3111baf2f15000981ea22deea2ae6923.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

Communications Testing Michael Wagner Dominic Jonak Robotics Institute July 28, 2003 Life in the Atacama Carnegie Mellon

VHF Testing Purpose VHF communications are very dependent on noise and soil properties Pittsburgh region has numerous transmitters, the desert’s radio environment is quite different Pittsburgh and Atacama are geologically distinct Understand tradeoffs to design a very long-range, intermittent comm solution for subsequent years Life in the Atacama Carnegie Mellon
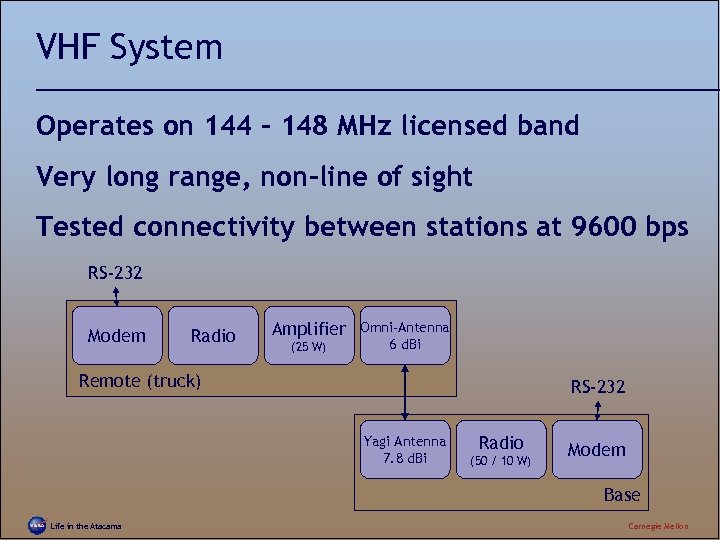
VHF System Operates on 144 – 148 MHz licensed band Very long range, non-line of sight Tested connectivity between stations at 9600 bps RS-232 Modem Radio Amplifier (25 W) Omni-Antenna 6 d. Bi Remote (truck) RS-232 Yagi Antenna 7. 8 d. Bi Radio (50 / 10 W) Modem Base Life in the Atacama Carnegie Mellon
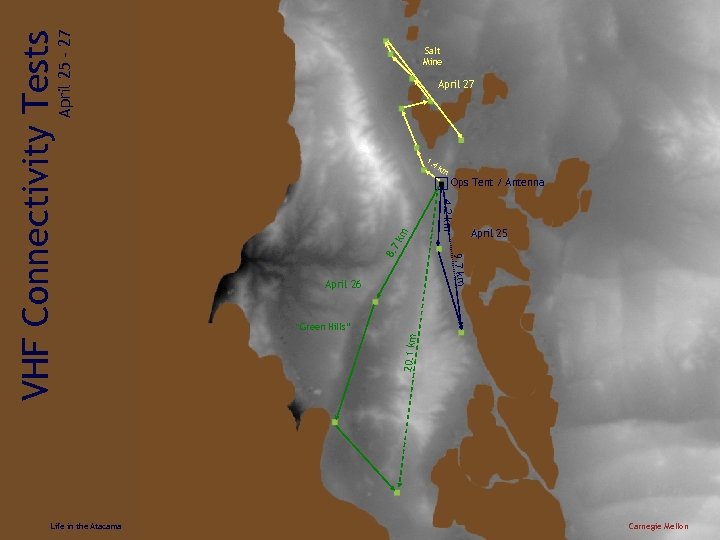
April 25 – 27 1. 4 k m 8. 7 km Ops Tent / Antenna April 25 9. 7 km April 26 “Green Hills” 20. 1 km VHF Connectivity Tests April 27 4. 2 km Life in the Atacama Salt Mine Carnegie Mellon
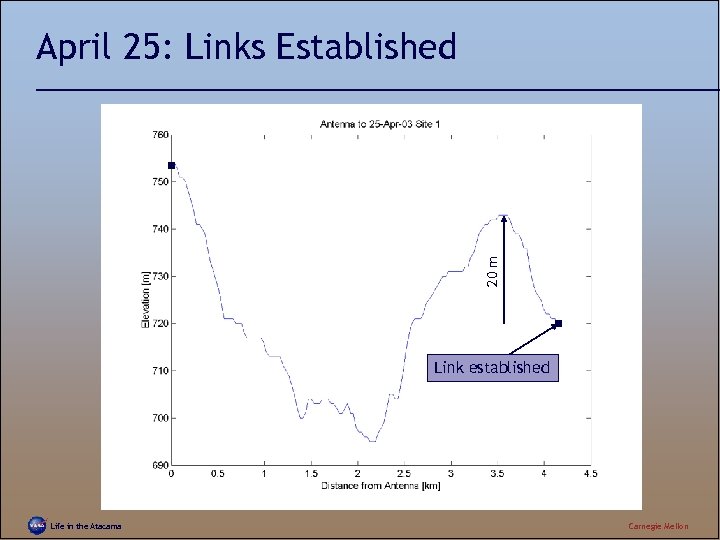
20 m April 25: Links Established Link established Life in the Atacama Carnegie Mellon
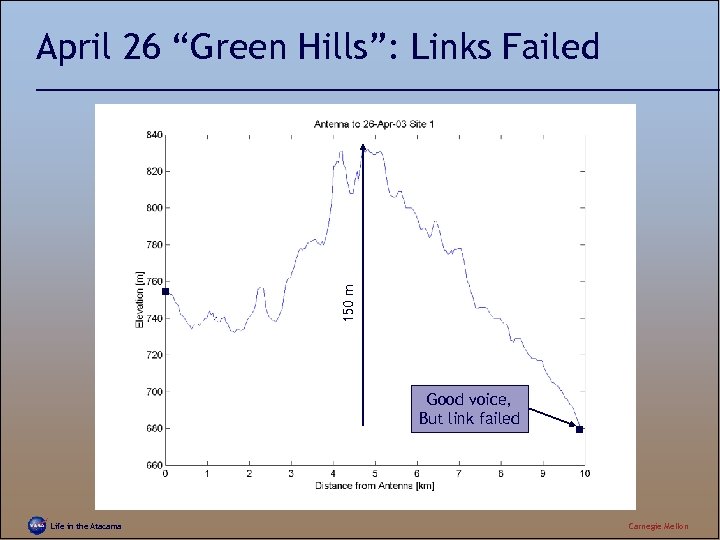
150 m April 26 “Green Hills”: Links Failed Good voice, But link failed Life in the Atacama Carnegie Mellon
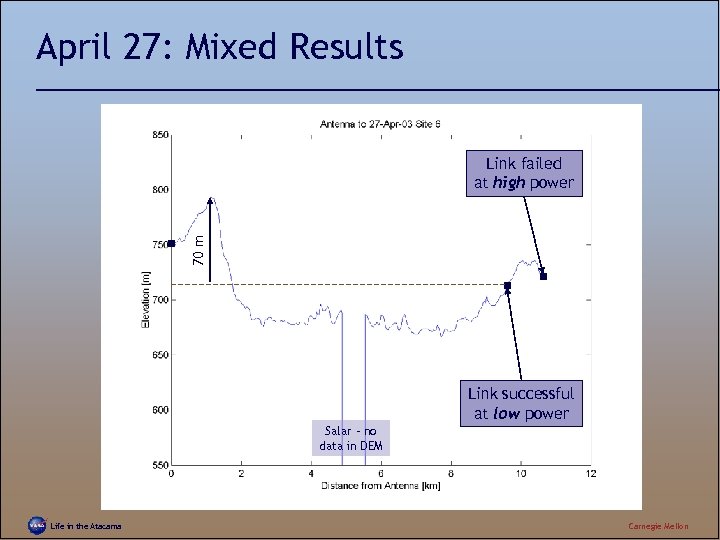
April 27: Mixed Results 70 m Link failed at high power Link successful at low power Salar – no data in DEM Life in the Atacama Carnegie Mellon
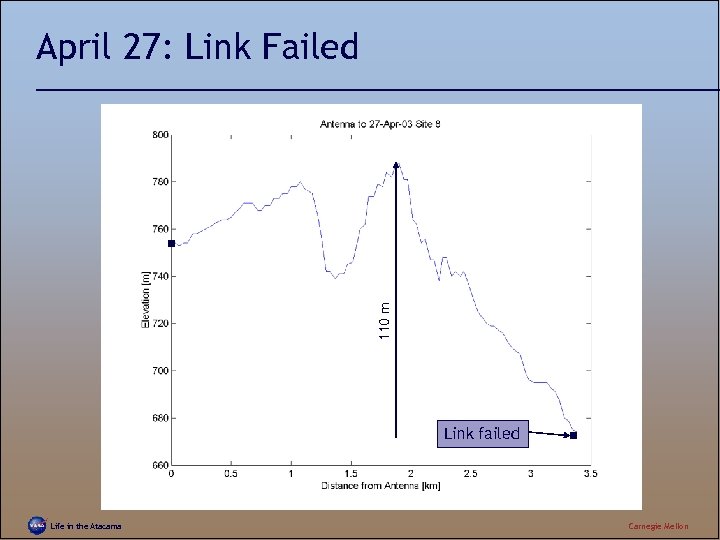
110 m April 27: Link Failed Link failed Life in the Atacama Carnegie Mellon

VHF Testing Conclusions The VHF comm system tested is capable of supporting intermittent, low data rate connections at ranges on the order of 10 km Much further range (>20 km) is likely with: A higher antenna mount (~20 ft) A higher-gain antenna (~13 d. Bi) Automated pointing at base camp (only 10 deg accuracy required) Comm-based mission planning onboard robot – based on LOS results from tests Life in the Atacama Carnegie Mellon

900 MHz Testing Purpose Understand suitability of 900 MHz system for a wireless Ethernet replacement Longer range, but lower data rates Life in the Atacama Carnegie Mellon
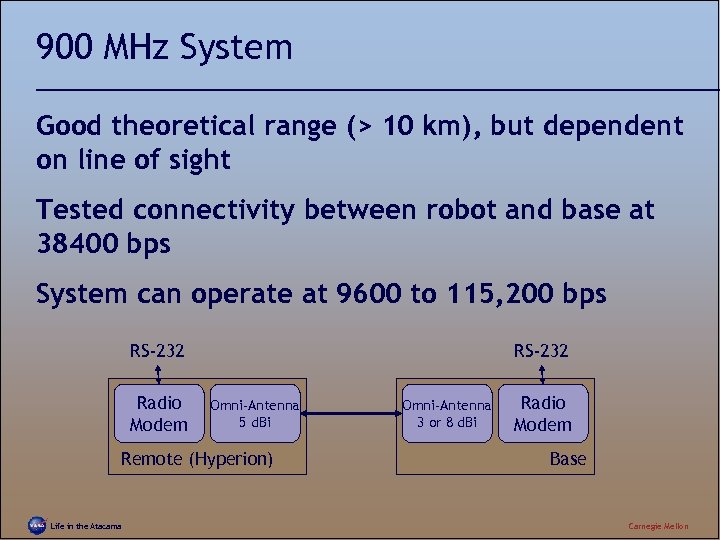
900 MHz System Good theoretical range (> 10 km), but dependent on line of sight Tested connectivity between robot and base at 38400 bps System can operate at 9600 to 115, 200 bps RS-232 Radio Modem RS-232 Omni-Antenna 5 d. Bi Remote (Hyperion) Life in the Atacama Omni-Antenna 3 or 8 d. Bi Radio Modem Base Carnegie Mellon
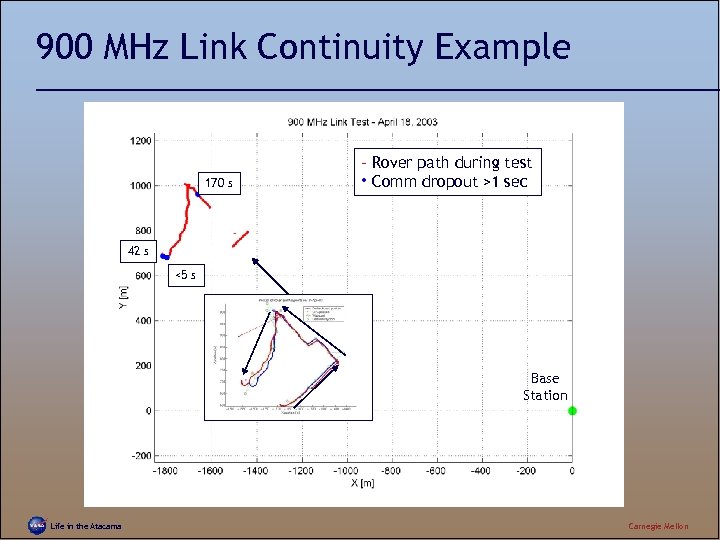
900 MHz Link Continuity Example 170 s – Rover path during test • Comm dropout >1 sec 42 s <5 s Base Station Life in the Atacama Carnegie Mellon
900 MHz Testing Conclusions Several advantages over 2. 4 GHz Small 3 d. Bi antenna matched range of high-gain 2. 4 GHz antennas, 8 d. Bi antenna should do far better Smaller antenna means less panel shadowing / mechanism interference Directionality still very important Did not collect enough data to determine relationship between distance and data rate Future 900 MHz systems should have: Very tall antenna mounts or well-placed repeaters Directional antennas with automated antenna pointing Comm-based mission planning onboard robot Life in the Atacama Carnegie Mellon
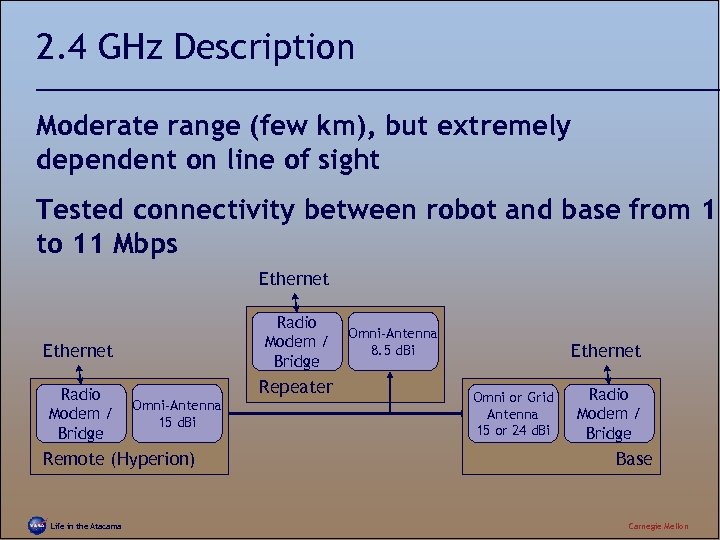
2. 4 GHz Description Moderate range (few km), but extremely dependent on line of sight Tested connectivity between robot and base from 1 to 11 Mbps Ethernet Radio Modem / Bridge Omni-Antenna 15 d. Bi Remote (Hyperion) Life in the Atacama Repeater Omni-Antenna 8. 5 d. Bi Ethernet Omni or Grid Antenna 15 or 24 d. Bi Radio Modem / Bridge Base Carnegie Mellon

2. 4 GHz Conclusions Needed to reposition repeater station very frequently, sometimes 3 or 4 times per day Repeater movements would interrupt operations for 20 – 60 minutes Automatically-maintained network maps were not reliable Life in the Atacama Carnegie Mellon

Telemetry Log Volume Collected telemetry logs over entire expedition Includes gigabytes of inter-process messages, commands and telemetry Does not include science data Analyzed the contents of logs over 10 days Over 2. 5 million messages logged Over 3 GB of data logged Life in the Atacama Carnegie Mellon
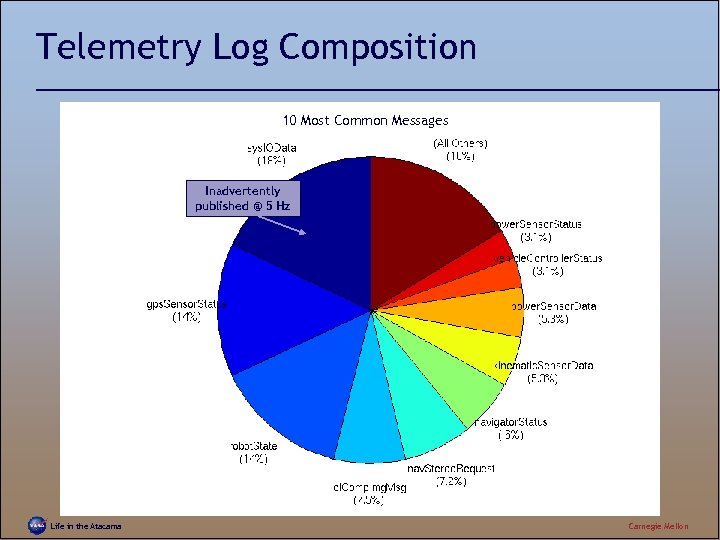
Telemetry Log Composition 10 Most Common Messages Inadvertently published @ 5 Hz Life in the Atacama Carnegie Mellon
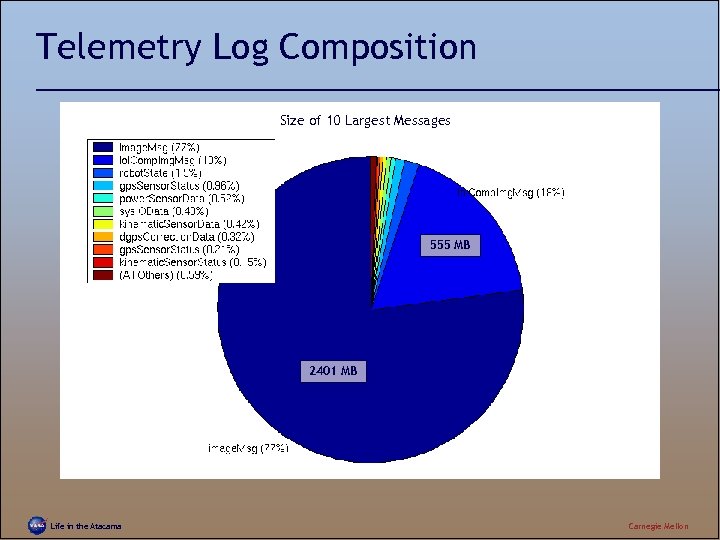
Telemetry Log Composition Size of 10 Largest Messages 555 MB 2401 MB Life in the Atacama Carnegie Mellon
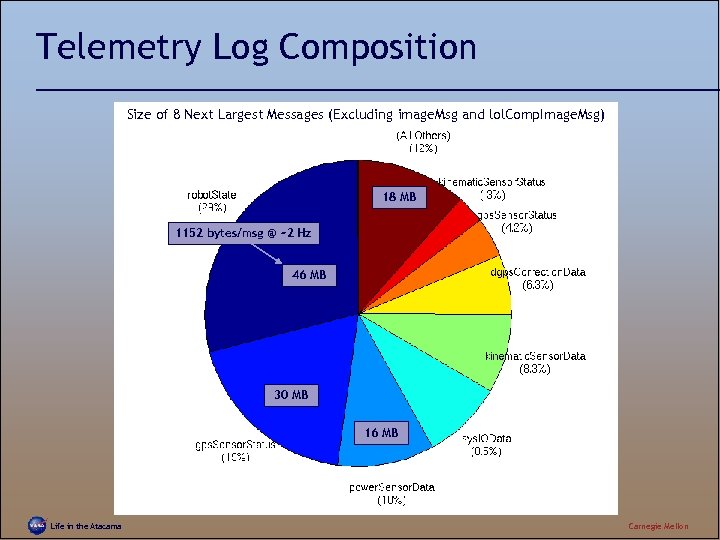
Telemetry Log Composition Size of 8 Next Largest Messages (Excluding image. Msg and lol. Comp. Image. Msg) 18 MB 1152 bytes/msg @ ~2 Hz 46 MB 30 MB 16 MB Life in the Atacama Carnegie Mellon
Telemetry Manager Improvements Must operate over low-bandwidth, intermittent communications link How to prioritize data for remote operators? Consider what tasks remote operators need to do Provide only the data that enables these tasks For instance, if pitch angle limits exceeded, return recent rover pose and terrain maps to assist recovery Will require that the TM cooperate with other software modules Life in the Atacama Carnegie Mellon
3111baf2f15000981ea22deea2ae6923.ppt