ffa5bea33787452954c62b15bf924a6a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

Communicating in Teams Guffey text Ch 2, Thill/Bovee text Ch 2, Robbins text Ch 8 -9

Why Use Teams? “Two together can accomplish more than two separately” ¡ When is this statement true? ¡ When is this statement not true?

Why Use Teams? ¡ Better decisions ¡ Faster response ¡ Increased productivity ¡ Greater “buy-in” ¡ Less resistance to change ¡ Improved employee morale ¡ Reduced risks

Beware: Teams Aren’t Always the Answer Three tests: 1) 2) 3) Is the work complex, requiring different perspectives? Does the work create a common purpose/set of goals? Is purpose as strong a motivator as existing individual goals? Are group members involved in interdependent tasks?

Characteristics of Successful Teams ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Small size, diverse makeup Agreement on purpose Agreement on procedures Ability to deal with conflict Use of good communication techniques Ability to collaborate rather than compete Shared leadership

4 Stages of Team Development ¡ ¡ FORMING STORMING NORMING PERFORMING Teams can get stuck, or repeat stages.

Roles Played by Team Members Task Roles • Initiator • Information seeker/giver • Opinion seeker/giver • Direction giver • Summarizer • Diagnoser

Roles Played by Team Members o Energizer o Gatekeeper o Reality tester What kinds of statements might be made by these role players?

Roles Played by Team Members Relationship Roles • • • Participation encourager Harmonizer/ tension reliever Emotional climate evaluator Praise giver Empathic listener What kinds of statements might be made by these role players?
Roles Played by Team Members Dysfunctional Roles • • • Blocker Attacker Recognition-seeker Joker Withdrawer What kinds of statements might be made by these role players?

Skills for Team Leaders/Facilitators Task Relationships • Goal setting • Agenda making • Clarifying • Summarizing • Verbalizing consensus • Establishing work patterns • Following procedures

Skills for Team Leaders/Facilitators Interpersonal Relationships • Regulating participation • Maintaining positive climate • Maintaining mutual respect • Instigating group self-analysis • Resolving conflict • Instigating conflict
Conflict: Functional vs. Dysfunctional
Types of Conflict

Task Conflict ¡ Low to moderate levels = functional ¡ Positive effect on group performance when stimulates discussion

Relationship Conflict ¡ Almost always dysfunctional ¡ Increases personality clashes ¡ Decreases understanding
Process Conflict ¡ At low levels = functional ¡ Becomes dysfunctional when Creates uncertainty about task roles l Increases time to complete tasks l Leads to members working at cross-purposes l

Conflict: When to Call the Boss ¡ ¡ Conflict source is external to team Dysfunctional task or process conflict remains unresolved l l ¡ team applies conflict management process no immediate and sustained improvement Relationship conflict remains unresolved or creates hostile workplace environment

Discussion: Communication Matters ¡ Workplace Communication

Managing Conflict ¡ Conflict management styles ¡ Six-step procedure for managing conflict ¡ Dealing with avoidance ¡ Group decision-making methods
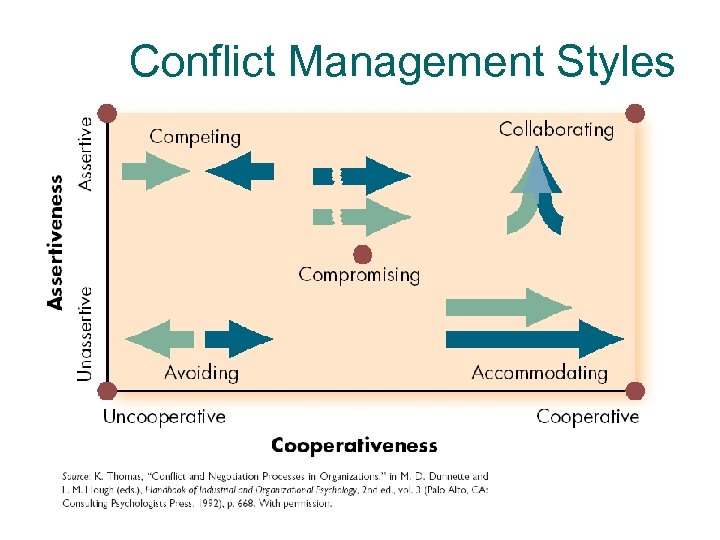
Conflict Management Styles

Conflict Style: Avoiding ¡ Behaviors l l l Avoiding people you find troublesome Avoiding issues that are unimportant, complex, or dangerous Postponing discussion until later

Conflict Style: Avoiding ¡ Benefits l l Reducing stress Saving time Steering clear of danger Setting up more favorable conditions ¡ Costs l l Declining working relationships Resentment Delays Degraded communication and decision making

Conflict Style: Competing ¡ Behaviors l l l Imposing of dictating a decision Arguing for a conclusion that fits your data Hard bargaining (making no concessions)

Conflict Style: Competing ¡ Benefits l l Asserting your position Quick victory potential Self-defense Testing assumptions ¡ Costs l l Strained work relationships Suboptimal decisions Decreased initiative and motivation Possible escalation of 4 horsemen

Conflict Style Accommodating ¡ Behaviors l l l Doing a favor to help someone Being persuaded Obeying an authority Deferring to another’s expertise Appeasing someone who is dangerous

Conflict Style: Accommodating ¡ Benefits l l Helping someone out Restoring harmony Building relationships Choosing a quick ending ¡ Costs l l l Sacrificed concerns Loss of respect Loss of motivation

Conflict Style: Compromising ¡ Behaviors l l l Soft bargaining (exchanging concessions) Taking turns Moderating your conclusions

Conflict Style: Compromising ¡ Benefits l l Pragmatism Speed and expediency Fairness Maintaining relationships ¡ Costs l l l Partially sacrificed concerns Suboptimal solutions Superficial understandings

Conflict Style: Collaborating ¡ Behaviors l l Reconciling interests through a win-win solution Combining insights into a richer understanding

Conflict Style: Collaborating ¡ Benefits l l High-quality decisions Learning and communication Resolution and commitment Strengthening relationships ¡ Costs l l Time and energy required Psychological demands Possibility of offending Vulnerability risk

Six-Step Procedure for Managing Conflict Goal: Collaborate or Compromise 1. Listen 2. Understand the other point of view 3. Show concern for the relationship 4. Look for common ground 5. Invent new problemsolving options 6. Reach a fair agreement

Dealing with Avoidance Clear the air If you’re on a team with someone who seems consistently irritated, a martyr, or passive-aggressive: l Ask for a private meeting l Solicit feedback l Listen without interrupting and with an open mind l Request permission to respond with equal openness

Group Decision-Making Methods ¡ Majority (vote) ¡ Consensus ¡ Minority (buy-in) (subgroup recommendation) ¡ Averaging ¡ Authority (compromise) rule with input What are the advantages and disadvantages of each method?

Productive Meetings

Is a Meeting Necessary? ¡ Topic is important ¡ Need for input/decision is urgent ¡ Requires an exchange of ideas A meeting is not necessary when: Objective=distribute information l No immediate feedback required l

Productive Meetings Before the meeting • Invite the right people those who have information • those who make decisions • those who implement decisions • • Distribute an agenda essential for introverts • include required pre-meeting preparation •

Productive Meetings During the Meeting Establish ground rules l Assign facilitator role l Start on time (watch socializing) l Introduce agenda, add items if needed or put on “parking lot” l Appoint a recorder l Encourage balanced participation l Confront conflict frankly l Summarize points of consensus l

Productive Meetings Ending the meeting • • • End on time Review meeting decisions Remind people of action items (identify who will do what by when) Following up • Distribute minutes of meeting • • • Absentees (for record) list of decisions action items

Organizing Team-Based Written and Oral Presentations ¡ See text (p. 53 -55) ¡ See consulting project on web site ¡ See boss (Loescher) Goal: Successful, meaningful, and FUN project

ffa5bea33787452954c62b15bf924a6a.ppt