89e1cd907e031207ac96ca0d6d7ef289.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Communications Studies and Personal Development - Damian Gordon -
Communications Studies and Personal Development - Damian Gordon -
 FIP FIRST IMPORTANT PRIORITIES
FIP FIRST IMPORTANT PRIORITIES
 FIP • The process of picking out the most important ideas, factors, objectives, consequences • To be used in conjunction with other techniques (e. g. CAF, APC ) • Purpose is to restore the balance in a deliberate manner. • FIP is a judgement situation and there are no absolute answers.
FIP • The process of picking out the most important ideas, factors, objectives, consequences • To be used in conjunction with other techniques (e. g. CAF, APC ) • Purpose is to restore the balance in a deliberate manner. • FIP is a judgement situation and there are no absolute answers.
 FIP: Example • FIP on scenario “A husband wife go to buy a used car for their family”
FIP: Example • FIP on scenario “A husband wife go to buy a used car for their family”
 FIP: Example 1. The person selling it actually owns it 2. The price of the car 3. The type of car and colour 4. The engine power and speed of the car 5. All the mechanical parts are working well 6. The car is big enough for a family 7. Has the car been in a crash? 8. It will be easy to get replacement parts 9. It has tax and NCT certificates 10. What is the potential resell value?
FIP: Example 1. The person selling it actually owns it 2. The price of the car 3. The type of car and colour 4. The engine power and speed of the car 5. All the mechanical parts are working well 6. The car is big enough for a family 7. Has the car been in a crash? 8. It will be easy to get replacement parts 9. It has tax and NCT certificates 10. What is the potential resell value?
 FIP: Example 1. The person selling it actually owns it 2. The price of the car 3. The type of car and colour 4. The engine power and speed of the car 5. All the mechanical parts are working well 6. The car is big enough for a family 7. Has the car been in a crash? 8. It will be easy to get replacement parts 9. It has tax and NCT certificates 10. What is the potential resell value?
FIP: Example 1. The person selling it actually owns it 2. The price of the car 3. The type of car and colour 4. The engine power and speed of the car 5. All the mechanical parts are working well 6. The car is big enough for a family 7. Has the car been in a crash? 8. It will be easy to get replacement parts 9. It has tax and NCT certificates 10. What is the potential resell value?
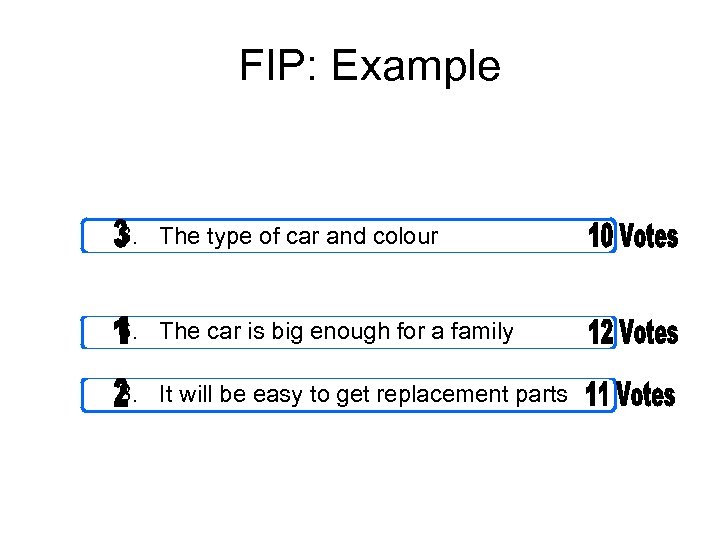 FIP: Example 1. The person selling it actually owns it 2. The price of the car 3. The type of car and colour 4. The engine power and speed of the car 5. All the mechanical parts are working well 6. The car is big enough for a family 7. Has the car been in a crash? 8. It will be easy to get replacement parts 9. It has tax and NCT certificates 10. What is the potential resell value?
FIP: Example 1. The person selling it actually owns it 2. The price of the car 3. The type of car and colour 4. The engine power and speed of the car 5. All the mechanical parts are working well 6. The car is big enough for a family 7. Has the car been in a crash? 8. It will be easy to get replacement parts 9. It has tax and NCT certificates 10. What is the potential resell value?
 FIP: Exercise • FIP on choosing hairstyle.
FIP: Exercise • FIP on choosing hairstyle.
 C&S CONSEQUENCES & SEQUELS
C&S CONSEQUENCES & SEQUELS
 C&S • The process of looking ahead to see the consequences of some action, plan, decision, rule, invention. • C&S deals with what may happen after the decision has been made. – Short-term (1 -2 years) – Medium-term (2 -5 years) – Long-term consequences (over 5 years).
C&S • The process of looking ahead to see the consequences of some action, plan, decision, rule, invention. • C&S deals with what may happen after the decision has been made. – Short-term (1 -2 years) – Medium-term (2 -5 years) – Long-term consequences (over 5 years).
 C&S: How to do it
C&S: How to do it
 C&S: How to do it
C&S: How to do it
 C&S: How to do it ST MT LT
C&S: How to do it ST MT LT
 C&S: How to do it ST MT LT
C&S: How to do it ST MT LT
 C&S: How to do it ST Faskmdf wkmfwef Rfa qrrtyj tu eyw weewtwrtjwryjyj wj 3446 j 46 j 46 je Sad. f/mr kiwmr r MT LT
C&S: How to do it ST Faskmdf wkmfwef Rfa qrrtyj tu eyw weewtwrtjwryjyj wj 3446 j 46 j 46 je Sad. f/mr kiwmr r MT LT
 C&S: How to do it ST MT Faskmdf wkmfwef Salkmvskfvmaslfkv Rfa qrrtyj tu eyw Fvkl’amfapwwrvm weewtwrtjwryjyj We weew; vws; vwp wj 3446 j 46 j 46 je Fsvwmwwefwe; l, Sad. f/mr kiwmr r Efwe, fwopropmgrt LT
C&S: How to do it ST MT Faskmdf wkmfwef Salkmvskfvmaslfkv Rfa qrrtyj tu eyw Fvkl’amfapwwrvm weewtwrtjwryjyj We weew; vws; vwp wj 3446 j 46 j 46 je Fsvwmwwefwe; l, Sad. f/mr kiwmr r Efwe, fwopropmgrt LT
 C&S: How to do it ST MT LT Faskmdf wkmfwef Salkmvskfvmaslfkv Sadfmewpmfeow Rfa qrrtyj tu eyw Fvkl’amfapwwrvm Wefwe; lfmsdom weewtwrtjwryjyj We weew; vws; vwp Efw[p, pwefwew wj 3446 j 46 j 46 je Fsvwmwwefwe; l, Wef; ewsefsd[ee Sad. f/mr kiwmr r Efwe, fwopropmgrt Weflwef, we; , efl
C&S: How to do it ST MT LT Faskmdf wkmfwef Salkmvskfvmaslfkv Sadfmewpmfeow Rfa qrrtyj tu eyw Fvkl’amfapwwrvm Wefwe; lfmsdom weewtwrtjwryjyj We weew; vws; vwp Efw[p, pwefwew wj 3446 j 46 j 46 je Fsvwmwwefwe; l, Wef; ewsefsd[ee Sad. f/mr kiwmr r Efwe, fwopropmgrt Weflwef, we; , efl
 C&S: Example • An Australian man introduces rabbits into the country to provide hunting for his friends.
C&S: Example • An Australian man introduces rabbits into the country to provide hunting for his friends.
 C&S: Example • Short-Term consequences – friends have plenty to shoot at, – rabbit is alternative source of food, – lots of fun had, – lots of guns sold
C&S: Example • Short-Term consequences – friends have plenty to shoot at, – rabbit is alternative source of food, – lots of fun had, – lots of guns sold
 C&S: Example • Medium-Term consequences – rabbits have multiplied, – they have become a pest
C&S: Example • Medium-Term consequences – rabbits have multiplied, – they have become a pest
 C&S: Example • Long-Term consequences – rabbits have spread all over Australia – do a lot of damage to crops
C&S: Example • Long-Term consequences – rabbits have spread all over Australia – do a lot of damage to crops
 C&S: Exercise • “A new device has been created to immediately tell if someone is telling lies”
C&S: Exercise • “A new device has been created to immediately tell if someone is telling lies”
 AGO AIMS, GOALS & OBJECTIVES
AGO AIMS, GOALS & OBJECTIVES
 AGO • To introduce and emphasise the idea of purpose • Focus directly and deliberately on the intention behind actions. – Aim is the general direction – Goal is an ultimate destination – Objectives are recognisable points of achievement along the way
AGO • To introduce and emphasise the idea of purpose • Focus directly and deliberately on the intention behind actions. – Aim is the general direction – Goal is an ultimate destination – Objectives are recognisable points of achievement along the way
 AGO: Example • “A developer is building a new shopping centre”
AGO: Example • “A developer is building a new shopping centre”
 AGO: Example • Aim – Make all arrangements for building • Goal – Complete the shopping centre • Objectives – – – to make a profit, build a successful shopping centre, pleasing potential shoppers, fitting in with planning authorities, work well in time and in budget
AGO: Example • Aim – Make all arrangements for building • Goal – Complete the shopping centre • Objectives – – – to make a profit, build a successful shopping centre, pleasing potential shoppers, fitting in with planning authorities, work well in time and in budget
 AGO: Exercise • Develop an AGO for the police and put them in order of priority
AGO: Exercise • Develop an AGO for the police and put them in order of priority
 APC ALTERNATIVES, POSSIBILITIES & CHOICES
APC ALTERNATIVES, POSSIBILITIES & CHOICES
 APC • The process of deliberately trying to find alternatives. • An attempt to focus attention directly on exploring all the alternatives or choices or possibilities - beyond the obvious ones • Applies not only to action but also to explanations.
APC • The process of deliberately trying to find alternatives. • An attempt to focus attention directly on exploring all the alternatives or choices or possibilities - beyond the obvious ones • Applies not only to action but also to explanations.
 APC: Example • You arrive at school on Monday morning and see the goal posts have been removed. What could have happened?
APC: Example • You arrive at school on Monday morning and see the goal posts have been removed. What could have happened?
 APC: Example • Vandals cut them down • A car backed into a post badly splintering it and for safety sake it had to be removed. • The PE teacher had taken them down because they were not regulation size • The local football team borrowed them for a match • A pole vaulter needed to some quick practice • A Jousting contest had been held over the weekend and no one wanted to use real lances • A new school building is going to be built on the field
APC: Example • Vandals cut them down • A car backed into a post badly splintering it and for safety sake it had to be removed. • The PE teacher had taken them down because they were not regulation size • The local football team borrowed them for a match • A pole vaulter needed to some quick practice • A Jousting contest had been held over the weekend and no one wanted to use real lances • A new school building is going to be built on the field
 APC: Exercise • The brightest girl in class starts making mistakes in her work on purpose, what are the possible explanations ?
APC: Exercise • The brightest girl in class starts making mistakes in her work on purpose, what are the possible explanations ?
 Summary • • PMI = Plus, Minus, Interesting CAF = Consider All Factors OPV = Other People’s Views FIP = First Important Priorities C&S = Consequences & Sequels AGO = Aims, Goals, Objectives APC = Alternatives, Possibilities, Choices
Summary • • PMI = Plus, Minus, Interesting CAF = Consider All Factors OPV = Other People’s Views FIP = First Important Priorities C&S = Consequences & Sequels AGO = Aims, Goals, Objectives APC = Alternatives, Possibilities, Choices


