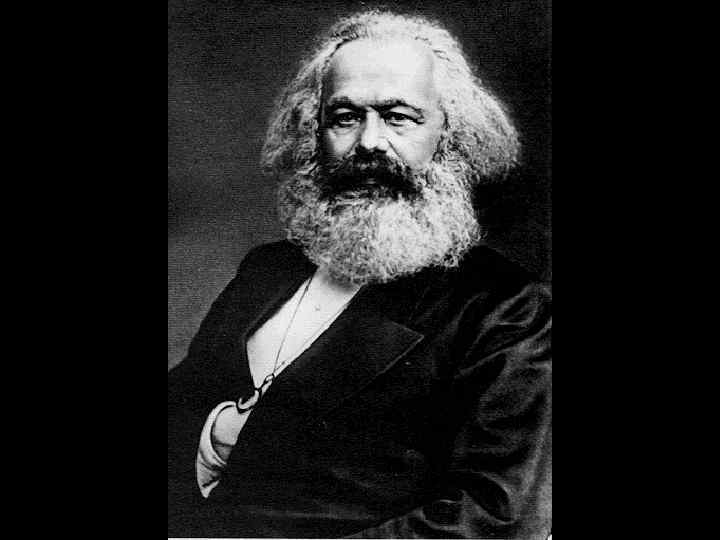
 What is communism? • Economic system. • Believes in collective (group) ownership and a planned economy. • The theory is that everybody pools their resources and labor to evenly distribute everything. • Karl Marx is “the” communist.
What is communism? • Economic system. • Believes in collective (group) ownership and a planned economy. • The theory is that everybody pools their resources and labor to evenly distribute everything. • Karl Marx is “the” communist.
 5 Key Points • Communism is the government when everything is distributed equally. • Dictatorship is the government when a group or one person has control over everyone. • The Cold War is when there was tension between the U. S and the Soviet Union. • The beginning of communism through the Industrial Revolution. • U. S. S. R. goal to expand communism through the countries.
5 Key Points • Communism is the government when everything is distributed equally. • Dictatorship is the government when a group or one person has control over everyone. • The Cold War is when there was tension between the U. S and the Soviet Union. • The beginning of communism through the Industrial Revolution. • U. S. S. R. goal to expand communism through the countries.
 Communist Manifesto 1. 2. 3. 4. Abolition of property Heavy, progressive taxes Abolition of inheritance Confiscation of property of all emigrants and rebels 5. Central banking 6. State-controlled communication and transportation 7. State-controlled education of the children
Communist Manifesto 1. 2. 3. 4. Abolition of property Heavy, progressive taxes Abolition of inheritance Confiscation of property of all emigrants and rebels 5. Central banking 6. State-controlled communication and transportation 7. State-controlled education of the children
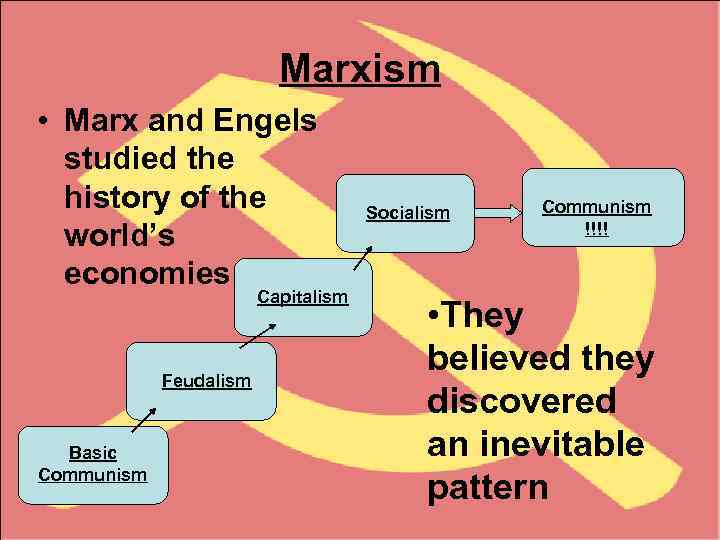 Marxism • Marx and Engels studied the history of the world’s economies Capitalism Feudalism Basic Communism Socialism Communism !!!! • They believed they discovered an inevitable pattern
Marxism • Marx and Engels studied the history of the world’s economies Capitalism Feudalism Basic Communism Socialism Communism !!!! • They believed they discovered an inevitable pattern
 Stage 1: Primitive Communism • This is how humans lived together before the emergence of largescale agriculture. • Small hunting and gathering tribes • Everything was shared amongst the tribe-food, jobs, belongings. • No one owned land no one is exploited for their labor. • Eventually one group comes to power which leads to Feudalism…
Stage 1: Primitive Communism • This is how humans lived together before the emergence of largescale agriculture. • Small hunting and gathering tribes • Everything was shared amongst the tribe-food, jobs, belongings. • No one owned land no one is exploited for their labor. • Eventually one group comes to power which leads to Feudalism…
 Stage 2: Primitive Communism - Feudalism • Under feudalism, a king becomes ruler over all the people. Exploitation begins. • The people are kept uneducated and told that god chose the king to rule. (? ) • The king gives land privileges to nobles who rule the people for him (? ) • As trade develops, some people get richer. This leads to Capitalism…
Stage 2: Primitive Communism - Feudalism • Under feudalism, a king becomes ruler over all the people. Exploitation begins. • The people are kept uneducated and told that god chose the king to rule. (? ) • The king gives land privileges to nobles who rule the people for him (? ) • As trade develops, some people get richer. This leads to Capitalism…
 Stage 3: Feudalism - Capitalism • Business owners or capitalists get richer while the workers do the work. • Capitalists get more power to serve their own interests. • Capitalism creates a large working-class of people who organize, create unions, and demand changes. This leads to Socialism…
Stage 3: Feudalism - Capitalism • Business owners or capitalists get richer while the workers do the work. • Capitalists get more power to serve their own interests. • Capitalism creates a large working-class of people who organize, create unions, and demand changes. This leads to Socialism…
 Stage 4: Capitalism-Socialism • In the Socialist revolution all the rulers lose power, wealth, and privilege. • Workers take control of the country to produce things for everyone. No one is exploited. • Nothing is made for profit therefore all people benefit. • These ideas spread across the world to create Communism…
Stage 4: Capitalism-Socialism • In the Socialist revolution all the rulers lose power, wealth, and privilege. • Workers take control of the country to produce things for everyone. No one is exploited. • Nothing is made for profit therefore all people benefit. • These ideas spread across the world to create Communism…
 Stage 5: Socialism-Communism • Capitalists will put up a fight but the will of the people will always win. • Everyone now works together, war eliminated, and armies are obsolete. • Everything is provided by the people so $ becomes a thing of the past. • All human activity goes towards benefiting each other-allowing all to live their lives to the fullest.
Stage 5: Socialism-Communism • Capitalists will put up a fight but the will of the people will always win. • Everyone now works together, war eliminated, and armies are obsolete. • Everything is provided by the people so $ becomes a thing of the past. • All human activity goes towards benefiting each other-allowing all to live their lives to the fullest.
 Communism/Socialism: What’s the difference? • Socialism is, “from each according to their ability, to each according to their DEEDS. ” – Socialism is the stage between Capitalism and Communism. It builds upon the previous system (Capitalism) by nationalizing the “means of production” (i. e. corporations, resources, banks, etc. ), but not by making everyone equal. People are paid wages based on several factors (social need, difficulty, amount of schooling required, etc. ), so not everyone will make the same wage. • Communism is “from each according to their ability to each according to their NEEDS. ”
Communism/Socialism: What’s the difference? • Socialism is, “from each according to their ability, to each according to their DEEDS. ” – Socialism is the stage between Capitalism and Communism. It builds upon the previous system (Capitalism) by nationalizing the “means of production” (i. e. corporations, resources, banks, etc. ), but not by making everyone equal. People are paid wages based on several factors (social need, difficulty, amount of schooling required, etc. ), so not everyone will make the same wage. • Communism is “from each according to their ability to each according to their NEEDS. ”


 Elements of Soviet Communism • 1) The State provided housing for everyone. • 2) Housing was always in short supply- The state never constructed enough housing to meet demand. • 3) People did not own their own housing, the state owned it • 4) The state owned all the land, farmers worked on collective farms- Since all workers were paid the same, there was no incentive to work hard. Soviet agriculture struggled to produce enough food. • 5) Workers were guaranteed a job, no one was unemployed • 6) The state provided free medical care. • 7) The state provided free vacations to spas and beach resorts along the Black Sea.
Elements of Soviet Communism • 1) The State provided housing for everyone. • 2) Housing was always in short supply- The state never constructed enough housing to meet demand. • 3) People did not own their own housing, the state owned it • 4) The state owned all the land, farmers worked on collective farms- Since all workers were paid the same, there was no incentive to work hard. Soviet agriculture struggled to produce enough food. • 5) Workers were guaranteed a job, no one was unemployed • 6) The state provided free medical care. • 7) The state provided free vacations to spas and beach resorts along the Black Sea.
 Elements of Soviet Communism • 7) The state provided free day care for women • 8) Women were not allowed to stay home and take care of their children, they had to work • 9) Since consumer goods were always in short supply, huge lines formed when people found out that was a shipment of shoes for example • 10) Money was not as important, as having access to scarce goods, important communist party members had the right to shop in special stores, or were given cars and houses by the state
Elements of Soviet Communism • 7) The state provided free day care for women • 8) Women were not allowed to stay home and take care of their children, they had to work • 9) Since consumer goods were always in short supply, huge lines formed when people found out that was a shipment of shoes for example • 10) Money was not as important, as having access to scarce goods, important communist party members had the right to shop in special stores, or were given cars and houses by the state
 Elements of Soviet Communism • 11) It was almost impossible to fire workers from their jobs. Factories had to many workers, because the objective was to employ people rather than make money. • 12) You were paid the same whether you worked hard or came in late to work drunk. • 13) The state choose your job, whether you liked it or not. You needed special permission to change job. • 14) Soviet agriculture was very inefficient, and used 25% of the population as compared 2 -3% in the U. S. • 15) If Soviet citizen’s saw a line they entered, because they knew there had to be something good at the end of the line.
Elements of Soviet Communism • 11) It was almost impossible to fire workers from their jobs. Factories had to many workers, because the objective was to employ people rather than make money. • 12) You were paid the same whether you worked hard or came in late to work drunk. • 13) The state choose your job, whether you liked it or not. You needed special permission to change job. • 14) Soviet agriculture was very inefficient, and used 25% of the population as compared 2 -3% in the U. S. • 15) If Soviet citizen’s saw a line they entered, because they knew there had to be something good at the end of the line.
 What’s good about communism? • Security, basic needs met. • Everyone would have a job, house, health care, etc.
What’s good about communism? • Security, basic needs met. • Everyone would have a job, house, health care, etc.
 What’s bad about communism? • Lack of choice • No reward for being a better worker or punishment for being a slacker. • Everyone expected to be the same.
What’s bad about communism? • Lack of choice • No reward for being a better worker or punishment for being a slacker. • Everyone expected to be the same.
 How’s this related to the Industrial Revolution? • Adam Smith’s capitalism dominated the Ind. Rev. Led to bad working conditions. • Karl Marx wrote about communism as solution to capitalism’s problems. – Marx said the workers would get fed up and overthrow their governments and start communism.
How’s this related to the Industrial Revolution? • Adam Smith’s capitalism dominated the Ind. Rev. Led to bad working conditions. • Karl Marx wrote about communism as solution to capitalism’s problems. – Marx said the workers would get fed up and overthrow their governments and start communism.