108499a0441a85706babe9215799a39f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 96
 Common Core State Standards (CCSS) “Connecting The Dots” Grades 3 -4 -5 Mathematics Written Taught Tested 1 Bob Trammel Math Consultant robertwtrammel@msn. com
Common Core State Standards (CCSS) “Connecting The Dots” Grades 3 -4 -5 Mathematics Written Taught Tested 1 Bob Trammel Math Consultant robertwtrammel@msn. com
 Introductions and Welcome 2
Introductions and Welcome 2
 Welcome to All l 3 Introductions - Name - School and District - Grade Level - Number of Years Teaching - What You Do For Fun
Welcome to All l 3 Introductions - Name - School and District - Grade Level - Number of Years Teaching - What You Do For Fun
 Ice Breaker Activity l l l 4 On the back of your agenda …………. . Write 4 simple statements about yourself. Make 3 of them true and 1 of them false in random order. Don’t make the statements too complicated. Keep these hidden please. In a couple of minutes we will have some fun.
Ice Breaker Activity l l l 4 On the back of your agenda …………. . Write 4 simple statements about yourself. Make 3 of them true and 1 of them false in random order. Don’t make the statements too complicated. Keep these hidden please. In a couple of minutes we will have some fun.
 Bob’s 4 Statements See if you can pick the false statement from the below list! 1. I like to play golf. 2. I like to fish. 3. I like to run. 4. I like to lift weights. 5
Bob’s 4 Statements See if you can pick the false statement from the below list! 1. I like to play golf. 2. I like to fish. 3. I like to run. 4. I like to lift weights. 5
 Objectives 6 Each participant will learn the cohesive design of the Common Core State Standards @ grades 3 -4 -5 mathematics. Each participant will learn how to identify which mathematical practices that apply for a given content standard. Participants will learn HOW to teach the content with the selected mathematical practices. Each participant will learn how to create assessments that align to the rigor demand by the Common Core State Standards. Each participant will learn how IDOE scores student work on the Applied Skills Portion of ISTEP+.
Objectives 6 Each participant will learn the cohesive design of the Common Core State Standards @ grades 3 -4 -5 mathematics. Each participant will learn how to identify which mathematical practices that apply for a given content standard. Participants will learn HOW to teach the content with the selected mathematical practices. Each participant will learn how to create assessments that align to the rigor demand by the Common Core State Standards. Each participant will learn how IDOE scores student work on the Applied Skills Portion of ISTEP+.
 Handouts for Today Indiana Common Core Standards Grade 3 Indiana Common Core Standards Grade 4 Indiana Common Core Standards Grade 5 7
Handouts for Today Indiana Common Core Standards Grade 3 Indiana Common Core Standards Grade 4 Indiana Common Core Standards Grade 5 7
 Handouts for Today • Handout #1: List for Vocabulary (Developed During Workshop) > Notes • Handout #2: Examples of Standards for Math Practices > Notes 8
Handouts for Today • Handout #1: List for Vocabulary (Developed During Workshop) > Notes • Handout #2: Examples of Standards for Math Practices > Notes 8
 Website Work Resources l l l 9 www. azed. gov Inside Mathematics Illustrative Mathematics doe. in. gov/commoncore parcconline. org katm. org
Website Work Resources l l l 9 www. azed. gov Inside Mathematics Illustrative Mathematics doe. in. gov/commoncore parcconline. org katm. org
 HERE 10
HERE 10
 Toolbox Site Morsels 11 doe. in. gov/commoncore Calendar
Toolbox Site Morsels 11 doe. in. gov/commoncore Calendar
 Let’s Get Crackin’ WHO is behind the Common Core State Standards Initiative? l l 12 NGA (National Governor’s Association) CCSSO (Council of Chief State School Officers) Workplace Readiness Post Secondary
Let’s Get Crackin’ WHO is behind the Common Core State Standards Initiative? l l 12 NGA (National Governor’s Association) CCSSO (Council of Chief State School Officers) Workplace Readiness Post Secondary
 Let’s Get Crackin’ WHAT is behind the Common Core State Standards Initiative? l l 13 Equity Issue From State to State Evaluation of NCLB Post Secondary Students are Struggling in the Workplace Post Secondary Students are Struggling in the 2 and 4 year Colleges
Let’s Get Crackin’ WHAT is behind the Common Core State Standards Initiative? l l 13 Equity Issue From State to State Evaluation of NCLB Post Secondary Students are Struggling in the Workplace Post Secondary Students are Struggling in the 2 and 4 year Colleges
 Let’s Get Crackin’ WHY does the Common Core State Standards Initiative make sense? l l 14 Today’s young adult will enter the workplace or the 2 or 4 year university away from their home base. We are definitely becoming a more transient society. Completely the opposite of my generation.
Let’s Get Crackin’ WHY does the Common Core State Standards Initiative make sense? l l 14 Today’s young adult will enter the workplace or the 2 or 4 year university away from their home base. We are definitely becoming a more transient society. Completely the opposite of my generation.
 Let’s Get Crackin’ WHEN is the Common Core State Standards Initiative going to be fully implemented? l l 15 l Grades K-11………school year 2014 -15. Grade K……School Year 2011 -12. Grade 1……. School Year 2012 -13 Grade 2……. School Year 2013 -14 Grades 3 -11. . School Year 2014 -15
Let’s Get Crackin’ WHEN is the Common Core State Standards Initiative going to be fully implemented? l l 15 l Grades K-11………school year 2014 -15. Grade K……School Year 2011 -12. Grade 1……. School Year 2012 -13 Grade 2……. School Year 2013 -14 Grades 3 -11. . School Year 2014 -15
 Other Points to Ponder l l 16 The US Math Curriculum is a mile wide and an inch deep. Teachers have been saying this for a long time. Technology must become interwoven in the mathematics curriculum. The process standards must be used more by teachers of mathematics.
Other Points to Ponder l l 16 The US Math Curriculum is a mile wide and an inch deep. Teachers have been saying this for a long time. Technology must become interwoven in the mathematics curriculum. The process standards must be used more by teachers of mathematics.
 Other Points to Ponder l l l 17 Sea of Change Transformation Less is More Deeper Understanding Making Connections Longer-Deeper Assessments
Other Points to Ponder l l l 17 Sea of Change Transformation Less is More Deeper Understanding Making Connections Longer-Deeper Assessments
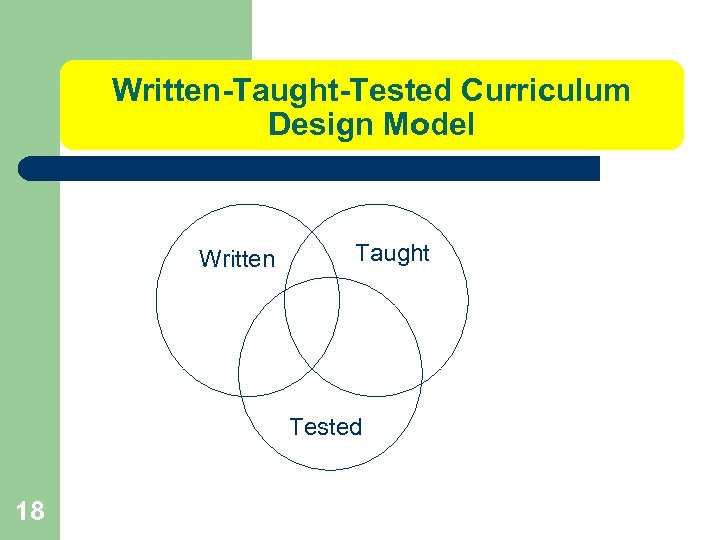 Written-Taught-Tested Curriculum Design Model Written Taught Tested 18
Written-Taught-Tested Curriculum Design Model Written Taught Tested 18
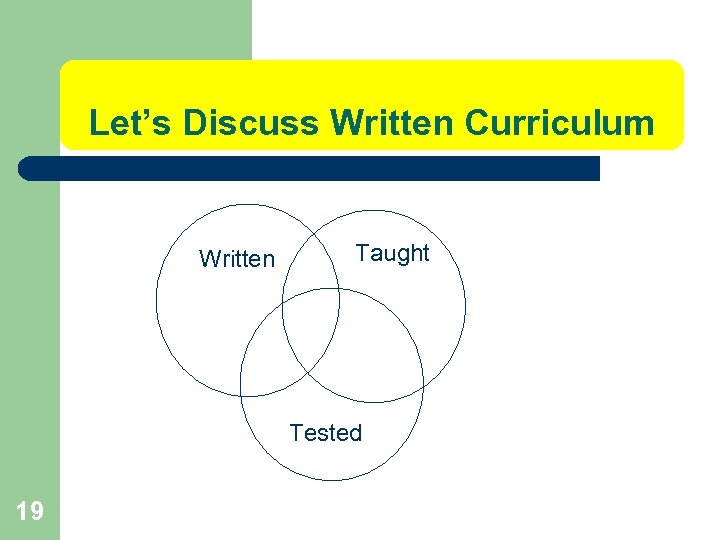 Let’s Discuss Written Curriculum Written Taught Tested 19
Let’s Discuss Written Curriculum Written Taught Tested 19
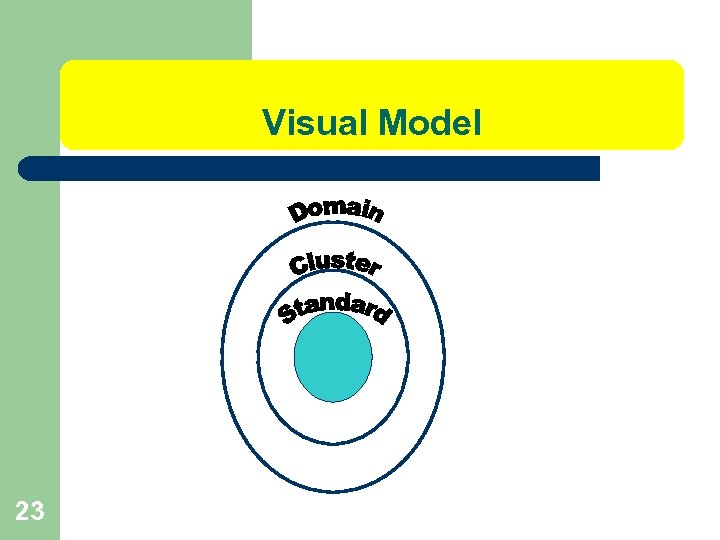
 Learn the Format and Design of Common Core State Standards (CCSS). Domain l Cluster l Standard l 20
Learn the Format and Design of Common Core State Standards (CCSS). Domain l Cluster l Standard l 20
 Domain l l l 21 A huge big idea that bridges across grade levels. Let’s look at the Common Core State Standards Document at Grade Level. Domain: Operations & Algebraic Thinking (OA)
Domain l l l 21 A huge big idea that bridges across grade levels. Let’s look at the Common Core State Standards Document at Grade Level. Domain: Operations & Algebraic Thinking (OA)
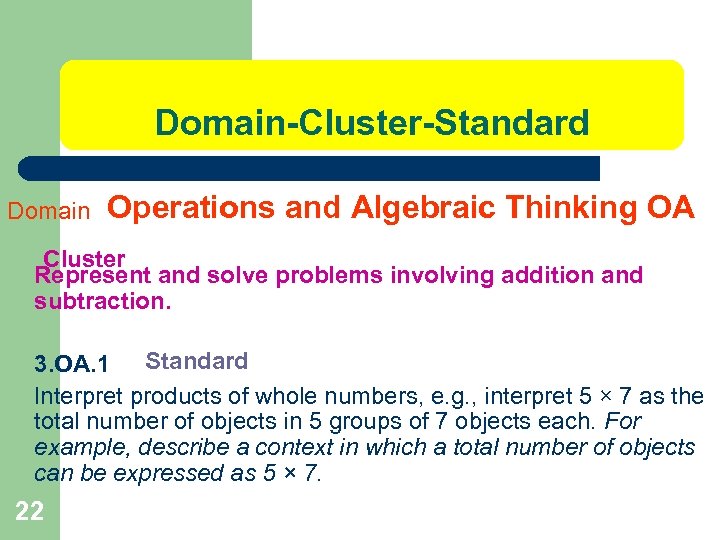 Domain-Cluster-Standard Domain Operations and Algebraic Thinking OA Cluster Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction. 3. OA. 1 Standard Interpret products of whole numbers, e. g. , interpret 5 × 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a total number of objects can be expressed as 5 × 7. 22
Domain-Cluster-Standard Domain Operations and Algebraic Thinking OA Cluster Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction. 3. OA. 1 Standard Interpret products of whole numbers, e. g. , interpret 5 × 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a total number of objects can be expressed as 5 × 7. 22
 Visual Model 23
Visual Model 23
 Listing of Domains Grades 3 -4 -5 Mathematics • (OA) • Number & Operations Base 10 (NBT) • Number Operations-Fractions (NF) • Measurement & Data (MD) • 24 Operations & Algebra Thinking Geometry (G)
Listing of Domains Grades 3 -4 -5 Mathematics • (OA) • Number & Operations Base 10 (NBT) • Number Operations-Fractions (NF) • Measurement & Data (MD) • 24 Operations & Algebra Thinking Geometry (G)
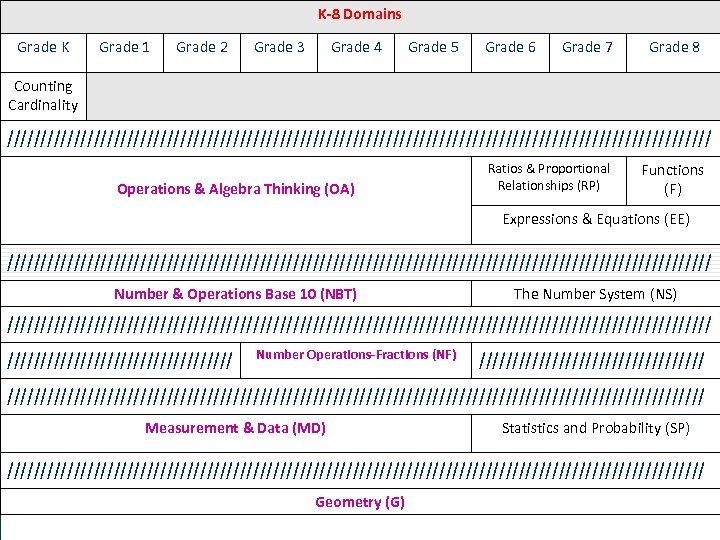 K-8 Domains Grade K Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Counting Cardinality ///////////////////////////////////////////////////// Operations & Algebra Thinking (OA) Ratios & Proportional Relationships (RP) Functions (F) Expressions & Equations (EE) ///////////////////////////////////////////////////// Number & Operations Base 10 (NBT) The Number System (NS) ///////////////////////////////////////////////////// Number Operations-Fractions (NF) ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Measurement & Data (MD) Statistics and Probability (SP) ///////////////////////////////////////////////////// 25 Geometry (G)
K-8 Domains Grade K Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Counting Cardinality ///////////////////////////////////////////////////// Operations & Algebra Thinking (OA) Ratios & Proportional Relationships (RP) Functions (F) Expressions & Equations (EE) ///////////////////////////////////////////////////// Number & Operations Base 10 (NBT) The Number System (NS) ///////////////////////////////////////////////////// Number Operations-Fractions (NF) ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Measurement & Data (MD) Statistics and Probability (SP) ///////////////////////////////////////////////////// 25 Geometry (G)
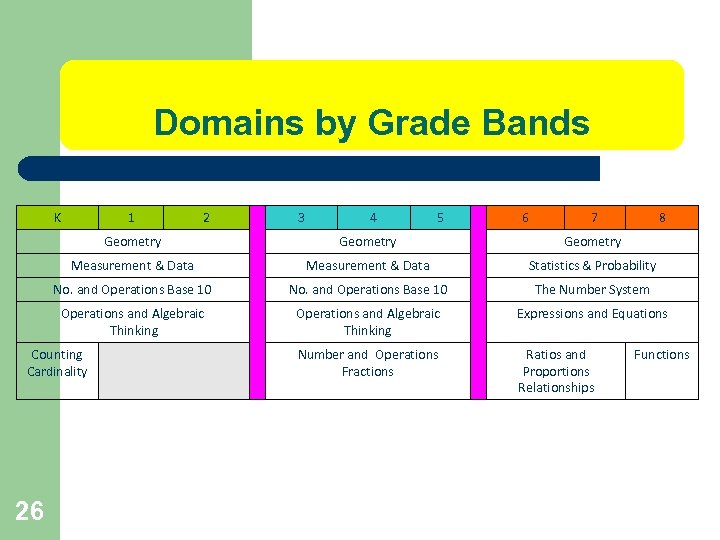 Domains by Grade Bands K 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Geometry Measurement & Data Statistics & Probability No. and Operations Base 10 The Number System Operations and Algebraic Thinking Expressions and Equations Number and Operations Fractions Ratios and Proportions Relationships Counting Cardinality 26 Functions
Domains by Grade Bands K 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Geometry Measurement & Data Statistics & Probability No. and Operations Base 10 The Number System Operations and Algebraic Thinking Expressions and Equations Number and Operations Fractions Ratios and Proportions Relationships Counting Cardinality 26 Functions
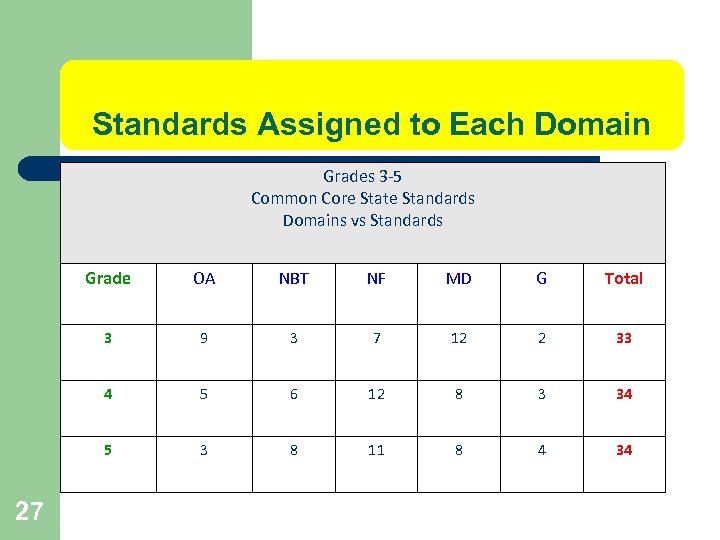 Standards Assigned to Each Domain Grades 3 -5 Common Core State Standards Domains vs Standards Grade NBT NF MD G Total 3 9 3 7 12 2 33 4 5 6 12 8 3 34 5 27 OA 3 8 11 8 4 34
Standards Assigned to Each Domain Grades 3 -5 Common Core State Standards Domains vs Standards Grade NBT NF MD G Total 3 9 3 7 12 2 33 4 5 6 12 8 3 34 5 27 OA 3 8 11 8 4 34
 Let’s Hear From You l What kind of professional development has been offered to you to learn information about the Common Core State Standards? Record Information by Tables l Report this information to us l 28
Let’s Hear From You l What kind of professional development has been offered to you to learn information about the Common Core State Standards? Record Information by Tables l Report this information to us l 28
 Learn the Cohesive Quality of CCSS Let’s Pick This Domain……. . NF …. Fractions 29
Learn the Cohesive Quality of CCSS Let’s Pick This Domain……. . NF …. Fractions 29
 Number and Operations- Fractions Cluster Comparison Grade 3 -4 -5 l l l 30 Grade 3 Develop understanding of fractions as numbers. Grade 4 Extend understanding of fraction equivalence and ordering. Build fractions from unit fractions by applying and extending previous understandings of operations on whole numbers. Understand decimal notation for fractions, and compare decimal fractions. Grade 5 Use equivalent fractions as a strategy to add and subtract fractions. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division to multiply and divide fractions.
Number and Operations- Fractions Cluster Comparison Grade 3 -4 -5 l l l 30 Grade 3 Develop understanding of fractions as numbers. Grade 4 Extend understanding of fraction equivalence and ordering. Build fractions from unit fractions by applying and extending previous understandings of operations on whole numbers. Understand decimal notation for fractions, and compare decimal fractions. Grade 5 Use equivalent fractions as a strategy to add and subtract fractions. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division to multiply and divide fractions.
 Number and Operations- Fractions Linked-Standard Comparison Grade 3 -4 -5 3. NF. 3 Explain equivalence of fractions in special cases, and compare fractions by reasoning about their size. 4. NF. 1 Explain why a fraction a/b is equivalent to a fraction (n × a)/(n × b) by using visual fraction models, with attention to how the number and size of the parts differ even though the two fractions themselves are the same size. Use this principle to recognize and generate equivalent fractions. 5. NF. 1 Add and subtract fractions with unlike denominators (including mixed numbers) by replacing given fractions with equivalent fractions in such a way as to produce an equivalent sum or difference of fractions with like denominators. For example, 2/3 + 5/4 = 8/12 + 15/12 = 23/12. 31
Number and Operations- Fractions Linked-Standard Comparison Grade 3 -4 -5 3. NF. 3 Explain equivalence of fractions in special cases, and compare fractions by reasoning about their size. 4. NF. 1 Explain why a fraction a/b is equivalent to a fraction (n × a)/(n × b) by using visual fraction models, with attention to how the number and size of the parts differ even though the two fractions themselves are the same size. Use this principle to recognize and generate equivalent fractions. 5. NF. 1 Add and subtract fractions with unlike denominators (including mixed numbers) by replacing given fractions with equivalent fractions in such a way as to produce an equivalent sum or difference of fractions with like denominators. For example, 2/3 + 5/4 = 8/12 + 15/12 = 23/12. 31
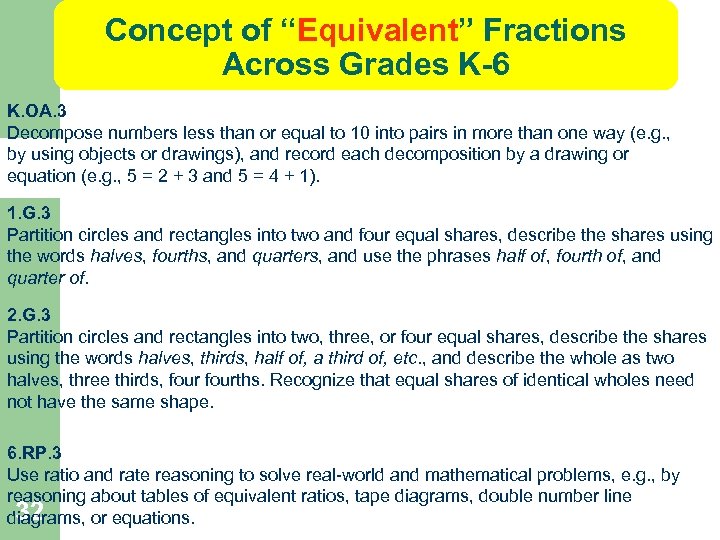 Concept of “Equivalent” Fractions Across Grades K-6 K. OA. 3 Decompose numbers less than or equal to 10 into pairs in more than one way (e. g. , by using objects or drawings), and record each decomposition by a drawing or equation (e. g. , 5 = 2 + 3 and 5 = 4 + 1). 1. G. 3 Partition circles and rectangles into two and four equal shares, describe the shares using the words halves, fourths, and quarters, and use the phrases half of, fourth of, and quarter of. 2. G. 3 Partition circles and rectangles into two, three, or four equal shares, describe the shares using the words halves, thirds, half of, a third of, etc. , and describe the whole as two halves, three thirds, fourths. Recognize that equal shares of identical wholes need not have the same shape. 6. RP. 3 Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve real-world and mathematical problems, e. g. , by reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line 32 diagrams, or equations.
Concept of “Equivalent” Fractions Across Grades K-6 K. OA. 3 Decompose numbers less than or equal to 10 into pairs in more than one way (e. g. , by using objects or drawings), and record each decomposition by a drawing or equation (e. g. , 5 = 2 + 3 and 5 = 4 + 1). 1. G. 3 Partition circles and rectangles into two and four equal shares, describe the shares using the words halves, fourths, and quarters, and use the phrases half of, fourth of, and quarter of. 2. G. 3 Partition circles and rectangles into two, three, or four equal shares, describe the shares using the words halves, thirds, half of, a third of, etc. , and describe the whole as two halves, three thirds, fourths. Recognize that equal shares of identical wholes need not have the same shape. 6. RP. 3 Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve real-world and mathematical problems, e. g. , by reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line 32 diagrams, or equations.
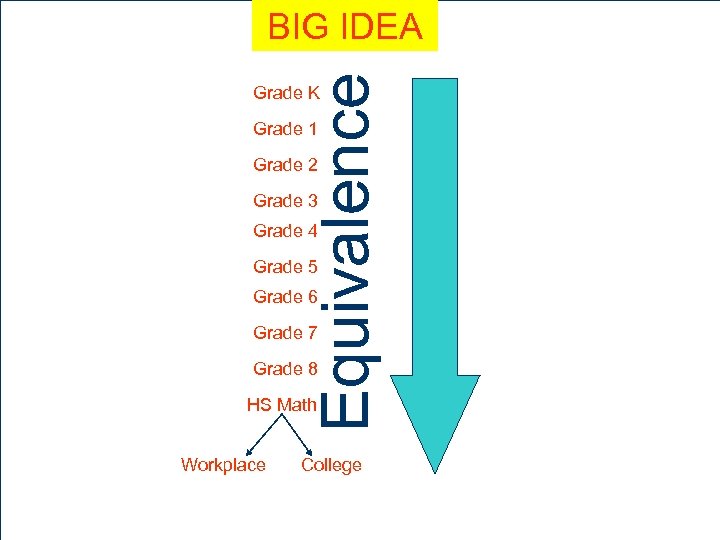 Equivalence BIG IDEA Grade K Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 HS Math Workplace 33 College
Equivalence BIG IDEA Grade K Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 HS Math Workplace 33 College
 Conclusion of Our Work The Common Core State Standards (CCSS) are design to teach CONCEPTS across grade levels. l These articulated standards by grade level are scaffold to develop a bigger and better understanding of mathematics. l 34
Conclusion of Our Work The Common Core State Standards (CCSS) are design to teach CONCEPTS across grade levels. l These articulated standards by grade level are scaffold to develop a bigger and better understanding of mathematics. l 34
 A True Story About Me l I could do the mathematics but didn’t know the concept. - Adding 2……two-digit numbers - 35 Rounding Numbers
A True Story About Me l I could do the mathematics but didn’t know the concept. - Adding 2……two-digit numbers - 35 Rounding Numbers
 Let’s Divide Into Grade Level Tables l l l 36 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
Let’s Divide Into Grade Level Tables l l l 36 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5
 Grade Level Activity At Grade Level Tables, examine the CCSS. Record the following information on chart paper. l l l 37 What Challenges Do You See? How Will CCSS Change Your Classroom Practices? How Do You See the Implementation Process?
Grade Level Activity At Grade Level Tables, examine the CCSS. Record the following information on chart paper. l l l 37 What Challenges Do You See? How Will CCSS Change Your Classroom Practices? How Do You See the Implementation Process?
 Learn How to Unpack CCSS l Select the Number and Operations-Fractions Domain Use Chart Paper to ……. l - Grade Level - Code the Standard - Paraphrase the Standards in Your Own Words - Show an Example or Two to Illustrate the Standard - Make a List of Vocabulary Words that We Need to Know for Understanding. (see handout #1) We will do a Gallery Walk first then debrief chart info l 38
Learn How to Unpack CCSS l Select the Number and Operations-Fractions Domain Use Chart Paper to ……. l - Grade Level - Code the Standard - Paraphrase the Standards in Your Own Words - Show an Example or Two to Illustrate the Standard - Make a List of Vocabulary Words that We Need to Know for Understanding. (see handout #1) We will do a Gallery Walk first then debrief chart info l 38
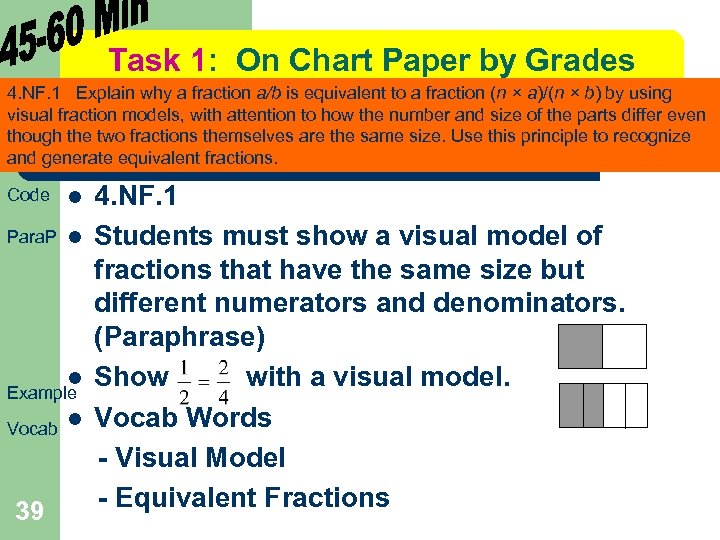 Task 1: On Chart Paper by Grades 4. NF. 1 Explain why a fraction a/b is equivalent to a fraction (n × a)/(n × b) by using visual fraction models, with attention to how the number and size of the parts differ even though the two fractions themselves are the same size. Use this principle to recognize and generate equivalent fractions. Code l Para. P l l Example Vocab l 39 4. NF. 1 Students must show a visual model of fractions that have the same size but different numerators and denominators. (Paraphrase) Show with a visual model. Vocab Words - Visual Model - Equivalent Fractions
Task 1: On Chart Paper by Grades 4. NF. 1 Explain why a fraction a/b is equivalent to a fraction (n × a)/(n × b) by using visual fraction models, with attention to how the number and size of the parts differ even though the two fractions themselves are the same size. Use this principle to recognize and generate equivalent fractions. Code l Para. P l l Example Vocab l 39 4. NF. 1 Students must show a visual model of fractions that have the same size but different numerators and denominators. (Paraphrase) Show with a visual model. Vocab Words - Visual Model - Equivalent Fractions
 Gallery Walk for View Charts Debrief Charts 40
Gallery Walk for View Charts Debrief Charts 40
 Information from Handout #1 What were some of your words or phrases? l What were some of your descriptions? (words and/or pictures) -------------------------------> Share within groups tablemates > Share with others too l 41
Information from Handout #1 What were some of your words or phrases? l What were some of your descriptions? (words and/or pictures) -------------------------------> Share within groups tablemates > Share with others too l 41
 Summary of Task #1 Number Operations with Fractions (NF) At grade tables…… l What do you see different about the NF domain? l What are the challenges? l How do you see yourself teaching the NF domain differently? 42
Summary of Task #1 Number Operations with Fractions (NF) At grade tables…… l What do you see different about the NF domain? l What are the challenges? l How do you see yourself teaching the NF domain differently? 42
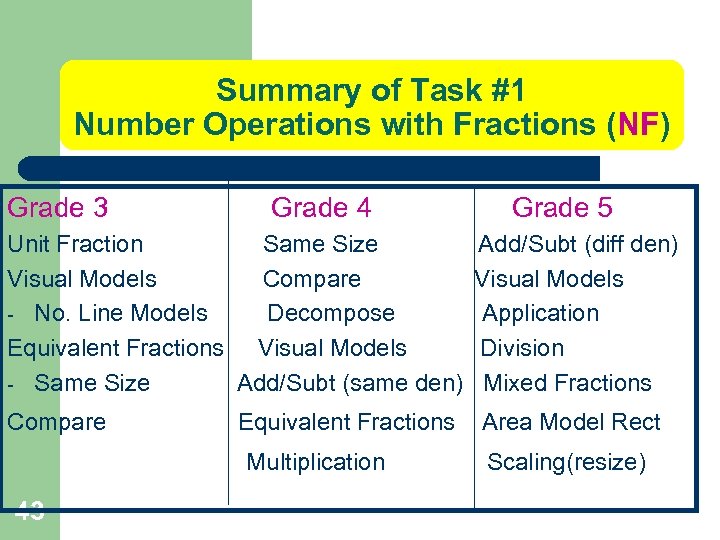 Summary of Task #1 Number Operations with Fractions (NF) Grade 3 Grade 4 Unit Fraction Same Size Visual Models Compare - No. Line Models Decompose Equivalent Fractions Visual Models - Same Size Add/Subt (same den) Compare Equivalent Fractions Multiplication 43 Grade 5 Add/Subt (diff den) Visual Models Application Division Mixed Fractions Area Model Rect Scaling(resize)
Summary of Task #1 Number Operations with Fractions (NF) Grade 3 Grade 4 Unit Fraction Same Size Visual Models Compare - No. Line Models Decompose Equivalent Fractions Visual Models - Same Size Add/Subt (same den) Compare Equivalent Fractions Multiplication 43 Grade 5 Add/Subt (diff den) Visual Models Application Division Mixed Fractions Area Model Rect Scaling(resize)
 Standards for Mathematical Practices (SMP) l l 44 See Grade Level CCSS Handout 8 Math Practices
Standards for Mathematical Practices (SMP) l l 44 See Grade Level CCSS Handout 8 Math Practices
 Standards Mathematical Practices (SMP) 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 4. Model with mathematics. 5. Use appropriate tools strategically. 6. Attend to precision. 7. Look for and make use of structure. 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. 45
Standards Mathematical Practices (SMP) 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 4. Model with mathematics. 5. Use appropriate tools strategically. 6. Attend to precision. 7. Look for and make use of structure. 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. 45
 Standards Mathematical Practices (SMP) SMP#1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. The teaching strategy here is to get students to “internalize problems” according to the student’s learning style. Students are to make sense of problems by working with other students, making connections, drawing pictures, asking questions, and any other way to enter the problem. Problem Solving strategies are big here. Persevere is a strong word in the SMP. “Persevere” means to stay with the problem until it is resolved. Students must learn from our teaching that problems can be solved by many entry level strategies. 46
Standards Mathematical Practices (SMP) SMP#1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. The teaching strategy here is to get students to “internalize problems” according to the student’s learning style. Students are to make sense of problems by working with other students, making connections, drawing pictures, asking questions, and any other way to enter the problem. Problem Solving strategies are big here. Persevere is a strong word in the SMP. “Persevere” means to stay with the problem until it is resolved. Students must learn from our teaching that problems can be solved by many entry level strategies. 46
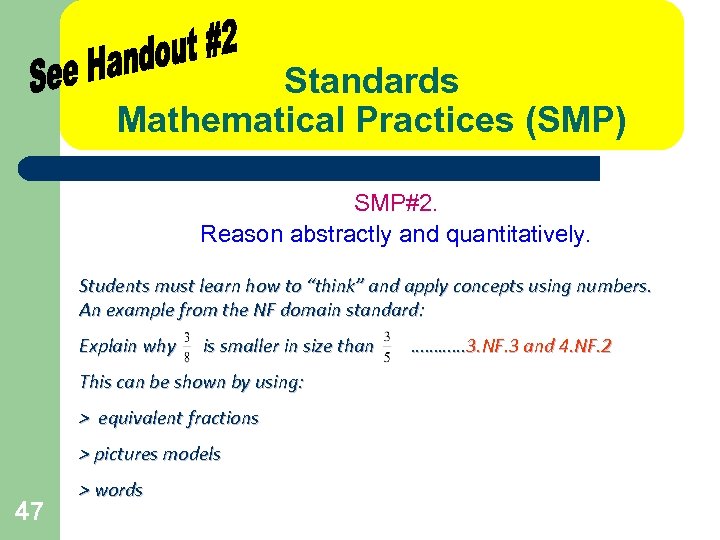 Standards Mathematical Practices (SMP) SMP#2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. Students must learn how to “think” and apply concepts using numbers. An example from the NF domain standard: Explain why is smaller in size than This can be shown by using: > equivalent fractions > pictures models 47 > words ………… 3. NF. 3 and 4. NF. 2
Standards Mathematical Practices (SMP) SMP#2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. Students must learn how to “think” and apply concepts using numbers. An example from the NF domain standard: Explain why is smaller in size than This can be shown by using: > equivalent fractions > pictures models 47 > words ………… 3. NF. 3 and 4. NF. 2
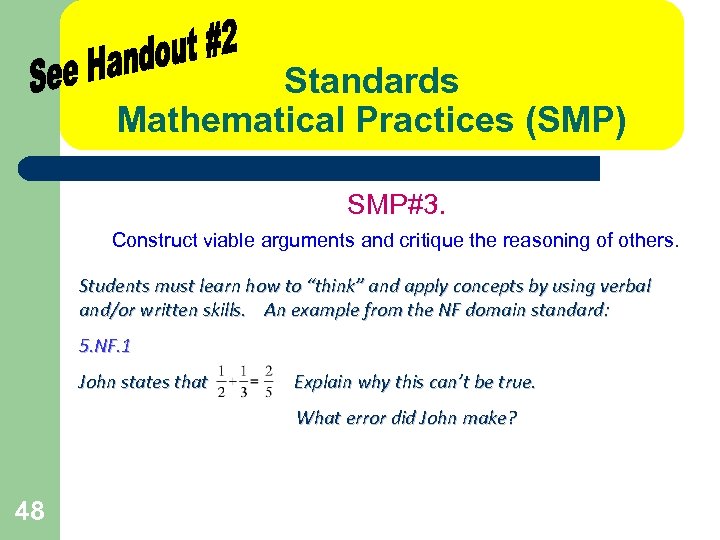 Standards Mathematical Practices (SMP) SMP#3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. Students must learn how to “think” and apply concepts by using verbal and/or written skills. An example from the NF domain standard: 5. NF. 1 John states that Explain why this can’t be true. What error did John make? 48
Standards Mathematical Practices (SMP) SMP#3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. Students must learn how to “think” and apply concepts by using verbal and/or written skills. An example from the NF domain standard: 5. NF. 1 John states that Explain why this can’t be true. What error did John make? 48
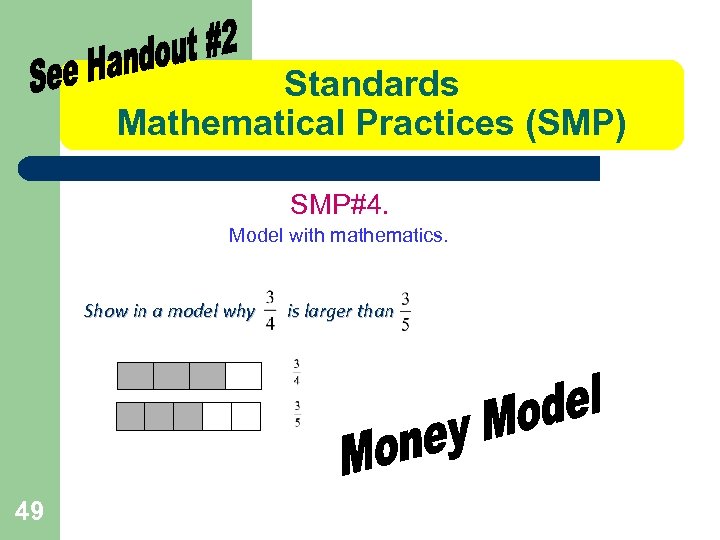 Standards Mathematical Practices (SMP) SMP#4. Model with mathematics. Show in a model why 49 is larger than
Standards Mathematical Practices (SMP) SMP#4. Model with mathematics. Show in a model why 49 is larger than
 Standards Mathematical Practices (SMP) SMP#5. Use appropriate tools strategically. Students must learn how to select the appropriate “tools” to solve problems. Ø Ruler Ø Manipulatives Ø ISTEP+ Punch-Outs Ø Technology 50
Standards Mathematical Practices (SMP) SMP#5. Use appropriate tools strategically. Students must learn how to select the appropriate “tools” to solve problems. Ø Ruler Ø Manipulatives Ø ISTEP+ Punch-Outs Ø Technology 50
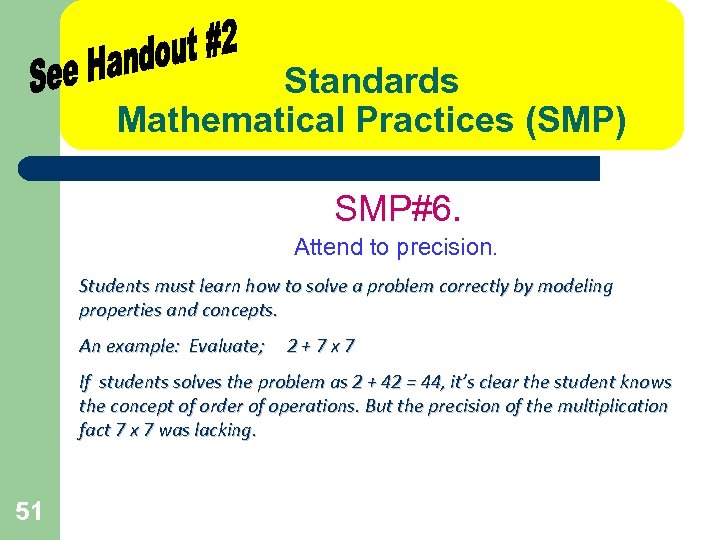 Standards Mathematical Practices (SMP) SMP#6. Attend to precision. Students must learn how to solve a problem correctly by modeling properties and concepts. An example: Evaluate; 2+7 x 7 If students solves the problem as 2 + 42 = 44, it’s clear the student knows the concept of order of operations. But the precision of the multiplication fact 7 x 7 was lacking. 51
Standards Mathematical Practices (SMP) SMP#6. Attend to precision. Students must learn how to solve a problem correctly by modeling properties and concepts. An example: Evaluate; 2+7 x 7 If students solves the problem as 2 + 42 = 44, it’s clear the student knows the concept of order of operations. But the precision of the multiplication fact 7 x 7 was lacking. 51
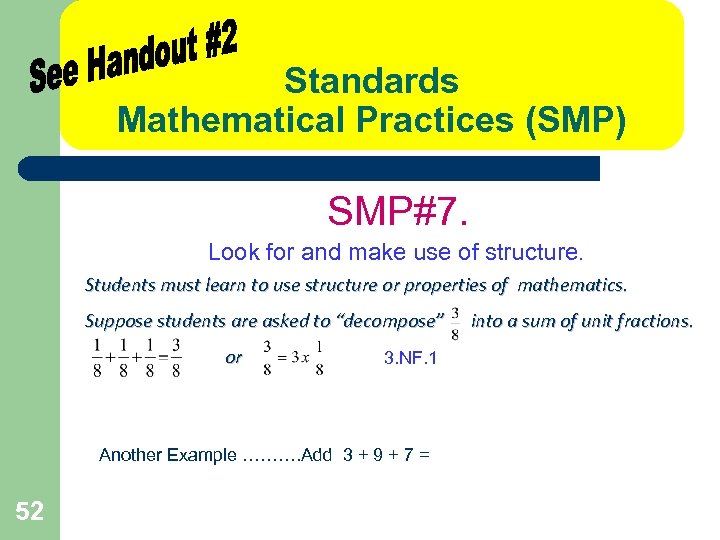 Standards Mathematical Practices (SMP) SMP#7. Look for and make use of structure. Students must learn to use structure or properties of mathematics. Suppose students are asked to “decompose” or 3. NF. 1 Another Example ………. Add 3 + 9 + 7 = 52 into a sum of unit fractions.
Standards Mathematical Practices (SMP) SMP#7. Look for and make use of structure. Students must learn to use structure or properties of mathematics. Suppose students are asked to “decompose” or 3. NF. 1 Another Example ………. Add 3 + 9 + 7 = 52 into a sum of unit fractions.
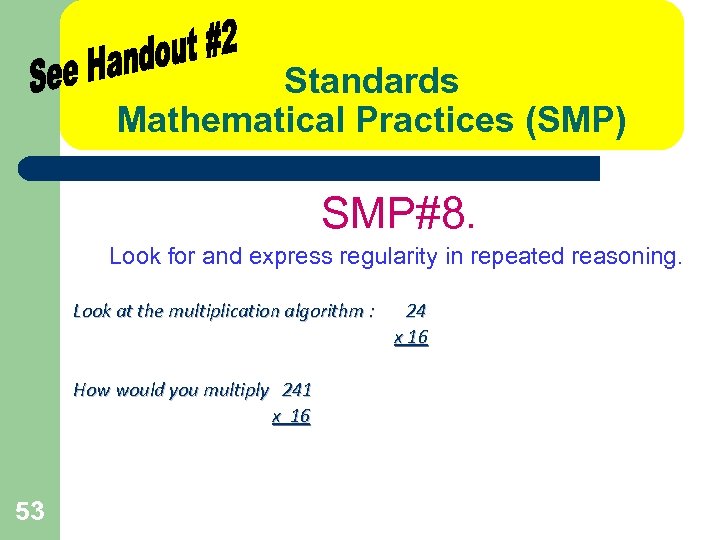 Standards Mathematical Practices (SMP) SMP#8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Look at the multiplication algorithm : How would you multiply 241 x 16 53 24 x 16
Standards Mathematical Practices (SMP) SMP#8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Look at the multiplication algorithm : How would you multiply 241 x 16 53 24 x 16
 Task 2 l l l 54 Let’s go back to our charts from Task 1. For each grade level standard in the NF domain, identify a few standards for mathematical practices (SMP). We will discuss your updated charts in a few minutes.
Task 2 l l l 54 Let’s go back to our charts from Task 1. For each grade level standard in the NF domain, identify a few standards for mathematical practices (SMP). We will discuss your updated charts in a few minutes.
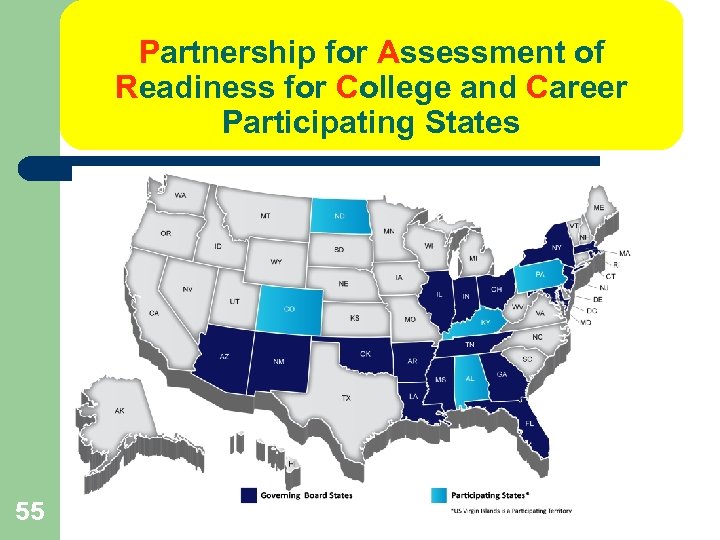 Partnership for Assessment of Readiness for College and Career Participating States 55
Partnership for Assessment of Readiness for College and Career Participating States 55
 Assessment PARCC Partnership for Assessment of Readiness for College and Career To address the priority purposes, PARCC will develop an assessment system comprised of four components. Each component will be computer-delivered and will use technology to incorporate innovations. 56
Assessment PARCC Partnership for Assessment of Readiness for College and Career To address the priority purposes, PARCC will develop an assessment system comprised of four components. Each component will be computer-delivered and will use technology to incorporate innovations. 56
 Assessment PARCC Partnership for Assessment of Readiness for College and Career PARCC will also use technology throughout the design and implementation of the assessment system. The overall assessment system design will include a mix of constructed response items, performance-based tasks, and computerenhanced, computer-scored items. The PARCC assessments will be administered via computer, and a combination of automated scoring and human scoring will be employed. 57
Assessment PARCC Partnership for Assessment of Readiness for College and Career PARCC will also use technology throughout the design and implementation of the assessment system. The overall assessment system design will include a mix of constructed response items, performance-based tasks, and computerenhanced, computer-scored items. The PARCC assessments will be administered via computer, and a combination of automated scoring and human scoring will be employed. 57
 Assessment PARCC Two Required Assessments Two summative, required assessment components designed to: > Make “college- and career-readiness” and “on-track” determinations, > Measure the full range of standards and full performance continuum, and Provide data for accountability uses, including measures of growth. 58
Assessment PARCC Two Required Assessments Two summative, required assessment components designed to: > Make “college- and career-readiness” and “on-track” determinations, > Measure the full range of standards and full performance continuum, and Provide data for accountability uses, including measures of growth. 58
 PARCC REQUIRED ASSESSMENTS l l 59 Performance-Based Assessment (PBA) Given close to the end of year. Math will focus on applied skills, concepts, and understandings to solve multi-step problems requiring abstract reasoning, precision, perseverance, and use of tools. End-of Year Assessment (EOY) Given 90% of the way during the school year. Math will be comprised of innovative, machine-scoreable items.
PARCC REQUIRED ASSESSMENTS l l 59 Performance-Based Assessment (PBA) Given close to the end of year. Math will focus on applied skills, concepts, and understandings to solve multi-step problems requiring abstract reasoning, precision, perseverance, and use of tools. End-of Year Assessment (EOY) Given 90% of the way during the school year. Math will be comprised of innovative, machine-scoreable items.
 Assessment PARCC l l 60 Two non-summative, optional assessment components designed to: Generate timely information for informing instruction, interventions, and professional development during the school year.
Assessment PARCC l l 60 Two non-summative, optional assessment components designed to: Generate timely information for informing instruction, interventions, and professional development during the school year.
 Technology and PARCC What technology is needed to administer the PARCC assessments, and how will states get ready? The PARCC assessments will be administered and scored via computer for students in grades 6 through high school. For grades 3 -5, the PARCC states plan to deliver the assessments via computer but have students respond to the assessment questions on paper and pencil, given potential concerns about younger students’ keyboarding abilities. Before making a final determination about grades 3 -5, research will be conducted to confirm the appropriate approach. 61
Technology and PARCC What technology is needed to administer the PARCC assessments, and how will states get ready? The PARCC assessments will be administered and scored via computer for students in grades 6 through high school. For grades 3 -5, the PARCC states plan to deliver the assessments via computer but have students respond to the assessment questions on paper and pencil, given potential concerns about younger students’ keyboarding abilities. Before making a final determination about grades 3 -5, research will be conducted to confirm the appropriate approach. 61
 PARCC and Teachers 62 How is PARCC involving teachers in the development of the assessments? The PARCC item development process will be extensive and involve educators and community members from all PARCC states. Review committees will consist of PARCC state K-12 and higher education officials; local education agency K-12 staff and higher education faculty; and citizens and educators from various backgrounds. In the item development process, teachers will be directly engaged as reviewers on local educator teams and teams that review potential test questions for bias and sensitivity issues. Teachers on the review committees will be tasked with ensuring that PARCC items are free of bias, culturally sensitive, age-appropriate, content accurate, and well-aligned to the CCSS. Item and reading passage review meetings will begin for teachers in the spring of 2012, and will be designed to ensure that 100% of PARCC items are reviewed prior to and following field tests, in preparation for operational testing in the 2014 -2015 school year.
PARCC and Teachers 62 How is PARCC involving teachers in the development of the assessments? The PARCC item development process will be extensive and involve educators and community members from all PARCC states. Review committees will consist of PARCC state K-12 and higher education officials; local education agency K-12 staff and higher education faculty; and citizens and educators from various backgrounds. In the item development process, teachers will be directly engaged as reviewers on local educator teams and teams that review potential test questions for bias and sensitivity issues. Teachers on the review committees will be tasked with ensuring that PARCC items are free of bias, culturally sensitive, age-appropriate, content accurate, and well-aligned to the CCSS. Item and reading passage review meetings will begin for teachers in the spring of 2012, and will be designed to ensure that 100% of PARCC items are reviewed prior to and following field tests, in preparation for operational testing in the 2014 -2015 school year.
 PARCC and Cut-Score How will cut scores on the PARCC assessments be determined? The PARCC states will set standards (cut scores) for the various performance levels they will use to report results of the PARCC assessments during the summer of 2015 – after the first full administration of the PARCC assessments in all the member states. At the high school level, PARCC will identify a performance level in both ELA/literacy and mathematics that will indicate that a student is collegeand career-ready. This level will serve as an anchor or reference point for articulating meaningful “on-track” performance levels for the earlier grades. 63
PARCC and Cut-Score How will cut scores on the PARCC assessments be determined? The PARCC states will set standards (cut scores) for the various performance levels they will use to report results of the PARCC assessments during the summer of 2015 – after the first full administration of the PARCC assessments in all the member states. At the high school level, PARCC will identify a performance level in both ELA/literacy and mathematics that will indicate that a student is collegeand career-ready. This level will serve as an anchor or reference point for articulating meaningful “on-track” performance levels for the earlier grades. 63
 Back to our Charts Task 3 l 64 For one standard in the NF grade-level, domain category, write an assessment that measures student learning. Keep in Mind - Higher Level Understanding
Back to our Charts Task 3 l 64 For one standard in the NF grade-level, domain category, write an assessment that measures student learning. Keep in Mind - Higher Level Understanding
 Transition Handout IDOE Instructional Priorities 2012 -13 Grade 3 -4 -5 l 65 Examine the Document
Transition Handout IDOE Instructional Priorities 2012 -13 Grade 3 -4 -5 l 65 Examine the Document
 In Groups Teams… Use the Transition IDOE Handout Ø Write one assessment for each standard: Grade 3 Team 3. MD. 1 Ø Grade 4 Team 4. OA. 2 Ø Grade 5 Team 5. NBT. 4 l 66
In Groups Teams… Use the Transition IDOE Handout Ø Write one assessment for each standard: Grade 3 Team 3. MD. 1 Ø Grade 4 Team 4. OA. 2 Ø Grade 5 Team 5. NBT. 4 l 66
 Website Work Resources l l l 67 www. azed. gov Inside Mathematics Illustrative Mathematics
Website Work Resources l l l 67 www. azed. gov Inside Mathematics Illustrative Mathematics
 68
68
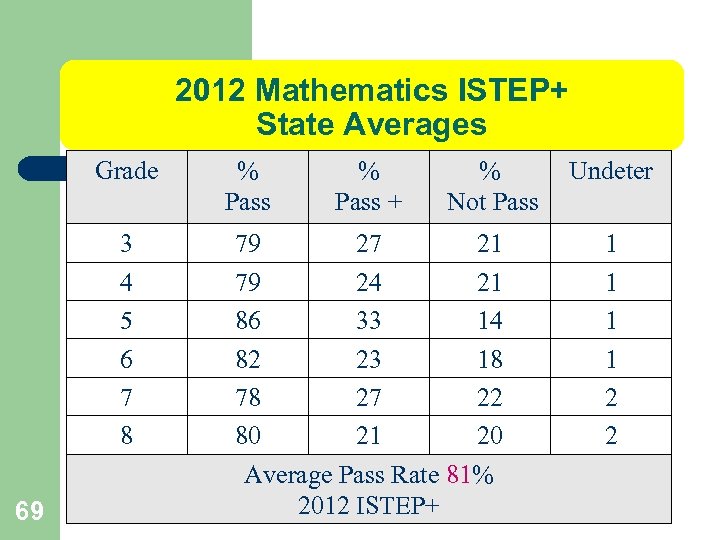 2012 Mathematics ISTEP+ State Averages Grade 3 4 5 6 7 8 69 % Pass + % Not Pass 79 27 21 79 24 21 86 33 14 82 23 18 78 27 22 80 21 20 Average Pass Rate 81% 2012 ISTEP+ Undeter 1 1 2 2
2012 Mathematics ISTEP+ State Averages Grade 3 4 5 6 7 8 69 % Pass + % Not Pass 79 27 21 79 24 21 86 33 14 82 23 18 78 27 22 80 21 20 Average Pass Rate 81% 2012 ISTEP+ Undeter 1 1 2 2
 ISTEP+ for School Year 2012 -13 See Applied Skills Handout l l l 70 Applied Skills Portion ……March 4 -13, 2013 Written Solutions (Problem Solving) Values of the Problems? Which Standards are Covered? How many problems? How long?
ISTEP+ for School Year 2012 -13 See Applied Skills Handout l l l 70 Applied Skills Portion ……March 4 -13, 2013 Written Solutions (Problem Solving) Values of the Problems? Which Standards are Covered? How many problems? How long?
 ISTEP+ for School Year 2012 -13 l l l 71 Multiple Choices Assessment April 29 – May 8, 2013 Which Standards are Covered? How many problems? How long?
ISTEP+ for School Year 2012 -13 l l l 71 Multiple Choices Assessment April 29 – May 8, 2013 Which Standards are Covered? How many problems? How long?
 IDOE State Reports l l 72 Disaggregation Summary Report Applied Skills Frequency Distribution Report
IDOE State Reports l l 72 Disaggregation Summary Report Applied Skills Frequency Distribution Report
 Let’s Look at the 4 Applied Skills Problems at Grade Level l l 73 Browse over the four problems. Problems 1 -2 -3 are worth 4 points each (2 pts for content + 2 pts for problem solving) Problem 4 is worth 6 points (3 pts for content + 3 pts for problem solving) Look the 4 problems over!
Let’s Look at the 4 Applied Skills Problems at Grade Level l l 73 Browse over the four problems. Problems 1 -2 -3 are worth 4 points each (2 pts for content + 2 pts for problem solving) Problem 4 is worth 6 points (3 pts for content + 3 pts for problem solving) Look the 4 problems over!
 State Scoring Rubric l l 74 Constructed Response Problems #1 -2 -3 Extended Response Problem #4
State Scoring Rubric l l 74 Constructed Response Problems #1 -2 -3 Extended Response Problem #4
 Rubric for Applied Skills l l l l l l 75 Constructed Response Rubric Content Rubric 2 A score of two indicates a thorough understanding of the mathematical concepts embodied in the task. The response • shows algorithms, computations, and other content related work executed correctly and completely. 1 A score of one indicates a partial understanding of the mathematical concepts embodied in the task. The response • contains errors in the execution of algorithms, computations, and/or other content related work. 0 A score of zero indicates limited or no understanding of the mathematical concepts embodied in the task. Problem-Solving Rubric ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------2 A score of two indicates a thorough understanding of the problem-solving concepts embodied in the task. The response • shows an appropriate strategy to solve the problem, and the strategy is executed correctly and completely. • identifies all important elements of the problem and shows a complete understanding of the relationships among them. • provides clear and complete explanations and/or interpretations when required. 1 A score of one indicates a partial understanding of the problem-solving concepts embodied in the task. The response contains one or more of the following errors. The response • shows an appropriate strategy to solve the problem. However, the execution of the strategy contains errors and/or is incomplete. • identifies some of the important elements of the problem and shows a general understanding of the relationships among them. • provides incomplete, partial, or unclear explanations and/or interpretations when required. 0 A score of zero indicates limited or no understanding of the problem-solving concepts embodied in the task.
Rubric for Applied Skills l l l l l l 75 Constructed Response Rubric Content Rubric 2 A score of two indicates a thorough understanding of the mathematical concepts embodied in the task. The response • shows algorithms, computations, and other content related work executed correctly and completely. 1 A score of one indicates a partial understanding of the mathematical concepts embodied in the task. The response • contains errors in the execution of algorithms, computations, and/or other content related work. 0 A score of zero indicates limited or no understanding of the mathematical concepts embodied in the task. Problem-Solving Rubric ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------2 A score of two indicates a thorough understanding of the problem-solving concepts embodied in the task. The response • shows an appropriate strategy to solve the problem, and the strategy is executed correctly and completely. • identifies all important elements of the problem and shows a complete understanding of the relationships among them. • provides clear and complete explanations and/or interpretations when required. 1 A score of one indicates a partial understanding of the problem-solving concepts embodied in the task. The response contains one or more of the following errors. The response • shows an appropriate strategy to solve the problem. However, the execution of the strategy contains errors and/or is incomplete. • identifies some of the important elements of the problem and shows a general understanding of the relationships among them. • provides incomplete, partial, or unclear explanations and/or interpretations when required. 0 A score of zero indicates limited or no understanding of the problem-solving concepts embodied in the task.
 Samples for Item #1 IDOE March Applied Skills l l l 76 See the Handout with Grade Level Problems for item #1. Samples A, B, C In grade level pairs, score the student work based upon the IDOE rubric. Share table pair results. Share with the entire workshop too!
Samples for Item #1 IDOE March Applied Skills l l l 76 See the Handout with Grade Level Problems for item #1. Samples A, B, C In grade level pairs, score the student work based upon the IDOE rubric. Share table pair results. Share with the entire workshop too!
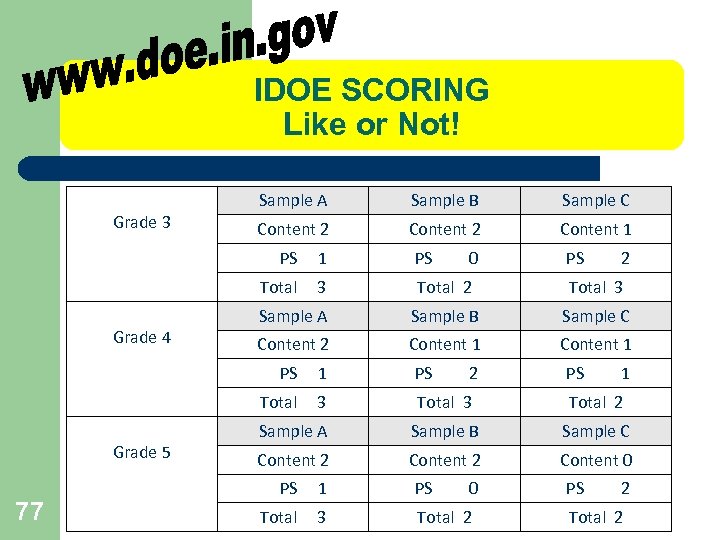 IDOE SCORING Like or Not! Grade 3 Sample A Sample B Sample C Content 2 Content 1 PS PS Total Grade 4 1 0 3 Total 2 Total 3 Sample A Sample B Sample C Content 2 Content 1 PS Total 77 1 3 Total 2 Sample A Sample B Sample C Content 2 Content 0 PS 1 PS 0 Total 3 Total 2 PS Grade 5 2 PS PS 1 2 Total 2
IDOE SCORING Like or Not! Grade 3 Sample A Sample B Sample C Content 2 Content 1 PS PS Total Grade 4 1 0 3 Total 2 Total 3 Sample A Sample B Sample C Content 2 Content 1 PS Total 77 1 3 Total 2 Sample A Sample B Sample C Content 2 Content 0 PS 1 PS 0 Total 3 Total 2 PS Grade 5 2 PS PS 1 2 Total 2
 Problem Solving Resources l l l 78 Ice Cream Jamie’s Cards Product Game
Problem Solving Resources l l l 78 Ice Cream Jamie’s Cards Product Game
 Website Work Resources l l l 79 www. azed. gov Inside Mathematics Illustrative Mathematics doe. in. gov/commoncore parcconline. org katm. org
Website Work Resources l l l 79 www. azed. gov Inside Mathematics Illustrative Mathematics doe. in. gov/commoncore parcconline. org katm. org
 Time for Personal Reflections l l 80 What did you learn the most about today? How are you feeling about the CCSS?
Time for Personal Reflections l l 80 What did you learn the most about today? How are you feeling about the CCSS?
 Objectives Looking Back and Assessing 81 Each participant will learn the cohesive design of the Common Core State Standards @ grades 3 -4 -5 mathematics. Each participant will learn how to identify which mathematical practices that apply for a given content standard. Participants will learn HOW to teach the content with the selected mathematical practices. Each participant will learn how to create assessments that align to the rigor demand by the Common Core State Standards. Each participant will learn how IDOE scores student work on the Applied Skills Portion of ISTEP+.
Objectives Looking Back and Assessing 81 Each participant will learn the cohesive design of the Common Core State Standards @ grades 3 -4 -5 mathematics. Each participant will learn how to identify which mathematical practices that apply for a given content standard. Participants will learn HOW to teach the content with the selected mathematical practices. Each participant will learn how to create assessments that align to the rigor demand by the Common Core State Standards. Each participant will learn how IDOE scores student work on the Applied Skills Portion of ISTEP+.
 Thanks For A Great Day! 82
Thanks For A Great Day! 82
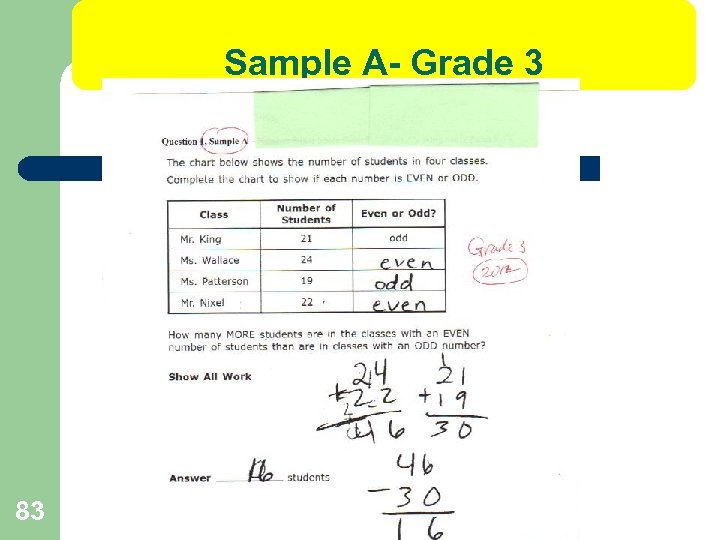 Sample A- Grade 3 83
Sample A- Grade 3 83
 Sample A - Grade 4 84
Sample A - Grade 4 84
 IDOE SCORING Grade 3 l 85 Sample B 2 pt Content 0 pts Problem Solving 2 pts Total Scoring Notes: This response shows a thorough understanding of the content skills and limited or no understanding of the problem solving concepts assessed by the question. The student was able to correctly identify which numbers were even or odd, but the student does not utilize an appropriate strategy to solve the problem. The student did not add both even classes and odd classes together before subtracting. Just as points can be awarded in problem-solving for a wrong answer with the correct process, this response indicates a correct understanding of number sense with a flawed process, which results in zero points for problem solving, while the content score is maintained.
IDOE SCORING Grade 3 l 85 Sample B 2 pt Content 0 pts Problem Solving 2 pts Total Scoring Notes: This response shows a thorough understanding of the content skills and limited or no understanding of the problem solving concepts assessed by the question. The student was able to correctly identify which numbers were even or odd, but the student does not utilize an appropriate strategy to solve the problem. The student did not add both even classes and odd classes together before subtracting. Just as points can be awarded in problem-solving for a wrong answer with the correct process, this response indicates a correct understanding of number sense with a flawed process, which results in zero points for problem solving, while the content score is maintained.
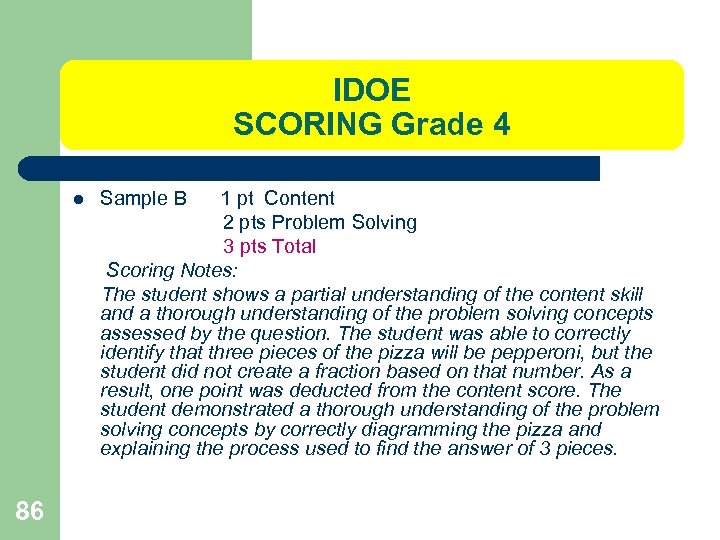 IDOE SCORING Grade 4 l 86 Sample B 1 pt Content 2 pts Problem Solving 3 pts Total Scoring Notes: The student shows a partial understanding of the content skill and a thorough understanding of the problem solving concepts assessed by the question. The student was able to correctly identify that three pieces of the pizza will be pepperoni, but the student did not create a fraction based on that number. As a result, one point was deducted from the content score. The student demonstrated a thorough understanding of the problem solving concepts by correctly diagramming the pizza and explaining the process used to find the answer of 3 pieces.
IDOE SCORING Grade 4 l 86 Sample B 1 pt Content 2 pts Problem Solving 3 pts Total Scoring Notes: The student shows a partial understanding of the content skill and a thorough understanding of the problem solving concepts assessed by the question. The student was able to correctly identify that three pieces of the pizza will be pepperoni, but the student did not create a fraction based on that number. As a result, one point was deducted from the content score. The student demonstrated a thorough understanding of the problem solving concepts by correctly diagramming the pizza and explaining the process used to find the answer of 3 pieces.
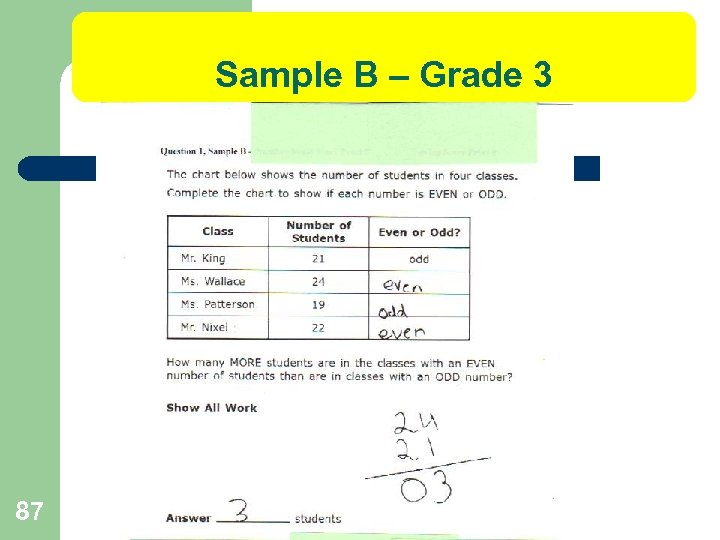 Sample B – Grade 3 87
Sample B – Grade 3 87
 Sample B – Grade 4 88
Sample B – Grade 4 88
 IDOE SCORING Grade 3 l 89 Sample B 2 pt Content 0 pts Problem Solving 2 pts Total Scoring Notes: This response shows a thorough understanding of the content skills and limited or no understanding of the problem solving concepts assessed by the question. The student was able to correctly identify which numbers were even or odd, but the student does not utilize an appropriate strategy to solve the problem. The student did not add both even classes and odd classes together before subtracting. Just as points can be awarded in problem-solving for a wrong answer with the correct process, this response indicates a correct understanding of number sense with a flawed process, which results in zero points for problem solving, while the content score is maintained.
IDOE SCORING Grade 3 l 89 Sample B 2 pt Content 0 pts Problem Solving 2 pts Total Scoring Notes: This response shows a thorough understanding of the content skills and limited or no understanding of the problem solving concepts assessed by the question. The student was able to correctly identify which numbers were even or odd, but the student does not utilize an appropriate strategy to solve the problem. The student did not add both even classes and odd classes together before subtracting. Just as points can be awarded in problem-solving for a wrong answer with the correct process, this response indicates a correct understanding of number sense with a flawed process, which results in zero points for problem solving, while the content score is maintained.
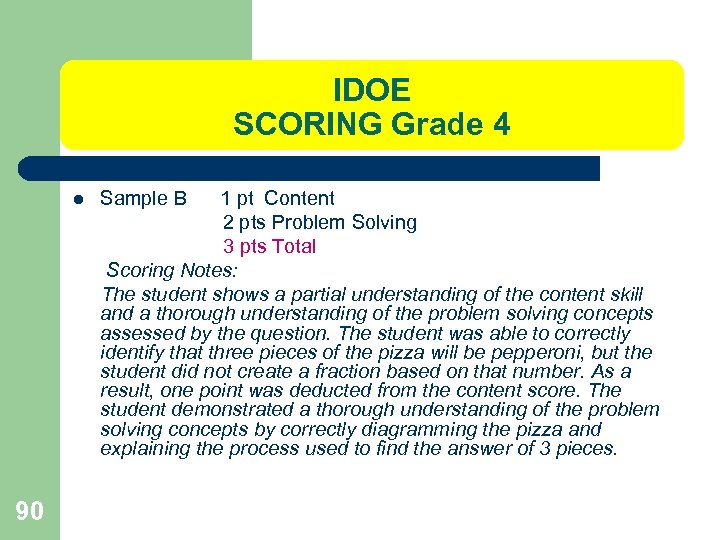 IDOE SCORING Grade 4 l 90 Sample B 1 pt Content 2 pts Problem Solving 3 pts Total Scoring Notes: The student shows a partial understanding of the content skill and a thorough understanding of the problem solving concepts assessed by the question. The student was able to correctly identify that three pieces of the pizza will be pepperoni, but the student did not create a fraction based on that number. As a result, one point was deducted from the content score. The student demonstrated a thorough understanding of the problem solving concepts by correctly diagramming the pizza and explaining the process used to find the answer of 3 pieces.
IDOE SCORING Grade 4 l 90 Sample B 1 pt Content 2 pts Problem Solving 3 pts Total Scoring Notes: The student shows a partial understanding of the content skill and a thorough understanding of the problem solving concepts assessed by the question. The student was able to correctly identify that three pieces of the pizza will be pepperoni, but the student did not create a fraction based on that number. As a result, one point was deducted from the content score. The student demonstrated a thorough understanding of the problem solving concepts by correctly diagramming the pizza and explaining the process used to find the answer of 3 pieces.
 Sample C – Grade 3 91
Sample C – Grade 3 91
 Sample C – Grade 4 92
Sample C – Grade 4 92
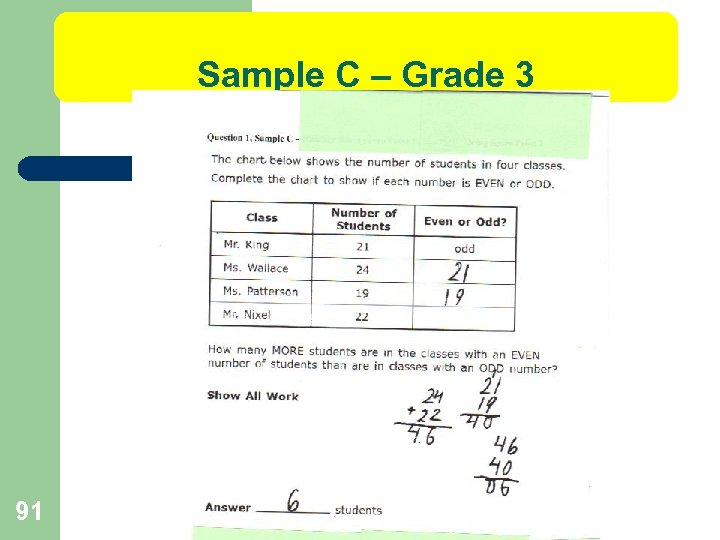
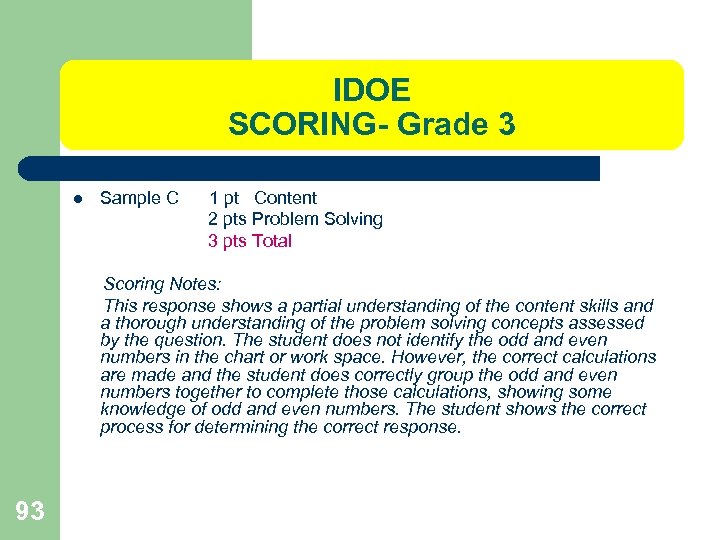 IDOE SCORING- Grade 3 l Sample C 1 pt Content 2 pts Problem Solving 3 pts Total Scoring Notes: This response shows a partial understanding of the content skills and a thorough understanding of the problem solving concepts assessed by the question. The student does not identify the odd and even numbers in the chart or work space. However, the correct calculations are made and the student does correctly group the odd and even numbers together to complete those calculations, showing some knowledge of odd and even numbers. The student shows the correct process for determining the correct response. 93
IDOE SCORING- Grade 3 l Sample C 1 pt Content 2 pts Problem Solving 3 pts Total Scoring Notes: This response shows a partial understanding of the content skills and a thorough understanding of the problem solving concepts assessed by the question. The student does not identify the odd and even numbers in the chart or work space. However, the correct calculations are made and the student does correctly group the odd and even numbers together to complete those calculations, showing some knowledge of odd and even numbers. The student shows the correct process for determining the correct response. 93
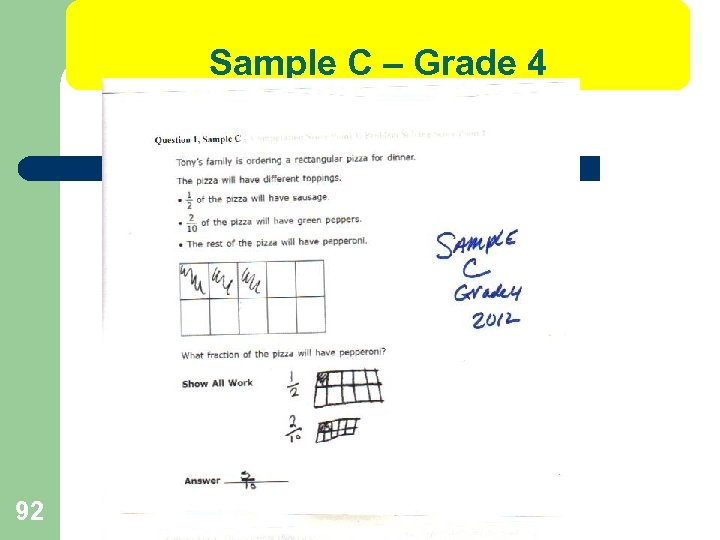
 IDOE SCORING- Grade 4 l Sample C 1 pt Content 1 pt Problem Solving 2 pts Total Scoring Notes: This response shows a partial understanding of the content skills and a partial understanding of the problem solving concepts assessed by the question. The student provided the correct response but lacked the necessary support that showed that the student understood how to appropriately determine the correct response. The student attempted to create diagrams of the data but incorrectly interpreted some of the information provided. As a result, one point was deducted from both the content and problem solving score. 94
IDOE SCORING- Grade 4 l Sample C 1 pt Content 1 pt Problem Solving 2 pts Total Scoring Notes: This response shows a partial understanding of the content skills and a partial understanding of the problem solving concepts assessed by the question. The student provided the correct response but lacked the necessary support that showed that the student understood how to appropriately determine the correct response. The student attempted to create diagrams of the data but incorrectly interpreted some of the information provided. As a result, one point was deducted from both the content and problem solving score. 94
 Problem Solving Resources l l l 95 Ice Cream Jamie’s Cards Product Game
Problem Solving Resources l l l 95 Ice Cream Jamie’s Cards Product Game
 Website Work Resources l l l 96 www. azed. gov Inside Mathematics Illustrative Mathematics doe. in. gov/commoncore parcconline. org katm. org
Website Work Resources l l l 96 www. azed. gov Inside Mathematics Illustrative Mathematics doe. in. gov/commoncore parcconline. org katm. org


