cb55c39e033b74628dae878a5151a027.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 Communication – Network Management Technologies KNOWLEDGE REPRESENTATION Ontologies Rashid Mijumbi Barcelona, April 2011
Communication – Network Management Technologies KNOWLEDGE REPRESENTATION Ontologies Rashid Mijumbi Barcelona, April 2011
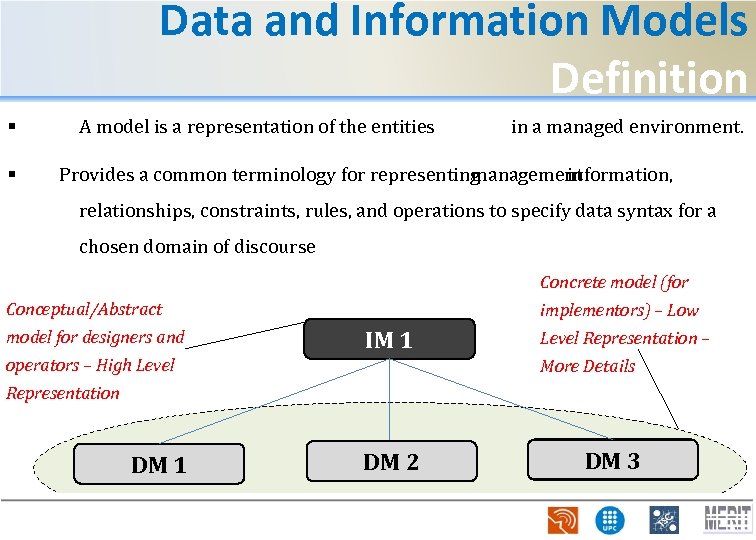 Data and Information Models Definition § § A model is a representation of the entities in a managed environment. Provides a common terminology for representing management information, relationships, constraints, rules, and operations to specify data syntax for a chosen domain of discourse Concrete model (for Conceptual/Abstract model for designers and implementors) – Low IM 1 operators – High Level Representation – More Details Representation DM 1 DM 2 DM 3
Data and Information Models Definition § § A model is a representation of the entities in a managed environment. Provides a common terminology for representing management information, relationships, constraints, rules, and operations to specify data syntax for a chosen domain of discourse Concrete model (for Conceptual/Abstract model for designers and implementors) – Low IM 1 operators – High Level Representation – More Details Representation DM 1 DM 2 DM 3
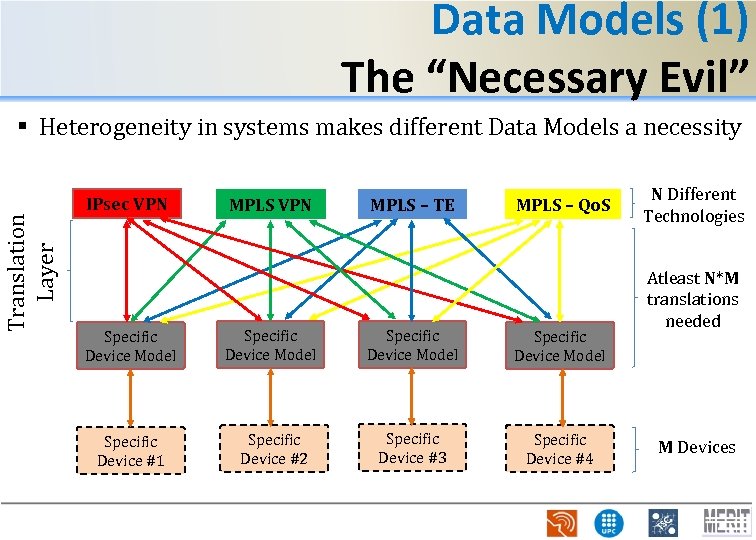 Data Models (1) The “Necessary Evil” Translation Layer § Heterogeneity in systems makes different Data Models a necessity IPsec VPN MPLS – TE MPLS – Qo. S Specific Device Model Specific Device #1 Specific Device #2 Specific Device #3 Specific Device #4 N Different Technologies Atleast N*M translations needed M Devices
Data Models (1) The “Necessary Evil” Translation Layer § Heterogeneity in systems makes different Data Models a necessity IPsec VPN MPLS – TE MPLS – Qo. S Specific Device Model Specific Device #1 Specific Device #2 Specific Device #3 Specific Device #4 N Different Technologies Atleast N*M translations needed M Devices
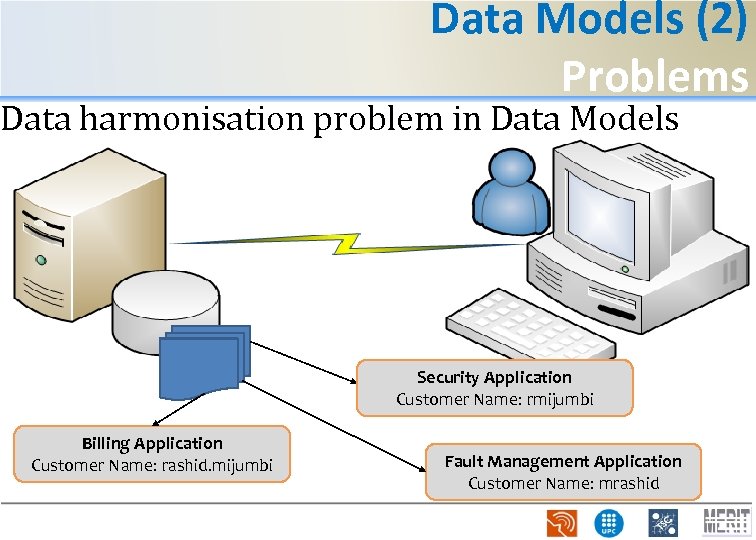 Data Models (2) Problems Data harmonisation problem in Data Models Security Application Customer Name: rmijumbi Billing Application Customer Name: rashid. mijumbi Fault Management Application Customer Name: mrashid
Data Models (2) Problems Data harmonisation problem in Data Models Security Application Customer Name: rmijumbi Billing Application Customer Name: rashid. mijumbi Fault Management Application Customer Name: mrashid
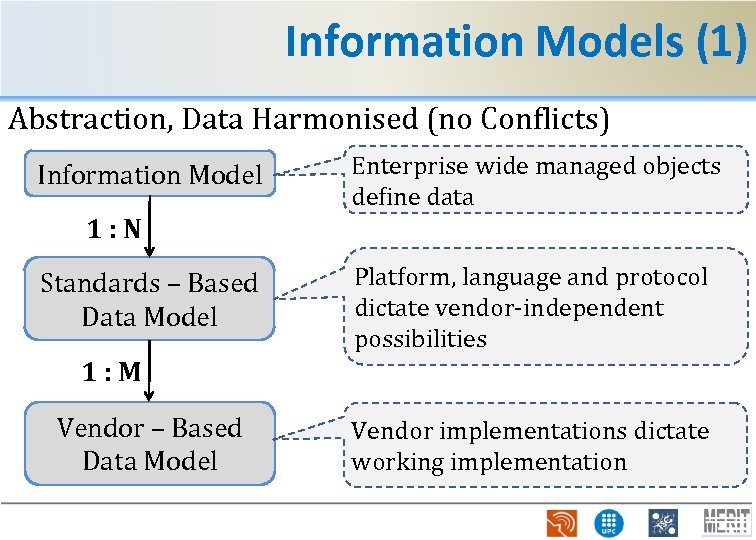 Information Models (1) Abstraction, Data Harmonised (no Conflicts) Information Model Enterprise wide managed objects define data 1: N Standards – Based Data Model Platform, language and protocol dictate vendor-independent possibilities 1: M Vendor – Based Data Model Vendor implementations dictate working implementation
Information Models (1) Abstraction, Data Harmonised (no Conflicts) Information Model Enterprise wide managed objects define data 1: N Standards – Based Data Model Platform, language and protocol dictate vendor-independent possibilities 1: M Vendor – Based Data Model Vendor implementations dictate working implementation
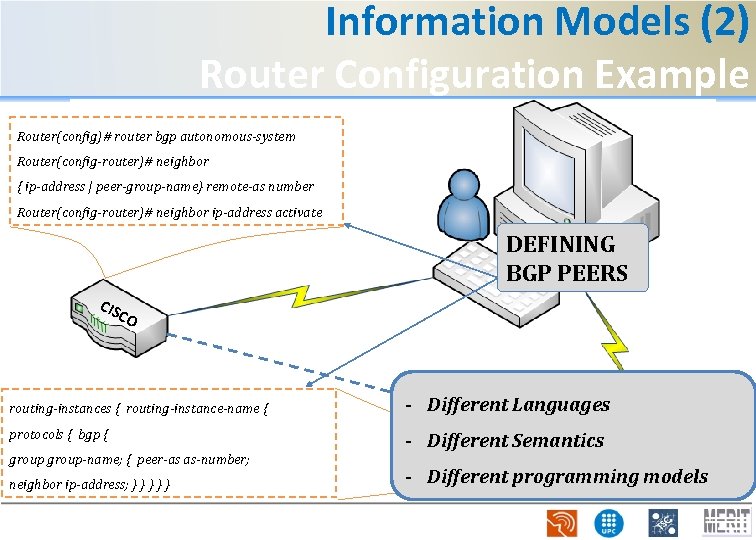 Information Models (2) Router Configuration Example Router(config)# router bgp autonomous-system Router(config-router)# neighbor { ip-address | peer-group-name} remote-as number Router(config-router)# neighbor ip-address activate DEFINING BGP PEERS CIS C O routing-instances { routing-instance-name { - Different Languages protocols { bgp { - Different Semantics group-name; { peer-as as-number; neighbor ip-address; } } } Jun ipe r - Different programming models
Information Models (2) Router Configuration Example Router(config)# router bgp autonomous-system Router(config-router)# neighbor { ip-address | peer-group-name} remote-as number Router(config-router)# neighbor ip-address activate DEFINING BGP PEERS CIS C O routing-instances { routing-instance-name { - Different Languages protocols { bgp { - Different Semantics group-name; { peer-as as-number; neighbor ip-address; } } } Jun ipe r - Different programming models
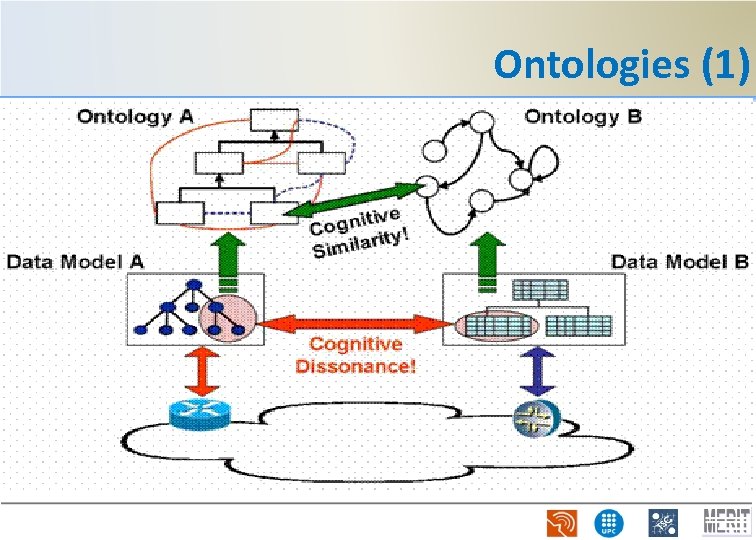 Ontologies (1)
Ontologies (1)
 Ontologies (2) § Ontology refers to the shared understanding of some domain of interest which may be used as a unifying framework – Uschold and Gruininger (1996) § An ontology is an explicit specification of a conceptualisation. – Gruber 1993 § Ontologies offer a formal mechanism for defining an understanding of data § Ontological Commitments § Ontology Requirements: Clarity, Coherence, Extensibility, Minimal encoding bias, Minimal ontological commitment
Ontologies (2) § Ontology refers to the shared understanding of some domain of interest which may be used as a unifying framework – Uschold and Gruininger (1996) § An ontology is an explicit specification of a conceptualisation. – Gruber 1993 § Ontologies offer a formal mechanism for defining an understanding of data § Ontological Commitments § Ontology Requirements: Clarity, Coherence, Extensibility, Minimal encoding bias, Minimal ontological commitment
 Ontology Languages An ontology language is made up of three components § syntax, § semantics (model theory), § proof theory. § The syntax of an ontology language is itself divided into three areas § Logic lexicon, non-logic lexicon and Grammar. § By Syntax § Cyc. L and KIF are examples of languages that support expressions in first-order logic. § By Structure § These languages use a markup scheme to encode knowledge, most commonly XML. § Ontology Inference Layer (OIL), OWL. §
Ontology Languages An ontology language is made up of three components § syntax, § semantics (model theory), § proof theory. § The syntax of an ontology language is itself divided into three areas § Logic lexicon, non-logic lexicon and Grammar. § By Syntax § Cyc. L and KIF are examples of languages that support expressions in first-order logic. § By Structure § These languages use a markup scheme to encode knowledge, most commonly XML. § Ontology Inference Layer (OIL), OWL. §
 Ontology Tools § Ontology development tools can be further distinguished as: those that are independent of an ontology language, and those that are dependent on one. § Protégé, Ontolingua. § Ontology merging tools § PROMPT, Chimaera. tightly
Ontology Tools § Ontology development tools can be further distinguished as: those that are independent of an ontology language, and those that are dependent on one. § Protégé, Ontolingua. § Ontology merging tools § PROMPT, Chimaera. tightly
 Semantic Web (1) § A new form of web content that is meaningful to computers - Berners-Lee 2001 User lives in Barcelona and Used. Cars Website
Semantic Web (1) § A new form of web content that is meaningful to computers - Berners-Lee 2001 User lives in Barcelona and Used. Cars Website
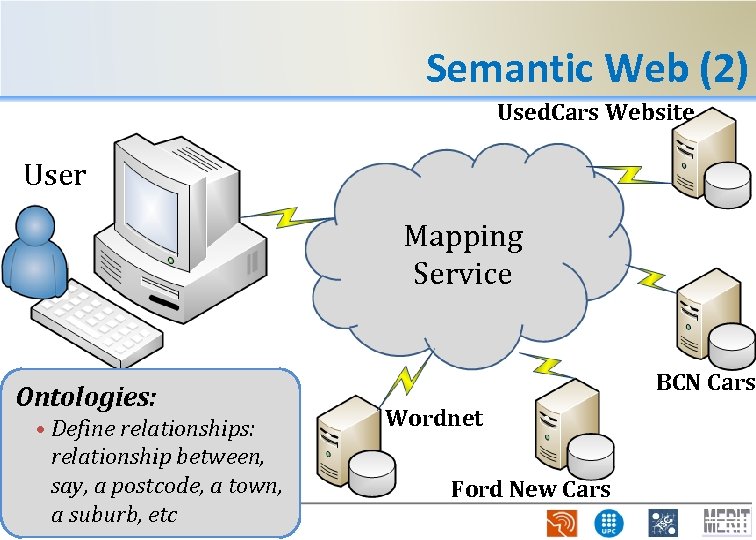 Semantic Web (2) Used. Cars Website User Mapping Service Ontologies: • Define relationships: relationship between, say, a postcode, a town, a suburb, etc BCN Cars Wordnet Ford New Cars
Semantic Web (2) Used. Cars Website User Mapping Service Ontologies: • Define relationships: relationship between, say, a postcode, a town, a suburb, etc BCN Cars Wordnet Ford New Cars


