7929487d0bac8b42ec1a36bc21955f76.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 Communications & Networks Standard Grade Revision: Networks
Communications & Networks Standard Grade Revision: Networks
 What is a Network? • A series of computers linked together so can send and receive data. • We use them for sending e-mails, downloading files, shopping, etc • They are divided into two types: – Local Area Network (LAN) – Wide Area Network (WAN)
What is a Network? • A series of computers linked together so can send and receive data. • We use them for sending e-mails, downloading files, shopping, etc • They are divided into two types: – Local Area Network (LAN) – Wide Area Network (WAN)
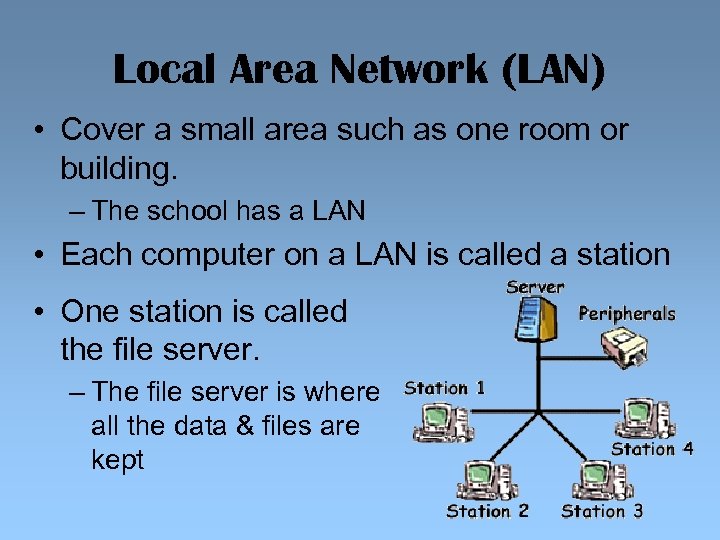 Local Area Network (LAN) • Cover a small area such as one room or building. – The school has a LAN • Each computer on a LAN is called a station • One station is called the file server. – The file server is where all the data & files are kept
Local Area Network (LAN) • Cover a small area such as one room or building. – The school has a LAN • Each computer on a LAN is called a station • One station is called the file server. – The file server is where all the data & files are kept
 Advantages of a LAN • • • Share data Share peripherals (resource sharing) E-mail Passwords keep data secure Different levels of access – stop unauthorised access • Flexible access – Use any station connected to the LAN • Many users can use same document at the same time (workgroup computing)
Advantages of a LAN • • • Share data Share peripherals (resource sharing) E-mail Passwords keep data secure Different levels of access – stop unauthorised access • Flexible access – Use any station connected to the LAN • Many users can use same document at the same time (workgroup computing)
 Transmission media for LAN • Stations can be connected by cables or wireless technology • Cables: –Unshielded Twisted Pair of copper wire (UTP) • Uses electrical signals to transmit data • Cheaper but can get interference –Optical fibre • Uses light beams to transmit data • Expensive but doesn't get interference
Transmission media for LAN • Stations can be connected by cables or wireless technology • Cables: –Unshielded Twisted Pair of copper wire (UTP) • Uses electrical signals to transmit data • Cheaper but can get interference –Optical fibre • Uses light beams to transmit data • Expensive but doesn't get interference
 Transmission media for LAN • Wireless – Infrared communication • Like the TV controls – Bluetooth • Range of about 10 metres – WIFI (Wireless Fidelity Alliance) • Range of about 12 -50 metres Bluetooth & WIFI use radio waves
Transmission media for LAN • Wireless – Infrared communication • Like the TV controls – Bluetooth • Range of about 10 metres – WIFI (Wireless Fidelity Alliance) • Range of about 12 -50 metres Bluetooth & WIFI use radio waves
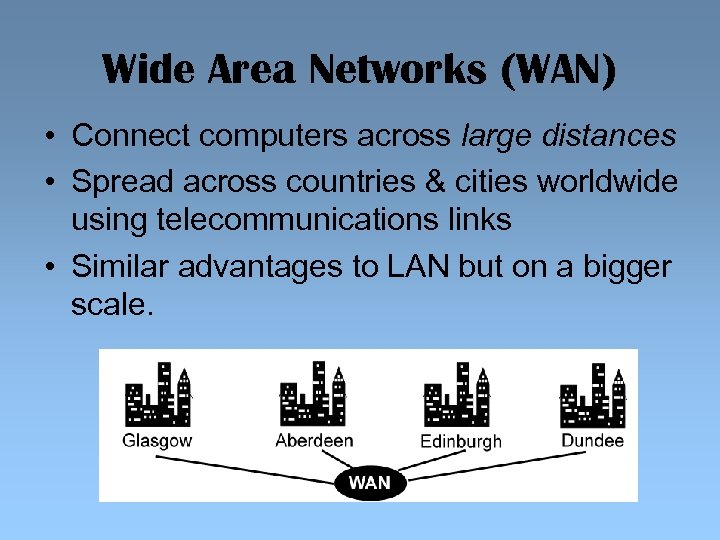 Wide Area Networks (WAN) • Connect computers across large distances • Spread across countries & cities worldwide using telecommunications links • Similar advantages to LAN but on a bigger scale.
Wide Area Networks (WAN) • Connect computers across large distances • Spread across countries & cities worldwide using telecommunications links • Similar advantages to LAN but on a bigger scale.
 Transmission Media for WANs • Telecommunications links – The communication of information over a distance using: • Microwave transmission • Satellite links • Optical Fibre
Transmission Media for WANs • Telecommunications links – The communication of information over a distance using: • Microwave transmission • Satellite links • Optical Fibre
 Network Security • Security methods include: – Passwords & user IDs – Encryption – Physical methods
Network Security • Security methods include: – Passwords & user IDs – Encryption – Physical methods
 Lesson Objectives • We will learn about: – Client Server Networks – Network Interface Cards – Multi-Access Computers – Social, Legal & Ethical Issues
Lesson Objectives • We will learn about: – Client Server Networks – Network Interface Cards – Multi-Access Computers – Social, Legal & Ethical Issues
 Recap - LAN • Area: • Stations & File Server • Transmission Medium: • Advantages of LANs – Share data – Resource sharing – Different levels of access – Flexible access – workgroup computing
Recap - LAN • Area: • Stations & File Server • Transmission Medium: • Advantages of LANs – Share data – Resource sharing – Different levels of access – Flexible access – workgroup computing
 Recap - WAN • Area: • Network Security: • Transmission Medium: – Telecommunications Links
Recap - WAN • Area: • Network Security: • Transmission Medium: – Telecommunications Links
 Client & Server Networks • A method of network organisation • Each workstation is called a client • Each workstation is connected to a central system called a server • The server can be used for: – Holding all the data files and application software – Organising printing on the network – Organising the clients’ access to the internet
Client & Server Networks • A method of network organisation • Each workstation is called a client • Each workstation is connected to a central system called a server • The server can be used for: – Holding all the data files and application software – Organising printing on the network – Organising the clients’ access to the internet
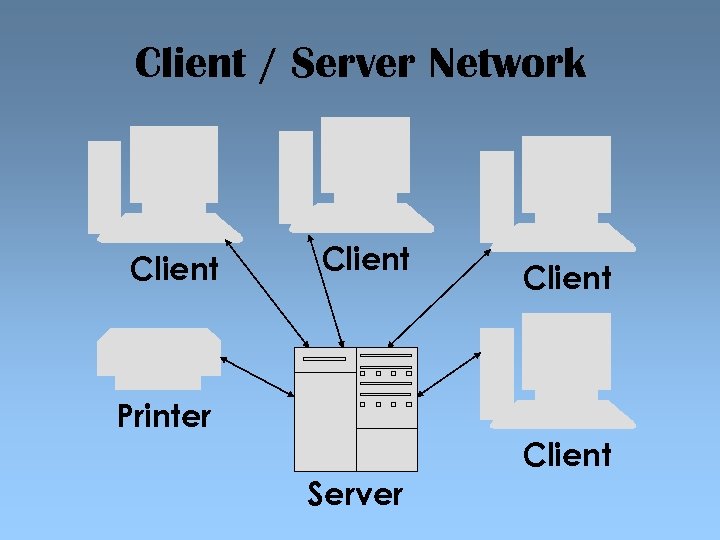 Client / Server Network Client Printer Client Server
Client / Server Network Client Printer Client Server
 Network Interface Card • Allows the computer system to communicate with the network • Every device that is connected to the LAN will need a NIC, for example, computer, printer and scanner. • It take the data sent by your computer – stores it in its own memory locations, – then adapts it ensuring it follows the communication rules
Network Interface Card • Allows the computer system to communicate with the network • Every device that is connected to the LAN will need a NIC, for example, computer, printer and scanner. • It take the data sent by your computer – stores it in its own memory locations, – then adapts it ensuring it follows the communication rules
 Multi-Access Computers • Enable many users to: – Access the system at the same time – Share the proccessing power of the system – Shave the available memory – Share the data on backing storage • The terminals attached to these computers useually have no processing power of their own. • The terminals would be made up of just a monitor and keyboard
Multi-Access Computers • Enable many users to: – Access the system at the same time – Share the proccessing power of the system – Shave the available memory – Share the data on backing storage • The terminals attached to these computers useually have no processing power of their own. • The terminals would be made up of just a monitor and keyboard
 Social Issues • Teleworking – Process of using a WAN to work from home • WANs can improve communications for people in remote areas • Some people can’t afford the cost so a gap could form between the “Information Rich” and the “Information Poor” • Some people believe that computers cause social isolation
Social Issues • Teleworking – Process of using a WAN to work from home • WANs can improve communications for people in remote areas • Some people can’t afford the cost so a gap could form between the “Information Rich” and the “Information Poor” • Some people believe that computers cause social isolation
 Legal & Ethical Issues • Legal: – Computer Misuse Act – Copyright, Designs & Patents Act – Data Protection Act • Ethical: – Invasion of personal privacy – Censorship & freedom of speech
Legal & Ethical Issues • Legal: – Computer Misuse Act – Copyright, Designs & Patents Act – Data Protection Act • Ethical: – Invasion of personal privacy – Censorship & freedom of speech
 Communications & Networks Electronic Communications
Communications & Networks Electronic Communications
 Lesson Objectives • Electronic Communication • Text/Instant Messaging • E-Mail • Advantages & Disadvantages • File Attachments • Netiquette
Lesson Objectives • Electronic Communication • Text/Instant Messaging • E-Mail • Advantages & Disadvantages • File Attachments • Netiquette
 Electronic Communication • The process of sending and receiving electronic messages. • Electronic messages include: – Electronic mail – Text messaging – File transfer (attachments)
Electronic Communication • The process of sending and receiving electronic messages. • Electronic messages include: – Electronic mail – Text messaging – File transfer (attachments)
 Text Messaging • Types: – Short text message. – Instant messaging. • Language used: – Casual/Informal – Abbreviations – Acronyms
Text Messaging • Types: – Short text message. – Instant messaging. • Language used: – Casual/Informal – Abbreviations – Acronyms
 E-mail • Advantages: – – – Fast compared to post Cheap – ISP connection only Web mail – access anywhere Send multiple copies (CC) Organise folders • Disadvantages: – Spam – Viruses – Lack of Netiquette • File Transfer – Files can be attached – Size limit – Attached viruses
E-mail • Advantages: – – – Fast compared to post Cheap – ISP connection only Web mail – access anywhere Send multiple copies (CC) Organise folders • Disadvantages: – Spam – Viruses – Lack of Netiquette • File Transfer – Files can be attached – Size limit – Attached viruses
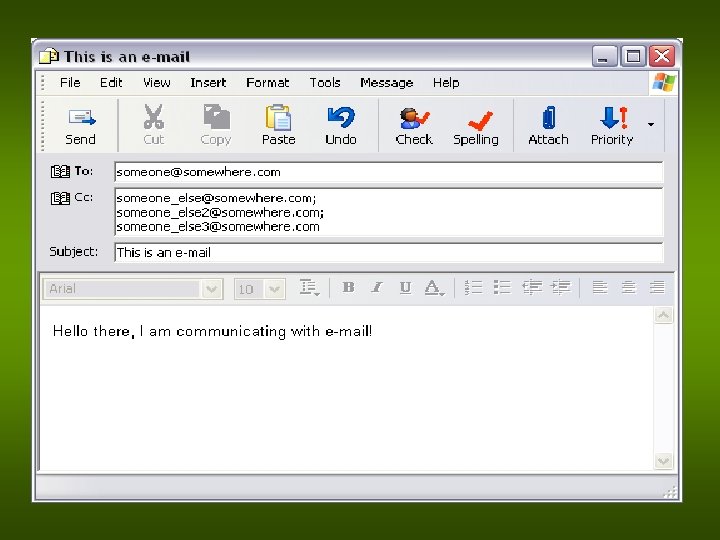
 Netiquette • Code of conduct used in e-communications • • DON’T WRITE IN CAPS! Don’t leave the Subject Field blank Don’t over use Formatting Don’t give out personal details Don’t start Flame Wars (Trolling) Use proper English in e-mails. Don’t send dumb jokes, chain mail, etc
Netiquette • Code of conduct used in e-communications • • DON’T WRITE IN CAPS! Don’t leave the Subject Field blank Don’t over use Formatting Don’t give out personal details Don’t start Flame Wars (Trolling) Use proper English in e-mails. Don’t send dumb jokes, chain mail, etc
 Communications & Networks The Internet
Communications & Networks The Internet
 Lesson Objectives • Internet Services • Accessing the Internet • The World Wide Web • Search Engines
Lesson Objectives • Internet Services • Accessing the Internet • The World Wide Web • Search Engines
 The Internet • Enables computers and networks worldwide to connect with each other • The network of networks
The Internet • Enables computers and networks worldwide to connect with each other • The network of networks
 Internet Services • World Wide Web (www or just web) – Used for browsing or searching • E-mail – Communication & exchange of information • File transfer – Sending & receiving large amounts of information
Internet Services • World Wide Web (www or just web) – Used for browsing or searching • E-mail – Communication & exchange of information • File transfer – Sending & receiving large amounts of information
 Accessing the Internet • Internet ready computer • Internet Service Provider (ISP) – A company that provides access to the internet • Browser – Software used to view web pages • Email client – Program for sending and receiving email
Accessing the Internet • Internet ready computer • Internet Service Provider (ISP) – A company that provides access to the internet • Browser – Software used to view web pages • Email client – Program for sending and receiving email
 Accessing the Internet • Modem – The telephone line doesn’t understand binary – A modem is needed to translate for the computer • Dial-Up – Uses a modem and an ordinary phone line to dial up the number of your ISP that connects you to the internet. • Broadband – Uses either a digital subscriber line (DSL) or a cable modem
Accessing the Internet • Modem – The telephone line doesn’t understand binary – A modem is needed to translate for the computer • Dial-Up – Uses a modem and an ordinary phone line to dial up the number of your ISP that connects you to the internet. • Broadband – Uses either a digital subscriber line (DSL) or a cable modem
 World Wide Web • Information is stored in web pages on web sites • These pages can be viewed in a browser • They are found by an address such as: – www. google. co. uk – www. msn. com • Hyperlinks are used to ‘travel’ around the web
World Wide Web • Information is stored in web pages on web sites • These pages can be viewed in a browser • They are found by an address such as: – www. google. co. uk – www. msn. com • Hyperlinks are used to ‘travel’ around the web
 The Web - HTML • Hyper Text Mark-up Language • The language used to write web pages <"http: //www. w 3. org/TR/html 4/loose. dtd">
The Web - HTML • Hyper Text Mark-up Language • The language used to write web pages <"http: //www. w 3. org/TR/html 4/loose. dtd">
 Search Engine • Special web site to help you find information • A big database! • Some of the main search engines:
Search Engine • Special web site to help you find information • A big database! • Some of the main search engines:
 Lesson Objectives • Software on the internet • Video conferencing • Streaming media • Internet services • Mobile Internet
Lesson Objectives • Software on the internet • Video conferencing • Streaming media • Internet services • Mobile Internet
 Software on the Internet • Freeware – Free software but the author still holds the copyright – You are not allowed to change it • Shareware – 30 -Day trial period – After that either pay for it or delete it
Software on the Internet • Freeware – Free software but the author still holds the copyright – You are not allowed to change it • Shareware – 30 -Day trial period – After that either pay for it or delete it
 Software on the Internet • Commercial – Pay full price up front – Limited to one backup copy – Licence agreements are very detailed
Software on the Internet • Commercial – Pay full price up front – Limited to one backup copy – Licence agreements are very detailed
 Video Conferencing • Using networks to send audio and visual data. • Enables people to have face-to-face meetings • Saves time and money • No need to travel long distances for business
Video Conferencing • Using networks to send audio and visual data. • Enables people to have face-to-face meetings • Saves time and money • No need to travel long distances for business
 VideoAudio Streaming • The internet is used to send data one way • Online radio stations do this • Uses large amount of network bandwidth
VideoAudio Streaming • The internet is used to send data one way • Online radio stations do this • Uses large amount of network bandwidth
 Other Internet Services • Chat & instant messaging – Text based communication – Communication is in real time (instant) • Weblogging (Blog) – A type of online diary – Used for both business & personal • Bulletin boards – Electronic notice board
Other Internet Services • Chat & instant messaging – Text based communication – Communication is in real time (instant) • Weblogging (Blog) – A type of online diary – Used for both business & personal • Bulletin boards – Electronic notice board
 Mobile Internet • Using the internet while on the move – Walk ‘N’ Surf • Devices include – Mobile phones, Laptops, palmtops
Mobile Internet • Using the internet while on the move – Walk ‘N’ Surf • Devices include – Mobile phones, Laptops, palmtops


